Daphne Genkwa Sieb. et Zucc. Water-Soluble Extracts Act on Enterovirus 71 by Inhibiting Viral Entry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Water-Soluble Fraction of D. genkwa Inhibits Viral Replication
| Title | Concentration (mg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CC50a | EC50b | SI c | |
| Cytotoxic effect | |||
| RD cells | 1.444 ± 0.193 | ||
| MDCK cells | 1.603 ± 0.091 | ||
| HFF3 cells | 2.354 ± 0.018 | ||
| A549 cells | >2 | ||
| EV71d, TW/2231/98 (genotype C) | 0.163 ± 0.013 | 8.859 | |
| EV71, BrCr (genotype A) | 0.182 ± 0.027 | 7.934 | |
| EV71, TW/71552/05 (subgenotype C4) | 0.824 ± 0.004 | 1.752 | |
| EV71, TW/1101/08 (subgenotype B5) | >1 | – | |
| CV-B1 d | >1 | – | |
| CV-B2 | >1 | – | |
| CV-B3 | >1 | – | |
| CV-B4 | >1 | – | |
| CV-B5 | >1 | – | |
| Influenza virus A/WSN/33 | 0.838 ± 0.026 | 1.913 | |
| Adenovirus | >2 | – | |
| HSV-1 d | >2 | – | |

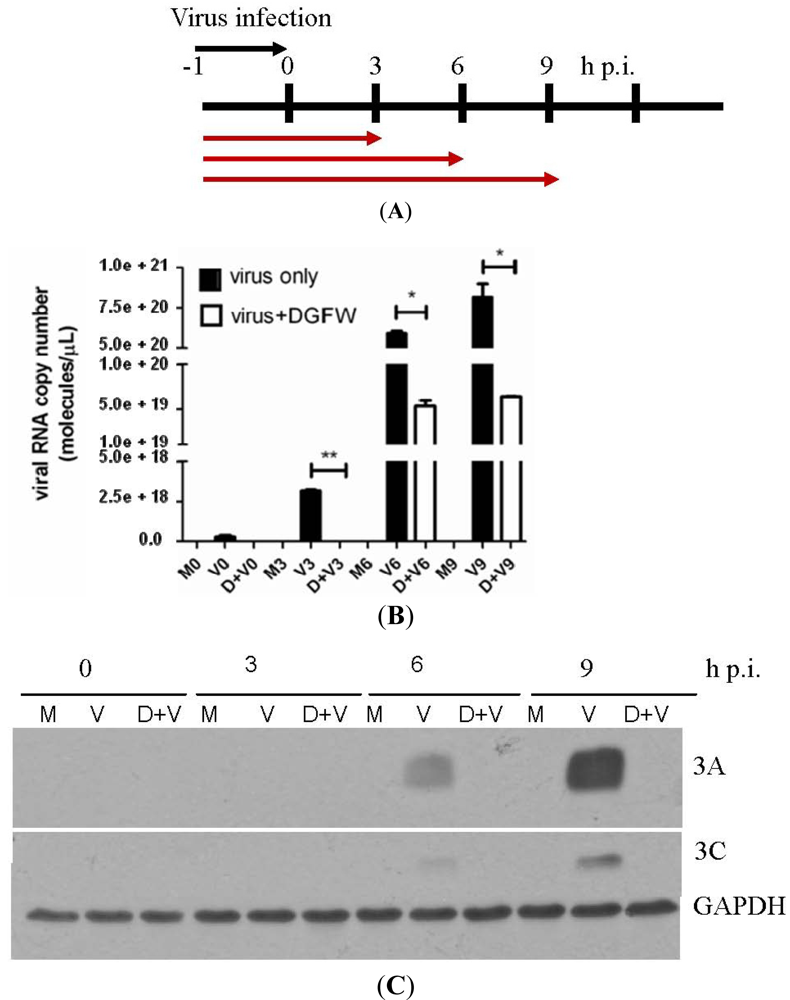
2.2. DGFW Inhibits Early Stages of Replication

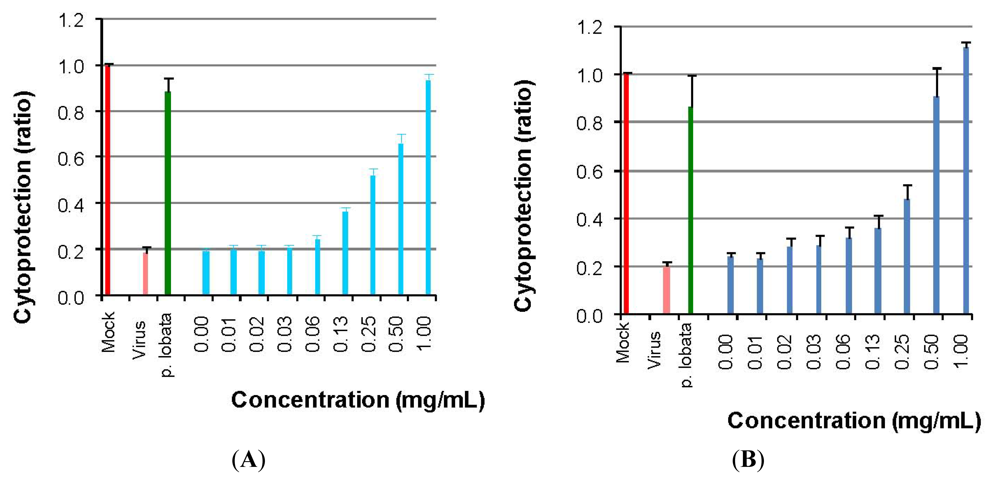
2.3. DGFW Inhibits Viral Attachment and Penetration
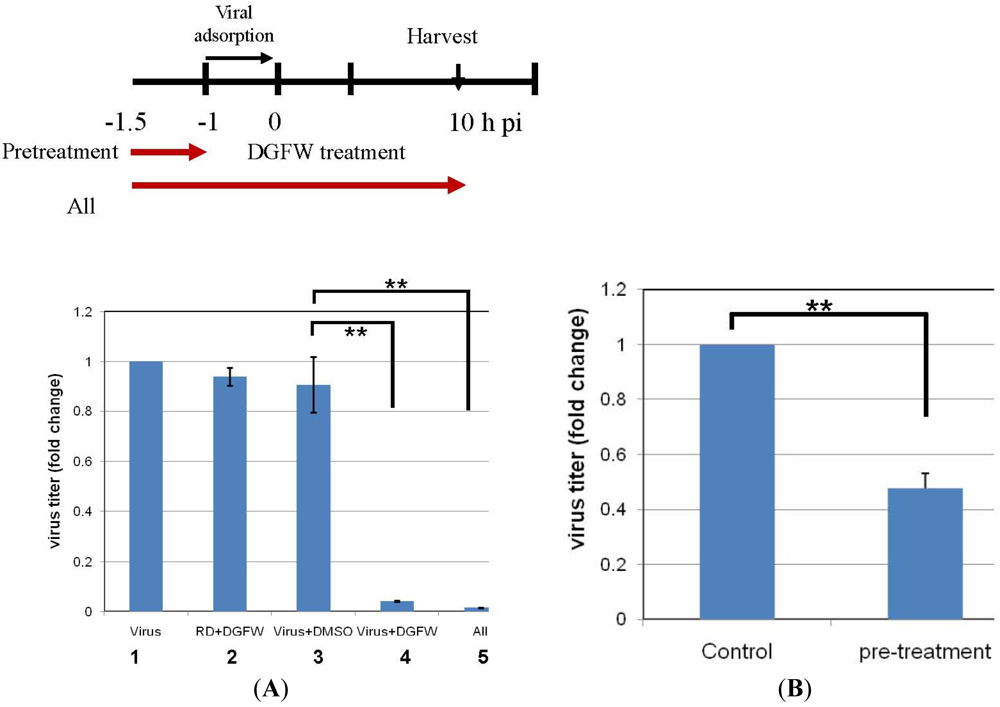
2.4. DGFW Targets the Virus Directly but not the Host Cells
2.5. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Virus and Cell Culture and Viral Amplification
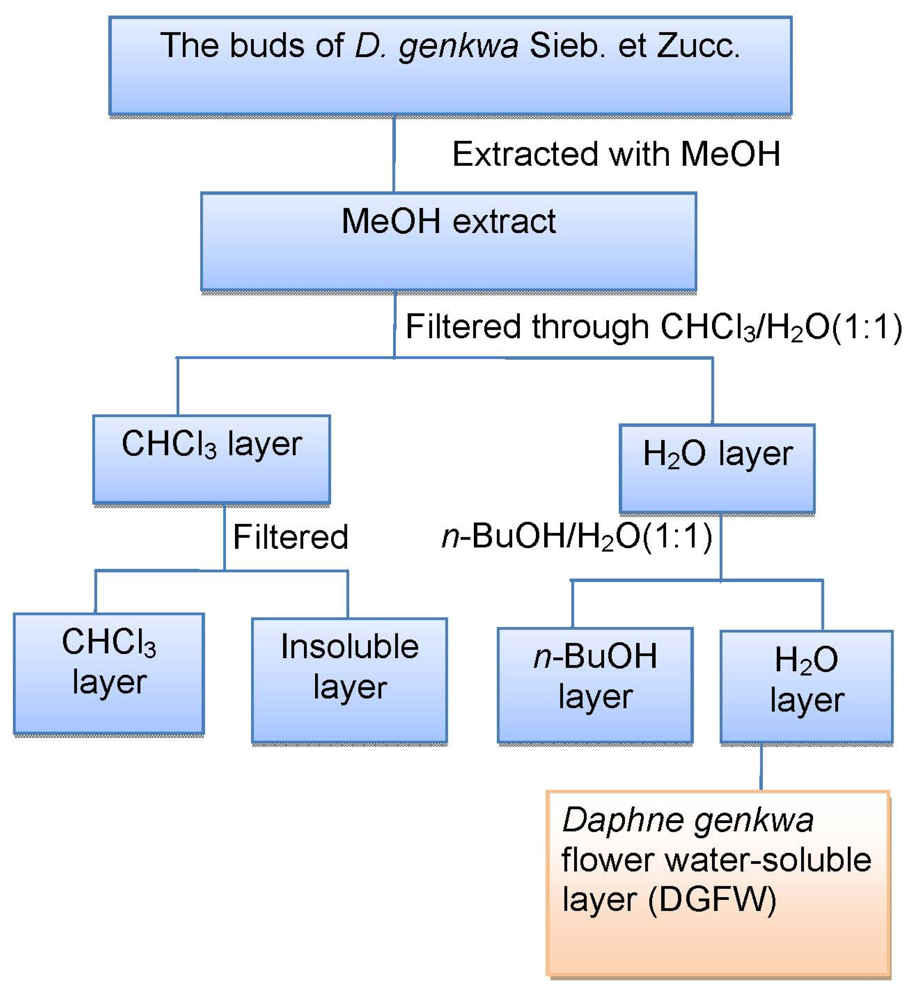
3.2. Plant Material
3.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.5. Plaque Assay
3.6. Western Blotting
3.7. CPE Testing
3.8. Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification and Absolute Quantitative (q)PCR
3.9. Time-of-Addition Assay
3.10. Attachment Assay
3.11. Penetration Assay
3.12. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflict of Interest
References
- Lin, J.Y.; Chen, T.C.; Weng, K.F.; Chang, S.C.; Chen, L.L.; Shih, S.R. Viral and host proteins involved in picornavirus life cycle. J. Biomed. Sci. 2009, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Racaniello, V.R. Picornaviridae: The Viruses and Their Replication. In Fields Virology, 5th; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Martin, M.A., Griffin, D.E., Lamb, R.A., Roizman, B., Straus, S.E., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; Volume 1, pp. 795–838. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.Y.; Huang, L.M.; Gau, S.S.; Wu, Y.Y.; Hsia, S.H.; Fan, T.Y.; Lin, K.L.; Huang, Y.C.; Lu, C.Y.; Lin, T.Y. Neurodevelopment and cognition in children after enterovirus 71 infection. New Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Chang, L.Y.; Hsia, S.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Chiu, C.H.; Hsueh, C.; Shih, S.R.; Liu, C.C.; Wu, M.H. The 1998 enterovirus 71 outbreak in Taiwan: Pathogenesis and management. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2002, 34, S52–S57. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, Y.; Shimojima, M.; Tano, Y.; Miyamura, T.; Wakita, T.; Shimizu, H. Human P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 is a functional receptor for enterovirus 71. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamayoshi, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Li, J.; Hanagata, N.; Minowa, T.; Takemura, T.; Koike, S. Scavenger receptor B2 is a cellular receptor for enterovirus 71. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 798–801. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Chuang, H.; Yang, K.D. Sialylated glycans as receptor and inhibitor of enterovirus 71 infection to DLD-1 intestinal cells. Virol. J. 2009, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.W.; Pan, T.L.; Leu, Y.L.; Chang, Y.K.; Tai, P.J.; Lin, K.H.; Horng, J.T. Antiviral effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) against enterovirus 71. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2007, 35, 153–168. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Jheng, J.R.; Tsai, H.P.; Jan, J.T.; Wong, W.R.; Horng, J.T. Anti-enterovirus 71 activity screening of chinese herbs with anti-infection and inflammation activities. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2009, 37, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.N. Some progress on the chemistry of natural bioactive terpenoids from Chinese medicinal plants. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1991, 86, 219–226. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.Y.; Park, B.Y.; Kwon, O.K.; Yuk, J.E.; Oh, S.R.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, H.K.; Ahn, K.S. Anti-inflammatory activity of (−)-aptosimon isolated from Daphne genkwa in RAW264.7 cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.Y.; Min, B.S.; Ahn, K.S.; Kwon, O.K.; Joung, H.; Bae, K.H.; Lee, H.K.; Oh, S.R. Daphnane diterpene esters isolated from flower buds of Daphne genkwa induce apoptosis in human myelocytic HL-60 cells and suppress tumor growth in Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC)-inoculated mouse model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 111, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, K.M.; Leong, K.L.; Ng, M.M.; Chu, J.J. The essential role of clathrin-mediated endocytosis in the infectious entry of human enterovirus 71. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 309–321. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, H.Y.; Cheng, M.L.; Weng, S.F.; Chang, L.; Yeh, T.T.; Shih, S.R.; Chiu, D.T. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency enhances enterovirus 71 infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinlay, M.A. Discovery and development of antipicornaviral agents. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. Suppl. 1993, 88, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Phelps, D.K.; Post, C.B. A novel basis of capsid stabilization by antiviral compounds. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 254, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shia, K.S.; Li, W.T.; Chang, C.M.; Hsu, M.C.; Chern, J.H.; Leong, M.K.; Tseng, S.N.; Lee, C.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, S.J.; Peng, K.C.; Tseng, H.Y.; Chang, Y.L.; Tai, C.L.; Shih, S.R. Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationship of pyridyl imidazolidinones: a novel class of potent and selective human enterovirus 71 inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 1644–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, B.A.; Oberste, M.S.; Alexander, J.P., Jr.; Kennett, M.L.; Pallansch, M.A. Molecular epidemiology and evolution of enterovirus 71 strains isolated from 1970 to 1998. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9969–9975. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.W.; Hsu, Y.W.; Smith, D.J.; Kiang, D.; Tsai, H.P.; Lin, K.H.; Wang, S.M.; Liu, C.C.; Su, I.J.; Wang, J.R. Reemergence of enterovirus 71 in 2008 in taiwan: dynamics of genetic and antigenic evolution from 1998 to 2008. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 3653–3662. [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido, T.; Ohmoto, T.; Sankawa, U. Inhibitors of adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate phosphodiesterase in Daphne genkwa Sieb. et Zucc. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noro, T.; Oda, Y.; Miyase, T.; Ueno, A.; Fukushima, S. Inhibitors of xanthine oxidase from the flowers and buds of Daphne genkwa. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1983, 31, 3984–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, R.; Lee, K.H.; Huang, H.C. Genkwadaphnin, a potent antileukemic diterpene from Daphne genkwa. Phytochemistry 1981, 20, 2592–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yu, C.; Yan, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C.; Wen, X. Antiviral flavonoids from Mosla scabra. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 429–433. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.L.; Liu, B.; Qin, H.L.; Lee, S.M.; Wang, Y.T.; Du, G.H. Anti-influenza virus activities of flavonoids from the medicinal plant Elsholtzia rugulosa. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.B.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.; Nguyen, T.T.; Park, S.J.; Chang, J.S.; Park, K.H.; Rho, M.C.; Lee, W.S. Biflavonoids from Torreya nucifera displaying SARS-CoV 3CL(pro) inhibition. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 7940–7947. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Sun, L.M.; Liu, X.Q.; Li, B.; Wang, Q.; Dong, J.X. Anti-HBV active flavone glucosides from Euphorbia humifusa Willd. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelik, B.; Kartal, M.; Orhan, I. Cytotoxicity, antiviral and antimicrobial activities of alkaloids, flavonoids, and phenolic acids. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 49, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhong, J.M.; Ye, S.Q.; Ni, Z.Y.; Miao, X.Q.; Mo, Y.K.; Li, Z.L. Screening of Epstein-Barr virus early antigen expression inducers from Chinese medicinal herbs and plants. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 1994, 7, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Niedobitek, G. Epstein-Barr virus infection in the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol. Pathol. 2000, 53, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.T.; Yeh, J.Y.; Lin, T.J.; Li, M.L.; Wu, M.S.; Hsieh, C.F.; Chou, Y.C.; Tang, W.F.; Lau, K.S.; Hung, H.C.; Fang, M.Y.; Ko, S.; Hsieh, H.P.; Horng, J.T. Identification of BPR3P0128 as an Inhibitor of Cap-Snatching Activities of Influenza Virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 647–657. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.F.; Yang, S.Y.; Wu, B.W.; Jheng, J.R.; Chen, Y.L.; Shih, C.H.; Lin, K.H.; Lai, H.C.; Tang, P.; Horng, J.T. Reticulon 3 binds the 2C protein of enterovirus 71 and is required for viral replication. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 5888–5898. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, K.F.; Li, M.L.; Hung, C.T.; Shih, S.R. Enterovirus 71 3C protease cleaves a novel target CstF-64 and inhibits cellular polyadenylation. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.M.; Chang, J.S.; Wang, K.C.; Tsai, J.J.; Chiang, L.C. A water extract of Pueraria lobata inhibited cytotoxicity of enterovirus 71 in a human foreskin fibroblast cell line. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2008, 24, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Logu, A.; Loy, G.; Pellerano, M.L.; Bonsignore, L.; Schivo, M.L. Inactivation of HSV-1 and HSV-2 and prevention of cell-to-cell virus spread by Santolina insularis essential oil. Antivir. Res. 2000, 48, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Albin, R.; Chase, R.; Risano, C.; Lieberman, M.; Ferrari, E.; Skelton, A.; Buontempo, P.; Cox, S.; DeMartino, J.; Wright-Minogue, J.; Jirau-Lucca, G.; Kelly, J.; Afonso, A.; Kwong, A.D.; Rozhon, E.J.; O’Connell, J.F. SCH 43478 and analogs: in vitro activity and in vivo efficacy of novel agents for herpesvirus type 2. Antivir. Res. 1997, 35, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal, K.S.; Perez, R.; Hodnichak, C. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 penetration by cytochalasins B and D. J. Gen. Virol. 1985, 66, 1601–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard, K.M.; Semler, B.L. Regulation of picornavirus gene expression. Microbes Infect. Inst. Pasteur 2004, 6, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Supplementary Files
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, C.-W.; Leu, Y.-L.; Horng, J.-T. Daphne Genkwa Sieb. et Zucc. Water-Soluble Extracts Act on Enterovirus 71 by Inhibiting Viral Entry. Viruses 2012, 4, 539-556. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4040539
Chang C-W, Leu Y-L, Horng J-T. Daphne Genkwa Sieb. et Zucc. Water-Soluble Extracts Act on Enterovirus 71 by Inhibiting Viral Entry. Viruses. 2012; 4(4):539-556. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4040539
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Chia-Wen, Yan-Lii Leu, and Jim-Tong Horng. 2012. "Daphne Genkwa Sieb. et Zucc. Water-Soluble Extracts Act on Enterovirus 71 by Inhibiting Viral Entry" Viruses 4, no. 4: 539-556. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4040539
APA StyleChang, C.-W., Leu, Y.-L., & Horng, J.-T. (2012). Daphne Genkwa Sieb. et Zucc. Water-Soluble Extracts Act on Enterovirus 71 by Inhibiting Viral Entry. Viruses, 4(4), 539-556. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4040539




