High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals the Mycoviral Diversity of the Pathogenic Grape Fungus Penicillium astrolabium During Postharvest
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Isolates and Culture Conditions
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction and Isolates Harboring Mycoviruses Screening
2.3. RNA Extraction, Sequencing Library Preparation, and RNA-Seq
2.4. High-Throughput Sequencing and Data Processing and Analysis
2.5. Analysis of Conserved Domains of Viral RdRps and Phylogenetic Tree Construction
3. Results
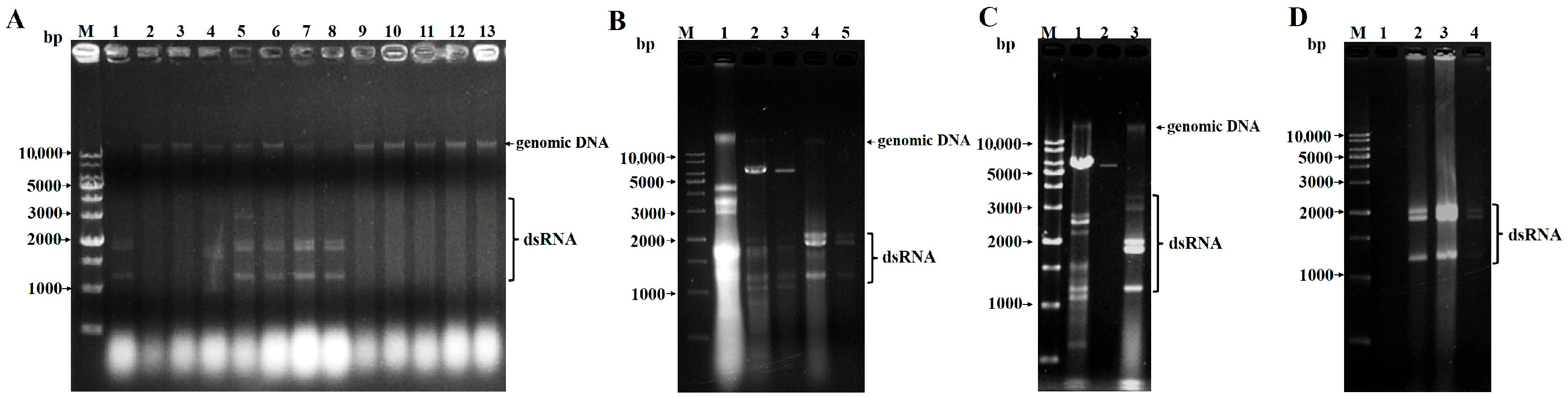
3.1. Screening of P. astrolabium Strains Harboring Viruses
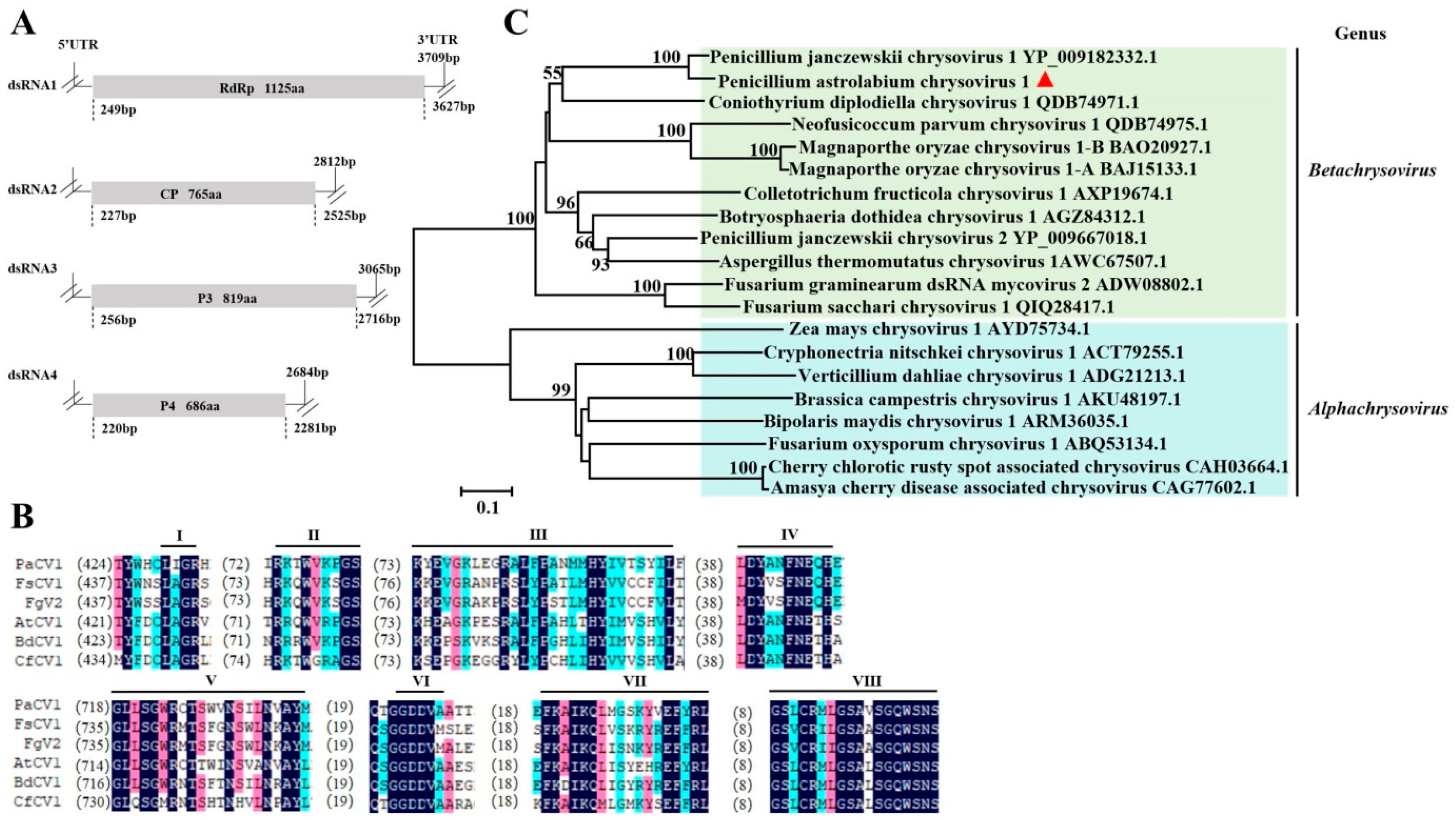
3.2. Sequence Analysis of the Chrysoviridae Virus
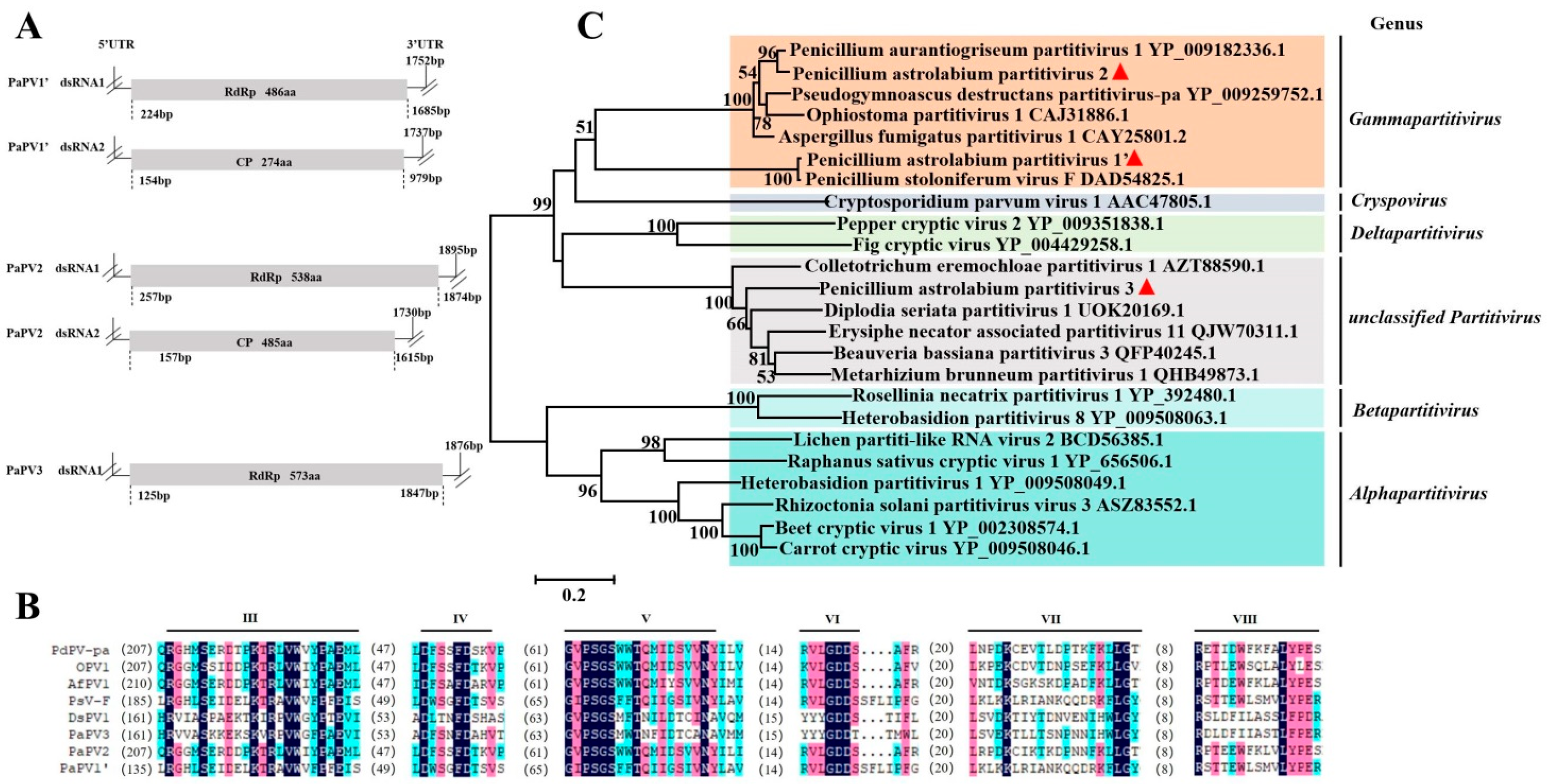
3.3. Sequence Analysis of the Partitiviridae Virus
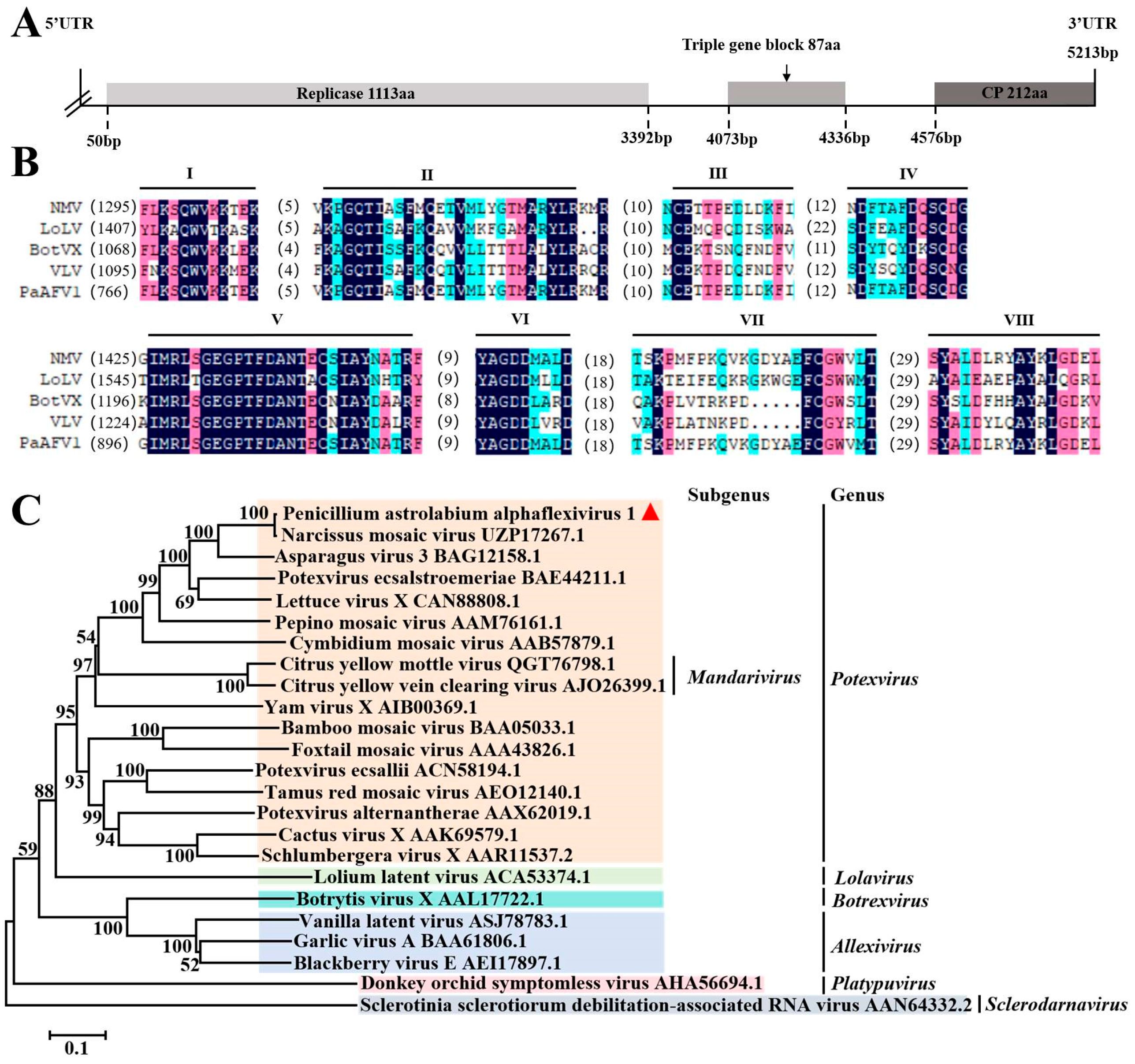
3.4. Sequence Analysis of the Alphaflexiviridae Virus
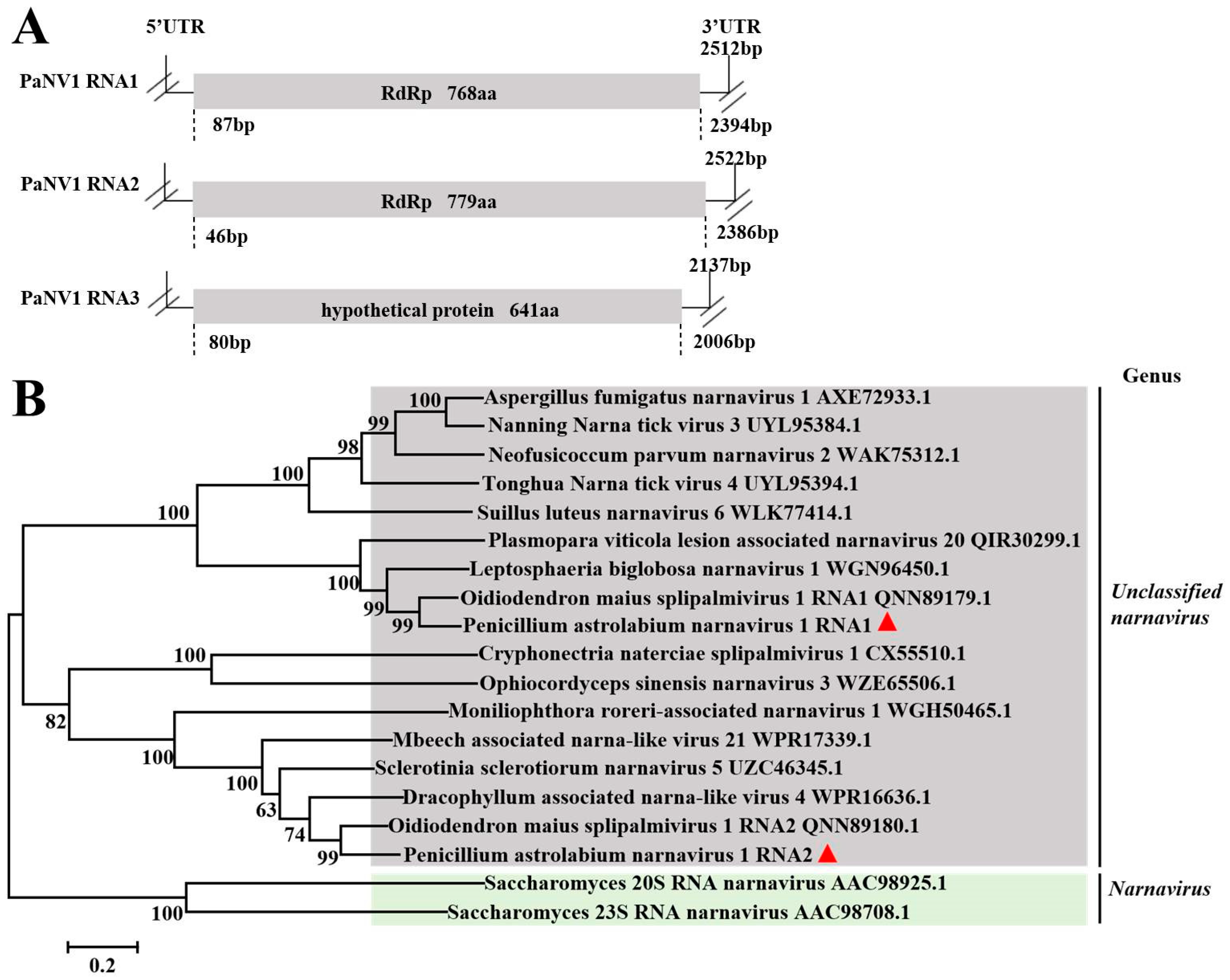
3.5. Sequence Analysis of the Narnaviridae Virus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| +ssRNA | positive single-stranded RNA |
| aa | amino acid |
| AfPV1 | Aspergillus fumigatus partitivirus 1 |
| AtCV1 | Aspergillus thermomutatus chrysovirus 1 |
| BdCV1 | Botryosphaeria dothidea chrysovirus 1 |
| BotVX | Botrytis virus X |
| CfCV1 | Colletotrichum fructicola chrysovirus 1 |
| CHV1 | Cryphonectria hypovirus 1 |
| CMV | cucumber mosaic virus |
| CP | coat protein |
| DsPV1 | Diplodia seriata partitivirus 1 |
| dsRNA | double-stranded RNA |
| FgV2 | Fusarium graminearum dsRNA mycovirus 2 |
| FsCV1 | Fusarium sacchari chrysovirus 1 |
| ICTV | International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses |
| LoLV | Lolium latent virus |
| NGS | next-generation sequencing |
| NMV | Narcissus mosaic virus |
| NP1 | nonstructural protein 1 |
| OPV1 | Ophiostoma partitivirus 1 |
| ORF | open reading frame |
| PaAFV1 | Penicillium astrolabium alphaflexivirus 1 |
| PaCV1 | Penicillium astrolabium chrysovirus 1 |
| PaNV1 RNA1 | Penicillium astrolabium narnavirus 1 RNA1 |
| PaNV1 RNA2 | Penicillium astrolabium narnavirus 1 RNA2 |
| PaPV1ʹ | Penicillum astrolabium partitivirus 1ʹ |
| PaPV2 | Penicillum astrolabium partitivirus 2 |
| PaPV3 | Penicillum astrolabium partitivirus 3 |
| PcV | Penicillium chrysogenum virus |
| PdNLV1 | Penicillium digitatum Narna-like virus 1 |
| PdPMV1 | Penicillium digitatum polymycovirus 1 |
| PdPV-pa | Pseudogymnoascus destructans partitivirus-pa |
| PdV | Penicillium discovirus |
| PjCV1 | Penicillium janczewskii chrysovirus 1 |
| PrNssV1 | Penicillium roseopurpureum negative ssRNA virus 1 |
| PsV-F | Penicillium stoloniferum virus F |
| PsV-S | Penicillium stoloniferum virus S |
| RdRp | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| Rep | replicase |
| ssDNA | single-stranded DNA |
| SsHADV-1 | Sclerotinia sclerotiorum hypovirulence-associated DNA virus 1 |
| SsHADV1_PO | Sclerotinia sclerotiorum hypovirulence-associated DNA virus 1_Penicillium olsonii |
| -ssRNA | negative single-stranded RNA |
| ssRNA-RT | reverse-transcribing single-stranded RNA |
| TGB1 | Triple Gene Block 1 |
| VLV | Vanilla latent virus |
| SsPV1 | Sclerotinia sclerotiorum partitivirus 1 |
References
- Jiang, C.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, C. Inhibition of Aspergillus carbonarius and fungal contamination in table grapes using Bacillus subtilis. Food Control 2014, 35, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Zhang, T.; Wen, G.; Song, B.; Jiang, S. First report of Penicillium olsonii causing postharvest fruit rot of grape (Vitis vinifera) in China. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, R.; Peterson, S.W. Penicillium astrolabium and Penicillium neocrassum, two new species isolated from grapes and their phylogenetic placement in the P. olsonii and P. brevicompactum clade. Mycologia 2007, 99, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.X.; Jiang, T.; Gong, L.Z.; Sun, Z.H.; Lyu, L.A. Diversity of Botrytis cinerea in major grape production regions of Hubei Province. J. South. Agric. 2022, 5, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabrial, S.A.; Suzuki, N.J. Viruses of plant pathogenic fungi. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2009, 47, 353–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollings, M. Viruses associated with a die-back disease of cultivated mushroom. Nature 1962, 196, 962–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabrial, S.; Suzuki, N. Fungal viruses. In Encyclopedia of Virology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 1–5, pp. V2-284–V2-291. [Google Scholar]
- Nuss, D.L. Hypovirulence: Mycoviruses at the fungal–plant interface. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostakis, S.L. Biological control of chestnut blight. Science 1982, 215, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, S.; Salaipeth, L.; Lin, Y.H.; Sasaki, A.; Kanematsu, S.; Suzuki, N. A novel bipartite double-stranded RNA mycovirus from the white root rot fungus Rosellinia necatrix: Molecular and biological characterization, taxonomic considerations, and potential for biological control. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12801–12812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, B.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Li, G.; Peng, Y.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Huang, J.; et al. A geminivirus-related DNA mycovirus that confers hypovirulence to a plant pathogenic fungus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8387–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, B.; Fu, Y.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Li, G.; Yi, X.; Jiang, D. Extracellular transmission of a DNA mycovirus and its use as a natural fungicide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xie, J.; Fu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Qu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Cheng, S.; Chen, T.; Li, B.; Wang, Q.; et al. A 2-kb mycovirus converts a pathogenic fungus into a beneficial endophyte for Brassica protection and yield enhancement. Mol. Plant. 2020, 13, 1420–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Kotta-Loizou, I.; Dong, K.; Li, S.; Ni, D.; Hong, N.; Wang, G.; Xu, W. A mycovirus modulates the endophytic and pathogenic traits of a plant associated fungus. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1893–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Xie, J.; Chen, T.; Li, B.; Jiang, D. Transcriptional responses of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum to the infection by SsHADV-1. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghabrial, S.A.; Castón, J.R.; Coutts, R.H.A.; Hillman, B.I.; Jiang, D.; Kim, D.H.; Moriyama, H. Corrigendum: ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Chrysoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andika, I.B.; Tian, M.; Bian, R.; Cao, X.; Luo, M.; Kondo, H.; Sun, L. Cross-kingdom interactions between plant and fungal viruses. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2023, 1, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotta-Loizou, I.; Castón, J.R.; Coutts, R.H.A.; Hillman, B.I.; Jiang, D.; Kim, D.H.; Moriyama, H.; Suzuki, N. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Chrysoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.B.; Lu, W.H.; Lin, Y.; Luo, J.Z. Development and application of transcriptome sequencing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 35, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, K.B.; Holcomb, E.E.; Allscheid, R.L.; Carrington, J.C. Hiding in plain sight: New virus genomes discovered via a systematic analysis of fungal public transcriptomes. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, K.M. Genome organization and expression of the Penicillium stoloniferum virus S. Virus Genes 2003, 27, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Li, N.; Yuan, Y.; Cao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Tan, B.; Li, G.; Liu, D. Blue-white colony selection of virus-infected isogenic recipients based on a chrysovirus isolated from Penicillium italicum. Virol. Sin. 2019, 34, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Mao, J.; Yang, Z.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, D. Characterization of two novel mycoviruses from Penicillium digitatum and the related fungicide resistance analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerva, L.; Ciuffo, M.; Vallino, M.; Margaria, P.; Varese, G.C.; Gnavi, G.; Turina, M. Multiple approaches for the detection and characterization of viral and plasmid symbionts from a collection of marine fungi. Virus Res. 2016, 219, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Geng, H.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, M.; Mao, J.; Zhang, T.; Niu, Y.; Liu, D. Molecular characterization of a new gammapartitivirus isolated from the citrus-pathogenic fungus Penicillium digitatum. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 3185–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, D. Isolation and characterization of a novel mycovirus from Penicillium digitatum. Virology 2016, 494, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerva, L.; Silvestri, A.; Ciuffo, M.; Palmano, S.; Varese, G.C.; Turina, M. Transmission of Penicillium aurantiogriseum partiti-like virus 1 to a new fungal host (Cryphonectria parasitica) confers higher resistance to salinity and reveals adaptive genomic changes. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 4480–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, K.W.; Girvan, R.F. Comparison of the biophysical and biochemical properties of Penicillium cyaneo-fulvum virus and Penicillium chrysogenum virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1977, 34, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, H.; Bozarth, R.F.; Mislivec, P.B. Viruslike particles associated with an isolate of Penicillium brevi-compactum. Virology 1971, 44, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Choi, E.Y.; Lee, J.I. Genome organization and expression of the Penicillium stoloniferum virus F. Virus Genes 2005, 31, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Pappu, H.R.; Vandemark, G.J.; Chen, W. Genome sequence of sclerotinia sclerotiorum hypovirulence-associated DNA virus 1 found in the fungus penicillium olsonii isolated from Washington State, USA. Microbiol. Resour. Ann. 2022, 11, e00019-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Ghabrial, S.A. Molecular characterization of Penicillium chrysogenum virus: Reconsideration of the taxonomy of the genus Chrysovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, T.J.; Dodds, J.A. Isolation and analysis of double-stranded RNA from virus-infected plant and fungal tissue. Phytopathology 1979, 69, 854–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Toh, H. Recent developments in the MAFFT multiple sequence alignment program. Brief. Bioinform. 2008, 9, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vainio, E.J.; Chiba, S.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Maiss, E.; Roossinck, M.; Sabanadzovic, S.; Suzuki, N.; Xie, J.; Nibert, M. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Partitiviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuze, J.F.; Vaira, A.M.; Menzel, W.; Candresse, T.; Zavriev, S.K.; Hammond, J.; Hyun Ryu, K. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Alphaflexiviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 699–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutela, S.; Forgia, M.; Vainio, E.J.; Chiapello, M.; Daghino, S.; Vallino, M.; Martino, E.; Girlanda, M.; Perotto, S.; Turina, M. The virome from a collection of endomycorrhizal fungi reveals new viral taxa with unprecedented genome organization. Virus Evol. 2020, 6, veaa076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poimala, A.; Parikka, P.; Hantula, J.; Vainio, E.J. Viral diversity in Phytophthora cactorum population infecting strawberry. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 5200–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Li, N.; Cao, Q.; Li, G.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, D. Molecular characterization of a chrysovirus isolated from the citrus pathogen Penicillium crustosum and related fungicide resistance analysis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, H.; Urayama, S.I.; Higashiura, T.; Le, T.M.; Komatsu, K. Chrysoviruses in Magnaporthe oryzae. Viruses 2018, 10, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Q.; Yao, Z. The Interaction between hypovirulence-associated chrysoviruses and their host Fusarium species. Viruses 2024, 16, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzanetakis, I.E.; Price, R.; Martin, R.R. Nucleotide sequence of the tripartite Fragaria chiloensis cryptic virus and presence of the virus in the Americas. Virus Genes 2008, 36, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Cheng, J.; Tang, J.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Baker, T.S.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Xie, J. A novel partitivirus that confers hypovirulence on plant pathogenic fungi. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10120–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghabrial, S.A.; Castón, J.R.; Jiang, D.; Nibert, M.L.; Suzuki, N. 50-plus years of fungal viruses. Virology 2015, 479, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roossinck, M.J. Evolutionary and ecological links between plant and fungal viruses. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Kondo, H.; Andika, I.B. Cross-kingdom virus infection. In Encyclopedia of Virology, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 1–5, pp. 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wei, D.; Jiang, D.; Fu, Y.; Li, G.; Ghabrial, S.; Peng, Y. Characterization of debilitation-associated mycovirus infecting the plant-pathogenic fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howitt, R.L.J.; Beever, R.E.; Pearson, M.N.; Forster, R.L.S. Genome characterization of Botrytis virus F, a flexuous rod-shaped mycovirus resembling plant ‘potex-like’ viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howitt, R.L.J.; Beever, R.E.; Pearson, M.N.; Forster, R.L.S. Genome characterization of a flexuous rod-shaped mycovirus, Botrytis virus X, reveals high amino acid identity to genes from plant ‘potex-like’ viruses. Arch. Virol. 2006, 151, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Liu, J.; Pang, J.; Kondo, H.; Chi, S.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Andika, I.B. Common but nonpersistent acquisitions of plant viruses by plant-associated fungi. Viruses 2022, 14, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andika, I.B.; Wei, S.; Cao, C.; Salaipeth, L.; Kondo, H.; Sun, L. Phytopathogenic fungus hosts a plant virus: A naturally occurring cross-kingdom viral infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12267–12272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espino-Vázquez, A.N.; Bermúdez-Barrientos, J.R.; Cabrera-Rangel, J.F.; Córdova-López, G.; Cardoso-Martínez, F.; Martínez-Vázquez, A.; Camarena-Pozos, D.A.; Mondo, S.J.; Pawlowska, T.E.; Abreu-Goodger, C.; et al. Narnaviruses: Novel players in fungal-bacterial symbioses. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1743–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, B.I.; Cai, G. The family narnaviridae: Simplest of RNA viruses. Adv. Virus. Res. 2013, 86, 149–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Wen, G.; Liu, X.; Luo, Y.; Chang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, T. High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals the Mycoviral Diversity of the Pathogenic Grape Fungus Penicillium astrolabium During Postharvest. Viruses 2025, 17, 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081053
Wang R, Wen G, Liu X, Luo Y, Chang Y, Li G, Zhang T. High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals the Mycoviral Diversity of the Pathogenic Grape Fungus Penicillium astrolabium During Postharvest. Viruses. 2025; 17(8):1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081053
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Rui, Guoqin Wen, Xiaohong Liu, Yingqing Luo, Yanhua Chang, Guoqi Li, and Tingfu Zhang. 2025. "High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals the Mycoviral Diversity of the Pathogenic Grape Fungus Penicillium astrolabium During Postharvest" Viruses 17, no. 8: 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081053
APA StyleWang, R., Wen, G., Liu, X., Luo, Y., Chang, Y., Li, G., & Zhang, T. (2025). High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals the Mycoviral Diversity of the Pathogenic Grape Fungus Penicillium astrolabium During Postharvest. Viruses, 17(8), 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081053





