Pegiviruses and Coronavirus: Biomolecular Prevalence and Phylogenetic Analysis of Strains Detected in Italian Horse Populations
Abstract
1. Background
2. Introduction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Extraction and Molecular Detection of Viral RNA
3.2.1. Molecular Detection of Pegivirus caballi and equi
3.2.2. Molecular Detection of ECoV
3.3. Sequencing
3.3.1. Sequencing of Pegivirus-Positive Samples
3.3.2. Sequencing of ECoV-Positive Samples
3.3.3. Sequence Analysis
| For | Reagent | ID | Sequence 5′–3′ | Target | Purpose | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equine Pegiviruses | Primers fw | EVT-146 | AGGGTTCTTCGGGTAAATCC | 5′UTR | Duplex real-time RT-PCR | [16,37] |
| Primers rv | EPgV-314 | TCGKCGAGCYACAGACCGT | 5′UTR | Duplex real-time RT-PCR | [37] | |
| Probes | EPgV1WST-189 | 6FAM-TGTTGTGATTGTGTTAGGGCAGGTGGCA-BHQ-1 | Pegivirus caballi 5′UTR | Duplex real-time RT-PCR | [37] | |
| Probes | TDAV-199 | TEX-TGTTTTGGGTTCAGGGCAGTAG-BHQ-2 | Pegivirus equi 5′UTR | Duplex real-time RT-PCR | [37] | |
| Equine Pegiviruses | Primers | TDAV-3744 Fw | GGAGCCCGGAGGGCATGGGTA | NS3 | Conventional PCR | [37] |
| Primers | TDAV-4098 Rv | TGGCAGGGACAAGGGTGGACT | NS3 | Conventional PCR | [37] | |
| ECoV | Primers | ECoV-380f | TGGGAACAGGCCCGC | Gene N | Real-Time PCR | [63] |
| Primers | ECoV-522r | CCTAGTCGGAATAGCCTCATCAC | Gene N | Real-Time PCR | [63] | |
| Probes | ECoV-436p | 6FAM-TGGGTCGCTAACAAG-TAMRA | Gene N | Real-Time PCR | [63] | |
| ECoV | Primers Ext-Fw | Primers Ext-Fw | AAATTTTATGGCGGCTGG | ORF1AB | Nested-PCR | [85] |
| Primers Ext-Rv | Primers Ext-Rv | GGACCTCATGAATTCTGTTC | ORF1AB | Nested-PCR | [85] | |
| Primers Int-Fw | Primers Int-Fw | GGTTGGGATTACCCTAAGTGTGA | ORF1AB | Nested-PCR | [85] | |
| Primers Int-Rv | Primers Int-Rv | ATGATGATTTTGAGTGATGATGG | ORF1AB | Nested-PCR | [85] |
3.4. Phylogenetic Tree Construction
4. Results
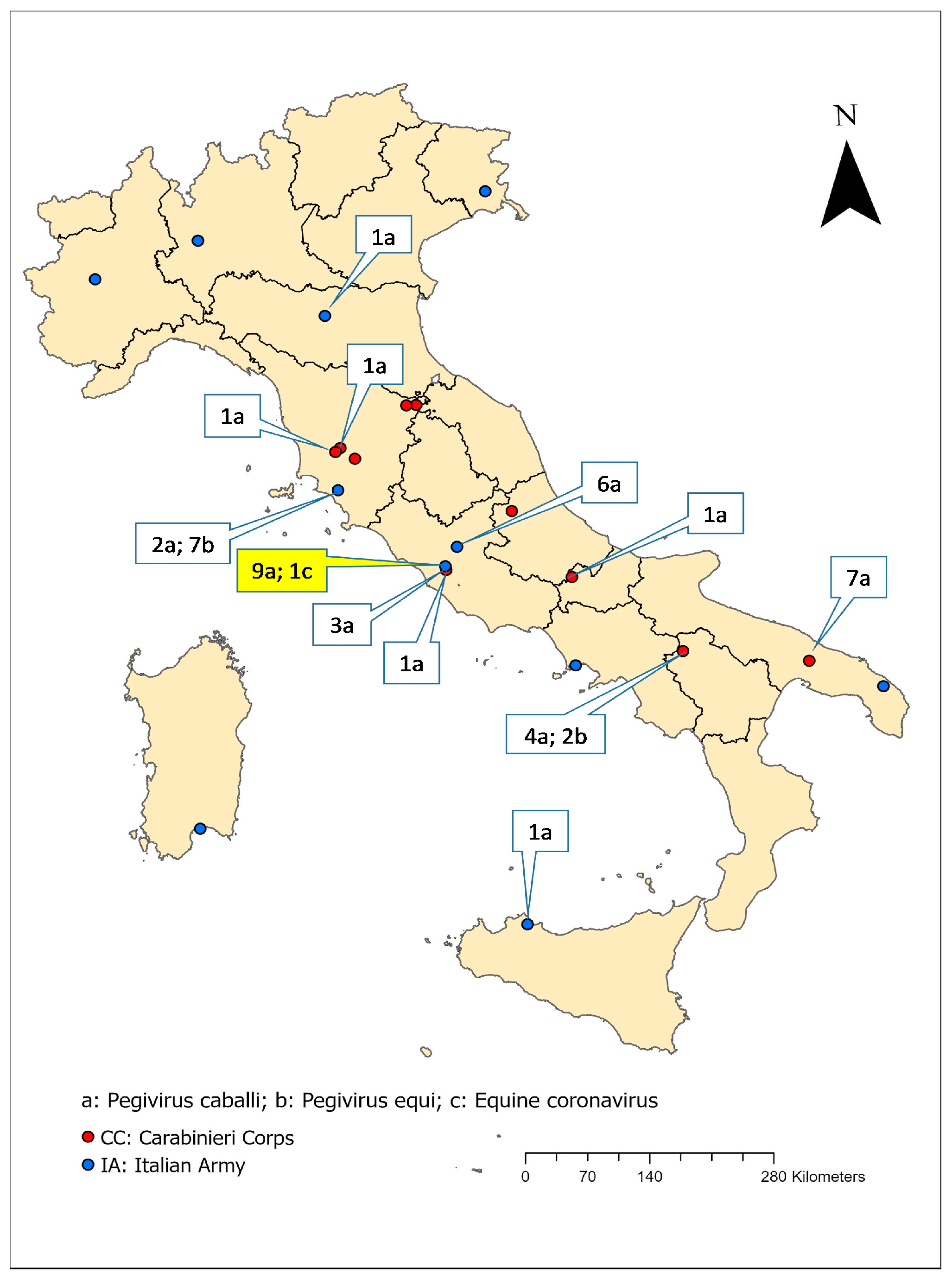
4.1. The Sampling Population
4.2. Extraction and Molecular Detection of Viral RNA
4.2.1. Molecular Detection of Pegivirus caballi and equi
4.2.2. Molecular Detection of ECoV
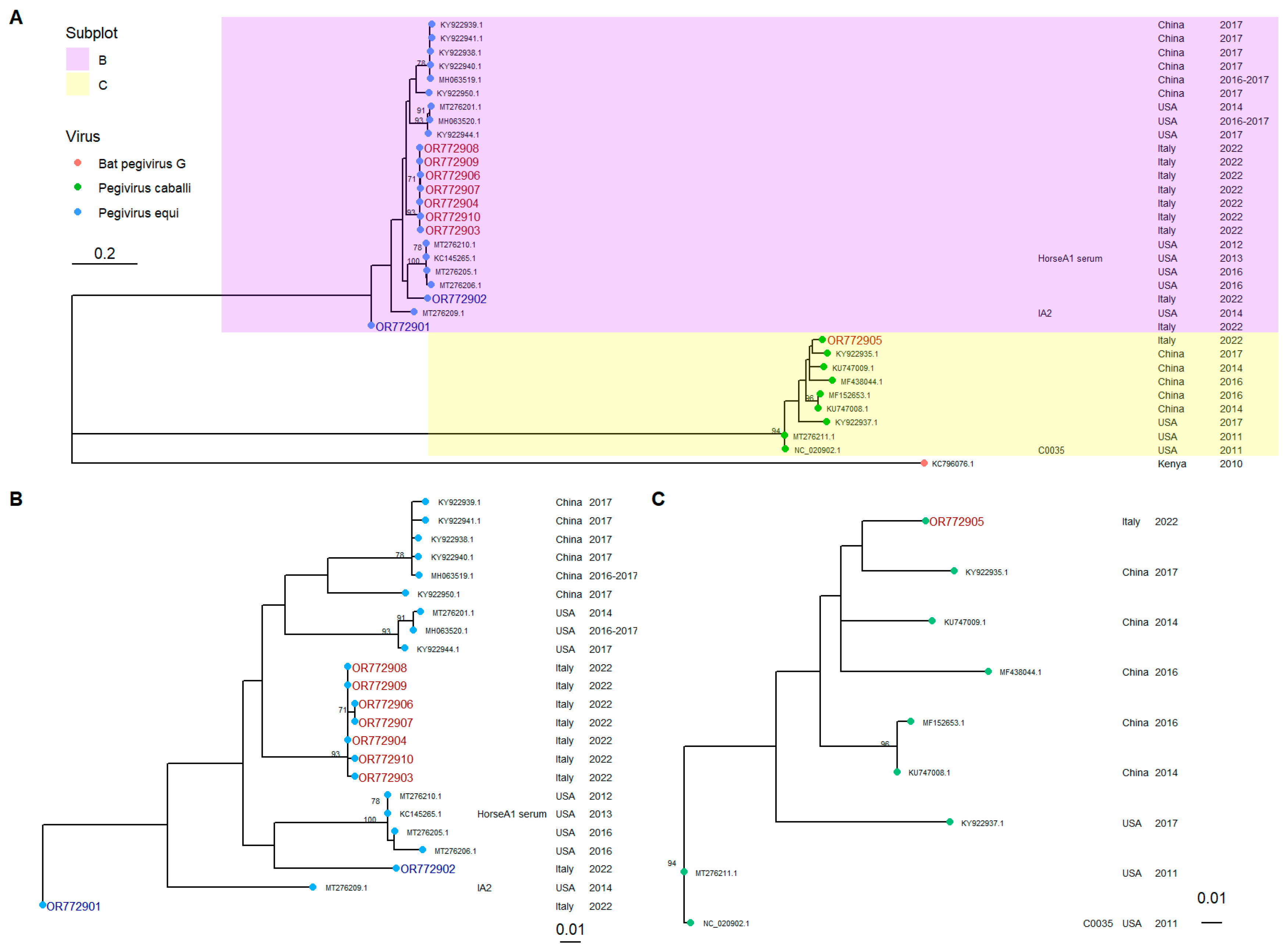
4.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.4. Phylogenetic Tree Construction
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, J.; Marlin, D. Foreword—Emerging issues in equestrian practice. Comp. Exerc. Physiol. 2020, 16, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillot, R. Special issue “equine Viruses”: Old “friends” and new foes? Viruses 2020, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.L.; Jones, J.H.; Hornof, W.J.; Miles, J.A.; Longworth, K.E.; Willits, N.H. Effects of road transport on indices of stress in horses. Equine Vet. J. 1996, 28, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandin, T. Assessment of Stress during Handling and Transport. J. Anim. Sci. 1997, 75, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Biau, S.; Möstl, E.; Becker-Birck, M.; Morillon, B.; Aurich, J.; Faure, J.M.; Aurich, C. Changes in cortisol release and heart rate variability in sport horses during long-distance road transport. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2010, 38, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichert, C.; Campe, A.; Walter, S.; Pfaender, S.; Welsch, K.; Ruddat, I.; Sieme, H.; Feige, K.; Steinmann, E.; Cavalleri, J.M.V. Frequent occurrence of nonprimate hepacivirus infections in Thoroughbred breeding horses—A cross-sectional study for the occurrence of infections and potential risk factors. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 203, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoney, P.J. Factors influencing the international spread of equine diseases. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2000, 16, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, K.L.; O’Sullivan, T.L.; Poljak, Z.; Greer, A.L. Descriptive and network analyses of the equine contact network at an equestrian show in Ontario, Canada and implications for disease spread. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, M.; Mapitse, N.J.; Akerström, G.; Devolz, R.; Mcewen, J.; Stewart, B.; Lam, K. The HHP Framework, for Certified High-Health-Status Equine Athlete; Bulletin De L’OMSA; OIE: Paris, France, 2019; p. 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, T.M. A brief introduction to equine influenza and equine influenza viruses. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2123, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlock, F.; Murcia, P.R.; Newton, J.R. A Review on Equine Influenza from a Human Influenza Perspective. Viruses 2022, 14, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, E.; Rush, B.R.; Cox, J.; DeBey, B.; Kapil, S. Neonatal enterocolitis associated with coronavirus infection in a foal: A case report. J. Vet. Diagnostic Investig. 2000, 12, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, J.S.; Breslin, J.J.; Breuhaus, B.; Vivrette, S.; Smith, L.G. Characterization of a coronavirus isolated from a diarrheic foal. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 4523–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burbelo, P.D.; Dubovi, E.J.; Simmonds, P.; Medina, J.L.; Henriquez, J.A.; Mishra, N.; Wagner, J.; Tokarz, R.; Cullen, J.M.; Iadarola, M.J.; et al. Serology-Enabled Discovery of Genetically Diverse Hepaciviruses in a New Host. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6171–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, A.; Simmonds, P.; Cullen, J.M.; Scheel, T.K.H.; Medina, J.L.; Giannitti, F.; Nishiuchi, E.; Brock, K.V.; Burbelo, P.D.; Rice, C.M.; et al. Identification of a Pegivirus (GB Virus-Like Virus) That Infects Horses. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7185–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandriani, S.; Skewes-Cox, P.; Zhong, W.; Ganem, D.E.; Divers, T.J.; Van Blaricum, A.J.; Tennant, B.C.; Kistler, A.L. Identification of a previously undescribed divergent virus from the Flaviviridae family in an outbreak of equine serum hepatitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E1407–E1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postler, T.S.; Beer, M.; Blitvich, B.J.; Bukh, J.; de Lamballerie, X.; Drexler, J.F.; Imrie, A.; Kapoor, A.; Karganova, G.G.; Lemey, P.; et al. Renaming of the genus Flavivirus to Orthoflavivirus and extension of binomial species names within the family Flaviviridae. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divers, T.J.; Tennant, B.C.; Kumar, A.; McDonough, S.; Cullen, J.; Bhuva, N.; Jain, K.; Chauhan, L.S.; Scheel, T.K.H.; Lipkin, W.I.; et al. New parvovirus associated with serum hepatitis in horses after inoculation of common biological product. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasche, A.; Lehmann, F.; Goldmann, N.; Nagel, M.; Moreira-Soto, A.; Nobach, D.; de Oliveira Carneiro, I.; Osterrieder, N.; Greenwood, A.D.; Steinmann, E.; et al. A hepatitis B virus causes chronic infections in equids worldwide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2013982118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprety, T.; Sreenivasan, C.C.; Hause, B.M.; Li, G.; Odemuyiwa, S.O.; Locke, S.; Morgan, J.; Zeng, L.; Gilsenan, W.F.; Slovis, N.; et al. Identification of a ruminant origin group b rotavirus associated with diarrhea outbreaks in foals. Viruses 2021, 13, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, P.; Becher, P.; Bukh, J.; Gould, E.A.; Meyers, G.; Monath, T.; Muerhoff, S.; Pletnev, A.; Rico-Hesse, R.; Smith, D.B.; et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Flaviviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, J.E.; Wolfisberg, R.; Fahnøe, U.; Sharma, H.; Renshaw, R.W.; Nielsen, L.; Nishiuchi, E.; Holm, C.; Dubovi, E.; Rosenberg, B.R.; et al. Equine pegiviruses cause persistent infection of bone marrow and are not associated with hepatitis. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wan, Z.; Wang, J.H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C. Review of human pegivirus: Prevalence, transmission, pathogenesis, and clinical implication. Virulence 2022, 13, 324–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, S.D.; Lauck, M.; Bailey, A.L.; Hyeroba, D.; Tumukunde, A.; Weny, G.; Chapman, C.A.; O’Connor, D.H.; Goldberg, T.L.; Friedrich, T.C. Discovery and characterization of distinct simian pegiviruses in three wild African old world monkey species. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, A.F.; Pettersson, J.H.O.; Chang, W.S.; Harvey, E.; Rose, K.; Shi, M.; Eden, J.S.; Buchmann, J.; Moritz, C.; Holmes, E.C. Novel hepaci- And pegi-like viruses in native Australian wildlife and non-human primates. Virus Evol. 2020, 6, veaa064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffron, A.S.; Lauck, M.; Somsen, E.D.; Townsend, E.C.; Bailey, A.L.; Sosa, M.; Eickhoff, J.; Capuano, S.; Newman, C.M.; Kuhn, J.H.; et al. Discovery of a novel simian pegivirus in common marmosets (Callithrix jacchus) with lymphocytic enterocolitis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, P.L.; Firth, C.; Conte, J.M.; Williams, S.H.; Zambrana-Torrelio, C.M.; Anthony, S.J.; Ellison, J.A.; Gilbert, A.T.; Kuzmin, I.V.; Niezgoda, M.; et al. Bats are a major natural reservoir for hepaciviruses and pegiviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8194–8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nguyen, D.; Van Nguyen, C.; Bonsall, D.; Ngo, T.T.; Carrique-Mas, J.; Pham, A.H.; Bryant, J.E.; Thwaites, G.; Baker, S.; Woolhouse, M.; et al. Detection and characterization of homologues of human hepatitis viruses and pegiviruses in rodents and bats in Vietnam. Viruses 2018, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, C.; Bhat, M.; Firth, M.A.; Williams, S.H.; Frye, M.J.; Simmonds, P.; Conte, J.M.; Ng, J.; Garcia, J.; Bhuva, N.P.; et al. Detection of zoonotic pathogens and characterization of novel viruses carried by commensal Rattus norvegicus in New York city. mBio 2014, 5, e01933-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, A.; Simmonds, P.; Scheel, T.K.H.; Hjelle, B.; Cullen, J.M.; Burbelo, P.D.; Chauhan, L.V.; Duraisamy, R.; Sanchez Leon, M.; Jain, K.; et al. Identification of rodent homologs of hepatitis C virus and pegiviruses. mBio 2013, 4, e00216-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Yang, J.; Lu, S.; Huang, Y.; Jin, D.; Pu, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Shi, M.; Xu, J. Novel pegiviruses infecting wild birds and rodents. Virol. Sin. 2022, 37, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baechlein, C.; Grundhoff, A.; Fischer, N.; Alawi, M.; Hoeltig, D.; Waldmann, K.H.; Becher, P. Pegivirus infection in domestic pigs, Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1312–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, T.; Usui, R.; Narabu, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Murata, K.; Okamoto, H. Identification of a novel pegivirus in pet cats (Felis silvestris catus) in Japan. Virus Res. 2021, 301, 198452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, S.; Kapoor, A.; Schneider, B.S.; Wolfe, N.D.; Culshaw, G.; Corcoran, B.; Durham, A.E.; Burden, F.; McGorum, B.C.; Simmonds, P. Viraemic frequencies and seroprevalence of non-primate hepacivirus and equine pegiviruses in horses and other mammalian species. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- De Souza, A.J.S.; Malheiros, A.P.; de Sousa, E.R.P.; Moreira, A.C.N.; Silva, A.L.; das Chagas, A.A.C.; Freitas, P.E.B.; Gemaque, B.S.; de Figueiredo, H.F.; de Sá, L.R.M.; et al. First report of equine Pegivirus in South America, Brazil. Acta Trop. 2015, 152, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Sun, L.; Xu, T.; He, D.; Wang, Z.; Ou, S.; Jia, K.; Yuan, L.; Li, S. First description of hepacivirus and pegivirus infection in domestic Horses in China: A study in guangdong province, heilongjiang province and Hong Kong district. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postel, A.; Cavalleri, J.M.V.; Pfaender, S.; Walter, S.; Steinmann, E.; Fischer, N.; Feige, K.; Haas, L.; Becher, P. Frequent presence of hepaci and pegiviruses in commercial equine serum pools. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 182, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Fu, C.; Huang, J.; Xu, H.; Wu, P.; Ping, X.; Li, S. Molecular characterization of a genetically divergent equine pegivirus strain identified in China. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Zhu, N.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Wan, Z.; Cai, Q.; Yu, S.; Tang, S. Identification and genetic characterization of equine Pegivirus in China. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.S.; de Moraes, M.V.D.S.; Soares, C.C.; Chalhoub, F.L.L.; de Filippis, A.M.B.; dos Santos, D.R.L.; de Almeida, F.Q.; Godoi, T.L.O.S.; de Souza, A.M.; Burdman, T.R.; et al. First description of Theiler’s disease-associated virus infection and epidemiological investigation of equine pegivirus and equine hepacivirus coinfection in Brazil. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1737–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.C.S.; Subramaniam, K.; McCulloch, S.D.; Goldstein, J.D.; Schaefer, A.M.; Fair, P.A.; Reif, J.S.; Bossart, G.D.; Waltzek, T.B. Genomic characterization of a novel pegivirus species from free-ranging bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in the Indian River Lagoon, Florida. Virus Res. 2019, 263, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Merits, A.; Simmonds, P.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; et al. The First Nonmammalian Pegivirus Demonstrates Efficient In Vitro Replication and High Lymphotropism. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01150-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divers, T.J.; Tomlinson, J.E.; Tennant, B.C. The history of Theiler’s disease and the search for its aetiology. Vet. J. 2022, 287, 105878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, J.E.; Tennant, B.C.; Struzyna, A.; Mrad, D.; Browne, N.; Whelchel, D.; Johnson, P.J.; Jamieson, C.; Löhr, C.V.; Bildfell, R.; et al. Viral testing of 10 cases of Theiler’s disease and 37 in-contact horses in the absence of equine biologic product administration: A prospective study (2014–2018). J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, J.E.; Kapoor, A.; Kumar, A.; Tennant, B.C.; Laverack, M.A.; Beard, L.; Delph, K.; Davis, E.; Schott, H.; Lascola, K.; et al. Viral testing of 18 consecutive cases of equine serum hepatitis: A prospective study (2014–2018). J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Huang, J.; Yang, Q.; Xu, H.; Wu, P.; Fu, C.; Li, S. Identification and genetic characterization of hepacivirus and pegivirus in commercial equine serum products in China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altan, E.; Li, Y.; Sabino-Santos, G., Jr.; Sawaswong, V.; Barnum, S.; Pusterla, N.; Deng, X.; Delwart, E. Viruses in Horses with Neurologic and Respiratory Diseases. Viruses 2019, 11, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paim, W.P.; Weber, M.N.; Cibulski, S.P.; da Silva, M.S.; Puhl, D.E.; Budaszewski, R.F.; Varela, A.P.M.; Mayer, F.Q.; Canal, C.W. Characterization of the viral genomes present in commercial batches of horse serum obtained by high-throughput sequencing. Biologicals 2019, 61, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalleri, J.M.V.; Korbacska-Kutasi, O.; Leblond, A.; Paillot, R.; Pusterla, N.; Steinmann, E.; Tomlinson, J. European College of Equine Internal Medicine consensus statement on equine flaviviridae infections in Europe. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2022, 36, 1858–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, M.; Oue, Y.; Murakami, S.; Kanno, T.; Bannai, H.; Tsujimura, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Kondo, T. Complete genome analysis of equine coronavirus isolated in Japan. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 2903–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusterla, N.; Vin, R.; Leutenegger, C.; Mittel, L.D.; Divers, T.J. Equine coronavirus: An emerging enteric virus of adult horses. Equine Vet. Educ. 2016, 28, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; De Groot, R.J.; Haagmans, B.; Lau, S.K.P.; Neuman, B.W.; Perlman, S.; Sola, I.; Van Der Hoek, L.; Wong, A.C.P.; Yeh, S.H. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Coronaviridae 2023. J. Gen. Virol. 2023, 104, 001843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzo, G.; Drigo, M.; Legnardi, M.; Grassi, L.; Pasotto, D.; Menandro, M.L.; Cecchinato, M.; Tucciarone, C.M. Bovine coronavirus: Variability, evolution, and dispersal patterns of a no longer neglected betacoronavirus. Viruses 2020, 12, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlasova, A.N.; Saif, L.J. Bovine Coronavirus and the Associated Diseases. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 643220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Díaz, J.C.; Piñeyro, P.E.; Houston, E.; Zimmerman, J.; Giménez-Lirola, L.G. Porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus: A review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Vlasova, A.N.; Kenney, S.P.; Saif, L.J. Emerging and re-emerging coronaviruses in pigs. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, S.J.; Weiss, S.R. Pathogenesis of murine coronavirus in the central nervous system. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010, 5, 336–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, S.; Ludewig, B.; Pikor, N.B. Insights into coronavirus immunity taught by the murine coronavirus. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Kulcsar, K.; Misra, V.; Frieman, M.; Mossman, K. Bats and coronaviruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Liu, Z.; Chen, D. Human coronaviruses: Origin, host and receptor. J. Clin. Virol. 2022, 155, 105246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guy, J.S.; Snijder, E.J.; Denniston, D.A.; Timoney, P.J.; Balasuriya, U.B.R. Genomic characterization of equine coronavirus. Virology 2007, 369, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oue, Y.; Ishihara, R.; Edamatsu, H.; Morita, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Yoshima, M.; Hatama, S.; Murakami, K.; Kanno, T. Isolation of an equine coronavirus from adult horses with pyrogenic and enteric disease and its antigenic and genomic characterization in comparison with the NC99 strain. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 150, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusterla, N.; Mapes, S.; Wademan, C.; White, A.; Ball, R.; Sapp, K.; Burns, P.; Ormond, C.; Butterworth, K.; Bartol, J.; et al. Emerging outbreaks associated with equine coronavirus in adult horses. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miszczak, F.; Tesson, V.; Kin, N.; Dina, J.; Balasuriya, U.B.R.; Pronost, S.; Vabret, A. First detection of equine coronavirus (ECoV) in Europe. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slovis, N.M.; Elam, J.; Estrada, M.; Leutenegger, C.M. Infectious agents associated with diarrhoea in neonatal foals in central Kentucky: A comprehensive molecular study. Equine Vet. J. 2014, 46, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijman, L.J.; James, K.; Mapes, S.M.; Theelen, M.J.P.; Pusterla, N. Seroprevalence and risk factors for infection with equine coronavirus in healthy horses in the USA. Vet. J. 2017, 220, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, J.; Marr, C.M.; MacKenzie, C.J.; Mair, T.S.; Fletcher, A.; Cash, R.; Phillips, M.; Pusterla, N.; Mapes, S.; Foote, A.K. Detection of equine coronavirus in horses in the United Kingdom. Vet. Rec. 2019, 184, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusterla, N.; James, K.; Mapes, S.; Bain, F. Frequency of molecular detection of equine coronavirus in faeces and nasal secretions in 277 horses with acute onset of fever. Vet. Rec. 2019, 184, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, M.G.; Kwon, S.Y.; Pusterla, N.; Gold, J.R.; Bain, F.; Evermann, J. Evaluation of equine coronavirus fecal shedding among hospitalized horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattei, D.N.; Kopper, J.J.; Sanz, M.G. Equine Coronavirus-Associated Colitis in Horses: A Retrospective Study. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2020, 87, 102906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambayashi, Y.; Bannai, H.; Tsujimura, K.; Hirama, A.; Ohta, M.; Nemoto, M. Outbreak of equine coronavirus infection among riding horses in Tokyo, Japan. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 77, 101668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schvartz, G.; Tirosh-Levy, S.; Barnum, S.; David, D.; Sol, A.; Pusterla, N.; Steinman, A. Seroprevalence and risk factors for exposure to equine coronavirus in apparently healthy horses in israel. Animals 2021, 11, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouché, N.; Remy-Wohlfender, F.; Blau, D.; Franzen, J.; Gurtner, C.; Seuberlich, T.; Unger, L.; Gerber, V. Characterization of an outbreak of equine coronavirus infection in adult horses in Switzerland. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2022, 164, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusterla, N.; Vin, R.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Mittel, L.D.; Divers, T.J. Enteric coronavirus infection in adult horses. Vet. J. 2018, 231, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berryhill, E.H.; Magdesia, K.G.; Aleman, M.; Pusterla, N. Clinical presentation, diagnostic findings, and outcome of adult horses with equine coronavirus infection at a veterinary teaching hospital: 33 cases (2012–2018). Vet. J. 2019, 248, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambayashi, Y.; Nemoto, M.; Tsujimura, K.; Ohta, M.; Bannai, H. Serosurveillance of equine coronavirus infection among Thoroughbreds in Japan. Equine Vet. J. 2023, 55, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusterla, N. Equine Coronaviruses. Vet. Clin. N. Am.—Equine Pract. 2023, 39, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, C.L.; Higgins, J.K.; Higgins, J.C.; Mcintosh, S.; Scott, E.; Giannitti, F.; Mete, A.; Pusterla, N. Disease Associated with Equine Coronavirus Infection and High Case Fatality Rate. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannitti, F.; Diab, S.; Mete, A.; Stanton, J.B.; Fielding, L.; Crossley, B.; Sverlow, K.; Fish, S.; Mapes, S.; Scott, L.; et al. Necrotizing Enteritis and Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy Associated With Equine Coronavirus Infection in Equids. Vet. Pathol. 2015, 52, 1148–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, M.; Oue, Y.; Morita, Y.; Kanno, T.; Kinoshita, Y.; Niwa, H.; Ueno, T.; Katayama, Y.; Bannai, H.; Tsujimura, K.; et al. Experimental inoculation of equine coronavirus into Japanese draft horses. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 3329–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, E.; Harms, C.; Viner, M.; Barnum, S.; Pusterla, N. Investigation of an experimental infection model of equine coronavirus in adult horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 2099–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambayashi, Y.; Kishi, D.; Ueno, T.; Ohta, M.; Bannai, H.; Tsujimura, K.; Kinoshita, Y.; Nemoto, M. Distribution of equine coronavirus RNA in the intestinal and respiratory tracts of experimentally infected horses. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusterla, N.; Holzenkaempfer, N.; Mapes, S.; Kass, P. Prevalence of equine coronavirus in nasal secretions from horses with fever and upper respiratory tract infection. Vet. Rec. 2015, 177, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepworth-Warren, K.L.; Erwin, S.J.; Moore, C.B.; Talbot, J.R.; Young, K.A.S.; Neault, M.J.; Haugland, J.C.; Robertson, J.B.; Blikslager, A.T. Risk factors associated with an outbreak of equine coronavirus at a large farm in North Carolina. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1060759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzewnioková, P.; Festa, F.; Panzarin, V.; Lelli, D.; Moreno, A.; Zecchin, B.; De Benedictis, P.; Leopardi, S. Best molecular tools to investigate coronavirus diversity in mammals: A comparison. Viruses 2021, 13, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausch, T.; Fritz, M.H.Y.; Untergasser, A.; Benes, V. Tracy: Basecalling, alignment, assembly and deconvolution of sanger chromatogram trace files. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, L.; Luo, X.; Chen, M.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; Dai, Z.; Lam, T.T.; Guan, Y.; Yu, G. Ggtree: A serialized data object for visualization of a phylogenetic tree and annotation data. iMeta 2022, 1, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaev, A.S.; Chong, S.; Novikov, A.; Kongpachith, A.; Masiarz, F.R.; Lim, M.; Kim, J.P. Hepatitis G Virus Encodes Protease Activities Which Can Effect Processing of the Virus Putative Nonstructural Proteins. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, P.F.; Gao, X.Y.; Ji, J.K.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.H.; Cheng, K.H.; Cui, N.; Zhu, M.L.; Hu, T.; Dong, X.; et al. Identification of a recombinant equine coronavirus in donkey, China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, J.D.; Evanoff, R.; Wilkinson, T.E.; Divers, T.J.; Knowles, D.P.; Mealey, R.H. Experimental transmission of equine hepacivirus in horses as a model for hepatitis C virus. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample ID | Horse Population | Virus Identified | Accession Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50638/48 | CC | Equine coronavirus | OR166386 |
| 2 | 8844/46 | CC | Pegivirus equi | OR772901 |
| 3 | 8844/48 | CC | Pegivirus equi | OR772902 |
| 4 | 75424/6 | IA | Pegivirus equi | OR772903 |
| 5 | 75424/5 | IA | Pegivirus equi | OR772904 |
| 6 | 84400/11 | IA | Pegivirus caballi | OR772905 |
| 7 | 77362/13 | IA | Pegivirus equi | OR772906 |
| 8 | 76019/16 | IA | Pegivirus equi | OR772907 |
| 9 | 75424/11 | IA | Pegivirus equi | OR772908 |
| 10 | 76019/22 | IA | Pegivirus equi | OR772909 |
| 11 | 76019/23 | IA | Pegivirus equi | OR772910 |
| Protein A.N. | Query Cover | E-Value | Ident% | Nucleotide A.N. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPE03507.1 | 100% | 2 × 10−87 | 100.00 | OR772908.1 |
| WPE03501.1 | 99% | 1 × 10−86 | 100.00 | OR772902.1 |
| WPE03509.1 | 97% | 3 × 10−85 | 100.00 | OR772910.1 |
| WPE03502.1 | 97% | 3 × 10−85 | 100.00 | OR772903.1 |
| AGH70217.1 | 100% | 2 × 10−77 | 99.15 | KC145265.1 |
| Nucleotide A.N. | Query Cover | E-Value | Ident% | Isolate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC061273.1 | 100% | 0.0 | 99.49 | Obihiro12-1 |
| LC061274.1 | 100% | 0.0 | 99.49 | Obihiro12-2 |
| MZ562881.1 | 100% | 0.0 | 99.24 | CH21 isolate Haribo |
| EF446615.1 | 100% | 0.0 | 99.24 | NC99 |
| LC061272.1 | 100% | 0.0 | 98.99 | Tokachi09 |
| KY458232.1 | 100% | 0.0 | 98.48 | |
| OL770366.1 | 100% | 0.0 | 97.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ricci, I.; Rosone, F.; Pacchiarotti, G.; Manna, G.; Cersini, A.; Carvelli, A.; La Rocca, D.; Cammalleri, E.; Giordani, R.; Tofani, S.; et al. Pegiviruses and Coronavirus: Biomolecular Prevalence and Phylogenetic Analysis of Strains Detected in Italian Horse Populations. Viruses 2025, 17, 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081076
Ricci I, Rosone F, Pacchiarotti G, Manna G, Cersini A, Carvelli A, La Rocca D, Cammalleri E, Giordani R, Tofani S, et al. Pegiviruses and Coronavirus: Biomolecular Prevalence and Phylogenetic Analysis of Strains Detected in Italian Horse Populations. Viruses. 2025; 17(8):1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081076
Chicago/Turabian StyleRicci, Ida, Francesca Rosone, Giulia Pacchiarotti, Giuseppe Manna, Antonella Cersini, Andrea Carvelli, Davide La Rocca, Elisa Cammalleri, Roberta Giordani, Silvia Tofani, and et al. 2025. "Pegiviruses and Coronavirus: Biomolecular Prevalence and Phylogenetic Analysis of Strains Detected in Italian Horse Populations" Viruses 17, no. 8: 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081076
APA StyleRicci, I., Rosone, F., Pacchiarotti, G., Manna, G., Cersini, A., Carvelli, A., La Rocca, D., Cammalleri, E., Giordani, R., Tofani, S., Conti, R., Rombolà, P., Nardini, R., Minniti, C. A., Caforio, R., Linardi, B., & Scicluna, M. T. (2025). Pegiviruses and Coronavirus: Biomolecular Prevalence and Phylogenetic Analysis of Strains Detected in Italian Horse Populations. Viruses, 17(8), 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081076







