Non-Coding RNAs and Immune Evasion in Human Gamma-Herpesviruses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MicroRNAs
2.1. Viral microRNAs
2.2. Cellular miRNA and Mimicry by v-miRNA
2.3. Extracellular Vesicle-Associated miRNA
2.4. miRNA–mRNA Network Discovery
3. Long Non-Coding RNAs
3.1. KSHV lncRNA: PAN
3.2. EBV lncRNA: BARTs and BHLF1
3.3. Circular RNAs (circRNAs)
3.4. Post-Transcriptional Regulation of miRNAs via lncRNAs
4. Other ncRNAs
4.1. EBERs
4.2. sisRNAs
4.3. TMERs
5. RNA Modifications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| KSHV | Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus |
| ncRNA | non-coding RNA |
| lncRNA | long non-coding RNA |
| NPC | nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
| EBVaGC | EBV-associated gastric carcinoma |
| DLBCL | diffuse large B cell lymphoma |
| KS | Kaposi’s Sarcoma |
| PEL | primary effusion lymphoma |
| MCD | multicentric Castleman’s disease |
| KICS | KSHV inflammatory cytokine syndrome |
| LANA | latency associated nuclear antigen protein |
| PRR | pattern recognition receptor |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| MHC | major histocompatibility complex |
| NK | natural killer cells |
| IL | interleukins |
| IFN | interferon |
| ORF | open reading frame |
| BHRF1 | BamHI fragment H rightward open reading frame 1 |
| BART | BamHI fragment A rightward transcript |
| v-miRs | viral microRNAs |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| MICB | major histocompatibility complex class I-related chain B protein |
| NLRs | NOD-like receptors |
| LMP1 | latent membrane protein |
| BZLF1 | BamHI-Z leftward reading frame 1 |
| RBP | RNA binding protein |
| GO | gene ontology |
| rLCV | rhesus lymphocryptovirus |
| RRV | rhesus rhadinovirus |
| EV, EVP | extracellular vesicle, extracellular vesicle and particle |
| AGO | Argonaute |
| RISC | RNA-induced silencing complex |
| MVB | multivesicular bodies |
| LECs | lymphatic endothelial cells |
| AGO-CLIP | Argonaute-cross-linking and immunoprecipitation |
| CLASH, qCLASH | Cross-Linking, Ligation and Sequencing of Hybrids, quantitative approach of CLASH |
| IL2RB | interleukin 2 receptor subunit beta |
| K-LEC | KSHV-infected lymphatic endothelial cell |
| ENE | expression and nuclear retention element |
| IRF | interferon regulatory factor |
| EBER | EBV encoded RNA |
| TR | terminal repeat |
| sisRNA | stable intronic sequence RNA |
| TMER | transfer RNA (tRNA)-miRNA encoding RNA molecules |
| circRNA | circular RNA |
| MHV68 | murine gammaherpesvirus 68 |
| lincRNAs | long intergenic non-coding RNAs |
| HCMV | human cytomegalovirus |
| ecircRNA | exonic circRNA |
| ciRNA | circular intronic RNA |
| EIcircRNA | exon-intron circRNAs |
| vIRF | viral interferon regulatory factor |
| PAN | long non-coding polyadenylated nuclear RNA |
| TDMD | target RNA-directed microRNA degradation |
| ceRNA | competing endogenous RNA |
| La protein | lupus erythematosus-associated antigen |
| Pre-miRNAs | miRNA precursors |
| HVS | herpesvirus saimiri |
| HHV | human herpesvirus |
| m6A | N6-methyladenosine RNA modification |
| m5C | 5-methylcytosine RNA modification |
| Ac4C | N4-acetylcytidine modification |
| RLR | RIG-1-like receptor signaling |
| sORFs | short open reading frames |
References
- Ye, R.; Wang, A.; Bu, B.; Luo, P.; Deng, W.; Zhang, X.; Yin, S. Viral Oncogenes, Viruses, and Cancer: A Third-Generation Sequencing Perspective on Viral Integration into the Human Genome. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1333812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausen, H.Z.; Schulte-Holthausen, H.; Wolf, H.; Dörries, K.; Egger, H. Attempts to Detect Virus-Specific DNA in Human Tumors. II. Nucleic Acid Hybridizations with Complementary RNA of Human Herpes Group Viruses. Int. J. Cancer 1974, 13, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). World Cancer Report: Cancer Research for Cancer Prevention; IARC: Lyon, France, 2020; Volume 199, ISBN 978-92-832-0447-3.
- Shannon-Lowe, C.; Rickinson, A. The Global Landscape of EBV-Associated Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 466112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarchoan, R.; Uldrick, T.S. HIV-Associated Cancers and Related Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benfield, T. Noninfectious Conditions in Patients with Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. In Clinical Respiratory Medicine: Fourth Edition; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Tian, T.; Wang, B.; Lu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lin, Y.F.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Zou, H. Global Patterns and Trends in Kaposi Sarcoma Incidence: A Population-Based Study. Lancet. Glob. Health 2023, 11, e1566–e1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesarman, E.; Damania, B.; Krown, S.E.; Martin, J.; Bower, M.; Whitby, D. Kaposi Sarcoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumeyer, S.; Tagawa, T. The Kaposi Sarcoma Herpesvirus Control of Monocytes, Macrophages, and the Tumour Microenvironment. Virology 2025, 601, 110286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münz, C. Epstein–Barr Virus Pathogenesis and Emerging Control Strategies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, J.R. Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Reactivation and Therapeutic Inhibitors. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 72, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhu, P.K.; Damania, B. The Regulation of KSHV Lytic Reactivation by Viral and Cellular Factors. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2022, 52, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ressing, M.E.; Gram, A.M.; Gram, A.M.; Hooykaas, M.J.G.; Piersma, S.J.; Wiertz, E.J.H.J. Immune Evasion by Epstein-Barr Virus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 391, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purushothaman, P.; Uppal, T.; Verma, S.C. Molecular Biology of KSHV Lytic Reactivation. Viruses 2015, 7, 116–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Usherwood, E.J. Immune Escape of γ-Herpesviruses from Adaptive Immunity. Rev. Med. Virol. 2014, 24, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. TLR Signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gent, M.; Braem, S.G.E.; de Jong, A.; Delagic, N.; Peeters, J.G.C.; Boer, I.G.J.; Moynagh, P.N.; Kremmer, E.; Wiertz, E.J.; Ovaa, H.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus Large Tegument Protein BPLF1 Contributes to Innate Immune Evasion through Interference with Toll-Like Receptor Signaling. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, B.D.; Gram, A.M.; Mulder, A.; Van Leeuwen, D.; Claas, F.H.J.; Wang, F.; Ressing, M.E.; Wiertz, E. EBV BILF1 Evolved To Downregulate Cell Surface Display of a Wide Range of HLA Class I Molecules through Their Cytoplasmic Tail. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 1672–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spriggs, M.K.; Armitage, R.J.; Comeau, M.R.; Strockbine, L.; Farrah, T.; Macduff, B.; Ulrich, D.; Alderson, M.R.; Ju, J.; Mu llberg, J.; et al. The Extracellular Domain of the Epstein-Barr Virus BZLF2 Protein Binds the HLA-DR Beta Chain and Inhibits Antigen Presentation. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 5557–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coscoy, L.; Ganem, D. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Encodes Two Proteins That Block Cell Surface Display of MHC Class I Chains by Enhancing Their Endocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8051–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polizzotto, M.N.; Uldrick, T.S.; Hu, D.; Yarchoan, R. Clinical Manifestations of Kaposi Sarcoma Herpesvirus Lytic Activation: Multicentric Castleman Disease (KSHV-MCD) and the KSHV Inflammatory Cytokine Syndrome. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 21628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Host, K.M.; Jacobs, S.R.; West, J.A.; Zhang, Z.; Costantini, L.M.; Stopford, C.M.; Dittmer, D.P.; Damania, B. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Increases PD-L1 and Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression in Human Monocytes. mBio 2017, 8, e00917-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensoli, B.; Stürzl, M. Inflammatory Cytokines, Angiogenic Factors and Viral Agents. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1998, 9, 63–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohga, S.; Nomura, A.; Takada, H.; Ihara, K.; Kawakami, K.; Yanai, F.; Takahata, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Kasuga, N.; Hara, T. Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Load and Cytokine Gene Expression in Activated T Cells of Chronic Active EBV Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbist, K.C.; Nichols, K.E. Cytokine Storm Syndromes Associated with Epstein–Barr Virus. In Cytokine Storm Syndrome; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Malefyt, R.D.W.; Briere, F.; Parham, C.; Bridon, J.M.; Banchereau, J.; Moore, K.W.; Xu, J. The EBV IL-10 homologue is a selective agonist with impaired binding to the IL-10 receptor. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, D.-H.; Malefyt, R.D.W.; Fiorentino, D.F.; Dang, M.-N.; Vieira, P.; deVries, J.; Spits, H.; Mosmann, T.R.; Moore, K.W. Expression of Interleukin-10 Activity by Epstein-Barr Virus Protein BCRF1. Science 1990, 250, 830–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.; Liu, Z.F. Long Non-Coding RNAs: Novel Players in Regulation of Immune Response upon Herpesvirus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 341310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattick, J.S.; Amaral, P.P.; Carninci, P.; Carpenter, S.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, L.L.; Chen, R.; Dean, C.; Dinger, M.E.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Long Non-Coding RNAs: Definitions, Functions, Challenges and Recommendations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hombach, S.; Kretz, M. Non-Coding RNAs: Classification, Biology and Functioning. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 937, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, K.; Bayraktar, R.; Ferracin, M.; Calin, G.A. Non-Coding RNAs in Disease: From Mechanisms to Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2024, 25, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withers, J.B.; Mondol, V.; Pawlica, P.; Rosa-Mercado, N.A.; Tycowski, K.T.; Ghasempur, S.; Torabi, S.F.; Steitz, J.A. Idiosyncrasies of Viral Noncoding RNAs Provide Insights into Host Cell Biology. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2019, 6, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmik, D.; Zhu, F. Evasion of Intracellular DNA Sensing by Human Herpesviruses. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 647992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; He, S.; Zhai, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y. Viral Oncogenesis in Cancer: From Mechanisms to Therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.; Thakur, N.; Monga, I.; Thakur, A.; Kumar, M. VIRmiRNA: A Comprehensive Resource for Experimentally Validated Viral MiRNAs and Their Targets. Database 2014, 2014, bau103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samols, M.A.; Hu, J.; Skalsky, R.L.; Renne, R. Cloning and Identification of a MicroRNA Cluster within the Latency-Associated Region of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, S.; Sewer, A.; Lagos-Quintana, M.; Sheridan, R.; Sander, C.; Grässer, F.A.; van Dyk, L.F.; Kiong Ho, C.; Shuman, S.; Chien, M.; et al. Identification of MicroRNAs of the Herpesvirus Family. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Gonzalez, C.M.; Damania, B.; Cullen, B.R. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Expresses an Array of Viral MicroRNAs in Latently Infected Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5570–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Cullen, B.R. Transcriptional Origin of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus MicroRNAs. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 2234–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umbach, J.L.; Cullen, B.R. In-Depth Analysis of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus MicroRNA Expression Provides Insights into the Mammalian MicroRNA-Processing Machinery. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, E.; Moosmann, A.; Grömminger, S.; Walz, N.; Grundhoff, A.; Hammerschmidt, W. Micro RNAS of Epstein-Barr Virus Promote Cell Cycle Progression and Prevent Apoptosis of Primary Human B Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feederle, R.; Linnstaedt, S.D.; Bannert, H.; Lips, H.; Bencun, M.; Cullen, B.R.; Delecluse, H.J. A Viral MicroRNA Cluster Strongly Potentiates the Transforming Properties of a Human Herpesvirus. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feederle, R.; Haar, J.; Bernhardt, K.; Linnstaedt, S.D.; Bannert, H.; Lips, H.; Cullen, B.R.; Delecluse, H.-J. The Members of an Epstein-Barr Virus MicroRNA Cluster Cooperate to Transform B Lymphocytes. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9801–9810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundhoff, A.; Sullivan, C.S.; Ganem, D. A Combined Computational and Microar-ray-Based Approach Identifies Novel MicroRNAs Encoded by Human Gam-ma-Herpesviruses. RNA 2006, 12, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.J.; Chen, G.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Chang, K.P.; Chang, Y.S.; Chen, H.C. Characterization of Epstein-Barr Virus MiRNAome in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Deep Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Schäfer, A.; Lu, S.; Bilello, J.P.; Desrosiers, R.C.; Edwards, R.; Raab-Traub, N.; Cullen, B.R. Epstein-Barr Virus MicroRNAs Are Evolutionarily Conserved and Differ-entially Expressed. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, 0236–0247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachmani, D.; Stern-Ginossar, N.; Sarid, R.; Mandelboim, O. Diverse Herpesvirus Mi-croRNAs Target the Stress-Induced Immune Ligand MICB to Escape Recognition by Natural Killer Cells. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 5, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, M.; Tagawa, T.; Bouvet, M.; Maliqi, L.; Lutter, D.; Hoser, J.; Hastreiter, M.; Hayes, M.; Sugden, B.; Martin, L.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus MicroRNAs Reduce Immune Surveillance by Virus-Specific CD8+ T Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6467–E6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagawa, T.; Albanese, M.; Bouvet, M.; Moosmann, A.; Mautner, J.; Heissmeyer, V.; Zielinski, C.; Lutter, D.; Hoser, J.; Hastreiter, M.; et al. Epstein-Barr Viral MiRNAs Inhibit Antiviral CD4+ T Cell Responses Targeting IL-12 and Peptide Processing. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 2065–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, A.K.F.; To, K.F.; Lo, K.W.; Lung, R.W.M.; Hui, J.W.Y.; Liao, G.; Hayward, S.D. Modulation of LMP1 Protein Expression by EBV-Encoded MicroRNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, B. Epstein–Barr Virus MiRNA-BART16 Modulates Cell Proliferation by Targeting LMP1. Virus Res. 2018, 256, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooykaas, M.J.G.; van Gent, M.; Soppe, J.A.; Kruse, E.; Boer, I.G.J.; van Leenen, D.; Groot Koerkamp, M.J.A.; Holstege, F.C.P.; Ressing, M.E.; Wiertz, E.J.H.J.; et al. EBV MicroRNA BART16 Suppresses Type I IFN Signaling. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 4062–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvet, M.; Voigt, S.; Tagawa, T.; Albanese, M.; Chen, Y.F.A.; Chen, Y.; Fachko, D.N.; Pich, D.; Göbel, C.; Skalsky, R.L.; et al. Multiple Viral Micrornas Regulate Interferon Release and Signaling Early during Infection with Epstein-Barr Virus. mBio 2021, 12, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.T.; Lin, C.W. EBV-Encoded MiR-BART20-5p and MiR-BART8 Inhibit the IFN-γ–STAT1 Pathway Associated with Disease Progression in Nasal NK-Cell Lymphoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, C.M.; Ivanov, N.S.; Barr, S.A.; Chen, Y.; Skalsky, R.L. An Epstein-Barr Virus MicroRNA Blocks Interleukin-1 (IL-1) Signaling by Targeting IL-1 Receptor 1. J. Virol. 2017, 91, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Lu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wei, L.; Peng, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Ou, C.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus MiR-BART6-3p Inhibits the RIG-I Pathway. J. Innate Immun. 2017, 9, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, C.J.; Chang, M.S.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, W.; Koo, B.K.; Yun, S.C.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Woo, J.H. Epstein–Barr Virus-Encoded MiR-BART5-5p Upregulates PD-L1 through PIAS3/PSTAT3 Modulation, Worsening Clinical Outcomes of PD-L1-Positive Gastric Carcinomas. Gastric Cancer 2020, 23, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abend, J.R.; Ramalingam, D.; Kieffer-Kwon, P.; Uldrick, T.S.; Yarchoan, R.; Ziegelbauer, J.M. Kaposi’s Sar-coma-Associated Herpesvirus MicroRNAs Target IRAK1 and MYD88, Two Components of the Toll-like Receptor/Interleukin-1R Signaling Cascade, to Reduce Inflammatory-Cytokine Expression. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 11663–11674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Gao, Y.; Lin, X.; He, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Deng, Q.; Lan, K. A Human Herpesvirus MiRNA Attenuates Interferon Signaling and Contributes to Maintenance of Viral Latency by Targeting IKKε. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottwein, E.; Mukherjee, N.; Sachse, C.; Frenzel, C.; Majoros, W.H.; Chi, J.T.A.; Braich, R.; Manoharan, M.; Soutschek, J.; Ohler, U.; et al. A Viral MicroRNA Functions as an Orthologue of Cellular MiR-155. Nature 2007, 450, 1096–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalsky, R.L.; Samols, M.A.; Plaisance, K.B.; Boss, I.W.; Riva, A.; Lopez, M.C.; Baker, H.V.; Renne, R. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Encodes an Ortholog of MiR-155. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12836–12845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Bai, Z.; Ye, F.; Xie, J.; Kim, C.G.; Huang, Y.; Gao, S.J. Regulation of NF-KappaB Inhibitor IkappaBalpha and Viral Replication by a KSHV MicroRNA. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Kearney, P.; Plaisance, K.; Parsons, C.H. Pivotal Advance: Kaposi’s Sar-coma-Associated Herpesvirus (KSHV)-Encoded MicroRNA Specifically Induce IL-6 and IL-10 Secretion by Macrophages and Monocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.C.; Li, Z.; Chu, C.Y.; Feng, J.; Feng, J.; Sun, R.; Rana, T.M. MicroRNAs Encoded by Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Regulate Viral Life Cycle. EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Liang, D.; He, Z.; Deng, Q.; Robertson, E.S.; Lan, K. MiR-K12-7-5p Encoded by Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Stabilizes the Latent State by Targeting Viral ORF50/RTA. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellare, P.; Ganem, D. Regulation of KSHV Lytic Switch Protein Expression by a Virus-Encoded MicroRNA: An Evolutionary Adaptation That Fine-Tunes Lytic Reactiva-tion. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 6, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.-J.; Choi, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.K. MicroRNA MiR-BART20-5p Stabilizes Epstein-Barr Virus Latency by Directly Targeting BZLF1 and BRLF1. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 9027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iizasa, H.; Wulff, B.E.; Alla, N.R.; Maragkakis, M.; Megraw, M.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.; Iwakiri, D.; Takada, K.; Wiedmer, A.; Showe, L.; et al. Editing of Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded BART6 MicroRNAs Controls Their Dicer Targeting and Consequently Affects Viral Latency. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fachko, D.N.; Chen, Y.; Skalsky, R.L. Epstein-Barr Virus MiR-BHRF1-3 Targets the BZLF1 3’UTR and Regulates the Lytic Cycle. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e01495-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.C.; Liu, T.Y.; Hsu, S.M.; Lin, C.W. Epstein-Barr Virus–Encoded MiR-BART20-5p Inhibits T-Bet Translation with Secondary Suppression of P53 in Invasive Nasal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1865–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haneklaus, M.; Gerlic, M.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Rainey, A.-A.; Pich, D.; McInnes, I.B.; Hammerschmidt, W.; O’Neill, L.A.J.; Masters, S.L. Cutting Edge: MiR-223 and EBV MiR-BART15 Regulate the NLRP3 Inflammasome and IL-1β Production. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3795–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vereide, D.T.; Seto, E.; Chiu, Y.F.; Hayes, M.; Tagawa, T.; Grundhoff, A.; Hammerschmidt, W.; Sugden, B. Epstein-Barr Virus Maintains Lymphomas via Its MiRNAs. Oncogene 2013, 33, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, H.P. EBV-BART-6-3p and Cellular MicroRNA-197 Compromise the Immune Defense of Host Cells in EBV-Positive Burkitt Lymphoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris-Arnold, A.; Arnold, C.P.; Schaffert, S.; Hatton, O.; Krams, S.M.; Esquivel, C.O.; Martinez, O.M. Epstein-Barr Virus Modulates Host Cell MicroRNA-194 to Promote IL-10 Production and B Lymphoma Cell Survival. Am. J. Transpl. 2015, 15, 2814–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; McBride, J.; Fewell, C.; Lacey, M.; Wang, X.; Lin, Z.; Cameron, J.; Flemington, E.K. MicroRNA-155 Is an Epstein-Barr Virus-Induced Gene That Modulates Epstein-Barr Virus-Regulated Gene Expression Pathways. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Weidmer, A.; Liu, C.-G.; Volinia, S.; Croce, C.M.; Lieberman, P.M. Epstein-Barr Virus-Induced MiR-155 Attenuates NF-ΚB Signaling and Stabilizes Latent Virus Persistence. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 10436–10443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X. Composition of Seed Sequence Is a Major Determinant of MicroRNA Targeting Patterns. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottwein, E.; Corcoran, D.L.; Mukherjee, N.; Skalsky, R.L.; Hafner, M.; Nusbaum, J.D.; Shamulailatpam, P.; Love, C.L.; Dave, S.S.; Tuschl, T.; et al. Viral MicroRNA Targetome of KSHV-Infected Primary Effusion Lymphoma Cell Lines. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, M.; Shamulailatpam, P.; Raja, A.N.; Gottwein, E. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Encodes a Mimic of Cellular MiR-23. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 11821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, K.; Manzano, M.; Chung, K.; Schipma, M.J.; Bartom, E.T.; Gottwein, E. The Oncogenic Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Encodes a Mimic of the Tumor-Suppressive MiR-15/16 MiRNA Family. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 2961–2969.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Fachko, D.N.; Ivanov, N.S.; Skalsky, R.L. B Cell Receptor-Responsive MiR-141 Enhances Epstein-Barr Virus Lytic Cycle via FOXO3 Inhibition. Msphere 2021, 6, e00093-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Liu, K.H.; Hsu, J.T.; Chen, T.C.; Chiu, C.T.; Yeh, T.S. Sen Com-prehensive Profiling of Virus MicroRNAs of Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Carcinoma: Highlighting the Interactions of Ebv-Bart9 and Host Tumor Cells. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottwein, E.; Cullen, B.R. Viral and Cellular MicroRNAs as Determinants of Viral Pathogenesis and Immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, K.J.; Rabinowitz, G.S.; Yario, T.A.; Luna, J.M.; Darnell, R.B.; Steitz, J.A. EBV and Human MicroRNAs Co-Target Oncogenic and Apoptotic Viral and Human Genes during Latency. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, A.J.; Wang, L.; Dezube, B.J.; Harrington, W.J.; Damania, B.; Dittmer, D.P. Tumor Suppressor MicroRNAs Are Underrepresented in Primary Effusion Lymphoma and Kaposi Sarcoma. Blood 2009, 113, 5938–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazot, Q.; Paschos, K.; Skalska, L.; Kalchschmidt, J.S.; Parker, G.A.; Allday, M.J. Epstein-Barr Virus Proteins EBNA3A and EBNA3C Together Induce Expression of the Oncogenic MicroRNA Cluster MiR-221/MiR-222 and Ablate Expression of Its Target P57KIP2. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrázek, J.; Kreutmayer, S.B.; Gräser, F.A.; Polacek, N.; Huettenhofer, A. Subtractive Hybridization Identifies Novel Differentially Expressed NcRNA Species in EBV-Infected Human B Cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagos, D.; Pollara, G.; Henderson, S.; Gratrix, F.; Fabani, M.; Milne, R.S.B.; Gotch, F.; Boshoff, C. MiR-132 Regulates Antiviral Innate Immunity through Suppression of the P300 Transcriptional Co-Activator. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, J.E.; Yin, Q.; Fewell, C.; Lacey, M.; McBride, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, Z.; Schaefer, B.C.; Flemington, E.K. Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 Induces Cellular MicroRNA MiR-146a, a Modulator of Lymphocyte Signaling Pathways. J. Virol. 2007, 82, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.S.; Jain, V.; Krueger, B.; Marshall, V.; Kim, C.H.; Shisler, J.L.; Whitby, D.; Renne, R. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus (KSHV) Induces the Oncogenic MiR-17-92 Cluster and Down-Regulates TGF-β Signaling. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.C.; Kim, H.; Choi, H.; Chang, M.S.; Lee, S.K. Epstein-Barr Virus MiR-BART1-3p Regulates the MiR-17-92 Cluster by Targeting E2F3. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walz, N.; Christalla, T.; Tessmer, U.; Grundhoff, A. A Global Analysis of Evolutionary Conservation among Known and Predicted Gammaherpesvirus MicroRNAs. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, D.; Kieffer-Kwon, P.; Ziegelbauer, J.M. Emerging Themes from EBV and KSHV MicroRNA Targets. Viruses 2012, 4, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, N.; Okuyama, K.; Ogata, J.; Kanai, A.; Helwak, A.; Takamatsu, M.; Imadome, K.I.; Takakura, K.; Chanda, B.; Kurosaki, N.; et al. Novel Functional Small RNAs Are Selectively Loaded onto Mammalian Ago1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Fenix, A.M.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Zhang, Q.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Liebler, D.C.; Ping, J.; Liu, Q.; Evans, R.; et al. Reassessment of Exosome Compo-sition. Cell 2019, 177, 428–445.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogev, O.; Henderson, S.; Hayes, M.J.; Marelli, S.S.; Ofir-Birin, Y.; Regev-Rudzki, N.; Herrero, J.; Enver, T. Herpesviruses Shape Tumour Microenvironment through Exosomal Transfer of Viral MicroRNAs. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshina, S.; Sekizuka, T.; Kataoka, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Hamada, H.; Kuroda, M.; Katano, H. Profile of Exosomal and Intracellular MicroRNA in Gamma-Herpesvirus-Infected Lymphoma Cell Lines. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chugh, P.E.; Sin, S.H.; Ozgur, S.; Henry, D.H.; Menezes, P.; Griffith, J.; Eron, J.J.; Damania, B.; Dittmer, D.P. Systemically Circulating Viral and Tumor-Derived MicroRNAs in KSHV-Associated Malignancies. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Nanbo, A.; Sun, L.; Lin, Z. Extracellular Vesicles in Epstein-Barr Virus’ Life Cycle and Pathogenesis. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cone, A.S.; York, S.B.; Meckes, D.G. Extracellular Vesicles in Epstein-Barr Virus Pathogenesis. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2019, 6, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevillet, J.R.; Kang, Q.; Ruf, I.K.; Briggs, H.A.; Vojtech, L.N.; Hughes, S.M.; Cheng, H.H.; Arroyo, J.D.; Meredith, E.K.; Gallichotte, E.N.; et al. Quantitative and Stoichiometric Analysis of the MicroRNA Content of Exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14888–14893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, M.; Chen, Y.F.A.; Hüls, C.; Gärtner, K.; Tagawa, T.; Mejias-Perez, E.; Keppler, O.T.; Göbel, C.; Zeidler, R.; Shein, M.; et al. MicroRNAs Are Minor Constituents of Extracellular Vesicles That Are Rarely Delivered to Target Cells. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miceli, R.T.; Chen, T.Y.; Nose, Y.; Tichkule, S.; Brown, B.; Fullard, J.F.; Saulsbury, M.D.; Heyliger, S.O.; Gnjatic, S.; Kyprianou, N.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles, RNA Sequencing, and Bioinformatic Analyses: Challenges, Solutions, and Recommendations. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e70005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Jeppesen, D.K.; Yang, Y.P.; Li, W.; McKinley, E.T.; Graves-Deal, R.; Ping, J.; Britain, C.M.; Dorsett, K.A.; et al. Transfer of Functional Cargo in Exomeres. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Jeppesen, D.K.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Graves-Deal, R.; Trinh, V.Q.; Ramirez, M.A.; Sohn, Y.; Neininger, A.C.; Taneja, N.; McKinley, E.T.; et al. Supermeres Are Functional Extracellular Nanoparticles Replete with Disease Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 23, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Freitas, D.; Kim, H.S.; Fabijanic, K.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; Martin, A.B.; Bojmar, L.; et al. Identification of Distinct Nanoparticles and Subsets of Extracellular Vesicles by Asymmetric Flow Field-Flow Fractionation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, C.J.; Li, L.; Hiers, N.M.; Li, T.; Sheng, P.; Huda, T.; Shan, J.; Gay, L.; Gu, T.; Bian, J.; et al. Sequencing of Argonaute-Bound MicroRNA/MRNA Hybrids Reveals Regulation of the Unfolded Protein Response by MicroRNA-320a. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimson, A.; Farh, K.K.H.; Johnston, W.K.; Garrett-Engele, P.; Lim, L.P.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNA Targeting Specificity in Mammals: Determinants Beyond Seed Pairing. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viollet, C.; Davis, D.A.; Reczko, M.; Ziegelbauer, J.M.; Pezzella, F.; Ragoussis, J.; Yarchoan, R. Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis Reveals Differential Expression Profiles of MiRNA-MRNA Target Pairs in KSHV-Infected Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungerleider, N.; Bullard, W.; Kara, M.; Wang, X.; Roberts, C.; Renne, R.; Tibbetts, S.; Flemington, E.K. EBV MiRNAs Are Potent Effectors of Tumor Cell Transcriptome Remodeling in Promoting Immune Escape. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalsky, R.L.; Corcoran, D.L.; Gottwein, E.; Frank, C.L.; Kang, D.; Hafner, M.; Nusbaum, J.D.; Feederle, R.; Delecluse, H.J.; Luftig, M.A.; et al. The Viral and Cellular MicroRNA Targetome in Lymphoblastoid Cell Lines. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haecker, I.; Gay, L.A.; Yang, Y.; Hu, J.; Morse, A.M.; McIntyre, L.M.; Renne, R. Ago HITS-CLIP Expands Understanding of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus MiRNA Function in Primary Effusion Lymphomas. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, L.A.; Sethuraman, S.; Thomas, M.; Turner, P.C.; Renne, R. Modified Cross-Linking, Ligation, and Sequencing of Hybrids (QCLASH) Identifies Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus MicroRNA Targets in Endothelial Cells. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02138-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafner, M.; Landthaler, M.; Burger, L.; Khorshid, M.; Hausser, J.; Berninger, P.; Roth-baller, A.; Ascano, M.; Jungkamp, A.C.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Transcriptome-Wide Identification of RNA-Binding Protein and MicroRNA Target Sites by PAR-CLIP. Cell 2010, 141, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ule, J.; Jensen, K.B.; Ruggiu, M.; Mele, A.; Ule, A.; Darnell, R.B. CLIP Identifies Nova-Regulated RNA Networks in the Brain. Science 2003, 302, 1212–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helwak, A.; Tollervey, D. Mapping the MiRNA Interactome by Cross-Linking Ligation and Sequencing of Hybrids (CLASH). Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Movassagh, M.; Morton, S.U.; Hehnly, C.; Smith, J.; Doan, T.T.; Irizarry, R.; Broach, J.R.; Schiff, S.J.; Bailey, J.A.; Paulson, J.N. MirTarRnaSeq: An R/Bioconductor Statistical Package for MiRNA-MRNA Target Identification and Interaction Analysis. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, T.M.; Bryceson, Y.T. IL2RB Maintains Immune Harmony. J. Ex-Perimental. Med. 2019, 216, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A CeRNA Hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a Hidden RNA Language? Cell 2011, 146, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, C.; Weisburd, B.; Stern-Ginossar, N.; Mercier, A.; Madrid, A.S.; Bellare, P.; Holdorf, M.; Weissman, J.S.; Ganem, D. KSHV 2.0: A Comprehensive Annotation of the Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Genome Using Next-Generation Sequencing Reveals Novel Genomic and Functional Features. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitton-Fry, R.M.; DeGregorio, S.J.; Wang, J.; Steitz, T.A.; Steitz, J.A. Poly(A) Tail Recognition by a Viral RNA Element Through Assembly of a Triple Helix. Science 2010, 330, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withers, J.B.; Li, E.S.; Vallery, T.K.; Yario, T.A.; Steitz, J.A. Two Herpesviral Noncoding PAN RNAs Are Functionally Homologous but Do Not Associate with Common Chromatin Loci. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, C.C.; Pari, G.S. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Noncoding Polyadenylated Nuclear RNA Interacts with Virus- and Host Cell-Encoded Proteins and Suppresses Expression of Genes Involved in Immune Modulation. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 13290–13297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, C.C.; Tarrant-Elorza, M.; Verma, S.; Purushothaman, P.; Pari, G.S. Regulation of Viral and Cellular Gene Expression by Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Polyadenylated Nuclear RNA. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5540–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.H.; Liu, W.; Li, P.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Luo, B. Sequence Analysis of Epstein-Barr Virus RPMS1 Gene in Malignant Hematopathy of Northern China. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquitz, A.R.; Raab-Traub, N. The Role of MiRNAs and EBV BARTs in NPC. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2012, 22, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Song, Y.; Luo, B. Conservation and Polymorphism of EBV RPMS1 Gene in EBV-Associated Tumors and Healthy Individuals from Endemic and Non-Endemic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Areas in China. Virus Res. 2018, 250, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoeven, R.J.A.; Tong, S.; Mok, B.W.Y.; Liu, J.; He, S.; Zong, J.; Chen, Y.; Tsao, S.W.; Lung, M.L.; Chen, H. Epstein-Barr Virus Bart Long Non-Coding Rnas Function as Ep-igenetic Modulators in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoeven, R.J.A.; Tong, S.; Zhang, G.; Zong, J.; Chen, Y.; Jin, D.-Y.; Chen, M.-R.; Pan, J.; Chen, H. NF-ΚB Signaling Regulates Expression of Epstein-Barr Virus BART MicroRNAs and Long Noncoding RNAs in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6475–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, R.H.; Raab-Traub, N. Major Role for Cellular MicroRNAs, Long Noncoding RNAs (LncRNAs), and the Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded BART LncRNA during Tumor Growth in Vivo. mBio 2022, 13, e0065522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungerleider, N.; Concha, M.; Lin, Z.; Roberts, C.; Wang, X.; Cao, S.; Baddoo, M.; Moss, W.N.; Yu, Y.; Seddon, M.; et al. The Epstein Barr Virus CircRNAome. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennekamp, A.J.; Lieberman, P.M. Initiation of Epstein-Barr Virus Lytic Replication Requires Transcription and the Formation of a Stable RNA-DNA Hybrid Molecule at OriLyt. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2837–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yetming, K.D.; Lupey-Green, L.N.; Biryukov, S.; Hughes, D.J.; Marendy, E.M.; Miranda, J.L.; Sample, J.T. The BHLF1 Locus of Epstein-Barr Virus Contributes to Viral Latency and B-Cell Immortalization. J. Virol. 2020, 94, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, M.T.; Coca-Prados, M. Electron Microscopic Evidence for the Circular Form of RNA in the Cytoplasm of Eukaryotic Cells. Nature 1979, 280, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, I.; Chen, Y.G. Emerging Roles of Circular RNAs in Innate Immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 68, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, S.; Zhou, H.; Feng, Z.; Xu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Li, P.; Wu, M. CircRNA: Functions and Properties of a Novel Potential Biomarker for Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.X.; Xue, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yin, Q.F.; Wei, J.; Yao, R.W.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. Coordinated CircRNA Biogenesis and Function with NF90/NF110 in Viral Infection. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 214–227.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.X.; Li, X.; Nan, F.; Jiang, S.; Gao, X.; Guo, S.K.; Xue, W.; Cui, Y.; Dong, K.; Ding, H.; et al. Structure and Degradation of Circular RNAs Regulate PKR Activation in Innate Immunity. Cell 2019, 177, 865–880.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.G.; Kim, M.V.; Chen, X.; Batista, P.J.; Aoyama, S.; Wilusz, J.E.; Iwasaki, A.; Chang, H.Y. Sensing Self and Foreign Circular RNAs by Intron Identity. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesselhoeft, R.A.; Kowalski, P.S.; Parker-Hale, F.C.; Huang, Y.; Bisaria, N.; Anderson, D.G. RNA Circularization Diminishes Immunogenicity and Can Extend Translation Duration in Vivo. Mol. Cell 2019, 74, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.G.; Chen, R.; Ahmad, S.; Verma, R.; Kasturi, S.P.; Amaya, L.; Broughton, J.P.; Kim, J.; Cadena, C.; Pulendran, B.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine Modification Controls Circular RNA Immunity. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.T.; Chen, J.N.; Gong, L.P.; Bi, Y.H.; Liang, J.; Zhou, L.; He, D.; Shao, C.K. Identification of Virus-Encoded Circular RNA. Virology 2019, 529, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toptan, T.; Abere, B.; Nalesnik, M.A.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Ranganathan, S.; Lee, N.; Shair, K.H.; Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. Circular DNA Tumor Viruses Make Circular RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8737–E8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Shuai, M.; Xia, Y. Knockdown of EBV-Encoded CircRNA CircRPMS1 Suppresses Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cell Proliferation and Metastasis through Sponging Multiple MiRNAs. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 8023–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagawa, T.; Gao, S.; Koparde, V.N.; Gonzalez, M.; Spouge, J.L.; Serquiña, A.P.; Lurain, K.; Ramaswami, R.; Uldrick, T.S.; Yarchoan, R.; et al. Discovery of Kaposi’s Sarcoma Herpesvirus-Encoded Circular RNAs and a Human Antiviral Circular RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 12805–12810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, S.; Jain, V.; Stribling, D.; Gay, L.A.; Naeem, M.; Baddoo, M.; Flemington, E.K.; Tibbetts, S.A.; Renne, R. A Viral Circular RNA in Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Modulates Viral and Host Gene Expression during Latent and Lytic Replication. Explor. Target. Antitumor. Ther. 2025, 6, 1002320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, K.L.; Mottram, T.J.; Anene, C.A.; Foster, B.; Patterson, M.R.; McDonnell, E.; Macdonald, A.; Westhead, D.; Whitehouse, A. Dysregulation of the MiR-30c/DLL4 Axis by CircHIPK3 Is Essential for KSHV Lytic Replication. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e54117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Jia, X.; Wang, F.; Sheng, L.; Song, P.; Cao, Y.; Shi, H.; Fan, W.; Ding, X.; Gao, S.J.; et al. CircRNA ARFGEF1 Functions as a CeRNA to Promote Oncogenic KSHV-Encoded Viral Interferon Regulatory Factor Induction of Cell Invasion and Angiogenesis by Upregulating Glutaredoxin 3. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagawa, T.; Oh, D.; Dremel, S.; Mahesh, G.; Koparde, V.N.; Duncan, G.; Andresson, T.; Ziegelbauer, J.M. A Virus-Induced Circular RNA Maintains Latent Infection of Kaposi’s Sarcoma Herpesvirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2212864120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Wang, J.; Xiong, F.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, K.; Wang, Y.; Mo, Y.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, S.; He, Y.; et al. Epstein–Barr Virus–Encoded Circular RNA CircBART2.2 Promotes Immune Escape of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Regulating PD-L1. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 5074–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Chen, J.; Dong, M.; Xiao, Z.; Feng, Z.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bi, Y.; et al. Epstein–Barr Virus-derived Circular RNA LMP2A Induces Stemness in EBV-associated Gastric Cancer. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e49689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Wang, S.; Lin, K.; Zong, J.; Zheng, Q.; Su, Y.; Huang, T. Competitive Endogenous RNA Landscape in Epstein-Barr Virus Associated Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 782473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasda, E.; Parker, R. Circular RNAs Co-Precipitate with Extracellular Vesicles: A Possible Mechanism for Circrna Clearance. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, D.; Wu, Y.; Lian, J. Circular RNA Vaccine in Disease Prevention and Treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naipauer, J.; García Solá, M.E.; Salyakina, D.; Rosario, S.; Williams, S.; Coso, O.; Abba, M.C.; Mesri, E.A.; Lacunza, E. A Non-Coding RNA Network Involved in KSHV Tumorigenesis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 687629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Zeng, J.; Chao, W.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Deng, K.; Huang, Z.; Li, J.; Dai, M.; Chen, S.; et al. Serum Long Non-Coding RNAs MALAT1, AFAP1-AS1 and AL359062 as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 41166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.M.; Lian, G.Y.; Song, Y.; Huang, Y.F.; Gong, Y. LncRNA MALAT1 Promotes Tumorigenesis and Immune Escape of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma by Sponging MiR-195. Life Sci. 2019, 231, 116335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Wei, F.; Gong, Z.; Bo, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Xiang, B.; Guo, C.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded MiR-BART6-3p Inhibits Cancer Cell Metastasis and Invasion by Targeting Long Non-Coding RNA LOC553103. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethuraman, S.; Gay, L.A.; Jain, V.; Haecker, I.; Renne, R. MicroRNA Dependent and Independent Deregulation of Long Non-Coding RNAs by an Oncogenic Herpesvirus. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallen, A.N.; Zhou, X.B.; Xu, J.; Qiao, C.; Ma, J.; Yan, L.; Lu, L.; Liu, C.; Yi, J.S.; Zhang, H.; et al. The Imprinted H19 LncRNA Antagonizes Let-7 MicroRNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, D.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, X. Long Noncoding RNA H19 Competitively Binds MiR-17-5p to Regulate YES1 Expression in Thyroid Cancer. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 2326–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Cullen, B.R. The Imprinted H19 Noncoding RNA Is a Primary MicroRNA Precursor. RNA 2007, 13, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, S.; Zhao, M.; Luo, B. LMP1 Induces P53 Protein Expression via the H19/MiR-675-5p Axis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0000622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, L.; Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; He, Y.; Zhuang, R.; Gu, Y.; Yan, Q.; Li, W.; Lu, C. VFLIP-Regulated Competing Endogenous RNA (CeRNA) Networks Targeting Lytic Induction for KSHV-Associated Malignancies. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 2766–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wightman, F.F.; Giono, L.E.; Fededa, J.P.; De La Mata, M. Target RNAs Strike Back on MicroRNAs. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Mata, M.; Gaidatzis, D.; Vitanescu, M.; Stadler, M.B.; Wentzel, C.; Scheiffele, P.; Filipowicz, W.; Großhans, H. Potent Degradation of Neuronal Mi RNA s Induced by Highly Complementary Targets. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Song, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Hong, Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.; Baek, D.; Ahn, K. Selective Degradation of Host MicroRNAs by an Intergenic HCMV Noncoding RNA Accelerates Virus Production. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcinowski, L.; Tanguy, M.; Krmpotic, A.; Rädle, B.; Lisnić, V.J.; Tuddenham, L.; Chane-Woon-Ming, B.; Ruzsics, Z.; Erhard, F.; Benkartek, C.; et al. Degradation of Cellular MiR-27 by a Novel, Highly Abundant Viral Transcript Is Important for Efficient Virus Replication in Vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazalla, D.; Yario, T.; Steitz, J. Down-Regulation of a Host MicroRNA by a Herpesvirus Saimiri Noncoding RNA. Science 2010, 328, 1563–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennig, T.; Prusty, A.B.; Kaufer, B.B.; Whisnant, A.W.; Lodha, M.; Enders, A.; Thomas, J.; Kasimir, F.; Grothey, A.; Klein, T.; et al. Selective Inhibition of MiRNA Processing by a Herpesvirus-Encoded MiRNA. Nature 2022, 605, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, J.A.; Liang, Z.; Xu, J.K.; Gottwein, E. Retargeting Target-Directed MicroRNA-Decay Sites to Highly Expressed Viral or Cellular MiRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, 14171–14183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Pimienta, G.; Steitz, J.A. AUF1/HnRNP D Is a Novel Protein Partner of the EBER1 Noncoding RNA of Epstein-Barr Virus. RNA 2012, 18, 2073–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez-Calvillo, G.; Martin, S.; Hamm, C.; Sztuba-Solinska, J. The Structure-To-Function Relationships of Gammaherpesvirus-Encoded Long Non-Coding RNAs and Their Con-tributions to Viral Pathogenesis. Noncoding RNA 2018, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, M.; Iwakiri, D.; Kanda, T.; Imaizumi, T.; Takada, K. EB Virus-Encoded RNAs Are Recognized by RIG-I and Activate Signaling to Induce Type I IFN. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakiri, D. Multifunctional Non-Coding Epstein-Barr Virus Encoded RNAs (EBERs) Contribute to Viral Pathogenesis. Virus Res. 2016, 212, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakiri, D.; Zhou, L.; Samanta, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Ebihara, T.; Seya, T.; Imai, S.; Fujieda, M.; Kawa, K.; Takada, K. Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-Encoded Small RNA Is Released from EBV-Infected Cells and Activates Signaling from Toll-like Receptor 3. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 2091–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, N.; Goto, M.; Kurozumi, K.; Maruo, S.; Fukayama, M.; Naoe, T.; Yasukawa, M.; Hino, K.I.; Suzuki, T.; Todo, S.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded Poly(A)(-) RNA Supports Burkitt’s Lymphoma Growth through Interleukin-10 Induction. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 6742–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Moss, W.N.; Yario, T.A.; Steitz, J.A. EBV Noncoding RNA Binds Nascent RNA to Drive Host PAX5 to Viral DNA. Cell 2015, 160, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; He, X.; Silva, E. Stable Intronic Sequence RNAs (SisRNAs) Are Selected Regions in Introns with Distinct Properties. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, I.; Tay, M.L.I.; Pek, J.W. Stable Intronic Sequence RNAs (SisRNAs): A New Layer of Gene Regulation. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-Intron Circular RNAs Regulate Transcription in the Nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tompkins, V.S.; Valverde, D.P.; Moss, W.N. Human Regulatory Proteins Associate with Non-Coding RNAs from the EBV IR1 Region. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymula, A.; Palermo, R.D.; Bayoumy, A.; Groves, I.J.; Ba abdullah, M.; Holder, B.; White, R.E. Epstein-Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen EBNA-LP Is Essential for Transforming Naïve B Cells, and Facilitates Recruitment of Transcription Factors to the Viral Genome. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, W.N.; Steitz, J.A. Genome-Wide Analyses of Epstein-Barr Virus Reveal Conserved RNA Structures and a Novel Stable Intronic Sequence RNA. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, E.R.; Kara, M.; Coleman, C.B.; Grau, K.R.; Oko, L.M.; Krueger, B.J.; Renne, R.; van Dyk, L.F.; Tibbetts, S.A. Virus-Encoded MicroRNAs Facilitate Gammaherpesvirus Latency and Pathogenesis In Vivo. mBio 2014, 5, e00981-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullard, W.L.; Kara, M.; Gay, L.A.; Sethuraman, S.; Wang, Y.; Nirmalan, S.; Esemenli, A.; Feswick, A.; Hoffman, B.A.; Renne, R.; et al. Identification of Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68 MiRNA-MRNA Hybrids Reveals MiRNA Target Conservation among Gam-maherpesviruses Including Host Translation and Protein Modification Machinery. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diebel, K.W.; Smith, A.L.; Van Dyk, L.F. Mature and Functional Viral MiRNAs Tran-scribed from Novel RNA Polymerase III Promoters. RNA 2010, 16, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, E.R.; Kara, M.; Oko, L.M.; Grau, K.R.; Krueger, B.J.; Zhang, J.; Feng, P.; van Dyk, L.F.; Renne, R.; Tibbetts, S.A. A Gammaherpesvirus Noncoding RNA Is Essential for Hematogenous Dissemination and Establishment of Peripheral Latency. Msphere 2016, 1, e00105-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kara, M.; Tibbetts, S.A. Evaluation of Immune Sensor Responses to a Viral Small Noncoding RNA. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1459256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, B.A.; Wang, Y.; Feldman, E.R.; Tibbetts, S.A. Epstein-Barr Virus EBER1 and Murine Gammaherpesvirus TMER4 Share Conserved in Vivo Function to Promote B Cell Egress and Dissemination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 25392–25394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aufgebauer, C.J.; Bland, K.M.; Horner, S.M. Modifying the Antiviral Innate Immune Response by Selective Writing, Erasing, and Reading of M6A on Viral and Cellular RNA. Cell Chem. Biol. 2024, 31, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, T.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, W.; Chen, M.; Ye, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A.; et al. N(6)-methyladenosine-binding Protein YTHDF1 Suppresses EBV Replication and Promotes EBV RNA Decay. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e50128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, F.; Singh, R.K.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, K.; Robertson, E.S. EBV Epitranscriptome Reprogramming by METTL14 Is Critical for Viral-Associated Tumorigenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Y.; Peng, Q.; Lu, J.; Wei, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Wu, Y.; et al. RNA M6A Methylation Regulates Virus–Host Interaction and EBNA2 Expression during Epstein–Barr Virus Infection. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2021, 9, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagi, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Hara, Y.; Sato, Y.; Kimura, H.; Murata, T. EBV Exploits RNA M6A Modification to Promote Cell Survival and Progeny Virus Production During Lytic Cycle. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 870816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, D.; Lin, X.; Gao, L.; Wei, Z.; Pei, Y.; Robertson, E.S. Attenuation of IFN Signaling Due to M6A Modification of the Host Epitranscriptome Promotes EBV Lytic Reactivation. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, B.A.; Kanarek, J.P.; Kotter, A.; Helm, M.; Lee, N. 5-Methylcytosine Modification of an Epstein–Barr Virus Noncoding RNA Decreases Its Stability. RNA 2020, 26, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Kong, L.; Cheng, J.; Al Moussawi, K.; Chen, X.; Iqbal, A.; Wing, P.A.C.; Harris, J.M.; Tsukuda, S.; Embarc-Buh, A.; et al. Absolute Quantitative and Base-Resolution Sequencing Reveals Comprehensive Landscape of Pseudouridine across the Human Transcriptome. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 2024–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, F.; Chen, E.R.; Nilsen, T.W. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Utilizes and Manipulates RNA N 6-Adenosine Methylation To Promote Lytic Replication. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00466-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Da Silva, S.R.; Zhang, L.; Meng, J.; Cui, X.; Yuan, H.; Sorel, O.; Zhang, S.W.; et al. Viral and Cellular N6-Methyladenosine and N6,2′-O-Dimethyladenosine Epitranscriptomes in the KSHV Life Cycle. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 3, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ni, G.; Damania, B. ADAR1 Facilitates KSHV Lytic Reactivation by Modulating the RLR-Dependent Signaling Pathway. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendren, S.; Ye, X.; Dunker, W.; Richardson, A.; Karijolich, J. The Cellular and KSHV A-to-I RNA Editome in Primary Effusion Lymphoma and Its Role in the Viral Lifecycle. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Ding, X.; Ma, X.; Li, W.; Jia, X.; Gao, S.J.; Lu, C. NAT10-Dependent N 4-acetylcytidine Modification Mediates PAN RNA Stability, KSHV Reactivation, and IFI16-Related Inflammasome Activation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, A.; Winiarek, G.; Hołówka, O.; Godlewski, J.; Bronisz, A. Unlocking the Secrets of the Immunopeptidome: MHC Molecules, NcRNA Peptides, and Vesicles in Immune Response. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornesello, A.L.; Cerasuolo, A.; Starita, N.; Amiranda, S.; Cimmino, T.P.; Bonelli, P.; Tuccillo, F.M.; Buonaguro, F.M.; Buonaguro, L.; Tornesello, M.L. Emerging Role of Endogenous Peptides Encoded by Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer Biology. Noncoding RNA Res. 2025, 10, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.L. Towards Higher-Resolution and in Vivo Understanding of LncRNA Biogenesis and Function. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 1152–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani-Kukia, N.; Abbasi, A. New Insights on Circular RNAs and Their Potential Applications as Biomarkers, Therapeutic Agents, and Preventive Vaccines in Viral Infections: With a Glance at SARS-CoV-2. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 29, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iizasa, H.; Kim, H.; Kartika, A.V.; Kanehiro, Y.; Yoshiyama, H. Role of Viral and Host MicroRNAs in Immune Regulation of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 502282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, R.W.M.; Tong, J.H.M.; Sung, Y.M.; Leung, P.S.; Ng, D.C.H.; Chau, S.L.; Chan, A.W.H.; Ng, E.K.O.; Lo, K.W.; To, K.F. Modulation of LMP2A Expression by a Newly Identified Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded MicroRNA MiR-BART22. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalsky, R.L.; Cullen, B.R. EBV Noncoding RNAs. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 391, 181–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondada, M.S.; Yao, Y.; Nair, V. Multifunctional MiR-155 Pathway in Avian Oncogenic Virus-Induced Neoplastic Diseases. Non-Coding RNA 2019, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
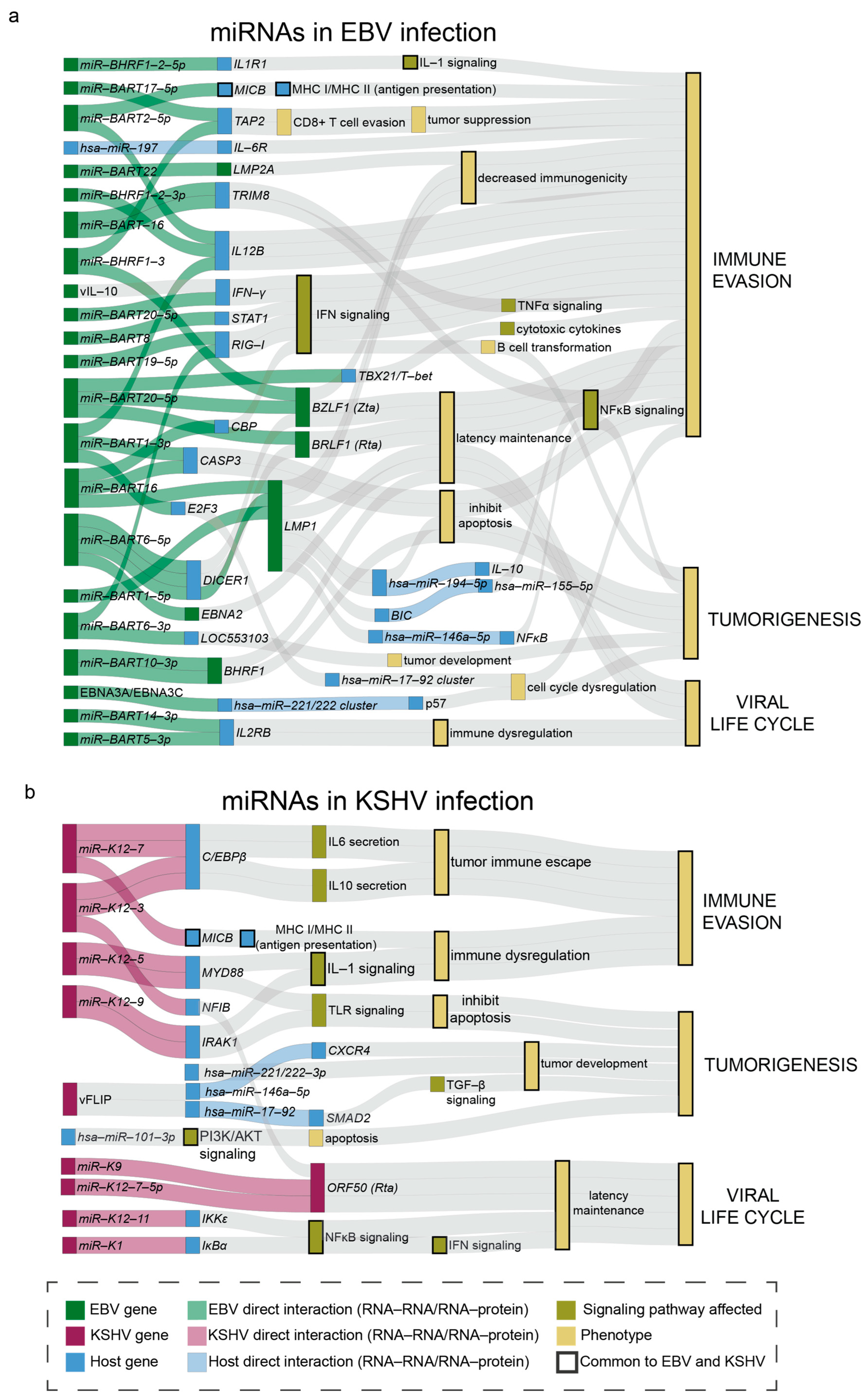

| Virus and Cell Line | Method | miRNA–mRNA Targets Identified | Validated Targets | Pathway Analysis—Top Pathways | Findings | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KSHV (BC-1, BC-3) | PAR-CLIP | Identified 1741 and 1409 target mRNAs in BC-1 and BC-3, respectively. KSHV miRNAs directly target more than 2000 cellular mRNAs. | Confirmed identified targets of miR-155. Confirmed 12 out of 29 KSHV miRNA targets, with expression >40%. | Regulation of transcription, intracellular signaling cascade, and protein localization. | It was found that 58% of mRNAs targeted by KSHV are also targeted by EBV miRNAs. KSHV encodes a viral miRNA that mimics cellular miR-142-3p function. | [78] |
| KSHV (BC-1, BC-3) | HITS-CLIP | Identified 1170 and 950 cellular KSHV miRNA targets from BCBL-1 and BC-3 cells. | Confirmed 10 of 12 miR-K11 targets. Validated vIL-6 as a miR-K12-10 target. | Apoptosis, glycolysis, and lymphocyte activation. | Only had 42% overlap with Gottwein method. | [112] |
| EBV (Jijoye) | HITS-CLIP | mRNA targets of 44 EBV and 310 human miRNAs. | LMP1 repression via BART miRNAs and host miRs. miR-17 family targets were validated. | Transcription, apoptosis, Wnt signaling, and the cell cycle. | miRNAs do not control the latent/lytic switch by targeting EBV lytic genes. | [84] |
| EBV (LCLs) | PAR-CLIP | Identified 500 EBV miRNA targets. | Tested 29 miRNA:3’UTR combinations, identified by PAR-CLIP. There was >20% KD of luciferase expression for 21 out of the 29 PAR-CLIP-identified miRNA:3’UTR pairs. | p53 feedback loops, B cell activation, and apoptosis. | At least 14 EBV miRNAs, including those not encoded by B95-8, share seed sequence homology with cellular miRNAs. | [111] |
| KSHV (endothelial cells) | qCLASH | Identified 3324 target genes in 2 of 3 replicates, 1433 in 3 replicates. | Validated 30 of 54 identified miR-K11 targets. | Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway, apoptosis, cell cycle control, and glycolysis. | When looking at existing HITS-CLIP, 223 and 169 targets were shared with BC-1 and BC-3 cells, respectively. | [113] |
| EBV (Akata, SNU719) | qCLASH | Over 1700 viral and cellular targets. | In vivo validation—higher targeting efficacies of EBV miRNAs likely translate into stronger functional influences on their targets. | Antigen processing and presentation (MHC class I), ubiquitin and proteasome degradation, IFN-stimulated genes, and ISG15 antiviral mechanisms. | EBV miRNAs regulate the tumor cell phenotype and the immune cell microenvironment. | [110] |
| Element (ncRNA/Protein) | Type | Origin | Immune Target(s) | Mechanism | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ebv-miR-BART1-3p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | IL12B, miR-17, CASP3 (Caspase 3) | Reduces CD4+ T cell differentiation, inhibits E2F3, decreasing miR-17, increases cell survival. | [45,49,72] |
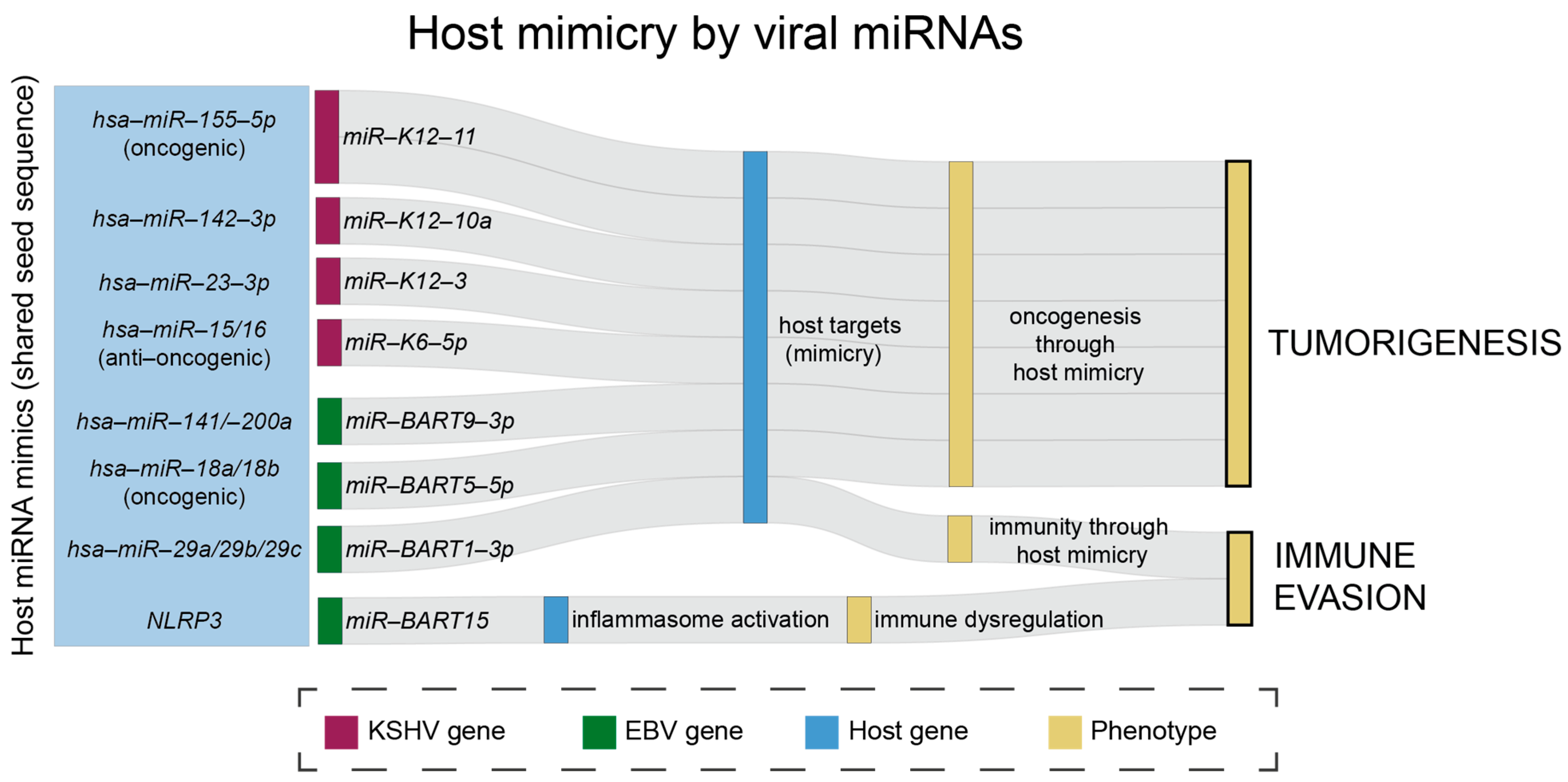
| ebv-miR-BART1-3p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | miR-29a/b/c | Mimic, downregulated in NPC to increase cell migration/DNA methylation. | [45] |
| ebv-miR-BART1-5p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | LMP1, IL12B | Reduces EBV immunogenicity/evades immunity. | [49,50] |
| ebv-miR-BART2 -5p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | IL12B, MICB | Reduces CD4+ T cell differentiation, MHC I presentation. | [47,49] |
| ebv-miR-BART5-5p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | miR-18a/b | Mimic, upregulated in NPC; they are part of the oncogenic miR-17-92 cluster. | [45] |
| ebv-miR-BART5-3p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | IL2RB | Affects interleukin pathways | [117] |
| ebv-miR-BART6-5p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | Dicer, Rta, Zta, EBNA2 | Establishment/maintenance of latency. | [68] |
| ebv-miR-BART6-3p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | RIG-I pathway, lncRNA-LOC553103 | Downregulates IFN response (RIG-I genes), downregulates lncRNA-LOC553103, inhibits the metabolism and migration of tumor cells. | [56,158] |
| ebv-miR-BART8 | miRNA | viral (EBV) | STAT1 | Downregulates IFN response (IFN-γ-STAT1 signaling pathway). | [54] |
| ebv-miR-BART9-3p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | miR-141, -200a | Mimics, downregulates 141/200a to promote tumor. | [45] |
| ebv-miR-BART10-3p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | BHRF1 | Increases BHRF1 protein levels and apoptosis. | [84] |
| ebv-miR-BART14-3p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | IL2RB | Affects interleukin pathways. | [117] |
| ebv-miR-BART15 | miRNA | viral (EBV) | NLRP3 | Restricts inflammasome activation. | [71] |
| ebv-miR-BART16 | miRNA | viral (EBV) | LMP1, CBP (CREB binding protein), TRIM8, CASP3 | Reduces EBV immunogenicity/evades immunity, downregulates IFN response, reduces antiviral immunity, increase cell survival. | [52,72,110,208] |
| ebv-miR-BART17-5p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | TAP2 | CD8+ cell evasion. | [48] |
| ebv-miR-BART19-5p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | DDX58 (RIG-1) | Decreases RIG-1 PRR expression. | [53] |
| ebv-miR-BART20-5p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | TBX21/T-bet, IFN- γ, BZLF1, BRLF1 | Decreases cytotoxic cytokine production, downregulates IFN response (IFN-γ-STAT1 signaling pathway), promotes latency. | [54,70,208] |
| ebv-miR-BART22 | miRNA | viral (EBV) | LMP2A | Decreases immunogenicity, promotes evasion/oncogenesis. | [209] |
| ebv-miR-BHRF1-2-3p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | IL12B | Reduces CD4+ T cell differentiation. | [49] |
| ebv-miR-BHRF1-2-5p | miRNA | viral (EBV) | IL1R1 | Blocks IL-1 signaling. | [55] |
| ebv-miR-BHRF1-3 | miRNA | viral (EBV) | TAP2, BZLF1 | CD8+ cell evasion, suppresses lytic replication and gene expression. | [48,69] |
| hsa-miR-197 | miRNA | host (EBV) | IL-6R | Upregulated in EBV BL, decreasing IL-6R. | [73] |
| circRPMS1_E4_E3a | lncRNA (circRNA) | viral (EBV) | unknown mechanism | Downregulates 11 cellular miRNAs, increased cell migration. | [142] |
| circLMP2A | lncRNA (circRNA) | viral (EBV) | miR-3908 (TDMD) | miR-3908/TRIM59/p53 axis. miR-3908 downregulated, TRIM59 upregulated, p53 degraded. Promotes invasion, metastasis and EMT | [151] |
| circBART2.2 | lncRNA (circRNA) | viral (EBV) | RIG-I protein, IRF3 | Activates PD-L1 and promotes tumor immune escape. Activates NF-κB, promotes tumor development. | [150] |
| circRELL1(4,5,6).1 | lncRNA (circRNA) | host (KSHV) (EBV, HCMV) | TTI1 | Causes pro-latency phenotypes via maintaining PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway (KSHV). Also induced by EBV and HCMV. | [145,149] |
| circACADM(7,8,9,10).1 | lncRNA (circRNA) | host (EBV) | miR-221-3p | miR-221-3p/CDKN1B axis for cell cycle dysregulation in EBV (increases miR-221, lowers CDKN1B). | [152] |
| circMDM2(6,7,8).1 | lncRNA (circRNA) | host (EBV) | miR-589-5p | miR-589-5p/RPGR axis. Potential regulatory role in cancer. | [152] |
| circWDFY1(7,8,9).1 | lncRNA (circRNA) | host (EBV) | no known mechanism | Upregulated in EBV NPC. | [152] |
| MALAT1 | lncRNA | host (EBV) | miR-195 | Sponges miR-195, increases PD-L1 and EBV tumor escape. | [157] |
| LMP1 | protein | viral (EBV) | H19, BIC, miR-194, miR-146a | LMP1/H19/miR-675-5p/p53. Decreases H19 and miR-675-5p, increasing p53, promoting latency. Induces miR-155 activation in B-lymphocytes. Downregulates miR-194, which downregulates IL-10, and induces apoptosis. Induces miR-146a, inducing NF-κB. | [74,76,89,160,161] |
| EBNA3A, EBNA3C | protein | viral (EBV) | miR-222/221 | Binds and activates miR-222/221. | [86] |
| EBER1 | ncRNA | viral (EBV) | La protein IL-10 | TLR3 activation, inflammation, activates RIG-1. | [176,177] |
| EBER2 | ncRNA | viral (EBV) | PAX5 | Promotes lytic infection, activates RIG-1. | [178] |
| miR-155 | miRNA | host (KSHV/EBV) | NF-κB | Mimicked in KSHV. Activated in EBV. | [61,75,76,210,211] |
| miR-K12-1 | miRNA | viral (KSHV) | NF-κB | Suppresses RTA to maintain latency. | [62] |
| kshv-miR-K12-3 | miRNA | viral (KSHV) | nuclear factor I/B,C/EBPβ, hsa-miR-23 | Suppresses lytic replication and gene expression; suppresses RTA to maintain latency. Increases IL-6 and IL-10 secretion. Hsa-miR-23 mimic. | [63,64,79] |
| kshv-miR-K12-5 | miRNA | viral (KSHV) | MYD88 | TLR/IL1-R signaling. | [58] |
| kshv-miR-K12-6-5p | miRNA | viral (KSHV) | miR-15/16 | Mimics, inhibits cell cycle progression, decreases tumor | [80] |
| kshv-miR-K12-7-5p | miRNA | viral (KSHV) | RTA | Maintains latency. | [65] |
| kshv-miR-K12-7 | miRNA | viral (KSHV) | MICB, C/EBPβ | MHC I. Increases IL-6 and IL-10 secretion. | [63] |
| kshv-miR-K12-9 | miRNA | viral (KSHV) | IRAK1, RTA | TLR/IL1-R signaling. Maintains latency. | [58,66] |
| kshv-miR-K12-10a | miRNA | viral (KSHV) | miR-142-3p | Mimic of miR-142-3p | [79] |
| kshv-miR-K12-11 | miRNA | viral (KSHV) | IKKɛ, miR-155 | Maintains latency, controls IFN signaling (NF-κB), miR-155 mimic impacting B cell development. | [59,60] |
| circvIRF4 | lncRNA (circRNA) | viral (KSHV) | Unknown | Potentially regulates gene expression. | [146] |
| miR-222/221 | miRNA | host (KSHV) | p57KIP2 | Downregulated in KSHV. | [85] |
| circHIPK3(2).1 | lncRNA (circRNA) | host (KSHV) | miR-29b and miR-30c | ceRNA network circHIPK3(2).1/miR-29b/DLL4, to regulate cell cycle. Upregulated in KSHV (unknown how). | [147] |
| PAN | lncRNA | viral (KSHV) | JMJD3, UTX, PRC2 | Regulates late gene expression, induces IL-4 level, decreases IFN-γ and IL-18 levels. | [123,124] |
| circPAN | lncRNA (circRNA) | viral (KSHV) | Unknown | Function not yet known. | [143,145] |
| vFLIP (K13) | protein | viral (KSHV) | miR-17, miR-146a. circSHROOM3(5).1, AL031123.1 | Induces miR-17 to decrease TGF-β signaling pathway, promotes tumor. Downregulates CXCR4, upregulating miR-146a. circSHROOM3(5).1/hsa-miR-378i/SPEG/FOXQ1. Increase in miR-378i to inhibit KSHV reactivation. AL031123.1/hsa-miR-378i/SPEG/FOXQ1. increase in miR-378i to inhibit KSHV reactivation. | [90,164] |
| vIRF1 | protein | viral (KSHV) | LEF1 | Induces circARFGEF1(2,3,4).1, which degrades miR-125a-3p, inducing GLRX3, increasing cell proliferation and angiogenesis. | [148] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Media, T.S.; Cano-Aroca, L.; Tagawa, T. Non-Coding RNAs and Immune Evasion in Human Gamma-Herpesviruses. Viruses 2025, 17, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071006
Media TS, Cano-Aroca L, Tagawa T. Non-Coding RNAs and Immune Evasion in Human Gamma-Herpesviruses. Viruses. 2025; 17(7):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071006
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedia, Tablow S., Laura Cano-Aroca, and Takanobu Tagawa. 2025. "Non-Coding RNAs and Immune Evasion in Human Gamma-Herpesviruses" Viruses 17, no. 7: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071006
APA StyleMedia, T. S., Cano-Aroca, L., & Tagawa, T. (2025). Non-Coding RNAs and Immune Evasion in Human Gamma-Herpesviruses. Viruses, 17(7), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071006






