Abstract
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) is a tick-borne bunyavirus with a mortality rate of up to 30%. There is no specific treatment for SFTSV. This article systematically reviews the progress of major anti-SFTSV drugs. The nucleotide analogues (favipiravir, 4′-fluorouridine diphosphate prodrug VV261) have shown clinical potential. Calcium channel blockers (nifedipine, etc.) block virus invasion by inhibiting calcium influx. Monoclonal antibody (S2A5/SNB02) has achieved targeted therapy, and SNB02 nanoantibody has entered clinical trials. However, many candidate agents predominantly focus on a single target, such as viral RdRp or host calcium channels, which makes it difficult to block the entire viral replication cycle and may accelerate the accumulation of resistant mutations. In addition, the low bioavailability of small-molecule drugs, the obstacles to industrial-scale production of antibody-based therapies, and the lack of Phase III clinical evidence severely restrict their clinical translation. Future research should focus on exploring viral replication mechanisms, developing drugs against key viral proteins, and designing multi-target combination therapies and novel drug delivery systems.
1. Introduction
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS), caused by the severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV), is an acute febrile illness characterized by thrombocytopenia and leukopenia. In severe cases, it may trigger cytokine storms leading to multiple organ failure and death [1]. Clinical laboratory findings frequently demonstrate elevated serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) [2].
SFTSV, also designated Dabie bandavirus, belongs to the genus Bandavirus within the family Phenuiviridae and the order Bunyavirales [3,4]. The primary vector for transmission is the hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis [5]. Exhibiting broad host tropism and zoonotic potential, SFTSV transmits not only via tick bites but also through direct blood exposure [6]. Since its initial identification in China in 2009 [2,7], the virus has spread to regions including South Korea, Japan, and Vietnam, with a global case fatality rate approximating 30% [8,9,10].
The absence of approved vaccines or targeted therapeutics poses a substantial threat to public health should large-scale outbreaks occur. Consequently, the WHO designated SFTSV as a priority pathogen in 2017 and reaffirmed its status as a high-risk agent under the Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) framework in 2024. Elucidating the viral pathogenesis and developing effective countermeasures remain imperative.
2. Genomic Characteristics of SFTSV
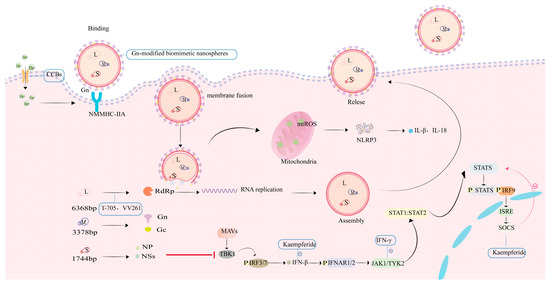
SFTSV is a segmented, single-stranded, negative-sense RNA virus with spherical virions measuring 80–100 nm in diameter [2,11]. The viral genome comprises three distinct segments designated as small, medium, and large segments [12]. Structurally, each genomic segment is flanked by non-translated regions (NTRs) that form panhandle-like secondary structures at the 5’ and 3’ termini [13]. The large (L) segment has a full length of approximately 6368 base pairs (bp) and primarily encodes the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). This enzyme represents the primary target for nucleoside analogue-based antivirals [2,13]. The M segment (3378 bp) expresses a glycoprotein precursor processed into Gn and Gc glycoproteins—key targets for vaccine development. Gn facilitates cellular entry by binding the host receptor non-muscle myosin heavy chain IIA (NMMHC-IIA), while Gc mediates pH-dependent membrane fusion [14]. The S segment, approximately 1744 bp in length, encodes both the nonstructural protein (NS) and nucleoprotein (NP) [13]. NS antagonizes IFN-β production through TBK1 sequestration and impedes NF-κB signaling, processes that provoke dysregulated cytokine release and hyperinflammation. Concurrently, the oligomerization of NP into ring-like structures encapsulates the viral RNA-RdRp complex, assembling stable RNPs essential for genomic protection and viral replication. The open reading frame (ORF) within the S segment exhibits significantly lower conservation than its counterpart in the L segment [13]. Driven by genetic instability, NSs undergo frequent mutations that can mediate resistance to selected antiviral therapies. Hence, in the process of drug development, it is important to thoroughly account for the potential impact of viral genomic mutations, design NS-targeted drugs to counter mutation-driven resistance, and explore the Gn/Gc fusion mechanism as a dual-target inhibitor (Figure 1, Table 1).
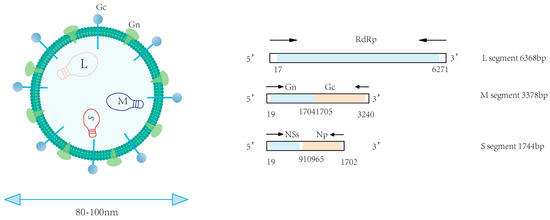
Figure 1.
Genomic organization of SFTSV.

Table 1.
SFTSV genomic segments and encoded proteins.
4. Summary and Outlook
This review summarizes the recent advances in SFTSV antiviral drugs. At present, most of the drug research on SFTSV is still in the stage of in vitro experiments or animal models, and few have advanced into clinical trials. Nucleoside analogues like ribavirin and favipiravir are primarily effective early in infection or at low viral loads, though efficacy is often limited by emerging resistance. Calcium channel blockers are promising host-targeted drugs, with evidence from retrospective studies; however, their efficacy lacks confirmation from randomized controlled trials. Caffeic acid exhibits antiviral activity only at the cellular level, and its in vivo efficacy and safety remain to be fully evaluated. Despite demonstrated antiviral efficacy in vitro, the suboptimal oral bioavailability of amodiaquine substantially curtails its clinical translation potential. Vitamin D derivatives have demonstrated antiviral activity in both laboratory and animal studies and exhibit a synergistic effect when combined with favipiravir. However, this potential has not yet been validated in human subjects. The long-term administration of IFN-γ and its inducers necessitates rigorous risk assessment for therapy-limiting effects, including acquired resistance mediated by JAK-STAT pathway dysregulation and dose-dependent hepatotoxicity. Metabolic disturbances, particularly hyperglycemia, have been recognized as significant contributors to poor outcomes in SFTS. Early clinical observations indicate that metformin may help normalize glucose levels, lower viral burden, and correlate with improved survival. Yet, current evidence is based on small cohorts, and its therapeutic relevance in patients without hyperglycemia has not been established. But the SNB02 monoclonal nanobody demonstrates high efficacy in animal models and has advanced to preclinical and clinical investigations, representing one of the most promising translational strategies currently available.
Based on the above analysis, the majority of drug studies remain at the stage of in vitro experiments or animal models. In the future, it is imperative to conduct in-depth investigations into key viral proteins, such as NSs and Gn/Gc, as well as host factors, to facilitate the development of multi-target inhibitors. Moreover, advancing siRNA nanodelivery systems and self-assembling nanoparticle platforms must proceed in parallel, accelerating the clinical translation of vaccines through rigorous safety and efficacy evaluation, while establishing both SFTS rapid diagnostics and robust tick vector surveillance systems. These advances constitute pivotal scientific underpinnings for confronting SFTSV threats, forming the bedrock for sustainable safeguards of global health security.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.D. and Y.T.; investigation, H.D., L.Z. and Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, H.D.; writing—review and editing, S.X., L.L. and Y.T.; visualization, H.D., L.Z. and Y.W.; supervision, S.X. and Y.T.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liang, S.; Xie, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, N.; Wang, X.; Qin, Y.; Bao, C.; Hu, J. Analysis of Fatal Cases of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in Jiangsu Province, China, between 2011 and 2022: A Retrospective Study. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1076226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.-J.; Liang, M.-F.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.-D.; Sun, Y.-L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.-F.; Popov, V.L.; Li, C.; et al. Fever with Thrombocytopenia Associated with a Novel Bunyavirus in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, J.H.; Adkins, S.; Alioto, D.; Alkhovsky, S.V.; Amarasinghe, G.K.; Anthony, S.J.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Ayllón, M.A.; Bahl, J.; Balkema-Buschmann, A.; et al. 2020 Taxonomic Update for Phylum Negarnaviricota (Riboviria: Orthornavirae), Including the Large Orders Bunyavirales and Mononegavirales. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 3023–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Min, Y.-Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Deng, F.; Wang, H.; Ning, Y.-J. Animal Model of Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 797189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Tang, F.; Cui, N.; Qin, S.; Wang, B.; Liu, W. Survey and genetic analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus from Haemaphysalis longicornis. J. Pathog. Biol. 2014, 9, 629–632. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jung, I.Y.; Choi, W.; Kim, J.; Wang, E.; Park, S.-W.; Lee, W.-J.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Uh, Y.; Kim, Y.K. Nosocomial Person-to-Person Transmission of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 633.e1–633.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhou, D.J.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, X.P.; He, Y.W.; Sun, Q.; Yu, B.; Li, J.; Dai, Y.A.; Tian, J.H.; et al. Hemorrhagic fever caused by a novel tick-borne Bunyavirus in Huaiyangshan, China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2011, 32, 209–220. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, X.C.; Yun, Y.; Van An, L.; Kim, S.-H.; Thao, N.T.P.; Man, P.K.C.; Yoo, J.R.; Heo, S.T.; Cho, N.-H.; Lee, K.H. Endemic Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome, Vietnam. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1029–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.S.; Woo, J.H. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome: Tick-Mediated Viral Disease. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2013, 28, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Maeda, K.; Suzuki, T.; Ishido, A.; Shigeoka, T.; Tominaga, T.; Kamei, T.; Honda, M.; Ninomiya, D.; Sakai, T.; et al. The First Identification and Retrospective Study of Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in Japan. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chai, C.; Wang, C.; Amer, S.; Lv, H.; He, H.; Sun, J.; Lin, J. Systematic Review of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome:Virology, Epidemiology, and Clinical Characteristics. Rev. Med. Virol. 2014, 24, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-W.; Kim, D.; Yun, N.; Kim, D.-M. Clinical Update of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Viruses 2021, 13, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guu, T.S.Y.; Zheng, W.; Tao, Y.J. Bunyavirus: Structure and Replication. In Viral Molecular Machines; Rossmann, M.G., Rao, V.B., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 726, pp. 245–266. ISBN 978-1-4614-0979-3. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Qi, Y.; Liu, C.; Gao, W.; Chen, P.; Fu, L.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; Jing, Z.; Zhong, G.; et al. Nonmuscle Myosin Heavy Chain IIA Is a Critical Factor Contributing to the Efficiency of Early Infection of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China; National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Diagnosis and treatment scheme for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (2023 Edition). Chin. J. Infect. Control. 2024, 23, 819–929. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Miao, W.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in Hefei: Clinical Features, Risk Factors, and Ribavirin Therapeutic Efficacy. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 3516–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama-Ito, M.; Saijo, M. Antiviral Drugs Against Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graci, J.D.; Cameron, C.E. Mechanisms of Action of Ribavirin against Distinct Viruses. Rev. Med. Virol. 2006, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimojima, M.; Fukushi, S.; Tani, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Fukuma, A.; Taniguchi, S.; Suda, Y.; Maeda, K.; Takahashi, T.; Morikawa, S.; et al. Effects of Ribavirin on Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus In Vitro. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 67, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Kim, K.-H.; Yi, J.; Choi, S.J.; Choe, P.G.; Park, W.B.; Kim, N.J.; Oh, M. In Vitro Antiviral Activity of Ribavirin against Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2017, 32, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lu, Q.-B.; Cui, N.; Li, H.; Wang, L.-Y.; Liu, K.; Yang, Z.-D.; Wang, B.-J.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; et al. Case-Fatality Ratio and Effectiveness of Ribavirin Therapy Among Hospitalized Patients in China Who Had Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, Q.-B.; Xing, B.; Zhang, S.-F.; Liu, K.; Du, J.; Li, X.-K.; Cui, N.; Yang, Z.-D.; Wang, L.-Y.; et al. Epidemiological and Clinical Features of Laboratory-Diagnosed Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in China, 2011–2017: A Prospective Observational Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delang, L.; Abdelnabi, R.; Neyts, J. Favipiravir as a Potential Countermeasure against Neglected and Emerging RNA Viruses. Antivir. Res. 2018, 153, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraki, K.; Daikoku, T. Favipiravir, an Anti-Influenza Drug against Life-Threatening RNA Virus Infections. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 209, 107512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Jiang, X.-M.; Cui, N.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, S.-F.; Lu, Q.-B.; Yang, Z.-D.; Xin, Q.-L.; Song, Y.-B.; Zhang, X.-A.; et al. Clinical Effect and Antiviral Mechanism of T-705 in Treating Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Sig. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangawa, H.; Komeno, T.; Nishikawa, H.; Yoshida, A.; Takahashi, K.; Nomura, N.; Furuta, Y. Mechanism of Action of T-705 Ribosyl Triphosphate against Influenza Virus RNA Polymerase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5202–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, H.; Fukuma, A.; Fukushi, S.; Taniguchi, S.; Yoshikawa, T.; Iwata-Yoshikawa, N.; Sato, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Nagata, N.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. Efficacy of T-705 (Favipiravir) in the Treatment of Infections with Lethal Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus. mSphere 2016, 1, e00061-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, M.; Toyama, M.; Sakakibara, N.; Okamoto, M.; Arima, N.; Saijo, M. Establishment of an Antiviral Assay System and Identification of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Inhibitors. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2017, 25, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suemori, K.; Saijo, M.; Yamanaka, A.; Himeji, D.; Kawamura, M.; Haku, T.; Hidaka, M.; Kamikokuryo, C.; Kakihana, Y.; Azuma, T.; et al. A Multicenter Non-Randomized, Uncontrolled Single Arm Trial for Evaluation of the Efficacy and the Safety of the Treatment with Favipiravir for Patients with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jian, X.; Wen, Y.; Xu, M.; Jin, R.; Wu, X.; Zhou, F.; Cao, J.; Xiao, G.; Peng, K.; et al. A Nanoluciferase SFTSV for Rapid Screening Antivirals and Real-Time Visualization of Virus Infection in Mice. eBioMedicine 2024, 99, 104944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Hu, T.; Xue, H.; Pan, W.; Xie, Y.; Shen, J. Synthesis and Evaluation of NHC Derivatives and 4′-Fluorouridine Prodrugs. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2023, 21, 2754–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zheng, W.; Dong, X.; Sun, T.; Xu, M.; Xiang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Jian, X.; Yu, J.; et al. Design and Development of a Novel Oral 4′-Fluorouridine Double Prodrug VV261 against SFTSV. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 68, 9811–9826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, L.-K.; Li, S.-F.; Zhang, S.-F.; Wan, W.-W.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Xin, Q.-L.; Dai, K.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Z.-B.; et al. Calcium Channel Blockers Reduce Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus (SFTSV) Related Fatality. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urata, S.; Yoshikawa, R.; Yasuda, J. Calcium Influx Regulates the Replication of Several Negative-Strand RNA Viruses Including Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e00015-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Yan, X.; Yang, S.; Ren, S.; Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Shao, Y.; Li, W.; Li, S.; et al. Antiviral Activity of Vitamin D Derivatives against Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus in Vitro and in Vivo. Virol. Sin. 2024, 39, S1995820X24001342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, M.; Shirasago, Y.; Ando, S.; Shimojima, M.; Saijo, M.; Fukasawa, M. Caffeic Acid, a Coffee-Related Organic Acid, Inhibits Infection by Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus in Vitro. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Shirasago, Y.; Tanida, I.; Kakuta, S.; Uchiyama, Y.; Shimojima, M.; Hanada, K.; Saijo, M.; Fukasawa, M. Structural Basis of Antiviral Activity of Caffeic Acid against Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus. J. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 27, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, M.; Okamoto, M.; Toyama, M.; Sakakibara, N.; Shimojima, M.; Saijo, M.; Niwa, T.; Yagi, Y. Amodiaquine Derivatives as Inhibitors of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus (SFTSV) Replication. Antivir. Res. 2023, 210, 105479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Sun, J.; Kuang, W.; Yu, F.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Deng, W.; Xu, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, H.; et al. A Broadly Protective Antibody Targeting Glycoprotein Gn Inhibits Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, B.; Ma, X.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, N.; Xu, S.; Nawaz, W.; Xu, C.; Wu, Z. A Single-Domain Antibody Inhibits SFTSV and Mitigates Virus-Induced Pathogenesis in Vivo. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e136855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y-Clone Medical Science Co., Ltd. Technology Transfer and R&D Collaboration Agreement on SNB02 . Available online: www.y-clone.com (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Hoffmann, H.-H.; Schneider, W.M.; Rice, C.M. Interferons and Viruses: An Evolutionary Arms Race of Molecular Interactions. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, K.; Hertzog, P.J.; Ravasi, T.; Hume, D.A. Interferon-γ: An Overview of Signals, Mechanisms and Functions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 163–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.-J.; Mo, Q.; Feng, K.; Min, Y.-Q.; Li, M.; Hou, D.; Peng, C.; Zheng, X.; Deng, F.; Hu, Z.; et al. Interferon-γ-Directed Inhibition of a Novel High-Pathogenic Phlebovirus and Viral Antagonism of the Antiviral Signaling by Targeting STAT1. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yan, Y.; Dai, Q.; Yin, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Zhong, W.; Cao, R.; Li, S. Tilorone Confers Robust In Vitro and In Vivo Antiviral Effects against Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus. Virol. Sin. 2022, 37, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, R.; Sun, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.; Anirudhan, V.; Cui, Q.; Wang, H.; Rong, L.; Ning, Y.-J. Kaempferide Enhances Type I Interferon Signaling as a Novel Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Agent. Antivir. Res. 2025, 237, 106141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Peng, X.; Wang, G.; Gong, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; et al. Impact of Glycemia and Insulin Treatment in Fatal Outcome of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 119, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, X.; Ge, H.; Cui, N.; Lin, L.; Yue, M.; Zhu, C.; Zhou, Q.; Song, P.; Shang, X.; et al. Metformin as Antiviral Therapy Protects Hyperglycemic and Diabetic Patients. mBio 2025, 16, e00634-25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaer, W.; Zureigat, H.; Al Karaki, A.; Al-Kadash, A.; Gharaibeh, L.; Hatmal, M.M.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Awidi, A. siRNA: Mechanism of Action, Challenges, and Therapeutic Approaches. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 905, 174178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Shang, S. Gn-Modified Biomimetic Nanospheres for Targeted siRNA Delivery and Their in Vitro Activity against Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 309, 142955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).