Characterization of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus Integration in the Horse Genome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Preparation and Infection
2.2. Cloning and Sequencing of Integration Sites
2.3. Sequences Analysis and Mapping of Integration Sites in the Host Genome
| Group | Virus or Vector | Cell Type | Number of Integration Sites | Accession Numbers (GenBank) | Source of Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV-1 | HIV-1 vector | HEK 293T a | 146 b (162 c) | DQ498202–DQ498347 | [33] |
| EIAV | EIAV vector | HEK 293T | 416 (458) | DQ498348–DQ498763 | [33] |
| EIAV-Ssp I | EIAVFDDV13 d | FED e | 287 | KO454413–KO454699 | This study |
| EIAV-Dra I | EIAVFDDV13 | FED | 190 | KO454223–KO454412 | This study |
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
3. Results
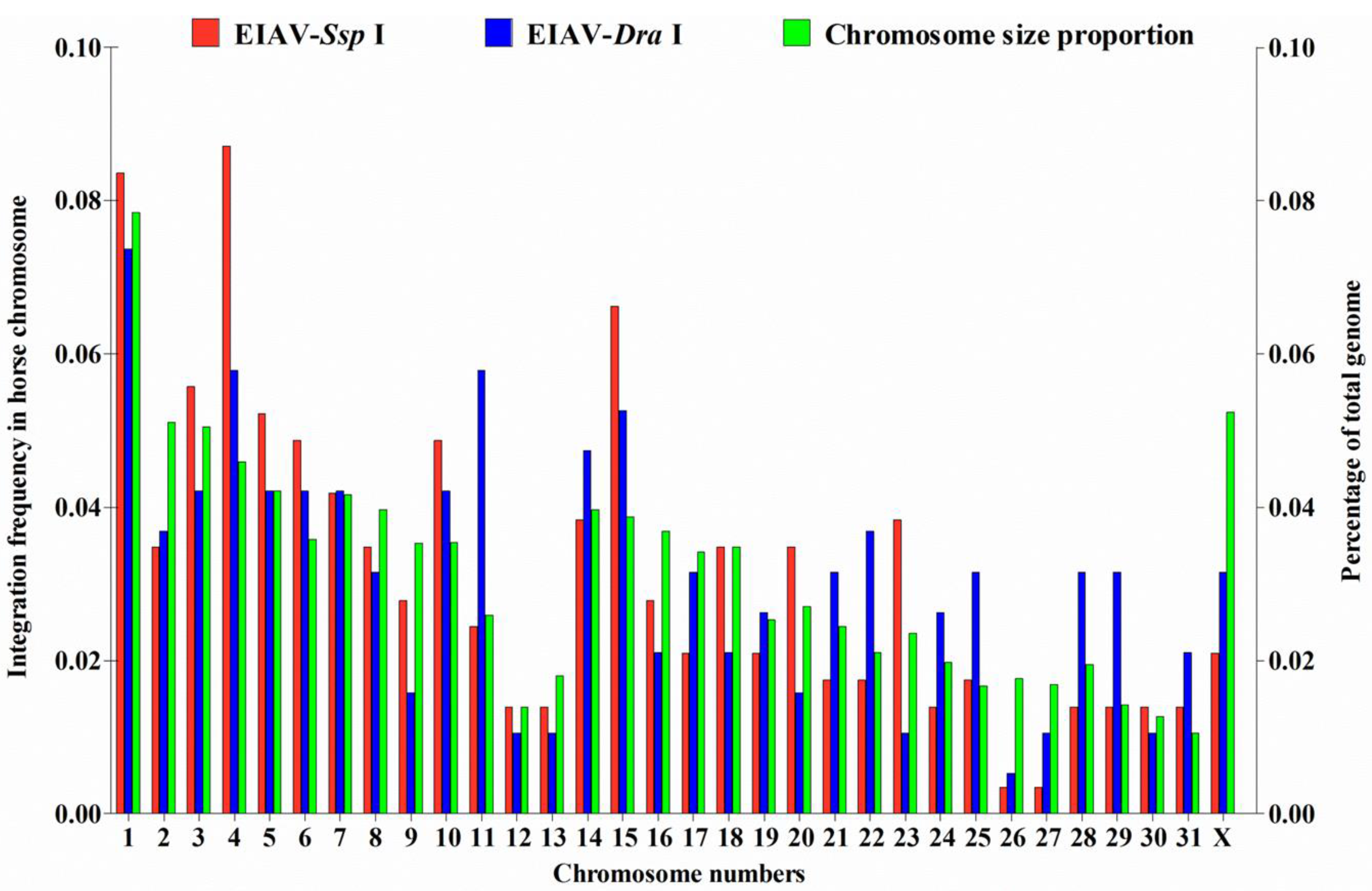
3.1. Distribution of EIAV Provirus Integration Sites in Horse Chromosomes
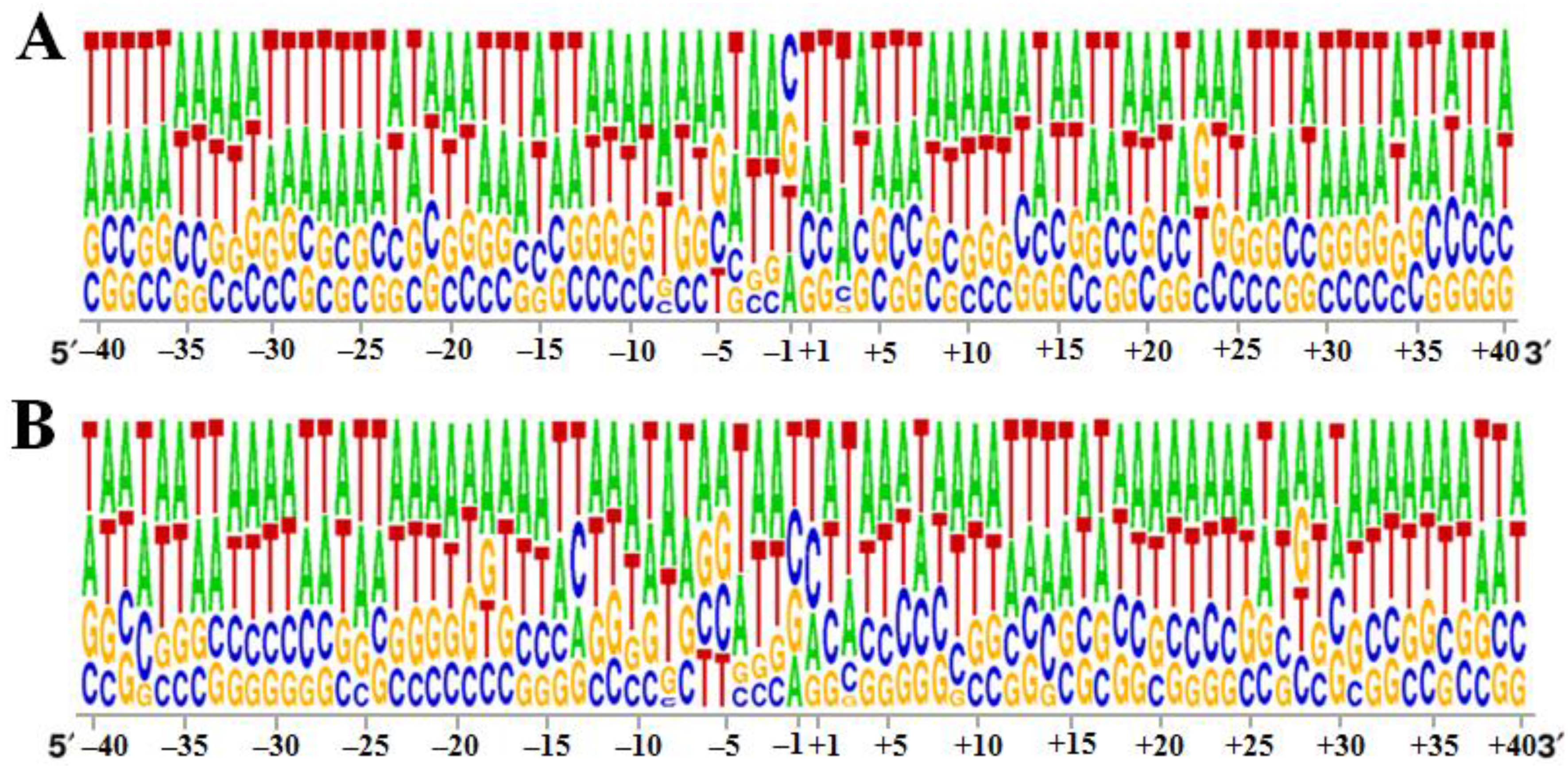
3.2. Specificity of the 40 bp Region around the Integration Sites
3.3. EIAVFDDV13 Provirus Tended to Integrate into Host RefSeq Genes
| Random | HIV-1 vector | EIAV vector | EIAV-Ssp I group | EIAV-Dra I group | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. (%) | No. (%) | No. (%) | P2 d | No. (%) | P1 c | P2 d | P3 e | No. (%) | P1 c | P2 d | P3 e | P4 f | |
| Total | 10000 (100.0) | 146 (100.0) | 416 (100.0) | NA | 287 (100.0) | NA | NA | NA | 190 (100.0) | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| In RefSeq genes a | 3315 (33.2) | 113 (77.4) | 313 (75.2) | NS | 152 (53.0) | ** | ** | ** | 105 (55.3) | ** | ** | ** | NS |
| Sense b | ND (ND) | 65 (57.5) | 149 (47.6) | NS | 79 (52.0) | NA | NS | NS | 63 (60.0) | NA | NS | * | NS |
3.4. EIAVFDDV13 Integration Targeted Low Gene Density Regions and Avoided the TSS
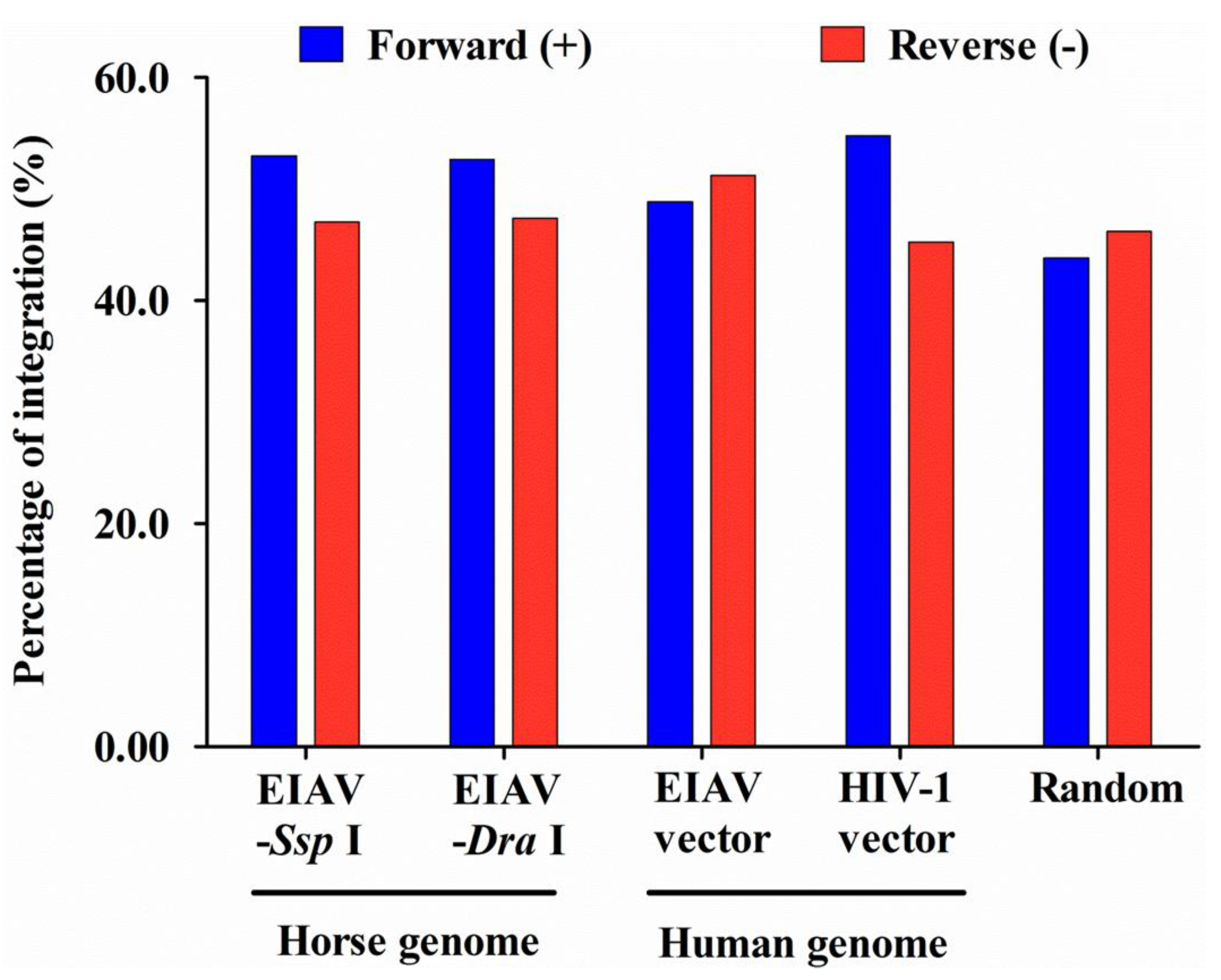
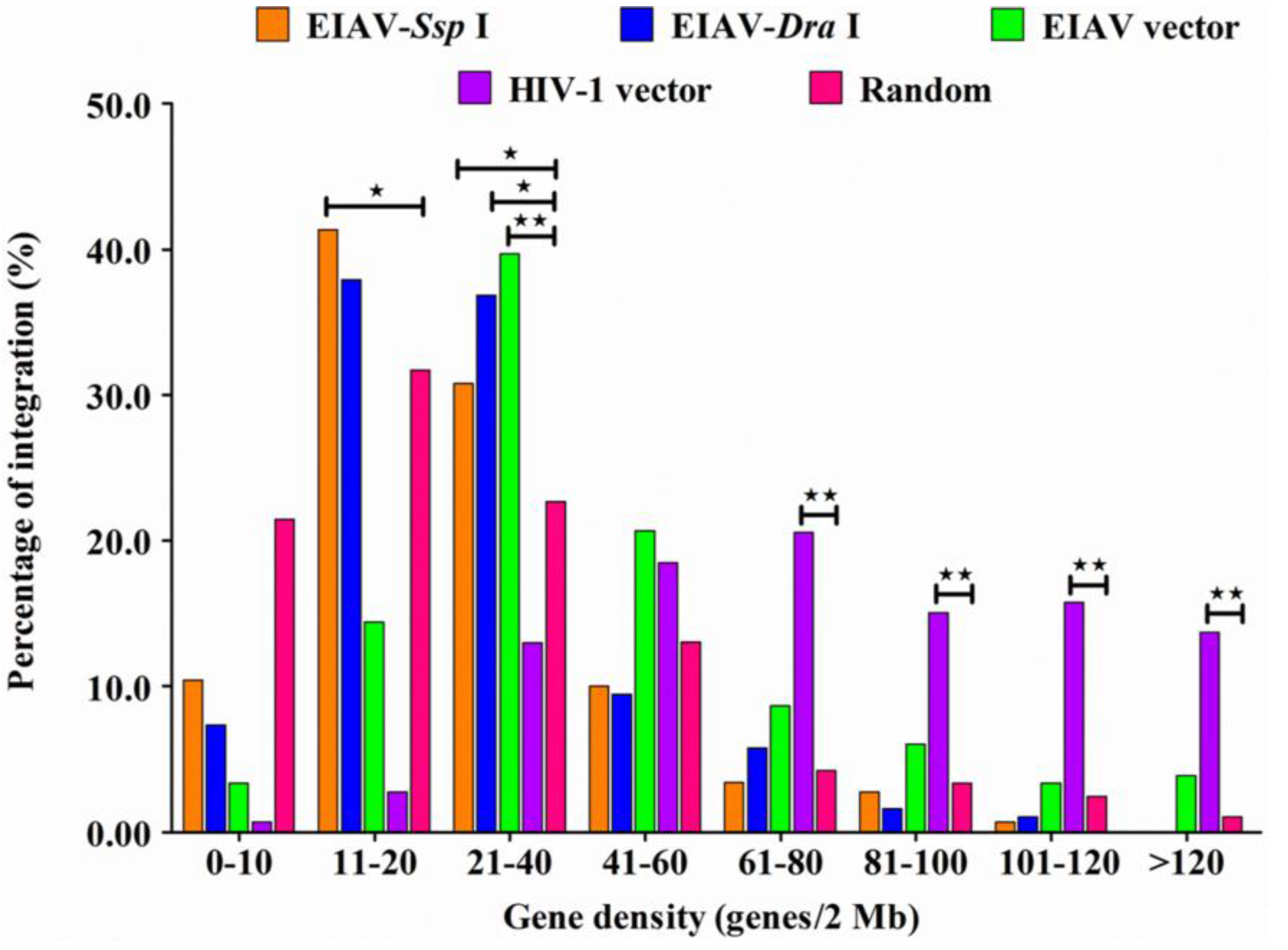
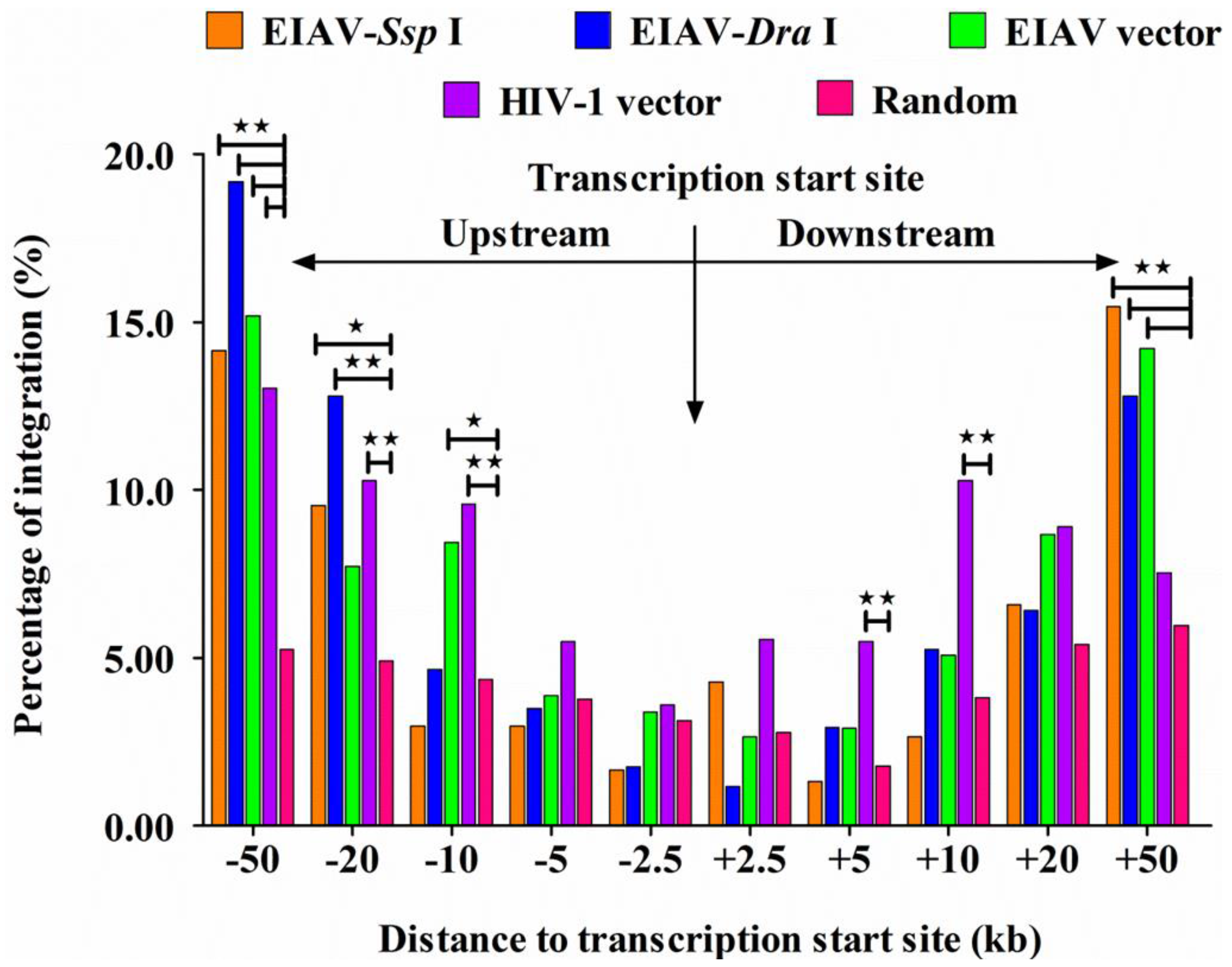
3.5. Integration Frequency of EIAVFDDV13 in Repetitive Sequences
| Random control | EIAV-Ssp I | EIAV-Dra I | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. (%) a | No. (%) | P1 c | No. (%) | P1 c | P2 d | |
| Total b | 4876 | 120 | 69 | |||
| LINEs | 1848 (37.9) | 69 (57.5) | ** | 38 (55.1) | ** | NS |
| SINEs | 675 (13.8) | 15 (12.5) | NS | 9 (13.0) | NS | NS |
| DNA transposons | 322 (6.6) | 21 (17.5) | ** | 15 (21.7) | ** | NS |
| LTR transposons | 658 (13.5) | 11 (9.2) | NS | 6 (8.7) | NS | NS |
4. Discussion
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coffin, J.M.; Hughes, S.H.; Varmus, H.E. The Interactions of Retroviruses and their Hosts. In Retroviruses; Coffin, J.M., Hughes, S.H., Varmus, H.E., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Van Maele, B.; Debyser, Z. HIV-1 integration: An interplay between HIV-1 integrase, cellular and viral proteins. AIDS Rev. 2005, 7, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Debyser, Z.; Christ, F.; De Rijck, J.; Gijsbers, R. Host factors for retroviral integration site selection. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasco, L.; Baricordi, C.; Aiuti, A. Retroviral integrations in gene therapy trials. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2012, 20, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boztug, K.; Dewey, R.A.; Klein, C. Development of hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Curr. Opin. Mol. Therapeutics 2006, 8, 390–395. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, A.; Hacein-Bey-Abina, S.; Cavazzana-Calvo, M. Gene therapy for primary adaptive immune deficiencies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 1356–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivat, C.; Santilli, G.; Gaspar, H.B.; Thrasher, A.J. Gene therapy for primary immunodeficiencies. Hum. Gene Ther. 2012, 23, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, I.M.; Weitzman, M.D. Gene therapy: Twenty-first century medicine. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2005, 74, 711–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pike-Overzet, K.; van der Burg, M.; Wagemaker, G.; van Dongen, J.J.; Staal, F.J. New insights and unresolved issues regarding insertional mutagenesis in X-linked SCID gene therapy. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2007, 15, 1910–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavazzana-Calvo, M.; Fischer, A. Gene therapy for severe combined immunodeficiency: Are we there yet? J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, K.; Izsvak, Z.; Ivics, Z. Targeted gene insertion for molecular medicine. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 86, 1205–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacein-Bey-Abina, S.; Von Kalle, C.; Schmidt, M.; McCormack, M.P.; Wulffraat, N.; Leboulch, P.; Lim, A.; Osborne, C.S.; Pawliuk, R.; Morillon, E.; et al. LMO2-associated clonal T cell proliferation in two patients after gene therapy for SCID-X1. Science 2003, 302, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacein-Bey-Abina, S.; Garrigue, A.; Wang, G.P.; Soulier, J.; Lim, A.; Morillon, E.; Clappier, E.; Caccavelli, L.; Delabesse, E.; Beldjord, K.; et al. Insertional oncogenesis in 4 patients after retrovirus-mediated gene therapy of SCID-X1. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3132–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacein-Bey-Abina, S.; von Kalle, C.; Schmidt, M.; Le Deist, F.; Wulffraat, N.; McIntyre, E.; Radford, I.; Villeval, J.L.; Fraser, C.C.; Cavazzana-Calvo, M.; Fischer, A. A serious adverse event after successful gene therapy for X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.P.; Garrigue, A.; Ciuffi, A.; Ronen, K.; Leipzig, J.; Berry, C.; Lagresle-Peyrou, C.; Benjelloun, F.; Hacein-Bey-Abina, S.; Fischer, A.; Cavazzana-Calvo, M.; Bushman, F.D. DNA bar coding and pyrosequencing to analyze adverse events in therapeutic gene transfer. Nucl. Acids Res. 2008, 36, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.P.; Levine, B.L.; Binder, G.K.; Berry, C.C.; Malani, N.; McGarrity, G.; Tebas, P.; June, C.H.; Bushman, F.D. Analysis of lentiviral vector integration in HIV+ study subjects receiving autologous infusions of gene modified CD4+ T cells. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2009, 17, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montini, E.; Cesana, D.; Schmidt, M.; Sanvito, F.; Bartholomae, C.C.; Ranzani, M.; Benedicenti, F.; Sergi, L.S.; Ambrosi, A.; Ponzoni, M.; Doglioni, C.; di Serio, C.; von Kalle, C.; Naldini, L. The genotoxic potential of retroviral vectors is strongly modulated by vector design and integration site selection in a mouse model of HSC gene therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papayannakos, C.; Daniel, R. Understanding lentiviral vector chromatin targeting: Working to reduce insertional mutagenic potential for gene therapy. Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, A.R.; Shinn, P.; Chen, H.; Berry, C.; Ecker, J.R.; Bushman, F. HIV-1 integration in the human genome favors active genes and local hotspots. Cell 2002, 110, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crise, B.; Li, Y.; Yuan, C.; Morcock, D.R.; Whitby, D.; Munroe, D.J.; Arthur, L.O.; Wu, X. Simian immunodeficiency virus integration preference is similar to that of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 12199–12204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Moressi, C.J.; Scheetz, T.E.; Xie, L.; Tran, D.T.; Casavant, T.L.; Ak, P.; Benham, C.J.; Davidson, B.L.; McCray, P.B., Jr. Integration site choice of a feline immunodeficiency virus vector. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 8820–8823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Crise, B.; Burgess, S.M. Transcription start regions in the human genome are favored targets for MLV integration. Science 2003, 300, 1749–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narezkina, A.; Taganov, K.D.; Litwin, S.; Stoyanova, R.; Hayashi, J.; Seeger, C.; Skalka, A.M.; Katz, R.A. Genome-wide analyses of avian sarcoma virus integration sites. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 11656–11663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, R.S.; Beitzel, B.F.; Schroder, A.R.; Shinn, P.; Chen, H.; Berry, C.C.; Ecker, J.R.; Bushman, F.D. Retroviral DNA integration: ASLV, HIV, and MLV show distinct target site preferences. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craigo, J.K.; Montelaro, R.C. Lessons in AIDS vaccine development learned from studies of equine infectious, anemia virus infection and immunity. Viruses 2013, 5, 2963–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroux, C.; Cadore, J.L.; Montelaro, R.C. Equine Infectious Anemia Virus (EIAV): What has HIV’s country cousin got to tell us? Vet. Res. 2004, 35, 485–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrold, S.M.; Cook, S.J.; Cook, R.F.; Rushlow, K.E.; Issel, C.J.; Montelaro, R.C. Tissue sites of persistent infection and active replication of equine infectious anemia virus during acute disease and asymptomatic infection in experimentally infected equids. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 3112–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, Y.; Hirasawa, K.; Fukunaga, Y.; Taniguchi, T. Recrudescence of equine infectious anemia by treatment with immunosuppressive drugs. Natl. Inst. Anim. Health Q. 1976, 16, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Craigo, J.K.; Leroux, C.; Howe, L.; Steckbeck, J.D.; Cook, S.J.; Issel, C.J.; Montelaro, R.C. Transient immune suppression of inapparent carriers infected with a principal neutralizing domain-deficient equine infectious anaemia virus induces neutralizing antibodies and lowers steady-state virus replication. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lewinski, M.K.; Bisgrove, D.; Shinn, P.; Chen, H.; Hoffmann, C.; Hannenhalli, S.; Verdin, E.; Berry, C.C.; Ecker, J.R.; Bushman, F.D. Genome-wide analysis of chromosomal features repressing human immunodeficiency virus transcription. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6610–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, M.J.; Graf, E.H.; Agosto, L.M.; Mexas, A.M.; Male, F.; Brady, T.; Bushman, F.D.; O’Doherty, U. Directly infected resting CD4+ T cells can produce HIV Gag without spreading infection in a model of HIV latency. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Lassen, K.; Monie, D.; Sedaghat, A.R.; Shimoji, S.; Liu, X.; Pierson, T.C.; Margolick, J.B.; Siliciano, R.F.; Siliciano, J.D. Resting CD4+ T cells from human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-infected individuals carry integrated HIV-1 genomes within actively transcribed host genes. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6122–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacker, C.V.; Vink, C.A.; Wardell, T.W.; Lee, S.; Treasure, P.; Kingsman, S.M.; Mitrophanous, K.A.; Miskin, J.E. The integration profile of EIAV-based vectors. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2006, 14, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, H.M.; Ronen, K.; Berry, C.; Llano, M.; Sutherland, H.; Saenz, D.; Bickmore, W.; Poeschla, E.; Bushman, F.D. Role of PSIP1/LEDGF/p75 in lentiviral infectivity and integration targeting. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Shi, N.; Jiang, C.G.; Lin, Y.Z.; Wang, X.F.; Wang, S.; Lv, X.L.; Zhao, L.P.; Shao, Y.M.; Kong, X.G.; Zhou, J.H.; Shen, R.X. A proviral derivative from a reference attenuated EIAV vaccine strain failed to elicit protective immunity. Virology 2011, 410, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Wang, S.S.; Lin, Y.Z.; Liu, H.F.; Wei, H.M.; Du, C.; Wang, X.F.; Zhou, J.H. An attenuated EIAV strain and its molecular clone strain differentially induce the expression of Toll-like receptors and type-I interferons in equine monocyte-derived macrophages. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, C.; Ma, J.; Zhao, L.; Lv, X.; Shen, R.; Wang, F.; Kong, X.; Su, Z.; Zhou, J. Genomic analysis of an effective lentiviral vaccine-attenuated equine infectious anemia virus vaccine EIAV FDDV13. Virus Genes 2010, 41, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shiraigol, W.; Li, B.; Bai, D.; Ye, W.; Daidiikhuu, D.; Yang, L.; Jin, B.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Analysis of horse genomes provides insight into the diversification and adaptive evolution of karyotype. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, C.M.; Giulotto, E.; Sigurdsson, S.; Zoli, M.; Gnerre, S.; Imsland, F.; Lear, T.L.; Adelson, D.L.; Bailey, E.; Bellone, R.R.; et al. Genome sequence, comparative analysis, and population genetics of the domestic horse. Science 2009, 326, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.G.; Gao, X.; Ma, J.; Lin, Y.Z.; Wang, X.F.; Zhao, L.P.; Hua, Y.P.; Liu, D.; Zhou, J.H. C-terminal truncation of the transmembrane protein of an attenuated lentiviral vaccine alters its in vitro but not in vivo replication and weakens its potential pathogenicity. Virus Res. 2011, 158, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, C.D.; Park, J.; Wakefield, J.K. Viral gene products and replication of the human immunodeficiency type 1 virus. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, C1135–C1156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ranki, A.; Lagerstedt, A.; Ovod, V.; Aavik, E.; Krohn, K.J. Expression kinetics and subcellular localization of HIV-1 regulatory proteins Nef, Tat and Rev in acutely and chronically infected lymphoid cell lines. Arch. Virol. 1994, 139, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciuffi, A.; Ronen, K.; Brady, T.; Malani, N.; Wang, G.; Berry, C.C.; Bushman, F.D. Methods for integration site distribution analyses in animal cell genomes. Methods 2009, 47, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciuffi, A.; Barr, S.D. Identification of HIV integration sites in infected host genomic DNA. Methods 2011, 53, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, A.G.; Coffin, J.M. Symmetrical base preferences surrounding HIV-1, avian sarcoma/leukosis virus, and murine leukemia virus integration sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6103–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.P.; Ciuffi, A.; Leipzig, J.; Berry, C.C.; Bushman, F.D. HIV integration site selection: Analysis by massively parallel pyrosequencing reveals association with epigenetic modifications. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venter, J.C.; Adams, M.D.; Myers, E.W.; Li, P.W.; Mural, R.J.; Sutton, G.G.; Smith, H.O.; Yandell, M.; Evans, C.A.; Holt, R.A.; et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science 2001, 291, 1304–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, C.; Hannenhalli, S.; Leipzig, J.; Bushman, F.D. Selection of target sites for mobile DNA integration in the human genome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2006, 2, e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldarelli, F.; Wu, X.; Su, L.; Simonetti, F.R.; Shao, W.; Hill, S.; Spindler, J.; Ferris, A.L.; Mellors, J.W.; Kearney, M.F.; Coffin, J.M.; Hughes, S.H. HIV latency. Specific HIV integration sites are linked to clonal expansion and persistence of infected cells. Science 2014, 345, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Yang, H.C.; Rabi, S.A.; Bravo, H.C.; Shroff, N.S.; Irizarry, R.A.; Zhang, H.; Margolick, J.B.; Siliciano, J.D.; Siliciano, R.F. Influence of host gene transcription level and orientation on HIV-1 latency in a primary-cell model. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5384–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohn, L.B.; Silva, I.T.; Oliveira, T.Y.; Rosales, R.A.; Parrish, E.H.; Learn, G.H.; Hahn, B.H.; Czartoski, J.L.; McElrath, M.J.; Lehmann, C.; et al. HIV-1 integration landscape during latent and active infection. Cell 2015, 160, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrill-Mix, S.; Lewinski, M.K.; Famiglietti, M.; Bosque, A.; Malani, N.; Ocwieja, K.E.; Berry, C.C.; Looney, D.; Shan, L.; Agosto, L.M.; et al. HIV latency and integration site placement in five cell-based models. Retrovirology 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciuffi, A.; Mohammadi, P.; Golumbeanu, M.; di Iulio, J.; Telenti, A. Bioinformatics and HIV Latency. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2015, 12, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desfarges, S.; Ciuffi, A. Retroviral integration site selection. Viruses 2010, 2, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ravin, S.S.; Su, L.; Theobald, N.; Choi, U.; Macpherson, J.L.; Poidinger, M.; Symonds, G.; Pond, S.M.; Ferris, A.L.; Hughes, S.H.; Malech, H.L.; Wu, X. Enhancers are major targets for murine leukemia virus vector integration. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 4504–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukahara, T.; Agawa, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Matsuda, M.; Ueno, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Yamada, K.; Tanaka, N.; Kojima, K.; Takeshita, T. Murine leukemia virus vector integration favors promoter regions and regional hot spots in a human T-cell line. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 345, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewinski, M.K.; Yamashita, M.; Emerman, M.; Ciuffi, A.; Marshall, H.; Crawford, G.; Collins, F.; Shinn, P.; Leipzig, J.; Hannenhalli, S.; Berry, C.C.; Ecker, J.R.; Bushman, F.D. Retroviral DNA integration: Viral and cellular determinants of target-site selection. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvaratskhelia, M.; Sharma, A.; Larue, R.C.; Serrao, E.; Engelman, A. Molecular mechanisms of retroviral integration site selection. Nucl. Acids Res. 2014, 42, 10209–10225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busschots, K.; Vercammen, J.; Emiliani, S.; Benarous, R.; Engelborghs, Y.; Christ, F.; Debyser, Z. The interaction of LEDGF/p75 with integrase is lentivirus-specific and promotes DNA binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 17841–17847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherepanov, P. LEDGF/p75 interacts with divergent lentiviral integrases and modulates their enzymatic activity in vitro. Nucl. Acids Res. 2007, 35, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaller, T.; Ocwieja, K.E.; Rasaiyaah, J.; Price, A.J.; Brady, T.L.; Roth, S.L.; Hue, S.; Fletcher, A.J.; Lee, K.; KewalRamani, V.N.; et al. HIV-1 capsid-cyclophilin interactions determine nuclear import pathway, integration targeting and replication efficiency. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rijck, J.; de Kogel, C.; Demeulemeester, J.; Vets, S.; El Ashkar, S.; Malani, N.; Bushman, F.D.; Landuyt, B.; Husson, S.J.; Busschots, K.; Gijsbers, R.; Debyser, Z. The BET family of proteins targets moloney murine leukemia virus integration near transcription start sites. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.S.; Maetzig, T.; Maertens, G.N.; Sharif, A.; Rothe, M.; Weidner-Glunde, M.; Galla, M.; Schambach, A.; Cherepanov, P.; Schulz, T.F. Bromo- and extraterminal domain chromatin regulators serve as cofactors for murine leukemia virus integration. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 12721–12736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Larue, R.C.; Plumb, M.R.; Malani, N.; Male, F.; Slaughter, A.; Kessl, J.J.; Shkriabai, N.; Coward, E.; Aiyer, S.S.; et al. BET proteins promote efficient murine leukemia virus integration at transcription start sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12036–12041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, A.F. Interspersed repeats and other mementos of transposable elements in mammalian genomes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1999, 9, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.S.; Szak, S.T.; Boeke, J.D. Transcriptional disruption by the L1 retrotransposon and implications for mammalian transcriptomes. Nature 2004, 429, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Lopez, M.; Garcia-Perez, J.L. DNA transposons: Nature and applications in genomics. Curr. Genomics 2010, 11, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yant, S.R.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; Garrison, B.; Burgess, S.M.; Kay, M.A. High-resolution genome-wide mapping of transposon integration in mammals. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Wang, X.-F.; Ma, J.; He, X.-J.; Wang, X.-J.; Zhou, J.-H. Characterization of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus Integration in the Horse Genome. Viruses 2015, 7, 3241-3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7062769
Liu Q, Wang X-F, Ma J, He X-J, Wang X-J, Zhou J-H. Characterization of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus Integration in the Horse Genome. Viruses. 2015; 7(6):3241-3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7062769
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qiang, Xue-Feng Wang, Jian Ma, Xi-Jun He, Xiao-Jun Wang, and Jian-Hua Zhou. 2015. "Characterization of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus Integration in the Horse Genome" Viruses 7, no. 6: 3241-3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7062769
APA StyleLiu, Q., Wang, X.-F., Ma, J., He, X.-J., Wang, X.-J., & Zhou, J.-H. (2015). Characterization of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus Integration in the Horse Genome. Viruses, 7(6), 3241-3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7062769






