Entry of Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus into Human Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells by Ultrasound
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells
2.2. Viral Infection
2.3. Ultrasound Exposure
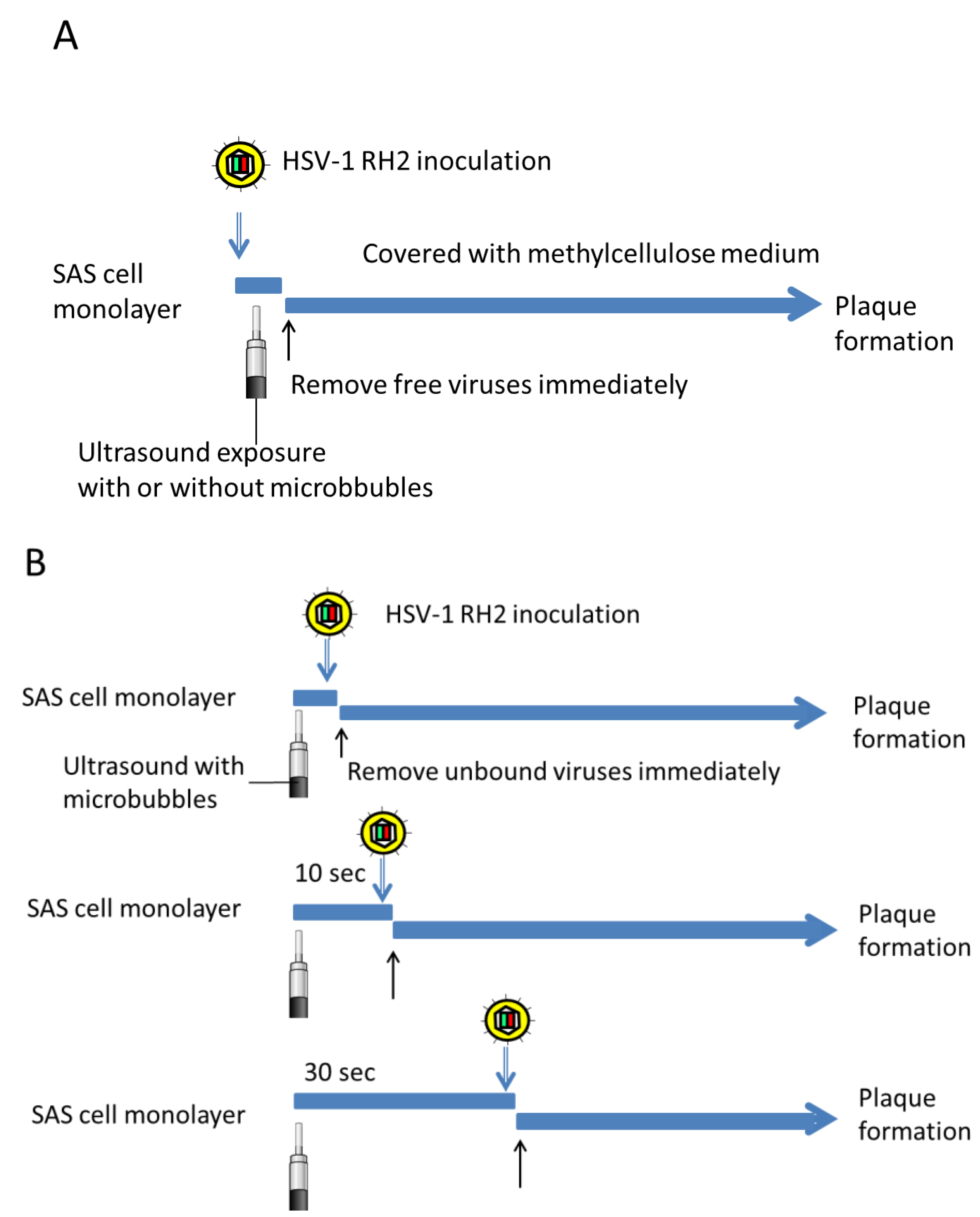
2.4. Plaque Formation in Combination with Ultrasound
2.5. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyl-Tetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Assay
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Ultrasound on the Growth of Oral SCC Cells
3.2. Effects of Ultrasound Exposure Immediately after Viral Inoculation on HSV-1 Plaque Formation and Cell Viability


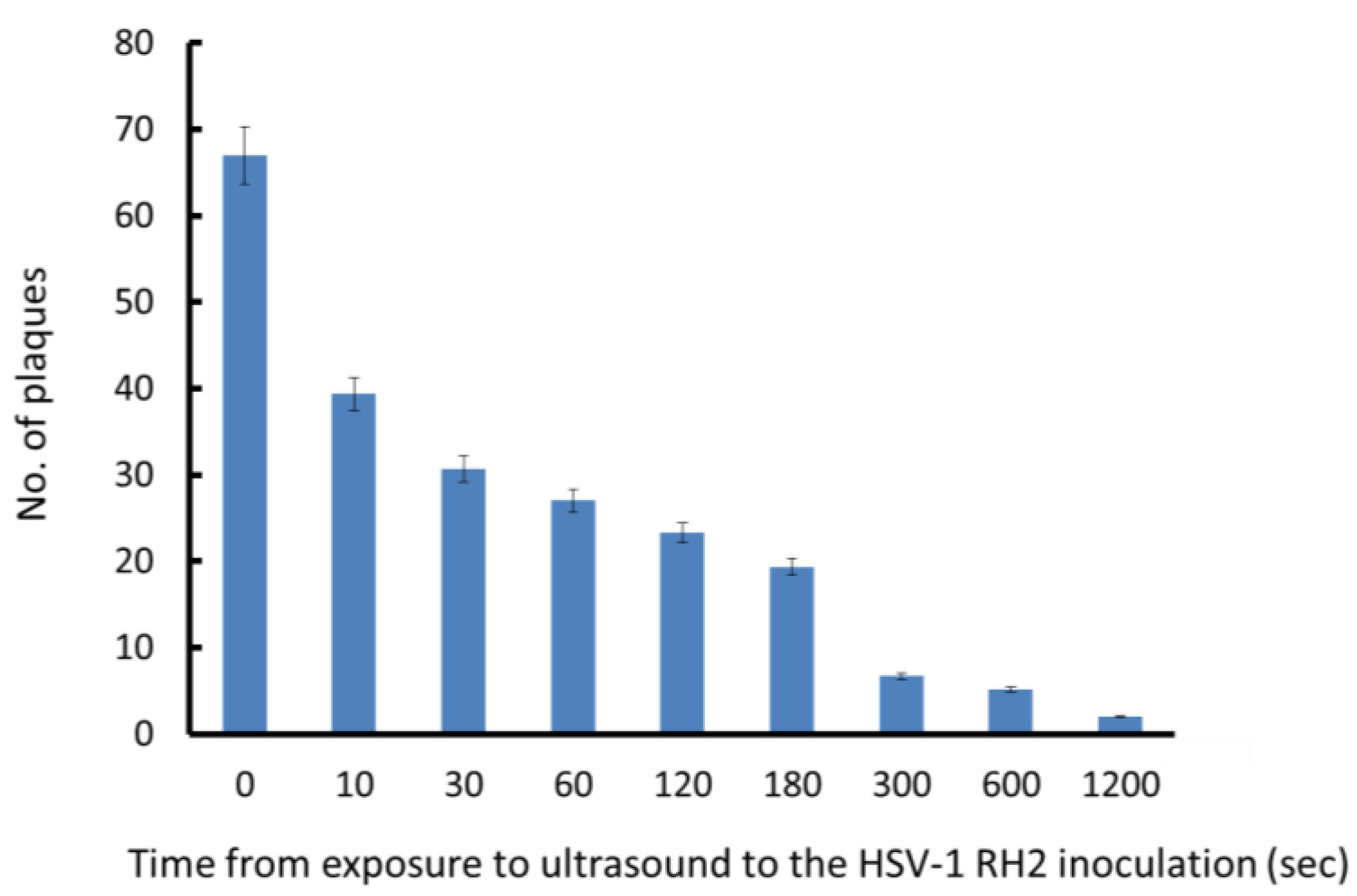
3.3. Effects of the Interval from Ultrasound Exposure to Viral Inoculation on HSV-1 Plaque Formation
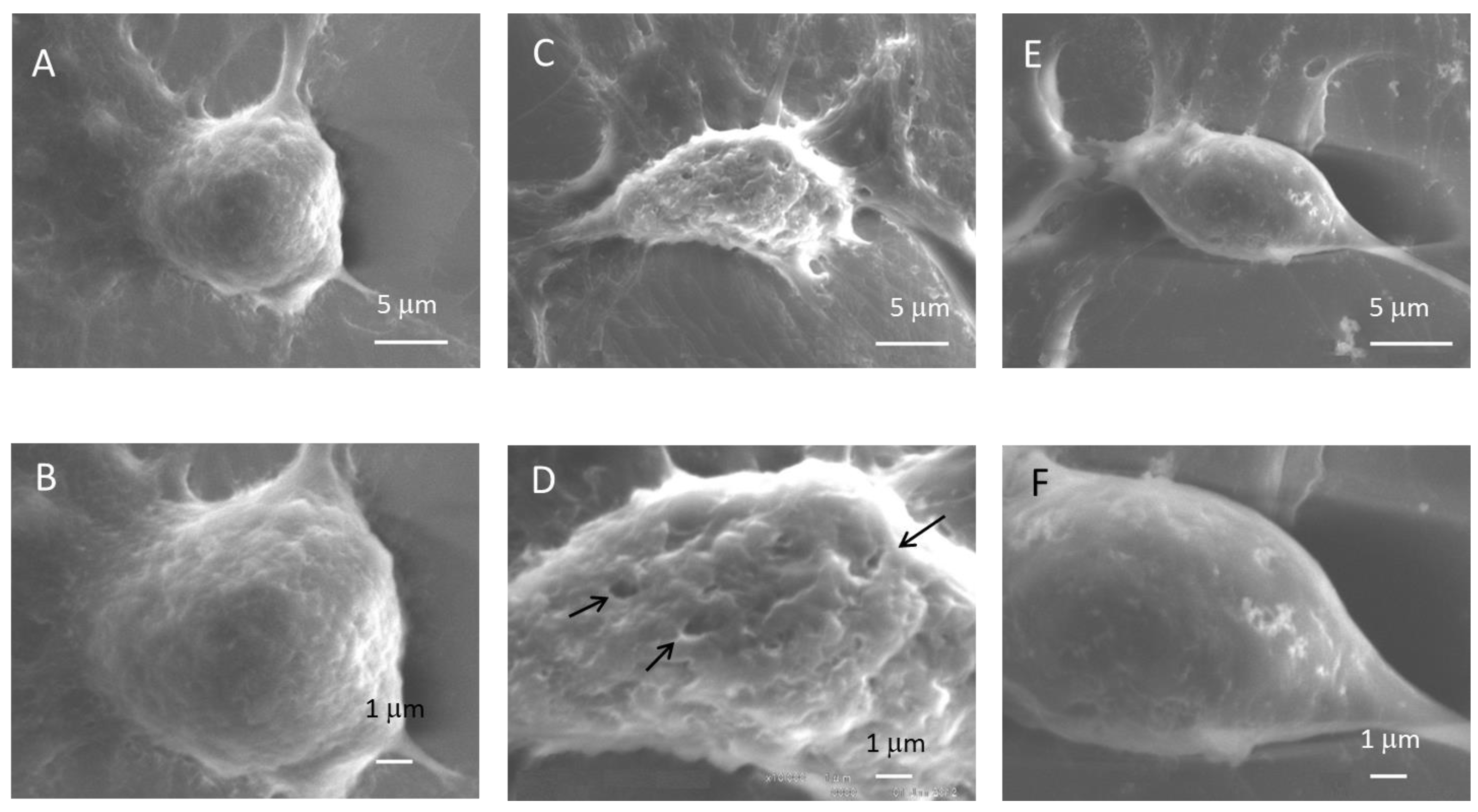
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscope of Oral SCC Cells Exposed to Ultrasound
4. Discussion
4.1. Increase of Virus Entry by Ultrasound in the Presence or Absence of Microbubbles
4.2. Scanning Electron Microscope of Oral SCC Cells
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, B.L.; Robinson, M.; Han, Z.Q.; Branston, R.H.; English, C.; Reay, P.; McGrath, Y.; Thomas, S.K.; Thornton, M.; Bullock, P.; Love, C.A.; et al. ICP34.5 deleted herpes simplex virus with enhanced oncolytic, immune stimulating, and anti-tumour properties. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senzer, N.N.; Kaufman, H.L.; Amatruda, T.; Nemunaitis, M.; Reid, T.; Daniels, G.; Gonzalez, R.; Glaspy, J.; Whitman, E.; Harrington, K.; et al. Phase II clinical trial of a granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-encoding, second-generation oncolytic herpesvirus in patients with unresectable metastatic melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5763–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, K.J.; Hingorani, M.; Tanay, M.A.; Hickey, J.; Bhide, S.A.; Clarke, P.M.; Renouf, L.C.; Thway, K.; Sibtain, A.; McNeish, I.A.; et al. Phase I/II study of oncolytic HSVGM-CSF in combination with radiotherapy and cisplatin in untreated stage III/IV squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 4005–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, Y.; Baxter, L.T.; Jain, R.K. Interstitial pressure gradients in tissue-isolated and subcutaneous tumors: Implications for therapy. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 4478–4484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.K. Normalization of tumor vasculature: An emerging concept inantiangiogenic therapy. Science 2005, 307, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozaki, T.; Ogawa, R.; Feril, L.B., Jr.; Kagiya, G.; Fuse, H.; Kondo, T. Enhancement of ultrasound-mediated gene transfection by membrane modification. J. Gene Med. 2003, 5, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenkel, V. Ultrasound mediated delivery of drugs and genes to solid tumors. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1193–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernot, S.; Klibanov, A.L. Microbubbles in ultrasound-triggered drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Aoi, A.; Horie, S.; Tomita, N.; Mori, S.; Morikawa, H.; Matsumura, Y.; Vassaux, G.; Kodama, T. Low-intensity ultrasound and microbubbles enhance the antitumor effect of cisplatin. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 2525–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintani, M.; Takahashi, G.; Hamada, M.; Okunaga, S.; Iwai, S.; Yura, Y. Effect of ultrasound on herpes simplex virus infection in cell culture. Virol. J. 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okunaga, S.; Takasu, A.; Meshii, N.; Imai, T.; Hamada, M.; Iwai, S.; Yura, Y. Ultrasound as a method to enhance antitumot ability of oncolytic herpes simplex virus for head and neck cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.L.; Du, L.F.; Wang, H.P.; Gu, Q. Comparative analysis of the effects of ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction on recombinant adeno-associated virus- and plasmid-mediated transgene expression in human retinal pigment epithelium cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2009, 2, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.L.; Zheng, X.Z.; Wang, H.P.; Li, F.; Wu, Y.; Du, L.F. Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction enhances AAV-mediated gene transfection in human RPE cells in vitro and rat retina in vivo. Gene Ther. 2009, 16, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaoka, H.; Takahashi, G.; Ogawa, F.; Imai, T.; Iwai, S.; Yura, Y. A novel fusogenic herpes simplex virus for oncolytic virotherapy of squamous cell carcinoma. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, G.; Meshii, N.; Hamada, M.; Iwai, S.; Yura, Y. Sequence of a fusogenic herpes simplex virus RH2 for oncolytic virotherapy. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczuk, L.; Boudinet, M.; El Sanharawi, M.; Touchard, E.; Naud, M.C.; Saïed, A.; Jeanny, J.C.; Behar-Cohen, F.; Laugier, P. In vivo gene transfer into the ocular ciliary muscle mediated by ultrasound and microbubbles. Ultrasound Med. Bol. 2011, 37, 1814–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, T.; Tomita, Y.; Koshiyama, K.; Blomley, M.J. Transfection effect of microbubbles on cells in superposed ultrasound waves and behavior of cavitation bubble. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2006, 32, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spear, P.G.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H. Three classes of cell surface receptors for alphaherpesvirus entry. Virology 2000, 275, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dollery, S.J.; Delboy, M.G.; Nicola, A.V. Low pH-induced conformational change in herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 3759–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geers, B.; Lentacker, I.; Alonso, A.; Sanders, N.N.; Demeester, J.; Meairs, S.; de Smedt, S.C. Elucidating the mechanisms behind sonoporation with adeno-associated virus-loaded microbubbles. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 2244–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehier-Humbert, S.; Bettinger, T.; Yan, F.; Guy, R.H. Plasma membrane poration induced by ultrasound exposure: Implication for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 104, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Kumon, R.E.; Cui, J.; Deng, C.X. The size of sonoporation pores on the cell membrane. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2009, 35, 1756–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Tominaga, K.; Iwanaga, K.; Nagao, F.; Habu, M.; Tsujisawa, T.; Seta, Y.; Toyoshima, K.; Fukuda, J.; Nishihara, T. Targeted drug delivery system for oral cancer therapy using sonoporation. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2009, 38, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okunaga, S.; Takasu, A.; Meshii, N.; Imai, T.; Hamada, M.; Iwai, S.; Yura, Y. Entry of Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus into Human Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells by Ultrasound. Viruses 2015, 7, 5610-5618. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7102890
Okunaga S, Takasu A, Meshii N, Imai T, Hamada M, Iwai S, Yura Y. Entry of Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus into Human Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells by Ultrasound. Viruses. 2015; 7(10):5610-5618. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7102890
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkunaga, Shusuke, Ayako Takasu, Noritoshi Meshii, Tomoaki Imai, Masakagu Hamada, Soichi Iwai, and Yoshiaki Yura. 2015. "Entry of Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus into Human Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells by Ultrasound" Viruses 7, no. 10: 5610-5618. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7102890
APA StyleOkunaga, S., Takasu, A., Meshii, N., Imai, T., Hamada, M., Iwai, S., & Yura, Y. (2015). Entry of Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus into Human Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells by Ultrasound. Viruses, 7(10), 5610-5618. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7102890




