HIV Eradication: Combinatorial Approaches to Activate Latent Viruses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Proof of Concept for a Functional Cure
3. Latency: The Consequence of a Block in HIV Gene Expression
3.1. First Block: Transcription Initiation
3.2. Second Block: Transcription Elongation; the Critical Role of Tat
4. Cell Model Systems in the Study of HIV Latency
5. Cellular Targets of Latency-Reversal Therapeutics
5.1. The PKC Pathway
5.2. The JNK Pathway
5.3. The Wnt Pathway
5.4. The AKT Pathway
5.5. Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)
5.6. Histone Methyl Transferases (HMTs)
5.7. DNA Methyltransferases
5.8. ATP-Dependent Chromatin Remodelers (BAF and CHD3)
5.9. Bromo-Domain-Containing (BET) Factors
5.10. HEXIM
6. Combinatorial Approaches to Activate Latent HIV
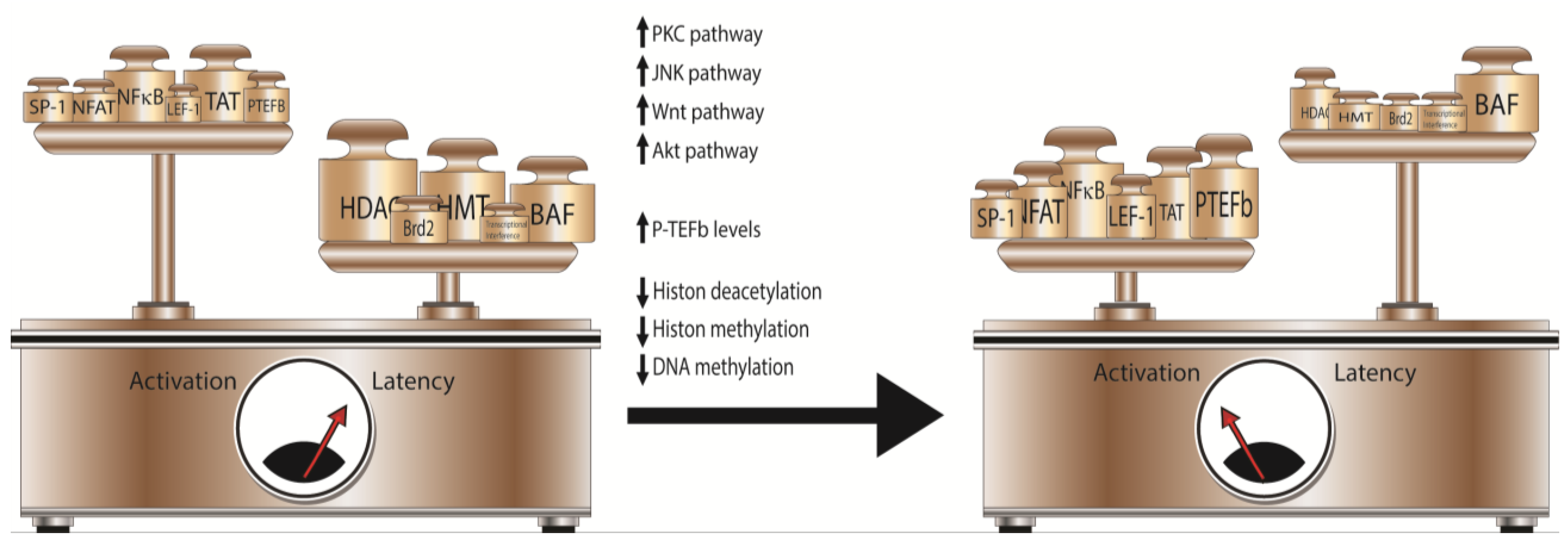
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Perelson, A.S.; Essunger, P.; Cao, Y.; Vesanen, M.; Hurley, A.; Saksela, K.; Markowitz, M.; Ho, D.D. Decay characteristics of HIV-1-infected compartments during combination therapy. Nature 1997, 387, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finzi, D.; Blankson, J.; Siliciano, J.D.; Margolick, J.B.; Chadwick, K.; Pierson, T.; Smith, K.; Lisziewicz, J.; Lori, F.; Flexner, C.; et al. Latent infection of CD4+ T cells provides a mechanism for lifelong persistence of HIV-1, even in patients on effective combination therapy. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finzi, D.; Hermankova, M.; Pierson, T.; Carruth, L.M.; Buck, C.; Chaisson, R.E.; Quinn, T.C.; Chadwick, K.; Margolick, J.; Brookmeyer, R.; et al. Identification of a reservoir for HIV-1 in patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy. Science 1997, 278, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siliciano, J.D.; Kajdas, J.; Finzi, D.; Quinn, T.C.; Chadwick, K.; Margolick, J.B.; Kovacs, C.; Gange, S.J.; Siliciano, R.F. Long-term follow-up studies confirm the stability of the latent reservoir for HIV-1 in resting CD4+ T cells. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 727–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankson, J.; Persaud, D.; Siliciano, R.F. Latent reservoirs for HIV-1. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 12, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, S.G.; Lewin, S.R.; Havlir, D.V. The end of aids: HIV infection as a chronic disease. Lancet 2013, 382, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maartens, G.; Celum, C.; Lewin, S.R. HIV infection: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention. Lancet 2014, 384, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, D.D.; Neumann, A.U.; Perelson, A.S.; Chen, W.; Leonard, J.M.; Markowitz, M. Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature 1995, 373, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Ghosh, S.K.; Taylor, M.E.; Johnson, V.A.; Emini, E.A.; Deutsch, P.; Lifson, J.D.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Nowak, M.A.; Hahn, B.H.; et al. Viral dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Nature 1995, 373, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomont, N.; DaFonseca, S.; Vandergeeten, C.; Ancuta, P.; Sekaly, R.P. Maintenance of CD4+ T-cell memory and HIV persistence: Keeping memory, keeping HIV. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2011, 6, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomont, N.; El-Far, M.; Ancuta, P.; Trautmann, L.; Procopio, F.A.; Yassine-Diab, B.; Boucher, G.; Boulassel, M.R.; Ghattas, G.; Brenchley, J.M.; et al. HIV reservoir size and persistence are driven by T cell survival and homeostatic proliferation. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisele, E.; Siliciano, R.F. Redefining the viral reservoirs that prevent HIV-1 eradication. Immunity 2012, 37, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinoso, J.B.; Kim, S.Y.; Wiegand, A.M.; Palmer, S.E.; Gange, S.J.; Cranmer, L.; O’Shea, A.; Callender, M.; Spivak, A.; Brennan, T.; et al. Treatment intensification does not reduce residual HIV-1 viremia in patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9403–9408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, R.T.; Coombs, R.W.; Chan, E.S.; Bosch, R.J.; Zheng, L.; Margolis, D.M.; Read, S.; Kallungal, B.; Chang, M.; Goecker, E.A.; et al. No effect of raltegravir intensification on viral replication markers in the blood of HIV-1-infected patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2012, 59, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joos, B.; Fischer, M.; Kuster, H.; Pillai, S.K.; Wong, J.K.; Boni, J.; Hirschel, B.; Weber, R.; Trkola, A.; Gunthard, H.F.; et al. HIV rebounds from latently infected cells, rather than from continuing low-level replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16725–16730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josefsson, L.; von Stockenstrom, S.; Faria, N.R.; Sinclair, E.; Bacchetti, P.; Killian, M.; Epling, L.; Tan, A.; Ho, T.; Lemey, P.; et al. The HIV-1 reservoir in eight patients on long-term suppressive antiretroviral therapy is stable with few genetic changes over time. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E4987–E4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allers, K.; Hutter, G.; Hofmann, J.; Loddenkemper, C.; Rieger, K.; Thiel, E.; Schneider, T. Evidence for the cure of HIV infection by CCR5Δ32/Δ32 stem cell transplantation. Blood 2011, 117, 2791–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrich, T.J.; Hu, Z.; Li, J.Z.; Sciaranghella, G.; Busch, M.P.; Keating, S.M.; Gallien, S.; Lin, N.H.; Giguel, F.F.; Lavoie, L.; et al. Long-term reduction in peripheral blood HIV type 1 reservoirs following reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrich, T.J.; Hanhauser, E.; Marty, F.M.; Sirignano, M.N.; Keating, S.; Lee, T.H.; Robles, Y.P.; Davis, B.T.; Li, J.Z.; Heisey, A.; et al. Antiretroviral-free HIV-1 remission and viral rebound after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: Report of 2 cases. Ann. Intern. Med. 2014, 161, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persaud, D.; Gay, H.; Ziemniak, C.; Chen, Y.H.; Piatak, M., Jr.; Chun, T.W.; Strain, M.; Richman, D.; Luzuriaga, K. Absence of detectable HIV-1 viremia after treatment cessation in an infant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1828–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). “Mississippi baby” now has detctable HIV, researchers find. Available online: http://www.niaid.nih.gov/news/newsreleases/2014/pages/mississippibabyhiv.aspx (accessed on 16 September 2014).
- Buzon, M.J.; Martin-Gayo, E.; Pereyra, F.; Ouyang, Z.; Sun, H.; Li, J.Z.; Piovoso, M.; Shaw, A.; Dalmau, J.; Zangger, N.; et al. Long-term antiretroviral treatment initiated at primary HIV-1 infection affects the size, composition, and decay kinetics of the reservoir of HIV-1-infected CD4 T cells. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10056–10065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hocqueloux, L.; Avettand-Fenoel, V.; Jacquot, S.; Prazuck, T.; Legac, E.; Melard, A.; Niang, M.; Mille, C.; Le Moal, G.; Viard, J.P.; et al. Long-term antiretroviral therapy initiated during primary HIV-1 infection is key to achieving both low HIV reservoirs and normal T cell counts. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamlyn, E.; Ewings, F.M.; Porter, K.; Cooper, D.A.; Tambussi, G.; Schechter, M.; Pedersen, C.; Okulicz, J.F.; McClure, M.; Babiker, A.; et al. Plasma HIV viral rebound following protocol-indicated cessation of art commenced in primary and chronic HIV infection. PLoS One 2012, 7, e43754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steingrover, R.; Pogany, K.; Fernandez Garcia, E.; Jurriaans, S.; Brinkman, K.; Schuitemaker, H.; Miedema, F.; Lange, J.M.; Prins, J.M. HIV-1 viral rebound dynamics after a single treatment interruption depends on time of initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Aids 2008, 22, 1583–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goujard, C.; Girault, I.; Rouzioux, C.; Lecuroux, C.; Deveau, C.; Chaix, M.L.; Jacomet, C.; Talamali, A.; Delfraissy, J.F.; Venet, A.; et al. HIV-1 control after transient antiretroviral treatment initiated in primary infection: Role of patient characteristics and effect of therapy. Antivir. Ther. 2012, 17, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saez-Cirion, A.; Bacchus, C.; Hocqueloux, L.; Avettand-Fenoel, V.; Girault, I.; Lecuroux, C.; Potard, V.; Versmisse, P.; Melard, A.; Prazuck, T.; et al. Post-treatment HIV-1 controllers with a long-term virological remission after the interruption of early initiated antiretroviral therapy anrs visconti study. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.L.; Rosenbloom, D.I.; Fu, F.; Nowak, M.A.; Siliciano, R.F. Predicting the outcomes of treatment to eradicate the latent reservoir for HIV-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13475–13480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archin, N.M.; Margolis, D.M. Emerging strategies to deplete the HIV reservoir. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 27, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siliciano, J.D.; Siliciano, R.F. Recent developments in the search for a cure for HIV-1 infection: Targeting the latent reservoir for HIV-1. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Lassen, K.; Monie, D.; Sedaghat, A.R.; Shimoji, S.; Liu, X.; Pierson, T.C.; Margolick, J.B.; Siliciano, R.F.; Siliciano, J.D. Resting CD4+ T cells from human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-infected individuals carry integrated HIV-1 genomes within actively transcribed host genes. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6122–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdin, E. DNAse I-hypersensitive sites are associated with both long terminal repeats and with the intragenic enhancer of integrated human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 6790–6799. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.A.; Bentley, K.; Peeters, A.; Churchill, M.J.; Deacon, N.J. A compilation of cellular transcription factor interactions with the HIV-1 LTR promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdin, E.; Van Lint, C. Internal transcriptional regulatory elements in HIV-1 and other retroviruses. Cell. Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-Grand, France) 1995, 41, 365–369. [Google Scholar]
- Verdin, E.; Paras, P., Jr.; Van Lint, C. Chromatin disruption in the promoter of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 during transcriptional activation. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3249–3259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Lint, C.; Emiliani, S.; Ott, M.; Verdin, E. Transcriptional activation and chromatin remodeling of the HIV-1 promoter in response to histone acetylation. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Mak, G.; Franza, B.R., Jr. In vitro study of functional involvement of sp1, NF-κB/Rel, and AP1 in phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-mediated HIV-1 long terminal repeat activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 30616–30619. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Baldauf, H.M.; Keppler, O.T.; Fackler, O.T. Restrictions to HIV-1 replication in resting CD4+ T lymphocytes. Cell. Res. 2013, 23, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ylisastigui, L.; Kaur, R.; Johnson, H.; Volker, J.; He, G.; Hansen, U.; Margolis, D. Mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate LSF occupancy at the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 5952–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coull, J.J.; Romerio, F.; Sun, J.M.; Volker, J.L.; Galvin, K.M.; Davie, J.R.; Shi, Y.; Hansen, U.; Margolis, D.M. The human factors YY1 and LSF repress the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat via recruitment of histone deacetylase 1. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6790–6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, W.; Barreto, K.; Raithatha, S.; Sadowski, I. An upstream YY1 binding site on the HIV-1 LTR contributes to latent infection. PLoS One 2013, 8, e77052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, M.; Karn, J. Cbf-1 promotes transcriptional silencing during the establishment of HIV-1 latency. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 4985–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donahue, D.A.; Wainberg, M.A. Cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the establishment of HIV-1 latency. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Shibata, H.; Handa, H. Transcription elongation factors DSIF and NELF: Promoter-proximal pausing and beyond. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1829, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadlowsky, J.K.; Wong, J.Y.; Graham, A.C.; Dobrowolski, C.; Devor, R.L.; Adams, M.D.; Fujinaga, K.; Karn, J. Negative elongation factor is required for the maintenance of proviral latency but does not induce promoter-proximal pausing of RNA polymerase II on the HIV long terminal repeat. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 1911–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, Y.H.; Rana, T.M. DSIF and NELF interact with RNA polymerase II elongation complex and HIV-1 Tat stimulates P-TEFB-mediated phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II and DSIF during transcription elongation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 12951–12958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, M.; Schiralli Lester, G.M.; Lee, C.; Missra, A.; Wasserman, G.A.; Steffen, M.; Gilmour, D.S.; Henderson, A.J. Negative elongation factor (NELF) coordinates RNA polymerase II pausing, premature termination, and chromatin remodeling to regulate HIV transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 25995–26003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhian, B.; Laguette, N.; Yatim, A.; Nakamura, M.; Levy, Y.; Kiernan, R.; Benkirane, M. HIV-1 Tat assembles a multifunctional transcription elongation complex and stably associates with the 7SK snRNP. Mol. Cell. 2010, 38, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Lin, C.; Shilatifard, A. The super elongation complex (SEC) family in transcriptional control. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 13, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isel, C.; Karn, J. Direct evidence that HIV-1 Tat stimulates RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal domain hyperphosphorylation during transcriptional elongation. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 290, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Bourgeois, C.F.; Isel, C.; Churcher, M.J.; Karn, J. Phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal domain by CDK9 is directly responsible for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat-activated transcriptional elongation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 4622–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, M.; Geyer, M.; Zhou, Q. The control of HIV transcription: Keeping RNA polymerase II on track. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yik, J.H.; Chen, R.; Nishimura, R.; Jennings, J.L.; Link, A.J.; Zhou, Q. Inhibition of P-TEFB (CDK9/cyclin T) kinase and RNA polymerase II transcription by the coordinated actions of hexim1 and 7SK snrna. Mol. Cell. 2003, 12, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhiraja, S.; Famiglietti, M.; Bosque, A.; Planelles, V.; Rice, A.P. Cyclin T1 and CDK9 T-loop phosphorylation are downregulated during establishment of HIV-1 latency in primary resting memory CD4+ T cells. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhiraja, S.; Rice, A.P. Reactivation of latent HIV: Do all roads go through P-TEFB? Future Virol. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, M.; Pearson, R.J.; Karn, J. Establishment of HIV latency in primary CD4+ cells is due to epigenetic transcriptional silencing and P-TEFB restriction. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 6425–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folks, T.M.; Justement, J.; Kinter, A.; Dinarello, C.A.; Fauci, A.S. Cytokine-induced expression of HIV-1 in a chronically infected promonocyte cell line. Science 1987, 238, 800–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emiliani, S.; Fischle, W.; Ott, M.; Van Lint, C.; Amella, C.A.; Verdin, E. Mutations in the Tat gene are responsible for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 postintegration latency in the U1 cell line. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 1666–1670. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Emiliani, S.; Van Lint, C.; Fischle, W.; Paras, P., Jr.; Ott, M.; Brady, J.; Verdin, E. A point mutation in the HIV-1 Tat responsive element is associated with postintegration latency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 6377–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeeninga, R.E.; Westerhout, E.M.; van Gerven, M.L.; Berkhout, B. HIV-1 latency in actively dividing human T cell lines. Retrovirology 2008, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, A.; Bisgrove, D.; Verdin, E. HIV reproducibly establishes a latent infection after acute infection of T cells in vitro. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1868–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duverger, A.; Jones, J.; May, J.; Bibollet-Ruche, F.; Wagner, F.A.; Cron, R.Q.; Kutsch, O. Determinants of the establishment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 latency. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 3078–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folks, T.M.; Clouse, K.A.; Justement, J.; Rabson, A.; Duh, E.; Kehrl, J.H.; Fauci, A.S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces expression of human immunodeficiency virus in a chronically infected T-cell clone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 2365–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wind-Rotolo, M.; Yang, H.C.; Siliciano, J.D.; Siliciano, R.F. Experimental approaches to the study of HIV-1 latency. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosque, A.; Planelles, V. Induction of HIV-1 latency and reactivation in primary memory CD4+ T cells. Blood 2009, 113, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.C.; Xing, S.; Shan, L.; O’Connell, K.; Dinoso, J.; Shen, A.; Zhou, Y.; Shrum, C.K.; Han, Y.; Liu, J.O.; et al. Small-molecule screening using a human primary cell model of HIV latency identifies compounds that reverse latency without cellular activation. J. Clin. Invest. 2009, 119, 3473–3486. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sahu, G.K.; Lee, K.; Ji, J.; Braciale, V.; Baron, S.; Cloyd, M.W. A novel in vitro system to generate and study latently HIV-infected long-lived normal CD4+ T-lymphocytes. Virology 2006, 355, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swiggard, W.J.; Baytop, C.; Yu, J.J.; Dai, J.; Li, C.; Schretzenmair, R.; Theodosopoulos, T.; O’Doherty, U. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 can establish latent infection in resting CD4+ T cells in the absence of activating stimuli. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14179–14188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassen, K.G.; Hebbeler, A.M.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Lobritz, M.A.; Greene, W.C. A flexible model of HIV-1 latency permitting evaluation of many primary CD4 T-cell reservoirs. PLoS One 2012, 7, e30176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spina, C.A.; Guatelli, J.C.; Richman, D.D. Establishment of a stable, inducible form of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 DNA in quiescent CD4 lymphocytes in vitro. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 2977–2988. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saleh, S.; Solomon, A.; Wightman, F.; Xhilaga, M.; Cameron, P.U.; Lewin, S.R. CCR7 ligands CCL19 and CCL21 increase permissiveness of resting memory CD4+ T cells to HIV-1 infection: A novel model of HIV-1 latency. Blood 2007, 110, 4161–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spina, C.A.; Anderson, J.; Archin, N.M.; Bosque, A.; Chan, J.; Famiglietti, M.; Greene, W.C.; Kashuba, A.; Lewin, S.R.; Margolis, D.M.; et al. An in-depth comparison of latent HIV-1 reactivation in multiple cell model systems and resting CD4+ T cells from aviremic patients. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archin, N.M.; Keedy, K.S.; Espeseth, A.; Dang, H.; Hazuda, D.J.; Margolis, D.M. Expression of latent human immunodeficiency type 1 is induced by novel and selective histone deacetylase inhibitors. Aids 2009, 23, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archin, N.M.; Liberty, A.L.; Kashuba, A.D.; Choudhary, S.K.; Kuruc, J.D.; Crooks, A.M.; Parker, D.C.; Anderson, E.M.; Kearney, M.F.; Strain, M.C.; et al. Administration of vorinostat disrupts HIV-1 latency in patients on antiretroviral therapy. Nature 2012, 487, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, Y.C.; Shan, L.; Hosmane, N.N.; Wang, J.; Laskey, S.B.; Rosenbloom, D.I.; Lai, J.; Blankson, J.N.; Siliciano, J.D.; Siliciano, R.F. Replication-competent noninduced proviruses in the latent reservoir increase barrier to HIV-1 cure. Cell 2013, 155, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiselinova, M.; Pasternak, A.O.; De Spiegelaere, W.; Vogelaers, D.; Berkhout, B.; Vandekerckhove, L. Comparison of droplet digital PCR and seminested real-time PCR for quantification of cell-associated HIV-1 RNA. PLoS One 2014, 9, e85999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullen, C.K.; Laird, G.M.; Durand, C.M.; Siliciano, J.D.; Siliciano, R.F. New ex vivo approaches distinguish effective and ineffective single agents for reversing HIV-1 latency in vivo. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laird, G.M.; Eisele, E.E.; Rabi, S.A.; Lai, J.; Chioma, S.; Blankson, J.N.; Siliciano, J.D.; Siliciano, R.F. Rapid quantification of the latent reservoir for HIV-1 using a viral outgrowth assay. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ylisastigui, L.; Archin, N.M.; Lehrman, G.; Bosch, R.J.; Margolis, D.M. Coaxing HIV-1 from resting CD4 T cells: Histone deacetylase inhibition allows latent viral expression. Aids 2004, 18, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archin, N.M.; Bateson, R.; Tripathy, M.K.; Crooks, A.M.; Yang, K.H.; Dahl, N.P.; Kearney, M.F.; Anderson, E.M.; Coffin, J.M.; Strain, M.C.; et al. HIV-1 expression within resting CD4+ T cells after multiple doses of vorinostat. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, T. The CLEAR Study Group. Panobinostat induces HIV transcription and plasma viremia in HIV patients on suppressive cart. In Proceedings of CROI, Boston, MA, USA, 3–6 March 2014.
- Spivak, A.M.; Andrade, A.; Eisele, E.; Hoh, R.; Bacchetti, P.; Bumpus, N.N.; Emad, F.; Buckheit, R., III; McCance-Katz, E.F.; Lai, J.; et al. A pilot study assessing the safety and latency-reversing activity of disulfiram in HIV-1-infected adults on antiretroviral therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouzioux, C.; Richman, D. How to best measure HIV reservoirs? Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2013, 8, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, S.; Graf, E.H.; Dahl, V.; Strain, M.C.; Yukl, S.A.; Lysenko, E.S.; Bosch, R.J.; Lai, J.; Chioma, S.; Emad, F.; et al. Comparative analysis of measures of viral reservoirs in HIV-1 eradication studies. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbonye, U.; Karn, J. Transcriptional control of HIV latency: Cellular signaling pathways, epigenetics, happenstance and the hope for a cure. Virology 2014, 454–455, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafeuillade, A.; Poggi, C.; Chadapaud, S.; Hittinger, G.; Chouraqui, M.; Pisapia, M.; Delbeke, E. Pilot study of a combination of highly active antiretroviral therapy and cytokines to induce HIV-1 remission. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2001, 26, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dybul, M.; Hidalgo, B.; Chun, T.W.; Belson, M.; Migueles, S.A.; Justement, J.S.; Herpin, B.; Perry, C.; Hallahan, C.W.; Davey, R.T.; et al. Pilot study of the effects of intermittent interleukin-2 on human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-specific immune responses in patients treated during recently acquired HIV infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Praag, R.M.; Prins, J.M.; Roos, M.T.; Schellekens, P.T.; Ten Berge, I.J.; Yong, S.L.; Schuitemaker, H.; Eerenberg, A.J.; Jurriaans, S.; de Wolf, F.; et al. OKT3 and IL-2 treatment for purging of the latent HIV-1 reservoir in vivo results in selective long-lasting CD4+ T cell depletion. J. Clin. Immunol. 2001, 21, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong-Starkesen, S.E.; Luciw, P.A.; Peterlin, B.M. Signaling through T lymphocyte surface proteins, TCR/CD3 and CD28, activates the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. J. Immunol. 1989, 142, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brooks, D.G.; Arlen, P.A.; Gao, L.; Kitchen, C.M.; Zack, J.A. Identification of T cell-signaling pathways that stimulate latent HIV in primary cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12955–12960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coiras, M.; Lopez-Huertas, M.R.; Rullas, J.; Mittelbrunn, M.; Alcami, J. Basal shuttle of NF-κB/IκBα in resting T lymphocytes regulates HIV-1 LTR dependent expression. Retrovirology 2007, 4, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cron, R.Q.; Bartz, S.R.; Clausell, A.; Bort, S.J.; Klebanoff, S.J.; Lewis, D.B. NFAT1 enhances HIV-1 gene expression in primary human CD4 T cells. Clin. Immunol. 2000, 94, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; May, M.J.; Jimi, E.; Ghosh, S. The phosphorylation status of nuclear NF-κB determines its association with CBP/p300 or HDAC-1. Mol. Cell. 2002, 9, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Rao, A. Nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT)-dependent transactivation regulated by the coactivators p300/CREB-binding protein (CBP). J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkosky, J.; Culnan, D.M.; Roman, J.; Dornadula, G.; Schnell, M.; Boyd, M.R.; Pomerantz, R.J. Prostratin: Activation of latent HIV-1 expression suggests a potential inductive adjuvant therapy for HAART. Blood 2001, 98, 3006–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korin, Y.D.; Brooks, D.G.; Brown, S.; Korotzer, A.; Zack, J.A. Effects of prostratin on T-cell activation and human immunodeficiency virus latency. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 8118–8123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.A.; Chen, L.F.; Kwon, H.; Fenard, D.; Bisgrove, D.; Verdin, E.; Greene, W.C. Prostratin antagonizes HIV latency by activating NF-κB. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 42008–42017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehla, R.; Bivalkar-Mehla, S.; Zhang, R.; Handy, I.; Albrecht, H.; Giri, S.; Nagarkatti, P.; Nagarkatti, M.; Chauhan, A. Bryostatin modulates latent HIV-1 infection via PKC and AMPK signaling but inhibits acute infection in a receptor independent manner. PLoS One 2010, 5, e11160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, T.L.; Rice, A.P. Effects of prostratin on cyclin T1/P-TEFB function and the gene expression profile in primary resting CD4+ T cells. Retrovirology 2006, 3, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beans, E.J.; Fournogerakis, D.; Gauntlett, C.; Heumann, L.V.; Kramer, R.; Marsden, M.D.; Murray, D.; Chun, T.W.; Zack, J.A.; Wender, P.A. Highly potent, synthetically accessible prostratin analogs induce latent HIV expression in vitro and ex vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11698–11703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, C.M.; Price, S.L.; Shirk, E.N.; Cunha, R.D.; Pianowski, L.F.; Clements, J.E.; Tanuri, A.; Gama, L. Dual role of novel ingenol derivatives from euphorbia tirucalli in HIV replication: Inhibition of de novo infection and activation of viral LTR. PLoS One 2014, 9, e97257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanuri, A.; Gama, L.; Santana, R.; Lewis, M.; Savarino, A.; Shytaj, I.; Clements, J.E.; Pianowski, L.F. Ing-B a potential PKC activator for HIV eradication is active in SIVmac251-infected macaques. In Proceedings of CROI, Boston, MA, USA, 3–6 March 2014.
- Micheva-Viteva, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Edelstein, L.C.; Pacchia, A.L.; Lee, H.L.; Graci, J.D.; Breslin, J.; Phelan, B.D.; Miller, L.K.; Colacino, J.M.; et al. High-throughput screening uncovers a compound that activates latent HIV-1 and acts cooperatively with a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 21083–21091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Lint, C.; Burny, A.; Verdin, E. The intragenic enhancer of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 contains functional AP-1 binding sites. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 7066–7072. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Colin, L.; Vandenhoudt, N.; de Walque, S.; Van Driessche, B.; Bergamaschi, A.; Martinelli, V.; Cherrier, T.; Vanhulle, C.; Guiguen, A.; David, A.; et al. The AP-1 binding sites located in the pol gene intragenic regulatory region of HIV-1 are important for viral replication. PLoS One 2011, 6, e19084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duverger, A.; Wolschendorf, F.; Zhang, M.; Wagner, F.; Hatcher, B.; Jones, J.; Cron, R.Q.; van der Sluis, R.M.; Jeeninga, R.E.; Berkhout, B.; et al. An AP-1 binding site in the enhancer/core element of the HIV-1 promoter controls the ability of HIV-1 to establish latent infection. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2264–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novis, C.L.; Archin, N.M.; Buzon, M.J.; Verdin, E.; Round, J.L.; Lichterfeld, M.; Margolis, D.M.; Planelles, V.; Bosque, A. Reactivation of latent HIV-1 in central memory CD4(+) T cells through TLR-1/2 stimulation. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallastegui, E.; Marshall, B.; Vidal, D.; Sanchez-Duffhues, G.; Collado, J.A.; Alvarez-Fernandez, C.; Luque, N.; Terme, J.M.; Gatell, J.M.; Sanchez-Palomino, S.; et al. Combination of biological screening in a cellular model of viral latency and virtual screening identifies novel compounds that reactivate HIV-1. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3795–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, B.; Dobrowolski, C.; Mao, H.; Powell, D.; Miller, M.; Hazuda, D.; Barnard, R.; Karn, J. Farnesyl transferase: A new target for eradication of latent HIV-1 provirus in jurkat T-cells. In Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on HIV Persistence during Therapy, Miami, FL, USA, 3–6 December 2013.
- Hazuda, D.; Barnard, R.; Wolkenberg, S.; Powell, D.; Karn, J.; Das, B.; Margolis, D.; Archin, N.; Holloway, K.; Wang, I.; et al. HIV latency drug discovery: Optimizing drugs to induce latent HIV expression. In Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on HIV Persistence during Therapy, Miami, FL, USA, 3–6 December 2013.
- Clevers, H.; Nusse, R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, P.L.; Sheline, C.T.; Cannon, K.; Voz, M.L.; Pazin, M.J.; Kadonaga, J.T.; Jones, K.A. Activation of the HIV-1 enhancer by the LEF-1 HMG protein on nucleosome-assembled DNA in vitro. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 2090–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafati, H.; LeMasters, E.; Lennert, V.D.D.; El-Sayyed, M.; Boucher, C.; Vries, R.; Mahmoudi, T. Activation of the Wnt pathway by natural ligands or small molecule inhibitors activates latent HIV. In Proceedings of the 7th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention (IAS), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 30 June–3 July 2013.
- Kameoka, M.; Kameoka, Y.; Utachee, P.; Kurosu, T.; Sawanpanyalert, P.; Ikuta, K.; Auwanit, W. Short communication: RNA interference directed against axin1 upregulates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gene expression by activating the Wnt signaling pathway in hela-derived J11.1 cells. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2009, 25, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, L.J.; Narasipura, S.D.; Adarichev, V.; Kashanchi, F.; Al-Harthi, L. Identification of novel T cell factor 4 (TCF-4) binding sites on the HIV long terminal repeat which associate with TCF-4, β-catenin, and smar1 to repress HIV transcription. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 9495–9503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, L.J.; Sharma, A.; Monaco, M.C.; Major, E.O.; Al-Harthi, L. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) transactivator of transcription through its intact core and cysteine-rich domains inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling in astrocytes: Relevance to HIV neuropathogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 16306–16313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasipura, S.D.; Henderson, L.J.; Fu, S.W.; Chen, L.; Kashanchi, F.; Al-Harthi, L. Role of β-catenin and TCF/LEFfamily members in transcriptional activity of HIV in astrocytes. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 1911–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wortman, B.; Darbinian, N.; Sawaya, B.E.; Khalili, K.; Amini, S. Evidence for regulation of long terminal repeat transcription by Wnt transcription factor TCF-4 in human astrocytic cells. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 11159–11165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll-Anzinger, D.; Kumar, A.; Adarichev, V.; Kashanchi, F.; Al-Harthi, L. Human immunodeficiency virus-restricted replication in astrocytes and the ability of gamma interferon to modulate this restriction are regulated by a downstream effector of the Wnt signaling pathway. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5864–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Zloza, A.; Moon, R.T.; Watts, J.; Tenorio, A.R.; Al-Harthi, L. Active β-catenin signaling is an inhibitory pathway for human immunodeficiency virus replication in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 2813–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, S.; Bullen, C.K.; Shroff, N.S.; Shan, L.; Yang, H.C.; Manucci, J.L.; Bhat, S.; Zhang, H.; Margolick, J.B.; Quinn, T.C.; et al. Disulfiram reactivates latent HIV-1 in a Bcl-2-transduced primary CD4+ T cell model without inducing global T cell activation. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6060–6064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyon, G.; Zerbato, J.; Mellors, J.W.; Sluis-Cremer, N. Disulfiram reactivates latent HIV-1 expression through depletion of the phosphatase and tensin homolog. Aids 2013, 27, F7–F11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmisano, I.; Della Chiara, G.; D’Ambrosio, R.L.; Huichalaf, C.; Brambilla, P.; Corbetta, S.; Riba, M.; Piccirillo, R.; Valente, S.; Casari, G.; et al. Amino acid starvation induces reactivation of silenced transgenes and latent HIV-1 provirus via down-regulation of histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2284–E2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keedy, K.S.; Archin, N.M.; Gates, A.T.; Espeseth, A.; Hazuda, D.J.; Margolis, D.M. A limited group of class I histone deacetylases acts to repress human immunodeficiency virus type 1 expression. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4749–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, K.; Margolis, D. Selective targeting of the repressive transcription factors YY1 and c-MYC to disrupt quiescent human immunodeficiency viruses. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2013, 29, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; Espeseth, A.; Hazuda, D.J.; Margolis, D.M. C-myc and sp1 contribute to proviral latency by recruiting histone deacetylase 1 to the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10914–10923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.A.; Chen, L.F.; Kwon, H.; Ruiz-Jarabo, C.M.; Verdin, E.; Greene, W.C. NF-κB p50 promotes HIV latency through HDAC recruitment and repression of transcriptional initiation. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelstein, L.C.; Micheva-Viteva, S.; Phelan, B.D.; Dougherty, J.P. Short communication: Activation of latent HIV type 1 gene expression by suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), an HDAC inhibitor approved for use to treat cutaneous T cell lymphoma. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2009, 25, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirakawa, K.; Chavez, L.; Hakre, S.; Calvanese, V.; Verdin, E. Reactivation of latent HIV by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 277–285. [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan, P.L.; Mayall, T.P.; Verdin, E.; Jones, K.A. Histone acetyltransferases regulate HIV-1 enhancer activity in vitro. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 3327–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrman, G.; Hogue, I.B.; Palmer, S.; Jennings, C.; Spina, C.A.; Wiegand, A.; Landay, A.L.; Coombs, R.W.; Richman, D.D.; Mellors, J.W.; et al. Depletion of latent HIV-1 infection in vivo: A proof-of-concept study. Lancet 2005, 366, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagot-Lerolle, N.; Lamine, A.; Chaix, M.L.; Boufassa, F.; Aboulker, J.P.; Costagliola, D.; Goujard, C.; Pallier, C.; Delfraissy, J.F.; Lambotte, O.; et al. Prolonged valproic acid treatment does not reduce the size of latent HIV reservoir. Aids 2008, 22, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steel, A.; Clark, S.; Teo, I.; Shaunak, S.; Nelson, M.; Gazzard, B.; Kelleher, P. No change to HIV-1 latency with valproate therapy. Aids 2006, 20, 1681–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, T.A.; Schmeltz Sogaard, O.; Brinkmann, C.; Wightman, F.; Lewin, S.R.; Melchjorsen, J.; Dinarello, C.; Ostergaard, L.; Tolstrup, M. Comparison of HDAC inhibitors in clinical development: Effect on HIV production in latently infected cells and T-cell activation. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2013, 9, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.G.; Chiang, V.; Fyne, E.; Balakrishnan, M.; Barnes, T.; Graupe, M.; Hesselgesser, J.; Irrinki, A.; Murry, J.P.; Stepan, G.; et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor romidepsin induces HIV expression in CD4 T cells from patients on suppressive antiretroviral therapy at concentrations achieved by clinical dosing. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wightman, F.; Lu, H.K.; Solomon, A.E.; Saleh, S.; Harman, A.N.; Cunningham, A.L.; Gray, L.; Churchill, M.; Cameron, P.U.; Dear, A.E.; et al. Entinostat is a histone deacetylase inhibitor selective for class 1 histone deacetylases and activates HIV production from latently infected primary T cells. Aids 2013, 27, 2853–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, F.; Ellenberg, P.; Churchill, M.; Lewin, S.R. HDAC inhibitors in HIV. Immunol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 90, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, J.; Solomon, A.; Wightman, F.; Smith, M.; Palmer, S.; Prince, M.; Watson, J.; Hoy, J.; McMahon, J.; Lewin, S.R. The safety and effect of multiple doses of vorinostat on HIV transcription in HIV-positive patients receiving cart. In Proceedings of CROI, Atlanta, GA, USA, 3–6 March 2013.
- Rasmussen, T.; Tolstrup, M.; Brinkmann, C.; Olesen, R.; Erikstrup, C.; Solomon, A.; Winckelmann, A.; Palmer, S.; Dinarello, C.; Buzon, M.; et al. Cyclic dosing of panobinostat to reverse HIV-latency: Findings from a clinical trial. In Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on HIV Persistence during Therapy, Miami, FL, USA, 3–6 December 2013.
- Lucera, M.B.; Tilton, C.A.; Mao, H.; Dobrowolski, C.; Tabler, C.O.; Haqqani, A.A.; Karn, J.; Tilton, J.C. The histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat (SAHA) increases the susceptibility of uninfected CD4+ T cells to HIV by increasing the kinetics and efficiency of postentry viral events. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10803–10812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.B.; O’Connor, R.; Mueller, S.; Foley, M.; Szeto, G.L.; Karel, D.; Lichterfeld, M.; Kovacs, C.; Ostrowski, M.A.; Trocha, A.; et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors impair the elimination of HIV-infected cells by cytotoxic t-lymphocytes. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.; Cho, W.K.; Chu, C.K.; Keedy, K.S.; Archin, N.M.; Margolis, D.M.; Karn, J. Epigenetic silencing of HIV-1 by the histone h3 lysine 27 methyltransferase enhancer of zeste 2. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9078–9089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, K.; Togami, H.; Okamoto, T. Involvement of histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9) methyltransferase G9a in the maintenance of HIV-1 latency and its reactivation by BIX01294. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 16538–16545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Chene, I.; Basyuk, E.; Lin, Y.L.; Triboulet, R.; Knezevich, A.; Chable-Bessia, C.; Mettling, C.; Baillat, V.; Reynes, J.; Corbeau, P.; et al. SUV39H1 and HP1gamma are responsible for chromatin-mediated HIV-1 transcriptional silencing and post-integration latency. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marban, C.; Suzanne, S.; Dequiedt, F.; de Walque, S.; Redel, L.; Van Lint, C.; Aunis, D.; Rohr, O. Recruitment of chromatin-modifying enzymes by ctip2 promotes HIV-1 transcriptional silencing. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, W.; Barreto, K.; Saunders, A.; Dahabieh, M.S.; Johnson, P.; Sadowski, I. The Suv39H1 methyltransferase inhibitor chaetocin causes induction of integrated HIV-1 without producing a T cell response. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 3549–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchat, S.; Gatot, J.S.; Kabeya, K.; Cardona, C.; Colin, L.; Herbein, G.; De Wit, S.; Clumeck, N.; Lambotte, O.; Rouzioux, C.; et al. Histone methyltransferase inhibitors induce HIV-1 recovery in resting CD4(+) T cells from HIV-1-infected HAART-treated patients. Aids 2012, 26, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauder, S.E.; Bosque, A.; Lindqvist, A.; Planelles, V.; Verdin, E. Epigenetic regulation of HIV-1 latency by cytosine methylation. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, G.; Zeichner, S.L. Cell line-dependent variability in HIV activation employing dnmt inhibitors. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazkova, J.; Trejbalova, K.; Gondois-Rey, F.; Halfon, P.; Philibert, P.; Guiguen, A.; Verdin, E.; Olive, D.; Van Lint, C.; Hejnar, J.; et al. CpG methylation controls reactivation of HIV from latency. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazkova, J.; Murray, D.; Justement, J.S.; Funk, E.K.; Nelson, A.K.; Moir, S.; Chun, T.W.; Fauci, A.S. Paucity of HIV DNA methylation in latently infected, resting CD4+ T cells from infected individuals receiving antiretroviral therapy. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5390–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cismasiu, V.B.; Paskaleva, E.; Suman Daya, S.; Canki, M.; Duus, K.; Avram, D. BCL11B is a general transcriptional repressor of the HIV-1 long terminal repeat in T lymphocytes through recruitment of the nurd complex. Virology 2008, 380, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafati, H.; Parra, M.; Hakre, S.; Moshkin, Y.; Verdin, E.; Mahmoudi, T. Repressive LTR nucleosome positioning by the BAF complex is required for HIV latency. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, T. The BAF complex and HIV latency. Transcription 2012, 3, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duyne, R.; Guendel, I.; Narayanan, A.; Gregg, E.; Shafagati, N.; Tyagi, M.; Easley, R.; Klase, Z.; Nekhai, S.; Kehn-Hall, K.; et al. Varying modulation of HIV-1 LTR activity by BAF complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 411, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boese, A.; Sommer, P.; Holzer, D.; Maier, R.; Nehrbass, U. Integrase interactor 1 (INI1/HSNF5) is a repressor of basal human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter activity. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2503–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dykhuizen, E.C.; Carmody, L.C.; Tolliday, N.; Crabtree, G.R.; Palmer, M.A. Screening for inhibitors of an essential chromatin remodeler in mouse embryonic stem cells by monitoring transcriptional regulation. J. Biomol. Screen 2012, 17, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.Y.; Chiang, C.M. The double bromodomain-containing chromatin adaptor BRD4 and transcriptional regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 13141–13145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yik, J.H.; Chen, R.; He, N.; Jang, M.K.; Ozato, K.; Zhou, Q. Recruitment of P-TEFB for stimulation of transcriptional elongation by the bromodomain protein BRD4. Mol. Cell. 2005, 19, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisgrove, D.A.; Mahmoudi, T.; Henklein, P.; Verdin, E. Conserved P-TEFB-interacting domain of BRD4 inhibits HIV transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13690–13695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Gaiha, G.D.; John, S.P.; Pertel, T.; Chin, C.R.; Gao, G.; Qu, H.; Walker, B.D.; Elledge, S.J.; Brass, A.L. Reactivation of latent HIV-1 by inhibition of BRD4. Cell. Rep. 2012, 2, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, D.; Calvanese, V.; Dar, R.D.; Xing, S.; Schroeder, S.; Martins, L.; Aull, K.; Li, P.C.; Planelles, V.; Bradner, J.E.; et al. Bet bromodomain-targeting compounds reactivate HIV from latency via a Tat-independent mechanism. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Q. The BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 activates HIV latency through antagonizing BRD4 inhibition of Tat-transactivation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, C.; Archin, N.; Michaels, D.; Belkina, A.C.; Denis, G.V.; Bradner, J.; Sebastiani, P.; Margolis, D.M.; Montano, M. Bet bromodomain inhibition as a novel strategy for reactivation of HIV-1. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, D.; Conrad, R.J.; Ott, M. Bromodomain proteins in HIV infection. Viruses 2013, 5, 1571–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, X.; Barboric, M.; Lenasi, T.; Peterlin, B.M. Hmba releases P-TEFB from HEXIM1 and 7SK snRNA via PI3k/AKT and activates HIV transcription. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schroder, A.R.; Shinn, P.; Chen, H.; Berry, C.; Ecker, J.R.; Bushman, F. HIV-1 integration in the human genome favors active genes and local hotspots. Cell 2002, 110, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Yang, H.C.; Rabi, S.A.; Bravo, H.C.; Shroff, N.S.; Irizarry, R.A.; Zhang, H.; Margolick, J.B.; Siliciano, J.D.; Siliciano, R.F. Influence of host gene transcription level and orientation on HIV-1 latency in a primary-cell model. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5384–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenasi, T.; Contreras, X.; Peterlin, B.M. Transcriptional interference antagonizes proviral gene expression to promote HIV latency. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 4, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrill-Mix, S.; Lewinski, M.K.; Famiglietti, M.; Bosque, A.; Malani, N.; Ocwieja, K.E.; Berry, C.C.; Looney, D.; Shan, L.; Agosto, L.M.; et al. HIV latency and integration site placement in five cell-based models. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Sluis, R.M.; Pollakis, G.; van Gerven, M.L.; Berkhout, B.; Jeeninga, R.E. Latency profiles of full length HIV-1 molecular clone variants with a subtype specific promoter. Retrovirology 2011, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, J.C.; Lim, K.I.; Calafi, A.; Rossi, J.J.; Schaffer, D.V.; Arkin, A.P. Combinatorial latency reactivation for HIV-1 subtypes and variants. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5958–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svicher, V.; Ceccherini-Silberstein, F.; Antinori, A.; Aquaro, S.; Perno, C.F. Understanding HIV compartments and reservoirs. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2014, 11, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, A.D.; Weinberger, L.S. Stochastic fate selection in HIV-infected patients. Cell 2013, 155, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, L.S.; Burnett, J.C.; Toettcher, J.E.; Arkin, A.P.; Schaffer, D.V. Stochastic gene expression in a lentiviral positive-feedback loop: HIV-1 Tat fluctuations drive phenotypic diversity. Cell 2005, 122, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dar, R.D.; Hosmane, N.N.; Arkin, M.R.; Siliciano, R.F.; Weinberger, L.S. Screening for noise in gene expression identifies drug synergies. Science 2014, 344, 1392–1396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ying, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Qu, X.; Wang, P.; Liu, S.; Lu, D.; Zhu, H. Selective histonedeacetylase inhibitor m344 intervenes in HIV-1 latency through increasing histone acetylation and activation of NF-kappaB. PLoS One 2012, 7, e48832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandelo Jose, D.; Bartholomeeusen, K.; da Cunha, R.D.; Abreu, C.M.; Glinski, J.; da Costa, T.B.; Bacchi Rabay, A.F.; Pianowski Filho, L.F.; Dudycz, L.W.; Ranga, U.; et al. Reactivation of latent HIV-1 by new semi-synthetic ingenol esters. Virology 2014, 462–463, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, R.; Wolkenberg, S.; Powell, D.; Karn, J.; Das, B.; Margolis, D.; Archin, N.; Holloway, K.; Wang, I.; Cook, E.; et al. Farnesyl-transferase inhibitors: Identification and validation of a class which reactivates HIV latent expression and is synergistic with other mechanisms in vitro. In Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on HIV Persistence during Therapy, Miami, FL, USA, 3–6 December 2013.
- Chen, L.; Fischle, W.; Verdin, E.; Greene, W.C. Duration of nuclear NF-κB action regulated by reversible acetylation. Science 2001, 293, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartholomeeusen, K.; Fujinaga, K.; Xiang, Y.; Peterlin, B.M. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACis) that release the positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFB) from its inhibitory complex also activate HIV transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 14400–14407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Crignis, E.; Mahmoudi, T. HIV Eradication: Combinatorial Approaches to Activate Latent Viruses. Viruses 2014, 6, 4581-4608. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6114581
De Crignis E, Mahmoudi T. HIV Eradication: Combinatorial Approaches to Activate Latent Viruses. Viruses. 2014; 6(11):4581-4608. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6114581
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Crignis, Elisa, and Tokameh Mahmoudi. 2014. "HIV Eradication: Combinatorial Approaches to Activate Latent Viruses" Viruses 6, no. 11: 4581-4608. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6114581
APA StyleDe Crignis, E., & Mahmoudi, T. (2014). HIV Eradication: Combinatorial Approaches to Activate Latent Viruses. Viruses, 6(11), 4581-4608. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6114581



