White-Tailed Deer Prion Protein Gene Variability Suggests Selection Against Chronic Wasting Disease in Canada’s Prairies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cervid Populations
2.2. DNA Extraction, Real-Time PCR Genotyping and Sanger Sequencing
2.3. Data Analysis
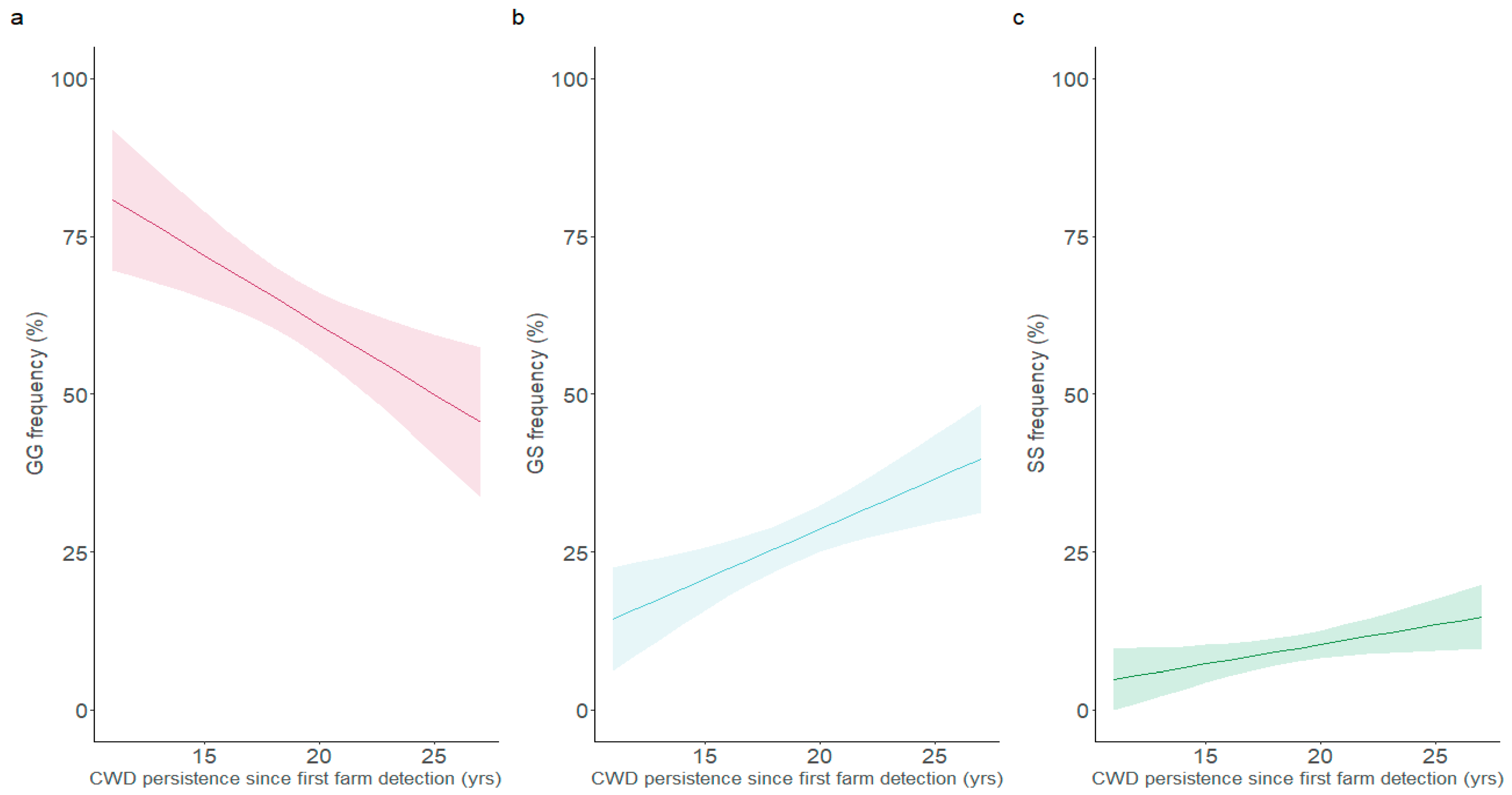
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFIA | Canadian Food Inspection Agency |
| CWD | Chronic wasting disease |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| PRNP | Prion protein gene |
| PrPC | Prion protein (cellular) |
| PrPCWD | Prion protein (infectious, chronic wasting disease) |
| PrPSc | Prion protein (infectious, general or scrapie) |
| RPLN(s) | Retropharyngeal lymph node(s) |
| TSE | Transmissible spongiform encephalopathy |
| USA | United States of America |
| WTD | White-tailed deer |
References
- Government of British Columbia. New Restrictions for Region Affected by Chronic Wasting Disease: Update. Available online: https://news.gov.bc.ca/releases/2024WLRS0007-000192 (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- United States Geological Survey. Expanding Distribution of Chronic Wasting Disease. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/centers/nwhc/science/expanding-distribution-chronic-wasting-disease (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Bollinger, T.; Caley, P.; Merrill, E.; Messier, F.; Miller, M.W.; Samuel, M.D.; Vanopdenbosch, E. Expert Scientific Panel on Chronic Wasting Disease. Available online: https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/icwdmccwhcnews/19/ (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Williams, E.S.; Young, S. Chronic wasting disease of captive mule deer: A spongiform encephalopathy. J. Wildl. Dis. 1980, 16, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.; Dubé, C.; Bates, L.; Balachandran, A. Chronic wasting disease in Canada: Part 1. Can. Vet. J. 2004, 45, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Argue, C.K.; Ribble, C.; Lees, V.W.; McLane, J.; Balachandran, A. Epidemiology of an outbreak of chronic wasting disease on elk farms in Saskatchewan. Can. Vet. J. 2007, 48, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Imran, M.; Mahmood, S. An overview of animal prion diseases. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, T.R.; Schätzl, H.M.; Gilch, S. Early detection of chronic wasting disease prions in urine of pre-symptomatic deer by real-time quaking-induced conversion assay. Prion 2013, 7, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennant, J.M.; Li, M.; Henderson, D.M.; Tyer, M.L.; Denkers, N.D.; Haley, N.J.; Mathiason, C.K.; Hoover, E.A. Shedding and stability of CWD prion seeding activity in cervid feces. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderon, D.M.; Denkers, N.D.; Hoover, C.E.; Garbino, N.; Mathiason, C.K.; Hoover, E.A. Longitudinal Detection of Prion Shedding in Saliva and Urine by Chronic Wasting Disease-Infected Deer by Real-Time Quaking-Induced Conversion. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9338–9347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgsson, G.; Sigurdarson, S.; Brown, P. Infectious agent of sheep scrapie may persist in the environment for at least 16 years. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 3737–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Ness, A.; Moffatt, E.; Bollinger, T.; McKenzie, D.; Stasiak, I.; Bahnson, C.S.; Aiken, J.M. Detection of Chronic Wasting Disease Prions in Prairie Soils from Endemic Regions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 10932–10940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.J.; Pederson, J.A.; Chappell, R.J.; McKenzie, D.; Aiken, J.M. Oral Transmissibility of Prion Disease Is Enhanced by Binding to Soil Particles. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritzkow, S.; Morales, R.; Moda, F.; Khan, U.; Telling, G.C.; Hoover, E.; Soto, C. Grass plants bind, retain, uptake, and transport infectious prions. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, T.A.; Pulford, B.; Wyckoff, A.C.; Meyerett, C.; Michel, B.; Gertig, K.; Hoover, E.A.; Jewell, J.E.; Telling, G.C.; Zabel, M.D. Detection of protease-resistant cervid prion protein in water from a CWD-endemic area. Prion 2009, 3, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigurdson, C.J.; Williams, E.S.; Miller, M.W.; Spraker, T.R.; O’Rourke, K.I.; Hoover, E.A. Oral transmission and early lymphoid tropism of chronic wasting disease PrPres in mule deer fawns (Odocoileus hemionus). J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 2757–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, J.A.; Telling, G.C. Molecular Mechanisms of Chronic Wasting Disease Prion Propagation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a024448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Manca, M.; Foutz, A.; Camacho, M.V.; Raymond, G.J.; Race, B.; Orru, C.D.; Yuan, J.; Shen, P.; Li, B.; et al. Early preclinical detection of prions in the skin of prion-infected animals. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, A.; Duque-Velásquez, C.; Johnson, C.; Herbst, A.; Bolea, R.; Badiola, J.J.; Aiken, J.; McKenzie, D. Prion protein polymorphisms associated with reduced CWD susceptibility limit peripheral PrPCWD deposition in orally infected white-tailed deer. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Schwabenlander, M.D.; Rowden, G.R.; Schefers, J.M.; Jennelle, C.S.; Carstensen, M.; Seelig, D.; Larsen, P.A. RT-QuIC detection of CWD prion seeding activity in white-tailed deer muscle tissues. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurson, C.J.; Bartz, J.C.; Glatzel, M. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Prion Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2019, 14, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, M.I.; Hannaoui, S.; Chang, S.C.; Thapa, S.; Schatzl, H.M.; Gilch, S. Cervid Prion Protein Polymorphisms: Role in Chronic Wasting Disease Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, N.J.; Merret, K.; Stein, A.B.; Simpson, D.; Carlson, A.; Mitchell, G.; Staskevicius, A.; Nichols, T.; Lehmkuhl, A.D.; Thomsen, B.V. Estimating relative CWD susceptibility and disease progression in farmed white-tailed deer with rare PRNP alleles. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, N.J.; Rielinger, R.; Davenport, K.A.; O’Rourke, K.; Mitchell, G.; Richt, J.A. Estimating chronic wasting disease susceptibility in cervids using real-time quaking-induced conversion. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2882–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazami-Goudarzi, K.; Andréoletti, O.; Vilotte, J.-L.; Béringue, V. Review on PRNP genetics and susceptibility to chronic wasting disease of Cervidae. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabury, C.M.; Lockwood, M.A.; Nichols, T.A. Genotype by environment interactions for chronic wasting disease in farmed US white-tailed deer. G3 2022, 12, jkac109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, D.R.; Kauffman, M.J.; Schumaker, B.A.; Lindzey, F.G.; Cook, W.E.; Kreeger, T.J.; Grogan, R.G.; Cornish, T.E. Chronic Wasting Disease Drives Population Decline of White-Tailed Deer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, G.A.; Nakada, S.M.; Bollinger, T.K.; Pybus, M.J.; Merrill, E.H.; Coltman, D.W. Polymorphisms at the PRNP Gene Influence Susceptibility to Chronic Wasting Disease in Two Species of Deer (Odocoileus spp.) in Western Canada. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2009, 72, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaCava, M.E.F.; Malmberg, J.L.; Edwards, W.H.; Johnson, L.N.L.; Allen, S.E.; Ernest, H.B. Spatio-temporal analyses reveal infectious disease-driven selection in a free-ranging ungulate. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 210802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketz, A.C.; Robinson, S.J.; Johnson, C.J.; Samuel, M.D. Pathogen-mediated selection and management implications for white-tailed deer exposed to chronic wasting disease. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 59, 982–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, K.I.; Spraker, T.R.; Hamburg, L.K.; Besser, T.E.; Brayton, K.A.; Knowles, D.P. Polymorphisms in the prion precursor functional gene but not the pseudogene are associated with susceptibility to chronic wasting disease in white-tailed deer. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürkner, P.-C. brms: An R Package for Bayesian Multilevel Models Using Stan. J. Stat. Soft 2017, 80, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stan Development Team. RStan: The R Interface to Stan, version 2.32.6. 2025. Available online: https://mc-stan.org/ (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Ghosh, J.; Li, Y.; Mitra, R. On the Use of Cauchy Prior Distributions for Bayesian Logistic Regression. Bayesian Anal. 2018, 13, 359–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehtari, A.; Gelman, A.; Simpson, D.; Carpenter, B.; Bürkner, P.-C. Rank-Normalization, Folding, and Localization: An Improved R for Assessing Convergence of MCMC (with Discussion). Bayesian Anal. 2021, 16, 667–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, R.L.; Roebroeck, A. Robust and Fast Markov Chain Monte Carlo Sampling of Diffusion MRI Microstruvture Models. Front. Neuroinform 2018, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpe, D. Chi-Square Test is Statistically Significant: Now What? Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2015, 20, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, Y.; Tian, T.; Brandt, A.L.; Kelly, A.C.; Shelton, P.; Roca, A.L.; Novakofski, J.; Mateus-Pinilla, N.E. Association of chronic wasting disease susceptibility with prion protein variation in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Prion 2020, 14, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Johnson, J.; Vanderloo, J.P.; Keane, D.; Aiken, J.M.; McKenzie, D. Prion protein polymorphisms in white-tailed deer influence susceptibility to chronic wasting disease. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 2109–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafin, T.K.; Douglas, M.R.; Martin, B.T.; Zbinden, Z.D.; Middaugh, C.R.; Ballard, J.R.; Gray, M.C.; White Jr, D.; Douglas, M.E. Age structuring and spatial heterogeneity in prion protein gene (PRNP) polymorphism in white-tailed deer. Prion 2020, 14, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, A.L.; Green, M.L.; Ishida, Y.; Roca, A.L.; Novakofski, J.; Mateus-Pinilla, N.E. Influence of the geographic distribution of prion protein gene sequence variation on patterns of chronic wasting disease spread in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Prion 2018, 12, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, A.L.; Kelly, A.C.; Green, M.L.; Shelton, P.; Novakofski, J.; Mateus-Pinilla, N.E. Prion protein gene sequence and chronic wasting disease susceptibility in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Prion 2015, 9, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidian, S.; Dorosh, L.; Duque-Velásquez, C.; Stepanova, M.; Aiken, J.; McKenzie, D.; Wille, H. Molecular dynamics simulations of cervid prion protein variants to assess protein stability and susceptibility towards chronic wasting disease. Found in: Prion 2019 emerging concepts. Prion 2019, 13, 140. [Google Scholar]
- Keane, D.P.; Barr, D.J.; Bochsler, P.N.; Hall, S.M.; Gidlewski, T.; O’Rourke, K.I.; Spraker, T.R.; Samuel, M.D. Chronic wasting disease in a Wisconsin white-tailed deer farm. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2008, 20, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.J.; Herbst, A.; Duque-Velásquez, C.; Vanderloo, J.P.; Bochsler, P.; Chappell, R.; McKenzie, D. Prion protein polymorphisms affect chronic wasting disease progression. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque-Velásquez, C.; Kim, C.; Haldiman, T.; Kim, C.; Herbst, A.; Aiken, J.; Safar, J.G.; McKenzie, D. Chronic wasting disease (CWD) pron strains evolve via adaptive diversification of conformers in hosts expression prion protein polymorphisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 4985–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, N.J.; Mathiason, C.K.; Carver, S.; Zabel, M.; Telling, G.C.; Hoover, E.A. Detection of Chronic Wasting Disease Prions in Salivary, Urinary and Intestinal Tissues of Deer: Potential Mechanisms of Prion Shedding and Transmission. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6309–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Risi, F.; Soto, P.; Benavente, P.; Nichols, T.A.; Morales, R. Dynamics of CWD prion detection in feces and blood from naturally infected white-tailed deer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, M.I.; Kaczmarczyk, L.; Zeng, D.; Hannaoui, S.; Lee, C.; Chang, S.C.; Mitchell, G.; McKenzie, D.; Beekes, M.; Jackson, W.; et al. Heterozygosity for cervid S138N polymorphism results in subclinical CWD in gene-targeted mice and progressive inhibition of prion conversion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2221060120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, M.A.; Unsworth, J.W.; Zager, P.; Hebblewhite, M.; Garton, E.O.; Montgomery, D.M.; Skalski, J.R.; Maycock, C.L. Demographic response of mule deer to experimental reduction of coyotes and mountain lions in southeastern Idaho. Wildl. Monogr. 2011, 178, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, C.; Leighton, P.A.; Beauchamp, G.; Nguon, S.; Trudel, L.; Milord, F.; Lindsay, L.R.; Bélanger, D.; Ogden, N.H. Harvested white-tailed deer as sentinel hosts for early establishing Ixodes scapularis populations and risk from vector-borne zoonoses in southeastern Canada. J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, N.; McGinn, R.; Soto, P.; Spraker, T.R.; Fischer, J.; VerCauteren, K.; Nichols, T.; Morales, R. Distribution of chronic wasting disease (CWD) prions in tissues from experimentally exposed coyotes (Canis latrans). PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0327485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, P.; Bravo-Risi, F.; Kramm, C.; Gamez, N.; Benavente, R.; Bonilla, D.L.; Reed, J.H.; Lockwood, M.; Spraker, T.J.; Nichols, T.; et al. Nasal bots carry relevant titers of CWD prions in naturally infected white-tailed deer. EMBO Rep. 2024, 25, 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzalaco, H.N.; Bravo-Risi, F.; Morales, R.; Walsh, D.P.; Storm, D.J.; Pederson, J.A.; Turner, W.C.; Lichtenberg, S.S. Ticks harbor and excrete chronic wasting disease prions. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, L.F.; Bedere, N.; Douhard, F.; Oliveira, H.R.; Arnal, M.; Peñagaricano, F.; Schinckel, A.P.; Baes, C.F.; Miglior, F. Review: Genetic selection of high-yielding dairy cattle toward sustainable farming systems in a rapidly changing world. Animal 2021, 15, 100292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, N.; Donner, R.; Merret, K.; Miller, M.; Senier, K. Selective Breeding for Disease-Resistant PRNP Variants to Manage Chronic Wasting Disease in Farmed Whitetail Deer. Genes 2021, 12, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monello, R.J.; Galloway, N.L.; Powers, J.G.; Madsen-Bouterse, S.A.; Edwards, W.H.; Wood, M.E.; O’Rourke, K.I.; Wild, M.A. Pathogen-mediated selection in free-ranging elk populations infected by chronic wasting disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12208–12212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzas, C.; Ayscue, P.; Ivanek, R.; Gröhn, Y.T. Model or meal? Farm animal populations as models for infectious diseases of humans. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 8, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, R.A.A.P.; Bollinger, T.K. Mule Deer (Odocoileus hemionus) Reproduction, Fawn Survival, and Exposure of Fawns to Infectious Agents in a Chronic Wasting Disease Endemic Area of Southern Saskatchewan. Master’s Thesis, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 17 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, K.A.; Jewell, J.E.; Williams, E.S.; Miller, M.W. Patterns of PrPCWD accumulation during the course of chronic wasting disease infection in orally inoculated mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus). J Gen Virol 2006, 87, 3451–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercauteren, K.C.; Lavelle, M.J.; Seward, N.W.; Fischer, J.W.; Phillips, G.E. Fence-Line Contact Between Wild and Farmed White-Tailed Deer in Michigan: Potential for Disease Transmission. J. Wildl. Manag. 2007, 71, 1603–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, P. Deer handling and transport. In Livestock Handling and Transport, 5th ed.; Grandin, T., Ed.; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK, 2009; pp. 370–403. [Google Scholar]

| Herd | Province | % CWD (Farm-Wide) | n | nWTD | nGenotyped | nSequenced |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | AB | 3.70 | 378 | 378 | 377 | 313 |
| B | AB | 0.00 | 306 | 306 | ND | 296 |
| C | AB | 11.89 | 143 | 136 | 136 | ND |
| D | AB | 4.66 | 686 | 402 | 388 | 29 |
| E | SK | 64.90 | 126 (+312) | 438 | 71 (+312) | 108 |
| F | SK | 1.09 | 274 | 274 | 271 | ND |
| G | SK | 11.77 | 20 | 12 | 12 | ND |
| H | SK | 90.00 | 20 | 20 | 18 | 9 |
| I | SK | 67.74 | 31 | 34 | 34 | ND |
| J | SK | 11.36 | 44 | 86 | 24 | ND |
| K | SK | 8.33 | 96 | 96 | 96 | 52 |
| L | SK | 85.71 | 21 | 31 | 31 | ND |
| M | SK | 31.40 | 121 | 24 | 24 | ND |
| N | SK | 6.7 | 179 | 157 | 157 | ND |
| O | SK | 47.62 | 23 | 21 | 21 | ND |
| P | SK | 21.26 | 414 | 395 | 381 | ND |
| Q | SK | 7.58 | 66 | 36 | 36 | ND |
| R | SK | 82.76 | 29 | 29 | 29 | ND |
| S | SK | 23.21 | 56 | 56 | 56 | ND |
| T | SK | 69.74 | 76 | 69 | 69 | ND |
| U | SK | 18.06 | 72 | 58 | 55 | ND |
| Herd | Wild-Type | 96GS | 96SS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CWD+ | CWD− | CWD+ | CWD− | CWD+ | CWD− | |
| A | 13 | 270 | 1 | 65 | * | 29 |
| B | * | 164 | * | 67 | * | 65 |
| C | 16 | 64 | 1 | 41 | * | 14 |
| D | 10 | 179 | 2 | 136 | * | 75 |
| E | 59 | 27 | 16 | 9 | * | 1 |
| F | 2 | 154 | * | 86 | 1 | 28 |
| G | 3 | 6 | * | 3 | * | * |
| H | 16 | 1 | 1 | 2 | * | * |
| I | 8 | 2 | 6 | 3 | * | * |
| J | 4 | 5 | 1 | 3 | * | * |
| K | 4 | 18 | 3 | 53 | 1 | 17 |
| L | 18 | 1 | * | 2 | * | * |
| Total | 153 | 891 | 31 | 470 | 2 | 229 |
| f (%) | 58.78 | 28.21 | 13.01 | |||
| Herd | Wild-Type | 96GS | 96SS | 116AG | 116GG | 95QH | 95HH | 96GS/ 116AG | 95QH/ 96GS | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CWD + | CWD − | CWD + | CWD − | CWD + | CWD − | CWD + | CWD − | CWD + | CWD − | CWD + | CWD − | CWD + | CWD − | CWD + | CWD − | CWD + | CWD − | |
| A | 13 | 211 | 1 | 49 | * | 22 | * | 7 | * | 4 | * | 1 | * | * | * | * | * | 4 |
| B | * | 145 | * | 63 | * | 65 | * | * | * | * | * | 9 | * | 10 | * | * | * | 4 |
| D | 8 | 8 | 2 | 7 | * | * | 1 | 1 | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 2 | * | * |
| E | 47 | 22 | 13 | 9 | * | 1 | 3 | 4 | * | * | 2 | * | * | * | 1 | * | 1 | * |
| H | 6 | 1 | 2 | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
| K | 1 | 18 | 1 | 20 | * | 10 | 1 | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |
| Total | 75 | 405 | 19 | 148 | 0 | 98 | 5 | 12 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 8 |
| f (%) | 60.00 | 20.88 | 12.25 | 2.13 | 0.50 | 1.50 | 1.25 | 0.38 | 1.13 | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pilot, W.; Arifin, M.I.; Staskevicius, A.; Haley, N.J.; Mitchell, G.; Guan, J. White-Tailed Deer Prion Protein Gene Variability Suggests Selection Against Chronic Wasting Disease in Canada’s Prairies. Viruses 2025, 17, 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081121
Pilot W, Arifin MI, Staskevicius A, Haley NJ, Mitchell G, Guan J. White-Tailed Deer Prion Protein Gene Variability Suggests Selection Against Chronic Wasting Disease in Canada’s Prairies. Viruses. 2025; 17(8):1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081121
Chicago/Turabian StylePilot, William, Maria I. Arifin, Antanas Staskevicius, Nicholas J. Haley, Gordon Mitchell, and Jiewen Guan. 2025. "White-Tailed Deer Prion Protein Gene Variability Suggests Selection Against Chronic Wasting Disease in Canada’s Prairies" Viruses 17, no. 8: 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081121
APA StylePilot, W., Arifin, M. I., Staskevicius, A., Haley, N. J., Mitchell, G., & Guan, J. (2025). White-Tailed Deer Prion Protein Gene Variability Suggests Selection Against Chronic Wasting Disease in Canada’s Prairies. Viruses, 17(8), 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081121







