Coxsackievirus B4 Can Infect Human Peripheral Blood-Derived Macrophages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Monocyte-Derived Macrophages
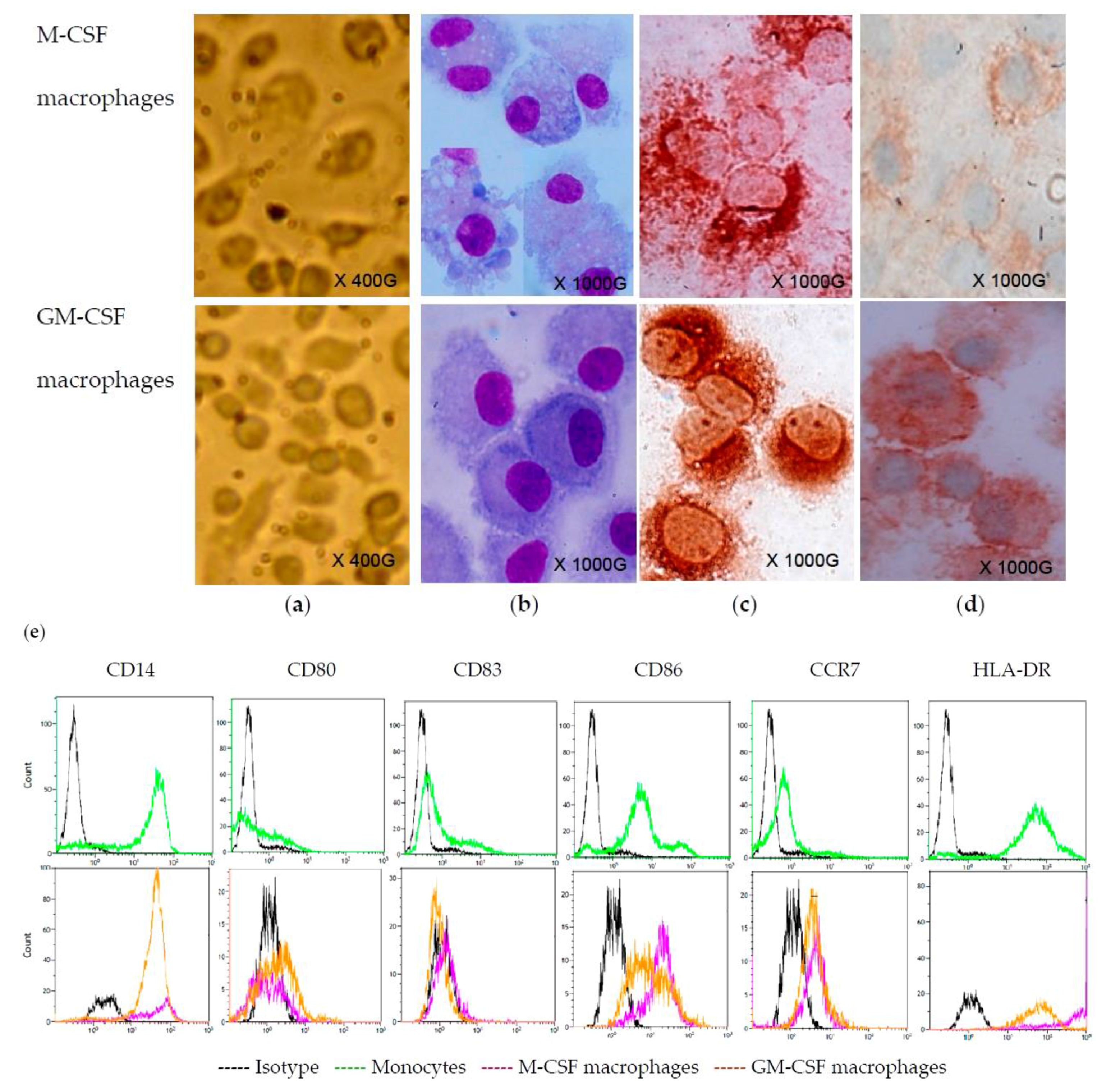
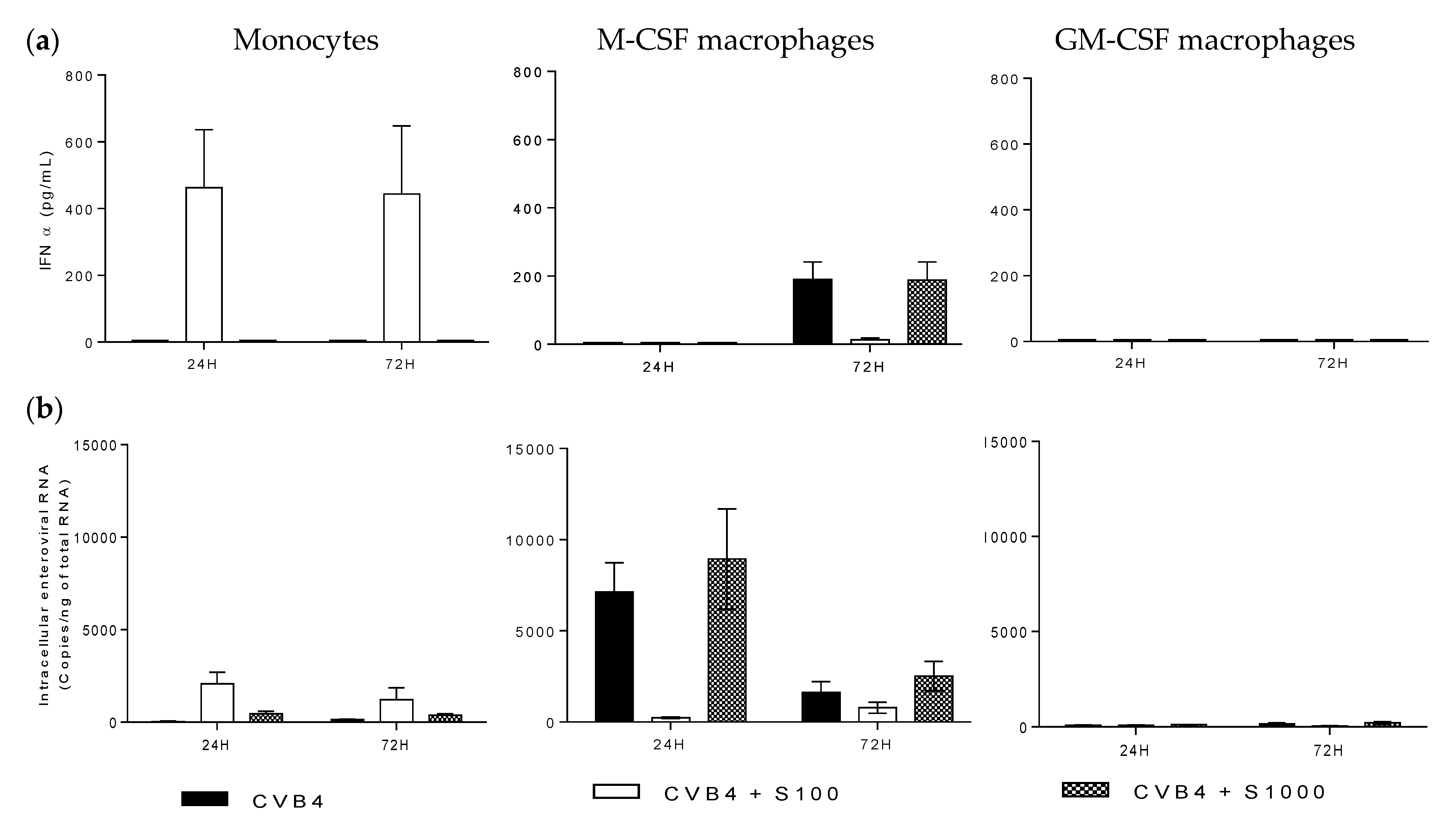
2.2. CVB4 Can Infect M-CSF-Treated Cells, but not GM-CSF-Treated Cells

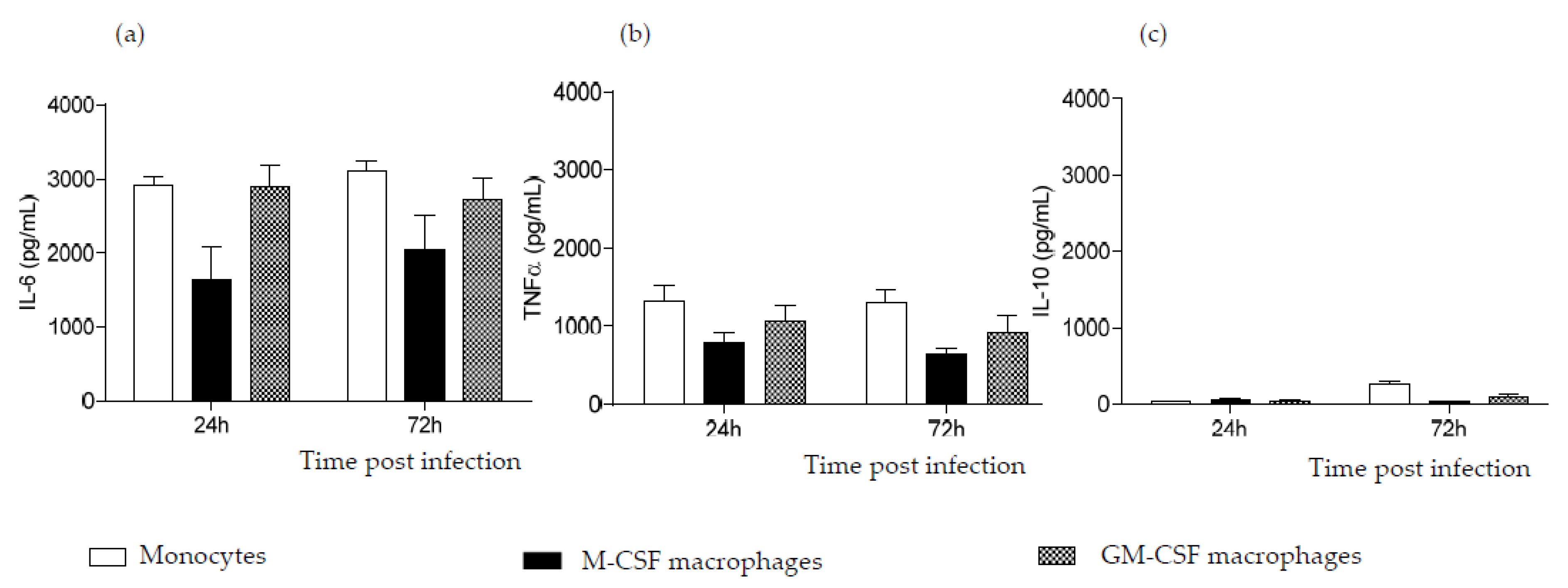
2.3. CVB4 Can Induce Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines MDM Induced with M-CSF and GM-CSF
2.4. CVB4 Can Replicate and Persist in M-CSF-Induced MDM

3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Virus Stocks
4.2. Peripheral Blood Monocyte-Derived Macrophages
4.3. Human Serum
4.4. May–Grunwald–Giemsa Staining and Immunocytochemistry
4.5. Flow Cytometry
4.6. Quantification of Cytokines
4.7. Viral Progeny
4.8. RNA Extraction
4.9. DNase Treatment
4.10. Enterovirus Real-Time Quantitative PCR
4.11. Quantification of Coxsackie and Adenovirus Receptor mRNA
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knowles, N.; Hovi, T; Hyypiä, T.; King, A.M.Q.; Lindberg, A.M.; Pallansch, M.A.; Palmenberg, A.C.; Simmonds, P.; Skern, T.; Stanway, G.; et al. Picornaviridae. In Virus Taxonomy: Classification and Nomenclature of Viruses: Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; King, A.M.Q., Adams, M.J., Carstens, E.B., Lefkowitz, E.J., Eds.; Publisher: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 855–880. [Google Scholar]
- Tapparel, C.; Siegrist, F.; Petty, T.J.; Kaiser, L. Picornavirus and enterovirus diversity with associated human diseases. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2013, 14, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, J.R. Pediatric group B coxsackievirus infections. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 323, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hober, D.; Alidjinou, E.K. Enteroviral pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes: Queries and answers. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 26, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hober, D.; Sauter, P. Pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes mellitus: Interplay between enterovirus and host. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Berg, A.-K.; Tuvemo, T.; Frisk, G. Enterovirus RNA is found in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in a majority of type 1 diabetic children at onset. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1964–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, B.M.; Bakkers, J.; Lanke, K.H.W.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Westerlaken, C.; Allebes, W.; Aanstoot, H.-J.; Bruining, G.J.; Adema, G.J.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; et al. Detection of enterovirus RNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of type 1 diabetic patients beyond the stage of acute infection. Viral Immunol. 2010, 23, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toniolo, A.; Maccari, G.; Federico, G.; Salvatoni, A.; Bianchi, G.; Baj, A. Are enterovirus infections linked to the early stages of Type 1 diabetes? Abstract. In Proceedings of the American Society of Microbiology Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 23–27 May 2010.
- Salvatoni, A.; Baj, A.; Bianchi, G.; Federico, G.; Colombo, M.; Toniolo, A. Intrafamilial spread of enterovirus infections at the clinical onset of type 1 diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2013, 14, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alidjinou, E.K.; Chehadeh, W.; Weill, J.; Vantyghem, M.-C.; Stuckens, C.; Decoster, A.; Hober, C.; Hober, D. Monocytes of patients with type 1 diabetes harbour enterovirus RNA. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 45, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hober, D.; Chehadeh, W.; Bouzidi, A.; Wattré, P. Antibody-dependent enhancement of coxsackievirus B4 infectivity of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells results in increased interferon-α synthesis. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 184, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goffard, A.; Alidjinou, E.K.; Sané, F.; Choteau, L.; Bouquillon, C.; Caloone, D.; Lobert, P.E.; Hober, D. Antibodies enhance the infection of phorbol-ester-differentiated human monocyte-like cells with coxsackievirus B4. Microbes Infect. Inst. Pasteur 2013, 15, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hober, D.; Chehadeh, W.; Weill, J.; Hober, C.; Vantyghem, M.-C.; Gronnier, P.; Wattré, P. Circulating and cell-bound antibodies increase coxsackievirus B4-induced production of IFN-α by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with type 1 diabetes. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 2169–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chehadeh, W.; Lobert, P.-E.; Sauter, P.; Goffard, A.; Lucas, B.; Weill, J.; Vantyghem, M.-C.; Alm, G.; Pigny, P.; Hober, D. Viral protein VP4 is a target of human antibodies enhancing coxsackievirus B4- and B3-induced synthesis of alpha interferon. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 13882–13891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alidjinou, E.K.; Sané, F.; Engelmann, I.; Hober, D. Serum-dependent enhancement of coxsackievirus B4-induced production of IFNα, IL-6 and TNFα by peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 5020–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Pamer, E.G. Monocyte recruitment during infection and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J.; Wynn, T.A. Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Y.; Akagawa, K.; Kimoto, H.; Suzuki, K.; Iwasaki, M.; Yasuda, S.; Häusser, G.; Hultgren, C.; Meyerhans, A.; Takemori, T. Monocyte-derived cultured dendritic cells are susceptible to human immunodeficiency virus infection and transmit virus to resting T cells in the process of nominal antigen presentation. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 4544–4547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Graaff, P.M.A.; de Jong, E.C.; van Capel, T.M.; van Dijk, M.E.A.; Roholl, P.J.M.; Boes, J.; Luytjes, W.; Kimpen, J.L.L.; van Bleek, G.M. Respiratory syncytial virus infection of monocyte-derived dendritic cells decreases their capacity to activate CD4 T cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 5904–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Nouën, C.; Munir, S.; Losq, S.; Winter, C.C.; McCarty, T.; Stephany, D.A.; Holmes, K.L.; Bukreyev, A.; Rabin, R.L.; Collins, P.L.; et al. Infection and maturation of monocyte-derived human dendritic cells by human respiratory syncytial virus, human metapneumovirus, and human parainfluenza virus type 3. Virology 2009, 385, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawle, D.J.; Setoh, Y.X.; Edmonds, J.H.; Khromykh, A.A. Comparison of attenuated and virulent West Nile virus strains in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells as a model of initial human infection. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, M.; Schulte, B.M.; Toonen, L.W.J.; de Bruijni, M.A.M.; Galama, J.M.D.; Adema, G.J.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M. Echovirus infection causes rapid loss-of-function and cell death in human dendritic cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, B.M.; Kers-Rebel, E.D.; Prosser, A.C.; Galama, J.M.D.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Adema, G.J. Differential susceptibility and response of primary human myeloid BDCA1(+) dendritic cells to infection with different Enteroviruses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosser, D.M.; Edwards, J.P. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willcox, A.; Richardson, S.J.; Bone, A.J.; Foulis, A.K.; Morgan, N.G. Analysis of islet inflammation in human type 1 diabetes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 155, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, W.; Liu, N.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Jin, Y.; Duan, Z. Excessive proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine responses of human monocyte-derived macrophages to enterovirus 71 infection. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElroy, A.K.; Nichol, S.T. Rift Valley fever virus inhibits a pro-inflammatory response in experimentally infected human monocyte derived macrophages and a pro-inflammatory cytokine response may be associated with patient survival during natural infection. Virology 2012, 422, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wati, S.; Li, P.; Burrell, C.J.; Carr, J.M. Dengue virus (DV) replication in monocyte-derived macrophages is not affected by tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and DV infection induces altered responsiveness to TNF-alpha stimulation. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10161–10171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauter, P.; Lobert, P.-E.; Lucas, B.; Varela-Calvino, R.; Alm, G.; Wattre, P.; Hober, D. Role of the capsid protein VP4 in the plasma-dependent enhancement of the Coxsackievirus B4E2-infection of human peripheral blood cells. Virus Res. 2007, 125, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, D.; Shepherd, N.; Lan, J.; Hu, N.; Amet, T.; Yang, K.; Desai, M.; Yu, Q. Primary human macrophages serve as vehicles for vaccinia virus replication and dissemination. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 6819–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaguin, M.; Houlbert, N.; Fardel, O.; Lecureur, V. Polarization profiles of human M-CSF-generated macrophages and comparison of M1-markers in classically activated macrophages from GM-CSF and M-CSF origin. Cell. Immunol. 2013, 281, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey-Giraud, F.; Hafner, M.; Ries, C.H. In vitro generation of monocyte-derived macrophages under serum-free conditions improves their tumor promoting functions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagawa, K.S. Functional heterogeneity of colony-stimulating factor-induced human monocyte-derived macrophages. Int. J. Hematol. 2002, 76, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagawa, K.S.; Komuro, I.; Kanazawa, H.; Yamazaki, T.; Mochida, K.; Kishi, F. Functional heterogeneity of colony-stimulating factor-induced human monocyte-derived macrophages. Respirology 2006, 11, S32–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellora, F.; Castriconi, R.; Dondero, A.; Reggiardo, G.; Moretta, L.; Mantovani, A.; Moretta, A.; Bottino, C. The interaction of human natural killer cells with either unpolarized or polarized macrophages results in different functional outcomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21659–21664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geissmann, F.; Manz, M.G.; Jung, S.; Sieweke, M.H.; Merad, M.; Ley, K. Development of monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Science 2010, 327, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.P.; Coyne, C.B.; Bergelson, J.M. Dynamin- and lipid raft-dependent entry of decay-accelerating factor (DAF)-binding and non-DAF-binding coxsackieviruses into nonpolarized cells. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 11064–11077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, S.; Akagawa, K.; Honda, M.; Yokota, Y.; Takebe, Y.; Takemori, T. Suppression of HIV replication in human monocyte-derived macrophages induced by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 1995, 11, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, P.; Thiruppathi, M.; Elshabrawy, H.A.; Alharshawi, K.; Kumar, P.; Prabhakar, B.S. GM-CSF: An immune modulatory cytokine that can suppress autoimmunity. Cytokine 2015, 75, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, W.Y.; Cheung, A.C.Y.; Tung, C.K.C.; Yeung, A.C.M.; Ngai, K.L.K.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Chan, P.K.S.; Tsui, S.K.W. miR-466 is putative negative regulator of Coxsackie virus and Adenovirus Receptor. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alidjinou, E.K.; Sané, F.; Trauet, J.; Copin, M.-C.; Hober, D. Coxsackievirus B4 Can Infect Human Peripheral Blood-Derived Macrophages. Viruses 2015, 7, 6067-6079. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7112924
Alidjinou EK, Sané F, Trauet J, Copin M-C, Hober D. Coxsackievirus B4 Can Infect Human Peripheral Blood-Derived Macrophages. Viruses. 2015; 7(11):6067-6079. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7112924
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlidjinou, Enagnon Kazali, Famara Sané, Jacques Trauet, Marie-Christine Copin, and Didier Hober. 2015. "Coxsackievirus B4 Can Infect Human Peripheral Blood-Derived Macrophages" Viruses 7, no. 11: 6067-6079. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7112924
APA StyleAlidjinou, E. K., Sané, F., Trauet, J., Copin, M.-C., & Hober, D. (2015). Coxsackievirus B4 Can Infect Human Peripheral Blood-Derived Macrophages. Viruses, 7(11), 6067-6079. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7112924





