The Biophysical Basis for Karyopherin-Dependent Ebola Virus VP24 Nuclear Transport
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Protein Constructs and Peptides
2.2. Immunofluorescence Imaging
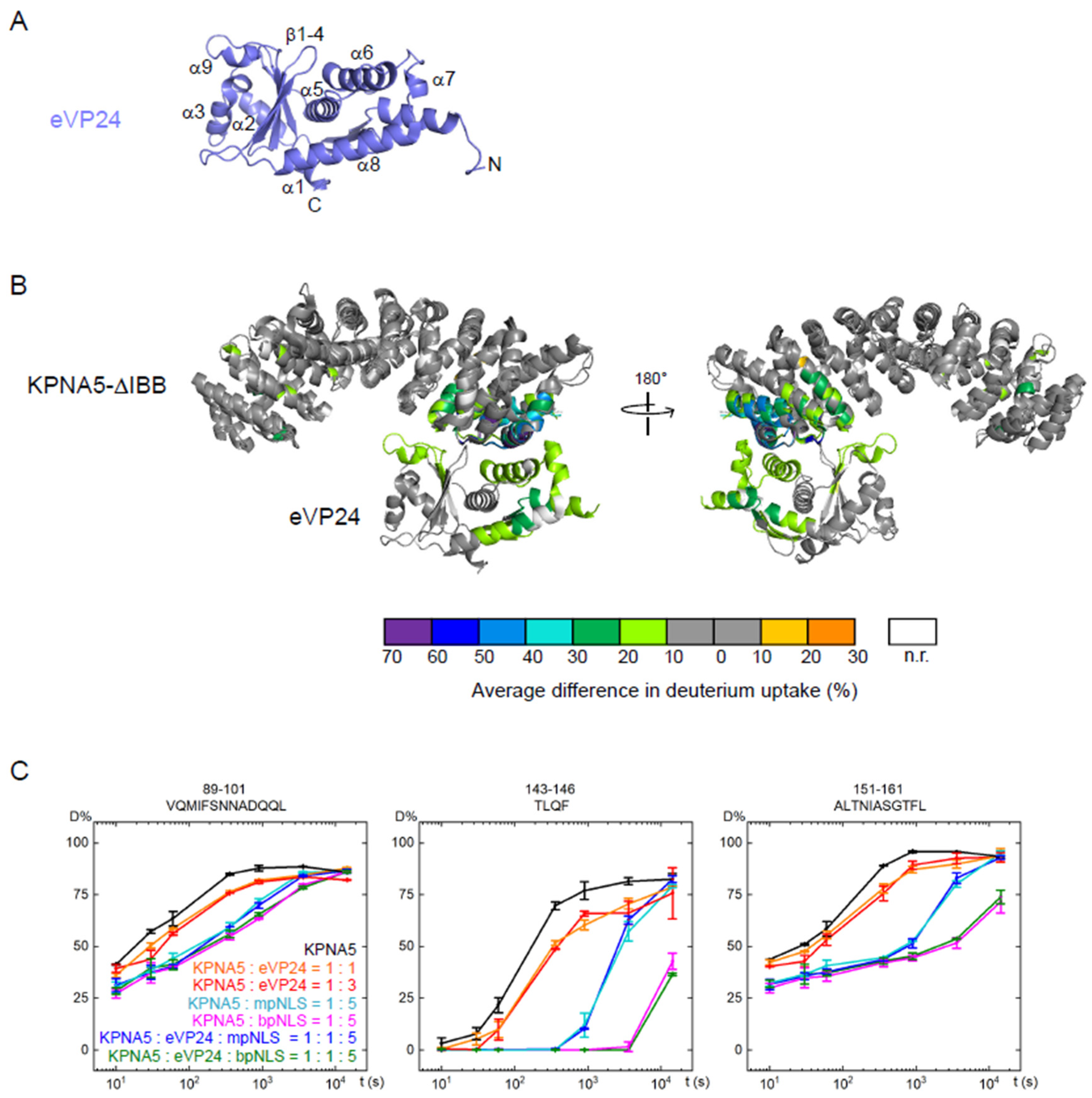
2.3. Hydrogen–Deuterium Exchange Mass Spectrometry (HDX-MS)
2.4. Native Mass Spectrometry
2.5. Fluorescence Polarization Assay
3. Results
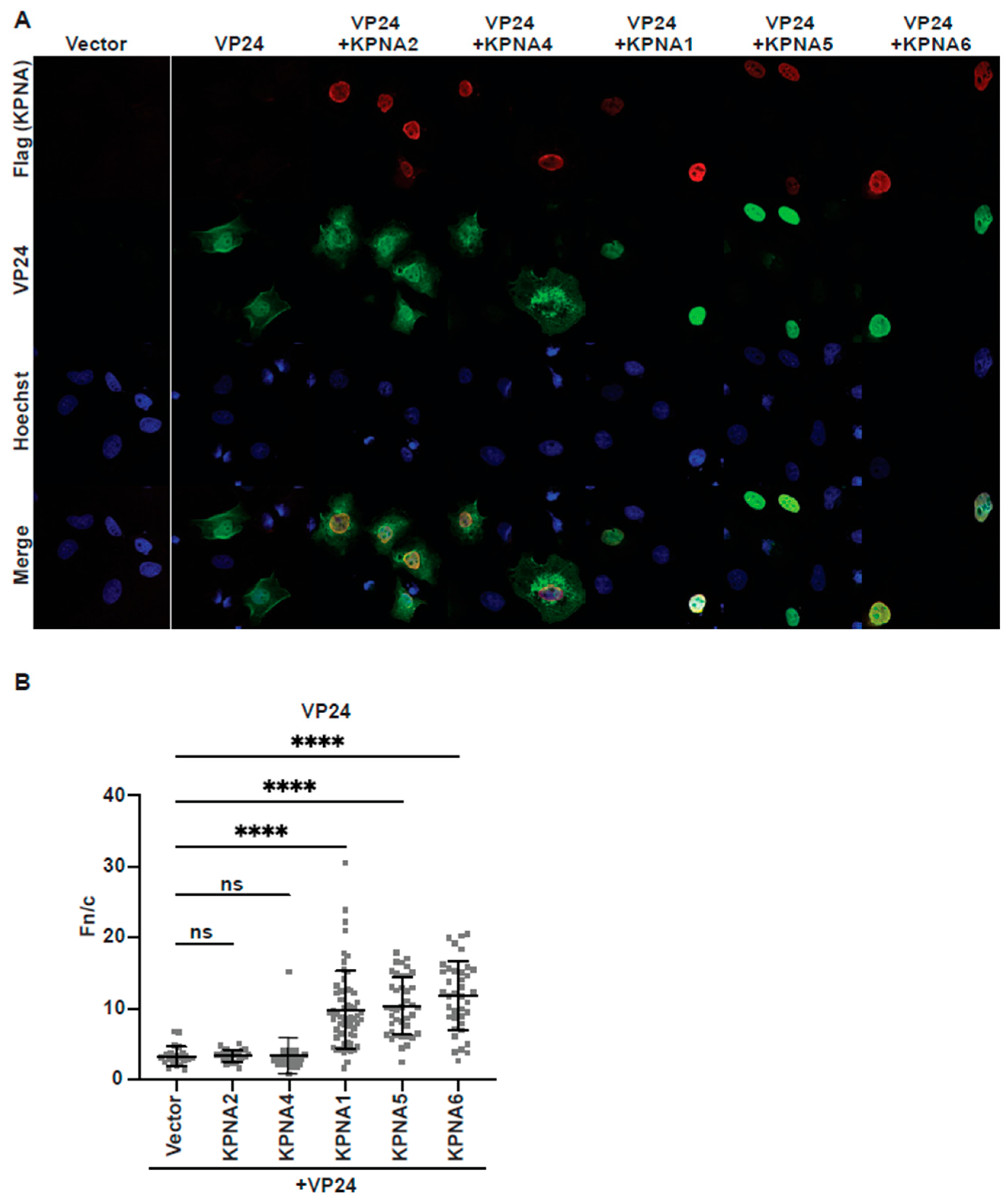
3.1. eVP24 Binding to C-Terminal ARMs of KPNA5 Is Not Sufficient for Nuclear Transport
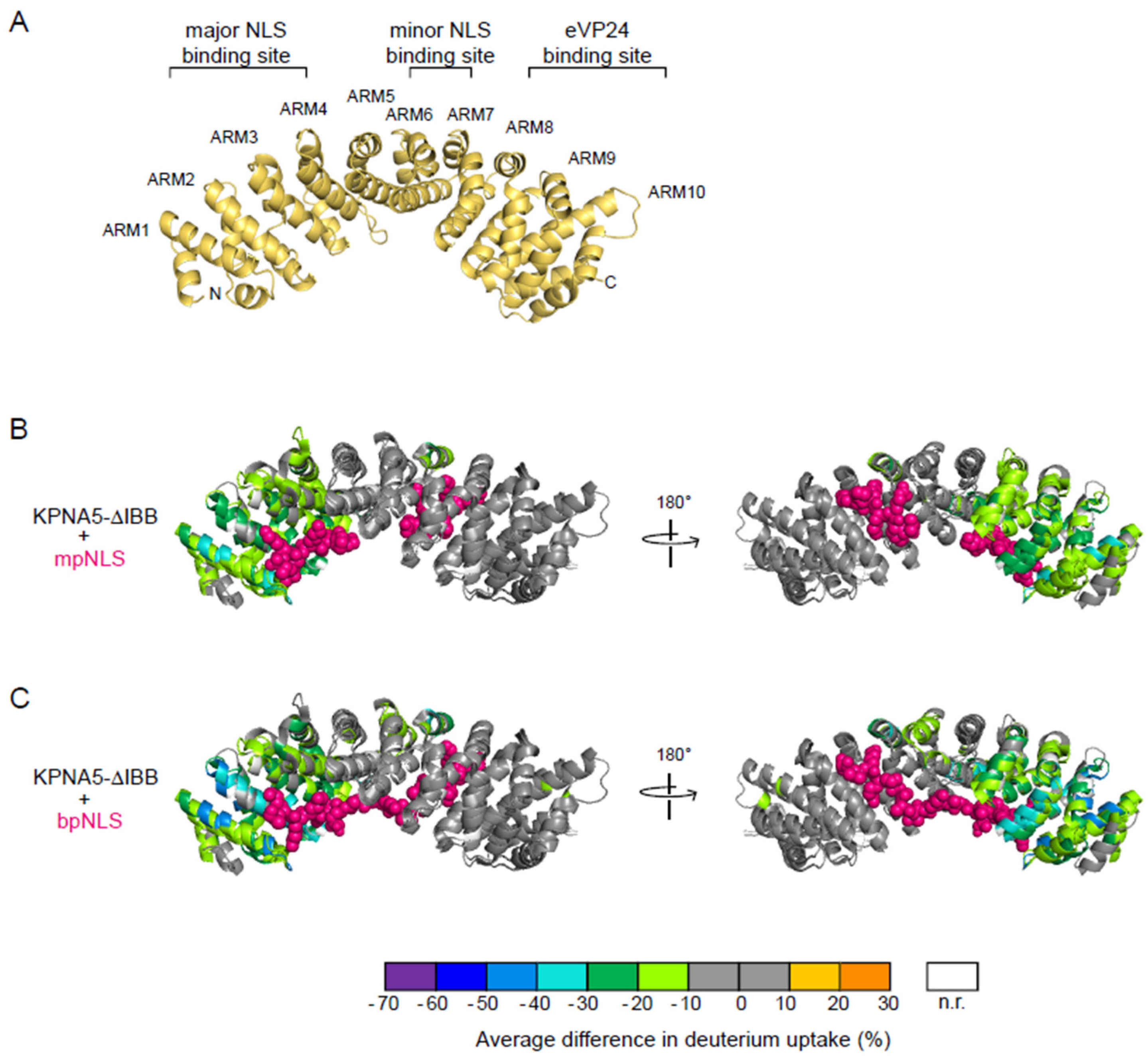
3.2. mpNLS and bpNLS Peptides Bind the N-Terminal ARMs of KPNA5
3.3. Binding of eVP24 Is Localized to the C-Terminal ARMs of KPNA5
3.4. Simultaneous Binding of eVP24 and cNLS Peptides on KPNA5
3.5. eVP24 Does Not Impact NLS Peptide Binding on KPNA5
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Letafati, A.; Ardekani, O.S.; Karami, H.; Soleimani, M. Ebola virus disease: A narrative review. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 181, 106213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobe, B. Autoinhibition by an internal nuclear localization signal revealed by the crystal structure of mammalian importin α. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1999, 6, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Yamada, K.; Yoneda, Y. Importin α: A key molecule in nuclear transport and non-transport functions. J. Biochem. 2016, 160, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, K.; Cingolani, G. The importin β binding domain as a master regulator of nucleocytoplasmic transport. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1578–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, E.; Uy, M.; Leighton, L.; Blobel, G.; Kuriyan, J. Crystallographic Analysis of the Recognition of a Nuclear Localization Signal by the Nuclear Import Factor Karyopherin α. Cell 1998, 94, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, E.; Kuriyan, J. Crystallographic analysis of the specific yet versatile recognition of distinct nuclear localization signals by karyopherin α. Structure 2000, 8, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, T.; Zhang, B.; Liu, S.; Song, W.; Qiao, J.; Ruan, H. Types of nuclear localization signals and mechanisms of protein import into the nucleus. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, L.; Chen, L.; Gong, B.; Jia, D.; Sun, Q. Nuclear transport proteins: Structure, function, and disease relevance. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, A.; Mills, R.E.; Lange, C.J.; Stewart, M.; Devine, S.E.; Corbett, A.H. Classical nuclear localization signals: Definition, function, and interaction with importin α. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 5101–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.H.C.; Briggs, L.J.; Hu, W.; Martin, T.J.; Gillespie, M.T.; Jans, D.A. Importin β Recognizes Parathyroid Hormone-related Protein with High Affinity and Mediates Its Nuclear Import in the Absence of Importin α. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 7391–7398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, K.M.; Banninger, G.; McDonald, C.; Reich, N.C. Regulated nuclear import of the STAT1 transcription factor by direct binding of importin-α. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, T.; Ebihara, H.; Muramoto, Y.; Fujii, K.; Takada, A.; Sagara, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kida, H.; Feldmann, H.; Kawaoka, Y. Assembly and Budding of Ebolavirus. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, A.; Moukambi, F.; Banadyga, L.; Groseth, A.; Callison, J.; Herwig, A.; Ebihara, H.; Feldmann, H.; Hoenen, T. A novel life cycle modeling system for Ebola virus shows a genome length-dependent role of VP24 in virus infectivity. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10511–10524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Boshra, H.; Sunyer, J.O.; Zwiers, S.H.; Paragas, J.; Harty, R.N. Biochemical and functional characterization of the Ebola virus VP24 protein: Implications for a role in virus assembly and budding. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banadyga, L.; Hoenen, T.; Ambroggio, X.; Dunham, E.; Groseth, A.; Ebihara, H. Ebola virus VP24 interacts with NP to facilitate nucleocapsid assembly and genome packaging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, Y.; Kolesnikova, L.; Becker, S. Ebola virus proteins NP, VP35, and VP24 are essential and sufficient to mediate nucleocapsid transport. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Zyla, D.; Parekh, D.; Hong, C.; Jones, Y.; Schendel, S.L.; Wan, W.; Castillon, G.; Saphire, E.O. Intracellular Ebola virus nucleocapsid assembly revealed by in situ cryo-electron tomography. Cell 2024, 187, 5587–5603.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita-Fujiharu, Y.; Hu, S.; Hirabayashi, A.; Takamatsu, Y.; Ng, Y.N.; Houri, K.; Muramoto, Y.; Nakano, M.; Sugita, Y.; Noda, T. Structural basis for Ebola virus nucleocapsid assembly and function regulated by VP24. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharat, T.A.; Noda, T.; Riches, J.D.; Kraehling, V.; Kolesnikova, L.; Becker, S.; Kawaoka, Y.; Briggs, J.A. Structural dissection of Ebola virus and its assembly determinants using cryo-electron tomography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4275–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, Y.; Matsunami, H.; Kawaoka, Y.; Noda, T.; Wolf, M. Cryo-EM structure of the Ebola virus nucleoprotein-RNA complex at 3.6Å resolution. Nature 2018, 563, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, A.L.; Bird, B.H.; Towner, J.S.; Antoniadou, Z.A.; Zaki, S.R.; Nichol, S.T. Inhibition of IRF-3 activation by VP35 is critical for the high level of virulence of ebola virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 2699–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.W.; Ginder, N.D.; Fulton, D.B.; Nix, J.; Basler, C.F.; Honzatko, R.B.; Amarasinghe, G.K. Structure of the Ebola VP35 interferon inhibitory domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.W.; Prins, K.C.; Borek, D.M.; Farahbakhsh, M.; Tufariello, J.M.; Ramanan, P.; Nix, J.C.; Helgeson, L.A.; Otwinowski, Z.; Honzatko, R.B.; et al. Structural basis for dsRNA recognition and interferon antagonism by Ebola VP35. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, K.C.; Binning, J.M.; Shabman, R.S.; Leung, D.W.; Amarasinghe, G.K.; Basler, C.F. Basic Residues Within the Ebolavirus VP35 Protein Are Required for Its Viral Polymerase Cofactor Function. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 10581–10591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.P.; Leung, L.W.; Hartman, A.L.; Martinez, O.; Shaw, M.L.; Carbonnelle, C.; Volchkov, V.E.; Nichol, S.T.; Basler, C.F. Ebola virus VP24 binds karyopherin α1 and blocks STAT1 nuclear accumulation. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5156–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, S.P.; Valmas, C.; Martinez, O.; Sanchez, F.M.; Basler, C.F. Ebola virus VP24 proteins inhibit the interaction of NPI-1 subfamily karyopherin α proteins with activated STAT1. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 13469–13477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyall, J.; Hart, B.J.; Postnikova, E.; Cong, Y.; Zhou, H.; Gerhardt, D.M.; Freeburger, D.; Michelotti, J.; Honko, A.N.; DeWald, L.E.; et al. Interferon-beta and Interferon-gamma Are Weak Inhibitors of Ebola Virus in Cell-Based Assays. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1416–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Edwards, M.R.; Borek, D.M.; Feagins, A.R.; Mittal, A.; Alinger, J.B.; Berry, K.N.; Yen, B.; Hamilton, J.; Brett, T.J.; et al. Ebola virus VP24 targets a unique NLS binding site on karyopherin alpha 5 to selectively compete with nuclear import of phosphorylated STAT1. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, T.M.; Edwards, M.R.; Diederichs, A.; Alinger, J.B.; Leung, D.W.; Amarasinghe, G.K.; Basler, C.F. VP24-Karyopherin Alpha Binding Affinities Differ between Ebolavirus Species, Influencing Interferon Inhibition and VP24 Stability. J. Virol. 2017, 91, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, M.; Reid, S.P.; Leung, L.W.; Basler, C.F.; Volchkov, V.E. Ebolavirus VP24 Binding to Karyopherins Is Required for Inhibition of Interferon Signaling. J. Virol. 2009, 84, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basler, C.F.; Amarasinghe, G.K. Evasion of Interferon Responses by Ebola and Marburg Viruses. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanan, P.; Shabman, R.S.; Brown, C.S.; Amarasinghe, G.K.; Basler, C.F.; Leung, D.W. Filoviral Immune Evasion Mechanisms. Viruses 2011, 3, 1634–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, A.R.; Todd, S.; Dearnley, M.; David, C.T.; Green, D.; Rawlinson, S.M.; Au, G.G.; Marsh, G.A.; Moseley, G.W. Antagonism of STAT3 signalling by Ebola virus. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes, M.R.M.; Teh, T.; Kobe, B. Structural basis of recognition of monopartite and bipartite nuclear localization sequences by mammalian importin-α 1 1 Edited by K. Nagai. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 297, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, N.K.; Rincon Pabon, J.P.; Gies, S.; Dastvan, R.; Gross, M.L. Kingfisher: An open-sourced web-based platform for the analysis of hydrogen exchange mass spectrometry data. Protein Sci. 2025, 34, e70096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.R.; Johnson, B.; Mire, C.E.; Xu, W.; Shabman, R.S.; Speller, L.N.; Leung, D.W.; Geisbert, T.W.; Amarasinghe, G.K.; Basler, C.F. The Marburg virus VP24 protein interacts with Keap1 to activate the cytoprotective antioxidant response pathway. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.P.; Bornholdt, Z.A.; Liu, T.; Abelson, D.M.; Lee, D.E.; Li, S.; Woods, V.L., Jr.; Saphire, E.O. The ebola virus interferon antagonist VP24 directly binds STAT1 and has a novel, pyramidal fold. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabman, R.S.; Gulcicek, E.E.; Stone, K.L.; Basler, C.F. The Ebola Virus VP24 Protein Prevents hnRNP C1/C2 Binding to Karyopherin α1 and Partially Alters its Nuclear Import. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204 (Suppl. 3), S904–S910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, J.; Hultquist, J.F.; Liu, D.; Shtanko, O.; Dollen, J.V.; Satkamp, L.; Jang, G.M.; Luthra, P.; Schwarz, T.M.; Small, G.I.; et al. Protein Interaction Mapping Identifies RBBP6 as a Negative Regulator of Ebola Virus Replication. Cell 2018, 175, 1917–1930.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Beri, N.R.; Zou, A.J.; Hubel, P.; Dorando, H.K.; Bergant, V.; Andrews, R.D.; Pan, J.; Andrews, J.M.; Sheehan, K.C.F.; et al. Nuclear-localized human respiratory syncytial virus NS1 protein modulates host gene transcription. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 109803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, T.N.; Pei, J.; Leung, D.W. Pathogenicity and virulence of human respiratory syncytial virus: Multifunctional nonstructural proteins NS1 and NS2. Virulence 2023, 2283897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalita, P.; Khatavkar, O.; Uwase, G.; Korshunova, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wagner, N.D.; Xu, J.; Pan, J.; Nix, J.C.; Gross, M.L.; et al. Molecular basis for human respiratory syncytial virus transcriptional regulator NS1 interactions with MED25. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.E.; Park, A.; Lake, M.; Pentecost, M.; Torres, B.; Yun, T.E.; Wolf, M.C.; Holbrook, M.R.; Freiberg, A.N.; Lee, B. Ubiquitin-regulated nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking of the Nipah virus matrix protein is important for viral budding. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Dorival, I.; Wu, W.; Dowall, S.; Armstrong, S.; Touzelet, O.; Wastling, J.; Barr, J.N.; Matthews, D.; Carroll, M.; Hewson, R.; et al. Elucidation of the Ebola virus VP24 cellular interactome and disruption of virus biology through targeted inhibition of host-cell protein function. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 5120–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Zhang, B.; Vogel, O.; Walker, B.W.; Ma, L.W.; Wagner, N.D.; Basler, C.F.; Leung, D.W.; Gross, M.L.; Amarasinghe, G.K. The Biophysical Basis for Karyopherin-Dependent Ebola Virus VP24 Nuclear Transport. Viruses 2025, 17, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081051
Zhao J, Zhang B, Vogel O, Walker BW, Ma LW, Wagner ND, Basler CF, Leung DW, Gross ML, Amarasinghe GK. The Biophysical Basis for Karyopherin-Dependent Ebola Virus VP24 Nuclear Transport. Viruses. 2025; 17(8):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081051
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Junjie, Bojie Zhang, Olivia Vogel, Benjamin W. Walker, Leonard W. Ma, Nicole D. Wagner, Christopher F. Basler, Daisy W. Leung, Michael L. Gross, and Gaya K. Amarasinghe. 2025. "The Biophysical Basis for Karyopherin-Dependent Ebola Virus VP24 Nuclear Transport" Viruses 17, no. 8: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081051
APA StyleZhao, J., Zhang, B., Vogel, O., Walker, B. W., Ma, L. W., Wagner, N. D., Basler, C. F., Leung, D. W., Gross, M. L., & Amarasinghe, G. K. (2025). The Biophysical Basis for Karyopherin-Dependent Ebola Virus VP24 Nuclear Transport. Viruses, 17(8), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081051






