Impact of Delayed Early Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation on Treatment Outcomes in Infant Macaques Exposed to SHIVAD8
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animals and Simian-Human Immunodeficiency Virus
2.3. Tissue Collection and Phenotyping
2.4. Nucleic Acid Extraction
2.5. Quantification of Plasma Viral Load and Cell-Associated SHIVAD8 DNA
2.6. SIV Neutralization Antibody Assay
2.7. SIV Gag-Specific CD8+ T Cell Assay
2.8. In Vivo CD8+ Lymphocyte Depletion
2.9. ELISA
2.10. ADCC Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
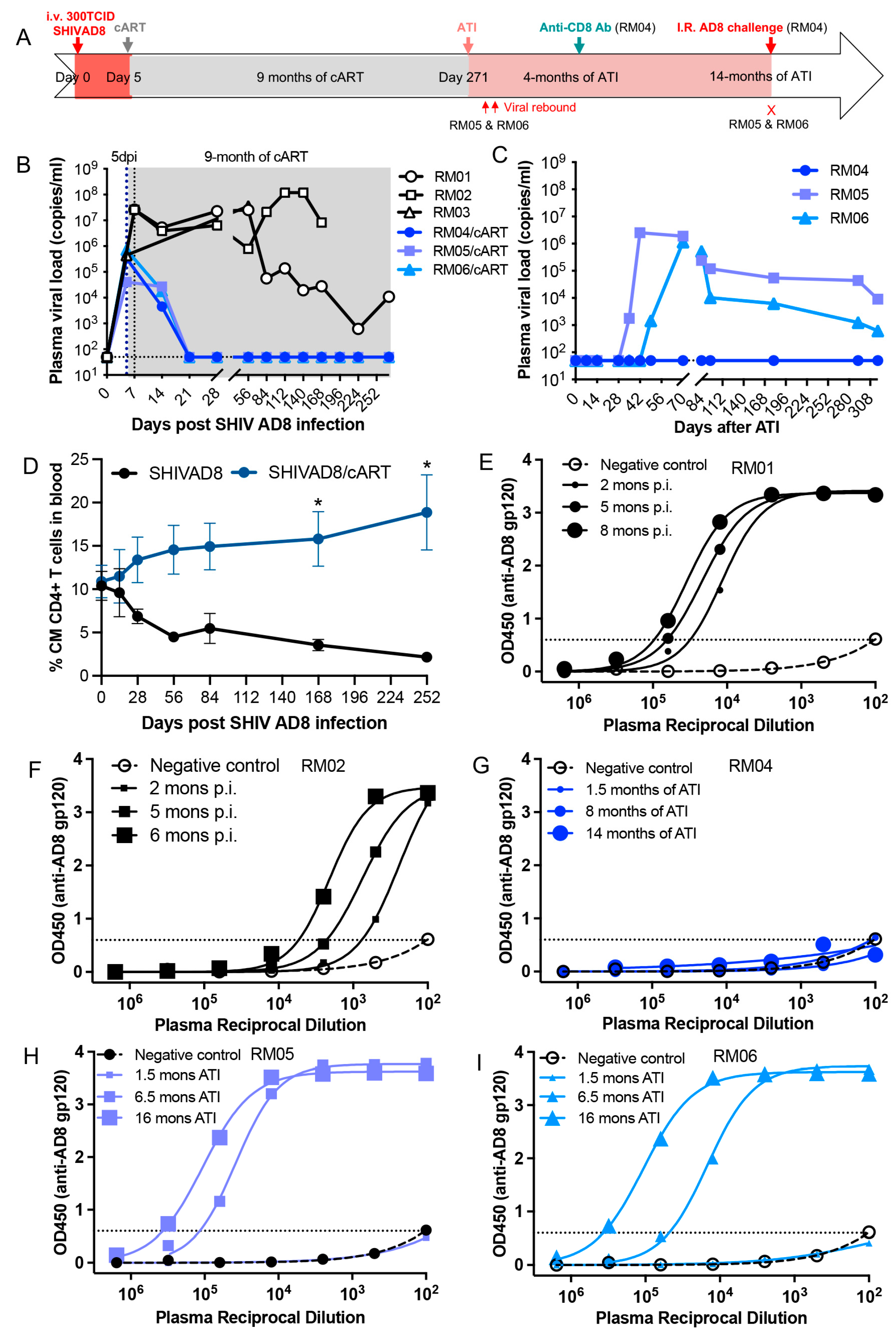
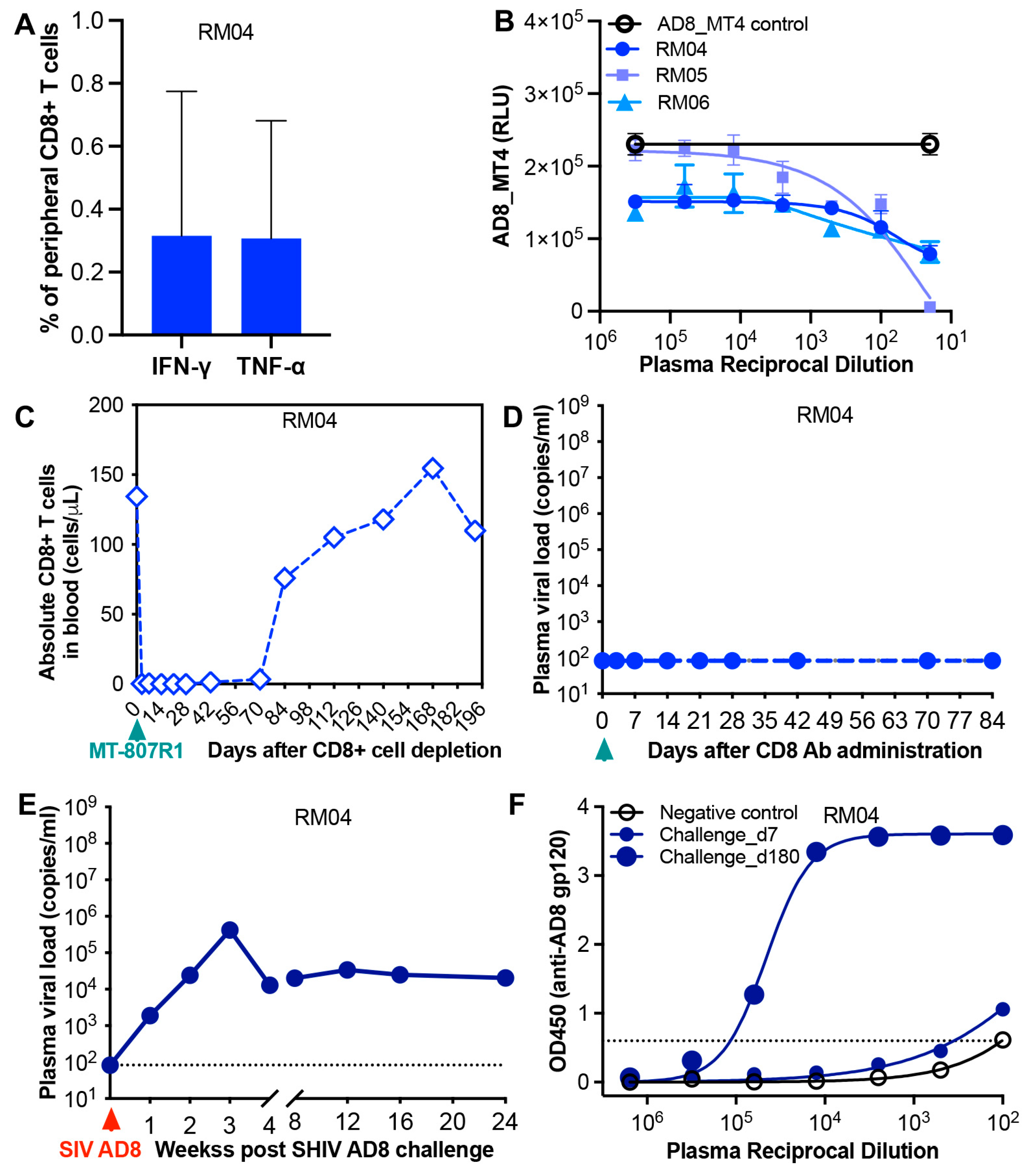
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ananworanich, J.; Chomont, N.; Eller, L.A.; Kroon, E.; Tovanabutra, S.; Bose, M.; Nau, M.; Fletcher, J.L.K.; Tipsuk, S.; Vandergeeten, C.; et al. HIV DNA Set Point is Rapidly Established in Acute HIV Infection and Dramatically Reduced by Early ART. EBioMedicine 2016, 11, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrich, T.J.; Hatano, H.; Bacon, O.; Hogan, L.E.; Rutishauser, R.; Hill, A.; Kearney, M.F.; Anderson, E.M.; Buchbinder, S.P.; Cohen, S.E.; et al. HIV-1 persistence following extremely early initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART) during acute HIV-1 infection: An observational study. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colby, D.J.; Trautmann, L.; Pinyakorn, S.; Leyre, L.; Pagliuzza, A.; Kroon, E.; Rolland, M.; Takata, H.; Buranapraditkun, S.; Intasan, J.; et al. Rapid HIV RNA rebound after antiretroviral treatment interruption in persons durably suppressed in Fiebig I acute HIV infection. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global HIV Programme. HIV Data and Statistics; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Muenchhoff, M.; Prendergast, A.J.; Goulder, P.J. Immunity to HIV in Early Life. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulder, P.J.; Lewin, S.R.; Leitman, E.M. Paediatric HIV infection: The potential for cure. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, J.B.; Lim, S.Y.; Osuna, C.E.; Kublin, J.L.; Chen, E.; Yoon, G.; Liu, P.T.; Abbink, P.; Borducci, E.N.; Hill, A.; et al. Prevention of SIVmac251 reservoir seeding in rhesus monkeys by early antiretroviral therapy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goo, L.; Chohan, V.; Nduati, R.; Overbaugh, J. Early development of broadly neutralizing antibodies in HIV-1-infected infants. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorin, V.; Fernandez, I.; Masse-Ranson, G.; Bouvin-Pley, M.; Molinos-Albert, L.M.; Planchais, C.; Hieu, T.; Pehau-Arnaudet, G.; Hrebik, D.; Girelli-Zubani, G.; et al. Epitope convergence of broadly HIV-1 neutralizing IgA and IgG antibody lineages in a viremic controller. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20212045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violari, A.; Cotton, M.F.; Gibb, D.M.; Babiker, A.G.; Steyn, J.; Madhi, S.A.; Jean-Philippe, P.; McIntyre, J.A.; Team, C.S. Early antiretroviral therapy and mortality among HIV-infected infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2233–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, M.F.; Violari, A.; Otwombe, K.; Panchia, R.; Dobbels, E.; Rabie, H.; Josipovic, D.; Liberty, A.; Lazarus, E.; Innes, S.; et al. Early time-limited antiretroviral therapy versus deferred therapy in South African infants infected with HIV: Results from the children with HIV early antiretroviral (CHER) randomised trial. Lancet 2013, 382, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzuriaga, K.; Tabak, B.; Garber, M.; Chen, Y.H.; Ziemniak, C.; McManus, M.M.; Murray, D.; Strain, M.C.; Richman, D.D.; Chun, T.W.; et al. HIV type 1 (HIV-1) proviral reservoirs decay continuously under sustained virologic control in HIV-1-infected children who received early treatment. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananworanich, J.; Puthanakit, T.; Suntarattiwong, P.; Chokephaibulkit, K.; Kerr, S.J.; Fromentin, R.; Bakeman, W.; Intasan, J.; Mahanontharit, A.; Sirivichayakul, S.; et al. Reduced markers of HIV persistence and restricted HIV-specific immune responses after early antiretroviral therapy in children. AIDS 2014, 28, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zyl, G.U.; Bedison, M.A.; van Rensburg, A.J.; Laughton, B.; Cotton, M.F.; Mellors, J.W. Early Antiretroviral Therapy in South African Children Reduces HIV-1-Infected Cells and Cell-Associated HIV-1 RNA in Blood Mononuclear Cells. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Bonet, M.; Puertas, M.C.; Fortuny, C.; Ouchi, D.; Mellado, M.J.; Rojo, P.; Noguera-Julian, A.; Munoz-Fernandez, M.A.; Martinez-Picado, J. Establishment and Replenishment of the Viral Reservoir in Perinatally HIV-1-infected Children Initiating Very Early Antiretroviral Therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainwater-Lovett, K.; Luzuriaga, K.; Persaud, D. Very early combination antiretroviral therapy in infants: Prospects for cure. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2015, 10, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Broncano, P.; Maddali, S.; Einkauf, K.B.; Jiang, C.; Gao, C.; Chevalier, J.; Chowdhury, F.Z.; Maswabi, K.; Ajibola, G.; Moyo, S.; et al. Early antiretroviral therapy in neonates with HIV-1 infection restricts viral reservoir size and induces a distinct innate immune profile. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaax7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendergast, A.; Mphatswe, W.; Tudor-Williams, G.; Rakgotho, M.; Pillay, V.; Thobakgale, C.; McCarthy, N.; Morris, L.; Walker, B.D.; Goulder, P. Early virological suppression with three-class antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected African infants. AIDS 2008, 22, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, D.; Gay, H.; Ziemniak, C.; Chen, Y.H.; Piatak, M., Jr.; Chun, T.W.; Strain, M.; Richman, D.; Luzuriaga, K. Absence of detectable HIV-1 viremia after treatment cessation in an infant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1828–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomet, V.; Trabattoni, D.; Zanchetta, N.; Biasin, M.; Gismondo, M.; Clerici, M.; Zuccotti, G. No cure of HIV infection in a child despite early treatment and apparent viral clearance. Lancet 2014, 384, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzuriaga, K.; Gay, H.; Ziemniak, C.; Sanborn, K.B.; Somasundaran, M.; Rainwater-Lovett, K.; Mellors, J.W.; Rosenbloom, D.; Persaud, D. Viremic relapse after HIV-1 remission in a perinatally infected child. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 786–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, K.M.; Gavin, P.; Coughlan, S.; Rochford, A.; Mc Donagh, S.; Cunningham, O.; Poulsom, H.; Watters, S.A.; Klein, N. Rapid viral rebound after 4 years of suppressive therapy in a seronegative HIV-1 infected infant treated from birth. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, e48–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateba Ndongo, F.; Texier, G.; Ida Penda, C.; Tejiokem, M.C.; Tetang Ndiang, S.; Ndongo, J.A.; Guemkam, G.; Sofeu, C.L.; Kfutwah, A.; Faye, A.; et al. Virologic Response to Early Antiretroviral Therapy in HIV-infected Infants: Evaluation After 2 Years of Treatment in the Pediacam Study, Cameroon. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, L.; Strehlau, R.; Shiau, S.; Patel, F.; Shen, Y.; Technau, K.G.; Burke, M.; Sherman, G.; Coovadia, A.; Aldrovandi, G.M.; et al. Early antiretroviral treatment of infants to attain HIV remission. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 18, 100241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wamalwa, D.; Benki-Nugent, S.; Langat, A.; Tapia, K.; Ngugi, E.; Moraa, H.; Maleche-Obimbo, E.; Otieno, V.; Inwani, I.; Richardson, B.A.; et al. Treatment interruption after 2-year antiretroviral treatment initiated during acute/early HIV in infancy. AIDS 2016, 30, 2303–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, S.; Strehlau, R.; Technau, K.G.; Patel, F.; Arpadi, S.M.; Coovadia, A.; Abrams, E.J.; Kuhn, L. Early age at start of antiretroviral therapy associated with better virologic control after initial suppression in HIV-infected infants. AIDS 2017, 31, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violari, A.; Cotton, M.F.; Kuhn, L.; Schramm, D.B.; Paximadis, M.; Loubser, S.; Shalekoff, S.; Da Costa Dias, B.; Otwombe, K.; Liberty, A.; et al. A child with perinatal HIV infection and long-term sustained virological control following antiretroviral treatment cessation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, H.; Chan, M.K.; Watters, S.A.; Otwombe, K.; Hsiao, N.Y.; Babiker, A.; Violari, A.; Cotton, M.F.; Gibb, D.M.; Klein, N.J. Early ART-initiation and longer ART duration reduces HIV-1 proviral DNA levels in children from the CHER trial. AIDS Res. Ther. 2021, 18, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, B.S.; Tierney, C.; Persaud, D.; Jao, J.; Cotton, M.F.; Bryson, Y.; Coletti, A.; Ruel, T.D.; Spector, S.A.; Reding, C.; et al. Infants Receiving Very Early Antiretroviral Therapy Have High CD4 Counts in the First Year of Life. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, e744–e747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitnun, A.; Samson, L.; Chun, T.W.; Kakkar, F.; Brophy, J.; Murray, D.; Justement, S.; Soudeyns, H.; Ostrowski, M.; Mujib, S.; et al. Early initiation of combination antiretroviral therapy in HIV-1-infected newborns can achieve sustained virologic suppression with low frequency of CD4+ T cells carrying HIV in peripheral blood. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscitelli, J.; Nikanjam, M.; Best, B.M.; Acosta, E.; Mirochnick, M.; Clarke, D.F.; Capparelli, E.V.; Momper, J.D. Optimizing Dolutegravir Initiation in Neonates Using Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Simulation. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2022, 89, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkova, A.; White, E.; Mujuru, H.A.; Kekitiinwa, A.R.; Kityo, C.M.; Violari, A.; Lugemwa, A.; Cressey, T.R.; Musoke, P.; Variava, E.; et al. Dolutegravir as First- or Second-Line Treatment for HIV-1 Infection in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2531–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuge, P.; Lugemwa, A.; Wynne, B.; Mujuru, H.A.; Violari, A.; Kityo, C.M.; Archary, M.; Variava, E.; White, E.; Turner, R.M.; et al. Once-daily dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapy in infants and children living with HIV from age 4 weeks: Results from the below 14 kg cohort in the randomised ODYSSEY trial. Lancet HIV 2022, 9, e638–e648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waalewijn, H.; Chan, M.K.; Bollen, P.D.J.; Mujuru, H.A.; Makumbi, S.; Kekitiinwa, A.R.; Kaudha, E.; Sarfati, T.; Musoro, G.; Nanduudu, A.; et al. Dolutegravir dosing for children with HIV weighing less than 20 kg: Pharmacokinetic and safety substudies nested in the open-label, multicentre, randomised, non-inferiority ODYSSEY trial. Lancet HIV 2022, 9, e341–e352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruel, T.D.; Acosta, E.P.; Liu, J.P.; Gray, K.P.; George, K.; Montanez, N.; Popson, S.; Buchanan, A.M.; Bartlett, M.; Dayton, D.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, safety, tolerability, and antiviral activity of dolutegravir dispersible tablets in infants and children with HIV-1 (IMPAACT P1093): Results of an open-label, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet HIV 2022, 9, e332–e340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amedee, A.M.; Phillips, B.; Jensen, K.; Robichaux, S.; Lacour, N.; Burke, M.; Piatak, M., Jr.; Lifson, J.D.; Kozlowski, P.A.; Van Rompay, K.K.A.; et al. Early Sites of Virus Replication After Oral SIV(mac251) Infection of Infant Macaques: Implications for Pathogenesis. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2018, 34, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessell, A.J.; Jaworski, J.P.; Epson, E.; Matsuda, K.; Pandey, S.; Kahl, C.; Reed, J.; Sutton, W.F.; Hammond, K.B.; Cheever, T.A.; et al. Early short-term treatment with neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies halts SHIV infection in infant macaques. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, M.B.; Cheever, T.; Malherbe, D.C.; Pandey, S.; Reed, J.; Yang, E.S.; Wang, K.; Pegu, A.; Chen, X.; Siess, D.; et al. Single-dose bNAb cocktail or abbreviated ART post-exposure regimens achieve tight SHIV control without adaptive immunity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.A.; McRaven, M.D.; Carias, A.M.; Anderson, M.R.; Matias, E.; Arainga, M.; Allen, E.J.; Rogers, K.A.; Gupta, S.; Kulkarni, V.; et al. Localization of infection in neonatal rhesus macaques after oral viral challenge. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregon-Perko, V.; Bricker, K.M.; Mensah, G.; Uddin, F.; Kumar, M.R.; Fray, E.J.; Siliciano, R.F.; Schoof, N.; Horner, A.; Mavigner, M.; et al. Simian-Human Immunodeficiency Virus SHIV.C.CH505 Persistence in ART-Suppressed Infant Macaques Is Characterized by Elevated SHIV RNA in the Gut and a High Abundance of Intact SHIV DNA in Naive CD4(+) T Cells. J. Virol. 2020, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.T.; Jaworski, J.P.; Jayaraman, P.; Sutton, W.F.; Delio, P.; Kuller, L.; Anderson, D.; Landucci, G.; Richardson, B.A.; Burton, D.R.; et al. Passive neutralizing antibody controls SHIV viremia and enhances B cell responses in infant macaques. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregon-Perko, V.; Bricker, K.M.; Mensah, G.; Uddin, F.; Rotolo, L.; Vanover, D.; Desai, Y.; Santangelo, P.J.; Jean, S.; Wood, J.S.; et al. Dynamics and origin of rebound viremia in SHIV-infected infant macaques following interruption of long-term ART. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e152526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrantelli, F.; Rasmussen, R.A.; Buckley, K.A.; Li, P.L.; Wang, T.; Montefiori, D.C.; Katinger, H.; Stiegler, G.; Anderson, D.C.; McClure, H.M.; et al. Complete protection of neonatal rhesus macaques against oral exposure to pathogenic simian-human immunodeficiency virus by human anti-HIV monoclonal antibodies. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 2167–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milush, J.M.; Kosub, D.; Marthas, M.; Schmidt, K.; Scott, F.; Wozniakowski, A.; Brown, C.; Westmoreland, S.; Sodora, D.L. Rapid dissemination of SIV following oral inoculation. AIDS 2004, 18, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Vincent, E.; Siddiqui, S.; Turnbull, K.; Lu, H.; Blair, R.; Wu, X.; Watkins, M.; Ziani, W.; Shao, J.; et al. Early treatment regimens achieve sustained virologic remission in infant macaques infected with SIV at birth. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, R.; Nelson, A.N.; Tu, J.J.; Dennis, M.; Feng, L.; Kumar, A.; Mangold, J.; Mangan, R.J.; Mattingly, C.; Curtis, A.D., 2nd; et al. Analytical Treatment Interruption after Short-Term Antiretroviral Therapy in a Postnatally Simian-Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Infant Rhesus Macaque Model. mBio 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavigner, M.; Habib, J.; Deleage, C.; Rosen, E.; Mattingly, C.; Bricker, K.; Kashuba, A.; Amblard, F.; Schinazi, R.F.; Lawson, B.; et al. Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Persistence in Cellular and Anatomic Reservoirs in Antiretroviral Therapy-Suppressed Infant Rhesus Macaques. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.; Nishimura, Y.; Lee, W.R.; Donau, O.; Buckler-White, A.; Shingai, M.; Sadjadpour, R.; Schmidt, S.D.; LaBranche, C.C.; Keele, B.F.; et al. Pathogenicity and mucosal transmissibility of the R5-tropic simian/human immunodeficiency virus SHIV(AD8) in rhesus macaques: Implications for use in vaccine studies. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 8516–8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Shingai, M.; Willey, R.; Sadjadpour, R.; Lee, W.R.; Brown, C.R.; Brenchley, J.M.; Buckler-White, A.; Petros, R.; Eckhaus, M.; et al. Generation of the pathogenic R5-tropic simian/human immunodeficiency virus SHIVAD8 by serial passaging in rhesus macaques. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 4769–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Navio, J.M.; Fuchs, S.P.; Pantry, S.N.; Lauer, W.A.; Duggan, N.N.; Keele, B.F.; Rakasz, E.G.; Gao, G.; Lifson, J.D.; Desrosiers, R.C. Adeno-Associated Virus Delivery of Anti-HIV Monoclonal Antibodies Can Drive Long-Term Virologic Suppression. Immunity 2019, 50, 567–575.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francica, J.R.; Sheng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Nishimura, Y.; Shingai, M.; Ramesh, A.; Keele, B.F.; Schmidt, S.D.; Flynn, B.J.; Darko, S.; et al. Analysis of immunoglobulin transcripts and hypermutation following SHIV(AD8) infection and protein-plus-adjuvant immunization. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Lynch, R.M.; Gautam, R.; Matus-Nicodemos, R.; Schmidt, S.D.; Boswell, K.L.; Darko, S.; Wong, P.; Sheng, Z.; Petrovas, C.; et al. Quality and quantity of TFH cells are critical for broad antibody development in SHIVAD8 infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 298ra120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shingai, M.; Donau, O.K.; Schmidt, S.D.; Gautam, R.; Plishka, R.J.; Buckler-White, A.; Sadjadpour, R.; Lee, W.R.; LaBranche, C.C.; Montefiori, D.C.; et al. Most rhesus macaques infected with the CCR5-tropic SHIV(AD8) generate cross-reactive antibodies that neutralize multiple HIV-1 strains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19769–19774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Barnes, C.O.; Gautam, R.; Cetrulo Lorenzi, J.C.; Mayer, C.T.; Oliveira, T.Y.; Ramos, V.; Cipolla, M.; Gordon, K.M.; Gristick, H.B.; et al. A broadly neutralizing macaque monoclonal antibody against the HIV-1 V3-Glycan patch. Elife 2020, 9, e61991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, W.E.; Sanford, H.; Schwall, L.; Burton, D.R.; Parren, P.W.; Robinson, J.E.; Desrosiers, R.C. Assorted mutations in the envelope gene of simian immunodeficiency virus lead to loss of neutralization resistance against antibodies representing a broad spectrum of specificities. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 9993–10003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, W.W.; Rahman, I.; Hraber, P.; Coffey, R.T.; Nevidomskyte, D.; Giri, A.; Asmal, M.; Miljkovic, S.; Daniels, M.; Whitney, J.B.; et al. Autologous neutralizing antibodies to the transmitted/founder viruses emerge late after simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac251 infection of rhesus monkeys. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 6018–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Gautam, R.; Chun, T.W.; Sadjadpour, R.; Foulds, K.E.; Shingai, M.; Klein, F.; Gazumyan, A.; Golijanin, J.; Donaldson, M.; et al. Early antibody therapy can induce long-lasting immunity to SHIV. Nature 2017, 543, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziani, W.; Bauer, A.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Bar, K.J.; Li, H.; Liu, D.; Shaw, G.M.; Veazey, R.S.; et al. Immune Responses and Viral Persistence in Simian/Human Immunodeficiency Virus SHIV.C.CH848-Infected Rhesus Macaques. J. Virol. 2021, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Lackner, A.A.; Veazey, R.S. CD8 down-regulation and functional impairment of SIV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in lymphoid and mucosal tissues during SIV infection. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 93, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Russell-Lodrigue, K.E.; Ratterree, M.S.; Veazey, R.S.; Xu, H. Chemokine receptor CCR5 correlates with functional CD8(+) T cells in SIV-infected macaques and the potential effects of maraviroc on T-cell activation. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 8905–8912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borducchi, E.N.; Liu, J.; Nkolola, J.P.; Cadena, A.M.; Yu, W.H.; Fischinger, S.; Broge, T.; Abbink, P.; Mercado, N.B.; Chandrashekar, A.; et al. Publisher Correction: Antibody and TLR7 agonist delay viral rebound in SHIV-infected monkeys. Nature 2018, 564, E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Rasmussen, T.; Pahar, B.; Poonia, B.; Alvarez, X.; Lackner, A.A.; Veazey, R.S. Massive infection and loss of CD4+ T cells occurs in the intestinal tract of neonatal rhesus macaques in acute SIV infection. Blood 2007, 109, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, D.R.; Mascola, J.R. Antibody responses to envelope glycoproteins in HIV-1 infection. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwata, T.; Miura, T.; Hayami, M. Using SHIVs to develop an anti-HIV-1 live-attenuated vaccine. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiau, S.; Abrams, E.J.; Arpadi, S.M.; Kuhn, L. Early antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected infants: Can it lead to HIV remission? Lancet HIV 2018, 5, e250–e258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.; Sharma, S.; Dobhal, A.; Kumar, S.; Chawla, H.; Singh, R.; Makhdoomi, M.A.; Das, B.K.; Lodha, R.; Kabra, S.K.; et al. Broadly neutralizing plasma antibodies effective against autologous circulating viruses in infants with multivariant HIV-1 infection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Animal ID | Months p.i. | Status | Neutralizing Antibody Titers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHIVCL7V3AD8 | SHIVAD8EO | |||
| RM01 | 3 | No cART | 1:51 | <1:20 |
| 6 | No cART | 1:312 | <1:20 | |
| 8 | No cART | 1:313 | <1:20 | |
| RM02 | 3 | No cART | <1:20 | <1:20 |
| 6 | No cART | <1:20 | <1:20 | |
| RM03 | 2 | No cART | <1:20 | <1:20 |
| RM04 | 12 | 3 mons ATI | <1:20 | <1:20 |
| RM05 | 12 | 3 mons ATI | 1:36 | <1:20 |
| RM06 | 12 | 3 mons ATI | <1:20 | <1:20 |
| Animal ID | Sample | 6 Months of cART | 8 Months of ATI | 14 Months of ATI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM04 | PBMCs | <20 | <20 | <20 |
| LNMCs | <12 | <9 | <5 | |
| Rec lymphocytes | NA | <6 | NA | |
| RM05 | LNMCs | NA | NA | 1.52 × 103 |
| RM06 | LNMCs | NA | NA | 5.41 × 102 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, L.; Nishimura, Y.; Wu, X.; Donau, O.; Vincent, E.; Lu, H.; Blair, R.V.; Doyle-Meyers, L.A.; Martin, M.; Veazey, R.S.; et al. Impact of Delayed Early Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation on Treatment Outcomes in Infant Macaques Exposed to SHIVAD8. Viruses 2025, 17, 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060849
Ma L, Nishimura Y, Wu X, Donau O, Vincent E, Lu H, Blair RV, Doyle-Meyers LA, Martin M, Veazey RS, et al. Impact of Delayed Early Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation on Treatment Outcomes in Infant Macaques Exposed to SHIVAD8. Viruses. 2025; 17(6):849. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060849
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Li, Yoshiaki Nishimura, Xueling Wu, Olivia Donau, Eunice Vincent, Hong Lu, Robert V. Blair, Lara A. Doyle-Meyers, Malcolm Martin, Ronald S. Veazey, and et al. 2025. "Impact of Delayed Early Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation on Treatment Outcomes in Infant Macaques Exposed to SHIVAD8" Viruses 17, no. 6: 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060849
APA StyleMa, L., Nishimura, Y., Wu, X., Donau, O., Vincent, E., Lu, H., Blair, R. V., Doyle-Meyers, L. A., Martin, M., Veazey, R. S., Xu, H., & Wang, X. (2025). Impact of Delayed Early Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation on Treatment Outcomes in Infant Macaques Exposed to SHIVAD8. Viruses, 17(6), 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060849








