Oral Application of T4 Phage Induces Weak Antibody Production in the Gut and in the Blood
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Induction of Anti-T4 Phage Antibodies in Mice Treated with the Phage per os
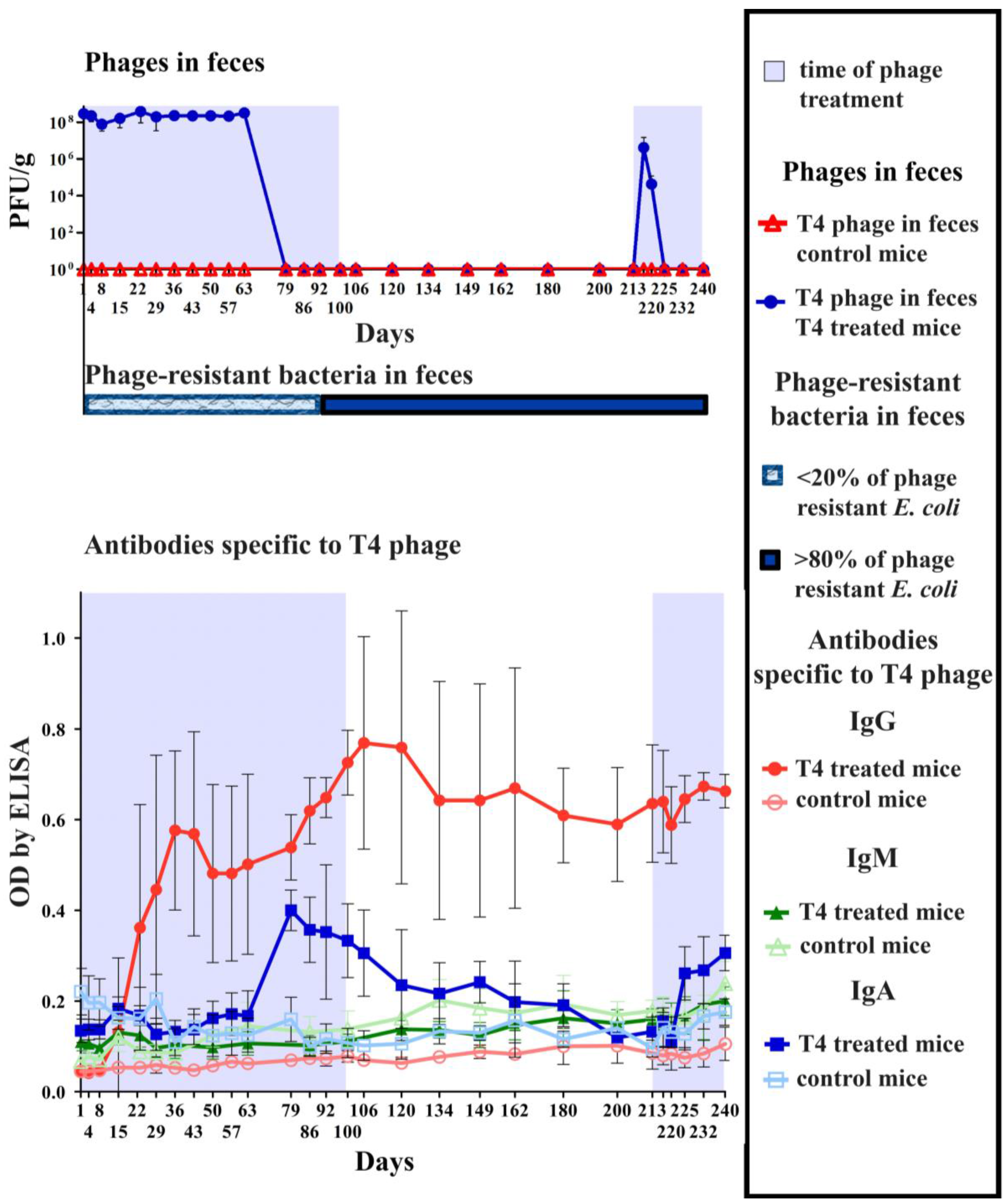
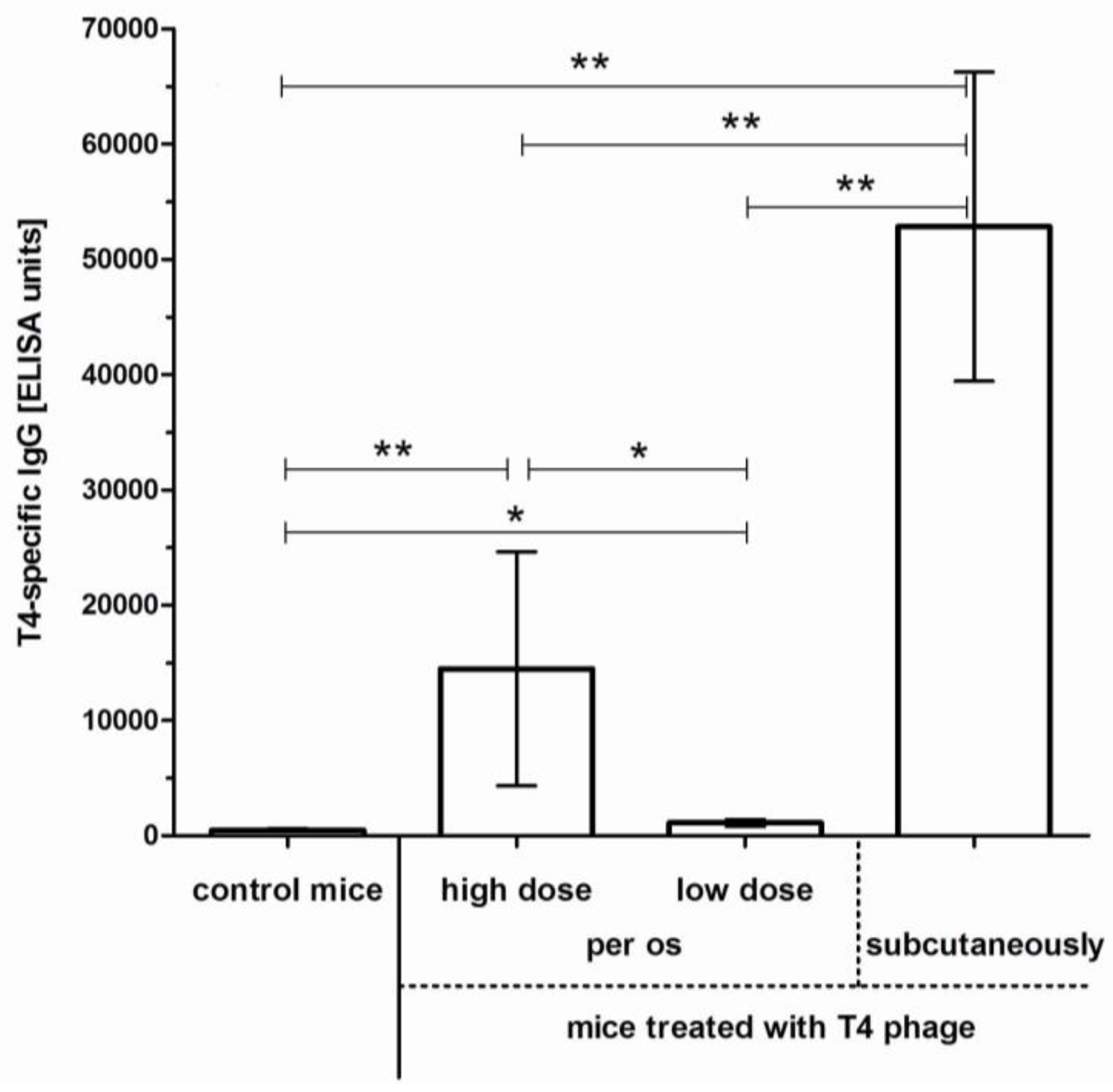
2.2. Individual Immunogenicity of Structural Proteins gp23*, gp24*, Hoc, Soc, and gp12 in Oral Application of T4 Phage
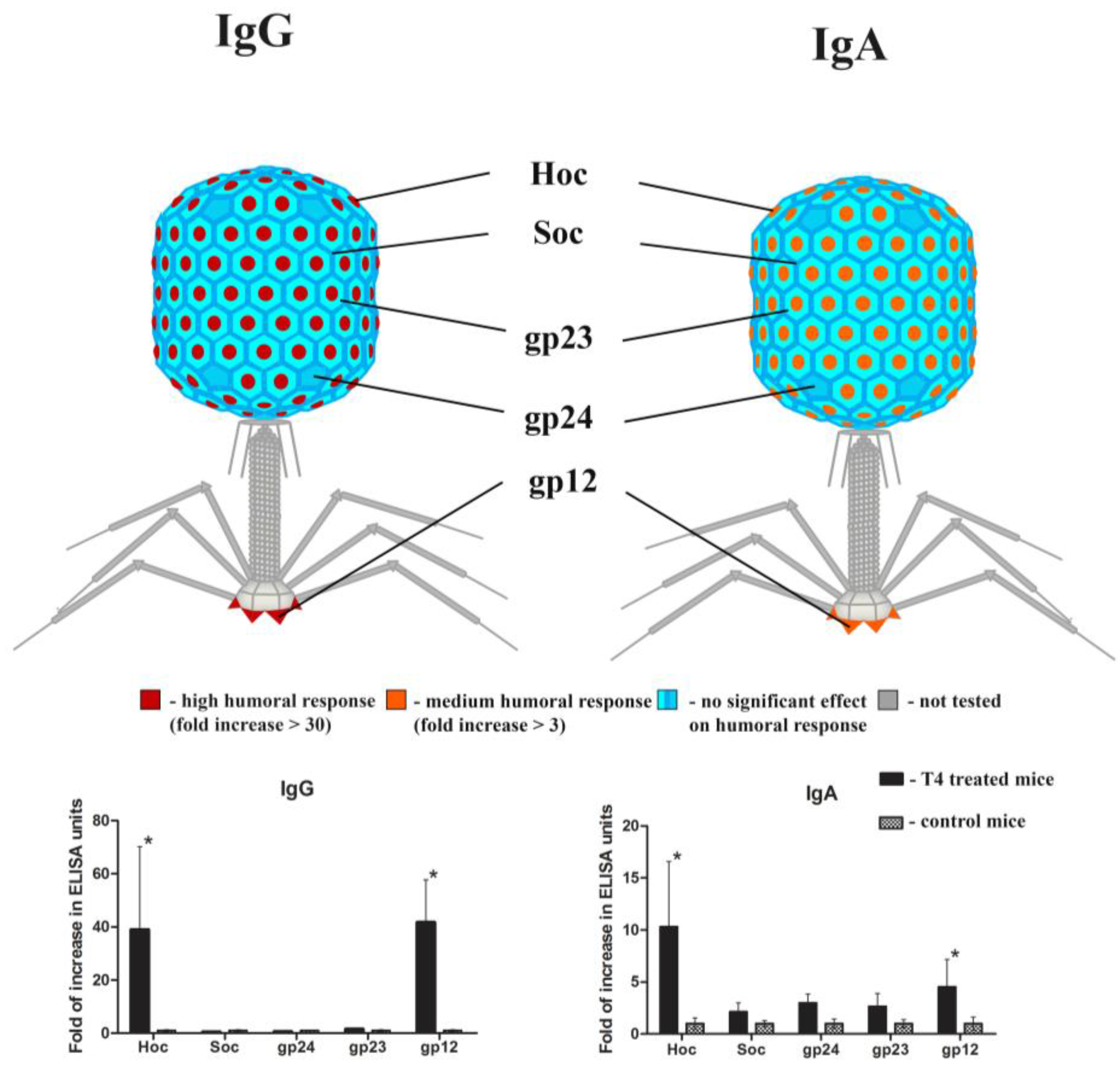
2.3. Immune Response to Foreign Antigens Presented as Fusions to Hoc Protein
| Class of Antibodies | Specificity of Antibodies | Type of Treatment | Immunization, ELISA Units | Statistical Significance (p < 0.05) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgA | anti-EB1 | T4_EB1 treatment | 106,681 (±13,892) | * |
| control | 30,778 (±10,853) | |||
| anti-T4 | T4_EB1 treatment | 175,507 (±61,845) | * | |
| control | 18,667 (±4628) | |||
| IgG | anti-EB1 | T4_EB1 treatment | 282 (±47) | |
| control | 295 (±29) | |||
| anti-T4 | T4_EB1 treatment | 18,047 (±4655) | * | |
| control | 557 (±24) |
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacteriophages
4.2. Bacteriophages Presenting Foreign Peptides
4.3. Phage Proteins
4.4. LPS Content Determination
4.5. Immunization of Mice
4.6. Ethics Statements
4.7. Specific Antibody Level Measurement by ELISA
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abedon, S.T.; Kuhl, S.J.; Blasdel, B.G.; Kutter, E.M. Phage treatment of human infections. Bacteriophage 2011, 1, 66–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruttin, A.; Brüssow, H. Human volunteers receiving Escherichia coli phage T4 orally: A safety test of phage therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2874–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutter, E.; de Vos, D.; Gvasalia, G.; Alavidze, Z.; Gogokhia, L.; Kuhl, S.; Abedon, S.T. Phage therapy in clinical practice: Treatment of human infections. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2010, 11, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Międzybrodzki, R.; Borysowski, J.; Weber-Dąbrowska, B.; Fortuna, W.; Letkiewicz, S.; Szufnarowski, K.; Pawełczyk, Z.; Rogóż, P.; Kłak, M.; Wojtasik, E.; et al. Clinical aspects of phage therapy. Adv. Virus Res. 2012, 83, 73–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sarker, S.A.; McCallin, S.; Barretto, C.; Berger, B.; Pittet, A.C.; Sultana, S.; Krause, L.; Huq, S.; Bibiloni, R.; Bruttin, A.; et al. Oral T4-like phage cocktail application to healthy adult volunteers from Bangladesh. Virology 2012, 434, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolska, K.; Kot, B.; Piechota, M.; Frankowska, A. Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to antibiotics. Postep. Hig. Med. Dosw. 2013, 67, 1300–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylski, M.; Borysowski, J.; Jakubowska-Zahorska, R.; Weber-Dąbrowska, B.; Górski, A. T4 bacteriophage-mediated inhibition of adsorption and replication of human adenovirus in vitro. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Abu-Shilbayeh, L.; Rao, V.B. Display of a PorA peptide from Neisseria meningitidis on the bacteriophage T4 capsid surface. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 4770–4777. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shivachandra, S.B.; Rao, M.; Janosi, L.; Sathaliyawala, T.; Matyas, G.R.; Alving, C.R.; Leppla, S.H.; Rao, V.B. In vitro binding of anthrax protective antigen on bacteriophage T4 capsid surface through Hoc-capsid interactions: A strategy for efficient display of large full-length proteins. Virology 2006, 345, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivachandra, S.B.; Li, Q.; Peachman, K.K.; Matyas, G.R.; Leppa, S.H.; Alving, C.R.; Rao, M.; Rao, V.B. Multicomponent anthrax toxin display and delivery using bacteriophage T4. Vaccine 2007, 25, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.J.; Lewis, G.K.; Wingfield, P.T.; Locke, E.G.; Steven, A.C.; Black, L.W. Phage display of intact domains at high copy number: A system based on Soc, the small outer capsid protein of bacteriophage T4. Protein Sci. 1996, 5, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathaliyawala, T.; Rao, M.; Maclean, D.M.; Birx, D.L.; Alving, C.R.; Rao, V.B. Assembly of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antigens on bacteriophage T4: A novel in vitro approach to construct multicomponent HIV vaccines. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7688–7698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamme, C. Antibodies against staphylococcal bacteriophages in human sera. I. Assay of antibodies in healthy individuals and in patients with staphylococcal infections. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. B Microbiol. Immunol. 1973, 81, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, H.W.; Huggins, M.B.; Shaw, K.M. Factors influencing the survival and multiplication of bacteriophages in calves and in their environment. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1987, 133, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górski, A.; Międzybrodzki, R.; Borysowski, J.; Dąbrowska, K.; Wierzbicki, P.; Ohams, M.; Korczak-Kowalska, G.; Olszowska-Zaremba, N.; Łusiak-Szelachowska, M.; Kłak, M.; et al. Phage as a modulator of immune responses: Practical implications for phage therapy. Adv. Virus Res. 2012, 83, 41–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Górski, A.; Wazna, E.; Dabrowska, B.W.; Dabrowska, K.; Switała-Jeleń, K.; Miedzybrodzki, R. Bacteriophage translocation. FEMS Immunol Med. Microbiol. 2006, 46, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łusiak-Szelachowska, M.; Zaczek, M.; Weber-Dąbrowska, B.; Międzybrodzki, R.; Kłak, M.; Fortuna, W.; Letkiewicz, S.; Rogóż, P.; Szufnarowski, K.; Jończyk-Matysiak, E.; et al. Phage neutralization by sera of patients receiving phage therapy. Viral Immunol. 2014, 27, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dąbrowska, K.; Miernikiewicz, P.; Piotrowicz, A.; Hodyra, K.; Owczarek, B.; Lecion, D.; Kaźmierczak, Z.; Letarov, A.; Górski, A. Immunogenicity studies of proteins forming the T4 phage head surface. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 12551–12557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huff, W.E.; Huff, G.R.; Rath, N.C.; Donoghue, A.M. Immune interference of bacteriophage efficacy when treating colibacillosis in poultry. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, A.; Semenkovich, N.P.; Whiteson, K.; Rohwer, F.; Gordon, J.I. Going viral: Next-generation sequencing applied to phage populations in the human gut. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, A.; Wu, M.; McNulty, N.P.; Rohwer, F.L.; Gordon, J.I. Gnotobiotic mouse model of phage-bacterial host dynamics in the human gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20236–20241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmasso, M.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. Exploiting gut bacteriophages for human health. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duerkop, B.A.; Hooper, L.V. Resident viruses and their interactions with the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabrowska, K.; Switała-Jelen, K.; Opolski, A.; Weber-Dabrowska, B.; Gorski, A. Bacteriophage penetration in vertebrates. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 98, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, K.; Orcutt, A.C.; Muratova, O.V.; Miller, L.H.; Saul, A.; Long, C.A. Development and characterization of a standardized ELISA including a reference serum on each plate to detect antibodies induced by experimental malaria vaccines. Vaccine 2008, 26, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, K.; Takashima, E.; Deng, B.; Tullo, G.; Diouf, A.; Moretz, S.E.; Nikolaeva, D.; Diakite, M.; Fairhurst, R.M.; Fay, M.P.; et al. Functional comparison of Plasmodium falciparum transmission-blocking vaccine candidates by the standard membrane-feeding assay. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 4377–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceglarek, I.; Piotrowicz, A.; Lecion, D.; Miernikiewicz, P.; Owczarek, B.; Hodyra, K.; Harhala, M.; Górski, A.; Dąbrowska, K. A novel approach for separating bacteriophages from other bacteriophages using affinity chromatography and phage display. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber-Dabrowska, B.; Dabrowski, M.; Slopek, S. Studies on bacteriophage penetration in patients subjected to phage therapy. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 1987, 35, 563–568. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, R.; Engley, F.B. Fate of bacteriophage particles introduced into mice by various routes. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1958, 98, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M. Animal experiments on the mucosal passage and absorption viremia of T3 phages after oral, tracheal and rectal administration. Zentralbl. Bacteriol. Orig. 1965, 198, 371–390. [Google Scholar]
- Fogelman, I.; Davey, V.; Ochs, H.D.; Elashoff, M.; Feinberg, M.B.; Mican, J.; Siegel, J.P.; Sneller, M.; Lane, H.C. Evaluation of CD4 T cell function in vivo in HIV-infected patients as measured by bacteriophage phiX174 immunization. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 182, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merril, C.R.; Biswas, B.; Carlton, R.M.; Jensen, N.C.; Creed, G.J.; Zullo, S.; Adhya, S. Long-circulating bacteriophage as antibacterial agents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 3188–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geier, M.R.; Trigg, M.E.; Merril, C.R. Fate of bacteriophage lambda in non-immune germ-free mice. Nature 1973, 246, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borysowski, J.; Górski, A. Is phage therapy acceptable in the immunocompromised host? Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 12, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mordenti, J.; Chen, S.A.; Moore, J.A.; Ferraiolo, B.L.; Green, J.D. Interspecies scaling of clearance and volume of distribution data for five therapeutic proteins. Pharm Res. 1991, 8, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulakvelidze, A.; Alavidze, Z.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Bacteriophage therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maura, D.; Debarbieux, L. On the interactions between virulent bacteriophages and bacteria in the gut. Bacteriophage 2012, 2, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.; Denou, E.; Bruttin, A.; Serra-Moreno, R.; Dillmann, M.L.; Brüssow, H. In vivo replication of T4 and T7 bacteriophages in germ-free mice colonized with Escherichia coli. Virology 2009, 393, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.R.; March, J.B. Bacteriophages and biotechnology: Vaccines, gene therapy and antibacterials. Trends Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.R.; March, J.B. Bacteriophage mediated nucleic acid immunisation. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 40, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Sanchez, A.; Yang, Z.; Zaki, S.R.; Nabel, E.G.; Nichol, S.T.; Nabel, G.J. Immunization for Ebola virus infection. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shedlock, D.J.; Aviles, J.; Talbott, K.T.; Wong, G.; Wu, S.J.; Villarreal, D.O.; Myles, D.J.; Croyle, M.A.; Yan, J.; Kobinger, G.P.; et al. Induction of broad cytotoxic T cells by protective DNA vaccination against Marburg and Ebola. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becquart, P.; Mahlakõiv, T.; Nkoghe, D.; Leroy, E.M. Identification of continuous human B-cell epitopes in the VP35, VP40, nucleoprotein and glycoprotein of Ebola virus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miernikiewicz, P.; Owczarek, B.; Piotrowicz, A.; Boczkowska, B.; Rzewucka, K.; Figura, G.; Letarov, A.; Kulikov, E.; Kopciuch, A.; Świtała-Jeleń, K.; et al. Recombinant expression and purification of T4 phage Hoc, Soc, gp23, gp24 proteins in native conformations with stability studies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miernikiewicz, P.; Institute of Immunology and Experimental Therapy, Polish Academy of Sciences, Wrocław, Poland. Personal Communication, 2013.
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- StatSoft, Inc. STATISTICA (data analysis software system), version 8.0. Available online: http://www.statsoft.com (accessed on 20 April 2015).
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Majewska, J.; Beta, W.; Lecion, D.; Hodyra-Stefaniak, K.; Kłopot, A.; Kaźmierczak, Z.; Miernikiewicz, P.; Piotrowicz, A.; Ciekot, J.; Owczarek, B.; et al. Oral Application of T4 Phage Induces Weak Antibody Production in the Gut and in the Blood. Viruses 2015, 7, 4783-4799. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7082845
Majewska J, Beta W, Lecion D, Hodyra-Stefaniak K, Kłopot A, Kaźmierczak Z, Miernikiewicz P, Piotrowicz A, Ciekot J, Owczarek B, et al. Oral Application of T4 Phage Induces Weak Antibody Production in the Gut and in the Blood. Viruses. 2015; 7(8):4783-4799. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7082845
Chicago/Turabian StyleMajewska, Joanna, Weronika Beta, Dorota Lecion, Katarzyna Hodyra-Stefaniak, Anna Kłopot, Zuzanna Kaźmierczak, Paulina Miernikiewicz, Agnieszka Piotrowicz, Jarosław Ciekot, Barbara Owczarek, and et al. 2015. "Oral Application of T4 Phage Induces Weak Antibody Production in the Gut and in the Blood" Viruses 7, no. 8: 4783-4799. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7082845
APA StyleMajewska, J., Beta, W., Lecion, D., Hodyra-Stefaniak, K., Kłopot, A., Kaźmierczak, Z., Miernikiewicz, P., Piotrowicz, A., Ciekot, J., Owczarek, B., Kopciuch, A., Wojtyna, K., Harhala, M., Mąkosa, M., & Dąbrowska, K. (2015). Oral Application of T4 Phage Induces Weak Antibody Production in the Gut and in the Blood. Viruses, 7(8), 4783-4799. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7082845






