Japanese Encephalitis Virus Upregulates the Expression of SOCS3 in Mouse Brain and Raw264.7 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus and Antibodies
2.2. Cell Lines and Mice
2.3. Virus Infection
2.4. Gene Chip and Bioinformatics
2.5. RNA Extraction, Semiquantitative RT-PCR and QRT-PCR
| Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5'-3')F= Forward, R= Reverse |
|---|---|
| SOCS3 | F=5'-GAGCGGATTCTACTGGAGCG-3' |
| R=5'-TGGATGCGTAGGTTCTTGGTC-3' | |
| GAPDH | F=5'-GCCCAAGATGCCCTTCAGT-3' |
| R=5'-CCTTCCGTGTTCCTACCCC-3' |
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Histological Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gene Expression Profiles in Raw264.7 Cells Infected with JEV
| Pathway Name | No. of Genes | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| IFN alpha signaling pathway | 2 | 0.0026 |
| IFN gamma signaling pathway | 2 | 0.0014 |
| IL-10 Anti-inflammatory signaling pathway | 2 | 0.0026 |
| p38 MAPK signaling pathway | 3 | 0.0018 |
| Cell cycle | 14 | 0.0 |
| Chemokine signaling pathway | 9 | 0.0 |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | 13 | 0.0 |
| Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | 10 | 0.0 |
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | 6 | 0.0012 |
| Metabolic pathways | 41 | 0.0 |
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 6 | 0.0 |
| p53 signaling pathway | 7 | 0.0 |
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | 5 | 2.0 × 10−4 |
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 7 | 0.0 |
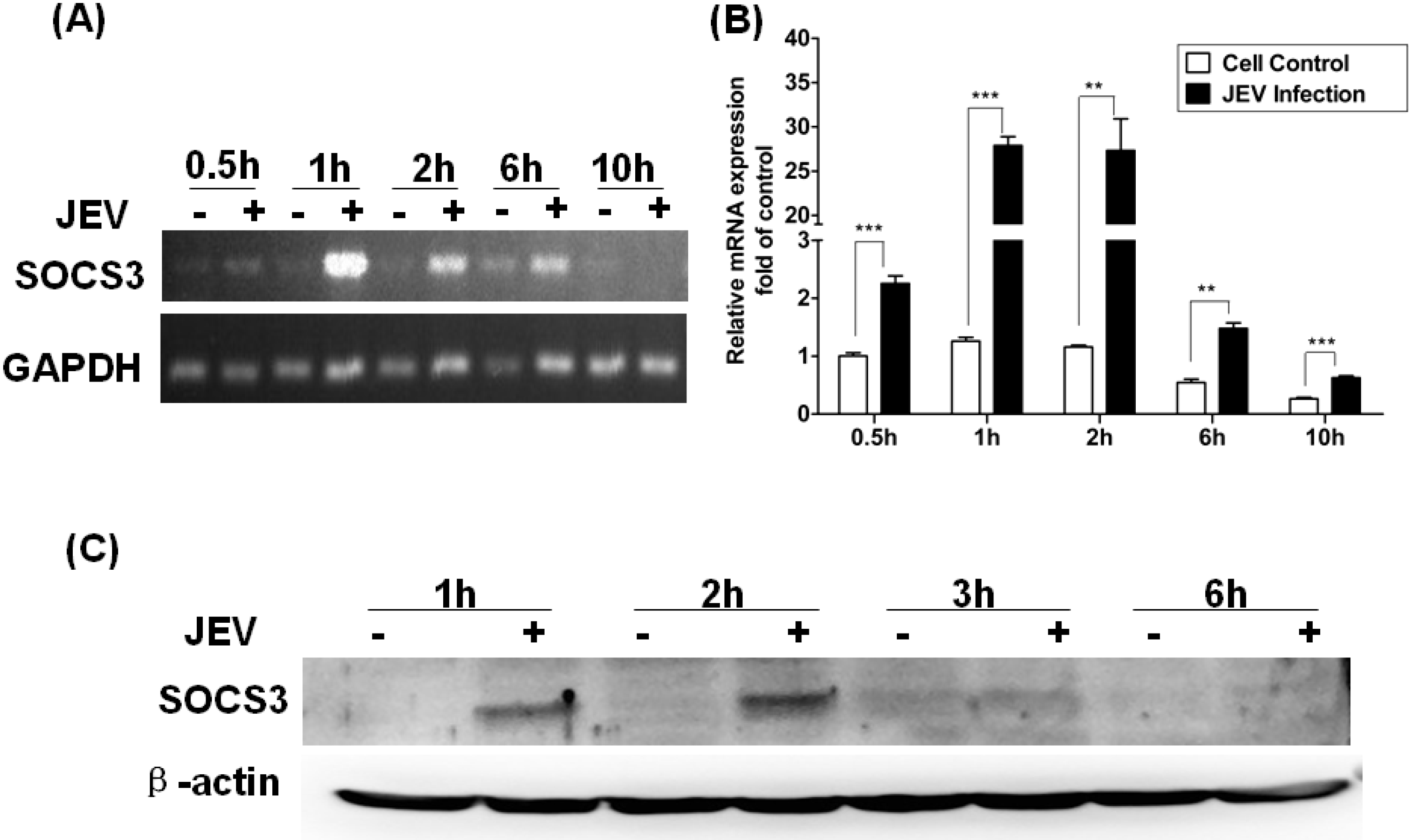
3.2. Change of SOCS3Expression in Raw264.7 Cells Infected with JEV
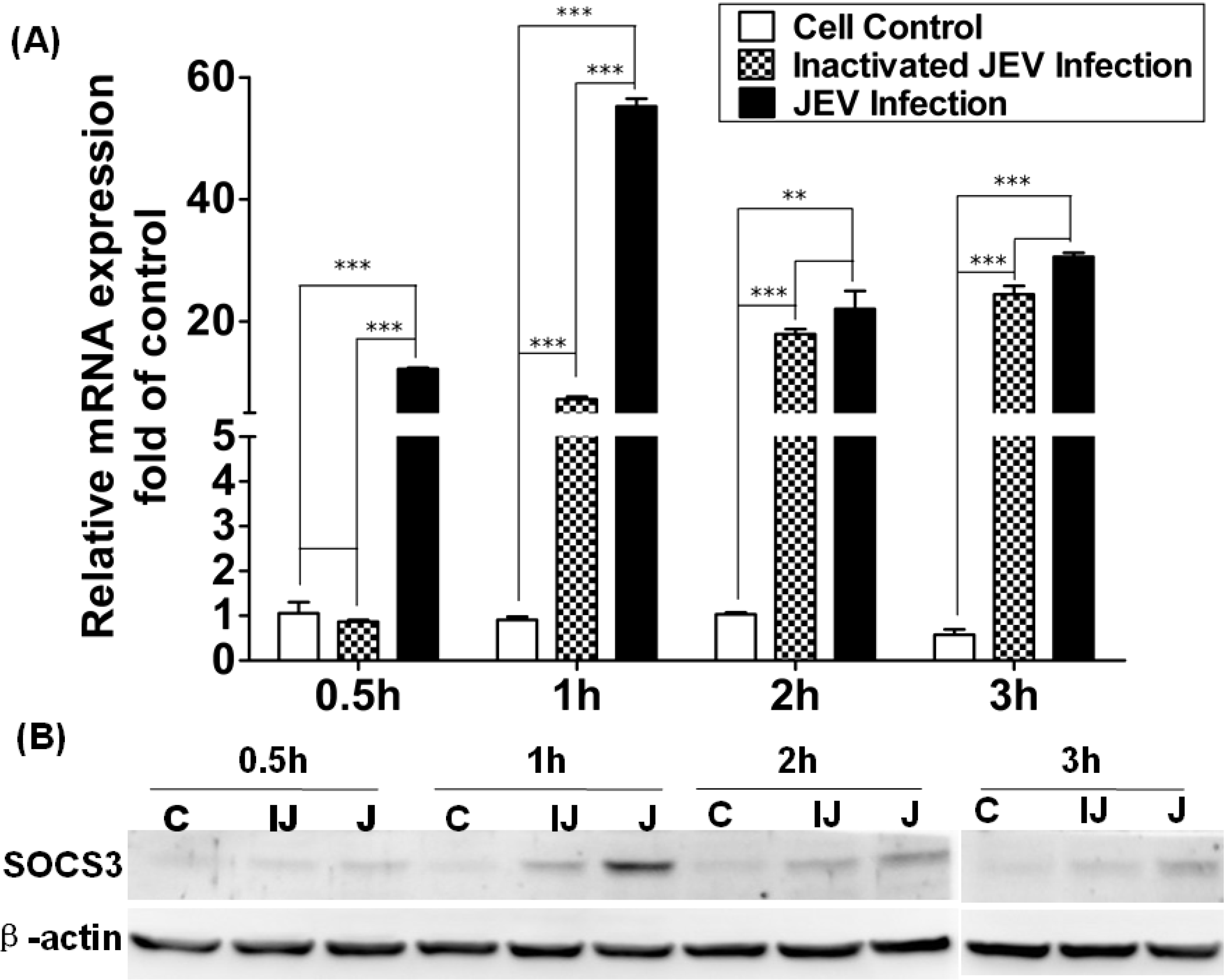
3.3. Level of Expression of SOCS3 in Raw264.7 Cells Infected with Inactivated JEV
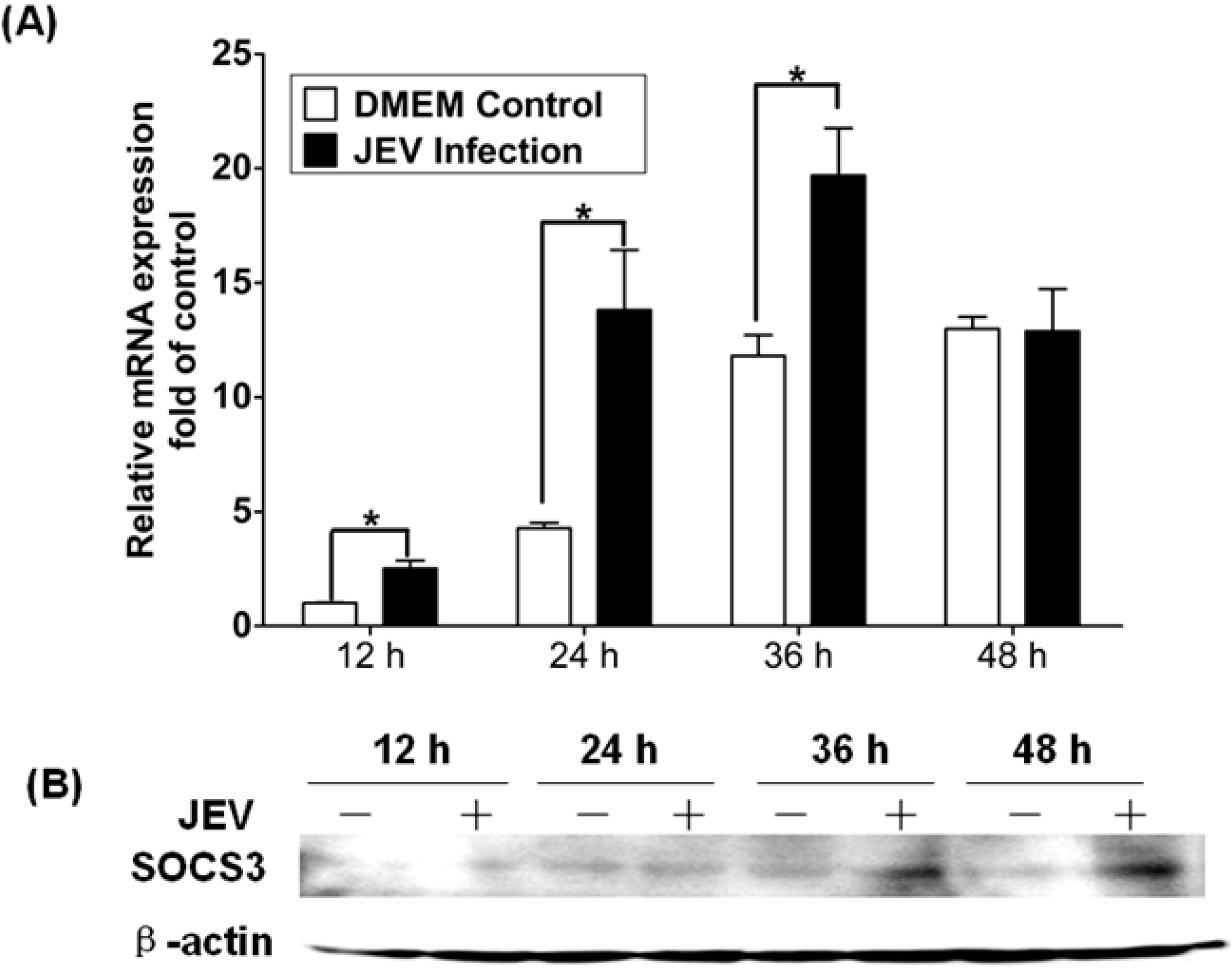
3.4. Expression of SOCS3 in Mouse Brain Infected with JEV
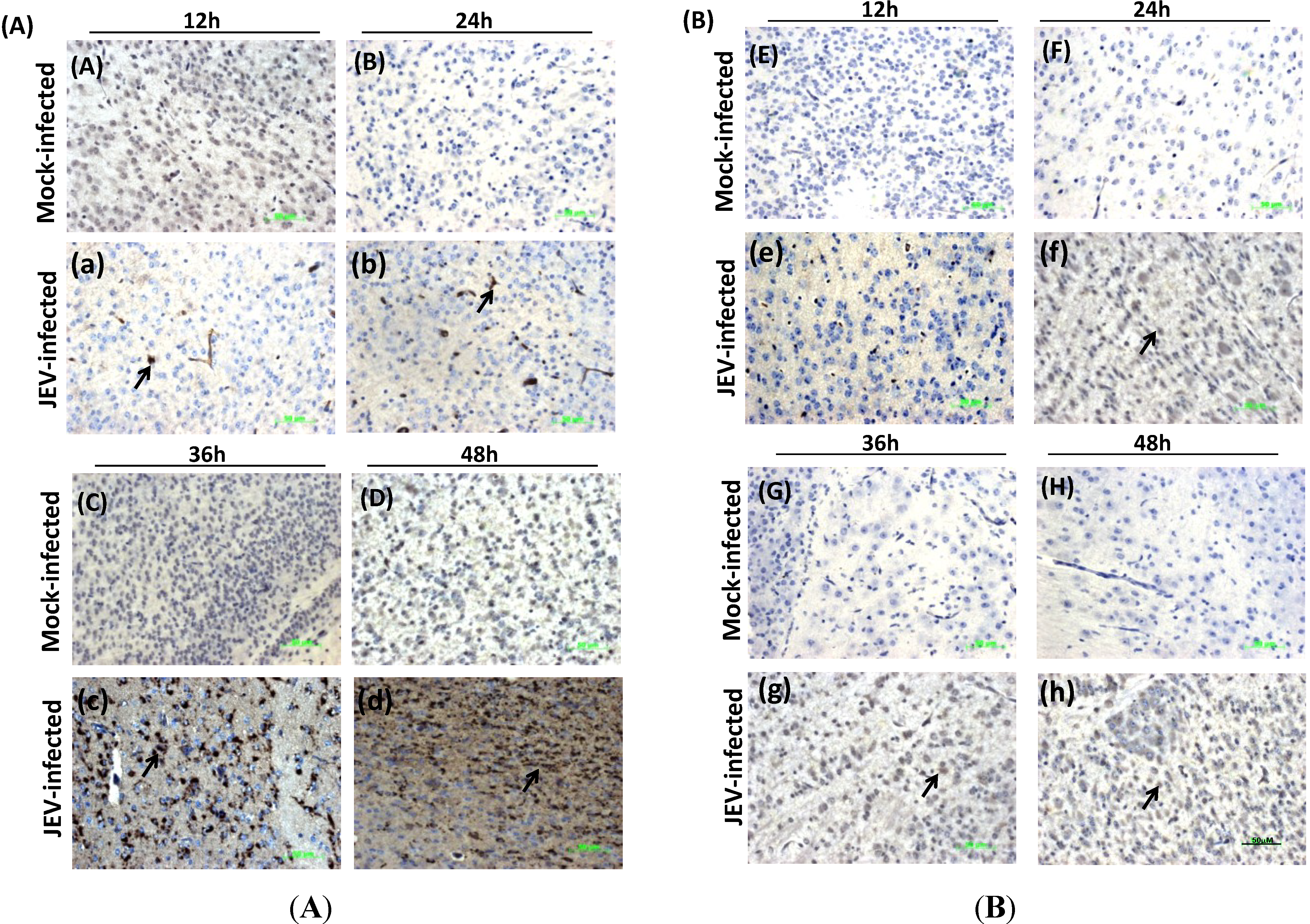
3.5. Histological Analysis and IHC Detection of Mouse Brain Infected with JEV
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Venugopal, K.; Goulrd, E.A. Towards a new generation of flavivirus vaccines. Vaccine 1994, 12, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.I.; Lee, Y.M. Japanese Encephalitis: The virus and vaccines. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2013, 10, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; Basu, A. Japanese Encephalitis-Pathological and Clinical Perspective. PLoS. Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, S.K. Japanese encephalitis: Perspective and new developments. Future Neurol. 2008, 3, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.B.; He, M.H.; Liu, X.D.; Li, X.Y.; Fan, B.; Zhao, S.H. Japanese encephalitis virus infects porcine kidney epithelial PK15 cells via clathrin- and cholesterol-dependent endocytosis. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, J.; Yang, X.; Jiang, R.; Chen, H.; Cao, S. Japanese encephalitis virus infection induces changes of mRNA profile of mouse spleen and brain. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randall, R.E.; Goodbourn, S. Interferons and viruses: An interplay between induction, signalling, antiviral responses and virus countermeasures. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, O.; Weber, F. Pathogenic viruses: Smart manipulators of the interferon system. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 316, 315–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.J.; Roehrig, J.T. New mouse model for dengue virus vaccine testing. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diamond, M.S.; Roberts, T.G.; Edgil, D.; Lu, B.; Ernst, J.; Harris, E. Modulation of Dengue virus infection in human cells by alpha, beta, and gamma interferons. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 4957–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.J.; Liao, C.L.; Lin, E.; Lin, Y.L. Blocking of the alpha interferon-induced Jak-Stat signaling pathway by Japanese encephalitis virus infection. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9285–9294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.J.; Chang, B.L.; Yu, H.P.; Liao, C.L.; Lin, Y.L. Blocking of interferon-induced Jak-Stat signaling by Japanese encephalitis virus NS5 through a protein tyrosine phosphatase-mediated mechanism. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5908–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, B.J.; Akhtar, L.N.; Benveniste, E.N. SOCS1 and SOCS3 in the control of CNS immunity. Trends. Immunol. 2009, 30, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croker, B.A.; Kiu, H.; Nicholson, S.E. SOCS regulation of the JAK/STAT signalling pathway. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2008, 19, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, K.; Liu, B. Regulation of JAK-STAT signalling in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, L.N.; Qin, H.; Muldowney, M.T.; Yanagisawa, L.L.; Kutsch, O.; Clements, J.E.; Benveniste, E.N. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 inhibits antiviral IFN-beta signaling to enhance HIV-1 replication in macrophages. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 2393–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kershaw, N.J.; Murphy, J.M.; Lucet, I.S.; Nicola, N.A.; Babon, J.J. Regulation of Janus kinases by SOCS proteins. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, W.S.; Hilton, D.J. The role of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins in regulation of the immune response. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 503–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Roberts, K.L.; Niyongere, S.A.; Cong, Y.; Elson, C.O.; Benveniste, E.N. Molecular mechanism of lipopolysaccharide-induced SOCS-3 gene expression in macrophages and microglia. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 5966–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, K.; Dutta, K.; Nazmi, A.; Basu, A. Japanese encephalitis virus infection modulates the expression of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) in macrophages: Implications for the hosts’ innate immune response. Cell. Immunol. 2013, 285, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.S.; Li, X.M.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Wang, D.D.; Chen, H.C.; Qian, P. Isolation and molecular characterization of genotype 1 Japanese encephalitis virus, SX09S-01, from pigs in China. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, L.N.; Benveniste, E.N. Viral exploitation of host SOCS protein functions. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 1912–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasukawa, H.; Yajima, T.; Duplain, H.; Iwatate, M.; Kido, M.; Hoshijima, M.; Weitzman, M.D.; Nakamura, T.; Woodard, S.; Xiong, D.; et al. The suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 (SOCS1) is a novel therapeutic target for enterovirus-induced cardiac injury. J. Clin. Invest. 2003, 111, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, J.G.; Ludwig, S.; Ehrhardt, C.; Albrecht, U.; Erhardt, A.; Schaper, F.; Heinrich, P.C.; Häussinger, D. IFN-alpha antagonistic activity of HCV core protein involves induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling-3. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 488–490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koeberlein, B.; zur Hausen, A.; Bektas, N.; Zentgraf, H.; Chin, R.; Nguyen, L.T.; Kandolf, R.; Torresi, J.; Bock, C.T. Hepatitis B virus overexpresses suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 (SOCS3) thereby contributing to severity of inflammation in the liver. Virus Res. 2010, 148, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, S.; Yokosawa, N.; Okabayashi, T.; Suzutani, T.; Miura, S.; Jimbow, K.; Fujii, N. Induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 by herpes simplex virus type 1 contributes to inhibition of the interferon signaling pathway. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6282–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, S.; Yokosawa, N.; Okabayashi, T.; Suzutani, T.; Fujii, N. Induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 by herpes simplex virus type 1 confers efficient viral replication. Virology 2005, 338, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.C.; Yan, T.; Li, L.; You, S.; Zhang, C. Respiratory syncytial virus inhibits interferon-alpha-inducible signaling in macrophage-like U937 cells. J. Infect. 2007, 54, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Ishibashi, K.; Ishioka, K.; Zhao, D.; Sato, M.; Ohara, S.; Abe, Y.; Kawasaki, Y.; Sato, Y.; Yokota, S.; et al. RSV replication is attenuated by counteracting expression of the suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) molecules. Virology 2009, 391, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, E.K.; Schmolke, M.; Wolff, T.; Viemann, D.; Roth, J.; Bode, J.G.; Ludwig, S. Influenza A virus inhibits type I IFN signaling via NF-kappaB-dependent induction of SOCS-3 expression. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothlichet, J.; Chignard, M.; Si-Tahar, M. Cutting edge: Innate immune response triggered by influenza A virus is negatively regulated by SOCS1 and SOCS3 through a RIG-I/IFNAR1-dependent pathway. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 2034–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansfield, K.L.; Johnson, N.; Cosby, S.L.; Solomon, T.; Fooks, A.R. Transcriptional upregulation of SOCS 1 and suppressors of cytokine signaling 3 mRNA in the absence of suppressors of cytokine signaling 2 mRNA after infection with West Nile virus or tick-borne encephalitis virus. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhu, Q.; Cao, Q.; Chen, H.; Qian, P. Japanese Encephalitis Virus Upregulates the Expression of SOCS3 in Mouse Brain and Raw264.7 Cells. Viruses 2014, 6, 4280-4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6114280
Li X, Zhu Q, Cao Q, Chen H, Qian P. Japanese Encephalitis Virus Upregulates the Expression of SOCS3 in Mouse Brain and Raw264.7 Cells. Viruses. 2014; 6(11):4280-4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6114280
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiangmin, Qiaoyan Zhu, Qishu Cao, Huanchun Chen, and Ping Qian. 2014. "Japanese Encephalitis Virus Upregulates the Expression of SOCS3 in Mouse Brain and Raw264.7 Cells" Viruses 6, no. 11: 4280-4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6114280
APA StyleLi, X., Zhu, Q., Cao, Q., Chen, H., & Qian, P. (2014). Japanese Encephalitis Virus Upregulates the Expression of SOCS3 in Mouse Brain and Raw264.7 Cells. Viruses, 6(11), 4280-4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6114280




