The Replication Function of Rabies Virus P Protein Is Regulated by a Novel Phosphorylation Site in the N-Terminal N Protein-Binding Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Plasmids
2.2. Cell Culture, Transfection and Treatments
2.3. Luciferase Reporter Gene Assays
2.4. Cell Imaging
2.5. Mass Spectrometry
2.6. Western Analysis of Cell Lysates
2.7. Protein Expression and Purification
2.8. Protein Crystallisation, Data Collection, and Processing
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
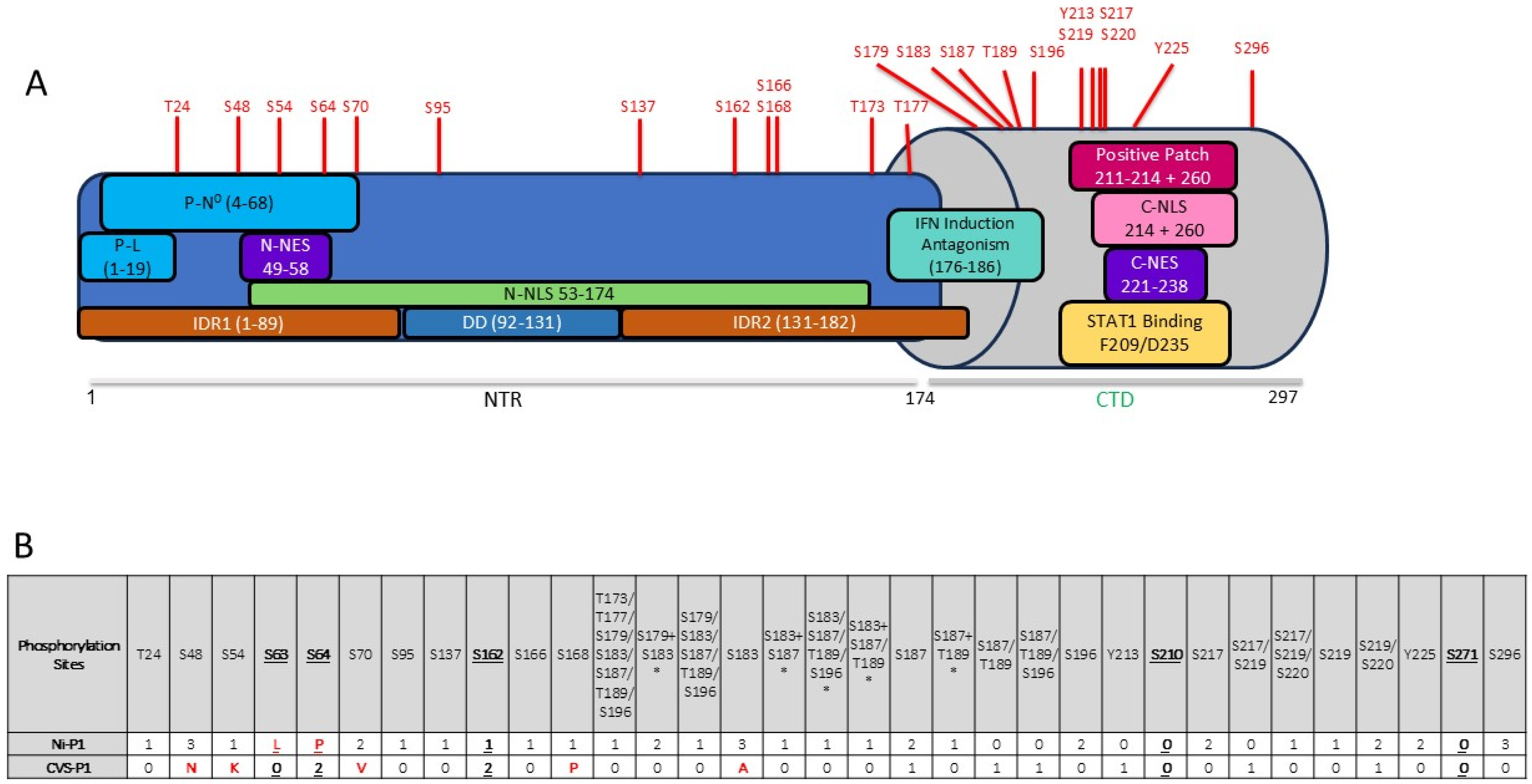
3.1. P Protein Is Phosphorylated in Multiple Regions Including at Novel Sites
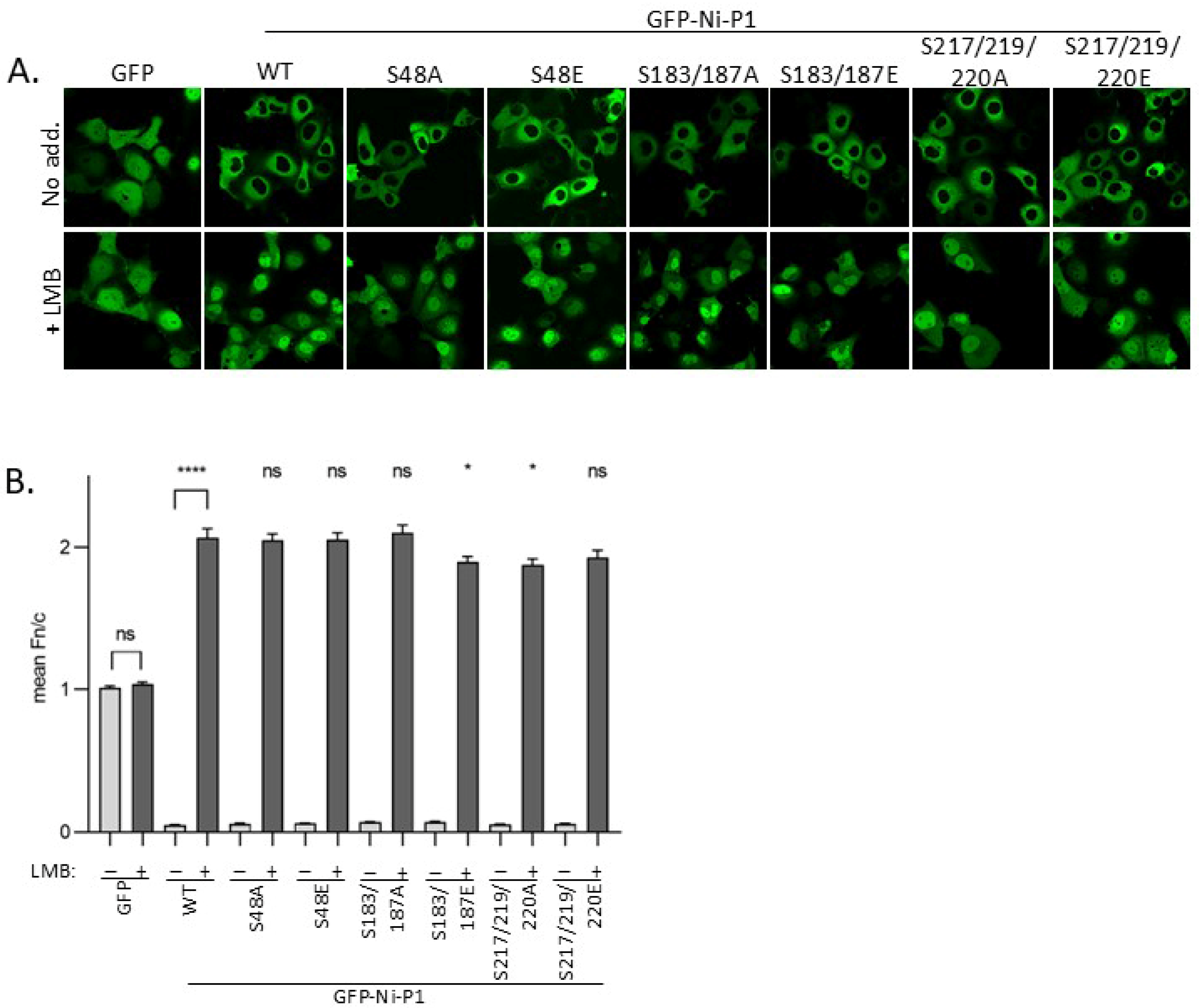
3.2. Modification of Selected Phosphorylation Sites Does Not Substantially Alter P1 Nuclear Localization
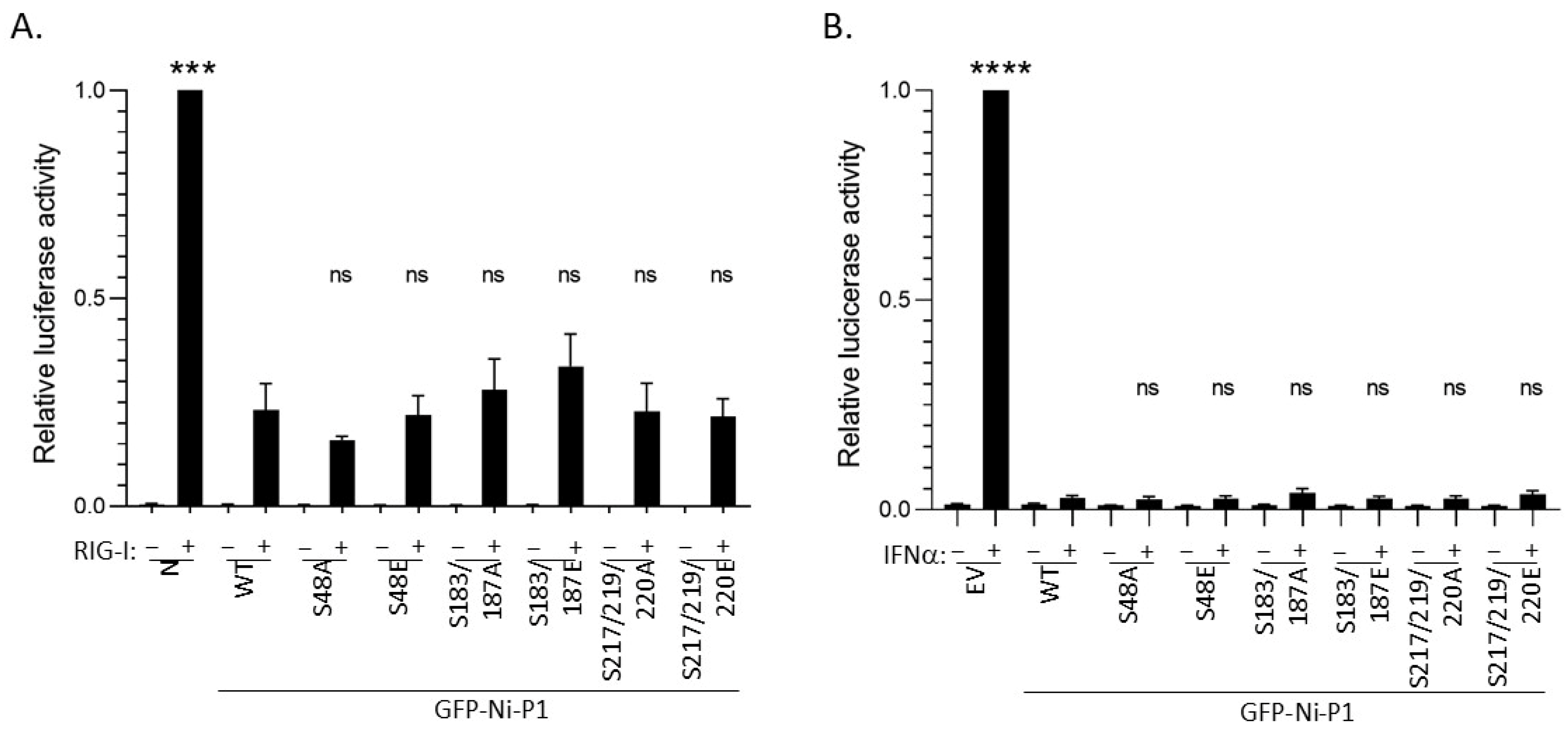
3.3. Modification of Selected Phosphorylation Sites Does Not Significantly Impact on IFN Antagonist Functions of P1
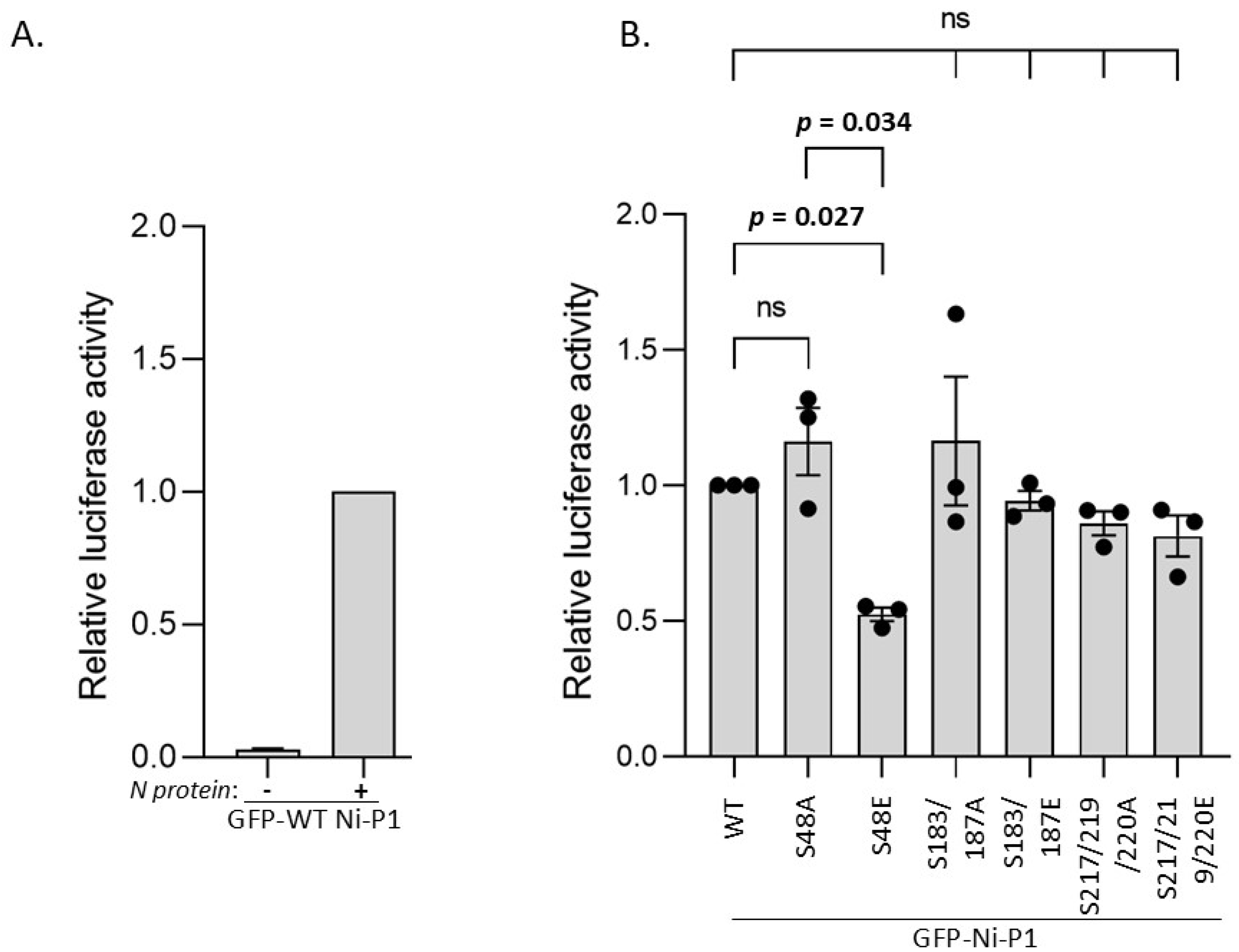
3.4. S48E Impacts on P Protein Function in Transcription/Replication
3.5. Modification at Ser48 Impacts on the Formation of Negri Body-like Structures
3.6. Expression and Crystallisation of Recombinant N0-P1−52 Complexes
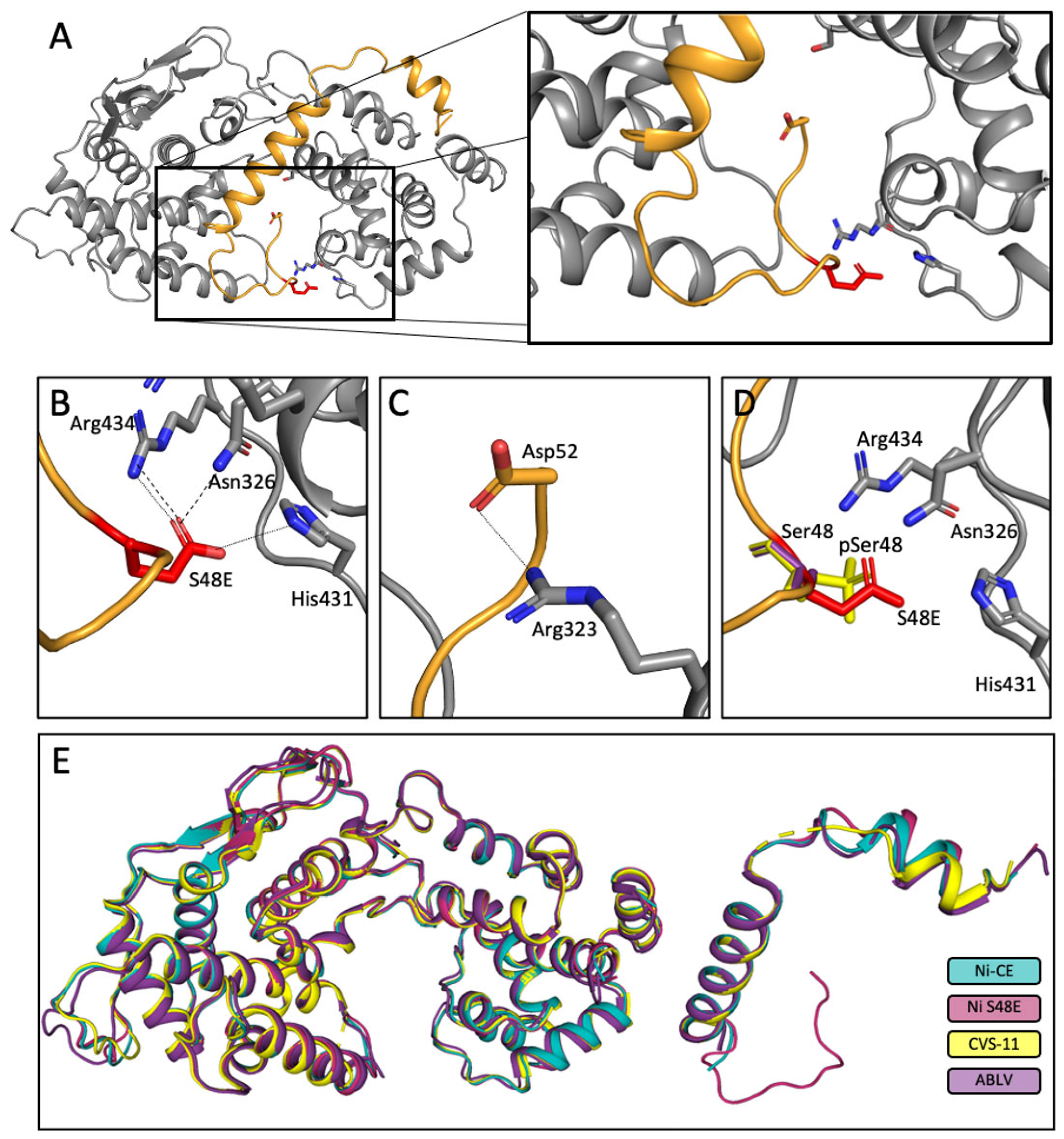
3.7. Crystal Structures of Ni-CE N0-P and Ni N0-P-S48E
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Rabies. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/rabies (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Pringle, C.R. The order Mononegavirales. Arch. Virol. 1991, 117, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B. Structures of the Mononegavirales Polymerases. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00175-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, N.; Moseley, G.W.; Sugiyama, M. The importance of immune evasion in the pathogenesis of rabies virus. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 78, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audsley, M.D.; Jans, D.A.; Moseley, G.W. Roles of nuclear trafficking in infection by cytoplasmic negative-strand RNA viruses: Paramyxoviruses and beyond. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2463–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, A.R.; Moseley, G.W. The Dynamic Interface of Viruses with STATs. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00856-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenik, M.; Schnell, M.; Conzelmann, K.K.; Blondel, D. Mapping the interacting domains between the rabies virus polymerase and phosphoprotein. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 1925–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, Y.; Real, E.; Tordo, N. Functional interaction map of lyssavirus phosphoprotein: Identification of the minimal transcription domains. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 9613–9622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksayan, S.; Ito, N.; Moseley, G.; Blondel, D. Subcellular Trafficking in Rhabdovirus Infection and Immune Evasion: A Novel Target for Therapeutics. Infect. Disord.—Drug TargetsDisorders 2012, 12, 38–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, A.R.; Lieu, K.G.; Larrous, F.; Ito, N.; Bourhy, H.; Moseley, G.W. Lyssavirus P-protein selectively targets STAT3-STAT1 heterodimers to modulate cytokine signalling. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brice, A.M.; Watts, E.; Hirst, B.; Jans, D.A.; Ito, N.; Moseley, G.W. Implication of the nuclear trafficking of rabies virus P3 protein in viral pathogenicity. Traffic 2021, 22, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlinson, S.M.; Zhao, T.; Ardipradja, K.; Zhang, Y.; Veugelers, P.F.; Harper, J.A.; David, C.T.; Sundaramoorthy, V.; Moseley, G.W. Henipaviruses and lyssaviruses target nucleolar treacle protein and regulate ribosomal RNA synthesis. Traffic 2022, 24, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brice, A.M.; Rozario, A.M.; Rawlinson, S.M.; David, C.T.; Wiltzer-Bach, L.; Jans, D.A.; Ito, N.; Bell, T.D.M.; Moseley, G.W. Lyssavirus P Protein Isoforms Diverge Significantly in Subcellular Interactions Underlying Mechanisms of Interferon Antagonism. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0139622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manokaran, G.; Audsley, M.D.; Funakoda, H.; David, C.T.; Garnham, K.A.; Rawlinson, S.M.; Deffrasnes, C.; Ito, N.; Moseley, G.W. Deactivation of the antiviral state by rabies virus through targeting and accumulation of persistently phosphorylated STAT1. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, A.; Rawlinson, S.M.; Dubey, A.; Ang, C.S.; Choi, Y.H.; Yan, F.; Okada, K.; Rozario, A.M.; Brice, A.M.; Ito, N.; et al. Structural insights into the multifunctionality of rabies virus P3 protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2217066120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, J.A.; Jenni, S.; Harrison, S.C.; Whelan, S.P.J. Structure of a rabies virus polymerase complex from electron cryo-microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Harrison, A.R.; Portelli, S.; Nguyen, T.B.; Kojima, I.; Zheng, S.; Yan, F.; Masatani, T.; Rawlinson, S.M.; Sethi, A.; et al. Definition of the immune evasion-replication interface of rabies virus P protein. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Koprowski, H.; Dietzschold, B.; Fu, Z.F. Phosphorylation of Rabies Virus Nucleoprotein Regulates Viral RNA Transcription and Replication by Modulating Leader RNA Encapsidation. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1661–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Chakraborty, S.; Sethi, A.; Mok, Y.-F.; Yan, F.; Moseley, G.W.; Gooley, P.R. Analysis of mechanisms of the rabies virus P protein-nucleocapsid interaction using engineered N-protein peptides and potential applications in antivirals design. Antivir. Res. 2025, 234, 106075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrakis, M.; Méhouas, S.; Réal, E.; Iseni, F.; Blondel, D.; Tordo, N.; Ruigrok, R.W. Rabies virus chaperone: Identification of the phosphoprotein peptide that keeps nucleoprotein soluble and free from non-specific RNA. Virology 2006, 349, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gérard, F.C.A.; Bourhis, J.-M.; Mas, C.; Branchard, A.; Vu, D.D.; Varhoshkova, S.; Leyrat, C.; Jamin, M. Structure and Dynamics of the Unassembled Nucleoprotein of Rabies Virus in Complex with Its Phosphoprotein Chaperone Module. Viruses 2022, 14, 2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moseley, G.W.; Filmer, R.P.; DeJesus, M.A.; Jans, D.A. Nucleocytoplasmic distribution of rabies virus P-protein is regulated by phosphorylation adjacent to C-terminal nuclear import and export signals. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 12053–12061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, C.L.; Wagstaff, K.M.; Oksayan, S.; Glover, D.J.; Jans, D.A.; Moseley, G.W. Nuclear Trafficking of the Rabies Virus Interferon Antagonist P-Protein Is Regulated by an Importin-Binding Nuclear Localization Sequence in the C-Terminal Domain. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiltzer, L.; Okada, K.; Yamaoka, S.; Larrous, F.; Kuusisto, H.V.; Sugiyama, M.; Blondel, D.; Bourhy, H.; Jans, D.A.; Ito, N.; et al. Interaction of rabies virus P-protein with STAT proteins is critical to lethal rabies disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 1744–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Larrous, F.; Rawlinson, S.M.; Zhan, J.; Sethi, A.; Ibrahim, Y.; Aloi, M.; Lieu, K.G.; Mok, Y.F.; Griffin, M.D.W.; et al. Structural Elucidation of Viral Antagonism of Innate Immunity at the STAT1 Interface. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 1934–1945.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raux, H.; Flamand, A.; Blondel, D. Interaction of the rabies virus P protein with the LC8 dynein light chain. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10212–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouquet, B.; Nikolic, J.; Larrous, F.; Bourhy, H.; Wirblich, C.; Lagaudriere-Gesbert, C.; Blondel, D. Focal adhesion kinase is involved in rabies virus infection through its interaction with viral phosphoprotein P. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 1640–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, N.; Real, E.; Gaudin, Y.; Vaney, M.-C.; King, S.; Jacob, Y.; Tordo, N.; Blondel, D. Molecular basis for the interaction between rabies virus phosphoprotein P and the dynein light chain LC8: Dissociation of dynein-binding properties and transcriptional functionality of P. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 2691–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasdeloup, D.; Poisson, N.; Raux, H.; Gaudin, Y.; Ruigrok, R.W.; Blondel, D. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the rabies virus P protein requires a nuclear localization signal and a CRM1-dependent nuclear export signal. Virology 2005, 334, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Ito, N.; Yamaoka, S.; Masatani, T.; Ebihara, H.; Goto, H.; Nakagawa, K.; Mitake, H.; Okadera, K.; Sugiyama, M. Roles of the Rabies Virus Phosphoprotein Isoforms in Pathogenesis. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 8226–8237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriguchi, Y.; Toriumi, H.; Kawai, A. Studies on the rabies virus RNA polymerase: 3. Two-dimensional electrophoretic analysis of the multiplicity of non-catalytic subunit (P protein). Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 46, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, F.; Asakawa, N.; Morimoto, K.; Takeuchi, K.; Eriguchi, Y.; Toriumi, H.; Kawai, A. Studies on the rabies virus RNA polymerase: 2. Possible relationships between the two forms of the non-catalytic subunit (P protein). Microbiol. Immunol. 1998, 42, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Blondel, D.; Choudhary, S.; Banerjee, A.K. The phosphoprotein of rabies virus is phosphorylated by a unique cellular protein kinase and specific isomers of protein kinase C. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sui, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, M.; Chen, H.; Fu, Z.F.; Zhao, L. Substitution of S179P in the Lyssavirus Phosphoprotein Impairs Its Interferon Antagonistic Function. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e01125-01122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, J.; Watts, E.; Brice, A.M.; Metcalfe, R.D.; Rozario, A.M.; Sethi, A.; Yan, F.; Bell, T.D.M.; Griffin, M.D.W.; Moseley, G.W.; et al. Molecular Basis of Functional Effects of Phosphorylation of the C-Terminal Domain of the Rabies Virus P Protein. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0011122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brice, A.; Whelan, D.R.; Ito, N.; Shimizu, K.; Wiltzer-Bach, L.; Lo, C.Y.; Blondel, D.; Jans, D.A.; Bell, T.D.; Moseley, G.W. Quantitative Analysis of the Microtubule Interaction of Rabies Virus P3 Protein: Roles in Immune Evasion and Pathogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, N.; Moseley, G.W.; Blondel, D.; Shimizu, K.; Rowe, C.L.; Ito, Y.; Masatani, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Jans, D.A.; Sugiyama, M. Role of interferon antagonist activity of rabies virus phosphoprotein in viral pathogenicity. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 6699–6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltzer, L.; Larrous, F.; Oksayan, S.; Ito, N.; Marsh, G.A.; Wang, L.F.; Blondel, D.; Bourhy, H.; Jans, D.A.; Moseley, G.W. Conservation of a unique mechanism of immune evasion across the Lyssavirus genus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 10194–10199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Ito, N.; Mita, T.; Yamada, K.; Hosokawa-Muto, J.; Sugiyama, M.; Minamoto, N. Involvement of nucleoprotein, phosphoprotein, and matrix protein genes of rabies virus in virulence for adult mice. Virus Res. 2007, 123, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audsley, M.D.; Marsh, G.A.; Lieu, K.G.; Tachedjian, M.; Joubert, D.A.; Wang, L.-F.; Jans, D.A.; Moseley, G.W. The immune evasion function of J and Beilong virus V proteins is distinct from that of other paramyxoviruses, consistent with their inclusion in the proposed genus Jeilongvirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemesh, M.; Aktepe, T.E.; Deerain, J.M.; McAuley, J.L.; Audsley, M.D.; David, C.T.; Purcell, D.F.J.; Urin, V.; Hartmann, R.; Moseley, G.W.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 suppresses IFNβ production mediated by NSP1, 5, 6, 15, ORF6 and ORF7b but does not suppress the effects of added interferon. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, C.M.; Stewart, M.; Roby, J.A.; Sundaramoorthy, V.; Forwood, J.K. Structural Determination of the Australian Bat Lyssavirus Nucleoprotein and Phosphoprotein Complex. Viruses 2023, 16, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, K.; Khoo, J.J.; Sadler, A.; Piganis, R.; Wang, D.; Borg, N.A.; Hjerrild, K.; Gould, J.; Thomas, B.J.; Nagley, P.; et al. Mitochondrially localised MUL1 is a novel modulator of antiviral signaling. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2013, 91, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audsley, M.D.; Jans, D.A.; Moseley, G.W. Nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of Nipah virus W protein involves multiple discrete interactions with the nuclear import and export machinery. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 479, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bern, M.; Kil, Y.J.; Becker, C. Byonic: Advanced peptide and protein identification software. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2012, 40, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studier, F.W.; Moffatt, B.A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J. Mol. Biol. 1986, 189, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPhillips, T.M.; McPhillips, S.E.; Chiu, H.J.; Cohen, A.E.; Deacon, A.M.; Ellis, P.J.; Garman, E.; Gonzalez, A.; Sauter, N.K.; Phizackerley, R.P.; et al. Blu-Ice and the Distributed Control System: Software for data acquisition and instrument control at macromolecular crystallography beamlines. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2002, 9 Pt 6, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch, W. XDS. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D 2010, 66, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clabbers, M.T.B.; Gruene, T.; Parkhurst, J.M.; Abrahams, J.P.; Waterman, D.G. Electron diffraction data processing with DIALS. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D 2018, 74, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, P.R.; Murshudov, G.N. How good are my data and what is the resolution? Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2013, 69 Pt 7, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40 Pt 4, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonine, P.V.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Echols, N.; Headd, J.J.; Moriarty, N.W.; Mustyakimov, M.; Terwilliger, T.C.; Urzhumtsev, A.; Zwart, P.H.; Adams, P.D. Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenix.refine. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D 2012, 68, 352–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Jabłońska, J.; Pravda, L.; Vařeková, R.S.; Thornton, J.M. PDBsum: Structural summaries of PDB entries. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, F.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Lee, J.; Eusebi, A.; Niewielska, A.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Lopez, R.; Butcher, S. The EMBL-EBI Job Dispatcher sequence analysis tools framework in 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W521–W525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelbi-Alix, M.K.; Vidy, A.; El Bougrini, J.; Blondel, D. Rabies viral mechanisms to escape the IFN system: The viral protein P interferes with IRF-3, Stat1, and PML nuclear bodies. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2006, 26, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseley, G.W.; Lahaye, X.; Roth, D.M.; Oksayan, S.; Filmer, R.P.; Rowe, C.L.; Blondel, D.; Jans, D.A. Dual modes of rabies P-protein association with microtubules: A novel strategy to suppress the antiviral response. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122 Pt 20, 3652–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzózka, K.; Finke, S.; Conzelmann, K.K. Inhibition of interferon signaling by rabies virus phosphoprotein P: Activation-dependent binding of STAT1 and STAT2. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 2675–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, M.; Brzózka, K.; Pfaller, C.K.; Cox, J.H.; Stitz, L.; Conzelmann, K.-K. Genetic Dissection of Interferon-Antagonistic Functions of Rabies Virus Phosphoprotein: Inhibition of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 Activation Is Important for Pathogenicity. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzózka, K.; Finke, S.; Conzelmann, K.-K. Identification of the Rabies Virus Alpha/Beta Interferon Antagonist: Phosphoprotein P Interferes with Phosphorylation of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7673–7681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masatani, T.; Ozawa, M.; Yamada, K.; Ito, N.; Horie, M.; Matsuu, A.; Okuya, K.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K.; Sugiyama, M.; Nishizono, A. Contribution of the interaction between the rabies virus P protein and I-kappa B kinase ϵ to the inhibition of type I IFN induction signalling. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrima, N.; Le Bars, R.; Nevers, Q.; Glon, D.; Chevreux, G.; Civas, A.; Blondel, D.; Lagaudrière-Gesbert, C.; Gaudin, Y. Rabies virus P protein binds to TBK1 and interferes with the formation of innate immunity-related liquid condensates. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidy, A.; Chelbi-Alix, M.; Blondel, D. Rabies virus P protein interacts with STAT1 and inhibits interferon signal transduction pathways. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14411–14420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, V.; Ellegast, J.; Kim, S.; Brzózka, K.; Jung, A.; Kato, H.; Poeck, H.; Akira, S.; Conzelmann, K.K.; Schlee, M.; et al. 5′-Triphosphate RNA is the ligand for RIG-I. Science 2006, 314, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masatani, T.; Ito, N.; Shimizu, K.; Ito, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Sawaki, Y.; Koyama, H.; Sugiyama, M. Rabies Virus Nucleoprotein Functions To Evade Activation of the RIG-I-Mediated Antiviral Response. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 4002–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrakis, M.; McCarthy, A.A.; Roche, S.; Blondel, D.; Ruigrok, R.W. Structure and function of the C-terminal domain of the polymerase cofactor of rabies virus. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugai, A.; Sato, H.; Yoneda, M.; Kai, C. Phosphorylation of measles virus phosphoprotein at S86 and/or S151 downregulates viral transcriptional activity. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 3900–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Banerjee, A.K.; Chen, M. N-terminal phosphorylation of phosphoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus is required for preventing nucleoprotein from binding to cellular RNAs and for functional template formation. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3177–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahaye, X.; Vidy, A.; Pomier, C.; Obiang, L.; Harper, F.; Gaudin, Y.; Blondel, D. Functional characterization of Negri bodies (NBs) in rabies virus-infected cells: Evidence that NBs are sites of viral transcription and replication. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7948–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolic, J.; Civas, A.; Lama, Z.; Lagaudrière-Gesbert, C.; Blondel, D. Rabies Virus Infection Induces the Formation of Stress Granules Closely Connected to the Viral Factories. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchdoerfer, R.N.; Abelson, D.M.; Li, S.; Wood, M.R.; Saphire, E.O. Assembly of the Ebola Virus Nucleoprotein from a Chaperoned VP35 Complex. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guryanov, S.G.; Liljeroos, L.; Kasaragod, P.; Kajander, T.; Butcher, S.J. Crystal Structure of the Measles Virus Nucleoprotein Core in Complex with an N-Terminal Region of Phosphoprotein. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 2849–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, M.; Bertinelli, M.; Leyrat, C.; Paesen, G.C.; Saraiva de Oliveira, L.F.; Huiskonen, J.T.; Grimes, J.M. Nucleocapsid assembly in pneumoviruses is regulated by conformational switching of the N protein. eLife 2016, 5, e12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertini, A.A.V.; Wernimont, A.K.; Muziol, T.; Ravelli, R.B.G.; Clapier, C.R.; Schoehn, G.; Weissenhorn, W.; Ruigrok, R.W.H. Crystal Structure of the Rabies Virus Nucleoprotein-RNA Complex. Science 2006, 313, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Data Collection and Processing | Ni-CE N0P | Ni N0P-S48E |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength (Å) | 0.9537 | 0.9537 |
| Resolution range (Å) | 29.90–2.00 (2.05–2.00) | 29.88–2.10 (2.16–2.10) |
| Space group | P 21 21 21 | P 21 21 21 |
| Unit cell (Å, °) | 42.17 74.50 154.72, 90 90 90 | 41.89 75.39 154.99, 90 90 90 |
| Total reflections | 388,562 (22,768) | 138,385 (10,791) |
| Unique reflections | 33,217 (2309) | 29,538 (2335) |
| Multiplicity | 11.7 (9.9) | 4.7 (4.6) |
| Completeness (%) | 98.1 (95.1) | 99.9 (99.8) |
| Mean I/sigma(I) | 12.4 (1.8) | 5.9 (2.0) |
| Wilson B-factor Å2 | 23.177 | 21.811 |
| R-merge % | 0.141 (1.380) | 0.138 (0.854) |
| R-pim % | 0.042 (0.428) | 0.071 (0.456) |
| CC1/2 | 0.997 (0.656) | 0.989 (0.849) |
| Refinement | ||
| Resolution range (Å) | 20.0–2.0 | 20.0–2.15 |
| Number of reflections | 33,008 | 27,965 |
| Number of R-free reflections | 1718 | 1474 |
| R-work % | 18.22 | 18.28 |
| R-free | 21.70 | 21.48 |
| RMS (bonds) | 0.003 | 0.003 |
| RMS (angles) | 0.60 | 0.58 |
| Ramachandran plot | ||
| favoured (%) | 98.26 | 98.10 |
| allowed (%) | 1.74 | 1.90 |
| outliers (%) | 0 | 0 |
| Validation | ||
| Clash score | 0.62 | 2.22 |
| MolProbity score (percentile) | 0.71 (100) | 1.00 (100) |
| PDB accession code | 8U0A | 8U0B |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tudhope, E.; Donnelly, C.M.; Sethi, A.; David, C.; Williamson, N.; Stewart, M.; Forwood, J.K.; Gooley, P.R.; Moseley, G.W. The Replication Function of Rabies Virus P Protein Is Regulated by a Novel Phosphorylation Site in the N-Terminal N Protein-Binding Region. Viruses 2025, 17, 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081075
Tudhope E, Donnelly CM, Sethi A, David C, Williamson N, Stewart M, Forwood JK, Gooley PR, Moseley GW. The Replication Function of Rabies Virus P Protein Is Regulated by a Novel Phosphorylation Site in the N-Terminal N Protein-Binding Region. Viruses. 2025; 17(8):1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081075
Chicago/Turabian StyleTudhope, Ericka, Camilla M. Donnelly, Ashish Sethi, Cassandra David, Nicholas Williamson, Murray Stewart, Jade K. Forwood, Paul R. Gooley, and Gregory W. Moseley. 2025. "The Replication Function of Rabies Virus P Protein Is Regulated by a Novel Phosphorylation Site in the N-Terminal N Protein-Binding Region" Viruses 17, no. 8: 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081075
APA StyleTudhope, E., Donnelly, C. M., Sethi, A., David, C., Williamson, N., Stewart, M., Forwood, J. K., Gooley, P. R., & Moseley, G. W. (2025). The Replication Function of Rabies Virus P Protein Is Regulated by a Novel Phosphorylation Site in the N-Terminal N Protein-Binding Region. Viruses, 17(8), 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081075






