The Multigene Family Genes-Encoded Proteins of African Swine Fever Virus: Roles in Evolution, Cell Tropism, Immune Evasion, and Pathogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of the MGFs
3. The Driving Factors of Diversity During the ASFV Pandemic
4. The Diversity and Significance of the MGFs-Encoded Proteins
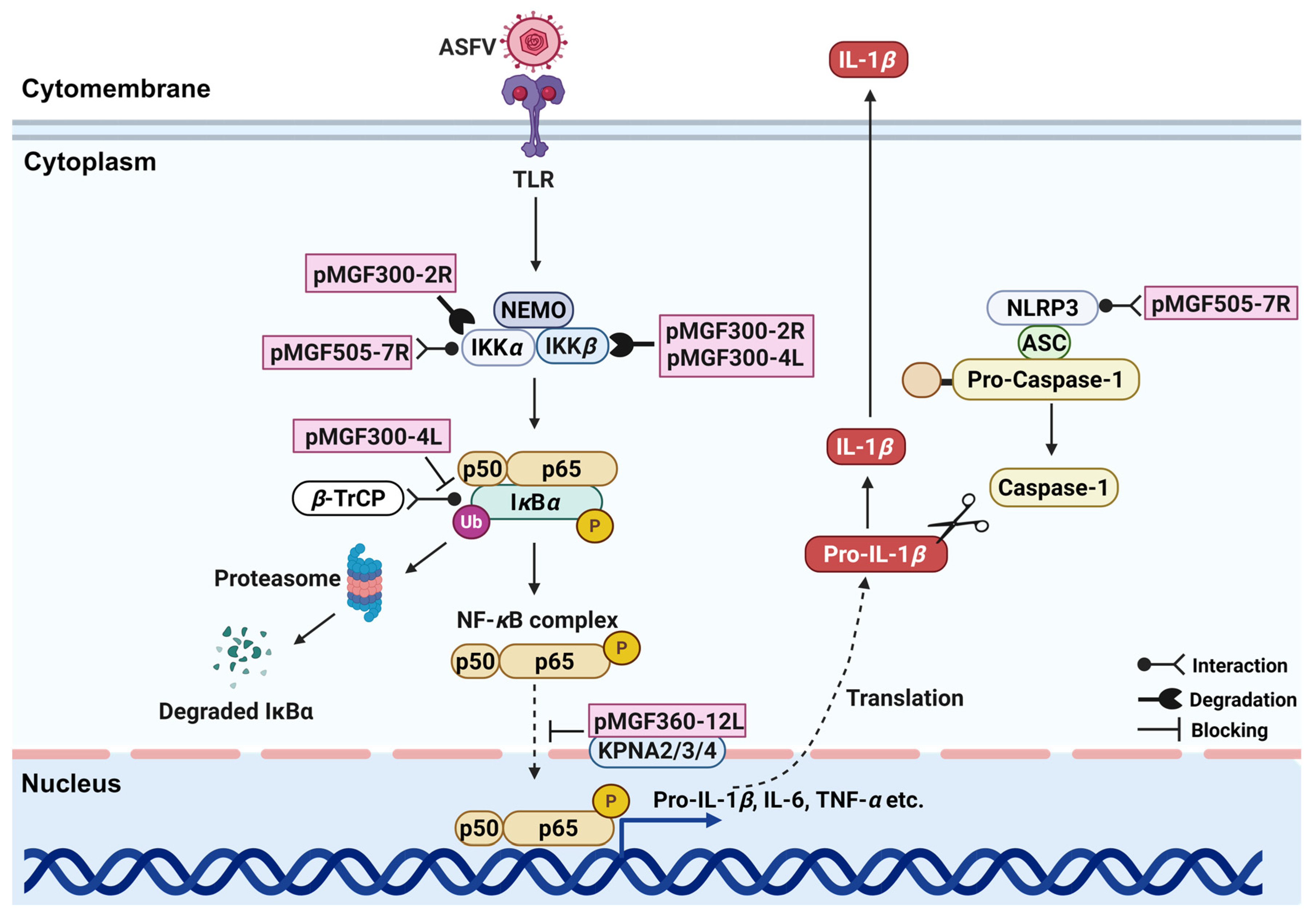
4.1. Immunomodulatory Factors: Regulating IFNs and Inflammatory Responses
4.2. Important Virulence-Associated Factors: Regulation of ASFV Infectivity and Pathogenicity
4.3. Viral Cell Tropism Determinants
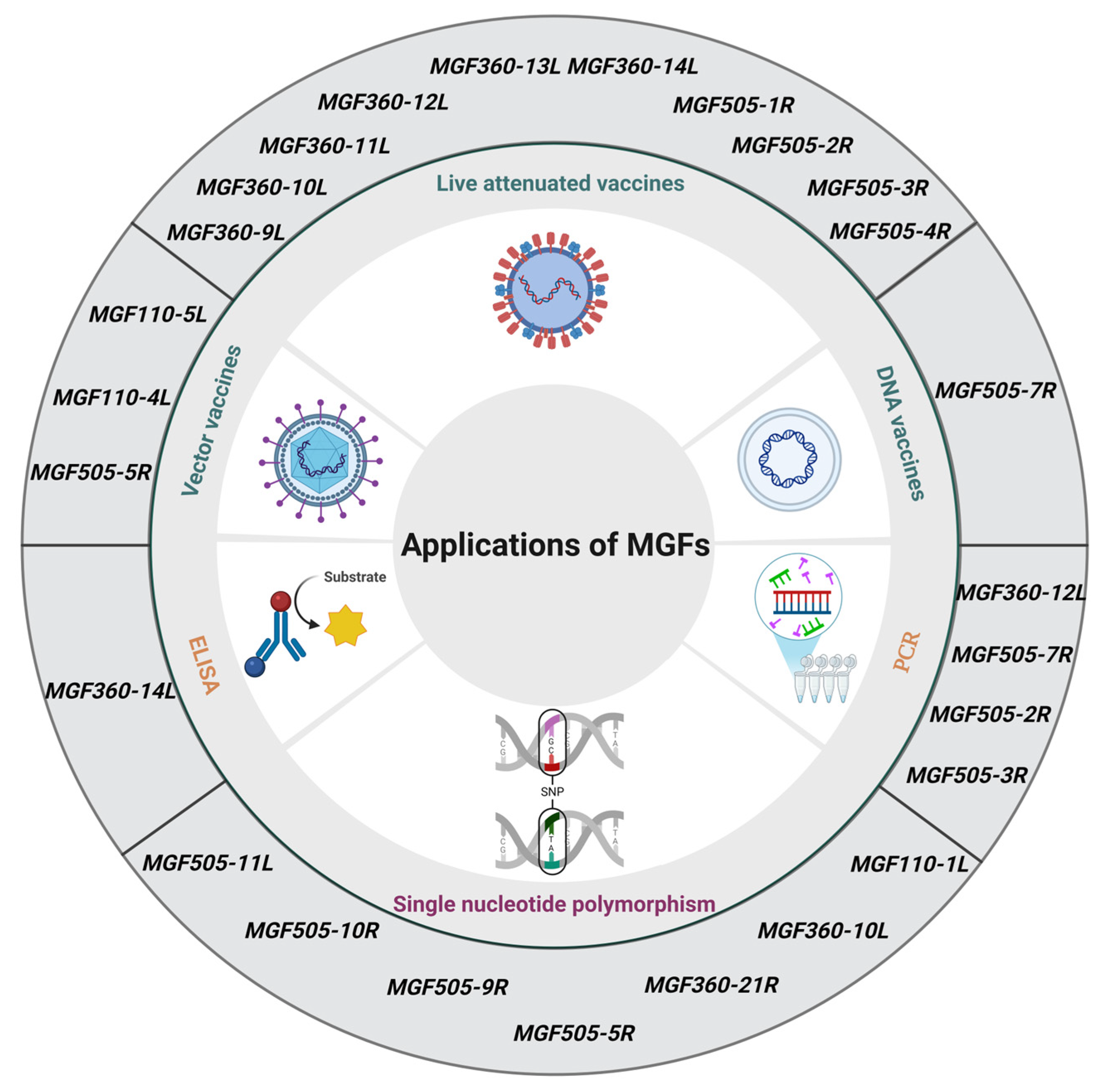
5. Translational Applications of MGFs-Related Research
5.1. Molecular Markers of Genetic Evolution in ASFV
5.2. Early Detection and Differential Diagnosis Targets
5.3. New Targets for Designing Vaccines
6. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, H.J. African swine fever: An unprecedented disaster and challenge to China. Infect. Dis. 2018, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Sun, E.; Huang, L.; Ding, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shen, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, T.; et al. Highly lethal genotype I and II recombinant African swine fever viruses detected in pigs. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, V.P.; Nguyen, V.T.; Le, T.B.; Mai, N.T.A.; Nguyen, V.D.; Than, T.T.; Lai, T.N.H.; Cho, K.H.; Hong, S.K.; Kim, Y.H.; et al. Detection of recombinant African swine fever virus strains of p72 genotypes I and II in domestic pigs. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, T.; Luo, R.; Lu, Z.; Lan, J.; Sun, Y.; Fu, Q.; Qiu, H.J. Genetic variations of African swine fever virus: Major challenges and prospects. Viruses 2024, 16, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, L.K.; Chapman, D.A.; Netherton, C.L.; Upton, C. African swine fever virus replication and genomics. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsak, L.; Lu, Z.; Kutish, G.F.; Neilan, J.G.; Rock, D.L. An African swine fever virus virulence-associated gene NL-S with similarity to the herpes simplex virus ICP34.5 gene. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 8865–8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilan, J.G.; Zsak, L.; Lu, Z.; Kutish, G.F.; Afonso, C.L.; Rock, D.L. Novel swine virulence determinant in the left variable region of the African swine fever virus genome. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 3095–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathakrishnan, A.; Connell, S.; Petrovan, V.; Moffat, K.; Goatley, L.C.; Jabbar, T.; Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Reis, A.L.; Dixon, L.K. Differential effect of deleting members of African swine fever virus MGF360 and MGF505 from the genotype II Georgia 2007/1 isolate on virus replication, virulence, and induction of protection. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0189921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, C.L.; Piccone, M.E.; Zaffuto, K.M.; Neilan, J.; Kutish, G.F.; Lu, Z.; Balinsky, C.A.; Gibb, T.R.; Bean, T.J.; Zsak, L.; et al. African swine fever virus MGF360 and MGF530 genes affect host interferon response. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 1858–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, R.; Agüero, M.; Almendral, J.M.; Viñuela, E. Variable and constant regions in African swine fever virus DNA. Virology 1989, 168, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almendral, J.M.; Almazán, F.; Blasco, R.; Viñuela, E. Multigene families in African swine fever virus: Family 110. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 2064–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Calvo, V.; Almazán, F.; Almendral, J.M.; Ramírez, J.C.; De la Vega, I.; Blasco, R.; Viñuela, E. Multigene families in African swine fever virus: Family 360. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 2073–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vydelingum, S.; Baylis, S.A.; Bristow, C.; Smith, G.L.; Dixon, L.K. Duplicated genes within the variable right end of the genome of a pathogenic isolate of African swine fever virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1993, 74, 2125–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.M.; Yañez, R.J.; Pan, R.; Rodríguez, J.F.; Salas, M.L.; Viñuela, E. Multigene families in African swine fever virus: Family 505. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 2746–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yozawa, T.; Kutish, G.F.; Afonso, C.L.; Lu, Z.; Rock, D.L. Two novel multigene families, 530 and 300, in the terminal variable regions of African swine fever virus genome. Virology 1994, 202, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, T.; Zou, Y.; Peng, Y. Classification and characterization of multigene family proteins of African swine fever viruses. Brief Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, L.K.; Islam, M.; Nash, R.; Reis, A.L. African swine fever virus evasion of host defences. Virus Res. 2019, 266, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, L.K.; Sun, H.; Roberts, H. African swine fever. Antivir. Res. 2019, 165, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.L.X.; McVey, D.S. Recent progress on gene-deleted live-attenuated African swine fever virus vaccines. NPJ Vaccines 2024, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, S.; Ribeiro, G.; Costa, J.V. Sequence and organization of the left multigene family 110 region of the Vero-adapted L60V strain of African swine fever virus. Virus Genes 1997, 15, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.M.; Moreno, L.T.; Alejo, A.; Lacasta, A.; Rodríguez, F.; Salas, M.L. Genome sequence of African swine fever virus BA71, the virulent parental strain of the nonpathogenic and tissue-culture adapted BA71V. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; Pan, L.; Yang, J.; Sun, M.; Zhou, P.; Sun, Y.; Bi, Y.; Qiu, H.J. Adaptation of African swine fever virus to HEK293T cells. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 2853–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, P.W.; Holinka, L.G.; O’Donnell, V.; Reese, B.; Sanford, B.; Fernandez-Sainz, I.; Gladue, D.P.; Arzt, J.; Rodriguez, L.; Risatti, G.R.; et al. The progressive adaptation of a Georgian isolate of African swine fever virus to Vero cells leads to a gradual attenuation of virulence in swine corresponding to major modifications of the viral genome. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2324–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Qi, X.; Wen, Y.; Li, P.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Liu, Z. African swine fever virus MGF-110-9L-deficient mutant has attenuated virulence in pigs. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Peng, J.; Wu, J.; Yi, J.; Wu, P.; Qi, X.; Ren, J.; Peng, G.; Duan, X.; Ru, Y.; et al. African swine fever virus MGF-360-10L is a novel and crucial virulence factor that mediates ubiquitination and degradation of JAK1 by recruiting the E3 ubiquitin ligase HERC5. mBio 2023, 14, e0060623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Luo, R.; Zhang, J.; Lan, J.; Lu, Z.; Zhai, H.; Li, L.F.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, H.J. The African swine fever virus MGF300-4L protein is associated with viral pathogenicity by promoting the autophagic degradation of IKKβ and increasing the stability of IκBα. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2333381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Luo, R.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Z.; Li, L.F.; Zheng, Y.H.; Pan, L.; Lan, J.; Zhai, H.; Huang, S.; et al. The MGF300-2R protein of African swine fever virus is associated with viral pathogenicity by promoting the autophagic degradation of IKKα and IKKβ through the recruitment of TOLLIP. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farlow, J.; Donduashvili, M.; Kokhreidze, M.; Kotorashvili, A.; Vepkhvadze, N.G.; Kotaria, N.; Gulbani, A. Intra-epidemic genome variation in highly pathogenic African swine fever virus from the country of Georgia. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur-Panasiuk, N.; Walczak, M.; Juszkiewicz, M.; Woźniakowski, G. The spillover of African swine fever in western Poland revealed its estimated origin on the basis of O174L, K145R, MGF 505-5R and IGR I73R/I329L genomic sequences. Viruses 2020, 12, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloum, A.; Van Schalkwyk, A.; Shotin, A.; Igolkin, A.; Shevchenko, I.; Gruzdev, K.N.; Vlasova, N. Comparative analysis of full genome sequences of African swine fever virus isolates taken from wild boars in Russia in 2019. Pathogens 2021, 10, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Tracing the origin of genotype II African swine fever virus in China by genomic epidemiology analysis. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2023, 4820809, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanh, T.T.; Duc, T.A.; Viet, L.D.; Van, H.T.; Thi, N.C.; Thi, C.N.; Thi, N.H.; Vu, D.H. Rapid identification for serotyping of African swine fever virus based on the short fragment of the EP402R gene encoding for CD2-like protein. Acta Vet. 2021, 71, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qi, C.; Ge, S.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Qian, Y. Genetic variation and evolution of attenuated African swine fever virus strain isolated in the field: A review. Virus Res. 2022, 319, 198874. [Google Scholar]
- Portugal, R.; Coelho, J.; Höper, D.; Little, N.S.; Smithson, C.; Upton, C.; Martins, C.; Leitão, A.; Keil, G.M. Related strains of African swine fever virus with different virulence: Genome comparison and analysis. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, E.G.; Riera, E.; Nogal, M.; Gallardo, C.; Fernández, P.; Bello-Morales, R.; López-Guerrero, J.A.; Chitko-McKown, C.G.; Richt, J.A.; Revilla, Y. Phenotyping and susceptibility of established porcine cells lines to African swine fever virus infection and viral production. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borca, M.V.; Rai, A.; Ramirez-Medina, E.; Silva, E.; Velazquez-Salinas, L.; Vuono, E.; Pruitt, S.; Espinoza, N.; Gladue, D.P. A cell culture-adapted vaccine virus against the current African swine fever virus pandemic strain. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0012321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaweerattanasinp, T.; Kaewborisuth, C.; Viriyakitkosol, R.; Saenboonrueng, J.; Wanitchang, A.; Tanwattana, N.; Sonthirod, C.; Sangsrakru, D.; Pootakham, W.; Tangphatsornruang, S.; et al. Adaptation of African swine fever virus to MA-104 cells: Implications of unique genetic variations. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 291, 110016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrini, S.; Righi, C.; Mészáros, I.; D’Errico, F.; Tamás, V.; Pela, M.; Olasz, F.; Gallardo, C.; Fernandez-Pinero, J.; Göltl, E.; et al. The production of recombinant African swine fever virus Lv17/WB/Rie1 strains and their in vitro and in vivo characterizations. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Lyu, J.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Hu, H.; Zhao, L.; Pan, M. Laminaran potentiates cGAS-STING signaling to enhance antiviral responses. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 147, 114014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.Y.; He, X.B.; Jia, H.J.; Chen, G.H.; Jin, Q.W.; Long, Z.L.; Jing, Z.Z. The cGAS-STING signaling pathway is required for the innate immune response against ectromelia virus. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Hu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, R.F. Function and regulation of cGAS-STING signaling in infectious diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1130423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.; Cao, H.; Li, W.; Hu, Z.; Rong, Z.; Yin, M.; Tian, L.; Hu, D.; Li, X.; Qian, P. African swine fever virus MGF505-6R attenuates type I interferon production by targeting STING for degradation. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1380220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Huang, Q.; Wang, R.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, M.; Xue, Y.; Shi, C.; Ye, L.; Yang, W.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Corrigendum to African swine fever virus MGF505-11R inhibits type I interferon production by negatively regulating the cGAS-STING-mediated signaling pathway. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 285, 109723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Luo, J.; Duan, Y. African swine fever virus MGF505-3R inhibits cGAS-STING-mediated IFN-β pathway activation by degrading TBK1. Anim. Dis. 2022, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhai, W.; Tao, C.; Chu, Y.; Pang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, P.; Jia, H. African swine fever virus MGF360-4L protein attenuates type I interferon response by suppressing the phosphorylation of IRF3. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1382675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Subasinghe, A.; Kim, Y.; Kwon, H.I.; Cho, Y.; Chathuranga, K.; Cha, J.W.; Moon, J.Y.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, J.; et al. Development and characterization of high-efficiency cell-adapted live attenuated vaccine candidate against African swine fever. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2432372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Fan, S.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Jiang, D.; Han, S.; Wan, B.; Zhang, G. African swine fever virus MGF110-7L induces host cell translation suppression and stress granule formation by activating the PERK/PKR-eIF2α pathway. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0328222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Li, D.; Zhu, G.; Yang, W.; Ru, Y.; Feng, T.; Qin, X.; Hao, R.; Duan, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Deletion of MGF-110-9L gene from African swine fever virus weakens autophagic degradation of TBK1 as a mechanism for enhancing type I interferon production. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e22934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Luo, R.; Lan, J.; Chen, S.; Qiu, H.J.; Wang, T.; Sun, Y. The MGF300-2R protein of African swine fever virus promotes IKKβ ubiquitination by recruiting the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM21. Viruses 2024, 16, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, M.; Tian, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, J.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. The African swine fever virus gene MGF_360-4L inhibits interferon signaling by recruiting mitochondrial selective autophagy receptor SQSTM1 degrading MDA5 antagonizing innate immune responses. mBio 2025, 16, e0267724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, B.; Shen, C.; Zhang, T.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Shi, X.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; et al. MGF360-9L is a major virulence factor associated with the African swine fever virus by antagonizing the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. mBio 2022, 13, e0233021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yang, B.; Hao, Y.; Shi, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, D.; Yan, W.; Chen, L.; Bie, X.; et al. African swine fever virus MGF360-9L promotes viral replication by degrading the host protein HAX1. Virus Res. 2023, 336, 199198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Xue, Y.; Niu, H.; Shi, C.; Cheng, M.; Wang, J.; Zou, B.; Wang, J.; Niu, T.; Bao, M.; et al. African swine fever virus MGF360-11L negatively regulates cGAS-STING-mediated inhibition of type I interferon production. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Y.; Guo, Z.; Ba, T.; Zhang, C.; He, L.; Zeng, C.; Dai, H. African swine fever virus MGF360-12L inhibits type I interferon production by blocking the interaction of Importin α and NF-κB signaling pathway. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, X.X.; Jiang, S.W.; Gao, X.T.; Huang, S.Y.; Liang, Y.; Jia, H.; Zhu, H.F. MGF360-12L of ASFV-SY18 is an immune-evasion protein that inhibits host type I IFN, NF-κB, and JAK/STAT pathways. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2023, 26, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Cheng, M.; Duan, Y.; Xing, X.; Lu, M.; Sun, Y.; Shi, C.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Li, X.; et al. African swine fever virus encoded protein MGF360-13L inhibits cGAS-STING-mediated IFN-I signaling pathway. Gene 2023, 874, 147490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, S.; Xin, T.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Chen, S.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, X.; et al. African swine fever virus MGF360-14L negatively regulates type I interferon signaling by targeting IRF3. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 818969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Medina, E.; Vuono, E.A.; Velazquez-Salinas, L.; Silva, E.; Rai, A.; Pruitt, S.; Berggren, K.A.; Zhu, J.; Borca, M.V.; Gladue, D.P. The MGF360-16R ORF of African swine fever virus strain Georgia encodes for a nonessential gene that interacts with host proteins SERTAD3 and SDCBP. Viruses 2020, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Weng, W.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Jiang, F.; Qu, Y.; Li, Q.; Gao, P.; Zhou, L.; et al. The African swine fever virus MGF360-16R protein functions as a mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis inducer by competing with BAX to bind to the HSP60 protein. J. Virol. 2025, 99, e0140124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunwoo, S.Y.; García-Belmonte, R.; Walczak, M.; Vigara-Astillero, G.; Kim, D.M.; Szymankiewicz, K.; Kochanowski, M.; Liu, L.; Tark, D.; Podgórska, K.; et al. Deletion of MGF505-2R gene activates the cGAS-STING pathway leading to attenuation and protection against virulent African swine fever virus. Vaccines 2024, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupré, J.; Le Dimna, M.; Hutet, E.; Dujardin, P.; Fablet, A.; Leroy, A.; Fleurot, I.; Karadjian, G.; Roesch, F.; Caballero, I.; et al. Exploring type I interferon pathway: Virulent vs. attenuated strain of African swine fever virus revealing a novel function carried by MGF505-4R. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1358219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, M.; Dang, W.; Liu, H.; Xu, F.; Huang, H.; Sun, Y.; Li, T.; Pei, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Combinational deletions of MGF360-9L and MGF505-7R attenuated highly virulent African swine fever virus and conferred protection against homologous challenge. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0032922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Song, J.; Kang, L.; Huang, L.; Zhou, S.; Hu, L.; Zheng, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; et al. pMGF505-7R determines pathogenicity of African swine fever virus infection by inhibiting IL-1β and type I IFN production. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Li, D.; Weng, C. Multifunctional pMGF505-7R is a key virulence-related factor of African swine fever virus. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 852431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Cao, H.; Zeng, F.; Lin, S.; Chen, J.; Luo, Y.; You, J.; Kong, C.; Mai, Z.; Deng, J.; et al. African swine fever virus MGF505-7R interacts with interferon regulatory factor 9 to evade the type I interferon signaling pathway and promote viral replication. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0197722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarino, A.V.; Kanno, Y.; Ferdinand, J.R.; O’Shea, J.J. Mechanisms of JAK/STAT signaling in immunity and disease. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, H.; Matsui, K.; Tsuji, H.; Tamura, A.; Suzuki, K. Immunolocalisation of the Janus kinases (JAK)-signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) pathway in human epidermis. J. Anat. 2001, 198, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, V.; Holinka, L.G.; Gladue, D.P.; Sanford, B.; Krug, P.W.; Lu, X.; Arzt, J.; Reese, B.; Carrillo, C.; Risatti, G.R.; et al. African swine fever virus Georgia isolate harboring deletions of MGF360 and MGF505 genes is attenuated in swine and confers protection against challenge with virulent parental virus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6048–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhao, D.; He, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Shan, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. A seven-gene-deleted African swine fever virus is safe and effective as a live attenuated vaccine in pigs. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.L.; Abrams, C.C.; Goatley, L.C.; Netherton, C.; Chapman, D.G.; Sanchez-Cordon, P.; Dixon, L.K. Deletion of African swine fever virus interferon inhibitors from the genome of a virulent isolate reduces virulence in domestic pigs and induces a protective response. Vaccine 2016, 34, 4698–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ren, J.; Zhu, G.; Wu, P.; Yang, W.; Ru, Y.; Feng, T.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Peng, J.; et al. Deletions of MGF110-9L and MGF360-9L from African swine fever virus are highly attenuated in swine and confer protection against homologous challenge. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yang, W.; Li, L.; Li, P.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, J.; Qi, X.; Ren, J.; Ru, Y.; Niu, Q.; et al. African swine fever virus MGF-505-7R negatively regulates cGAS–STING-mediated signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 1844–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, Z.; Ao, Q.; Di, D.; Yu, W.; Lv, L.; Zhong, Q.; Song, Y.; Liao, X.; et al. Development and in vivo evaluation of MGF100-1R deletion mutant in an African swine fever virus Chinese strain. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 261, 109208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Medina, E.; Vuono, E.; Pruitt, S.; Rai, A.; Silva, E.; Espinoza, N.; Zhu, J.; Velazquez-Salinas, L.; Borca, M.V.; Gladue, D.P. Development and in vivo evaluation of a MGF110-1L deletion mutant in African swine fever strain Georgia. Viruses 2021, 13, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Medina, E.; Vuono, E.; Silva, E.; Rai, A.; Valladares, A.; Pruitt, S.; Espinoza, N.; Velazquez-Salinas, L.; Borca, M.V.; Gladue, D.P. Evaluation of the deletion of MGF110-5L-6L on swine virulence from the pandemic strain of African swine fever virus and use as a DIVA marker in vaccine candidate ASFV-G-ΔI177L. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0059722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamás, V.; Righi, C.; Mészáros, I.; D’Errico, F.; Olasz, F.; Casciari, C.; Zádori, Z.; Magyar, T.; Petrini, S.; Feliziani, F. Involvement of the MGF 110-11L gene in the African swine fever replication and virulence. Vaccines 2023, 11, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Medina, E.; Vuono, E.A.; Rai, A.; Pruitt, S.; Silva, E.; Velazquez-Salinas, L.; Zhu, J.; Gladue, D.P.; Borca, M.V. Evaluation in swine of a recombinant African swine fever virus lacking the MGF-360-1L gene. Viruses 2020, 12, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.L.; Goatley, L.C.; Jabbar, T.; Sanchez-Cordon, P.J.; Netherton, C.L.; Chapman, D.A.G.; Dixon, L.K. Deletion of the African swine fever virus gene DP148R does not reduce virus replication in culture but reduces virus virulence in pigs and induces high levels of protection against challenge. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01428–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsak, L.; Lu, Z.; Burrage, T.G.; Neilan, J.G.; Kutish, G.F.; Moore, D.M.; Rock, D.L. African swine fever virus multigene family 360 and 530 genes are novel macrophage host range determinants. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 3066–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrage, T.G. African swine fever virus infection in Ornithodoros ticks. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrage, T.G.; Lu, Z.; Neilan, J.G.; Rock, D.L.; Zsak, L. African swine fever virus MGF360 genes affect virus replication and generalization of infection in Ornithodoros porcinus ticks. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Tian, X.; Lai, R.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Current detection methods of African swine fever virus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1289676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Q.; Xiong, C.; Mo, S.; Zhou, H.; Long, F.; Wei, H.; Hu, L.; Mo, M. The development of a multiplex real-time quantitative PCR assay for the differential detection of the wild-type strain and the MGF505-2R, EP402R and I177L gene-deleted strain of the African swine fever virus. Animals 2022, 12, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, X.; Peng, G.; Xia, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; et al. A quadruple fluorescence quantitative PCR method for the identification of wild strains of African swine fever and gene-deficient strains. Virol. J. 2023, 20, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Madera, R.; Pantua, H.; Craig, A.; Muro, N.; Li, D.; Retallick, J.; Ferreyra, F.M.; et al. Specific detection of African swine fever virus variants: Novel quadplex real-time PCR assay with internal control. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Peng, Z.; Song, W.; Zhang, C.; Fan, J.; Chen, H.; Hua, L.; Pei, J.; Tang, X.; Chen, H.; et al. A triplex real-time PCR method to detect African swine fever virus gene-deleted and wild type strains. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 943099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez-Salinas, L.; Ramirez-Medina, E.; Rai, A.; Pruitt, S.; Vuono, E.A.; Espinoza, N.; Gladue, D.P.; Borca, M.V. Development real-time PCR assays to genetically differentiate vaccinated pigs from infected pigs with the Eurasian strain of African swine fever virus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 768869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, K.; Qiao, S.; Chen, X.X.; Deng, R.; Zhang, G. Development and evaluation of duplex TaqMan real-time PCR assay for detection and differentiation of wide-type and MGF505-2R gene-deleted African swine fever viruses. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, L.; Ge, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. Development and application of a TaqMan-based real-time PCR method for the detection of the ASFV MGF505-7R gene. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1093733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Zhao, K.; Wei, H.; Zhou, Q.; Shi, Y.; Mo, S.; Long, F.; Hu, L.; Feng, S.; Mo, M. Triplex crystal digital PCR for the detection and differentiation of the wild-type strain and the MGF505-2R and I177L gene-deleted strain of African swine fever virus. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Lai, R.; Tian, X.; Guan, R.; Li, X. A duplex fluorescent quantitative PCR assay to distinguish the genotype I, II and I/II recombinant strains of African swine fever virus in China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1422757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, V.; Holinka, L.G.; Sanford, B.; Krug, P.W.; Carlson, J.; Pacheco, J.M.; Reese, B.; Risatti, G.R.; Gladue, D.P.; Borca, M.V. African swine fever virus Georgia isolate harboring deletions of 9GL and MGF360/505 genes is highly attenuated in swine but does not confer protection against parental virus challenge. Virus Res. 2016, 221, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Di, D.; Liu, J.; Gong, L.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J.; Ye, Z.; et al. Evaluation of an I177L gene-based five-gene-deleted African swine fever virus as a live attenuated vaccine in pigs. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2148560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Mi, S.; Xu, J.; Cao, J.; Hou, Y.; Wang, D.; Huo, X.; et al. Commercial E2 subunit vaccine provides full protection to pigs against lethal challenge with 4 strains of classical swine fever virus genotype 2. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 237, 108403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Hou, L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, D.; Cui, Y.; Feng, X.; Liu, J. Porcine circovirus type 2 vaccines: Commercial application and research advances. Viruses 2022, 14, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shan, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Ma, L.; Hu, L.; Huang, H.; Wei, K.; Zhu, R. Fused IgY Fc and polysaccharide adjuvant enhanced the immune effect of the recombinant VP2 and VP5 subunits-a prospect for improvement of infectious bursal disease virus subunit vaccine. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch-Camós, L.; López, E.; Collado, J.; Navas, M.J.; Blanco-Fuertes, M.; Pina-Pedrero, S.; Accensi, F.; Salas, M.L.; Mundt, E.; Nikolin, V.; et al. M448R and MGF505-7R: Two African swine fever virus antigens commonly recognized by ASFV-specific T-cells and with protective potential. Vaccines 2021, 9, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netherton, C.L.; Goatley, L.C.; Reis, A.L.; Portugal, R.; Nash, R.H.; Morgan, S.B.; Gault, L.; Nieto, R.; Norlin, V.; Gallardo, C.; et al. Identification and immunogenicity of African swine fever virus antigens. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goatley, L.C.; Reis, A.L.; Portugal, R.; Goldswain, H.; Shimmon, G.L.; Hargreaves, Z.; Ho, C.S.; Montoya, M.; Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Taylor, G.; et al. A pool of eight virally vectored African swine fever antigens protect pigs against fatal disease. Vaccines 2020, 8, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

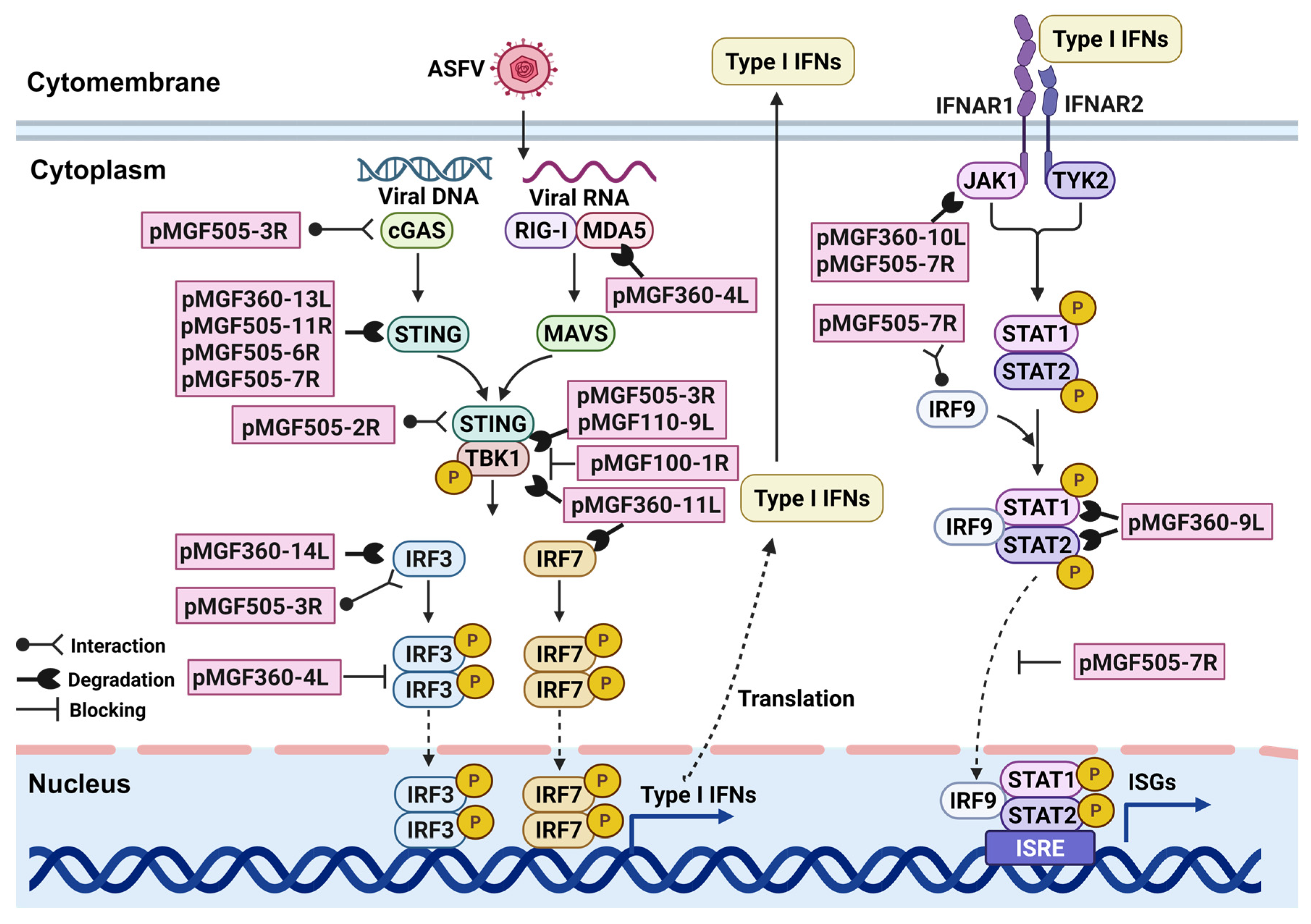
| Multigene Family | Members | Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| MGF100 | 1L | Unknown | / |
| 1R | Blocks the dimerization of TBK1 | [46] | |
| 3L | Unknown | / | |
| MGF110 | 1L | Unknown | / |
| 2L | Unknown | / | |
| 3L | Unknown | / | |
| 4L | Unknown | / | |
| 5L–6L | Unknown | / | |
| 7L | Induces translational repression and ISGs formation in host cells by activating the PERK/PKR-eIF2α pathway | [47] | |
| 8L | Unknown | / | |
| 9L | Facilitates TBK1 degradation by upregulating PIK3C2B | [48] | |
| 10L–14L | Unknown | / | |
| 12L | Unknown | / | |
| 13L | Unknown | / | |
| MGF300 | 1L | Unknown | / |
| 2R | Promotes K27-linked polyubiquitination of IKKα and IKKβ by recruiting the cargo receptor TOLLIP for selective autophagic degradation; Promotes IKKβ ubiquitination by recruiting the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM21 | [27,49] | |
| 4L | Promotes the autophagic degradation of IKKβ and increasing the stability of IκBα | [26] | |
| MGF360 | 1L | Unknown | / |
| 2L | Unknown | / | |
| 3L | Unknown | / | |
| 4L | Inhibits IRF3 phosphorylation; Interacts with MDA5 and recruits the mitochondrial selective autophagy receptor SQSTM1 (p62), leading to the degradation of MDA5 | [45,50] | |
| 6L | Unknown | / | |
| 8L | Unknown | / | |
| 9L | Interacts with STAT1 and STAT2 to induce degradation through apoptosis and the ubiquitin–proteasome pathways; Facilitates ASFV replication by degrading the host protein HAX1 | [51,52] | |
| 10L | Enhances the K48-linked ubiquitination of JAK1 by recruiting the E3 ubiquitin ligase HERC5 | [25] | |
| 11L | Facilitates the degradation of TBK1 and IRF7 | [53] | |
| 12L | Interferes with the interaction between p65 and importins, preventing nuclear localization | [54,55] | |
| 13L | Facilitates the autophagic degradation of STING | [56] | |
| 14L | Promotes IRF3 degradation by facilitating TRIM21-mediated K63-linked ubiquitination | [57] | |
| 15R | Unknown | / | |
| 16R | Interacts with the host proteins SERTAD3 and SDCBP, affecting viral replication and pathogenicity by regulating the transcriptional activity of host cell; Competes with BAX to bind HSP60, inducing apoptosis and affecting viral replication and pathogenicity by disrupting the HSP60-BAX complex | [58,59] | |
| 18R | Unknown | / | |
| 19R | Unknown | / | |
| 21R | Unknown | / | |
| MGF505 | 1R | Unknown | / |
| 2R | Interacts with STING | [60] | |
| 3R | Facilitates TBK1 degradation through autophagy | [44] | |
| 4R | Facilitates the autophagic degradation of TRAF3 | [61] | |
| 5R | Unknown | / | |
| 6R | Facilitates degradation through the autophagy-lysosomal pathway and inhibits the K63-linked polyubiquitination of STING | [42] | |
| 7R | Facilitates the autophagic degradation of STING; Inhibits IRF3 nuclear translocation; Suppresses the phosphorylation of IκBα; Upregulates the expression of the E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF125, promoting the degradation of JAK1 and JAK2 | [62,63,64,65] | |
| 9R | Unknown | / | |
| 10R | Unknown | / | |
| 11R | Facilitates STING degradation through the lysosome, ubiquitin–proteasome, and autophagy pathways | [43] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, R.; Luo, R.; Lan, J.; Lu, Z.; Qiu, H.-J.; Wang, T.; Sun, Y. The Multigene Family Genes-Encoded Proteins of African Swine Fever Virus: Roles in Evolution, Cell Tropism, Immune Evasion, and Pathogenesis. Viruses 2025, 17, 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060865
Huang R, Luo R, Lan J, Lu Z, Qiu H-J, Wang T, Sun Y. The Multigene Family Genes-Encoded Proteins of African Swine Fever Virus: Roles in Evolution, Cell Tropism, Immune Evasion, and Pathogenesis. Viruses. 2025; 17(6):865. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060865
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Ruojia, Rui Luo, Jing Lan, Zhanhao Lu, Hua-Ji Qiu, Tao Wang, and Yuan Sun. 2025. "The Multigene Family Genes-Encoded Proteins of African Swine Fever Virus: Roles in Evolution, Cell Tropism, Immune Evasion, and Pathogenesis" Viruses 17, no. 6: 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060865
APA StyleHuang, R., Luo, R., Lan, J., Lu, Z., Qiu, H.-J., Wang, T., & Sun, Y. (2025). The Multigene Family Genes-Encoded Proteins of African Swine Fever Virus: Roles in Evolution, Cell Tropism, Immune Evasion, and Pathogenesis. Viruses, 17(6), 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060865







