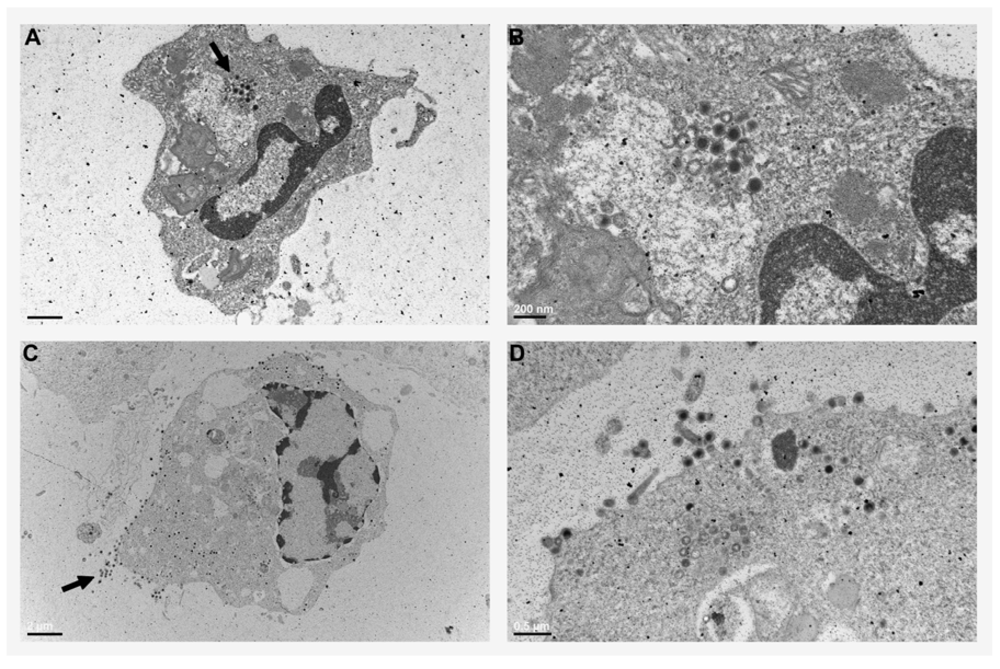
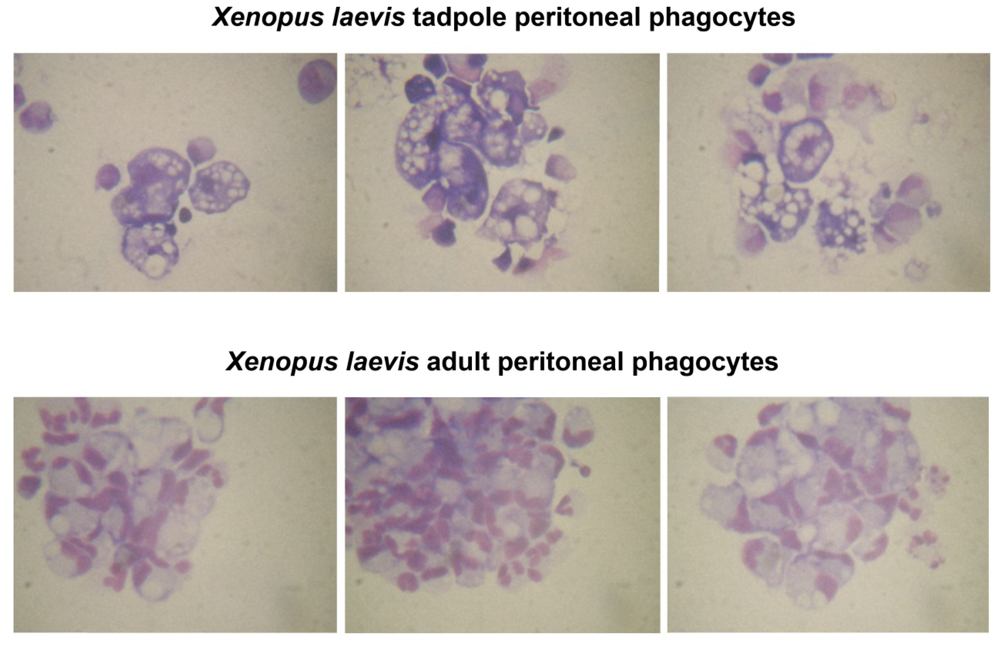
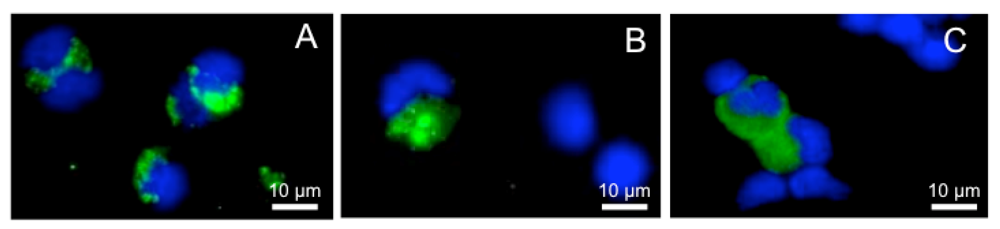
Abstract
Ranaviruses (RV, Iridoviridae) are large double-stranded DNA viruses that infect fish, amphibians and reptiles. For ecological and commercial reasons, considerable attention has been drawn to the increasing prevalence of ranaviral infections of wild populations and in aquacultural settings. Importantly, RVs appear to be capable of crossing species barriers of numerous poikilotherms, suggesting that these pathogens possess a broad host range and potent immune evasion mechanisms. Indeed, while some of the 95–100 predicted ranavirus genes encode putative evasion proteins (e.g., vIFα, vCARD), roughly two-thirds of them do not share significant sequence identity with known viral or eukaryotic genes. Accordingly, the investigation of ranaviral virulence and immune evasion strategies is promising for elucidating potential antiviral targets. In this regard, recombination-based technologies are being employed to knock out gene candidates in the best-characterized RV member, Frog Virus (FV3). Concurrently, by using animal infection models with extensively characterized immune systems, such as the African clawed frog, Xenopus laevis, it is becoming evident that components of innate immunity are at the forefront of virus-host interactions. For example, cells of the macrophage lineage represent important combatants of RV infections while themselves serving as targets for viral infection, maintenance and possibly dissemination. This review focuses on the recent advances in the understanding of the RV immune evasion strategies with emphasis on the roles of the innate immune system in ranaviral infections.
Keywords:
Iridovirus; ranavirus; FV3; frog virus 3; innate immunity; macrophage; anti-viral; immune-evasion; cytokines; inflammation Abbreviations
| [ATV] | Ambystoma tiginum virus |
| [BIV] | Bohle Iridovirus |
| [CARD] | caspase activation and recruitment domain |
| [CCV] | channel catfish herpes virus |
| [DE] | delayed early genes |
| [EHNV] | epizootic haematopoietic necrosis virus |
| [eIF2α] | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha |
| [FV3] | frog virus 3 |
| [HIV] | human immunodeficiency virus |
| [IE] | immediate early genes |
| [IFNγ] | interferon gamma |
| [IL-1β] | interleukin-1 beta |
| [IRF] | interferon regulatory factor |
| [L] | late genes |
| [MAPK] | mitogen activated protein kinase |
| [MX1] | Myxovirus-resistance1 |
| [ORF] | open reading frame |
| [PKR] | RNA-dependent protein kinase |
| [PL] | peritoneal leukocyte |
| [RCV-Z] | Rana (Lithobates) catesbeiana Virus Z |
| [RV] | ranavirus |
| [SGIV] | Singapore Grouper Iridovirus |
| [TGIV] | Taiwan Grouper Iridovirus |
| [TNFα] | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| [vIFα] | viral translation initiation factor-alpha homolog |
1. Introduction
Over the last two decades it has become increasingly apparent that amphibian species are facing a serious threat of extinction [], where roughly one-third (32%) of the 6593 amphibian species are diminishing as a result of complex, as of yet poorly understood causes. A number of possible escalating factors have been attributed to these die-offs, including destruction of habitats, increased levels of pollution, changes in climate as well as increasing ultraviolet irradiation [,]. While these may be underlining mechanisms, there is also a prevailing theory that the increasing amphibian declines stem from compromised immune systems of these animals coupled with elevated pathogenic threats [,], undoubtedly resulting from one or a combination of the above.
Until recently, it was believed that viral infections were a secondary contributing factor in these die-offs. However, currently members of the family Iridoviridae and particularly the genus Ranavirus (RVs, family Iridoviridae) have gained attention due to the dramatic rise in the prevalence of RV infections across pokilothermic species. In fact, ranaviruses are now considered the second most common infectious agent plaguing wild and cultured amphibian species [,], with half of the amphibian deaths in United States between 1996 and 2001 attributed to ranaviral infections [].
Ranaviruses are icosahedral, double-stranded DNA viruses with large genomes, ranging between 105 and 140 kilobase pairs in size. Specifically, members of the family Iridoviridae are known to infect three classes of ectothermic vertebrates: amphibians, bony fishes (teleosts) and reptiles []. To date three RV species that infect amphibians have been identified and grouped according to genetic and ecological parameters []. Amongst these, Bohle Iridovirus (BIV) infects Australian frogs and has so far remained confined to this region of the world. Ambystoma tiginum virus (ATV) infects salamanders and is primarily localized to United States and Canada. In contrast, the Frog Virus 3 (FV3), initially isolated from the leopard frog, Rana (Lithobates) pipiens, has been recognized worldwide as an amphibian pathogen. With a rapid increases in the prevalence and spread to multiple amphibian species, FV3 is believed to be a potential global threat to amphibian populations []. Although, FV3 is the greatest threat to pokilothermic vertebrates, information gained from studies dealing with the other two RV species and indeed from other members of the family Iridoviridae (generically referred to as “iridovirids” to distinguish them from members of the genus Iridovirus) should be recapitulated in order to better understand the mechanisms of infection and immunity within this family.
It is also becoming evident that RVs likely possess a plethora of immune evasion and host modulation mechanisms. A closer examination of the relationships between these viruses and their host immune systems is clearly warranted in light of increasing ranaviral prevalence and the potentially declining immune capacities of the ectothermic species that they infect. As compared to mammals, lower vertebrates such as those infected by iridovirids, possess functional but relatively less effective adaptive immune systems, with fewer antibody classes, poorer T lymphocyte expansion and generally less developed immunological memory responses (reviewed in reference []). Accordingly these organisms likely rely more heavily on innate immune components for pathogen clearance. In turn, cells of the macrophage lineage are indispensable for innate immune responses. In mammals, macrophages are long-lived, terminally differentiated cells of myeloid origin that exhibit limited proliferation capabilities and a high level of heterogeneity []. During certain viral infections, distinct macrophage subsets participate in anti-viral responses while in other instances mononuclear phagocytes may become productively infected and serve as long-term viral reservoirs and agents of viral dissemination. For example, during HIV infections macrophages are hijacked by the virus, store large numbers of virions and facilitate cell-to-cell spread of HIV [,,]. Conversely, as sentinels of the immune system, macrophages recognize viral infections through a repertoire of pattern recognition receptors [,,] and facilitate viral clearance by producing an array of bioactive molecules. Thus macrophages function in contrasting ways to either perpetuate virus replication or to eliminate it.
This review coalesces the current knowledge of the roles of innate immune components in ranaviral infections as well as recent advances in the understanding of ranavirus immune evasion strategies.
5. Concluding Remarks
Much remains to be learned regarding ranavirus gene regulation, cell invasion, the virus life cycle and immune evasion strategies. It is clear from the information presented here that there are definite gaps that must be bridged between what is currently known about the immune responses to these viruses, the viral infection strategies and the specifics of the mechanisms by which these pathogens so efficiently infiltrate hosts and even cross species barriers. These infectious agents encode an unprecedented number of putative gene products, several of which represent not only potential virulence factors but also the means to better understand both immune evasion strategies and the immune functions being manipulated. Ultimately, the study of ranaviruses in the context of their host immune systems holds the promise of providing insight into the pressures governing the evolution of both the viral invasion strategies as well as the host immune countermeasures.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
LG would like to thank the National Science and Engineering Council of Canada for a PDF Scholarship. Research support: 2 R24 Al 059830-06 from the NIH, and IOS-0923772 and IOS-0742711 from the NSF.
References
- Stuart, S.N.; Chanson, J.S.; Cox, N.A.; Young, B.E.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Fischman, D.L.; Waller, R.W. Status and trends of amphibian declines and extinctions worldwide. Science 2004, 306, 1783–1786. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, J.P. Amphibian decline and extinction: What we know and what we need to learn. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2010, 92, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daszak, P.; Berger, L.; Cunningham, A.A.; Hyatt, A.D.; Green, D.E.; Speare, R. Emerging infectious diseases and amphibian population declines. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 735–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.E.; Converse, K.A.; Schrader, A.K. Epizootiology of sixty-four amphibian morbidity and mortality events in the USA, 1996–2001. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 969, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.J.; Miller, D.L.; Hoverman, J.T. Ecology and pathology of amphibian ranaviruses. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2009, 87, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jancovich, J.K.; Jacobs, B.L. Innate immune evasion mediated by the Ambystoma tigrinum virus eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2alpha homologue. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5061–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchar, V.G.; Hyatt, A.; Miyazaki, T.; Williams, T. Family iridoviridae: Poor viral relations no longer. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 328, 123–170. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, J.; Ohta, Y. Comparative and developmental study of the immune system in Xenopus. Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 1249–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.; Martinez, F.O. Alternative activation of macrophages: Mechanism and functions. Immunity 2010, 32, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiras, M.; Lopez-Huertas, M.R.; Perez-Olmeda, M.; Alcami, J. Understanding HIV-1 latency provides clues for the eradication of long-term reservoirs. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 798–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gousset, K.; Ablan, S.D.; Coren, L.V.; Ono, A.; Soheilian, F.; Nagashima, K.; Ott, D.E.; Freed, E.O. Real-time visualization of HIV-1 GAG trafficking in infected macrophages. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Groot, F.; Welsch, S.; Sattentau, Q.J. Efficient HIV-1 transmission from macrophages to T cells across transient virological synapses. Blood 2008, 111, 4660–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Antiviral signaling through pattern recognition receptors. J. Biochem. 2007, 141, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. SnapShot: Pattern-recognition receptors. Cell 2007, 129. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, A.J.; Locarnini, S.A. Toll-like receptors, RIG-I-like RNA helicases and the antiviral innate immune response. Immunol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 85, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gut, J.P.; Anton, M.; Bingen, A.; Vetter, J.M.; Kirn, A. Frog virus 3 induces a fatal hepatitis in rats. Lab. Invest. 1981, 45, 218–228. [Google Scholar]
- Kirn, A.; Bingen, A.; Steffan, A.M.; Wild, M.T.; Keller, F.; Cinqualbre, J. Endocytic capacities of Kupffer cells isolated from the human adult liver. Hepatology 1982, 2, 216–222. [Google Scholar]
- Kirn, A.; Steffan, A.M.; Bingen, A. Inhibition of erythrophagocytosis by cultured rat Kupffer cells infected with frog virus 3. J. Reticuloendothel. Soc. 1980, 28, 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Hagmann, W.; Steffan, A.M.; Kirn, A.; Keppler, D. Leukotrienes as mediators in frog virus 3-induced hepatitis in rats. Hepatology 1987, 7, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubertin, A.M.; Hirth, C.; Travo, C.; Nonnenmacher, H.; Kirn, A. Preparation and properties of an inhibitory extract from frog virus 3 particles. J. Virol. 1973, 11, 694–701. [Google Scholar]
- Gendrault, J.L.; Steffan, A.M.; Bingen, A.; Kirn, A. Penetration and uncoating of frog virus 3 (FV3) in cultured rat Kupffer cells. Virology 1981, 112, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elharrar, M.; Hirth, C.; Blanc, J.; Kirn, A. Pathogenesis of the toxic hepatitis of mice provoked by FV3 (frog virus 3): Inhibition of the liver macromolecular synthesis. Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 1973, 319, 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Kirn, A.; Gut, J.P.; Elharrar, M. FV3 (Frog Virus 3) toxicity for the mouse. Nouv. Presse. Med. 1972, 1, 19–43. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, J.; Abramowitz, L.; Gantress, J.; Morales, H.D. Xenopus laevis: A possible vector of Ranavirus infection? J. Wildl. Dis. 2007, 43, 645–652. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, H.D.; Abramowitz, L.; Gertz, J.; Sowa, J.; Vogel, A.; Robert, J. Innate immune responses and permissiveness to ranavirus infection of peritoneal leukocytes in the frog Xenopus laevis. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 4912–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwicki, A.K.; Pozet, F.; Morand, M.; Volatier, C.; Terech-Majewska, E. Effects of iridovirus-like agent on the cell-mediated immunity in sheatfish (Silurus glanis)—An in vitro study. Virus. Res. 1999, 63, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.B.; Chen, C.Y.; Lai, Y.Y.; Lin, C.S.; Huang, H.T. Histological, ultrastructural, and in situ hybridization study on enlarged cells in grouper Epinephelus hybrids infected by grouper iridovirus in Taiwan (TGIV). Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2004, 58, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchar, V.G.; Wang, J.; Murti, G.; Carey, C.; Rollins-Smith, L. Inactivation of frog virus 3 and channel catfish virus by esculentin-2P and ranatuerin-2P, two antimicrobial peptides isolated from frog skin. Virology 2001, 288, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Cai, J.; Yan, Y.; Qin, Q. Roles of stress-activated protein kinases in the replication of Singapore grouper iridovirus and regulation of the inflammatory responses in grouper cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 92, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Maniero, G.D.; Morales, H.; Gantress, J.; Robert, J. Generation of a long-lasting, protective, and neutralizing antibody response to the ranavirus FV3 by the frog Xenopus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantress, J.; Maniero, G.D.; Cohen, N.; Robert, J. Development and characterization of a model system to study amphibian immune responses to iridoviruses. Virology 2003, 311, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, H.D.; Robert, J. Characterization of primary and memory CD8 T-cell responses against ranavirus (FV3) in Xenopus laevis. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 2240–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbertson, R.A.; Lang, R.A.; Coghlan, J.P. Macrophage products IL-1 alpha, TNF alpha and bFGF may mediate multiple cytopathic effects in the developing eyes of GM-CSF transgenic mice. Exp. Eye Res. 1990, 51, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, N.R.; Millet, I.; Paliwal, V.; Herzog, W.; Solomon, D.; Ramabhadran, R.; Askenase, P.W. Induction of macrophage TNF alpha, IL-1, IL-6, and PGE2 production by DTH-initiating factors. Cell. Immunol. 1991, 137, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, A.; Iizuka, K.; Natori, S. Induction of TNF-like factor by murine macrophage-like cell line J774.1 on treatment with Sarcophaga lectin. FEBS Lett. 1984, 175, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, F.Y.; Li, Y.; Millott, S. Tumour necrosis factor (TNF-alpha) in leishmaniasis. II. TNF-alpha-induced macrophage leishmanicidal activity is mediated by nitric oxide from L-arginine. Immunology 1990, 71, 556–559. [Google Scholar]
- McMasters, K.M.; Cheadle, W.G. Regulation of macrophage TNF alpha, IL-1 beta, and Ia (I-A alpha) mRNA expression during peritonitis is site dependent. J. Surg. Res. 1993, 54, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.J.; Pullen, J.K.; Ghildyal, N.; Eustis-Turf, E.; Schook, L.B. Regulation of IL-1 and TNF-alpha expression during the differentiation of bone marrow derived macrophage. J. Immunol. 1989, 142, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda, O.; Takeda, Y.; Woo, H.J.; Shimada, S.; Higuchi, M.; Osawa, T. A human macrophage hybridoma producing a cytotoxic factor distinct from TNF, LT, and IL-1. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 1988, 26, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Cassatella, M.A.; Bazzoni, F.; Flynn, R.M.; Dusi, S.; Trinchieri, G.; Rossi, F. Molecular basis of interferon-gamma and lipopolysaccharide enhancement of phagocyte respiratory burst capability. Studies on the gene expression of several NADPH oxidase components. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 20241–20246. [Google Scholar]
- Cassatella, M.A.; Cappelli, R.; Della Bianca, V.; Grzeskowiak, M.; Dusi, S.; Berton, G. Interferon-gamma activates human neutrophil oxygen metabolism and exocytosis. Immunology 1988, 63, 499–506. [Google Scholar]
- Corradin, S.B.; Buchmuller-Rouiller, Y.; Mauel, J. Phagocytosis enhances murine macrophage activation by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Eur. J. Immunol. 1991, 21, 2553–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fremond, C.M.; Togbe, D.; Doz, E.; Rose, S.; Vasseur, V.; Maillet, I.; Jacobs, M.; Ryffel, B.; Quesniaux, V.F. IL-1 receptor-mediated signal is an essential component of MyD88-dependent innate response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1178–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Grayfer, L.; Belosevic, M. Molecular characterization, expression and functional analysis of goldfish (Carassius auratus L.) interferon gamma. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayfer, L.; Garcia, E.G.; Belosevic, M. Comparison of macrophage antimicrobial responses induced by type II interferons of the goldfish (Carassius auratus L.). J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 23537–23547. [Google Scholar]
- Grayfer, L.; Walsh, J.G.; Belosevic, M. Characterization and functional analysis of goldfish (Carassius auratus L.) tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibe, K.; Yamanishi, T.; Wang, Y.; Osatomi, K.; Hara, K.; Kanai, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Oda, T. Comparative analysis of the production of nitric oxide (NO) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) from macrophages exposed to high virulent and low virulent strains of Edwardsiella tarda. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2009, 27, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, C.F.; Murray, H.W.; Wiebe, M.E.; Rubin, B.Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J. Exp. Med. 1983, 158, 670–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordas, M.C.; Costa, M.M.; Roca, F.J.; Lopez-Castejon, G.; Mulero, V.; Meseguer, J.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B. Turbot TNFalpha gene: Molecular characterization and biological activity of the recombinant protein. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 389–400. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, M.K.; Kurath, G.; Garver, K.A.; Herwig, R.P.; Winton, J.R. Quantitative expression profiling of immune response genes in rainbow trout following infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) infection or DNA vaccination. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2004, 17, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, M.K.; Nichols, K.M.; Winton, J.R.; Kurath, G.; Thorgaard, G.H.; Wheeler, P.; Hansen, J.D.; Herwig, R.P.; Park, L.K. Comprehensive gene expression profiling following DNA vaccination of rainbow trout against infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 2089–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhou, Z.C.; Chen, C.; Huo, W.L.; Yin, Z.X.; Weng, S.P.; Chan, S.M.; Yu, X.Q.; He, J.G. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene from mandarin fish, Siniperca chuatsi: Molecular cloning, cytotoxicity analysis and expression profile. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 3615–3622. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, S.; Wang, T.; Zou, J.; Cunningham, C.; Secombes, C.J. The first cytokine sequence within cartilaginous fish: IL-1 beta in the small spotted catshark (Scyliorhinus canicula). J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 3329–3340. [Google Scholar]
- Hirono, I.; Nam, B.H.; Kurobe, T.; Aoki, T. Molecular cloning, characterization, and expression of TNF cDNA and gene from Japanese flounder Paralychthys olivaceus. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 4423–4427. [Google Scholar]
- Igawa, D.; Sakai, M.; Savan, R. An unexpected discovery of two interferon gamma-like genes along with interleukin (IL)-22 and -26 from teleost: IL-22 and -26 genes have been described for the first time outside mammals. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, A.; Murata, E.; Akita, M.; Kaneko, K.; Moriya, O.; Tomita, M.; Hayashi, H. Roles of macrophages in programmed cell death and remodeling of tail and body muscle of Xenopus laevis during metamorphosis. Histochem. Cell Biol. 1998, 109, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Auffray, C.; Fogg, D.; Garfa, M.; Elain, G.; Join-Lambert, O.; Kayal, S.; Sarnacki, S.; Cumano, A.; Lauvau, G.; Geissmann, F. Monitoring of blood vessels and tissues by a population of monocytes with patrolling behavior. Science 2007, 317, 666–670. [Google Scholar]
- Nahrendorf, M.; Swirski, F.K.; Aikawa, E.; Stangenberg, L.; Wurdinger, T.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Libby, P.; Weissleder, R.; Pittet, M.J. The healing myocardium sequentially mobilizes two monocyte subsets with divergent and complementary functions. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 3037–3047. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Wong, W.C.; Sem, X.; Han, H.; Ong, S.M.; Tan, Y.C.; Yeap, W.H.; Gan, C.S.; Ng, K.Q.; et al. Identification of novel functional differences in monocyte subsets using proteomic and transcriptomic methods. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 4028–4038. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock, L. The CD14+ CD16+ blood monocytes: Their role in infection and inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flajnik, M.F.; Kaufman, J.F.; Hsu, E.; Manes, M.; Parisot, R.; Du Pasquier, L. Major histocompatibility complex-encoded class I molecules are absent in immunologically competent Xenopus before metamorphosis. J. Immunol. 1986, 137, 3891–3899. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, I.M.; Brown, R.E.; Hovanessian, A.G. Nature of inhibitor of cell-free protein synthesis formed in response to interferon and double-stranded RNA. Nature 1977, 268, 540–542. [Google Scholar]
- Meurs, E.; Chong, K.; Galabru, J.; Thomas, N.S.; Kerr, I.M.; Williams, B.R.; Hovanessian, A.G. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induced by interferon. Cell 1990, 62, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, W.K.; Hovanessian, A.; Brown, R.E.; Clemens, M.J.; Kerr, I.M. Interferon-mediated protein kinase and low-molecular-weight inhibitor of protein synthesis. Nature 1976, 264, 477–480. [Google Scholar]
- George, C.X.; Thomis, D.C.; McCormack, S.J.; Svahn, C.M.; Samuel, C.E. Characterization of the heparin-mediated activation of PKR, the interferon-inducible RNA-dependent protein kinase. Virology 1996, 221, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruvolo, P.P.; Gao, F.; Blalock, W.L.; Deng, X.; May, W.S. Ceramide regulates protein synthesis by a novel mechanism involving the cellular PKR activator RAX. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 11754–11758. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, J.; Alcami, J.; Esteban, M. Induction of apoptosis by double-stranded-RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) involves the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 and NF-kappaB. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 4653–4663. [Google Scholar]
- Langland, J.O.; Cameron, J.M.; Heck, M.C.; Jancovich, J.K.; Jacobs, B.L. Inhibition of PKR by RNA and DNA viruses. Virus. Res. 2006, 119, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essbauer, S.; Bremont, M.; Ahne, W. Comparison of the eIF-2alpha homologous proteins of seven ranaviruses (Iridoviridae). Virus Genes 2001, 23, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ward, B.M.; Yu, K.H.; Chinchar, V.G.; Robert, J. Improved knockout methodology reveals that frog virus 3 mutants lacking either the 18K immediate-early gene or the truncated vIF-2alpha gene are defective for replication and growth in vivo. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11131–11138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenburg, S.; Chinchar, V.G.; Dever, T.E. Characterization of a ranavirus inhibitor of the antiviral protein kinase PKR. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Majji, S.; Thodima, V.; Sample, R.; Whitley, D.; Deng, Y.; Mao, J.; Chinchar, V.G. Transcriptome analysis of Frog virus 3, the type species of the genus Ranavirus, family Iridoviridae. Virology 2009, 391, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, D.S.; Sample, R.C.; Sinning, A.R.; Henegar, J.; Chinchar, V.G. Antisense approaches for elucidating ranavirus gene function in an infected fish cell line. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).