BK Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy and Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Transplant Recipients—What We Understand and What Remains Unclear
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. BK Virus Overview
1.2. Epidemiology and Risk Factors for BKPyV-HC
2. Literature Review Methodology
3. Pathogenicity of BK Virus on the Urinary System
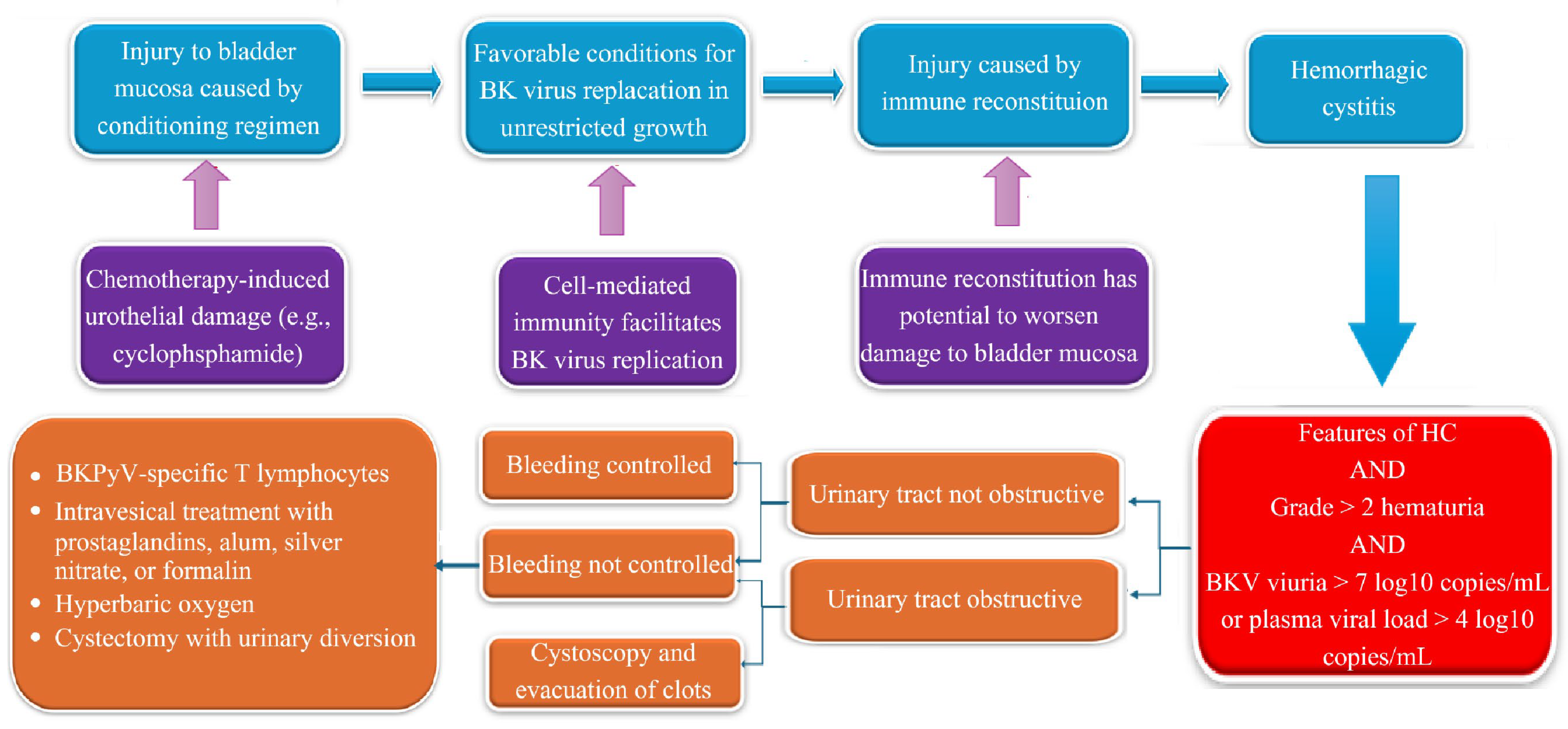
3.1. Cellular Tropism and Reactivation
3.2. Immunopathogenesis of BK Virus Reactivation
3.3. Immunopathological Mechanisms
3.4. Emerging Insights
4. Differences in Pathogenesis and Monitoring: BKPyVN vs. BKPyV-HC
4.1. Clinical Manifestations
4.2. Differential Diagnosis and Alternative Etiologies
4.3. Treatment and Outcomes of BKPyV-HC
5. Role of BKPyV Monitoring and Risk Stratification in HCT Recipients
- Virologic factors: high pre-transplant viruria, certain BKPyV genotypes, and rapid viral load kinetics have been associated with more aggressive disease courses [32].
6. Preventive Strategies for BKPyV-HC
6.1. Supportive Measures and Monitoring Strategies
6.2. Pharmacologic and Antiviral Prophylaxis
6.3. Emerging and Investigational Therapies
6.3.1. Recombinant Growth Factors and Antivirals
Keratinocyte Growth Factor (KGF/Palifermin)
Brincidofovir
6.3.2. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
6.3.3. Adoptive Cellular Therapies
BK Virus-Specific CTLs
Donor Lymphocyte Infusion (DLI)
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs)
6.3.4. Other Agents
Vidarabine
Estrogen Therapy
KGF Rescue Therapy
7. Intravesical Therapy for BKPyV-Associated Hemorrhagic Cystitis
8. Surgical Management of Refractory BKPyV-HC
9. Current Guidelines and Consensus Statements
10. Therapeutic Advances
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AE | Adverse Event |
| AST | American Society of Transplantation |
| BKPyV | BK Polyomavirus |
| BKPyVN | BK Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy |
| BKPyV-HC | BK Polyomavirus-Associated Hemorrhagic Cystitis |
| CD4+ | Cluster of Differentiation 4 Positive T Cell |
| CD8+ | Cluster of Differentiation 8 Positive T Cell |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
| CTL | Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| DLI | Donor Lymphocyte Infusion |
| ECIL | European Conference on Infections in Leukaemia |
| GVHD | Graft-Versus-Host Disease |
| HBOT | Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy |
| HC | Hemorrhagic Cystitis |
| HCT | Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation |
| IFN-γ | Interferon Gamma |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-11 | Interleukin-11 |
| IU/mL | International Units per Milliliter |
| IV | Intravenous |
| IVIG | Intravenous Immunoglobulin |
| JCPyV KDIGO | JC Polyomavirus Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes |
| KGF | Keratinocyte Growth Factor |
| KTR | Kidney Transplant Recipients |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal Stromal Cells |
| MPyV | Murine Polyomavirus |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PDGF | Platelet-Derived Growth Factor |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| PRP | Platelet-Rich Plasma |
| PTCy | Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide |
| qPCR | Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
| STAT3 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 |
| SVAE | Selective Vesical Artery Embolization |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| WUPyV | WU Polyomavirus |
References
- Furmaga, J.; Kowalczyk, M.; Zapolski, T.; Furmaga, O.; Krakowski, L.; Rudzki, G.; Jaroszyński, A.; Jakubczak, A. BK Polyomavirus-Biology, Genomic Variation and Diagnosis. Viruses 2021, 13, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilworth, S.M. Polyoma virus middle T antigen and its role in identifying cancer-related molecules. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauhiainen, M.K.; Mohanraj, U.; Lehecka, M.; Niemelä, M.; Hirvonen, T.P.; Pratas, D.; Perdomo, M.F.; Söderlund-Venermo, M.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Sinkkonen, S.T. Herpesviruses, polyomaviruses, parvoviruses, papillomaviruses, and anelloviruses in vestibular schwannoma. J. Neurovirol. 2023, 29, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuypers, J.; Campbell, A.P.; Guthrie, K.A.; Wright, N.L.; Englund, J.A.; Corey, L.; Boeckh, M. WU and KI polyomaviruses in respiratory samples from allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant recipients. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egli, A.; Infanti, L.; Dumoulin, A.; Buser, A.; Samaridis, J.; Stebler, C.; Gosert, R.; Hirsch, H.H. Prevalence of polyomavirus BK and JC infection and replication in 400 healthy blood donors. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dybko, J.; Piekarska, A.; Agrawal, S.; Makuch, S.; Urbaniak-Kujda, D.; Biernat, M.; Rybka, B.; Dutka, M.; Sadowska-Klasa, A.; Giebel, S.; et al. BKV Related Hemorrhagic Cystitis-An Insight into Risk Factors and Later Complications-An Analysis on Behalf of Polish Adult Leukemia Group. Cancers 2022, 14, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldiwani, M.; Tharakan, T.; Al-Hassani, A.; Gibbons, N.; Pavlu, J.; Hrouda, D. BK Virus Associated Haemorrhagic Cystitis. A Systematic Review of Current Prevention and Treatment Strategies. Int. J. Surg. 2019, 63, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorão, P.; Villalba, M.; Balaguer-Roselló, A.; Montoro, J.; Granados, P.; Gilabert, C.; Panadero, F.; Pardal, A.A.; González, E.M.; de Cossio, S.; et al. Incidence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of BK Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation From HLA-Matched and Haploidentical Donors with Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2025, 31, 182.e1–182.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, D.; Samuels, D.; Chen, J.; Koller, P.B.; Al Malki, M.M. A Clinical Review of the Different Strategies to Minimize Hemorrhagic Cystitis Associated with the Use of Post-Transplantation Cyclophosphamide in an Allogeneic Transplant. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2022, 28, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copelan, O.R.; Sanikommu, S.R.; Trivedi, J.S.; Butler, C.; Ai, J.; Ragon, B.K.; Jacobs, R.; Knight, T.G.; Usmani, S.Z.; Grunwald, M.R.; et al. Higher Incidence of Hemorrhagic Cystitis Following Haploidentical Related Donor Transplantation Compared with Matched Related Donor Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandial, A.; Mishra, K.; Sandal, R.; Sahu, K.K. Management of BK Virus-Associated Haemorrhagic Cystitis in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, 2049936121991377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaphan, E.; Germi, R.; Bailly, S.; Bulabois, C.E.; Carré, M.; Cahn, J.Y.; Thiebaut-Bertrand, A. Risk Factors of BK Viral Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Allogenic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2021, 23, e13601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Randhawa, P.S. BK Polyomavirus in Solid Organ Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13 (Suppl. S4), 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldo, C.H.; Hirsch, H.H. The Human Polyomaviruses: An Overview. Clin. Virol. 2007, 44, 306–313. [Google Scholar]
- Abend, J.R.; Low, J.A.; Imperiale, M.J. Inhibitory Effect of Gamma Interferon on BK Virus Gene Expression and Replication. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drachenberg, C.B.; Papadimitriou, J.C. Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy: Update in Diagnosis. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2006, 8, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, R.R.; Shah, K.V.; Baust, S.J.; Santos, G.W.; Saral, R. Association of BK viruria with hemorrhagic cystitis in recipients of bone marrow transplants. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskin, B.L.; Goebel, J.; Davies, S.M.; Yin, H.J. BK Virus Infection: An Update on Diagnosis and Treatment. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2009, 24, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Nickeleit, V.; Mihatsch, M.J. Polyomavirus Nephropathy in Renal Transplant Patients: An Update. Transpl. Int. 2006, 19, 960–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Brennan, D.C.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Ginevri, F.; Gordon, J.; Limaye, A.P.; Mihatsch, M.J.; Nickeleit, V.; Ramos, E.; Randhawa, P.; et al. Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy in Renal Transplantation: Interdisciplinary Analyses and Recommendations. Transplantation 2005, 79, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comoli, P.; Azzi, A.; Maccario, R.; Basso, S.; Botti, G.; Basile, G.; Fontana, I.; Labirio, M.; Cometa, A.; Poli, F.; et al. Polyomavirus BK-Specific Immunity after Kidney Transplantation. Transplantation 2004, 78, 1229–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhoff, E.; Gutteberg, T.J.; Sandvik, K.; Hirsch, H.H.; Rinaldo, C.H. Cidofovir Inhibits Polyomavirus BK Replication in Human Renal Tubular Cells Downstream of Viral Early Gene Expression. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abend, J.R.; Low, J.A.; Imperiale, M.J. BK Virus and the DNA Damage Response: Expanding Virus-Host Interactions. Trends. Microbiol. 2010, 18, 583–590. [Google Scholar]
- Moens, U.; Krumbholz, A.; Ehlers, B.; Zell, R.; Johne, R.; Calvignac-Spencer, S.; Lauber, C. Biology, Evolution, and Medical Importance of Polyomaviruses: An Update. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 54, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesaro, S.; Facchin, C.; Tridello, G.; Messina, C.; Calore, E.; Biasolo, M.A.; Pillon, M.; Varotto, S.; Brugiolo, A.; Mengoli, C.; et al. A Prospective Study of BK-Virus-Associated Haemorrhagic Cystitis in Paediatric Patients Undergoing Allogeneic Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008, 41, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedi, A.; Miller, C.B.; Hanson, J.L.; Goodman, S.; Ambinder, R.F.; Charache, P.; Arthur, R.R.; Jones, R.J. Association of BK Virus with Failure of Prophylaxis against Hemorrhagic Cystitis following Bone Marrow Transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behzad-Behbahani, A.; Klapper, P.E.; Vallely, P.J.; Cleator, G.M.; Khoo, S.H. Detection of BK Virus and JC Virus DNA in Urine Samples from Immunocompromised (HIV-Infected) and Immunocompetent (HIV-Non-Infected) Patients Using Polymerase Chain Reaction and Microplate Hybridisation. J. Clin. Virol. 2004, 29, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarche, C.; Orio, J.; Collette, S.; Senécal, L.; Hébert, M.J.; Renoult, É.; Tibbles, L.A.; Delisle, J.S. BK Polyomavirus and the Transplanted Kidney: Immunopathology and Therapeutic Approaches. Transplantation 2016, 100, 2276–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.Y.; Yuen, K.Y.; Kwong, Y.L. Polyoma BK Virus and Haemorrhagic Cystitis in Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Changing Paradigm. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005, 36, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.C.; Ngwube, A.; Suresh, T.; Sowa, A.; Abraham, A.; Anderson, E.; Andreansky, M.; Bhatia, M.; Chaudhury, S.; Cuvelier, G.D.E.; et al. Impact of Abatacept Inclusive Graft Versus Host Disease Prophylaxis in Pediatric Stem Cell Transplantation for Hemoglobinopathy. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2025, in press. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorriceta, J.H.; Lopez Otbo, A.; Uehara, G.; Posadas Salas, M.A. BK Viral Infection: A Review of Management and Treatment. World J. Transplant. 2023, 13, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawinski, D.; Trofe-Clark, J. BK Virus Nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 1893–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambalathingal, G.R.; Francis, R.S.; Smyth, M.J.; Smith, C.; Khanna, R. BK Polyomavirus: Clinical Aspects, Immune Regulation, and Emerging Therapies. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 503–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaro, S.; Tridello, G.; Pillon, M.; Calore, E.; Abate, D.; Tumino, M.; Carucci, N.; Varotto, S.; Cannata, E.; Pegoraro, A.; et al. Prospective Study on the Predictive Value of Plasma BK Virus-DNA Load for Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Pediatric Patients After Stem Cell Transplantation. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2015, 4, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardinger, K.L.; Koch, M.J.; Bohl, D.J.; Storch, G.A.; Brennan, D.C. BK-Virus and the Impact of Pre-Emptive Immunosuppression Reduction: 5-Year Results. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funahashi, Y. BK Virus-Associated Nephropathy after Renal Transplantation. Pathogens 2021, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickeleit, V.; Singh, H.K. Polyomaviruses and disease: Is there more to know than viremia and viruria? Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2015, 20, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.S.; Heyenbruch, D.; Rubinstein, J.D.; Sabulski, A.; Jodele, S.; Thomas, S.; Lutzko, C.; Zhu, X.; Leemhuis, T.; Cancelas, J.A.; et al. Virus-specific T-cell therapy to treat BK polyomavirus infection in bone marrow and solid organ transplant recipients. Blood. Adv. 2020, 4, 5745–5754. [Google Scholar]
- Parajuli, S.; Jorgenson, M.; Meyers, R.O.; Djamali, A.; Galipeau, J. Role of Virus-Specific T Cell Therapy for Cytomegalovirus and BK Infections in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Kidney360 2021, 2, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peras, M.; Bilić, E.; Mareković, I. Recent Insights into the Pathogenesis, Diagnostics, and Treatment of BK Virus Infections in Children after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Pathogens 2025, 14, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.; Aziz, F.; Hafeeq, B.; Anoop, K.P.M.; Uvais, N.A.; Narayanan, R.; Gopinathan, J.C.; Ramachandran, R.; Krishnakumar, A.; Rahman, S. Early Detection Strategy of BK Polyoma Virus Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Indian J. Nephrol. 2024, 34, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.; Mittal, C.; Amer, S.; Khalid, F.; Patel, A.; Delbusto, R.; Samuel, L.; Alangaden, G.; Ramesh, M. Currently recommended BK virus (BKV) plasma viral load cutoff of ≥4 log10/mL underestimates the diagnosis of BKV-associated nephropathy: A single transplant center experience. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2014, 16, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajenda, S.; Hevesi, Z.; Eder, M.; Gerges, D.; Aiad, M.; Koldyka, O.; Winnicki, W.; Wagner, L.; Eskandary, F.; Schmidt, A. Lessons from Polyomavirus Immunofluorescence Staining of Urinary Decoy Cells. Life 2023, 13, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickeleit, V.; Davis, V.G.; Thompson, B.; Singh, H.K. The Urinary Polyomavirus-Haufen Test: A Highly Predictive Non-Invasive Biomarker to Distinguish “Presumptive” from “Definitive” Polyomavirus Nephropathy: How to Use It—When to Use It—How Does It Compare to PCR Based Assays? Viruses 2021, 13, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis, M.; Velay, A.; Porcher, R.; Domingo-Calap, P.; Soulier, E.; Joly, M.; Meddeb, M.; Kack-Kack, W.; Moulin, B.; Bahram, S.; et al. Neutralizing Antibody-Mediated Response and Risk of BK Virus-Associated Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, M.A.; Imlay, H. Polyomaviruses After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Viruses 2025, 17, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erard, V.; Storer, B.; Corey, L.; Nollkamper, J.; Huang, M.L.; Limaye, A.; Boeckh, M. BK Virus Infection in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients: Frequency, Risk Factors, and Association with Postengraftment Hemorrhagic Cystitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 1861–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imlay, H.; Xie, H.; Leisenring, W.M.; Duke, E.R.; Kimball, L.E.; Huang, M.L.; Pergam, S.A.; Hill, J.A.; Jerome, K.R.; Milano, F.; et al. Presentation of BK polyomavirus-associated hemorrhagic cystitis after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybul, M.; Fauci, A.S.; Bartlett, J.G.; Kaplan, J.E.; Pau, A.K. Panel on Clinical Practices for Treatment of HIV. Guidelines for Using Antiretroviral Agents among HIV-Infected Adults and Adolescents. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 137 Pt 2, 381–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, J.E.; Muller, W.J. BK Virus-Associated Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Pediatric Stem Cell Transplantation: A Case Report and Scoping Review. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 11, 1267678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, M.; Ranchon, F.; Gilis, L.; Schwiertz, V.; Vantard, N.; Ader, F.; Labussiere-Wallet, H.; Thomas, X.; Nicolini, F.E.; Wattel, E.; et al. Cidofovir in the Treatment of BK Virus-Associated Hemorrhagic Cystitis after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionel, S.A.; Abraham, A.; Mathews, V.; Lakshmi, K.; Abraham, A.M.; George, B. BK Polyomavirus Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2022, 14, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, R.J.; Walsh, A.; Ní Laoi, B.; Conneally, E.; Crowley, B. BK virus (BKV) plasma dynamics in patients with BKV-associated hemorrhagic cystitis following allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2013, 15, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.B.; Lall, C.; Tirkes, T.; Gulati, R.; Lamba, R.; Goodwin, S.C. Chemotherapy-Related Complications in the Kidneys and Collecting System: An Imaging Perspective. Insights Imaging 2015, 6, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savona, M.R.; Newton, D.; Frame, D.; Levine, J.E.; Mineishi, S.; Kaul, D.R. Low-Dose Cidofovir Treatment of BK Virus-Associated Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Recipients of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007, 39, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Ahn, J.S.; Jung, S.H.; Ahn, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, S.J.; Jang, M.O.; Yang, D.H.; Kim, Y.K.; et al. Treatment of BK Virus-Associated Hemorrhagic Cystitis with Low-Dose Intravenous Cidofovir in Patients Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2015, 30, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Hino, T.; Honda, A.; Kurokawa, M. Fluoroquinolones for BK Viral Complication after Transplantation: Meta-Analysis. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2020, 22, e13433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhoff, E.; Tylden, G.D.; Kjerpeseth, L.J.; Gutteberg, T.J.; Hirsch, H.H.; Rinaldo, C.H. Leflunomide Inhibition of BK Virus Replication in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2150–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzay, A.; Gündoğdu, Y.; Koşan, B.; Yetiş, T.; Gür, H.; Okuturlar, Y.; Kartı, S.S. Daily Low Dose Intravesical Cidofovir for the Treatment of BK Virus-Associated Hemorrhagic Cystitis after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. J. Infect. Chemother. 2023, 29, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. NCT01295645. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01295645 (accessed on 17 March 2011).
- Schneidewind, L.; Neumann, T.; Dräger, D.L.; Kranz, J.; Hakenberg, O.W. Leflunomide in the Treatment of BK Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy in Kidney Transplanted Patients—A Systematic Review. Transplant. Rev. 2020, 34, 100565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T.; Shirai, H.; Tojimbara, T. Use of Leflunomide as an Antiviral Agent with Everolimus for BK Virus Nephropathy Patients after Kidney Transplantation: A Case Series. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e927367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Clinical Transplant Research Exchange (ECTR-X) 2023. Abstract #147. In: Proceedings of the ECTR-X 2023, 2023.
- Rasaei, N.; Malekmakan, L.; Gholamabbas, G.; Abdizadeh, P. Comparative Study of Intravenous Immunoglobulin and Leflunomide Combination Therapy with Intravenous Immunoglobulin Single Therapy in Kidney Transplant Patients with BK Virus Infection: Single-Center Clinical Trial. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2023, 21, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marty, F.M.; Ljungman, P.; Chemaly, R.F.; Maertens, J.; Dadwal, S.S.; Duarte, R.F.; Haider, S.; Ullmann, A.J.; Katayama, Y.; Brown, J.; et al. Letermovir Prophylaxis for Cytomegalovirus in Hematopoietic-Cell Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2433–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blijlevens, N.; Sonis, S. Palifermin (Recombinant Keratinocyte Growth Factor-1): A Pleiotropic Growth Factor with Multiple Biological Activities in Preventing Chemotherapy- and Radiotherapy-Induced Mucositis. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, V.A.; Smith, S.K.; Foster, S.; Li, Y.; Lanier, E.R.; Gates, I.; Trost, L.C.; Damon, I.K. In Vitro Efficacy of Brincidofovir against Variola Virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5570–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savva-Bordalo, J.; Pinho Vaz, C.; Sousa, M.; Branca, R.; Campilho, F.; Resende, R.; Baldaque, I.; Camacho, O.; Campos, A. Clinical effectiveness of hyperbaric oxygen therapy for BK-virus-associated hemorrhagic cystitis after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012, 47, 1095–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, K.; Yamazaki, H.; Nakamura, T.; Yoroidaka, T.; Imi, T.; Shima, Y.; Ohata, K.; Takamatsu, H.; Kotani, T.; Kondo, Y.; et al. Successful Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Refractory BK Virus-Associated Hemorrhagic Cystitis after Cord Blood Transplantation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2014, 16, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, A.; Lin, R.; Marin, D.; Rafei, H.; Bdaiwi, M.H.; Thall, P.F.; Basar, R.; Abudayyeh, A.; Banerjee, P.; Aung, F.M.; et al. Third-Party BK Virus-Specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Therapy for Hemorrhagic Cystitis Following Allotransplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2710–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukoulias, K.; Papayanni, P.G.; Leen, A.M.; Vasileiou, S. Virus-Specific T-Cell Therapy for the Management of Viral Infections in the Immunocompromised. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2024, 52, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morello, W.; Budelli, S.; Bernstein, D.A.; Montemurro, T.; Montelatici, E.; Lavazza, C.; Ghio, L.; Edefonti, A.; Peruzzi, L.; Molino, D.; et al. First Clinical Application of Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Children with Multi-Drug Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Okuda, T.; Shiraki, K. Synergistic Antiviral Activity of Acyclovir and Vidarabine against Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 and 2 and Varicella-Zoster Virus. Antivir. Res. 2006, 72, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rascon, J.; Verkauskas, G.; Pasauliene, R.; Zubka, V.; Bilius, V.; Rageliene, L. Intravesical Cidofovir to Treat BK Virus-Associated Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Children after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Pediatr. Transplant. 2015, 19, e111–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coomes, E.A.; Wolfe Jacques, A.; Michelis, F.V.; Kim, D.D.H.; Thyagu, S.; Viswabandya, A.; Lipton, J.H.; Messner, H.A.; Deotare, U. Efficacy of Cidofovir in Treatment of BK Virus-Induced Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 1901–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flammia, G.P.; Bove, P.; Cerretti, R.; Cudillo, L.; De Angelis, G.; Picardi, A.; Annibali, O.; Nobile, C.; Cerchiara, E.; Dentamaro, T.; et al. Rome Transplant Network. Fibrin Glue Therapy for Severe Hemorrhagic Cystitis after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014, 20, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, H.C. Intravesical Injections of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Refractory Interstitial Cystitis. Low Urin. Tract Symptoms 2023, 15, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegelmann, M.J.; Boorjian, S.A.; Joyce, D.D.; Montgomery, B.D.; Linder, B.J. Intravesical Formalin for Hemorrhagic Cystitis: A Contemporary Cohort. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2017, 11, E79–E82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Westerman, M.E.; Boorjian, S.A.; Linder, B.J. Safety and Efficacy of Intravesical Alum for Intractable Hemorrhagic Cystitis: A Contemporary Evaluation. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2016, 42, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braune, S.; Küpper, J.H.; Jung, F. Effect of Prostanoids on Human Platelet Function: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhou, C.G.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.L.; Shi, H.B.; Liu, S. Superselective Vesical Artery Embolization for Intractable Hemorrhagic Cystitis Following Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Single-Center Retrospective Study in 26 Patients. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2021, 44, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, S.; Osterberg, E.C.; Elliott, S.P.; Hittelman, A.B.; Breyer, B.N. Acute Bladder Necrosis after Pelvic Arterial Embolization for Pelvic Trauma: Lessons Learned from Two Cases of Immediate Postembolization Bladder Necrosis. Case Rep. Urol. 2016, 2016, 7594192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, A.; Lyons, G.R. Clinical Outcomes Following Percutaneous Urinary Diversion for Hemorrhagic Cystitis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 33, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, B.J.; Tarrell, R.F.; Boorjian, S.A. Cystectomy for Refractory Hemorrhagic Cystitis: Contemporary Etiology, Presentation and Outcomes. J. Urol. 2014, 192, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.; Seideman, C.; Wong, T.; Hakar, M.; Austin, J.C. Pediatric Cystectomy for Refractory Cystitis Post-Bone Marrow Transplant in Dyskeratosis Congenita: A Case Report. Urol. Case Rep. 2022, 44, 102163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesaro, S.; Dalianis, T.; Hanssen Rinaldo, C.; Koskenvuo, M.; Pegoraro, A.; Einsele, H.; Cordonnier, C.; Hirsch, H.H.; ECIL-6 Group. ECIL guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of BK polyomavirus-associated haemorrhagic cystitis in haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Randhawa, P.S.; AST Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. BK polyomavirus in solid organ transplantation-Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotton, C.N.; Kamar, N.; Wojciechowski, D.; Eder, M.; Hopfer, H.; Randhawa, P.; Sester, M.; Comoli, P.; Tedesco Silva, H.; Knoll, G.; et al. The Second International Consensus Guidelines on the Management of BK Polyomavirus in Kidney Transplantation. Transplantation 2024, 108, 1834–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneidewind, L.; Neumann, T.; Plis, A.; Brückmann, S.; Keiser, M.; Krüger, W.; Schmidt, C.A. Novel 3D organotypic urothelial cell culture model for identification of new therapeutic approaches in urological infections. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 124, 104283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourie, N.; Boueri, C.; Tran Minh, H.; Divard, G.; Lefaucheur, C.; Salmona, M.; Gressens, S.B.; Louis, K. BK Polyomavirus Infection in Kidney Transplantation: A Comprehensive Review of Current Challenges and Future Directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneidewind, L.; Neumann, T.; Krüger, W.; Hakenberg, O.W.; Schmidt, C.A. Targeting IL-11 in the Treatment of BK Virus-Associated Haemorrhagic Cystitis—A Promising New Approach. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 9097–9100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Feature | BKPyVN | BKPyV-HC |
|---|---|---|
| Primary patient population | Kidney transplant | Allogeneic HCT |
| Primary organ affected | Renal allograft (tubules/interstitium) | Bladder urothelium |
| Trigger for pathogenesis | Immunosuppression leading to viral replication | Urothelial injury from conditioning + viral reactivation |
| Clinical manifestation | Gradual rise in serum creatinine, renal dysfunction | Hematuria (ranging from microscopic to gross), dysuria, clot retention |
| Key timing | Usually >3 months post-kidney transplant | 2–8 weeks post-HCT (can be late-onset) |
| Monitoring focus | Plasma BK viral load and kidney function (routine screening) | Clinical signs and symptoms; BK viral load less predictive |
| Gold standard for diagnosis | Kidney biopsy | Clinical + high urine BK viral load; biopsy rarely needed |
| Agent/Strategy | Study Type and Size | Key Outcomes | Toxicity/Safety Findings | Evidence Level and Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cidofovir (IV) | Retrospective cohort (n = 27 HCT recipients with BKPyV-HC) | Complete response in 81.5%; partial response in 7.4% | ~30% developed renal impairment; ↓ creatinine clearance by 27% | Observational; no RCTs; single-dose protocol | [56] |
| Cidofovir (IV) | Retrospective series (n = 12 transplant recipients) | Significant reduction in HC severity | Not reported | Small sample; uncontrolled design | [60] |
| Cidofovir ± Intravesical | Single-center case series (n = 27 allo-HCT patients) | 60–100% of CRs observed independently of the dose or administration route. | The main toxicity reported was renal failure | Very small sample; emphasizes safety/dosing concerns | [52] |
| Cidofovir vs. Supportive Care | Ongoing RCT (NCT01295645) | Results pending | — | Awaiting results; randomized design promising | [61] |
| Leflunomide | Systematic review (12 studies; 267 KTR with BKPyVN) | BK viremia clearance ranged from 33–92%; ~10% graft loss | Hemolysis, thrombotic microangiopathy | Heterogeneous study protocols; risk of bias | [62] |
| Leflunomide + Everolimus | Case reports/series (n = 4–26 patients) | Reported viral clearance; stable graft function | High dose (>40 µg/mL) associated with hemolysis | No control group; variable dosing protocols | [63] |
| Leflunomide (Pediatrics) | Pediatric KTR case series (n ≈ unknown); ECTR-X 2023 abstract | All cleared viremia (~3.4 months); renal function preserved | No hepatotoxicity or anemia reported | Retrospective; limited cohort size | [64] |
| IVIG ± Leflunomide | RCT (n = 16 adult KTR with BKPyVN) | 7/8 cleared viremia in combo group vs. 3/7 with IVIG alone | Not reported | Small sample size; short-term follow-up | [65] |
| Brincidofovir | No BKPyV-specific trials; negative phase III in CMV/adenovirus | — | Increased gastrointestinal and severe adverse events | No data for BKPyV; clinical development discontinued | [66] |
| Guideline/Statement | Target Population | Key Recommendations | Evidence Level/Notes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECIL-6 (2015) | HCT recipients (focus on BKPyV-HC) |
| Based on expert consensus; no randomized controlled trials; emphasizes early detection and prevention | [87] |
| AST Infectious Diseases Community of Practice (2019) | KTR (BKPyVN) |
| Recommendations derived from observational studies and expert opinion | [88] |
| KDIGO Transplant Guidelines (2020) | KTR (BKPyVN) |
| Evidence-based guideline; emphasizes screening and early intervention | [89] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaing, T.-H.; Wang, Y.-L.; Chang, T.-Y. BK Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy and Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Transplant Recipients—What We Understand and What Remains Unclear. Viruses 2025, 17, 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091256
Jaing T-H, Wang Y-L, Chang T-Y. BK Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy and Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Transplant Recipients—What We Understand and What Remains Unclear. Viruses. 2025; 17(9):1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091256
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaing, Tang-Her, Yi-Lun Wang, and Tsung-Yen Chang. 2025. "BK Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy and Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Transplant Recipients—What We Understand and What Remains Unclear" Viruses 17, no. 9: 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091256
APA StyleJaing, T.-H., Wang, Y.-L., & Chang, T.-Y. (2025). BK Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy and Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Transplant Recipients—What We Understand and What Remains Unclear. Viruses, 17(9), 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091256








