Updates on Recent Advancements in Hepatitis D Virus Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
3. Pathogenesis
4. Prognostic Factors
4.1. Baseline Liver Injury
4.2. HDV Genotype
4.3. HBV Status
4.4. HDV RNA
5. Coinfection with HIV
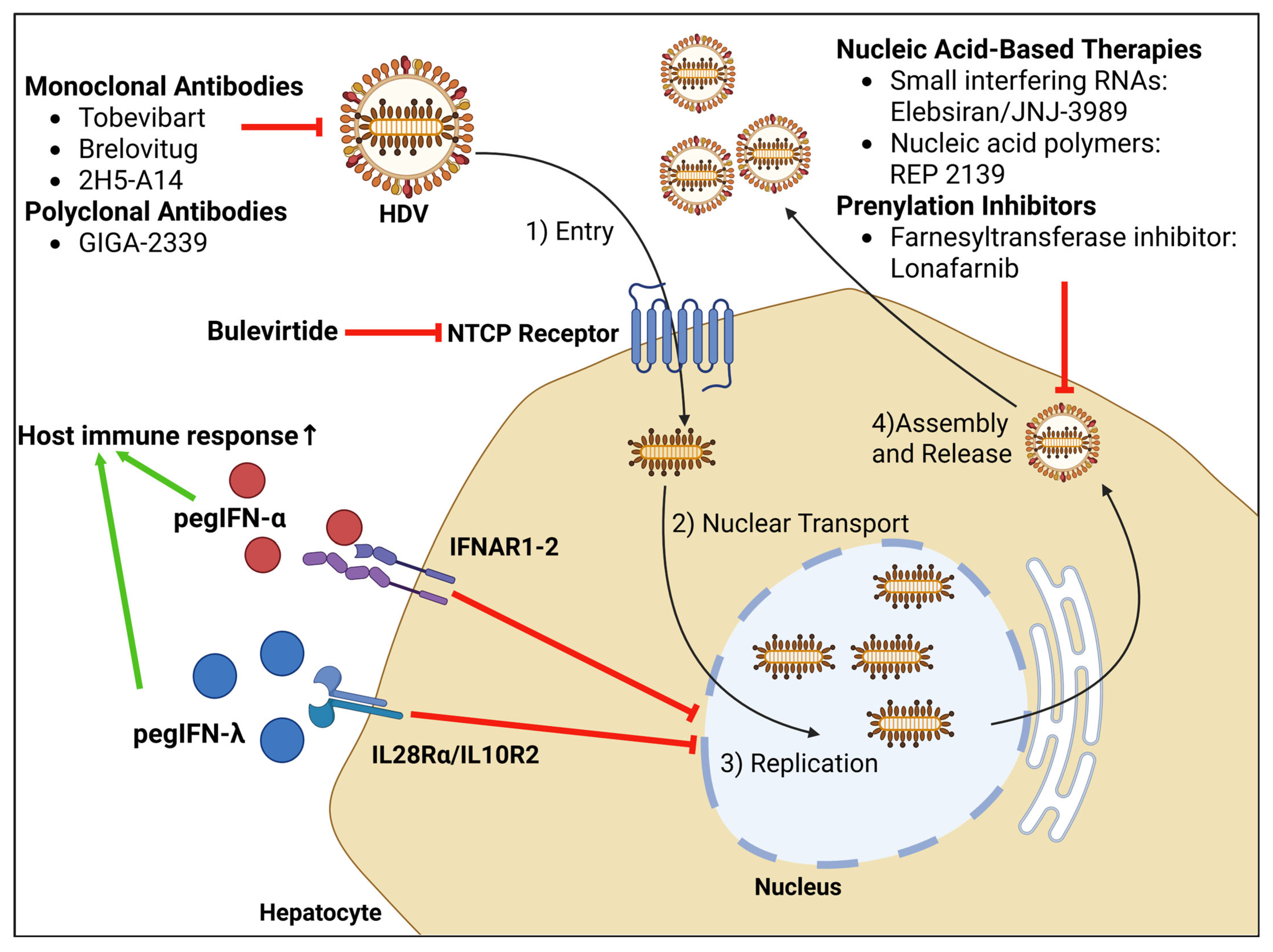
6. Treatment Options
6.1. Pegylated Interferon-α
6.2. Bulevirtide
6.3. Combination Therapy of Bulevirtide and PegIFN-α
6.4. Lonafarnib
6.5. Pegylated Interferon-λ (PegIFN-λ)
6.6. Nucleic Acid-Based Therapies
6.7. Monoclonal Antibodies
6.8. Polyclonal Antibodies
7. Liver Transplantation
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Rizzetto, M.; Canese, M.G.; Arico, S.; Crivelli, O.; Trepo, C.; Bonino, F.; Verme, G. Immunofluorescence detection of new antigen-antibody system (delta/anti-delta) associated to hepatitis B virus in liver and in serum of HBsAg carriers. Gut 1977, 18, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.S.; Choo, Q.L.; Weiner, A.J.; Ou, J.H.; Najarian, R.C.; Thayer, R.M.; Mullenbach, G.T.; Denniston, K.J.; Gerin, J.L.; Houghton, M. Structure, sequence and expression of the hepatitis delta (δ) viral genome. Nature 1986, 323, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzetto, M. Hepatitis D: Thirty years after. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farci, P.; Niro, G. Clinical Features of Hepatitis D. Semin. Liver. Dis. 2012, 32, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselah, T.; Rizzetto, M. Hepatitis D Virus Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patmore, L.A.; Spaan, M.; Agarwal, K.; Koc, Ö.M.; Blokzijl, H.; Brouwer, S.; Van Soest, H.; Van Hulzen, A.G.W.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Lammers, A.J.J.; et al. Prediction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Liver-related Events in Anti-hepatitis D Virus-positive Individuals. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, S1542–S3565, 00868-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ou, X.; Li, S.; Ma, Z.; Wang, W.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Liu, J.; Pan, Q. Estimating the Global Prevalence, Disease Progression, and Clinical Outcome of Hepatitis Delta Virus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 1677–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, B.V.; Bastaich, D.; Amoli, M.M.; Wong, R.J.; Evon, D.M.; Rogal, S.S.; Ross, D.B.; Morgan, T.R.; Spector, S.A.; Villada, G.; et al. Association of HDV infection and HCC, hepatic decompensation, and all-cause and liver-related death in a national cohort. Hepatology 2024, 81, 1822–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negro, F.; Lok, A.S. Hepatitis D: A Review. JAMA 2023, 330, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselah, T.; Chulanov, V.; Lampertico, P.; Wedemeyer, H.; Streinu-Cercel, A.; Pântea, V.; Lazar, S.; Placinta, G.; Gherlan, G.S.; Bogomolov, P.; et al. Bulevirtide Combined with Pegylated Interferon for Chronic Hepatitis D. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurdaydin, C. Treatment of Chronic Delta Hepatitis. Semin. Liver. Dis. 2012, 32, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Yurdaydin, C.; Hardtke, S.; Caruntu, F.A.; Curescu, M.G.; Yalcin, K.; Akarca, U.S.; Gürel, S.; Zeuzem, S.; Erhardt, A.; et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for hepatitis D (HIDIT-II): A randomised, placebo controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.F.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wranke, A.; Serrano, B.C.; Heidrich, B.; Kirschner, J.; Bremer, B.; Lehmann, P.; Hardtke, S.; Deterding, K.; Port, K.; Westphal, M.; et al. Antiviral treatment and liver-related complications in hepatitis delta. Hepatology 2017, 65, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Shen, D.T.; Ji, D.Z.; Han, P.C.; Zhang, W.-M.; Ma, J.-F.; Chen, W.-S.; Goyal, H.; Pan, S.; Xu, H.G. Prevalence and burden of hepatitis D virus infection in the global population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut 2019, 68, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockdale, A.J.; Kreuels, B.; Henrion, M.Y.R.; Giorgi, E.; Kyomuhangi, I.; de Martel, C.; Hutin, Y.; Geretti, A.M. The global prevalence of hepatitis D virus infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, A.; Le Gal, F.; Dziri, S.; Alloui, C.; Roulot, D.; Dény, P.; Sureau, C.; Brichler, S.; Gordien, E. Comprehensive Analysis of Hepatitis Delta Virus Assembly Determinants According to Genotypes: Lessons From a Study of 526 Hepatitis Delta Virus Clinical Strains. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 751531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salichos, L.; Minosse, C.; Visco-Comandini, U.; Taibi, C.; Zulian, V.; D’Offizi, G.; Pallothu, N.; McPhee, F.; Garbuglia, A.R. Phylogenetic and Phylodynamic Analysis of Delta Strains Circulating in Italy. Viruses 2023, 15, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, F.C.A.; Barros, T.M.; Angelice, G.P.; Costa, V.D.; Mello, V.M.; Pardini, M.I.M.C.; Lampe, E.; Lago, B.V.; Villar, L.M. Circulation of HDV Genotypes in Brazil: Identification of a Putative Novel HDV-8 Subgenotype. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e03965-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelice, G.P.; Barros, T.M.; Marques, V.A.; Villar, L.M.; Lago, B.V.; Mello, F.C.A. Exploring genetic diversity of hepatitis D virus full-length genome in Brazil: Discovery of a novel HDV-8 subgenotype beyond African borders. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2024, 125, 105671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Peng, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Ren, B.; Jing, Z.; Sui, J.; Li, W. Viral Entry of Hepatitis B and D Viruses and Bile Salts Transportation Share Common Molecular Determinants on Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3273–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. eLife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salpini, R.; D’Anna, S.; Piermatteo, L.; Svicher, V. Novel concepts on mechanisms underlying Hepatitis Delta virus persistence and related pathogenesis. J. Viral. Hepat. 2022, 29, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.B.; Lee, C.Z.; Lai, M.M.C. Hepatitis delta antigen expressed by recombinant baculoviruses: Comparison of biochemical properties and post-translational modifications between the large and small forms. Virology 1992, 190, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziri, S.; Rodriguez, C.; Gerber, A.; Brichler, S.; Alloui, C.; Roulot, D.; Dény, P.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; Gordien, E.; Le Gal, F. Variable In Vivo Hepatitis D Virus (HDV) RNA Editing Rates According to the HDV Genotype. Viruses 2021, 13, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turon-Lagot, V.; Saviano, A.; Schuster, C.; Baumert, T.F.; Verrier, E.R. Targeting the Host for New Therapeutic Perspectives in Hepatitis D. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiyagarajah, K.; Basic, M.; Hildt, E. Cellular Factors Involved in the Hepatitis D Virus Life Cycle. Viruses 2023, 15, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degasperi, E.; Sandmann, L.; Wedemeyer, H.; Lampertico, P.; the Delta Cure 2024 Working Group. Hepatitis D Virus Infection: Pathophysiology, Epidemiology and Treatment. Report From the Third Delta Cure Meeting 2024. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e70189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giersch, K.; Bhadra, O.D.; Volz, T.; Allweiss, L.; Riecken, K.; Fehse, B.; Lohse, A.W.; Petersen, J.; Sureau, C.; Urban, S.; et al. Hepatitis delta virus persists during liver regeneration and is amplified through cell division both in vitro and in vivo. Gut 2019, 68, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giersch, K.; Perez-Gonzalez, P.; Hendricks, L.; Goldmann, N.; Kolbe, J.; Hermanussen, L.; Bockmann, J.H.; Volz, T.; Volmari, A.; Allweiss, L.; et al. Strain-specific responsiveness of hepatitis D virus to interferon-alpha treatment. JHEP Rep. 2023, 5, 100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Walter, L.; Mutz, P.; Bartenschlager, R.; Urban, S. Hepatitis D virus-induced interferon response and administered interferons control cell division-mediated virus spread. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseligka, E.D.; Clément, S.; Negro, F. HDV Pathogenesis: Unravelling Ariadne’s Thread. Viruses 2021, 13, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberhardt, V.; Hofmann, M.; Thimme, R.; Neumann-Haefelin, C. Adaptive Immune Responses, Immune Escape and Immune-Mediated Pathogenesis during HDV Infection. Viruses 2022, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Filzmayer, C.; Ni, Y.; Sültmann, H.; Mutz, P.; Hiet, M.S.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Bartenschlager, R.; Urban, S. Hepatitis D virus replication is sensed by MDA5 and induces IFN-β/λ responses in hepatocytes. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chida, T.; Ishida, Y.; Morioka, S.; Sugahara, G.; Han, C.; Lam, B.; Yamasaki, C.; Sugahara, R.; Li, M.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Persistent hepatic IFN system activation in HBV-HDV infection determines viral replication dynamics and therapeutic response. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e162404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucifora, J.; Alfaiate, D.; Pons, C.; Michelet, M.; Ramirez, R.; Fusil, F.; Amirache, F.; Rossi, A.; Legrand, A.F.; Charles, E.; et al. Hepatitis D virus interferes with hepatitis B virus RNA production via interferon-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 958–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calle Serrano, B.; Großhennig, A.; Homs, M.; Heidrich, B.; Erhardt, A.; Deterding, K.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Bremer, B.; Koch, A.; Cornberg, M.; et al. Development and evaluation of a baseline-event-anticipation score for hepatitis delta. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, e154–e163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, U.; Vizzutti, F.; Corti, G.; Ambu, S.; Stasi, C.; Bresci, S.; Moscarella, S.; Boddi, V.; Petrarca, A.; Laffi, G.; et al. Acute viral hepatitis increases liver stiffness values measured by transient elastography. Hepatology 2008, 47, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulot, D.; Brichler, S.; Layese, R.; BenAbdesselam, Z.; Zoulim, F.; Thibault, V.; Scholtes, C.; Roche, B.; Castelnau, C.; Poynard, T.; et al. Origin, HDV genotype and persistent viremia determine outcome and treatment response in patients with chronic hepatitis delta. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1046–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaan, M.; Carey, I.; Bruce, M.; Shang, D.; Horner, M.; Dusheiko, G.; Agarwal, K. Hepatitis delta genotype 5 is associated with favourable disease outcome and better response to treatment compared to genotype 1. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caredda, F.; Rossi, E.; Monforte, A.D.; Zampini, L.; Re, T.; Meroni, B.; Moroni, M. Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Coinfection and Superinfection with Agent: Indistinguishable Disease with Different Outcome. J. Infect. Dis. 1985, 151, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gish, R.G.; Wong, R.J.; Di Tanna, G.L.; Kaushik, A.; Kim, C.; Smith, N.J.; Kennedy, P.T.F. Association of hepatitis delta virus with liver morbidity and mortality: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2024, 79, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringlander, J.; Skoglund, C.; Prakash, K.; Andersson, M.E.; Larsson, S.B.; Tang, K.; Rydell, G.E.; Abrahamsson, S.; Castedal, M.; Norder, H.; et al. Deep sequencing of liver explant transcriptomes reveals extensive expression from integrated hepatitis B virus DNA. J. Viral Hepat. 2020, 27, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringlander, J.; Strömberg, L.G.; Stenbäck, J.B.; Andersson, M.E.; Abrahamsson, S.; Skoglund, C.; Castedal, M.; Larsson, S.B.; Rydell, G.E.; Lindh, M. Enrichment Reveals Extensive Integration of Hepatitis B Virus DNA in Hepatitis Delta Virus-Infected Patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 230, e684–e693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palom, A.; Rodríguez-Tajes, S.; Navascués, C.A.; García-Samaniego, J.; Riveiro-Barciela, M.; Lens, S.; Rodríguez, M.; Esteban, R.; Buti, M. Long-term clinical outcomes in patients with chronic hepatitis delta: The role of persistent viraemia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furquim d’Almeida, A.; Ho, E.; Govaerts, L.; Michielsen, P.; Sersté, T.; Bourgeois, S.; Delwaide, J.; Moreno, C.; Orlent, H.; Van Vlierberghe, H.; et al. Severe Liver-Related Outcomes in Patients with Hepatitis Delta: Results From a Multi-Ethnic Multicenter Long-Term Follow-Up Study. J. Viral Hepat. 2025, 32, e14060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangia, A.; Squillante, M.M.; Fraticelli, F.; Cavorsi, M.C.; Paroni, G.; Zaffarano, L.; Piazzolla, A.V. HDV RNA Levels and Progression of Hepatitis Delta Infection: A 14 Year Follow Up Experience in Italy. Cells 2023, 12, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, H.; Westman, G.; Falconer, K.; Duberg, A.; Weiland, O.; Haverinen, S.; Wejstål, R.; Carlsson, T.; Kampmann, C.; Larsson, S.B.; et al. Long-Term Study of Hepatitis Delta Virus Infection at Secondary Care Centers: The Impact of Viremia on Liver-Related Outcomes. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, R.; Del Ninno, E.; Rumi, M.; Russo, A.; Sangiovanni, A.; De Franchis, R.; Ronchi, G.; Colombo, M. A 28-Year Study of the Course of Hepatitis Δ Infection: A Risk Factor for Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Leus, M.; Battersby, T.R.; Glenn, J.; Gordien, E.; Kamili, S.; Kapoor, H.; Kessler, H.H.; Lenz, O.; Lütgehetmann, M.; et al. HDV RNA assays: Performance characteristics, clinical utility, and challenges. Hepatology 2025, 81, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.; Han, P.; Ji, D.; Chen, H.; Cao, W.; Goyal, H.; Xu, H. Epidemiology estimates of hepatitis D in individuals co-infected with human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis B virus, 2002–2018: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Viral Hepat. 2021, 28, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, N.D.; Kallan, M.J.; Sukkestad, S.; Kodani, M.; Kitahata, M.M.; Cachay, E.R.; Bhattacharya, D.; Heath, S.; Napravnik, S.; Moore, R.D.; et al. Prevalence and determinants of hepatitis delta virus infection among HIV/hepatitis B-coinfected adults in care in the United States. J. Viral Hepat. 2023, 30, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béguelin, C.; Atkinson, A.; Boyd, A.; Falconer, K.; Kirkby, N.; Suter-Riniker, F.; Günthard, H.F.; Rockstroh, J.K.; Mocroft, A.; Rauch, A.; et al. Hepatitis delta infection among persons living with HIV in Europe. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancaccio, G.; Shanyinde, M.; Puoti, M.; Gaeta, G.B.; Monforte, A.D.; Vergori, A.; Rusconi, S.; Mazzarelli, A.; Castagna, A.; Antinori, A.; et al. Hepatitis delta coinfection in persons with HIV: Misdiagnosis and disease burden in Italy. Pathog. Glob. Health 2023, 117, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoye, A.A.; Picker, L.J. CD 4+ T-cell depletion in HIV infection: Mechanisms of immunological failure. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 254, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munier, M.L.; Kelleher, A.D. Acutely dysregulated, chronically disabled by the enemy within: T-cell responses to HIV-1 infection. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2007, 85, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liechti, T.; Kadelka, C.; Braun, D.L.; Kuster, H.; Böni, J.; Robbiani, M.; Günthard, H.F.; Trkola, A. Widespread B cell perturbations in HIV-1 infection afflict naive and marginal zone B cells. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 2071–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, A.; Zimmermann, K.; Oxenius, A. Antigen-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms of T and B Cell Hyperactivation during Chronic HIV-1 Infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 12102–12113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Patankar, V.; Kitchen, S.; Zhen, A. Examining Chronic Inflammation, Immune Metabolism, and T Cell Dysfunction in HIV Infection. Viruses 2024, 16, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokoya, T.; Steel, H.C.; Nieuwoudt, M.; Rossouw, T.M. HIV as a Cause of Immune Activation and Immunosenescence. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 6825493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zicari, S.; Sessa, L.; Cotugno, N.; Ruggiero, A.; Morrocchi, E.; Concato, C.; Rocca, S.; Zangari, P.; Manno, E.C.; Palma, P. Immune Activation, Inflammation, and Non-AIDS Co-Morbidities in HIV-Infected Patients under Long-Term ART. Viruses 2019, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Cao, W.; Li, T. HIV-Related Immune Activation and Inflammation: Current Understanding and Strategies. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 7316456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béguelin, C.; Moradpour, D.; Sahli, R.; Suter-Riniker, F.; Lüthi, A.; Cavassini, M.; Günthard, H.F.; Battegay, M.; Bernasconi, E.; Schmid, P.; et al. Hepatitis delta-associated mortality in HIV/HBV-coinfected patients. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.S.; Sun, H.Y.; Ho, S.Y.; Lin, K.Y.; Liu, W.D.; Sheng, W.H.; Hsieh, S.M.; Chuang, Y.C.; Su, L.H.; Su, Y.C.; et al. Incidence and Outcome of Hepatitis D Virus Infection in People with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Hepatitis B Virus Coinfection in the Era of Tenofovir-Containing Antiretroviral Therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2025, ciae655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horberg, M.; Thompson, M.; Agwu, A.; Colasanti, J.; Haddad, M.; Jain, M.; McComsey, G.; Radix, A.; Rakhmanina, N.; Short, W.R.; et al. Primary Care Guidance for Providers Who Care for Persons with Human Immunodeficiency Virus: 2024 Update by the HIV Medicine Association of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, ciae479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da, B.L. Clinical trials in hepatitis D virus: Measuring success. Hepatology 2023, 77, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.J.; McCoy, C. Peginterferon alfa-2a: A review of approved and investigational uses. Clin. Ther. 2004, 26, 991–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Youngster, S.; Grace, M.; Bausch, J.; Bordens, R.; Wyss, D.F. Structural and biological characterization of pegylated recombinant interferon alpha-2b and its therapeutic implications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 547–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandmann, L.; Wedemeyer, H. Interferon-based treatment of chronic hepatitis D. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giersch, K.; Homs, M.; Volz, T.; Helbig, M.; Allweiss, L.; Lohse, A.W.; Petersen, J.; Buti, M.; Pollicino, T.; Sureau, C.; et al. Both interferon alpha and lambda can reduce all intrahepatic HDV infection markers in HBV/HDV infected humanized mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Aleman, S.; Brunetto, M.R.; Blank, A.; Andreone, P.; Bogomolov, P.; Chulanov, V.; Mamonova, N.; Geyvandova, N.; Morozov, V.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomized Trial of Bulevirtide in Chronic Hepatitis D. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, K.; Mahgoub, S.; Al-Shakhshir, S.; Algieder, A.; Atabani, S.; Bannaga, A.; Elsharkawy, A.M. Recent treatment advances and practical management of hepatitis D virus. Clin. Med. 2023, 23, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidrich, B.; Yurdaydın, C.; Kabaçam, G.; Ratsch, B.A.; Zachou, K.; Bremer, B.; Dalekos, G.N.; Erhardt, A.; Tabak, F.; Yalcin, K.; et al. Late HDV RNA Relapse After Peginterferon Alpha-Based Therapy of Chronic Hepatitis Delta. Hepatology 2014, 60, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Yurdaydìn, C.; Dalekos, G.N.; Erhardt, A.; Çakaloğlu, Y.; Değertekin, H.; Gürel, S.; Zeuzem, S.; Zachou, K.; Bozkaya, H.; et al. Peginterferon plus Adefovir versus Either Drug Alone for Hepatitis Delta. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.W.; Dad Ullah, M.U.; Choudhry, M.; Ali, M.J.; Ali, M.A.; Lam, S.L.K.; Shah, P.A.; Kaur, S.P.; Lau, D.T.Y. Novel Therapies of Hepatitis B and D. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zakrzewicz, D.; Nosol, K.; Irobalieva, R.N.; Mukherjee, S.; Bang-Sørensen, R.; Goldmann, N.; Kunz, S.; Rossi, L.; Kossiakoff, A.A.; et al. Structure of antiviral drug bulevirtide bound to hepatitis B and D virus receptor protein NTCP. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelman, M.D.; Wettengel, J.M.; Protzer, U.; Oude Elferink, R.P.J.; Van De Graaf, S.F.J. Molecular regulation of the hepatic bile acid uptake transporter and HBV entry receptor NTCP. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 158960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goutam, K.; Ielasi, F.S.; Pardon, E.; Steyaert, J.; Reyes, N. Structural basis of sodium-dependent bile salt uptake into the liver. Nature 2022, 606, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asami, J.; Kimura, K.T.; Fujita-Fujiharu, Y.; Ishida, H.; Zhang, Z.; Nomura, Y.; Liu, K.; Uemura, T.; Sato, Y.; Ono, M.; et al. Structure of the bile acid transporter and HBV receptor NTCP. Nature 2022, 606, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, F.M.; Paulusma, C.C.; Huidekoper, H.; De Ru, M.; Lim, C.; Koster, J.; Ho-Mok, K.; Bootsma, A.H.; Groen, A.K.; Schaap, F.G.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (SLC10A1) deficiency: Conjugated hypercholanemia without a clear clinical phenotype. Hepatology 2015, 61, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slijepcevic, D.; Kaufman, C.; Wichers, C.G.K.; Gilglioni, E.H.; Lempp, F.A.; Duijst, S.; De Waart, D.R.; Oude Elferink, R.P.J.; Mier, W.; Stieger, B.; et al. Impaired uptake of conjugated bile acids and hepatitis b virus pres1-binding in na+-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide knockout mice. Hepatology 2015, 62, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.Y.; Wang, M.X.; Gong, J.Y.; Liu, L.L.; Setchell, K.D.R.; Xie, X.B.; Wang, N.L.; Li, W.; Wang, J.S. Abnormal Bilirubin Metabolism in Patients with Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide Deficiency. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 71, e138–e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.W.; Deng, M.; Cheng, Y.; Atif, R.M.; Lin, W.X.; Guo, L.; Li, H.; Song, Y.Z. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) deficiency: Identification of a novel SLC10A1 mutation in two unrelated infants presenting with neonatal indirect hyperbilirubinemia and remarkable hypercholanemia. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 106598–106607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watashi, K.; Shionoya, K.; Kobayashi, C.; Morita, T. Hepatitis B and D virus entry. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 23, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Cao, L.; Mu, A.; Fu, S.; Wang, P.; Gao, Y.; Ji, W.; Liu, Z.; Du, Z.; et al. Inherent symmetry and flexibility in hepatitis B virus subviral particles. Science 2024, 385, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, J.; Sato, K.; Ninomiya, M.; Masamune, A. Envelope Proteins of Hepatitis B Virus: Molecular Biology and Involvement in Carcinogenesis. Viruses 2021, 13, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureau, C.; Salisse, J. A conformational heparan sulfate binding site essential to infectivity overlaps with the conserved hepatitis B virus A-determinant. Hepatology 2013, 57, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.; Gripon, P.; Urban, S. Hepatitis B virus infection initiates with a large surface protein–dependent binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Mehrle, S.; Nkongolo, S.; Kaufman, C.; Fälth, M.; Stindt, J.; Königer, C.; Nassal, M.; Kubitz, R.; et al. Hepatitis B and D Viruses Exploit Sodium Taurocholate Co-transporting Polypeptide for Species-Specific Entry into Hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1070–1083.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Aleman, S.; Brunetto, M.; Blank, A.; Andreone, P.; Bogomolov, P.; Chulanov, V.; Mamonova, N.; Geyvandova, N.; Morozov, V.; et al. Bulevirtide monotherapy in patients with chronic HDV: Efficacy and safety results through week 96 from a phase III randomized trial. J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampertico, P.; Aleman, S.; Brunetto, M.; Blank, A.; Andreone, P.; Bogomolov, P.; Chulanov, V.; Mamonova, N.; Geyvandova, N.; Morozov, V.; et al. P135 Efficacy and Safety of 144 Weeks of Bulevirtide 2 Mg or 10 Mg Monotherapy from the Ongoing Phase 3 Study, MYR301; BMJ Publishing Group Ltd and British Society of Gastroenterology: London, UK, 2024; pp. A96–A97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollnberger, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Chang, S.; Martin, R.; Manhas, S.; Aeschbacher, T.; Han, B.; Yazdi, T.; May, L.; et al. No virologic resistance to bulevirtide monotherapy detected in patients through 24 weeks treatment in phase II and III clinical trials for chronic hepatitis delta. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleman, S.; Brunetto, M.; Blank, A.; Andreone, P.; Bogomolov, P.; Chulanov, V.; Mamonova, N.; Geyvandova, N.; Morozov, V.; Sagalova, O.; et al. OS-066 Predictors of undetectable hepatitis delta virus RNA at 48 weeks after end of treatment with bulevirtide monotherapy in the MYR 301 study. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, S48–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allweiss, L.; Volmari, A.; Suri, V.; Wallin, J.J.; Flaherty, J.F.; Manuilov, D.; Downie, B.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Bockmann, J.H.; Urban, S.; et al. Blocking viral entry with bulevirtide reduces the number of HDV-infected hepatocytes in human liver biopsies. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degasperi, E.; Anolli, M.P.; Jachs, M.; Reiberger, T.; De Ledinghen, V.; Metivier, S.; D’Offizi, G.; Di Maria, F.; Schramm, C.; Schmidt, H.; et al. Real-world effectiveness and safety of bulevirtide monotherapy for up to 96 weeks in patients with HDV-related cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degasperi, E.; Anolli, M.P.; Monico, S.; Jachs, M.; Reiberger, T.; Schramm, C.; Schmidt, H.; Zöllner, C.; Tacke, F.; Dietz-Fricke, C.; et al. TOP-265 Virological outcomes in patients with HDV-related compensated cirrhosis treated with Bulevirtide monotherapy for 144 weeks: A subanalysis of the retrospective multicenter european study (Save-D). J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, S810–S811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anolli, M.P.; Degasperi, E.; D’Offizi, G.; Rianda, A.; Loglio, A.; Vigano, M.; Ciancio, A.; Troshina, Y.; Brunetto, M.; Coco, B.; et al. WED-285-YI Real-world evidence shows comparable Bulevirtide effectiveness in hepatitis D patients with and without cirrhosis: Results from the prospective nationwide D-Shield multicenter study. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, S811–S812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degasperi, E.; Anolli, M.P.; Gheorghe, L.; Chitul, M.; Schramm, C.; Schmidt, H.; Jachs, M.; Reiberger, T.; Foucher, J.; Metivier, S.; et al. WED-291 Long risk of decompensation and HCC in patients with HDV- related compensated cirrhosis treated with Bulevirtide monotherapy for up to 144 weeks: The retrospective multicenter european study (Save-D). J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, S814–S815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz-Fricke, C.; Degasperi, E.; Jachs, M.; Maasoumy, B.; Reiter, F.P.; Geier, A.; Grottenthaler, J.M.; Berg, C.P.; Sprinzl, K.; Zeuzem, S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of off-label bulevirtide monotherapy in patients with HDV with decompensated Child-B cirrhosis—A real-world case series. Hepatology 2024, 80, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselah, T.; Lampertico, P.; Aleman, S.; Bourlière, M.; Streinu-Cercel, A.; Bogomolov, P.; Morozov, V.; Stepanova, T.; Lazar, S.; Manuilov, D.; et al. Bulevirtide Monotherapy Is Safe and Well Tolerated in Chronic Hepatitis Delta: An Integrated Safety Analysis of Bulevirtide Clinical Trials at Week 48. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e16174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Schöneweis, K.; Bogomolov, P.; Blank, A.; Voronkova, N.; Stepanova, T.; Sagalova, O.; Chulanov, V.; Osipenko, M.; Morozov, V.; et al. Safety and efficacy of bulevirtide in combination with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in patients with hepatitis B virus and hepatitis D virus coinfection (MYR202): A multicentre, randomised, parallel-group, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampertico, P.; Anolli, M.P.; Roulot, D.; Wedemeyer, H. Antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis delta: New insights from clinical trials and real-life studies. Gut 2024, 74, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, K.; Kamal, H.; Århem, K.; Cederberg, S.; Olsson, A.; Björkström, N.; Aleman, S. WED-294 Virological response and safety of combination treatment with bulevirtide and pegylated interferon in chronic hepatitis D patients with advanced fibrosis/cirrhosis: 48 weeks interim results from SEE-D trial. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, S816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoulim, F.; Asselah, T.; Aleman, S.; Brunetto, M.; Chulanov, V.; Streinu-Cercel, A.; Gherlan, G.S.; Bogomolov, P.; Stepanova, T.; Morozov, V.; et al. OS-070 Achieving undetectable hepatitis delta virus RNA at end of therapy with bulevirtide 10 mg/day with or without with pegylated interferon alpha is strongly associated with post-treatment virologic response in chronic hepatitis delta. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Laughlin, A.M.; De Mendizabal, N.V.; Caro, L.; Damoiseaux, D.; Lichtman, A.; Manuilov, D.; Mercier, R.-C.; Ni, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. WED-310 A mathematical viral load model characterises the exposure- response relationship between bulevirtide and hepatitis delta virus and identifies the minimum duration of on-treatment viral load monitoring required for accurate prediction of long-term virologic response. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, S822–S823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferkorn, M.; Rodemerk, H.; Degasperi, E.; Seltmann, J.; Drechsel, L.; Santisteve, S.S.; Matz-Soja, M.; Glebe, D.; Buti, M.; Renate, H.; et al. WED-306 The kinetic of HBsAg isoforms predicts response to BLV and pegylated interferon alfa2a in patients with chronic hepatitis delta. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, S820–S821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Lonafarnib: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Jeng, L.J.B.; Chefo, S.; Wang, Y.; Price, D.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Li, R.-J.; Ma, L.; Yang, Y.; et al. FDA approval summary for lonafarnib (Zokinvy) for the treatment of Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome and processing-deficient progeroid laminopathies. Genet. Med. 2023, 25, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurdaydin, C.; Keskin, O.; Yurdcu, E.; Çalişkan, A.; Önem, S.; Karakaya, F.; Kalkan, Ç.; Karatayli, E.; Karatayli, S.; Choong, I.; et al. A phase 2 dose-finding study of lonafarnib and ritonavir with or without interferon alpha for chronic delta hepatitis. Hepatology 2022, 75, 1551–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einav, S. Prenylation inhibitors: A novel class of antiviral agents. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordier, B.B.; Marion, P.L.; Ohashi, K.; Kay, M.A.; Greenberg, H.B.; Casey, J.L.; Glenn, J.S. A Prenylation Inhibitor Prevents Production of Infectious Hepatitis Delta Virus Particles. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 10465–10472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordier, B.B.; Ohkanda, J.; Liu, P.; Lee, S.-Y.; Salazar, F.H.; Marion, P.L.; Ohashi, K.; Meuse, L.; Kay, M.A.; Casey, J.L.; et al. In vivo antiviral efficacy of prenylation inhibitors against hepatitis delta virus. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.; Canini, L.; Dahari, H.; Zhao, X.; Uprichard, S.L.; Haynes-Williams, V.; Winters, M.A.; Subramanya, G.; Cooper, S.L.; Pinto, P.; et al. Oral prenylation inhibition with lonafarnib in chronic hepatitis D infection: A proof-of-concept randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2A trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurdaydin, C.; Keskin, O.; Kalkan, Ç.; Karakaya, F.; Çalişkan, A.; Karatayli, E.; Karatayli, S.; Bozdayi, A.M.; Koh, C.; Heller, T.; et al. Optimizing lonafarnib treatment for the management of chronic delta hepatitis: The LOWR HDV-1 study. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzion, O.; Hamid, S.S.; Asselah, T.; Gherlan, G.S.; Turcanu, A.; Petrivna, T.; Weissfeld, L.; Choong, I.; Hislop, C.; Apelian, D.; et al. Week 48 results of the phase 3 D-LIVR study, a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of Lonafarnib-boosted with Ritonavir with or without Peginterferon Alfa in patients with chronic hepatitis delta. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, H.H.; Dellgren, C.; Hamming, O.J.; Vends, S.; Paludan, S.R.; Hartmann, R. Interferon-λ Is Functionally an Interferon but Structurally Related to the Interleukin-10 Family. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 20869–20875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotenko, S.V.; Gallagher, G.; Baurin, V.V.; Lewis-Antes, A.; Shen, M.; Shah, N.K.; Langer, J.A.; Sheikh, F.; Dickensheets, H.; Donnelly, R.P. IFN-λs mediate antiviral protection through a distinct class II cytokine receptor complex. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, J.L.; Schneider, W.M.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Vercauteren, K.; Jude, K.M.; Xiong, A.; Moraga, I.; Horton, T.M.; Glenn, J.S.; De Jong, Y.P.; et al. The IFN-λ-IFN-λR1-IL-10Rβ Complex Reveals Structural Features Underlying Type III IFN Functional Plasticity. Immunity 2017, 46, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozhkov, A.A.; Klotchenko, S.A.; Ramsay, E.S.; Moshkoff, H.D.; Moshkoff, D.A.; Vasin, A.V.; Salvato, M.S. The Key Roles of Interferon Lambda in Human Molecular Defense against Respiratory Viral Infections. Pathogens 2020, 9, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemann, E.A.; Gale, M.; Savan, R. Interferon Lambda Genetics and Biology in Regulation of Viral Control. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, G.; Moreira Silva, E.A.S.; Medeiros Silva, D.C.; Thabane, L.; Campos, V.H.S.; Ferreira, T.S.; Santos, C.V.Q.; Nogueira, A.M.R.; Almeida, A.P.F.G.; Savassi, L.C.M.; et al. Early Treatment with Pegylated Interferon Lambda for COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Su, S.B. Interferon-λs: The modulators of antivirus, antitumor, and immune responses. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.L.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Chang, T.T.; Peng, C.-Y.; Wong, D.; Coffin, C.S.; Lim, S.G.; Chen, P.-J.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Marcellin, P.; et al. Peginterferon lambda for the treatment of HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: A randomized phase 2b study (LIRA-B). J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, A.J.; Shiffman, M.L.; Zaman, A.; Yoffe, B.; De La Torre, A.; Flamm, S.; Gordon, S.C.; Marotta, P.; Vierling, J.M.; Carlos Lopez-Talavera, J.; et al. Phase 1b Study of Pegylated Interferon Lambda 1 with or Without Ribavirin in Patients with Chronic Genotype 1 Hepatitis C Virus Infection†. Hepatology 2010, 52, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, A.J.; Arora, S.; Everson, G.; Flisiak, R.; George, J.; Ghalib, R.; Gordon, S.C.; Gray, T.; Greenbloom, S.; Hassanein, T.; et al. A randomized phase 2b study of peginterferon lambda-1a for the treatment of chronic HCV infection. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etzion, O.; Hamid, S.; Lurie, Y.; Gane, E.J.; Yardeni, D.; Duehren, S.; Bader, N.; Nevo-Shor, A.; Channa, S.M.; Cotler, S.J.; et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis D with peginterferon lambda—The phase 2 LIMT-1 clinical trial. Hepatology 2023, 77, 2093–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigica, A. Late-Stage Trial in Chronic Hepatitis D Discontinued Due to Safety Concerns. Available online: https://www.contagionlive.com/view/late-stage-trial-in-chronic-hepatitis-d-delta-eiger-discontinued-due-to-safety-concerns (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Vaillant, A. Oligonucleotide-Based Therapies for Chronic HBV Infection: A Primer on Biochemistry, Mechanisms and Antiviral Effects. Viruses 2022, 14, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collotta, D.; Bertocchi, I.; Chiapello, E.; Collino, M. Antisense oligonucleotides: A novel Frontier in pharmacological strategy. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1304342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, S.I.; Yamamoto, T.; Obika, S. XRN2 is required for the degradation of target RNAs by RNase H1-dependent antisense oligonucleotides. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 464, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Real, C.I.; Werner, M.; Paul, A.; Gerken, G.; Schlaak, J.F.; Vaillant, A.; Broering, R. Nucleic acid-based polymers effective against hepatitis B Virus infection in patients don’t harbor immunostimulatory properties in primary isolated liver cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumeier, J.; Meister, G. siRNA Specificity: RNAi Mechanisms and Strategies to Reduce Off-Target Effects. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 526455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, W.F.; De Hoyos, C.L.; Liang, X.; Crooke, S.T. RNA cleavage products generated by antisense oligonucleotides and siRNAs are processed by the RNA surveillance machinery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 3351–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejón, A.; Bartolomé, J.; Carreño, V. In vitro inhibition of the hepatitis delta virus replication mediated by interferon and trans-ribozyme or antisense probes. J. Hepatol. 1998, 29, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Taylor, J.M. Susceptibility of Human Hepatitis Delta Virus RNAs to Small Interfering RNA Action. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 9728–9731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, S.K.; Layden, T.J.; Gartel, A.L. RNA interference as a new strategy against viral hepatitis. Virology 2004, 323, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.F.; Lim, Y.S.; Yoon, K.T.; Lim, T.-H.; Heo, J.; Tangkijvanich, P.; Tak, W.Y.; Thanawala, V.; Cloutier, D.; Mao, S.; et al. VIR-2218 (elebsiran) plus pegylated interferon-alfa-2a in participants with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A phase 2 study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselah, T.; Streinu-Cercel, A.; Jucov, A.; Gane, E.J.; Wedemeyer, H.; Lampertico, P.; Chattergoon, M.A.; Wu, P.; Maciejewski, S.; Pilowa, C.; et al. OS-127 Efficacy and safety of tobevibart (VIR-3434) alone or in combination with elebsiran (VIR-2218) in participants with chronic hepatitis delta virus infection: Preliminary results from the phase 2 SOLSTICE trial in non-cirrhotic and compensated cirrhotic participants. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, S75–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Gane, E.J.; Agarwal, K.; Tabak, F.; Forns, X.; Akarca, U.; Viacheslav, M.; Aleman, S.; Buti, M.; Yilmaz, G.; et al. Treatment with siRNA JNJ-73763989 plus nucleos (t)ide analogue (NA) decreases HBsAg and HDV RNA levels in patients with chronic hepatitis D (CHD): Part 1 of the REEF-D study. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, K.; Buti, M.; Van Bömmel, F.; Lampertico, P.; Janczewska, E.; Bourliere, M.; Vanwolleghem, T.; Lenz, O.; Verbinnen, T.; Kakuda, T.N.; et al. JNJ-73763989 and bersacapavir treatment in nucleos(t)ide analogue-suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B: REEF-2. J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Lampertico, P.; Gane, E.J.; Agarwal, K.; Tabak, F.; Akarca, U.; Aleman, S.; Buti, M.; Sprinzl, K.; Donohue, K.; et al. LBP-044 Robust reduction of HBsAg and HDV RNA levels with low risk for ALT elevations in JNJ-73763989 treated patients with chronic hepatitis D (CHD) and baseline HBsAg levels below 10, 000 IU/ml: Part 2 of the REEF-D study. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.F.; Lim, S.G.; Plesniak, R.; Tsuji, K.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Pojoga, C.; Gadano, A.; Popescu, C.P.; Stepanova, T.; Asselah, T.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Bepirovirsen in Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1957–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, L.Y.; Hui, R.W.H.; Fung, J.; Seto, W.K.; Yuen, M.F. Bepirovirsen (GSK3228836) in chronic hepatitis B infection: An evaluation of phase II progress. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2023, 32, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulon, R.; Blanchet, M.; Lemasson, M.; Vaillant, A.; Labonté, P. Characterization of the antiviral effects of REP 2139 on the HBV lifecycle in vitro. Antivir. Res. 2020, 183, 104853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, M.; Pântea, V.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Albrecht, J.; Schmid, P.; Le Gal, F.; Gordien, E.; Krawczyk, A.; et al. Safety and efficacy of REP 2139 and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis D virus co-infection (REP 301 and REP 301-LTF): A non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, M.; Pântea, V.; Placinta, G.; Moscalu, I.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Iarovoi, L.; Smesnoi, V.; Musteata, T.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of 48 Weeks REP 2139 or REP 2165, Tenofovir Disoproxil, and Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2a in Patients with Chronic HBV Infection Naïve to Nucleos(t)ide Therapy. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 2180–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, M.; Pântea, V.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Anderson, M.; Gersch, J.; Holzmayer, V.; Elsner, C.; Krawczyk, A.; et al. Persistent Control of Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis Delta Virus Infection Following REP 2139-Ca and Pegylated Interferon Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus/Hepatitis Delta Virus Coinfection. Hepatol. Commun. 2021, 5, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, C.; Bourliere, M.; Loustaud-Ratti, V.; Bardou-Jacquet, E.; Alric, L.; Colombain, L.; Meszaros, M.; Metivier, S.; Mathurin, P.; Yurdaydin, C.; et al. OS-034 Safety and efficacy of REP 2139-Mg in hepatitis D patients with advanced liver disease: An international compassionate use program. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempp, F.A.; Volz, T.; Cameroni, E.; Benigni, F.; Zhou, J.; Rosen, L.E.; Noack, J.; Zatta, F.; Kaiser, H.; Bianchi, S.; et al. Potent broadly neutralizing antibody VIR-3434 controls hepatitis B and D virus infection and reduces HBsAg in humanized mice. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucov, A.; Asselah, T.; Streinu-Cercel, A.; Gane, E.J.; Wedemeyer, H.; Lampertico, P.; Chattergoon, M.A.; Bullard, B.; Huang, C.; Acosta, R.; et al. THU-243 SOLSTICE week 24 subgroup analysis: Impact of baseline viral parameters and cirrhosis status on virological and biochemical responses in participants with chronic hepatitis delta virus infection treated with tobevibart and elebsiran. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, S829–S830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gane, E.J.; Schwabe, C.; Smith, P.; Willeford, C.M.; Moore, C.; Grecko, R.; Chu, K.; Javanbakht, H.; Shulman, N. WED-374 Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of BJT-778, a monoclonal antibody for treatment of chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis D, following single ascending doses in healthy volunteers. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, S811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, K.; Dobryanska, M.; Jucov, A.; Kennedy, P.; Gane, E.; Yuen, M.-F.; Wong, G.; Strasser, S.; Holmes, J.; Roberts, S.; et al. BJT-778, Anti-Hbsag Monoclonal Antibody, Achieved 100% Virologic Response in Subjects with Chronic Hepatitis D (CHD): Phase 2 Study Results. In Hepatology; Agarwal, K., Ed.; Kings College Hospital: Kyiv, Ukraine, 2024; Volume 80, pp. S892–S893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Global, Randomized, Open-label, Multicenter, Phase 2b/3 Trial Evaluating BJT-778 vs. Delayed Treatment for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis Delta Infection (AZURE-1). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06907290 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- A Phase I Study to Investigate Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of RO7565020 in Healthy Participants and in Participants with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05763576 (accessed on 29 April 2023).
- Yuen, M.F.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Luk, A.O.Y.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Yeh, C.-T.; Bonacini, M.; Kim, D.J.; Leerapun, A.; Amado, L.E.M.; et al. THU-245 Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of RO7565020, a novel monoclonal antibody that targets the hepatitis B surface antigen: Results from a phase 1 single ascending dose study in healthy volunteers and participants with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, S830–S831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; He, W.; Liu, X.; Zheng, S.; Qi, Y.; Li, H.; Mao, F.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Pan, L.; et al. A potent human neutralizing antibody Fc-dependently reduces established HBV infections. eLife 2017, 6, e26738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yuan, L.Z.; Lan, Y.; Lo, Y.C.; Sun, C.P.; Wu, C.R.; Zhang, J.F.; et al. Prolonged suppression of HBV in mice by a novel antibody that targets a unique epitope on hepatitis B surface antigen. Gut 2016, 65, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemori, T.; Sugimoto-Ishige, A.; Nishitsuji, H.; Futamura, Y.; Harada, M.; Kimura-Someya, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Honma, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yaguchi, M.; et al. Establishment of a Monoclonal Antibody against Human NTCP That Blocks Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0168621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervolaraki, K.; Vanherck, J.C.; Marcadet, C.; Verhoye, L.; De Meyer, A.; Rasulova, M.; Lyoo, H.; Paulissen, J.; De Vos, K.; Bolt, I.; et al. TOP-363 A novel orally bioavailable small-molecule inhibitor of the sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide (NTCP) prevents HBV infection and ameliorates cholestasis in humanized mice models. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, S291–S292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, S.; Higgins, B.; Niedecken, A.; Chiang, Y.; Witte, P.; Sharda, R.; Lopez, Y.; Lucifora, J.; Durantel, D.; Vainorius, E.; et al. OS-074 Recombinant polyclonal antibody GIGA-2339 potently neutralizes hepatitis B and hepatitis D virus. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 1 Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of GIGA-2339 Administered as a Single Ascending Dose and Multiple Ascending Doses in Participants with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT07024641 (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- Muhammad, H.; Tehreem, A.; Hammami, M.B.; Ting, P.S.; Idilman, R.; Gurakar, A. Hepatitis D virus and liver transplantation: Indications and outcomes. World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, M.B.; Kohli, R.; Woreta, T.; Sulkowski, M.S.; Hamilton, J.P.; Toman, L.; Saberi, B.; Laurin, J.; Wang, J.G.; Philosophe, B.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus/Hepatitis D Virus–Coinfected Liver Transplant Candidate Receiving Hepatitis B Virus-Deoxyribonucleic Acid–Positive Allograft and Treated with High-Dose Hepatitis B Immune Globulin. ACG Case Rep. J. 2021, 8, e00582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelico, R.; Trapani, S.; Manzia, T.M.; Lenci, I.; Grossi, P.; Ricci, A.; Burra, P.; Andorno, E.; Agnes, S.; Bhoori, S.; et al. Liver transplantation for hepatitis D virus/hepatitis B virus coinfection in Italy: An intention-to-treat analysis of long-term outcomes. Am. J. Transplant. 2025, 25, 1502–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholongitas, E. Review of the pharmacological management of hepatitis B viral infection before and after liver transplantation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 9189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, S.; Tandoi, F.; Romagnoli, R.; Rizzetto, M. Liver Transplantation in Hepatitis B/Hepatitis D (Delta) Virus Coinfected Recipients. Transplantation 2022, 106, 1935–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Tajes, S.; García-Eliz, M.; Marcos, A.C.; Campos-Varela, I.; Ros, A.C.; Loinaz, C.; Gómez Bravo, M.Á.; Rodríguez-Perálvarez, M.; Fabrega, E.; González Diéguez, M.L.; et al. The role of HBIG in real life for patients undergoing liver transplantation due to HDV-related cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2024, 44, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistella, S.; Zanetto, A.; Gambato, M.; Germani, G.; Senzolo, M.; Burra, P.; Russo, F.P. The Role of Antiviral Prophylaxis in Preventing HBV and HDV Recurrence in the Setting of Liver Transplantation. Viruses 2023, 15, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, H.; Zaffar, D.; Tehreem, A.; Ting, P.-S.; Simsek, C.; Gokcan, H.; Gurakar, A.; Idilman, R. HBV/HDV management after liver transplantation: Review. J. Liver Transplant. 2021, 4, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serin, A.; Tokat, Y. Recurrence of Hepatitis D Virus in Liver Transplant Recipients with Hepatitis B and D Virus–Related Chronic Liver Disease. Transpl. Proc. 2019, 51, 2457–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushner, T.; Da, B.L.; Chan, A.; Dieterich, D.; Sigel, K.; Saberi, B. Liver Transplantation for Hepatitis D Virus in the United States: A UNOS Study on Outcomes in the MELD Era. Transpl. Direct. 2021, 8, e1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.P.; Battistella, S.; Zanetto, A.; Gambato, M.; Ferrarese, A.; Germani, G.; Senzolo, M.; Mescoli, C.; Piano, S.; D’Amico, F.E.; et al. Chronic Hepatitis B in the Transplant Setting: A 30-Year Experience in a Single Tertiary Italian Center. Viruses 2025, 17, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenci, P.; Reiberger, T.; Stadlbauer, V.; Zoller, H. Transplantation of hepatitis D virus patients: Lifelong hepatitis B immunoglobulins? Liver Int. 2023, 43, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manini, M.A.; Whitehouse, G.; Bruce, M.; Passerini, M.; Lim, T.Y.; Carey, I.; Considine, A.; Lampertico, P.; Suddle, A.; Heaton, N.; et al. Entecavir or tenofovir monotherapy prevents HBV recurrence in liver transplant recipients: A 5-year follow-up study after hepatitis B immunoglobulin withdrawal. Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholongitas, E.; Goulis, I.; Antoniadis, N.; Fouzas, I.; Imvrios, G.; Giakoustidis, D.; Giouleme, O.; Papanikolaou, V.; Akriviadis, E.; Vasiliadis, T. Nucleos(t)ide analog(s) prophylaxis after hepatitis B immunoglobulin withdrawal against hepatitis B and D recurrence after liver transplantation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2016, 18, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholongitas, E.; Oikonomou, T.; Bafa, K.; Sinakos, E.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Goulis, I. Efficacy of Newer Nucleos(t)ide Analogs After Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin Discontinuation Against Hepatitis B and D Recurrence in Liver Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2024, 108, e239–e244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenci, I.; Tariciotti, L.; Angelico, R.; Milana, M.; Signorello, A.; Manzia, T.M.; Toti, L.; Tisone, G.; Angelico, M.; Baiocchi, L. Successful clinical and virological outcomes of liver transplantation for HDV/HBV-related disease after long-term discontinuation of hepatitis B immunoglobulins. Clin. Transpl. 2023, 37, e14971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossami Saidy, R.R.; Sud, I.; Eurich, F.; Aydin, M.; Postel, M.P.; Dobrindt, E.M.; Pratschke, J.; Eurich, D. Discontinuation of Passive Immunization Is Safe after Liver Transplantation for Combined HBV/HDV Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfanidou, A.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Cholongitas, E. Antiviral prophylaxis against hepatitis B recurrence after liver transplantation: Current concepts. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 1448–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huprikar, S.; Danziger-Isakov, L.; Ahn, J.; Naugler, S.; Blumberg, E.; Avery, R.K.; Koval, C.; Lease, E.D.; Pillai, A.; Doucette, K.E.; et al. Solid Organ Transplantation From Hepatitis B Virus–Positive Donors: Consensus Guidelines for Recipient Management. Am. J. Transpl. 2015, 15, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Therapeutic Classes | Agent and Regimen(s) | Route | Key Antiviral Mechanism | Development/Regulatory Status | Typical Study Regimens † | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interferons | PegIFN-α-2a/-2b | SC | Broad immune activation | Approved for HBV/HCV → off-label HDV | 180 mcg qwk/1.5 mcg/kg qwk × 48 wk | SVR 23–57%; if no SVR → EVR < 5%; limited durability; contraindicated in decompensated cirrhosis; limited use due to side effects |
| PegIFN-λ | SC | Type III IFN, hepatocyte-selective | Phase 2/3 (LIMT-2 Phase 3 trial terminated due to liver decompensation in participants) | 120–180 mcg qwk × 48 wk | CR ≤ 30%; trial halted due to liver decompensation secondary to hepatobiliary toxicity | |
| Viral entry inhibition | Bulevirtide | SC | NTCP receptor inhibition | EMA-approved 2 mg qd | 2–10 mg qd; open-ended therapy | No dose-dependent differences in CR (~50% at week 48–144) or sustained HDV RNA negativity at post-treatment week 48; continued treatment needed for improved outcomes; delayed treatment linked to worse outcomes; better responses seen with lower baseline HDV RNA and HBsAg, on-treatment HBsAg loss or ≥1 log IU/mL decline, or ADA development; outcomes similar between patients with and without compensated cirrhosis. |
| Bulevirtide + PegIFN-α | NTCP receptor inhibition + immune activation | Phase 2 (MYR203, MYR204, SEE-D) | 2–10 mg qd + PegIFN-α × 96 wk | Undetectable HDV RNA at post-treatment week 48 in ~25–45%; higher efficacy observed with combination therapy than pegIFN-α or bulevirtide monotherapy, but with increased pegIFN-α-related side effects | ||
| Viral assembly inhibition | Lonafarnib + Ritonavir | PO | Inhibition L-HDAg prenylation → virion assembly | Phase 3 (D-LIVR) | 50 mg BID + Ritonavir × 48 wk | VR 14.6%, BR 24.7%, histologic improvement 33%; GI intolerance is dose-limiting; better bioavailability and tolerability with ritonavir (CYP3A4 inhibitor); compared to pegIFN-α monotherapy, better biochemical response but lower virologic and histologic outcomes |
| Lonafarnib + Ritonavir + PegIFN-α | Inhibition L-HDAg prenylation + immune activation | 50 mg BID + Ritonavir + PegIFN-α × 48 wk | VR 32%, BR 34.4%, histologic improvement 53%; triple regimen shows superior efficacy across all outcomes compared to dual therapy, but with increased pegIFN-α-related side effects | |||
| Nucleic-acid–directed therapies | Elebsiran (VIR-2218) + Tobevibart (VIR-3434) | SC | siRNA; silences HBV mRNA → ↓ HBsAg + mAb against HBsAg → HBsAg neutralisation | Phase 2 (SOLSTICE) → Phase 3 planned to commence in 2025 | 200 mg q4wk + Tobevibart × 24–60 wk | 100% VR at week 24; HDV RNA undetectable 41% at week 24, 64% at week 36, ≈80% at week 60 |
| JNJ-3989 (JNJ-73763989) | SC | siRNA; designed to silence all HBV RNA transcription and accordingly translation of HBV viral proteins | Phase 2 (REEF-D) | 100 mg q4wk + NA × 144 wk (results announced until wk 48) | At week 48, VR 52%, BR 41%; increased risk of ALT flares in patients with baseline HBsAg levels > 10,000 IU/mL; higher baseline levels of HBsAg and HDV RNA were associated with worse outcomes | |
| REP 2139-Ca/-Mg | IV/SC | NAP; binds host chaperones → blocking assembly and secretion of HBsAg | Phase 2 (REP 301, REP 301-LFT, RCAP ‡) | REP 2139-Ca: 500 mg IV qwk × 15 wk → 250 mg IV qwk + PegIFN-α × 15 wk → PegIFN-α × 33 wk (total 63 wk) REP 2139-Mg: 250 mg IV qwk ± PegIFN-α × 48 wk | REP 301: HDV RNA undetectable in 11/12 at end of therapy, 7/12 at 1 year post-treatment and 7/11 at 3.5 year post-treatment RCAP ‡: 76% VR and 61% HDV RNA undetectable at week 48; similar efficacy with/without pegIFN-α. | |
| Antibody-based therapies—Monoclonal | Brelovitug (BJT-778) | SC | Anti-HBsAg IgG1 → HBsAg neutralisation | Phase 2 ongoing; FDA BTD, EMA PRIME/Orphan; Phase 2b/3 (AZURE-1) enrolling | 300–600 mg qwk × 48 wk | 100% VR with 60% undetectable HDV RNA at week 28 with 300 mg weekly dosing; better results with 600 mg weekly dosing at week 12 with no available data for week 28 |
| Tobevibart (VIR-3434) ± Elebsiran (VIR-2218) | SC | Anti-HBsAg IgG1 → HBsAg neutralization + silencing of HBV mRNA | Phase 2 (SOLSTICE) | 300 mg q4wk + Elebsiran or 300 mg q2wk × 24–60 wk | Better results with combination therapy than monotherapy; see Elebsiran + Tobevibart | |
| RG-6449 (RO7565020), 2H5-A14, E6F6, N6HB426-20, CIM212930 (early mAbs) | Anti-HBsAg (RG-6449); preS1-NTCP block (2H5-A14); Fc-mediated HBsAg clearance (E6F6); direct NTCP block (N6HB426-20, CIM212930) | Phase 1/pre-clinical | — | — | ||
| Antibody-based therapies—Polyclonal | GIGA-2339 | IV | >1000 anti-HBsAg clones—broad neutralization | Phase 1 HBV; HDV pre-clinical | — | Potent in-vitro HDV neutralization |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bardak, A.E.; Ozturk, N.B.; Gurakar, M.; Sequeira, L.; Yildiz, E.; Ozmert, E.H.; Idilman, R.; Gurakar, A. Updates on Recent Advancements in Hepatitis D Virus Treatment. Viruses 2025, 17, 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081100
Bardak AE, Ozturk NB, Gurakar M, Sequeira L, Yildiz E, Ozmert EH, Idilman R, Gurakar A. Updates on Recent Advancements in Hepatitis D Virus Treatment. Viruses. 2025; 17(8):1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081100
Chicago/Turabian StyleBardak, Ali Emre, Nazli Begum Ozturk, Merve Gurakar, Lynette Sequeira, Eda Yildiz, Enis Hikmet Ozmert, Ramazan Idilman, and Ahmet Gurakar. 2025. "Updates on Recent Advancements in Hepatitis D Virus Treatment" Viruses 17, no. 8: 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081100
APA StyleBardak, A. E., Ozturk, N. B., Gurakar, M., Sequeira, L., Yildiz, E., Ozmert, E. H., Idilman, R., & Gurakar, A. (2025). Updates on Recent Advancements in Hepatitis D Virus Treatment. Viruses, 17(8), 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081100






