Biological, Molecular, and Physiological Characterization of Four Soybean Mosaic Virus Isolates Present in Argentine Soybean Crops
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inoculum Source
2.2. Biological Characterization
2.2.1. Pathogenicity Test
2.2.2. Aphid Transmission
2.2.3. Seed Transmission
2.3. Molecular Characterization
2.4. Physiological Parameters
2.4.1. Infection with SMV
2.4.2. Growth Parameters
2.4.3. Chlorophyll Fluorescence
2.4.4. Lipid Peroxidation
2.4.5. Total Soluble Sugars and Starch
2.4.6. Serological Virus Detection
2.4.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
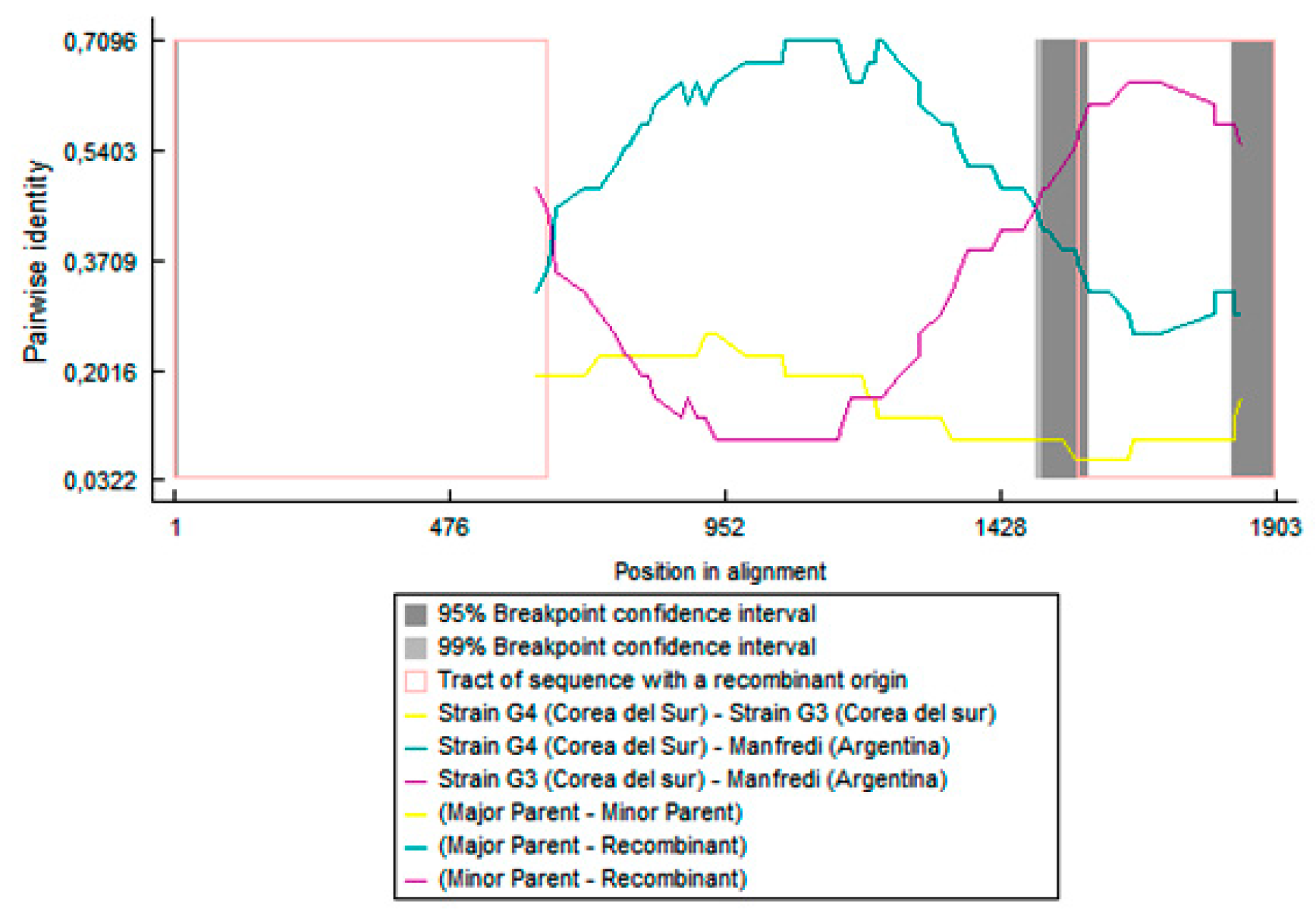
3.1. Phylogenetic Characterization and Recombination Analysis of the SMV Isolates
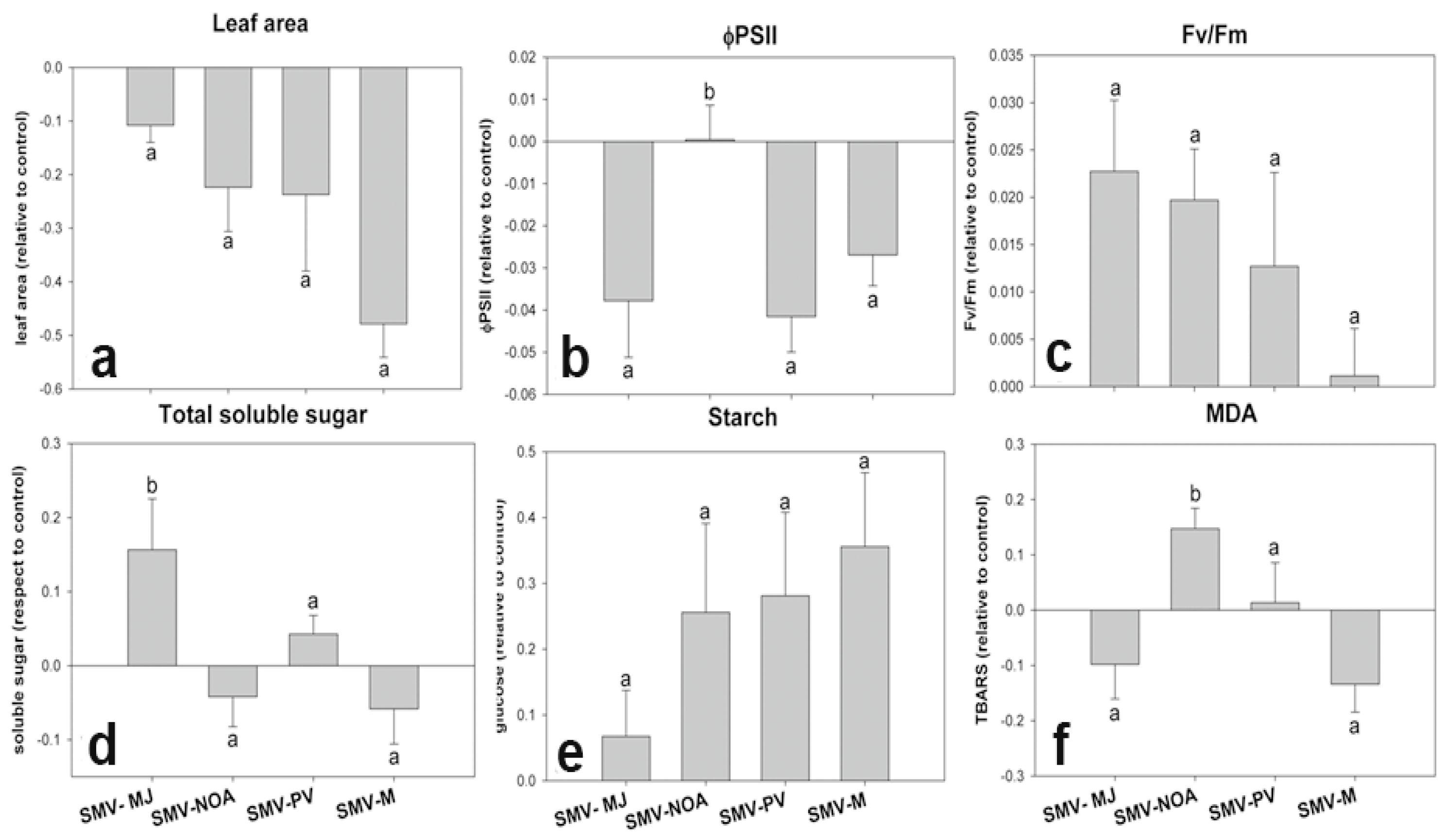
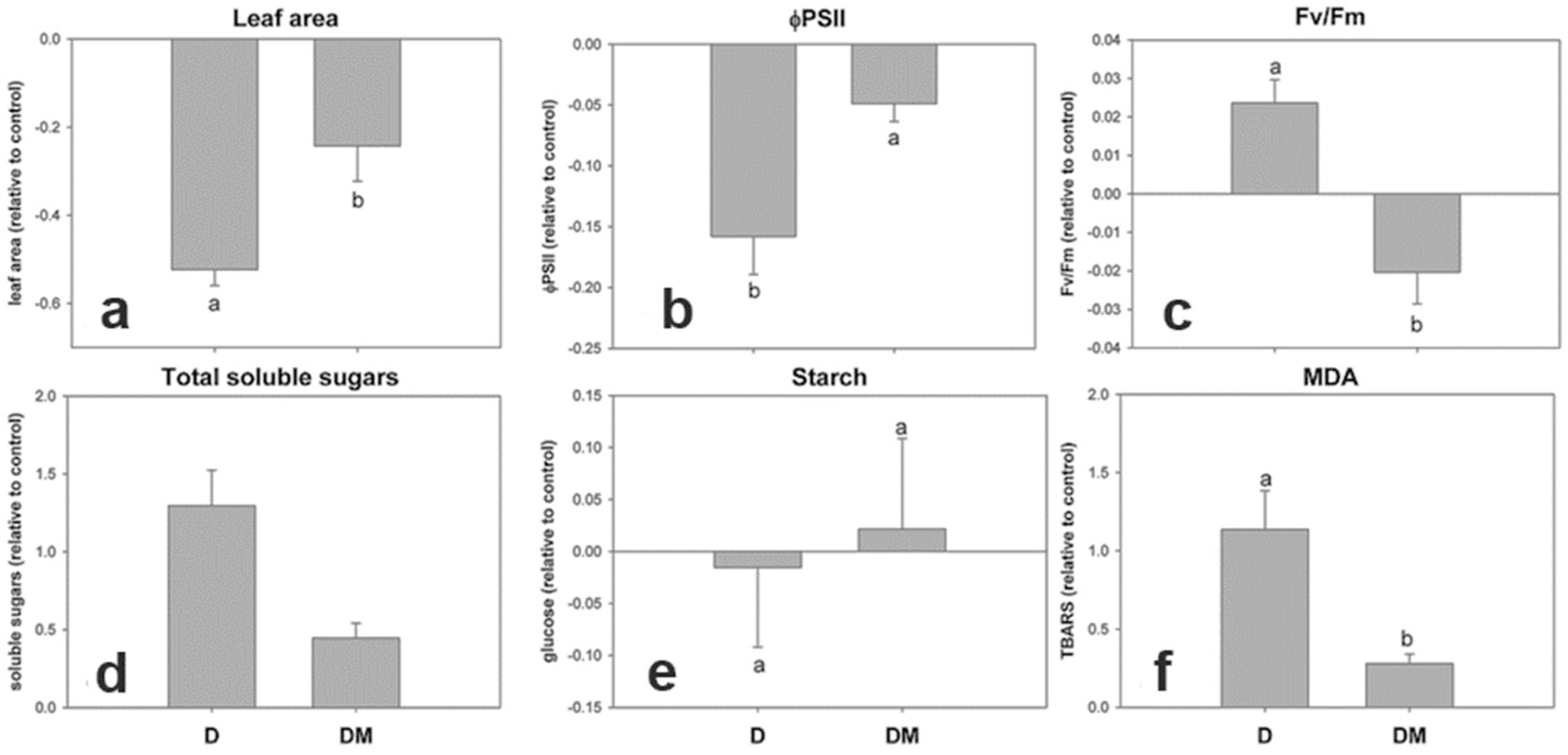
3.2. Early Physiological Alterations Caused by the Different Isolates of SMV
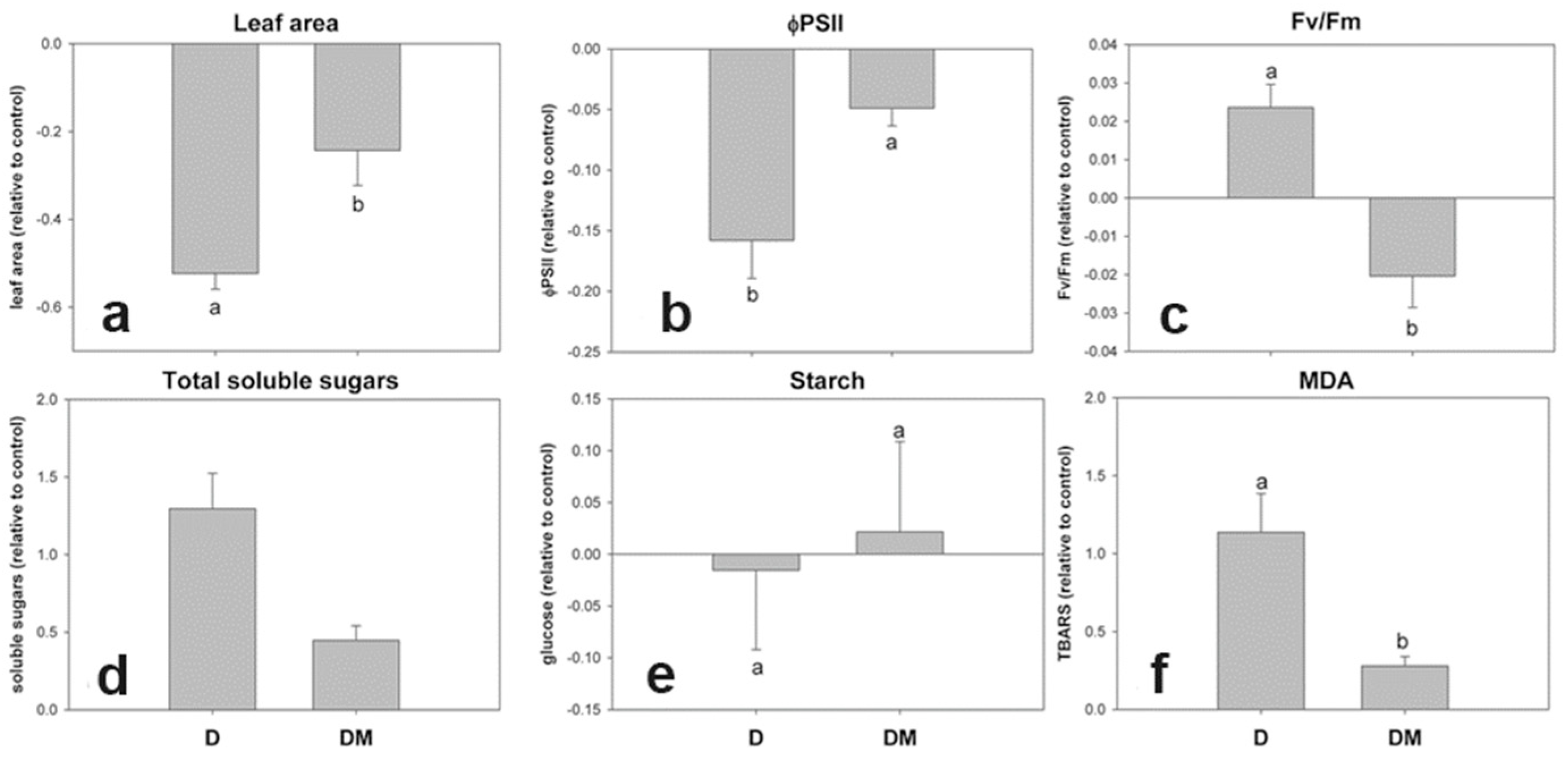
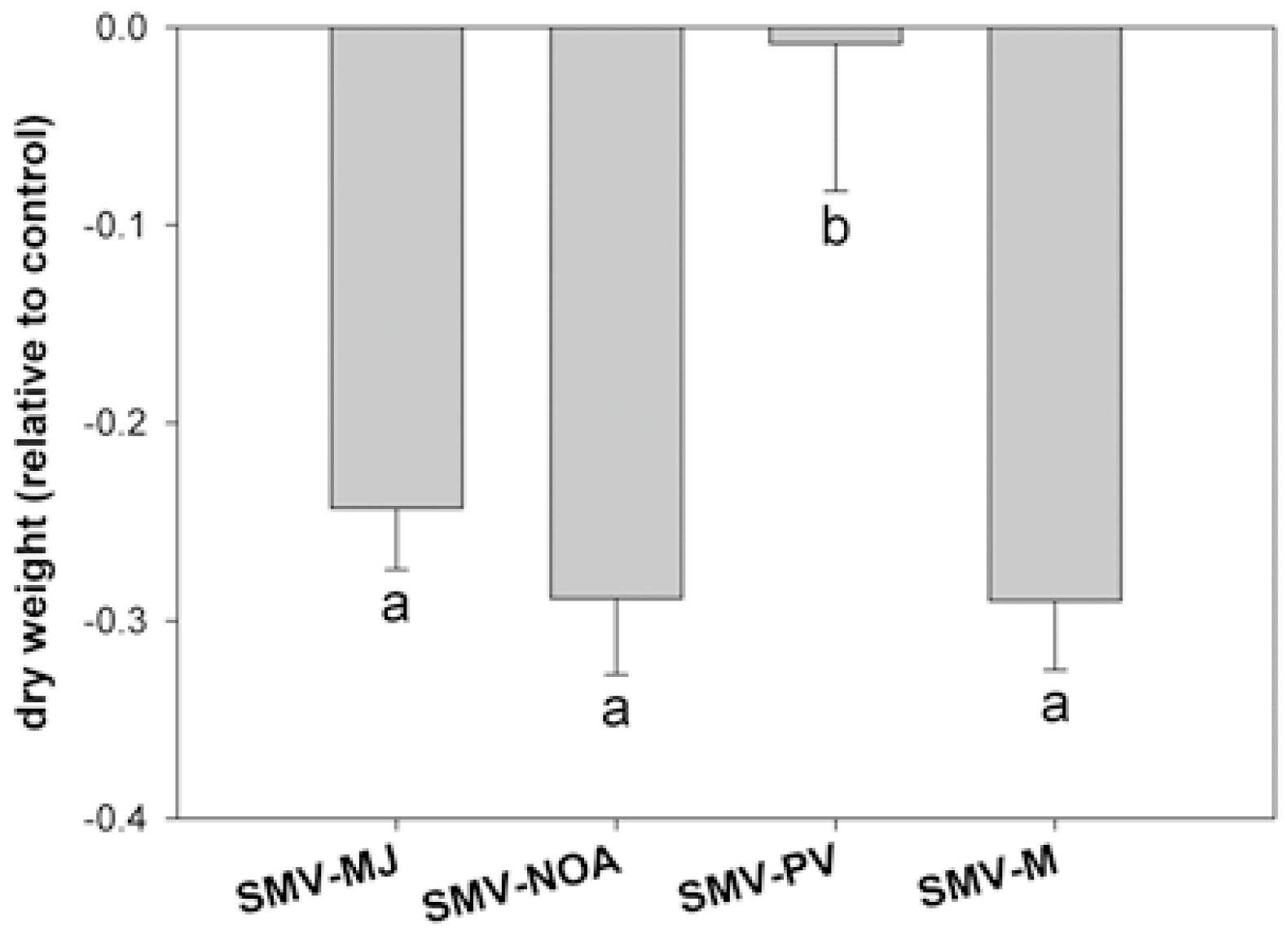
3.3. Physiological Alterations After Viral Symptom Development
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- Cui, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, A. Detection, Understanding and Control of Soybean Mosaic Virus; Soybean, M., Sudaric, A., Eds.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, J.H.; Whitham, S.A. Control of Virus Diseases in Soybeans. Adv. Virus Res. 2014, 90, 355–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Luo, J.; Ding, X.; Wang, T.; Hu, T.; Song, P.; Zhai, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, K.; Li, K.; et al. Soybean RNA Interference Lines Silenced for EIF4E Show Broad Potyvirus Resistance. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 21, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajimorad, M.R.; Domier, L.L.; Tolin, S.A.; Whitham, S.A.; Saghai Maroof, M.A. Soybean Mosaic Virus: A Successful Potyvirus with a Wide Distribution but Restricted Natural Host Range. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupe, J.; Luttrell, R.G. Effect of Pests and Diseases on Soybean Quality. In Soybeans: Chemistry, Production, Processing, and Utilization; Johnson, L.A., White, P.J., Galloway, R., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweets, L. Discolored Soybean Seed // Integrated Crop and Pest Management News Article // Integrated Pest Management, University of Missouri. Columbia, MO, USA. 2011. Available online: https://ipm.missouri.edu/IPCM/2011/9/Discolored-Soybean-Seed/ (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- Chung, B.Y.W.; Miller, W.A.; Atkins, J.F.; Firth, A.E. An Overlapping Essential Gene in the Potyviridae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5897–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, R.-H.; Hajimorad, M.R. Mutational Analysis of the Putative Pipo of Soybean Mosaic Virus Suggests Disruption of PIPO Protein Impedes Movement. Virology 2010, 400, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzzell, R.I.; Tu, J.C. Inheritance of Soybean Resistance to Soybean Mosaic Virus. J. Hered. 1984, 75, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.K.; Goodman, R.M. Evaluation of Resistance in Soybeans to Soybean Mosaic Virus Strains 1. Crop Sci. 1982, 22, 1133–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.Q.; Cao, Q.; Fang, D.C.; Xue, B.D.; Fang, Z.D. Identification of Strains of Soybean Mosaic Virus. Acta Phytophylacica Sin. 1982, 9, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.M. Resistance to Soybean Mosaic Virus in Soybeans. Phytopathology 1985, 75, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Zhi, H.J.; Yu, D.Y.; Gai, J.Y. Identification and Distribution of SMV Strains in Huang-Huai Valleys. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2006, 39, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.Z.; Fang, Y.; Pang, H. The Current Status of the Soybean-Soybean Mosaic Virus (SMV) Pathosystem. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usovsky, M.; Chen, P.; Li, D.; Wang, A.; Shi, A.; Zheng, C.; Shakiba, E.; Lee, D.; Vieira, C.C.; Lee, Y.C.; et al. Decades of Genetic Research on Soybean Mosaic Virus Resistance in Soybean. Viruses 2022, 14, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domier, L.L.; Latorre, I.J.; Steinlage, T.A.; McCoppin, N.; Hartman, G.L. Variability and Transmission by Aphis Glycines of North American and Asian Soybean Mosaic Virus Isolates. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 1925–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, K.H. Complete Genome Sequences of the Genomic RNA of Soybean Mosaic Virus Stranins G7H and G5. Plant Pathol. J. 2003, 19, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, J.-K.; Ohshima, K.; Lee, H.-G.; Son, M.; Choi, H.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Sohn, S.-H.; Kim, K.-H. Molecular Variability and Genetic Structure of the Population of Soybean Mosaic Virus Based on the Analysis of Complete Genome Sequences. Virology 2009, 393, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.K.; Koo, J.M.; Ahn, H.J.; Yum, H.J.; Choi, C.W.; Ryu, K.H.; Chen, P.; Tolin, S.A. Emergence of Rsv-Resistance Breaking Soybean Mosaic Virus Isolates from Korean Soybean Cultivars. Virus Res. 2005, 112, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagarinova, A.G.; Babu, M.; Strömvik, M.V.; Wang, A. Recombination Analysis of Soybean Mosaic Virus Sequences Reveals Evidence of RNA Recombination between Distinct Pathotypes. Virol. J. 2008, 5, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saruta, M.; Kikuchi, A.; Okabe, A.; Sasaya, T. Molecular Characterization of A2 and D Strains of Soybean Mosaic Virus, Which Caused a Recent Virus Outbreak in Soybean Cultivar Sachiyutaka in Chugoku and Shikoku Regions of Japan. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2005, 71, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.H.; Kadoury, D.; Gal-On, A.; Huet, H.; Wang, Y.; Raccah, B. Mutations in the HC-Pro Gene of Zucchini Yellow Mosaic Potyvirus: Effects on Aphid Transmission and Binding to Purified Virions. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jossey, S.; Hobbs, H.A.; Domier, L.L. Role of Soybean Mosaic Virus-Encoded Proteins in Seed and Aphid Transmission in Soybean. Phytopathology 2013, 103, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.; Kang, S.; Yoon Seo, B.; Kyo Jung, J.; Kim, K. Mutational Analysis of Interaction between Coat Protein and Helper Component-Proteinase of Soybean Mosaic Virus Involved in Aphid Transmission. Mol. Plant Path. 2010, 11, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bent, A.F.; Mackey, D. Elicitors, Effectors, and R Genes: The New Paradigm and a Lifetime Supply of Questions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2007, 45, 399–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, K.H. Strain-Specific Cylindrical Inclusion Protein of Soybean Mosaic Virus Elicits Extreme Resistance and a Lethal Systemic Hypersensitive Response in Two Resistant Soybean Cultivars. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggenberger, A.L.; Hajimorad, M.R.; Hill, J.H. Gain of Virulence on Rsv1-Genotype Soybean by an Avirulent Soybean Mosaic Virus Requires Concurrent Mutations in Both P3 and HC-Pro. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahangaran, A.; Habibi, M.K.; Mohammadi, G.H.M.; Winter, S.; García-Arenal, F. Analysis of Soybean Mosaic Virus Genetic Diversity in Iran Allows the Characterization of a New Mutation Resulting in Overcoming Rsv4-Resistance. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 2557–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreola, S.; Rodriguez, M.; Parola, R.; Alemano, S.; Lascano, R. Interactions between Soybean, Bradyrhizobium Japonicum and Soybean Mosaic Virus: The Effects Depend on the Interaction Sequence. Funct. Plant Biol. 2019, 46, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanini, A.A.; Di Feo, L.; Luna, D.F.; Paccioretti, P.; Collavino, A.; Rodriguez, M.S. Cassava Common Mosaic Virus Infection Causes Alterations in Chloroplast Ultrastructure, Function, and Carbohydrate Metabolism of Cassava Plants. Plant Pathol. 2021, 70, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loebenstain, G.; Carr, J.P. Natural Resistance Mechanisms of Plants to Viruses; Loebenstain, G., Carr, J.P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, A.M.R. Identificaçåo de Estirpes Do Virus Do Mosaico Comum Da Soja No Estado Do Paraná. Fitopatol. Bras. 1981, 6, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Shigemori, I. Studies on the Breeding on Soybeans for Resistance to Soybean Mosaic Virus (SMV). Bull. Nagano Chushin Agric. Exp. Stn. 1991, 10, 1–160. [Google Scholar]
- Converse, R.H.; Martin, R.R. ELISA Methods for Plant Viruses. In Serological Methods for Detection and Identification of Viral and Bacterial Plant Pathogens; Hampton, R., Ball, E., De Boer, S., Eds.; APS Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1990; pp. 179–196. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, O.S.; Roh, J.H.; Moon, J.K.; Sohn, S.I.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, J.Y. Identification of Soybean Mosaic Virus Strains by RT-PCR/RFLP Analysis of Cylindrical Inclusion Coding Region. Plant Dis. 2004, 88, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sherepitko, D.V.; Budzanivska, I.G.; Polischuk, V.P.; Boyko, A.L. Partial Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of Soybean Mosaic Virus Isolated in Ukraine. Biopolym. Cell 2011, 27, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and Analysis of Recombination Patterns in Virus Genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heath, R.L.; Packer, L. Photoperoxidation in Isolated Chloroplasts. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1968, 125, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.P.; Janes, H.W. Light Regulation of Sink Metabolism in Tomato Fruit I. Growth and Sugar Accumulation. Plant Physiol. 1991, 96, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FALES, F.W. The Assimilation and Degradation of Carbohydrates by Yeast Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneb, J.B.; Somers, G.F. The Watersoluble Polysaccharides of Sweet Corn. Arch. Biochem. 1944, 4, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Rienzo, J.A.; Casanoves, F.; Balzarini, M.G.; Gonzalez, L.; Tablada, M.; Robledo, C.W. Infostat. FCA, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba: Córdoba, Argentina 2020. Available online: http://www.infostat.com.ar (accessed on 27 May 2022).
- Widyasari, K.; Alazem, M.; Kim, K.H. Soybean Resistance to Soybean Mosaic Virus. Plants 2020, 9, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Chen, P.; Gergerich, R. Characterization of Resistance to Soybean Mosaic Virus in Diverse Soybean Germplasm. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 2503–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimorad, M.R.; Eggenberger, A.L.; Hill, J.H. Strain-Specific P3 of Soybean Mosaic Virus Elicits Rsv1-Mediated Extreme Resistance, but Absence of P3 Elicitor Function Alone Is Insufficient for Virulence on Rsv1-Genotype Soybean. Virology 2006, 345, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wen, R.H.; Khatabi, B.; Ashfield, T.; Maroof, M.A.S.; Hajimorad, M.R. The HC-Pro and P3 Cistrons of an Avirulent Soybean Mosaic Virus Are Recognized by Different Resistance Genes at the Complex Rsv1 Locus. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2013, 26, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atreya, C.D.; Raccah, B.; Pirone, T.P. A Point Mutation in the Coat Protein Abolishes Aphid Transmissibility of a Potyvirus. Virology 1990, 178, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Jo, Y.; Chung, H.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, S.-M.; Hong, J.-S.; Lee, B.C.; Cho, W.K. Phylogenetic and Phylodynamic Analyses of Soybean Mosaic Virus Using 305 Coat Protein Gene Sequences. Plants 2022, 11, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, C.; Shan, S.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Wei, Z.; Sun, Z. The Hypervariable N-Terminal of Soybean Mosaic Virus P1 Protein Influences Its Pathogenicity and Host Defense Responses. Phytopathol. Res. 2022, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Chen, J.; Hong, X.; Chen, J.; Adams, M.J. A Potyvirus P1 Protein Interacts with the Rieske Fe/S Protein of Its Host. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2007, 8, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Hong, Y.; Liu, Y. Chloroplast in Plant-Virus Interaction. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, M.; Taleisnik, E.; Lenardon, S.; Lascano, R. Are Sunflower Chlorotic Mottle Virus Infection Symptoms Modulated by Early Increases in Leaf Sugar Concentration? J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, M.; Muñoz, N.; Lenardon, S.; Lascano, R. The Chlorotic Symptom Induced by Sunflower Chlorotic Mottle Virus Is Associated with Changes in Redox-Related Gene Expression and Metabolites. Plant Sci. 2012, 196, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, M.C.; Luna, C.; Rodríguez, M.; Lenardon, S.; Taleisnik, E. Sunflower Chlorotic Mottle Virus in Compatible Interactions with Sunflower: ROS Generation and Antioxidant Response. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2005, 113, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.-K. Strains of Soybean Mosaic Virus: Classification Based on Virulence in Resistant Soybean Cultivars. Phytopathology 1979, 69, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cultivar | Genotype | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 | G6 | G7 | MJ | M | NOA | PV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | ||||||||||||
| Clark | rsv | -/M | -/M | -/M | -/M | -/MN | -/M | -/M | N/M | N/M | N/M | N/M |
| Davis | rsv | -/- | -/- | -/- | N/MN | -/M | -/M | -/M | N/MN | N/- | N/M | N/MN |
| York | Rsv-5 | -/- | -/- | -/- | N/MN | -/MN | -/M | -/M | N/MN | N/N | -/- | N/MN |
| Ogden | Rsv-1t | -/- | -/- | N/N | -/- | -/- | -/- | N/N | -/- | N/MN | -/- | -/N |
| Kwanggyo | Rsv-1K | -/- | -/- | -/- | -/- | N/N | N/N | N/N | N/N | -/- | N/N | N/MN |
| Buffalo | Rsv-1b | -/- | -/- | -/- | -/- | -/- | -/- | N/N | -/- | N/- | N/- | N/- |
| II | MS1 | MS2 | MS3 | |||||||||
| Clark | rsv | M | M | M | N/M | N/M | N/M | N/M | ||||
| Davis | rsv | - | - | M | N/MN | N/- | N/M | N/MN | ||||
| York | Rsv-5 | M | M | M | N/MN | N/N | -/- | N/MN | ||||
| Ogden | Rsv-1t | - | M N | M N | -/- | N/NM | -/- | -/N | ||||
| Kwanggyo | Rsv-1K | - | M LL | M | N/N | -/- | N/N | N/MN | ||||
| Buffalo | Rsv-1b | - | - | N | -/- | N/- | N/- | N/- | ||||
| III | A | B | C | D | E | |||||||
| Clark | rsv | M | M | M | M | M | M | M | M | M | ||
| Davis | rsv | M | M | N | N | - | M | N | ||||
| York | Rsv-5 | M | M | N | N | N | - | N | ||||
| Ogden | Rsv-1t | N | N | N | N | N | - | N | ||||
| Kwanggyo | Rsv-1K | M | M | N | N | - | N | N | ||||
| Buffalo | Rsv-1b | N | N | - | - | - | ||||||
| PI 96983 | Rsv-1t | N | N | - | - | N | ||||||
| PI 483084 | Rsv-1h | N | - | - | - |
| M | NOA | MJ | PV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 aphids per plant | 72 | 67 | 61 | 12.5 |
| 1 aphid per plant | 37.5 | 38 | 20 | 10 |
| Isolate | % of Not Spotted Seeds | % Spotted Seeds | Mottling Severity * | % Seed Transmission (PTA-ELISA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planta Vinosa | 65 | 35 | 1-2 | 7 |
| Marcos Juarez | 58 | 35 | 1-2 | 7 |
| NOA | 60 | 39 | 1-3 | 10 |
| Manfredi | 38 | 62 | 1-4 | 13 |
| Segment | Isolates | Similarity (%) | Divergence (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MJ | NOA | PV | MJ | NOA | PV | ||
| P1 | M | 95.9 | 53.1 | 53.6 | 4.2 | 31.4 | 30.6 |
| MJ | - | 51.1 | 51.4 | - | 32.3 | 31.9 | |
| NOA | - | - | 99.1 | - | - | 0.9 | |
| CI | M | 90.2 | 97.8 | 97.7 | 10.8 | 2.2 | 2.3 |
| MJ | - | 91 | 91 | - | 9.8 | 9.8 | |
| NOA | - | - | 99.5 | - | - | 0.6 | |
| CP | M | 92.8 | 94 | 95.2 | 7.8 | 6.4 | 5 |
| MJ | - | 96.7 | 94.2 | - | 3.4 | 6 | |
| NOA | - | - | 97.5 | - | - | 2.5 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maugeri, M.; Rodríguez, M.; Bejerman, N.; Laguna, I.G.; Rodríguez Pardina, P. Biological, Molecular, and Physiological Characterization of Four Soybean Mosaic Virus Isolates Present in Argentine Soybean Crops. Viruses 2025, 17, 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070995
Maugeri M, Rodríguez M, Bejerman N, Laguna IG, Rodríguez Pardina P. Biological, Molecular, and Physiological Characterization of Four Soybean Mosaic Virus Isolates Present in Argentine Soybean Crops. Viruses. 2025; 17(7):995. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070995
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaugeri, Mariel, Marianela Rodríguez, Nicolas Bejerman, Irma G. Laguna, and Patricia Rodríguez Pardina. 2025. "Biological, Molecular, and Physiological Characterization of Four Soybean Mosaic Virus Isolates Present in Argentine Soybean Crops" Viruses 17, no. 7: 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070995
APA StyleMaugeri, M., Rodríguez, M., Bejerman, N., Laguna, I. G., & Rodríguez Pardina, P. (2025). Biological, Molecular, and Physiological Characterization of Four Soybean Mosaic Virus Isolates Present in Argentine Soybean Crops. Viruses, 17(7), 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070995








