Adrenomedullin Therapy for Moderate-to-Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia: Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Phase 2a Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Randomization and Masking
2.4. Interventions
2.5. Data Assessment
2.6. Data Collection and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Randomization and Clinical Characteristics of Patients at Baseline
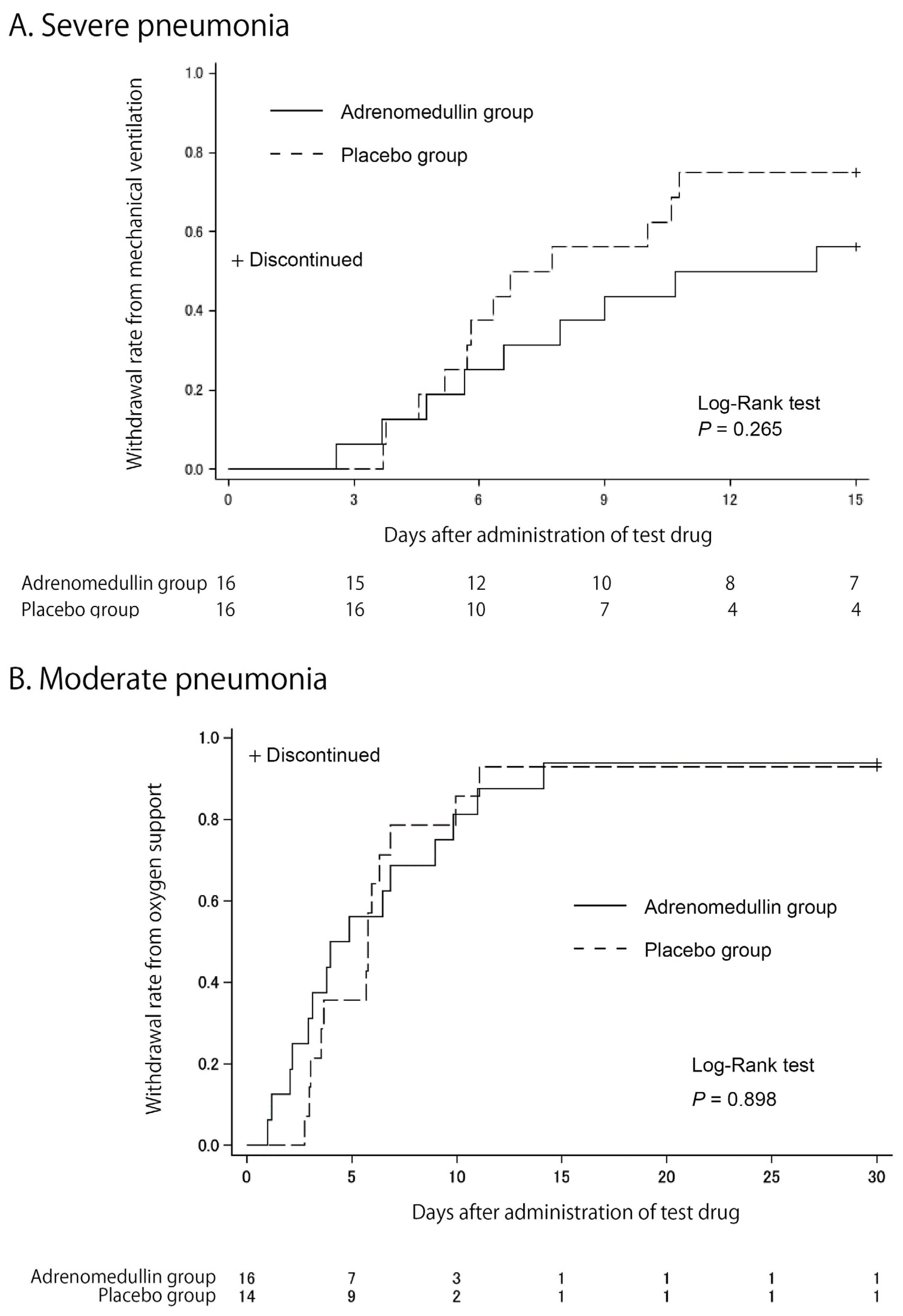
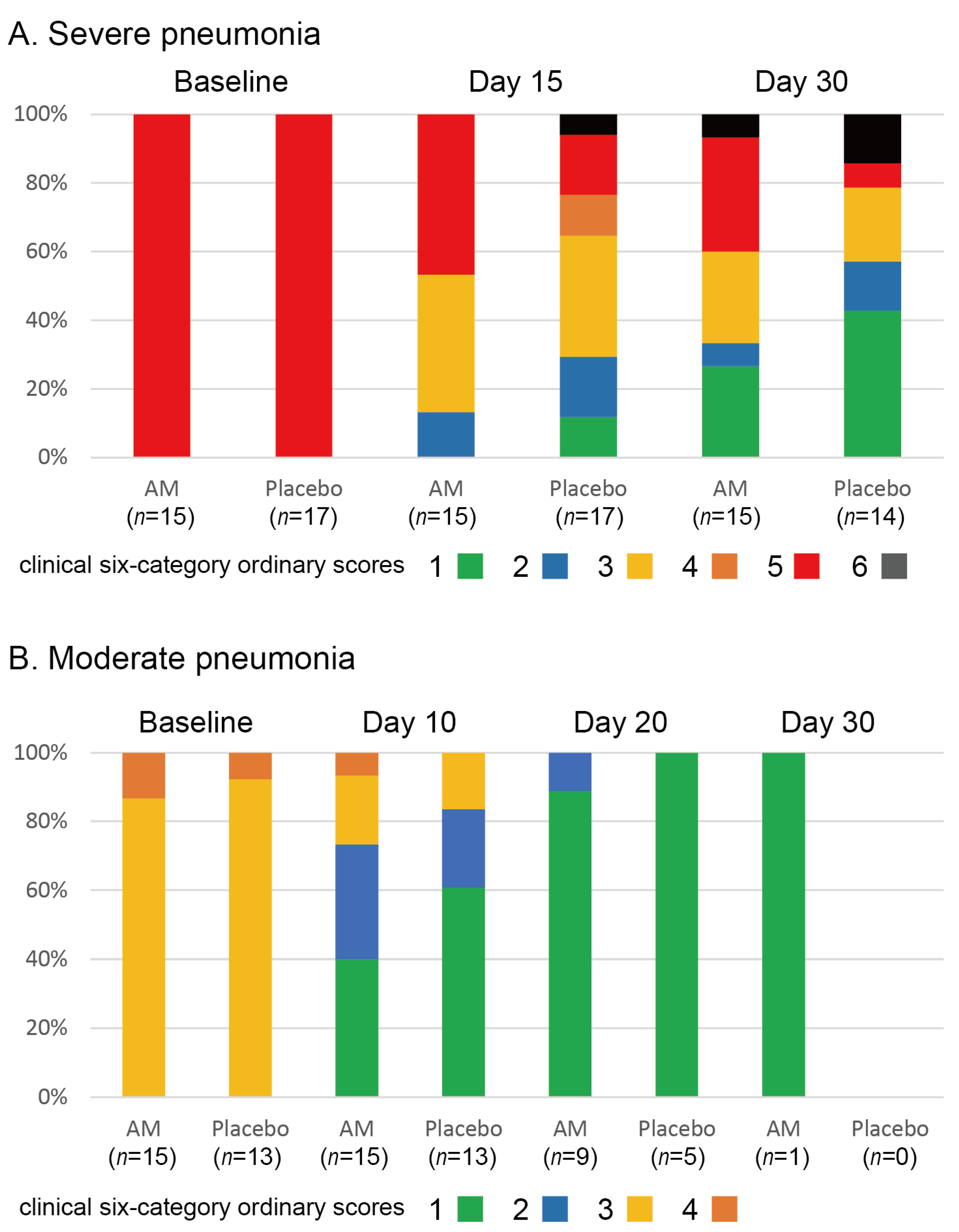
3.2. Clinical Efficacy
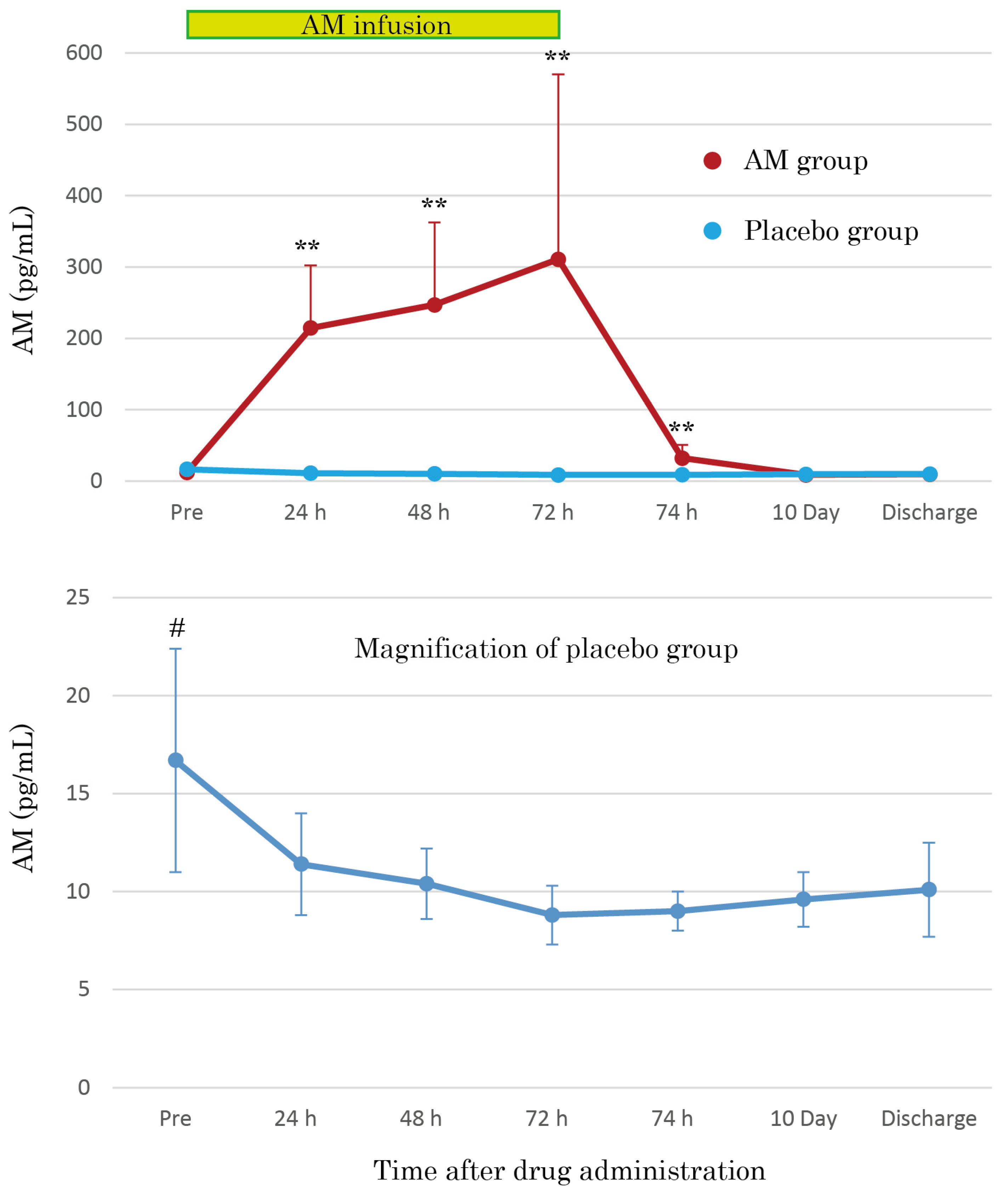
3.3. AM Plasma Concentrations
3.4. Safety Assessments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AM | Adrenomedullin |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| MV | Mechanical ventilation |
| VILI | Ventilator-induced lung injury |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| RFT | Respiratory function test |
| DLco | Carbon monoxide diffusion capacity |
| AE | Adverse event |
| FAS | Full primary analysis set |
References
- WHO. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Kita, T.; Kitamura, K. Adrenomedullin therapy in moderate to severe COVID-19. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eto, T.; Kato, J.; Kitamura, K. Regulation of production and secretion of adrenomedullin in the cardiovascular system. Regul. Pept. 2003, 112, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kita, T.; Kitamura, K. Translational studies of adrenomedullin and related peptides regarding cardiovascular diseases. Hypertens. Res. 2022, 45, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, T.P.; Stoppe, C.; Breuer, T.; Stiehler, L.; Dreher, M.; Kersten, A.; Kluge, S.; Karakas, M.; Zechendorf, E.; Marx, G.; et al. Prognostic value of bioactive adrenomedullin in critically ill patients with COVID-19 in Germany: An observational cohort study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, M.A.; Gualtieri, S.; Cordasco, F.; Tarallo, A.P.; Verrina, M.C.; Princi, A.; Bruni, A.; Garofalo, E.; Aquila, I. The role of adrenomedullin as a predictive marker of the risk of death and adverse clinical events: A review of the literature. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dackor, R.; Caron, K. Mice heterozygous for adrenomedullin exhibit a more extreme inflammatory response to endotoxin-induced septic shock. Peptides 2007, 28, 2164–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shindo, T.; Kurihara, H.; Maemura, K.; Kurihara, Y.; Kuwaki, T.; Izumida, T.; Minamino, N.; Ju, K.H.; Morita, H.; Oh-hashi, Y.; et al. Hypotension and resistance to lipopolysaccharide-induced shock in transgenic mice overexpressing adrenomedullin in their vasculature. Circulation 2000, 101, 2309–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wu, R.; Zhou, M.; Wang, P. Human adrenomedullin and its binding protein ameliorate sepsis-induced organ injury and mortality in jaundiced rats. Peptides 2010, 31, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Temmesfeld-Wollbrück, B.; Brell, B.; Dávid, I.; Dorenberg, M.; Adolphs, J.; Schmeck, B.; Suttorp, N.; Hippenstiel, S. Adrenomedullin reduces vascular hyperpermeability and improves survival in rat septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2007, 33, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Redetzky, H.C.; Will, D.; Hellwig, K.; Kummer, W.; Tschernig, T.; Pfeil, U.; Paddenberg, R.; Menger, M.D.; Kershaw, O.; Gruber, A.D.; et al. Mechanical ventilation drives pneumococcal pneumonia into lung injury and sepsis in mice: Protection by adrenomedullin. Crit. Care 2014, 18, R73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kita, T.; Kaji, Y.; Kitamura, K. Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of adrenomedullin in Healthy Males: A Randomized, Double-Blind, phase 1 Clinical Trial. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kita, T.; Ashizuka, S.; Ohmiya, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Kanai, T.; Motoya, S.; Hirai, F.; Nakase, H.; Moriyama, T.; Nakamura, M.; et al. Adrenomedullin for steroid-resistant ulcerative colitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase-2a clinical trial. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kita, T.; Ashizuka, S.; Takeda, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Ohmiya, N.; Nakase, H.; Motoya, S.; Ohi, H.; Mitsuyama, K.; Hisamatsu, T.; et al. Adrenomedullin for biologic-resistant Crohn’s disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2a clinical trial. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meesoontorn, S.; Pakdee, W.; Cheranakhorn, C.; Sangkaew, S. Understanding the change of in-hospital mortality and respiratory failure between Delta and Omicron waves from a tertiary hospital in Southern Thailand: A retrospective cohort study. IJID Reg. 2024, 13, 100446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R.; Yamasoba, D.; Kimura, I.; Wang, L.; Kishimoto, M.; Ito, J.; Morioka, Y.; Nao, N.; Nasser, H.; Uriu, K.; et al. Attenuated fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant. Nature 2022, 603, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, N.; Nakamori, Y.; Ogata, M.; Fukuda, N.; Yamura, A.; Ito, T. Aspiration pneumonia was the most frequent cause of death in older patients with SARS-CoV-2 omicron-related pneumonia in Japan. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2024, 72, 2234–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, T.; Saito, S.; Omae, K.; Tanaka, K.; Kita, T.; Kitamura, K.; Fukuma, K.; Washida, K.; Abe, S.; Ishiyama, H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of adrenomedullin for acute ischemic stroke (AMFIS): A phase 2, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. eClinicalMedicine 2024, 77, 102901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Trial | Severe Pneumonia | Moderate Pneumonia | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | AM | Placebo | AM | Placebo | |||
| Patient | N = 16 | N = 16 | p Value | N = 16 | N = 14 | p Value | |
| Demographic statistics | Age (years) | 61.3 ± 9.9 | 58.3 ± 8.0 | 0.35 | 53.4 ± 13.5 | 47.6 ± 14.1 | 0.26 |
| BMI | 27.5 ± 5.5 | 29.0 ± 5.2 | 0.46 | 27.2 ± 5.1 | 27.9 ± 4.0 | 0.71 | |
| Sex (male) | 13 (81.3%) | 13 (81.3%) | ― | 10 (62.5%) | 12 (85.7%) | 0.29 | |
| Smoking | 7 (43.8%) | 9 (56.3%) | 0.56 | 7 (43.8%) | 8 (57.1%) | 0.55 | |
| Complication(s) | Any | 15 (93.8%) | 16 (100%) | ― | 14 (87.5%) | 12 (85.7%) | 0.95 |
| Diabetes | 5 (31.3%) | 8 (50%) | 0.38 | 2 (12.5%) | 1 (7.1%) | 0.82 | |
| Hypertension | 7 (43.8%) | 11 (68.8%) | 0.24 | 6 (37.5%) | 4 (28.6%) | 0.70 | |
| Vaccination | Once/Twice | ― | ― | 0/4 | 1/2 | ||
| Clinical severity | SOFA | 4.9 ± 2.6 | 5.3 ± 2.5 | 0.68 | 2.3 ± 1.9 | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 0.33 |
| APACHE II | 12.0 ± 7.1 | 12.1 ± 6.5 | 0.98 | ― | ― | ||
| Laboratory test | IL-6 (pg/mL) | 467 ± 878 | 263 ± 371 | 0.40 | 54 ± 147 | 65 ± 112 | 0.83 |
| D-dimer (mg/mL) | 6.8 ± 11.2 | 3.2 ± 5.5 | 0.26 | 1.4 ± 2.4 | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 0.55 | |
| PTX-3 (ng/mL) | 56.5 ± 44.9 | 81.7 ± 95.5 | 0.35 | 53.0 ± 53.6 | 61.3 ± 45.7 | 0.66 | |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 5.1 ± 3.3 | 10.2 ± 9.6 | 0.054 | 6.1 ± 3.6 | 9.8 ± 7.5 | 0.11 | |
| Concomitant drug | Remdesivir | 13 (81.3%) | 16 (100%) | 0.38 | 15 (93.8%) | 13 (92.9%) | ― |
| Steroid | 16 (100%) | 16 (100%) | ― | 15 (93.8%) | 14 (100%) | 0.79 | |
| Anticoagulants | 15 (93.8%) | 15 (93.8%) | ― | 9 (56.3%) | 8 (57.1%) | ― | |
| Immunomodulator | 8 (50%) | 10 (62.5%) | 0.56 | 7 (43.8%) | 8 (57.1%) | 0.55 | |
| Before Treatment | After Continuous Infusion | After Intermittent Infusion | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | AM | Placebo | p Value | AM | Placebo | p Value | AM | Placebo | p Value | |
| N | 16 | 16 | 9 | 14 | 15 | 16 | ||||
| IL-1b | pg/mL | 0.9 ± 3.8 | 0 ± 0 | 0.33 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | ― | 0.9 ± 3.6 | 0.9 ± 3.8 | 0.998 |
| IL-6 | pg/mL | 467 ± 878 | 263 ± 371 | 0.40 | 802 ± 1783 | 729 ± 2016 | 0.93 | 578 ± 1524 | 1804 ± 4114 | 0.29 |
| IL-8 | pg/mL | 19.0 ± 21.9 | 13.5 ± 7.1 | 0.35 | 10.3 ± 8.6 | 12.9 ± 19.0 | 0.71 | 9.5 ± 16.0 | 18.1 ± 36.0 | 0.41 |
| IL-10 | pg/mL | 7.6 ± 11.9 | 10.9 ± 14.8 | 0.49 | 4.6 ± 5.6 | 1.3 ± 2.8 | 0.07 | 1.3 ± 3.8 | 1.4 ± 4.0 | 0.94 |
| TNF-a | pg/mL | 1.78 ± 1.07 | 1.89 ± 0.82 | 0.75 | 1.79 ± 0.91 | 2.31 ± 4.37 | 0.73 | 2.05 ± 1.81 | 2.40 ± 2.26 | 0.64 |
| INF-g | IU/mL | 0.11 ± 0.21 | 0.14 ± 0.28 | 0.67 | 0 ± 0 | 0.20 ± 0.69 | 0.40 | 0.03 ± 0.07 | 0.01 ± 0.05 | 0.52 |
| ATX | mg/L | 0.48 ± 0.20 | 0.62 ± 0.48 | 0.30 | 0.55 ± 0.29 | 0.61 ± 0.32 | 0.68 | 0.51 ± 0.25 | 0.60 ± 0.30 | 0.36 |
| FDP | mg/mL | 26.4 ± 50.4 | 9.9 ± 7.9 | 0.21 | 6.7 ± 2.1 | 26.1 ± 43.8 | 0.20 | 20.5 ± 37.2 | 24.4 ± 25.8 | 0.74 |
| D-dimer | mg/mL | 6.77 ± 11.15 | 3.22 ± 5.51 | 0.26 | 2.67 ± 1.66 | 7.69 ± 9.49 | 0.13 | 7.22 ± 10.11 | 10.61 ± 11.23 | 0.39 |
| tPA | U/L | 183 ± 125 | 166 ± 151 | 0.74 | 162 ± 169 | 163 ± 160 | 0.98 | 145 ± 107 | 227 ± 354 | 0.41 |
| PIC | mg/mL | 2.38 ± 3.27 | 1.76 ± 1.14 | 0.48 | 0.87 ± 0.50 | 1.81 ± 1.33 | 0.055 | 2.01 ± 2.08 | 2.21 ± 2.50 | 0.81 |
| PTX3 | ng/mL | 56.5 ± 44.9 | 81.7 ± 95.5 | 0.35 | 69.6 ± 58.4 | 36.3 ± 42.5 | 0.13 | 70.7 ± 60.6 | 31.6 ± 44.8 | 0.049 |
| Before Treatment | After Continuous Infusion | After Intermittent Infusion | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | AM | Placebo | p Value | AM | Placebo | p Value | AM | Placebo | p Value | |
| N | 16 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 15 | 13 | ||||
| IL-1b | pg/mL | 1.3 ± 3.4 | 2.4 ± 4.9 | 0.45 | 0.9 ± 3.0 | 2.2 ± 4.4 | 0.44 | 2.2 ± 6.3 | 2.4 ± 4.5 | 0.93 |
| IL-6 | pg/mL | 53.8 ± 147.2 | 64.5 ± 112.4 | 0.83 | 58.1 ± 146.6 | 19.1 ± 30.1 | 0.45 | 15.0 ± 36.0 | 14.4 ± 30.8 | 0.96 |
| IL-8 | pg/mL | 8.1 ± 7.1 | 9.3 ± 7.9 | 0.68 | 3.2 ± 5.2 | 3.4 ± 3.0 | 0.91 | 3.0 ± 2.9 | 2.4 ± 2.5 | 0.57 |
| IL-10 | pg/mL | 15.3 ± 27.7 | 10.3 ± 13.6 | 0.55 | 0.2 ± 0.6 | 0.4 ± 0.9 | 0.44 | 0.1 ± 0.5 | 0.6 ± 1.3 | 0.19 |
| TNF-a | pg/mL | 1.51 ± 0.82 | 1.50 ± 0.63 | 0.96 | 1.11 ± 0.56 | 1.10 ± 0.33 | 0.96 | 1.32 ± 0.59 | 1.11 ± 0.26 | 0.25 |
| INF-g | IU/mL | 0.46 ± 1.30 | 0.19 ± 0.24 | 0.44 | 0.01 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.04 | 0.44 | 0.01 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.04 | 0.48 |
| ATX | mg/L | 0.57 ± 0.20 | 0.61 ± 0.29 | 0.69 | 0.63 ± 0.24 | 0.51 ± 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.62 ± 0.21 | 0.56 ± 0.31 | 0.57 |
| FDP | mg/mL | 5.4 ± 3.7 | 5.6 ± 2.1 | 0.86 | 4.7 ± 5.1 | 5.1 ± 3.0 | 0.84 | 4.7 ± 1.5 | 5.0 ± 2.6 | 0.68 |
| D-dimer | mg/mL | 1.44 ± 2.45 | 1.03 ± 0.42 | 0.55 | 1.92 ± 3.53 | 1.66 ± 0.99 | 0.84 | 1.38 ± 1.21 | 1.79 ± 1.40 | 0.42 |
| tPA | U/L | 77 ± 64 | 123 ± 148 | 0.27 | 141 ± 125 | 76 ± 32 | 0.15 | 146 ± 300 | 91 ± 72 | 0.53 |
| PIC | mg/mL | 1.80 ± 0.64 | 2.10 ± 0.81 | 0.27 | 1.21 ± 0.37 | 1.38 ± 0.47 | 0.38 | 1.33 ± 0.50 | 1.44 ± 0.46 | 0.54 |
| PTX3 | ng/mL | 53.0 ± 53.6 | 61.3 ± 45.7 | 0.66 | 21.1 ± 18.8 | 15.1 ± 12.9 | 0.43 | 10.6 ± 17.6 | 13.6 ± 23.4 | 0.70 |
| Adrenomedullin Group | Placebo Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual Value/Standard Value (%) | N | Actual Value/Standard Value (%) | N | p Value | |
| Vital capacity | 85.7 ± 20.0 | 11 | 77.7 ± 10.2 | 7 | 0.34 |
| Forced expiratory volume in 1 s | 85.9 ± 13.4 | 11 | 74.4 ± 10.3 | 7 | 0.073 |
| Pulmonary diffusing capacity (DLco) | 77.5 ± 14.8 | 9 | 67.1 ± 13.3 | 7 | 0.15 |
| Trial | Severe Pneumonia | Moderate Pneumonia | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | AM | Placebo | AM | Placebo |
| No of Cases | N = 16 | N = 17 | N = 17 | N = 14 |
| Any adverse events | 15 (93.8%) | 16 (94.1%) | 14 (82.4%) | 10 (71.4%) |
| Serious adverse events | 3 (18.8%) | 4 (23.5%) | 1 (5.9%) | 1 (7.1%) |
| Death | 1 (6.3%) | 3 (17.6%) | 1 (5.9%) | 0 |
| AE occurring in >10% | ||||
| Sepsis | 3 (18.8%) | 2 (11.8%) | ― | ― |
| Bacterial pneumonia | 2 (12.5%) | 3 (17.6%) | 2 (11.8%) | 0 |
| Delirium | 1 (6.3%) | 4 (23.5%) | ― | ― |
| Insomnia | 2 (12.5%) | 1 (5.9%) | 1 (5.9%) | 1 (7.1%) |
| Headache | 0 | 1 (5.9%) | 4 (23.5%) | 0 |
| Bradycardia | 0 | 2 (11.8%) | 0 | 1 (7.1%) |
| Hypertension | 2 (12.5%) | 1 (5.9%) | ― | ― |
| Aspiration pneumonia | 1 (6.3%) | 2 (11.8%) | ― | ― |
| Respiratory failure | 1 (6.3%) | 3 (17.6%) | ― | ― |
| Organized pneumonia | 2 (12.5%) | 1 (5.9%) | 0 | 1 (7.1%) |
| Constipation | 4 (25.0%) | 3 (17.6%) | 2 (11.8%) | 2 (14.3%) |
| Diarrhea | 3 (18.8%) | 3 (17.6%) | 0 | 1 (7.1%) |
| Upper gastrointestinal bleeding | 2 (12.5%) | 0 | ― | ― |
| Rash | 2 (12.5%) | 2 (11.8%) | 1 (5.9%) | 1 (7.1%) |
| Renal dysfunction | 1 (6.3%) | 2 (11.8%) | 1 (5.9%) | 0 |
| Blood pressure lowering | 7 (43.8%) | 3 (17.6%) | 2 (11.8%) | 0 |
| QT prolongation (ECG) | 2 (12.5%) | 0 | 1 (5.9%) | 0 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 2 (12.5%) | 0 | ― | ― |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kita, T.; Ohmagari, N.; Saito, S.; Mukae, H.; Takazono, T.; Nakada, T.-A.; Shimada, T.; Hirai, Y.; Shindo, Y.; Komiya, K.; et al. Adrenomedullin Therapy for Moderate-to-Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia: Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Phase 2a Trial. Viruses 2025, 17, 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070982
Kita T, Ohmagari N, Saito S, Mukae H, Takazono T, Nakada T-A, Shimada T, Hirai Y, Shindo Y, Komiya K, et al. Adrenomedullin Therapy for Moderate-to-Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia: Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Phase 2a Trial. Viruses. 2025; 17(7):982. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070982
Chicago/Turabian StyleKita, Toshihiro, Norio Ohmagari, Sho Saito, Hiroshi Mukae, Takahiro Takazono, Taka-Aki Nakada, Tadanaga Shimada, Yuji Hirai, Yuichiro Shindo, Kosaku Komiya, and et al. 2025. "Adrenomedullin Therapy for Moderate-to-Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia: Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Phase 2a Trial" Viruses 17, no. 7: 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070982
APA StyleKita, T., Ohmagari, N., Saito, S., Mukae, H., Takazono, T., Nakada, T.-A., Shimada, T., Hirai, Y., Shindo, Y., Komiya, K., Saito, A., Yamato, M., Homma, K., Okamoto, M., Yamamoto, Y., Mutoh, Y., Hasegawa, C., Mori, N., Nakamura-Uchiyama, F., ... Kitamura, K. (2025). Adrenomedullin Therapy for Moderate-to-Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia: Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Phase 2a Trial. Viruses, 17(7), 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070982








