Detection and Characterization of a Novel Reassortant Mammalian Orthoreovirus in Bats in Europe
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sampling
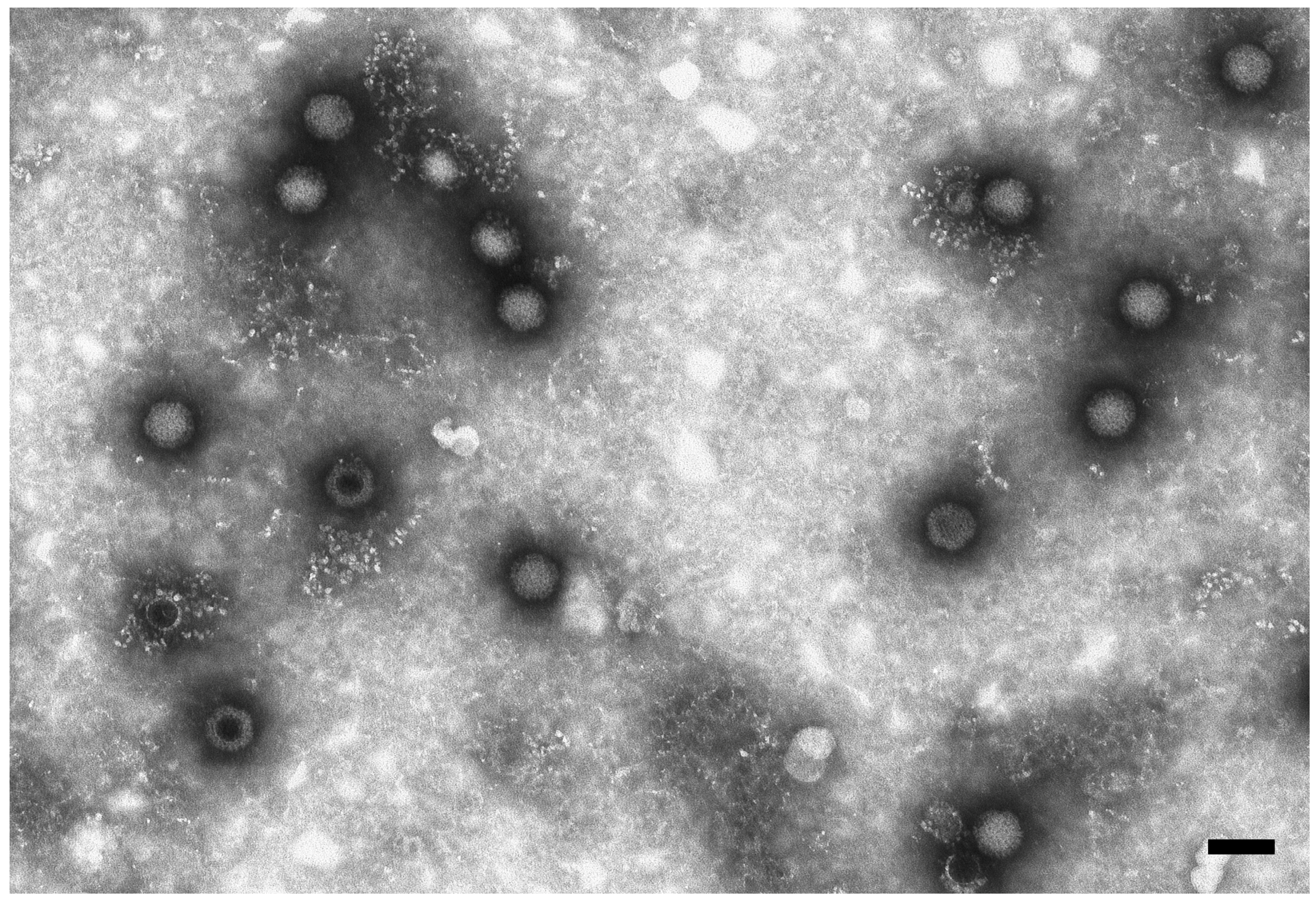
2.2. Virological Tests
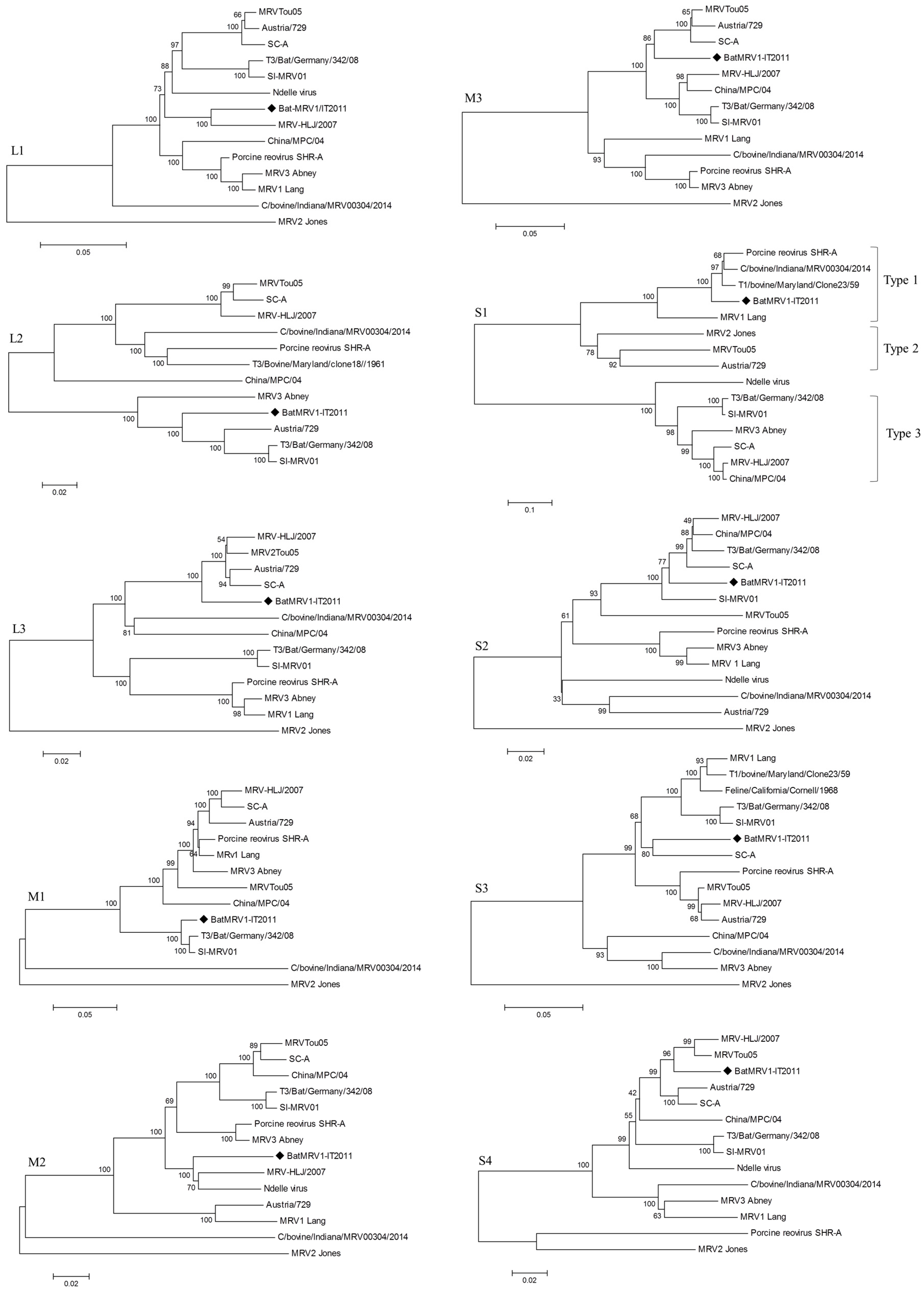
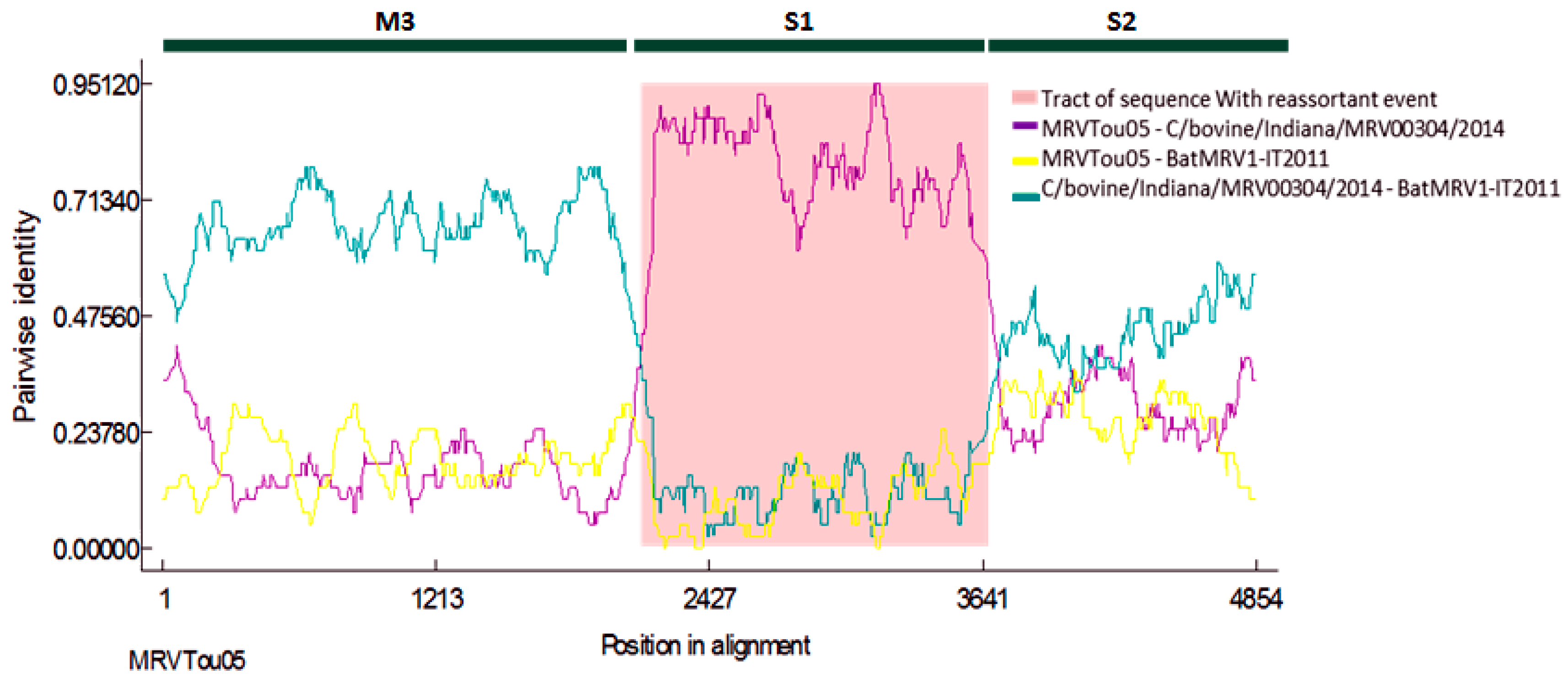
2.3. Genome Characterization of BatMRV1-IT2011
| BatMRV1-IT2011 | Similarity (%) | MRV Strain | Serotype | Host | Disease | Country | GenBank Accession No. | Encoding Protein and Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 93 | MRV-HLJ/2007 | 3 | Pig | Fever, respiratory illness | China | HQ642769.1 | λ3—RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| 90 | Porcine reovirus SHR-A | 1 | Pig | NA | China | JX415466.1 | ||
| L2 | 91 | Austria/729 | 2 | Pig | Encephalitis | Austria | JN799427.1 | λ2—Guanylyltransferase, methyltransferase |
| 90 | T3/bat/Germany/342/08 | 3 | Bat | Hemorrhagic enteritis | Germany | JQ412756.1 | ||
| 90 | SI-MRV01 | 3 | Human | Acute gastroenteritis | Slovenia | KF154725.1 | ||
| L3 | 95 | MRVTou05 | 2 | Human | Encephalitis | France | GU196308.1 | λ1—Helicase, binds dsRNA, NTPase |
| 94 | MRV-HLJ/2007 | 3 | Pig | Fever, respiratory illness | China | HQ642769.1 | ||
| M1 | 98 | T3/bat/Germany/342/08 | 3 | Bat | Hemorrhagic enteritis | Germany | JQ412758.1 | μ2—NTPase |
| 98 | SI-MRV01 | 3 | Human | Acute gastroenteritis | Slovenia | KF154727.1 | ||
| M2 | 92 | MRV-HLJ/2007 | 3 | Pig | Fever, respiratory illness | China | HQ642773.1 | μ1—Cell penetration, apoptosis |
| 92 | 4 Ndelle virus | Putative 4 | Mouse | NA | Cameroon | AF368034.1 | ||
| M3 | 93 | MRVTou05 | 2 | Human | Encephalitis | France | GU196314.1 | μNS—Nucleates viral inclusion bodies |
| 92 | Austria/729 | 2 | Pig | Encephalitis | Austria | JN799425.1 | ||
| S1 | 90 | T1/bovine/Maryland/Clone23/59 | 1 | Bovine | NA | USA | AY862134.1 | σ1, σ1s—Viral attachment |
| 88 | C/bovine/Indiana/MRV00304/2014 | 1 | Bovine | Diarrhea | USA | KJ676385.1 | ||
| S2 | 95 | China/MPC/04 | 3 | Civet | NA | China | GQ468273.1 | σ2—Inner capsid structural protein |
| 94 | T3/bat/Germany/342/08 | 3 | Bat | Hemorrhagic enteritis | Germany | JQ412762.1 | ||
| 94 | SI-MRV01 | 3 | Human | Acute gastroenteritis | Slovenia | KF154731.1 | ||
| 94 | MRV-HLJ/2007 | 3 | Pig | Fever, respiratory illness | China | HQ642776.1 | ||
| S3 | 91 | SC-A | 3 | Pig | Diarrhea | China | DQ411553.1 | σ2—ssRNA-binding |
| 91 | Feline/California/Cornell/1968 | 3 | Cat | NA | USA | U35362 | ||
| S4 | 95 | MRVTou05 | 2 | Human | Encephalitis | France | GU196313.1 | σ3—DS-RNA binding, modulation of cellular interferon response |
| 95 | MRV-HLJ/2007 | 2 | Pig | Fever, respiratory illness | China | HQ642778.1 |
2.4. VNTs for Virus Typing and Serology
| Immune Serum | Virus (100 TCID50/25 µL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRV1 Lang | MRV2 Jones | MRV3 Abney | BatMRV1-IT2011 | |
| MRV negative (rabbit) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MRV negative (guinea pig) | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| MRV1 Lang (guinea pig) | 1280 | 80 | 40 | 1280 |
| MRV2 Jones (rabbit) | 5 | 80 | 10 | 20 |
| MRV3 Abney (guinea pig) | 0 | 0 | 320 | 20 |
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling

4.2. Viral Isolation
4.3. Electron Microscopy
4.4. Molecular Testing and Analysis
4.5. Virus Neutralization Test
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- References Tyler, K.L. Mammalian Reoviruses. In Fields Virology, 4th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001; pp. 1729–1745. [Google Scholar]
- Sabin, A.B. Reoviruses: A new group of respiratory and enteric viruses formerly classified as ECHO type 10 is described. Science 1959, 130, 1387–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nibert, M.L.; Dermody, T.S.; Fields, B.N. Structure of the reovirus cell-attachment protein; a model for the domain organization of sigma 1. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 2976–2989. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weiner, H.L.; Fields, B.N. Neutralization of reovirus: The gene responsible for the neutralization antigen. J. Exp. Med. 1977, 146, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassel-Duby, R.; Spriggs, D.R.; Tyler, K.L.; Fields, B.N. Identification of attenuating mutations on the reovirus type 3 S1 double-stranded RNA segment with a rapid sequencing technique. J. Virol. 1986, 60, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dermody, T.S.; Nibert, M.L.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Fields, B.N. Sequence diversity in S1 genes and S1 translation products of 11 serotype 3 reovirus strains. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 4842–4850. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duncan, R. Extensive sequence divergence and phylogenetic relationships between the fusogenic and nonfusogenic orthoreovirus: A species proposal. Virology 1999, 260, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leary, T.P.; Erker, J.C.; Chalmers, M.L.; Wetzel, J.D.; Desai, S.M.; Mushahwar, I.K.; Dermody, T.S. Detection of reovirus by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction using primers corresponding to conserved regions of the viral L1 genome segment. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouattara, L.A.; Barin, F.; Barthez, M.A.; Bonnaud, B.; Roingeard, P.; Goudeau, A.; Castelnau, P.; Vernet, G.; Paranhos-Baccala, G.; Komurian-Pradel, F. Novel human reovirus isolated from children with acute necrotizing encephalopathy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.B.; Voon, K.; Crameri, G.; Tan, H.S.; Rosli, J.; McEachern, J.A.; Suluraju, S.; Yu, M.; Wang, L.F. Identification and characterization of a new orthoreovirus from patients with acute respiratory infections. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, K.B.; Voon, K.; Yu, M.; Keniscope, C.; Abdul Rasid, K.; Wang, L.F. Investigation of a potential zoonotic transmission of orthoreovirus associated with acute influenza-like illness in an adult patient. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Lau, C.S.; Lai, A.; Ho, E.; Leung, P.; Chan, F.; Wong, A.; Lim, W. A novel reovirus isolated from a patient with acute respiratory disease. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 45, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, L.; Embree, J.; Hazelton, P.; Wells, B.; Coombs, R.T. Reovirus type 2 isolated from cerebrospinal fluid. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2004, 373, 373–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, K.L.; Barton, E.S.; Ibach, M.L.; Robinson, C.; Campbell, J.A.; O’Donnell, S.M.; Valyi-Nagy, T.; Clarke, P.; Wetzel, J.D.; Dermody, T.S. Isolation and molecular characterization of novel type 3 reovirus from a child with meningitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 1664–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyer, A.; Gutiérrez-Aguire, I.; Kolenc, M.; Koren, S.; Kutnjak, D.; Pokorn, M.; Poljšak-Prijatelj, M.; Racki, N.; Ravnikar, M.; Sagadin, M.; et al. High similarity of novel orthoreovirus detected in a child hospitalized with acute gastroenteritis to mammalian orthoreoviruses found in bats in Europe. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3818–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelli, D.; Moreno, A.; Lavazza, A.; Bresaola, M.; Canelli, E.; Boniotti, M.B.; Cordioli, P. Identification of Mammalian orthoreovirus type 3 in Italian bats. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, C.; Lesnik, R.; Brinkmann, A.; Ebinger, A.; Radonic’, A.; Nitsche1, A.; Mu hldorfer, K.; Wibbelt, G.; Kurth, A. Isolation and characterization of three Mammalian orthoreoviruses from European bats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanappa, A.T.; Sooryanarain, H.; Deventhiran, J.; Cao, D.; Venkatachalam, B.A.; Kambiranda, D.; LeRoith, T.; Heffron, C.L.; Lindstrom, N.; Hall, K.; et al. A Novel pathogenic Mammalian orthoreovirus from diarrheic pigs and swine blood meal in the United States. mBio 2015, 6, e00593–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lorusso, A.; Teodori, L.; Leone, A.; Marcacci, M.; Mangone, I.; Orsini, M.; Capobianco-Dondona, A.; Camma’, C.; Monaco, F.; Savini, G. A new member of the pteropine orthoreovirus species isolated from fruit bats imported to Italy. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 30, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Wollenberg, D.J.M.; Dautzenberg, J.C.I.; van den Hengel, S.K.; Cramer, S.J.; de Groot, R.J.; Hoeben, R.C. Isolation of reovirus T3D mutants capable of infecting human tumor cells independent of junction adhesion molecule-A. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calisher, C.H.; Childs, J.E.; Field, H.E.; Holmes, K.V.; Schountz, T. Bats: Important reservoir hosts of emerging virus. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 19, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelli, D.; Moreno, A.; Prosperi, A.; Lavazza, A.; Boniotti, B.; Raffini, E.; Cordioli, P. Molecular characterization of orthoreovirus isolated from bats, dogs and cats. In Proceedings of the 8th Annual Meeting Epizone, Copenhagen, Denmark, 23–25 September 2014.
- Wang, L.; Fu, S.; Cao, L.; Lei, W.; Cao, Y.; Song, J.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Yang, W.; et al. Isolation and identification of a natural reassortant Mammalian orthoreovirus from least horseshoe bat in china. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodder, W.J.; de Roda Husman, A.M. Presence of noroviruses and other enteric viruses in sewage and surface waters in The Netherlands. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodder, W.J.; van den Berg, H.H.; Rutjes, S.A.; de Roda Husman, A.M. Presence of enteric viruses in source waters for drinking water production in The Netherlands. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5965–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinner, M.L.; di Giovanni, G.D. Detection and identification of mammalian reoviruses in surface water by combined cell culture and reverse transcription-PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3016–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irving, L.G.; Smith, F.A. One-year survey of enteroviruses, adenoviruses, and reoviruses isolated from effluent at an activated-sludge purification plant. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1981, 41, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fukumi, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Ishida, M.; Saito, H. Serological epidemiology of reovirus infection. J. Med. Sci. 1969, 22, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, T.; Kato, H. Reovirus antibody patterns in dogs: A trial for the application of principal component analysis to seroepidemiology. Natl. Inst. Anim. Health Q 1975, 15, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Osterhaus, A.; Berghuis-De Vries, J.; Steur, K. Antiviral antibodies in dogs in the Netherlands. Zentralbl. Veterinärmed. B. 1977, 24, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, L.; Abinanti, F.R.; Hovis, J.F. Further observations on the natural infection of cattle with reoviruses. Am. J. Hyg. 1963, 77, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hirahara, T.; Yasuhara, H.; Matsui, O.; Kodama, K.; Nakai, M.; Sasaki, N. Characteristics of reovirus type 1 from the respiratory tract of pigs in Japan. J. Vet. Sci. 1988, 50, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.R.; Agarwal, S.C. Sero-epidemiological study of reovirus infection amongst the normal population of the Chandigarh area-northern India. J. Hyg. 1968, 66, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor-Robinson, D. Respiratory virus antibodies in human sera from different regions of the world. Bull. World Health Organ. 1965, 32, 833–847. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lavazza, A.; Pascucci, S.; Gelmetti, D. Rod-shaped virus-like particles in intestinal contents of three avian species. Vet. Rec. 1990, 126, 581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- NCBI server. Available online: http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 20 July 2015).
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evolution. 2015, pp. 1–5. Available online: http://web.cbio.uct.ac.za/~darren/rdp.html (accessed on 20 July 2015). [CrossRef]
- Posada, D. Evaluation of methods for detecting recombination from DNA sequences: Empirical data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lelli, D.; Moreno, A.; Steyer, A.; Nagliˇc, T.; Chiapponi, C.; Prosperi, A.; Faccin, F.; Sozzi, E.; Lavazza, A. Detection and Characterization of a Novel Reassortant Mammalian Orthoreovirus in Bats in Europe. Viruses 2015, 7, 5844-5854. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7112908
Lelli D, Moreno A, Steyer A, Nagliˇc T, Chiapponi C, Prosperi A, Faccin F, Sozzi E, Lavazza A. Detection and Characterization of a Novel Reassortant Mammalian Orthoreovirus in Bats in Europe. Viruses. 2015; 7(11):5844-5854. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7112908
Chicago/Turabian StyleLelli, Davide, Ana Moreno, Andrej Steyer, Tina Nagliˇc, Chiara Chiapponi, Alice Prosperi, Francesca Faccin, Enrica Sozzi, and Antonio Lavazza. 2015. "Detection and Characterization of a Novel Reassortant Mammalian Orthoreovirus in Bats in Europe" Viruses 7, no. 11: 5844-5854. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7112908
APA StyleLelli, D., Moreno, A., Steyer, A., Nagliˇc, T., Chiapponi, C., Prosperi, A., Faccin, F., Sozzi, E., & Lavazza, A. (2015). Detection and Characterization of a Novel Reassortant Mammalian Orthoreovirus in Bats in Europe. Viruses, 7(11), 5844-5854. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7112908








