Detection and Genetic Characterization of Red-Spotted Grouper Nervous Necrosis Virus and a Novel Genotype of Nervous Necrosis Virus in Black Sea Bass from the U.S. Atlantic Coast
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Collection and Environmental Data
2.2. Viral Cell Culture Assays
2.3. Molecular Screening and Confirmation of Nervous Necrosis Virus
2.4. Genetic Sequencing
| Primer Name | Sequence | Target and Amp Size | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| RNA1_283-5′F | TAA CAT CAC CTT CTT GCT | RNA1 874 | [48] |
| RNA1_856-874R | GGT GCT CAC CCA TCT TGA | ||
| RNA1_684-705F | GAA CTA CAA CCA GGA TAC CAT G | RNA1 684 | [48] |
| RNA1_1346-1367R | GAC TCA CTT GGA AAT ACA | ||
| JRNV1_F1 | TCA CTT ACG CAA GGT TAC CG | RNA1 1122 | [49] |
| JRNV1_R1 | GAC CGG CGA ACA GTA TCT GAC | ||
| JRNV1_F1 | TCA CTT ACG CAA GGT TAC CG | RNA1 1973 | [49] |
| RNA1_1955-1973R | TGA CAG CAG GTG CTT GG | [48] | |
| JRNV1_F2 | AGT CTG GGY YTG GAR GGC | RNA1 1032 | [49] |
| JRNV1_R2 | GAC GAA AGC RTT DGC AAT GC | ||
| VNNV5 | GTT GAG GAT TAT CGC CAA CG | RNA1 953 | [50] |
| VNNV6 | ACC GGC GAA CAG TAT CTG AC | ||
| FOR521 | ACG TGG ACA TGC ATG AGT TG | RNA1 630 | [51] |
| VNNV6 | ACC GGC GAA CAG TAT CTG AC | [50,51] | |
| RNA1_1248-1267F | CTT GCK CGT CAT TAC CAA GC | RNA1 839 | This study |
| RNA1_2068-2087R | GCG ACC AGC AAG GTA TGA GA | ||
| JRNV1_F3 | TCC AAG CAC CWG CTG T | RNA1 1099 | [49] |
| JRNV1_R3 | GGG GTG GGA GCR GGC A | ||
| BF Pol 1698-1715F | GTC CAG CTA CAC CTA CGC | RNA1 785 | [48] |
| BF Pol 2465-2482R | AGT CTG CGT ATT GGA CCA | ||
| RNA2_283-5′F | TAA TCC ATC ACC GCT TTG | RNA2 593 | [48] |
| RNA2_578-597R | GCT GCC AAC ACA CAG GA | ||
| RNA2_8-21F | TCA YCG CTT TGC MAT CAC AA | RNA2 421 | This study |
| RNA2_410-429R | CGT TGT CAG TTG GAT CAG GC | ||
| VNNV1 * | ACA CTG GAG TTT GAA ATT CA | RNA2 605 | [45] |
| VNNV2 * | GTC TTG TTG AAG TTG TCC CA | ||
| VNNV3 ** | ATT GTG CCC CGC AAA CAC | RNA2 255 | [45] |
| VNNV4 ** | GAC ACG TTG ACC ACA TCA GT | ||
| RNA2_818-837F | CAT TGA CTA CAA CCT TGG AG | RNA2 409 | [48] |
| RNA2_1206-1227R | CAA TGG TAC CAA CAA TAG |
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis of Nervous Necrosis Virus Sequences
3. Results
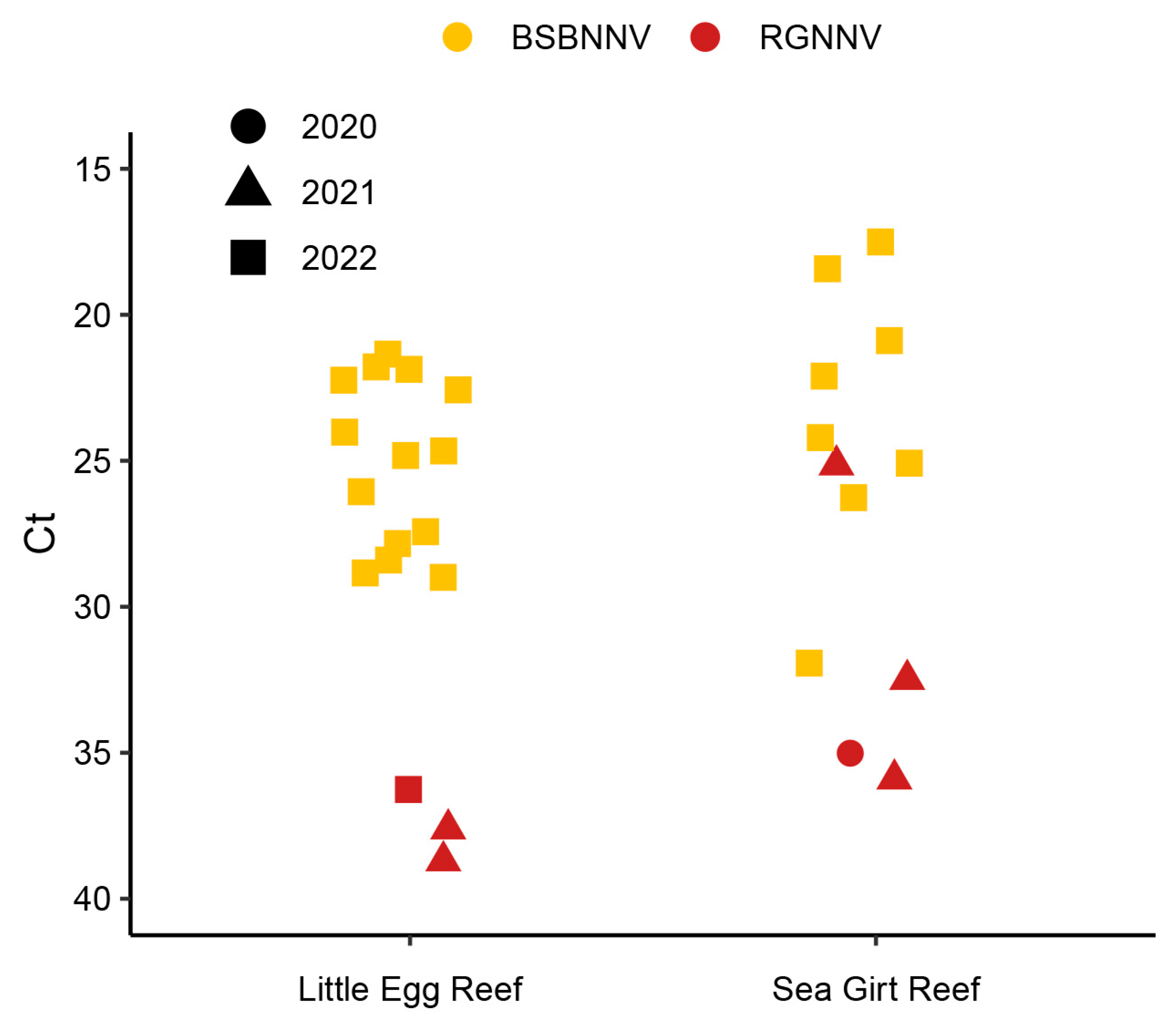
3.1. Virology and Nervous Necrosis Virus Findings in 2020
3.2. Nervous Necrosis Virus Findings in 2021
3.3. Nervous Necrosis Virus Findings in 2022
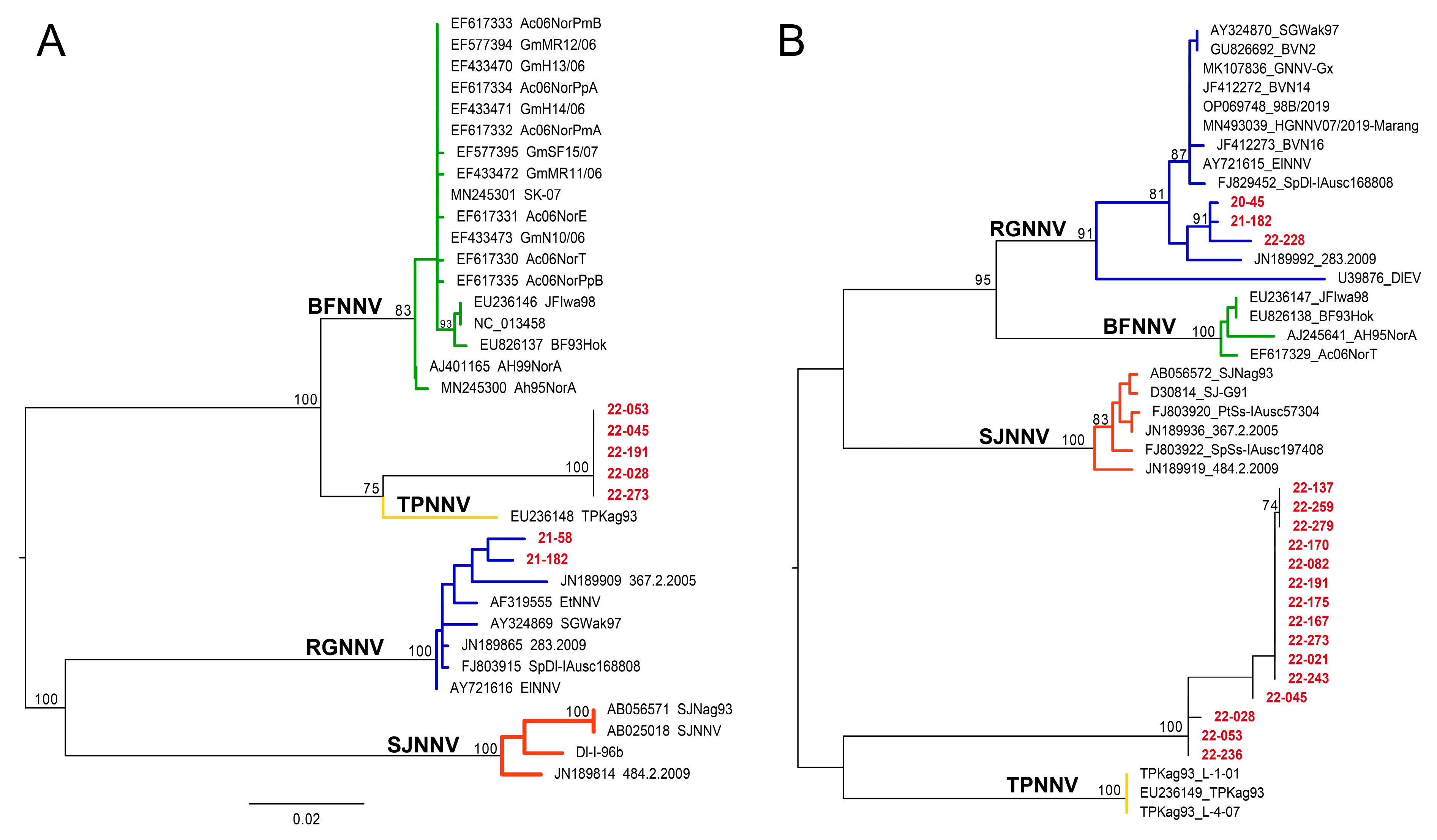
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of Nervous Necrosis Virus Sequences
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NNV | Nervous necrosis virus |
| VNN | Viral nervous necrosis |
| BFNNV | Barfin flounder nervous necrosis virus |
| RGNNV | Red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus |
| SJNNV | Striped jack nervous necrosis virus |
| TPNNV | Tiger puffer nervous necrosis virus |
| BSBNNV | Black sea bass nervous necrosis virus |
| rRT-PCR | Real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| RT-PCR | Endpoint/conventional reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| ICTV | International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses |
| CPE | Cytopathic effects |
| BF-2 | Bluegill fry-2 cells |
| EPC | Epithelioma papulosum cyprini cells |
| CHSE-214 | Chinook salmon embryo-214 cells |
| SSN-1 | Striped snakehead-1 cells |
| E-11 | Clone of striped snakehead cells |
| CT | Cycle threshold |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| HBSS | Hanks’ balanced salt solution |
| MEM | Minimum essential medium |
| nt | Nucleotide |
| AA | Amino acid |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| TL | Total length |
| YOY | Young of the year |
| BLAS | Nucleotide basic local alignment search tool |
References
- Sahul Hameed, A.; Ninawe, A.; Nakai, T.; Chi, S.; Johnson, K.; Consortium, I.R. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Nodaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.-I.; Nakai, T.; Muroga, K.; Arimoto, M.; Mushiake, K.; Furusawa, I. Properties of a new virus belonging to nodaviridae found in larval striped jack (Pseudocaranx dentex) with nervous necrosis. Virology 1992, 187, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peducasse, S.; Castric, J.; Thiery, R.; Jeffroy, J.; Le Ven, A.; Laurencin, F.B. Comparative study of viral encephalopathy and retinopathy in juvenile sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax infected in different ways. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 36, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nagai, T.; Nishizawa, T. Sequence of the non-structural protein gene encoded by RNA1 of striped jack nervous necrosis virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 3019–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, T.; Mori, K.-i.; Furuhashi, M.; Nakai, T.; Furusawa, I.; Muroga, K. Comparison of the coat protein genes of five fish nodaviruses, the causative agents of viral nervous necrosis in marine fish. J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.N.; Johnson, K.L.; Dasgupta, R.; Gratsch, T.; Ball, L.A. Comparisons among the larger genome segments of six nodaviruses and their encoded RNA replicases. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 1855–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, T.; Furuhashi, M.; Nagai, T.; Nakai, T.; Muroga, K. Genomic classification of fish nodaviruses by molecular phylogenetic analysis of the coat protein gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 1633–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, T.; Okinaka, Y.; Mise, K.; Mori, K.-I.; Arimoto, M.; Okuno, T.; Nakai, T. Identification of host-specificity determinants in betanodaviruses by using reassortants between striped jack nervous necrosis virus and sevenband grouper nervous necrosis virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.-C.; Lin, S.-C.; Su, H.-M.; Hu, W.-W. Temperature effect on nervous necrosis virus infection in grouper cell line and in grouper larvae. Virus Res. 1999, 63, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, N.; Okinaka, Y.; Iwamoto, T.; Kawato, Y.; Mori, K.-I.; Nakai, T. Identification of RNA regions that determine temperature sensitivities in betanodaviruses. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, S.; Olveira, J.G.; Bandín, I. Influence of temperature on Betanodavirus infection in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 179, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspehavg, V. The phylogenetic relationship of nervous necrosis virus from Halibut. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 1999, 19, 196. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, D.E.; MacKinnon, A.-M.; Boston, L.; Burt, M.D.; Cone, D.K.; Speare, D.J.; Griffiths, S.; Cook, M.; Ritchie, R.; Olivier, G. First report of piscine nodavirus infecting wild winter flounder Pleuronectes americanus in Passamaquoddy Bay, New Brunswick, Canada. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2002, 49, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.C.; Sperker, S.A.; Leggiadro, C.T.; Groman, D.B.; Griffiths, S.G.; Ritchie, R.J.; Cook, M.D.; Cusack, R.R. Identification and characterization of a piscine neuropathy and nodavirus from juvenile Atlantic cod from the Atlantic coast of North America. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2002, 14, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Mekuchi, T.; Imura, K.; Nakai, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Muroga, K. Occurrence of viral nervous necrosis (VNN) in hatchery-reared juvenile Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish. Sci. 1994, 60, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bandín, I.; Souto, S. Betanodavirus and VER disease: A 30-year research review. Pathogens 2020, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, R.; Sommerset, I.; Tørud, B.; Korsnes, K.; Hjortaas, M.; Nilsen, F.; Nerland, A.; Dannevig, B. Characterization of nodavirus and viral encephalopathy and retinopathy in farmed turbot, Scophthalmus maximus (L.). J. Fish Dis. 2004, 27, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Kwon, W.J.; Min, J.G.; Kim, K.I.; Jeong, H.D. Complete genome sequence and pathogenic analysis of a new betanodavirus isolated from shellfish. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Breton, A.; Grisez, L.; Sweetman, J.; Ollevier, F. Viral nervous necrosis (VNN) associated with mass mortalities in cage-reared sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax (L.). J. Fish Dis. 1997, 20, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffan, A.; Pascoli, F.; Pretto, T.; Panzarin, V.; Abbadi, M.; Buratin, A.; Quartesan, R.; Gijón, D.; Padrós, F. Viral nervous necrosis in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) caused by reassortant betanodavirus RGNNV/SJNNV: An emerging threat for Mediterranean aquaculture. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendramin, N.; Zrncic, S.; Padrós, F.; Oraic, D.; Le Breton, A.; Zarza, C.; Olesen, N.J. Fish health in Mediterranean Aquaculture, past mistakes and future challenges. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2016, 36, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, Y.; HD, N.; Furuhashi, M.; Nakai, T. Mass mortality of cultured sevenband grouper, Epinephelus septemfasciatus, associated with viral nervous necrosis. Fish Pathol. 1996, 31, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikoshi, K.; Inoue, K. Viral nervous necrosis in hatchery-reared larvae and juveniles of Japanese parrotfish, Oplegnathus fasciatus (Temminck & Schlegel). J. Fish Dis. 1990, 13, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, S.; Lo, C.; Kou, G.; Chang, P.; Peng, S.; Chen, S. Mass mortalities associated with viral nervous necrosis (VNN) disease in two species of hatchery-reared grouper, Epinephelus fuscogutatus and Epinephelus akaara (Temminck & Schlegel). J. Fish Dis. 1997, 20, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Grotmol, S.; Nerland, A.H.; Biering, E.; Totland, G.K.; Nishizawa, T. Characterisation of the capsid protein gene from a nodavirus strain affecting the Atlantic halibut Hippoglossus hippoglossus and design of an optimal reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) detection assay. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2000, 39, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagné, N.; Johnson, S.; Cook-Versloot, M.; MacKinnon, A.; Olivier, G. Molecular detection and characterization of nodavirus in several marine fish species from the northeastern Atlantic. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2004, 62, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, P.; Drawbridge, M.; Iwamoto, T.; Nakai, T.; Hedrick, R.; Gendron, A. Nodavirus infection of juvenile white seabass, Atractoscion nobilis, cultured in southern California: First record of viral nervous necrosis (VNN) in North America. J. Fish Dis. 2001, 24, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, S.E.; Gentry, R.R.; Kappel, C.V.; White, C.; Gaines, S.D. Offshore aquaculture in the United States: Untapped potential in need of smart policy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7162–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurath, G.; Winton, J. Complex dynamics at the interface between wild and domestic viruses of finfish. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2011, 1, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendramin, N.; Patarnello, P.; Toffan, A.; Panzarin, V.; Cappellozza, E.; Tedesco, P.; Terlizzi, A.; Terregino, C.; Cattoli, G. Viral Encephalopathy and Retinopathy in groupers (Epinephelus spp.) in southern Italy: A threat for wild endangered species? BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, H.; Chaoui, L.; Derbal, F.; Zaidi, R.; Boisséson, C.d.; Baud, M.; Bigarré, L. Betanodavirus-associated mortalities of adult wild groupers Epinephelus marginatus (Lowe) and Epinephelus costae (Steindachner) in Algeria. J. Fish Dis. 2014, 37, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaramillo, D.; Hick, P.; Whittington, R. Age dependency of nervous necrosis virus infection in barramundi Lates calcarifer (Bloch). J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toffan, A.; Biasini, L.; Pretto, T.; Abbadi, M.; Buratin, A.; Franch, R.; Dalla Rovere, G.; Panzarin, V.; Marsella, A.; Bargelloni, L. Age dependency of RGNNV/SJNNV viral encephalo-retinopathy in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 2021, 539, 736605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, W.O.; Carroll, P.M.; Alam, M.S.; Dumas, C.F.; Gabel, J.E.; Davis, T.M.; Bentley, C.D. The status of black sea bass, Centropristis striata, as a commercially ready species for US marine aquaculture. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2021, 52, 541–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steimle, F.W.; Zetlin, C.A.; Berrien, P.L.; Chang, S. Essential Fish Habitat Source Document. Black Sea Bass, Centropristis Striata, Life History and Habitat Characteristics; Northeast Fisheries Science Center (U.S.); NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-NE; 1999; Volume 143. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, E.; Quattro, J.; Greig, T. Genetic management of Black Sea Bass: Influence of biogeographic barriers on population structure. Mar. Coast. Fish. 2012, 4, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, M.A.; Burton, M.L.; Lima, T.G. Mitochondrial DNA differentiation between populations of black sea bass (Centropristis striata) across Cape Hatteras, North Carolina (USA). J. Biogeogr. 2013, 40, 1386–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musick, J.A.; Mercer, L.P. Seasonal distribution of black sea bass, Centropristis striata, in the Mid-Atlantic Bight with comments on the ecology and fisheries of the species. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1977, 106, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, J.; Shepherd, G.R. Seasonal distribution and movement of black sea bass (Centropristis striata) in the Northwest Atlantic as determined from a mark-recapture experiment. J. Northwest Atl. Fish. Sci. 2009, 40, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steimle, F.W.; Zetlin, C. Reef habitats in the middle Atlantic bight: Abundance, distribution, associated biological communities, and fishery resource use. Mar. Fish. Rev. 2000, 62, 24–42. [Google Scholar]
- Lovy, J.; Lewis, N.L.; Friend, S.E.; Able, K.W.; Shaw, M.J.; Hinks, G.S.; Clarke, P.J. Host, seasonal and habitat influences on incidence of Lernaeenicus radiatus (Copepoda: Pennellidae) in the mid-Atlantic Bight. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 642, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Able, K.W.; Valenti, J.L.; Grothues, T.M. Fish larval supply to and within a lagoonal estuary: Multiple sources for Barnegat Bay, New Jersey. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2017, 100, 663–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, T.; Nakai, T.; Mori, K.-i.; Arimoto, M.; Furusawa, I. Cloning of the fish cell line SSN-1 for piscine nodaviruses. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2000, 43, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzarin, V.; Patarnello, P.; Mori, A.; Rampazzo, E.; Cappellozza, E.; Bovo, G.; Cattoli, G. Development and validation of a real-time TaqMan PCR assay for the detection of betanodavirus in clinical specimens. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalla Valle, L.; Zanella, L.; Patarnello, P.; Paolucci, L.; Belvedere, P.; Colombo, L. Development of a sensitive diagnostic assay for fish nervous necrosis virus based on RT-PCR plus nested PCR. J. Fish Dis. 2000, 23, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batts, W.N.; LaPatra, S.E.; Katona, R.; Leis, E.; Ng, T.F.F.; Brieuc, M.S.; Breyta, R.B.; Purcell, M.K.; Conway, C.M.; Waltzek, T.B. Molecular characterization of a novel orthomyxovirus from rainbow and steelhead trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Virus Res. 2017, 230, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzarin, V.; Cappellozza, E.; Mancin, M.; Milani, A.; Toffan, A.; Terregino, C.; Cattoli, G. In vitro study of the replication capacity of the RGNNV and the SJNNV betanodavirus genotypes and their natural reassortants in response to temperature. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Chen, X.; Fu, J.; Yi, M.; Chen, W.; Jia, K. Near-complete genome sequence of a fish nervous necrosis virus isolated from hybrid grouper in China. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e01453-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffolo, V.; Negrisolo, E.; Maltese, C.; Bovo, G.; Belvedere, P.; Colombo, L.; Dalla Valle, L. Phylogeny of betanodaviruses and molecular evolution of their RNA polymerase and coat proteins. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2007, 43, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovo, G.; Gustinelli, A.; Quaglio, F.; Gobbo, F.; Panzarin, V.; Fusaro, A.; Mutinelli, F.; Caffara, M.; Fioravanti, M. Viral encephalopathy and retinopathy outbreak in freshwater fish farmed in Italy. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2011, 96, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovy, J.; Batts, W.N. Surveillance for Nervous Necrosis Virus in Black Sea Bass from the U.S. Atlantic Coast; U.S. Geological Survey Data Release: Reston, VA, USA, 2025. [CrossRef]
- Panzarin, V.; Fusaro, A.; Monne, I.; Cappellozza, E.; Patarnello, P.; Bovo, G.; Capua, I.; Holmes, E.C.; Cattoli, G. Molecular epidemiology and evolutionary dynamics of betanodavirus in southern Europe. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knibb, W.; Luu, G.; Premachandra, H.; Lu, M.-W.; Nguyen, N.H. Regional genetic diversity for NNV grouper viruses across the Indo-Asian region–implications for selecting virus resistance in farmed groupers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kwon, W.; Min, J.; Jeong, H. Isolation and initial characterization of new betanodaviruses in shellfish. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsnes, K.; Devold, M.; Nerland, A.H.; Nylund, A. Viral encephalopathy and retinopathy (VER) in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar after intraperitoneal challenge with a nodavirus from Atlantic halibut Hippoglossus hippoglossus. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2005, 68, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, R.J.; Richardson, D.E.; Hare, J.A.; Lynch, P.D.; Fratantoni, P.S. Disentangling the effects of climate, abundance, and size on the distribution of marine fish: An example based on four stocks from the Northeast US shelf. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 72, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahan, M.D.; Sherwood, G.D.; Grabowski, J.H. Geographic variation in life-history traits of black sea bass (Centropristis striata) during a rapid range expansion. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 567758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olveira, J.G.; Souto, S.; Dopazo, C.P.; Thiéry, R.; Barja, J.L.; Bandin, I. Comparative analysis of both genomic segments of betanodaviruses isolated from epizootic outbreaks in farmed fish species provides evidence for genetic reassortment. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2940–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, I.E.; Cerame-Vivas, M.J. The Circulation of Surface Waters in Raleigh Bay, North Carolina 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1963, 8, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, W.O.; Dumas, C.F.; Carroll, P.M.; Resimius, C.M. Production economic analysis of black sea bass juveniles to support finfish mariculture growout industry development in the southeastern United States. Aquac. Econ. Manag. 2015, 19, 226–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, W.O.; Smith, T.I.; Berlinsky, D.L.; Woolridge, C.A.; Stuart, K.R.; Copeland, K.A.; Denson, M.R. Volitional spawning of Black Sea Bass Centropristis striata induced with pelleted luteinizing hormone releasing hormone-analogue. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2003, 34, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, C.F.; Walker, R.L.; Recicar, T.C. Effects of temperature and salinity on growth of juvenile black sea bass, with implications for aquaculture. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2003, 65, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, I.; Jithendran, K.; Shekhar, M.; Thirunavukkarasu, A.; De la Pena, L. Immunolocalisation of nervous necrosis virus indicates vertical transmission in hatchery produced Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer Bloch)—A case study. Aquaculture 2006, 255, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ransangan, J.; Manin, B.O. Mass mortality of hatchery-produced larvae of Asian seabass, Lates calcarifer (Bloch), associated with viral nervous necrosis in Sabah, Malaysia. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 145, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlinsky, D.L.; Taylor, J.C.; Howell, R.A.; Bradley, T.M.; Smith, T.I. The effects of temperature and salinity on early life stages of black sea bass Centropristis striata. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2004, 35, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
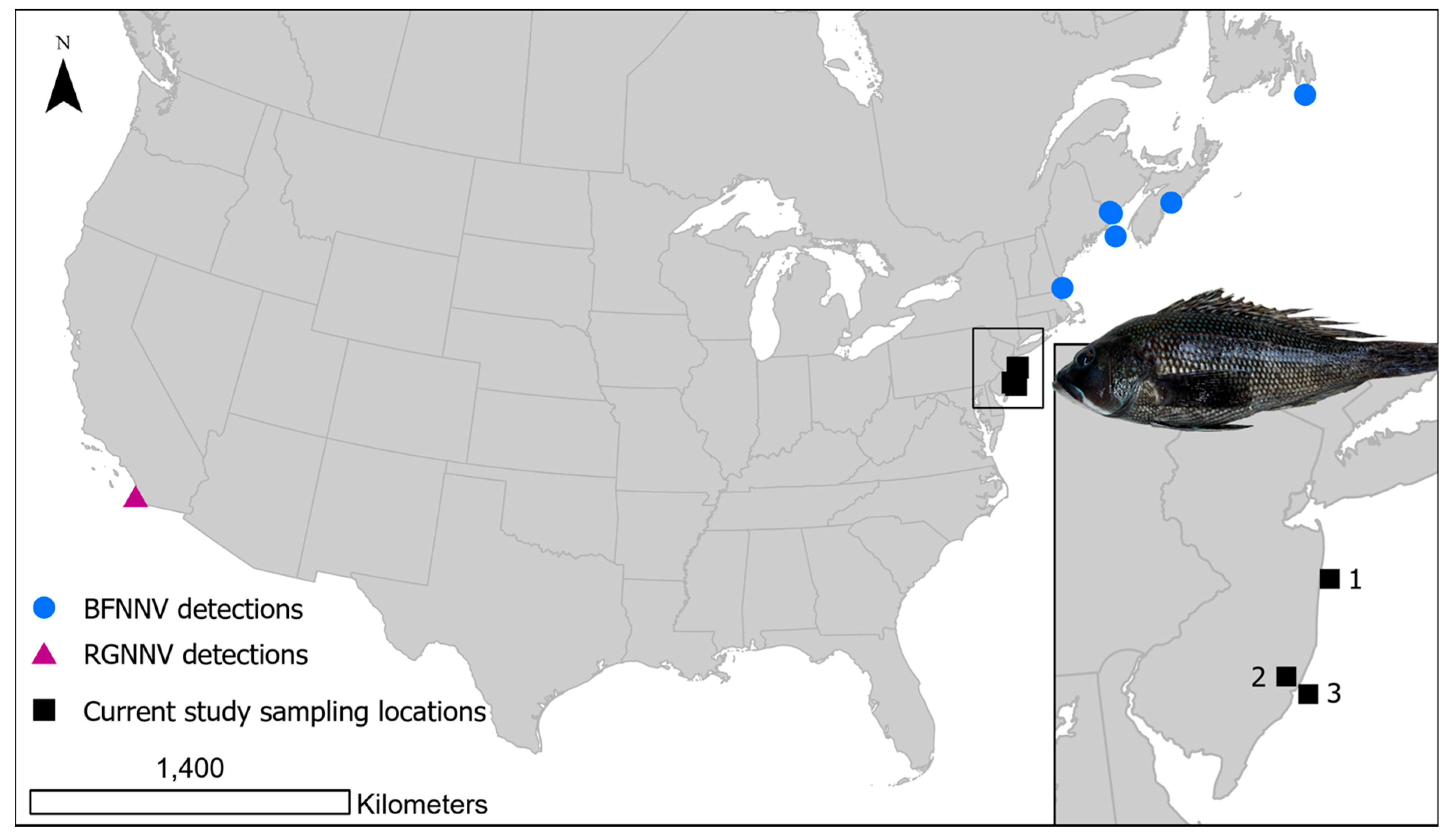

| Sampling Dates | Life Stage | Fish TL | Fish Weight | Method | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020—August–October | Adult | 246 ± 46 | 204 ± 113 | VI cell culture | 0/146 |
| 2020—March–August | YOY | 62 ± 11 | NA | rRT-PCR | 0/116 |
| 2020—August | Adult | 246 ± 46 | 203 ± 112 | rRT-PCR | 1/132 |
| 2020—October–November | Adult | 239 ± 50 | 203 ± 120 | rRT-PCR | 0/126 |
| 2021—April | Adult | 259 ± 25 | 220 ± 52 | rRT-PCR | 0/32 |
| 2021—July | Adult | 244 ± 38 | 193 ± 96 | rRT-PCR | 2/180 |
| 2021—October | Adult | 253 ± 38 | 225 ± 87 | rRT-PCR | 3/91 |
| 2022—July | Adult | 262 ± 44 | 258 ± 150 | rRT-PCR | 23/304 |
| Year | Strain ID | RNA1 | RNA2 | Year | Strain ID | RNA1 | RNA2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 20-045 | PV877385 | PV877386 | 2022 | 22-167 | PV993951 | PV993960 |
| 2021 | 21-058 | PV877388 | - | 22-170 | PV993952 | PV993961 | |
| 21-182 | PV877387 | PV877389 | 22-175 | PV993953 | PV993962 | ||
| 21-252 | Short* | Short* | 22-178 | Short* | - | ||
| 21-261 | - | Short* | 22-191 | PV877392 | PV993963 | ||
| 21-266 | - | Short* | 22-203 | Short* | - | ||
| 2022 | 22-021 | PV993948 | PV993956 | 22-213 | Short* | - | |
| 22-028 | PV877390 | PV877394 | 22-228 | - | PV877397 | ||
| 22-045 | PV877391 | PV877395 | 22-236 | PV993954 | PV993964 | ||
| 22-053 | PV993949 | PV993957 | 22-243 | Short* | PV993965 | ||
| 22-062 | PV993950 | Short* | 22-259 | - | PV993966 | ||
| 22-082 | - | PV993958 | 22-273 | PV993955 | PV993967 | ||
| 22-086 | Short* | - | 22-279 | - | PV993968 | ||
| 22-137 | Short* | PV877396 | 22-298 | PV877393 | - | ||
| 22-163 | - | Short* |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lovy, J.; Abbadi, M.; Toffan, A.; Das, N.; Neugebauer, J.N.; Batts, W.N.; Clarke, P.J. Detection and Genetic Characterization of Red-Spotted Grouper Nervous Necrosis Virus and a Novel Genotype of Nervous Necrosis Virus in Black Sea Bass from the U.S. Atlantic Coast. Viruses 2025, 17, 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091234
Lovy J, Abbadi M, Toffan A, Das N, Neugebauer JN, Batts WN, Clarke PJ. Detection and Genetic Characterization of Red-Spotted Grouper Nervous Necrosis Virus and a Novel Genotype of Nervous Necrosis Virus in Black Sea Bass from the U.S. Atlantic Coast. Viruses. 2025; 17(9):1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091234
Chicago/Turabian StyleLovy, Jan, Miriam Abbadi, Anna Toffan, Nilanjana Das, James N. Neugebauer, William N. Batts, and Peter J. Clarke. 2025. "Detection and Genetic Characterization of Red-Spotted Grouper Nervous Necrosis Virus and a Novel Genotype of Nervous Necrosis Virus in Black Sea Bass from the U.S. Atlantic Coast" Viruses 17, no. 9: 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091234
APA StyleLovy, J., Abbadi, M., Toffan, A., Das, N., Neugebauer, J. N., Batts, W. N., & Clarke, P. J. (2025). Detection and Genetic Characterization of Red-Spotted Grouper Nervous Necrosis Virus and a Novel Genotype of Nervous Necrosis Virus in Black Sea Bass from the U.S. Atlantic Coast. Viruses, 17(9), 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091234





