Vaccination against δ-Retroviruses: The Bovine Leukemia Virus Paradigm
Abstract
:1. Clinical Course

2. Molecular Mechanisms of Infection and Pathogenesis
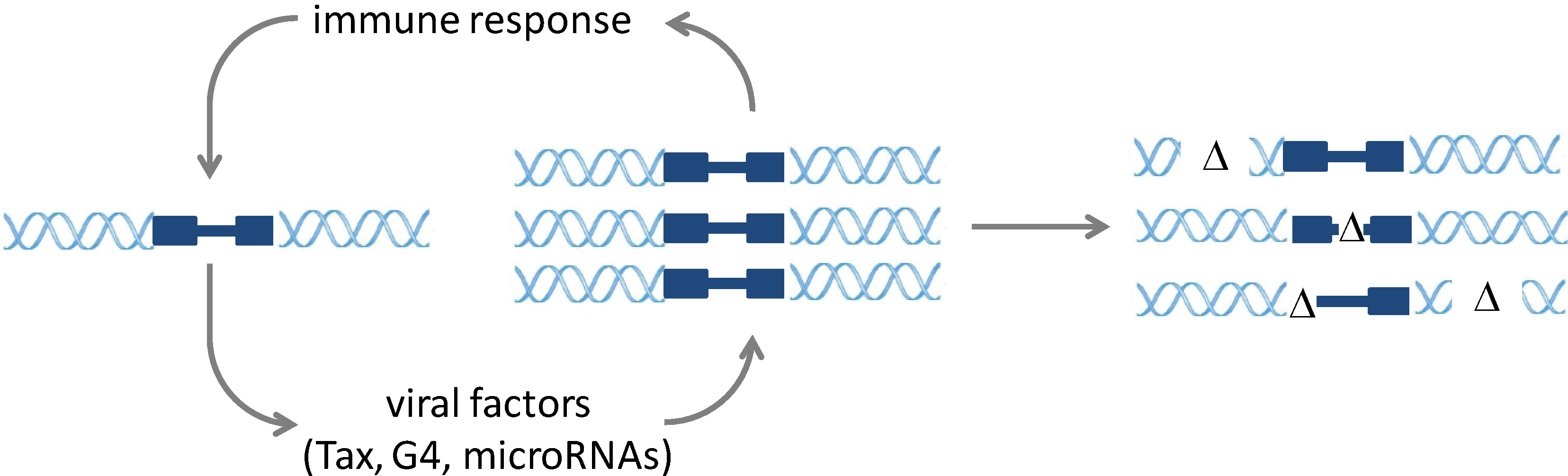
3. Preventive Strategies
4. Previous Failures in Vaccine Development against BLV
5. Competitive Attenuated Proviruses
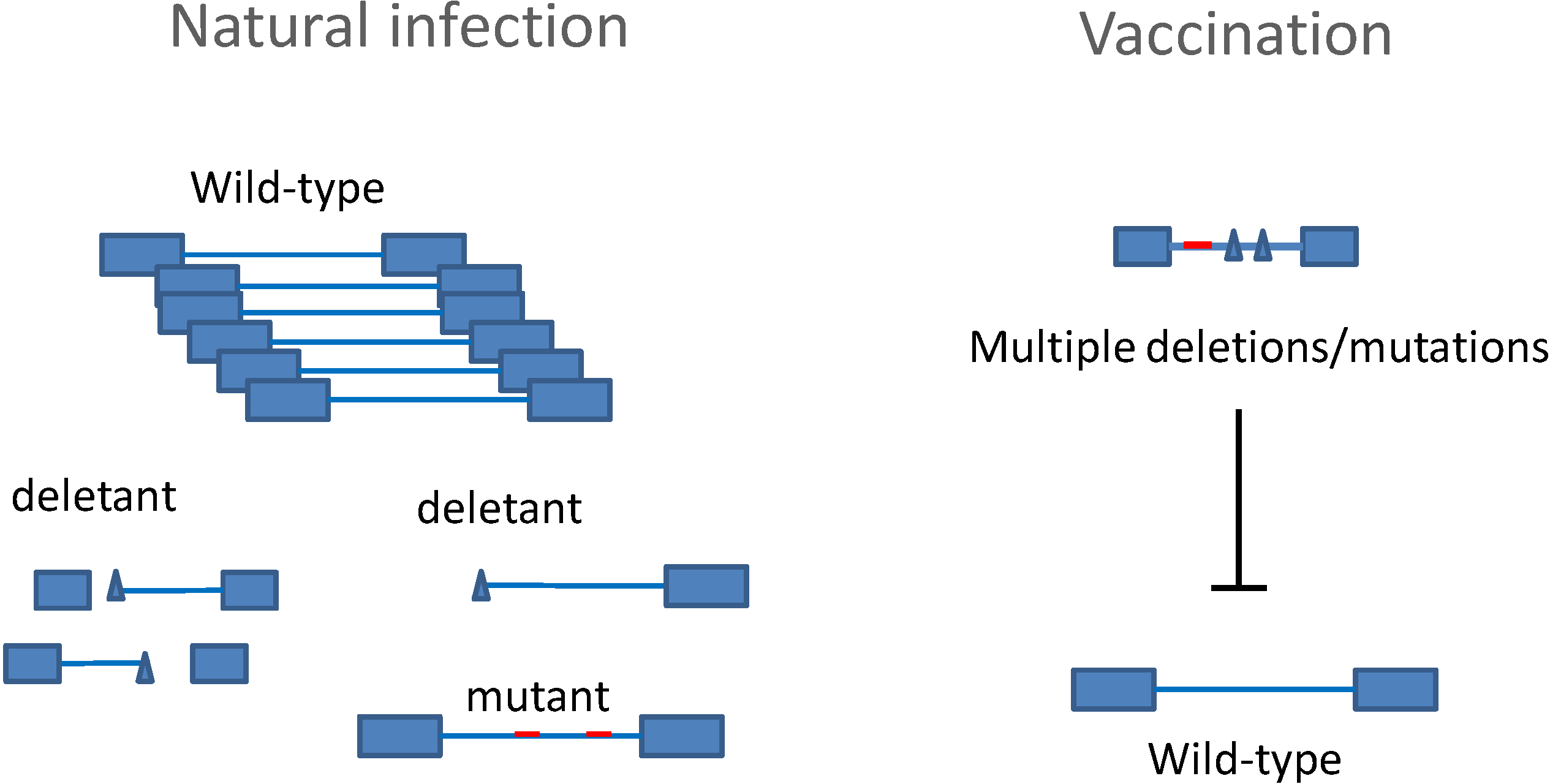
6. A BLV Vaccine as Vector Producing HTLV Neutralizing Antibodies
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interests
References and Notes
- Gillet, N.; Florins, A.; Boxus, M.; Burteau, C.; Nigro, A.; Vandermeers, F.; Balon, H.; Bouzar, A.B.; Defoiche, J.; Burny, A.; et al. Mechanisms of leukemogenesis induced by bovine leukemia virus: Prospects for novel anti-retroviral therapies in human. Retrovirology 2007, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burny, A.; Cleuter, Y.; Kettmann, R.; Mammerickx, M.; Marbaix, G.; Portetelle, D.; Van den Broeke, A.; Willems, L.; Thomas, R. Bovine leukaemia: Facts and hypotheses derived from the study of an infectious cancer. Cancer Surv. 1987, 6, 139–159. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer, J.F. Bovine lymphosarcoma. Adv. Vet. Sci. Comp. Med. 1980, 24, 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, S.; Konnai, S.; Okagawa, T.; Ikebuchi, R.; Shirai, T.; Sunden, Y.; Mingala, C.N.; Murata, S.; Ohashi, K. Expression analysis of foxp3 in t cells from bovine leukemia virus infected cattle. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 57, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okagawa, T.; Konnai, S.; Ikebuchi, R.; Suzuki, S.; Shirai, T.; Sunden, Y.; Onuma, M.; Murata, S.; Ohashi, K. Increased bovine tim-3 and its ligand expressions during bovine leukemia virus infection. Vet. Res. 2012, 43, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debacq, C.; Asquith, B.; Kerkhofs, P.; Portetelle, D.; Burny, A.; Kettmann, R.; Willems, L. Increased cell proliferation, but not reduced cell death, induces lymphocytosis in bovine leukemia virus-infected sheep. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10048–10053. [Google Scholar]
- Debacq, C.; Gillet, N.; Asquith, B.; Sanchez-Alcaraz, M.T.; Florins, A.; Boxus, M.; Schwartz-Cornil, I.; Bonneau, M.; Jean, G.; et al. Peripheral blood b-cell death compensates for excessive proliferation in lymphoid tissues and maintains homeostasis in bovine leukemia virus-infected sheep. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9710–9719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florins, A.; Gillet, N.; Asquith, B.; Boxus, M.; Burteau, C.; Twizere, J.C.; Urbain, P.; Vandermeers, F.; Debacq, C.; Sanchez-Alcaraz, M.T.; et al. Cell dynamics and immune response to blv infection: A unifying model. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 1520–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elemans, M.; Florins, A.; Willems, L.; Asquith, B. Rates of ctl killing in persistent viral infection in vivo. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarias, D.M.; Radke, K. Transcriptional activation of bovine leukemia virus in blood cells from experimentally infected, asymptomatic sheep with latent infections. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar]
- Cantor, G.H.; Pritchard, S.M.; Dequiedt, F.; Willems, L.; Kettmann, R.; Davis, W.C. Cd5 is dissociated from the b-cell receptor in b cells from bovine leukemia virus-infected, persistently lymphocytotic cattle: Consequences to b-cell receptor-mediated apoptosis. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derse, D. Bovine leukemia virus transcription is controlled by a virus-encoded trans-acting factor and by cis-acting response elements. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 2462–2471. [Google Scholar]
- Willems, L.; Gegonne, A.; Chen, G.; Burny, A.; Kettmann, R.; Ghysdael, J. The bovine leukemia virus p34 is a transactivator protein. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 3385–3389. [Google Scholar]
- Derse, D. Trans-acting regulation of bovine leukemia virus mrna processing. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen, S.; Carpenter, S.; Christensen, J.; Storgaard, T.; Viuff, B.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Belousov, J.; Roth, J.A. Identification of alternatively spliced mrnas encoding potential new regulatory proteins in cattle infected with bovine leukemia virus. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 39–52. [Google Scholar]
- Radke, K.; Sigala, T.J.; Grossman, D. Transcription of bovine leukemia virus in peripheral blood cells obtained during early infection in vivo. Microb. Pathog. 1992, 12, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkhofs, P.; Heremans, H.; Burny, A.; Kettmann, R.; Willems, L. In vitro and in vivo oncogenic potential of bovine leukemia virus g4 protein. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 2554–2559. [Google Scholar]
- Gillet, N.A.; Gutierrez, G.; Rodriguez, S.M.; de Brogniez, A.; Renotte, N.; Alvarez, I.; Trono, K.; Willems, L. Massive depletion of bovine leukemia virus proviral clones located in genomic transcriptionally active sites during primary infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kincaid, R.P.; Burke, J.M.; Sullivan, C.S. Rna virus microrna that mimics a b-cell oncomir. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3077–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosewick, N.; Momont, M.; Durkin, K.; Takeda, H.; Caiment, F.; Cleuter, Y.; Vernin, C.; Mortreux, F.; Wattel, E.; Burny, A.; et al. Deep sequencing reveals abundant noncanonical retroviral micrornas in b-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2306–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, N.; University of Liège, Liège, Belgium. Personnal communication, 2014.
- Boxus, M.; Willems, L. How the DNA damage response determines the fate of htlv-1 tax-expressing cells. Retrovirology 2012, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxus, M.; Twizere, J.C.; Legros, S.; Kettmann, R.; Willems, L. Interaction of htlv-1 tax with minichromosome maintenance proteins accelerates the replication timing program. Blood 2012, 119, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, S.M.; Florins, A.; Gillet, N.; de Brogniez, A.; Sanchez-Alcaraz, M.T.; Boxus, M.; Boulanger, F.; Gutierrez, G.; Trono, K.; Alvarez, I.; et al. Preventive and therapeutic strategies for bovine leukemia virus: Lessons for htlv. Viruses 2011, 3, 1210–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, P.V.; Ozden, S.; Prevost, M.C.; Schmitt, C.; Seilhean, D.; Weksler, B.; Couraud, P.O.; Gessain, A.; Romero, I.A.; Ceccaldi, P.E. Human blood-brain barrier disruption by retroviral-infected lymphocytes: Role of myosin light chain kinase in endothelial tight-junction disorganization. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2576–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooshiro, M.; Konnai, S.; Katagiri, Y.; Afuso, M.; Arakaki, N.; Tsuha, O.; Murata, S.; Ohashi, K. Horizontal transmission of bovine leukemia virus from lymphocytotic cattle, and beneficial effects of insect vector control. Vet. Rec. 2013, 173, 527. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, G.; Carignano, H.; Alvarez, I.; Martinez, C.; Porta, N.; Politzki, R.; Gammella, M.; Lomonaco, M.; Fondevila, N.; Poli, M.; et al. Bovine leukemia virus p24 antibodies reflect blood proviral load. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rola-Luszczak, M.; Pluta, A.; Olech, M.; Donnik, I.; Petropavlovskiy, M.; Gerilovych, A.; Vinogradova, I.; Choudhury, B.; Kuzmak, J. The molecular characterization of bovine leukaemia virus isolates from eastern europe and siberia and its impact on phylogeny. PLoS One 2013, 8, e58705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, J.F.; Piper, C.E. Role of colostrum and milk in the natural transmission of the bovine leukemia virus. Cancer Res. 1981, 41, 4906–4909. [Google Scholar]
- Onuma, M.; Hodatsu, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Higashihara, M.; Masu, S.; Mikami, T.; Izawa, H. Protection by vaccination against bovine leukemia virus infection in sheep. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1984, 45, 1212–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt, H.; Rosenthal, S.; Wittmann, W.; Starick, E.; Scholz, D.; Rosenthal, H.A.; Kluge, K.H. Immunization of young cattle with gp51 of the bovine leukosis virus and the subsequent experimental infection. Arch. Exp. Veterinarmed. 1989, 43, 933–942. [Google Scholar]
- Hislop, A.D.; Good, M.F.; Mateo, L.; Gardner, J.; Gatei, M.H.; Daniel, R.C.; Meyers, B.V.; Lavin, M.F.; Suhrbier, A. Vaccine-induced cytotoxic t lymphocytes protect against retroviral challenge. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohishi, K.; Kabeya, H.; Amanuma, H.; Onuma, M. Peptide-based bovine leukemia virus (blv) vaccine that induces blv-env specific th-1 type immunity. Leukemia 1997, 11, 223–226. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, K.; Sonoda, K.; Koyama, M.; Yin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Goryo, M.; Chen, S.L.; Kabeya, H.; Ohishi, K.; Onuma, M. Delayed-type hypersensitivity in sheep induced by synthetic peptides of bovine leukemia virus encapsulated in mannan-coated liposome. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2003, 65, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portetelle, D.; Limbach, K.; Burny, A.; Mammerickx, M.; Desmettre, P.; Riviere, M.; Zavada, J.; Paoletti, E. Recombinant vaccinia virus expression of the bovine leukaemia virus envelope gene and protection of immunized sheep against infection. Vaccine 1991, 9, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohishi, K.; Suzuki, H.; Yasutomi, Y.; Onuma, M.; Okada, K.; Numakunai, S.; Ohshima, K.; Ikawa, Y.; Sugimoto, M. Augmentation of bovine leukemia virus (blv)-specific lymphocyte proliferation responses in ruminants by inoculation with blv env-recombinant vaccinia virus: Their role in the suppression of blv replication. Microbiol. Immunol. 1992, 36, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkhofs, P.; Gatot, J.S.; Knapen, K.; Mammerickx, M.; Burny, A.; Portetelle, D.; Willems, L.; Kettmann, R. Long-term protection against bovine leukaemia virus replication in cattle and sheep. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 957–963. [Google Scholar]
- Reichert, M.; Cantor, G.H.; Willems, L.; Kettmann, R. Protective effects of a live attenuated bovine leukaemia virus vaccine with deletion in the r3 and g4 genes. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 965–969. [Google Scholar]
- Usui, T.; Konnai, S.; Tajima, S.; Watarai, S.; Aida, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Onuma, M. Protective effects of vaccination with bovine leukemia virus (blv) tax DNA against blv infection in sheep. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2003, 65, 1201–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boris-Lawrie, K.; Altanerova, V.; Altaner, C.; Kucerova, L.; Temin, H.M. In vivo study of genetically simplified bovine leukemia virus derivatives that lack tax and rex. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Kucerova, L.; Altanerova, V.; Altaner, C.; Boris-Lawrie, K. Bovine leukemia virus structural gene vectors are immunogenic and lack pathogenicity in a rabbit model. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 8160–8166. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, G.; Rodriguez, S.; University of Liège, Liège, Belgium. Personnal communication, 2014.
- Tamai, Y.; Hasegawa, A.; Takamori, A.; Sasada, A.; Tanosaki, R.; Choi, I.; Utsunomiya, A.; Maeda, Y.; Yamano, Y.; Eto, T.; et al. Potential contribution of a novel tax epitope-specific cd4+ t cells to graft-versus-tax effect in adult t cell leukemia patients after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4382–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez, G.; Rodríguez, S.M.; De Brogniez, A.; Gillet, N.; Golime, R.; Burny, A.; Jaworski, J.-P.; Alvarez, I.; Vagnoni, L.; Trono, K.; et al. Vaccination against δ-Retroviruses: The Bovine Leukemia Virus Paradigm. Viruses 2014, 6, 2416-2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6062416
Gutiérrez G, Rodríguez SM, De Brogniez A, Gillet N, Golime R, Burny A, Jaworski J-P, Alvarez I, Vagnoni L, Trono K, et al. Vaccination against δ-Retroviruses: The Bovine Leukemia Virus Paradigm. Viruses. 2014; 6(6):2416-2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6062416
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez, Gerónimo, Sabrina M. Rodríguez, Alix De Brogniez, Nicolas Gillet, Ramarao Golime, Arsène Burny, Juan-Pablo Jaworski, Irene Alvarez, Lucas Vagnoni, Karina Trono, and et al. 2014. "Vaccination against δ-Retroviruses: The Bovine Leukemia Virus Paradigm" Viruses 6, no. 6: 2416-2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6062416
APA StyleGutiérrez, G., Rodríguez, S. M., De Brogniez, A., Gillet, N., Golime, R., Burny, A., Jaworski, J.-P., Alvarez, I., Vagnoni, L., Trono, K., & Willems, L. (2014). Vaccination against δ-Retroviruses: The Bovine Leukemia Virus Paradigm. Viruses, 6(6), 2416-2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6062416





