Analysis of Epidemiological and Evolutionary Characteristics of Seasonal Influenza Viruses in Shenzhen City from 2018 to 2024
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Virus Isolation
2.2. Viral RNA Extraction and HA/NA Gene Sequencing Analysis
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
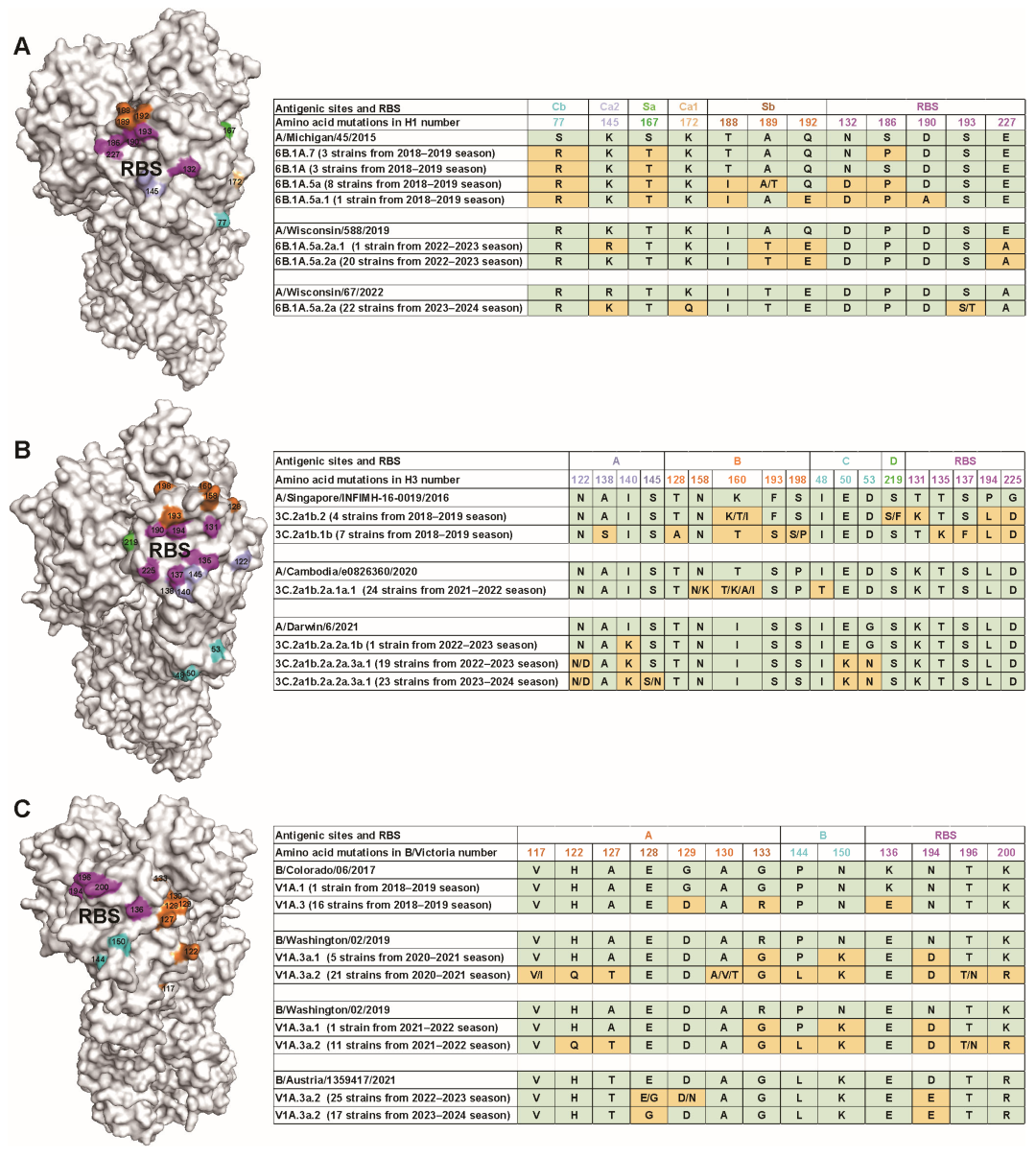
2.4. Amino Acid Substitution Analysis of Antigenic Sites and Receptor-Binding Site (RBS)
2.5. Hemagglutination (HA) Assay and Hemagglutination Inhibition (HI) Antibody Examination
3. Results
3.1. Epidemiological Surveillance of Seasonal Influenza Virus
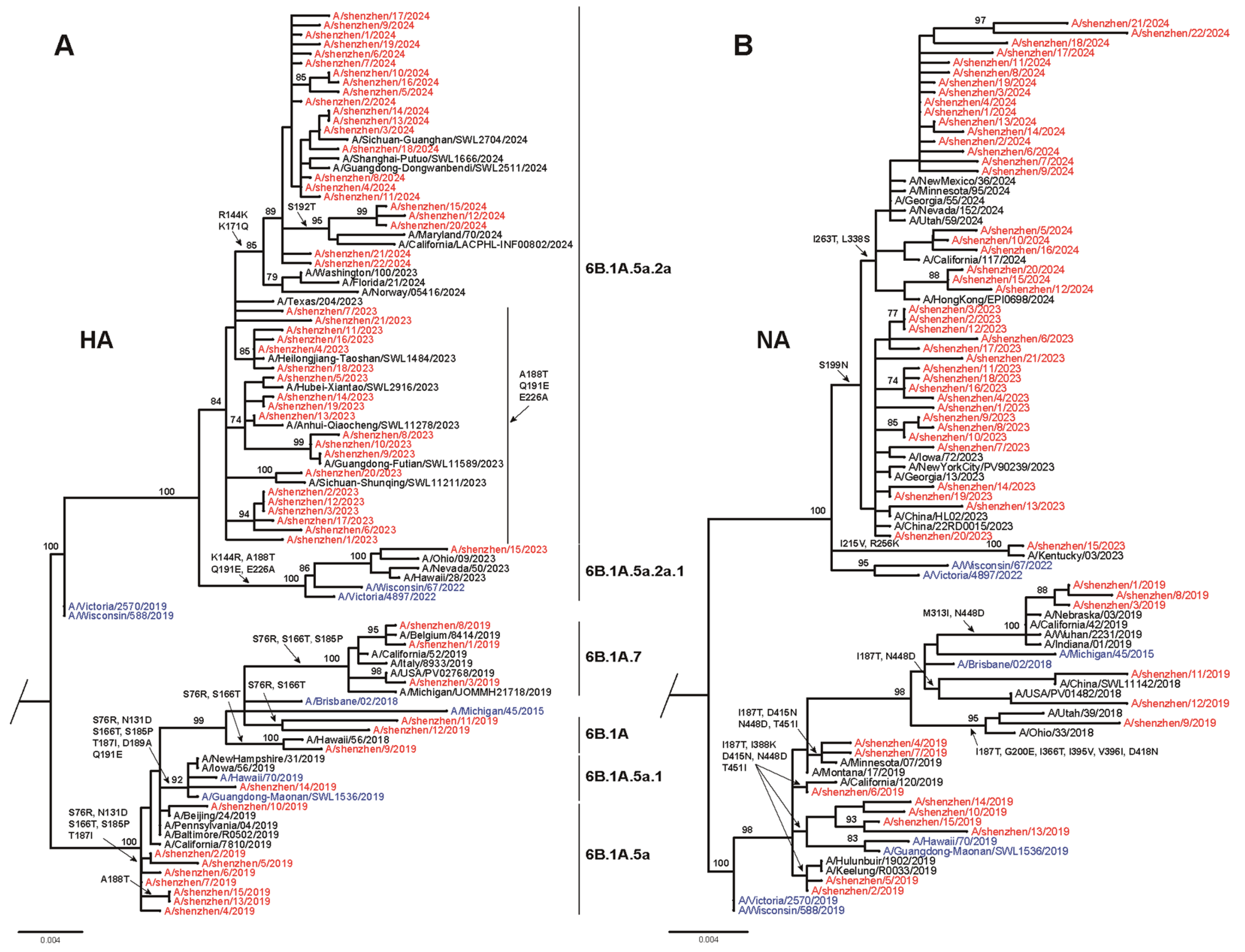
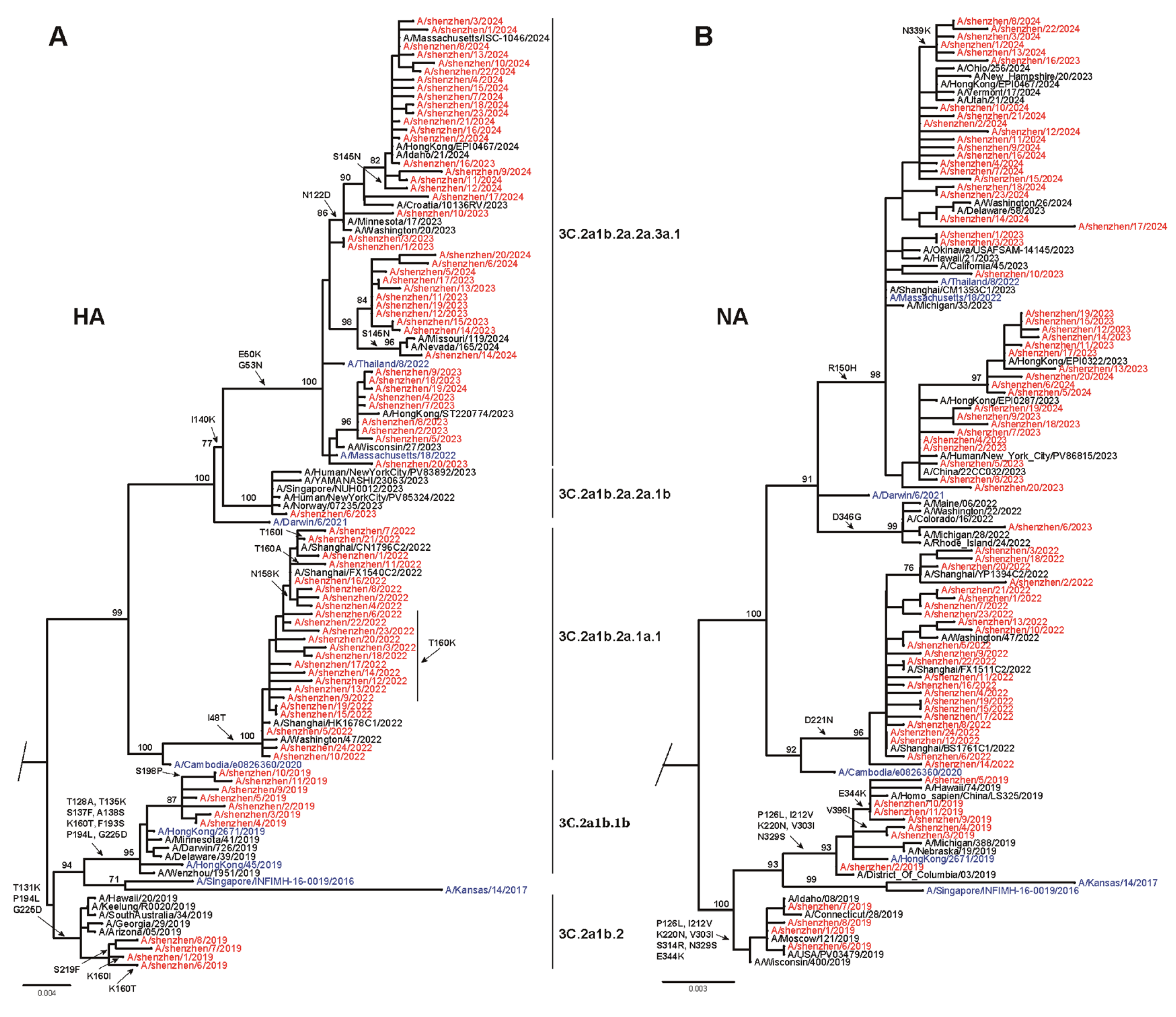
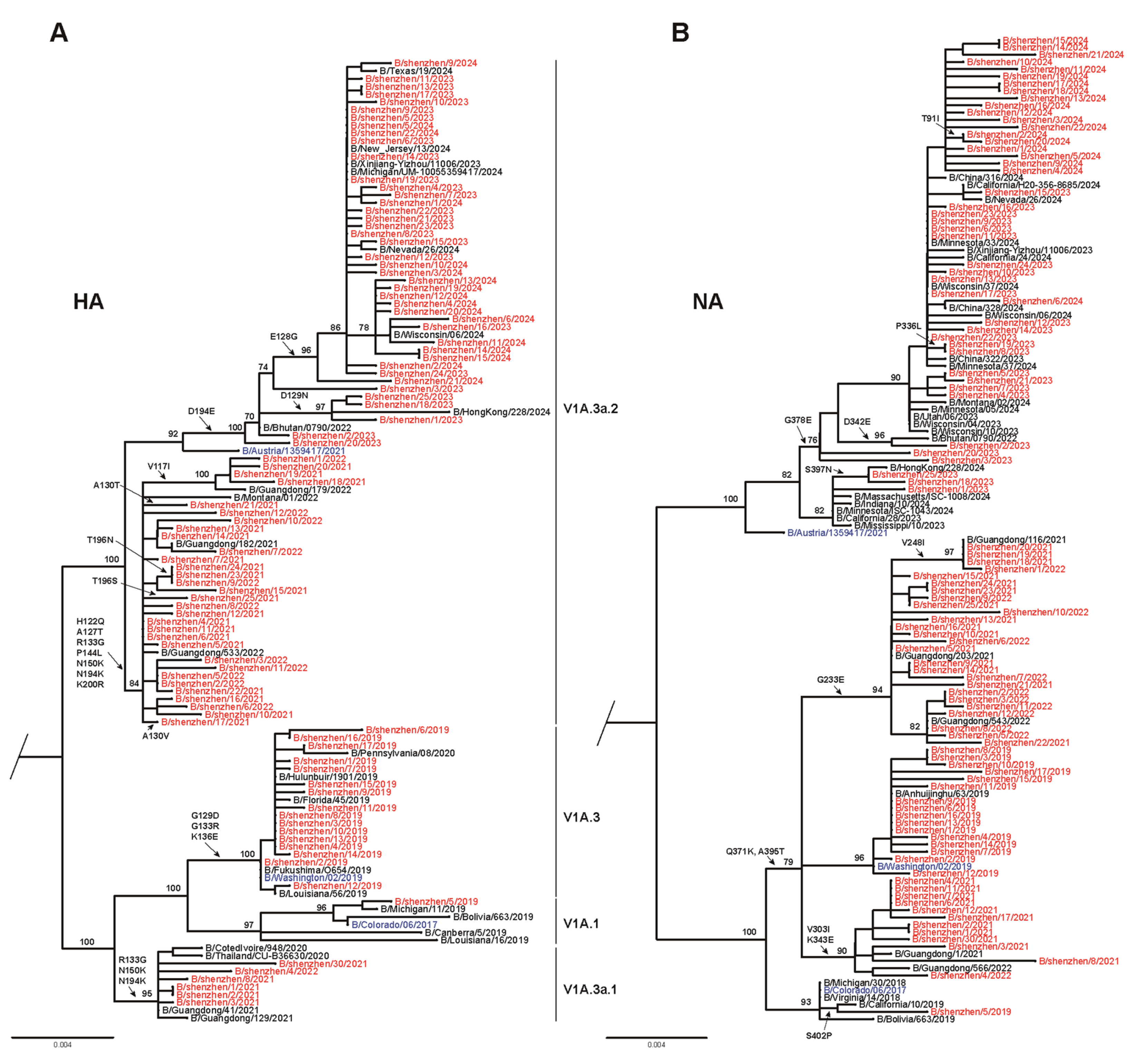
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of Seasonal Influenza Virus
3.3. Amino Acid Variations of Seasonal Influenza Viruses
3.4. Antigenic Characterization of Circulating Influenza Viruses
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iuliano, A.D.; Roguski, K.M.; Chang, H.H.; Muscatello, D.J.; Palekar, R.; Tempia, S.; Cohen, C.; Gran, J.M.; Schanzer, D.; Cowling, B.J.; et al. Estimates of global seasonal influenza-associated respiratory mortality: A modelling study. Lancet 2018, 391, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troeger, C.E.; Blacker, B.F.; Khalil, I.A.; Zimsen, S.R.M.; Albertson, S.B.; Abate, D.; Abdela, J.; Adhikari, T.B.; Aghayan, S.; Agrawal, S.; et al. Mortality, morbidity, and hospitalisations due to influenza lower respiratory tract infections, 2017: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Tsui, J.L.-H.; Gutierrez, B.; Moreno, S.B.; du Plessis, L.; Deng, X.; Cai, J.; Bajaj, S.; Suchard, M.A.; Pybus, O.G.; et al. COVID-19 pandemic interventions reshaped the global dispersal of seasonal influenza viruses. Science 2024, 386, eadq3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, S.J.; Winn, A.K.; Budd, A.P.; Prill, M.M.; Steel, J.; Midgley, C.M.; Kniss, K.; Burns, E.; Rowe, T.; Foust, A.; et al. Changes in Influenza and Other Respiratory Virus Activity During the COVID-19 Pandemic—United States, 2020–2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsakos, M.; Wheatley, A.K.; Laurie, K.; Kent, S.J.; Rockman, S. Influenza lineage extinction during the COVID-19 pandemic? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 741–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.F.; A Hoffmann, J.; Walzer, C.; Lu, J. Global public health crisis response: A roundtable discussion with Professor George Fu Gao, Professor Jules A Hoffmann, Professor Chris Walzer and Professor Jiahai Lu. hLife 2023, 1, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Ma, X.; Tan, K.; Wang, H.; Cong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, S.; Zhao, X.; Gao, G.F.; Deng, J. Evaluation of cross-neutralizing antibodies in children infected with omicron sub-variants. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2023, 40, 100939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Dou, C.; Tian, D.; Ma, Z.; Liu, W.; Gao, G.F.; Bi, Y. Genetic characteristics of H1N1 influenza virus outbreak in China in early 2023. Virol. Sin. 2024, 39, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Gu, L. Clinical, epidemiological, and genomic characteristics of a seasonal influenza A virus outbreak in Beijing: A descriptive study. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e29106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Dou, H.; Wang, X.; Song, T.; Jia, Y.; Yue, Y.; Li, L.; He, F.; Kong, L.; Wu, Z.; et al. Analysis of seasonal H3N2 influenza virus epidemic characteristics and whole genome features in Jining City from 2018 to 2023. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.-J.; Crank, M.C.; Shiver, J.; Graham, B.S.; Mascola, J.R.; Nabel, G.J. Next-generation influenza vaccines: Opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palese, P. Influenza: Old and new threats. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S82–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Ma, H.; Wang, X.; Bao, Z.; Tang, S.; Yi, C.; Sun, B. Broadly neutralizing antibodies to combat influenza virus infection. Antivir. Res. 2024, 221, 105785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekiert, D.C.; Kashyap, A.K.; Steel, J.; Rubrum, A.; Bhabha, G.; Khayat, R.; Lee, J.H.; Dillon, M.A.; O’Neil, R.E.; Faynboym, A.M.; et al. Cross-neutralization of influenza A viruses mediated by a single antibody loop. Nature 2012, 489, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.S.; Yoshida, R.; Ekiert, D.C.; Sakai, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Takada, A.; Wilson, I.A. Heterosubtypic antibody recognition of the influenza virus hemagglutinin receptor binding site enhanced by avidity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17040–17045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cho, M.; Shore, D.; Song, M.; Choi, J.; Jiang, T.; Deng, Y.-Q.; Bourgeois, M.; Almli, L.; Yang, H.; et al. A potent broad-spectrum protective human monoclonal antibody crosslinking two haemagglutinin monomers of influenza A virus. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallewaard, N.L.; Corti, D.; Collins, P.J.; Neu, U.; McAuliffe, J.M.; Benjamin, E.; Wachter-Rosati, L.; Palmer-Hill, F.J.; Yuan, A.Q.; Walker, P.A.; et al. Structure and Function Analysis of an Antibody Recognizing All Influenza A Subtypes. Cell 2016, 166, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, J.; Hwang, W.C.; Perez, S.; Wei, G.; Aird, D.; Chen, L.-M.; Santelli, E.; Stec, B.; Cadwell, G.; Ali, M.; et al. Structural and functional bases for broad-spectrum neutralization of avian and human influenza A viruses. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyfus, C.; Laursen, N.S.; Kwaks, T.; Zuijdgeest, D.; Khayat, R.; Ekiert, D.C.; Lee, J.H.; Metlagel, Z.; Bujny, M.V.; Jongeneelen, M.; et al. Highly conserved protective epitopes on influenza B viruses. Science 2012, 337, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Q.; Wohlbold, T.J.; Zheng, N.-Y.; Huang, M.; Huang, Y.; Neu, K.E.; Lee, J.; Wan, H.; Rojas, K.T.; Kirkpatrick, E.; et al. Influenza Infection in Humans Induces Broadly Cross-Reactive and Protective Neuraminidase-Reactive Antibodies. Cell 2018, 173, 417–429 e410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Peng, W.; Qi, J.; Chai, Y.; Song, H.; Bi, Y.; Rijal, P.; Wang, H.; Oladejo, B.O.; Liu, J.; et al. Structure-Based Modification of an Anti-neuraminidase Human Antibody Restores Protection Efficacy against the Drifted Influenza Virus. mBio 2020, 11, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rijal, P.; Wang, B.B.; Tan, T.K.; Schimanski, L.; Janesch, P.; Dong, T.; McCauley, J.W.; Daniels, R.S.; Townsend, A.R.; Huang, K.Y.A. Broadly Inhibiting Antineuraminidase Monoclonal Antibodies Induced by Trivalent Influenza Vaccine and H7N9 Infection in Humans. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01182-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, L.; McMahon, M.; Turner, H.L.; Zhu, X.; Turner, J.S.; Ozorowski, G.; Stadlbauer, D.; Vahokoski, J.; Schmitz, A.J.; Rizk, A.A.; et al. Human anti-N1 monoclonal antibodies elicited by pandemic H1N1 virus infection broadly inhibit HxN1 viruses in vitro and in vivo. Immunity 2023, 56, 1927–1938.e1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadlbauer, D.; Zhu, X.; McMahon, M.; Turner, J.S.; Wohlbold, T.J.; Schmitz, A.J.; Strohmeier, S.; Yu, W.; Nachbagauer, R.; Mudd, P.A.; et al. Broadly protective human antibodies that target the active site of influenza virus neuraminidase. Science 2019, 366, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momont, C.; Dang, H.V.; Zatta, F.; Hauser, K.; Wang, C.; di Iulio, J.; Minola, A.; Czudnochowski, N.; De Marco, A.; Branch, K.; et al. A pan-influenza antibody inhibiting neuraminidase via receptor mimicry. Nature 2023, 618, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Fu, G.; Jin, T.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Tian, W.; Li, J.; et al. Dominant subtype switch in avian influenza viruses during 2016–2019 in China. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A.; Ludwig, T.; Meier, H. RAxML-III: A fast program for maximum likelihood-based inference of large phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Ekiert, D.C.; Krause, J.C.; Hai, R.; Crowe, J.E.; Wilson, I.A. Structural basis of preexisting immunity to the 2009 H1N1 pandemic influenza virus. Science 2010, 328, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R.; Liang, W.; Ouyang, W.O.; Garcia, A.H.; Kikuchi, C.; Wang, S.; McBride, R.; Tan, T.J.C.; Sun, Y.; Chen, C.; et al. Epistasis mediates the evolution of the receptor binding mode in recent human H3N2 hemagglutinin. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tian, X.; Chen, X.; Ma, J. Structural basis for receptor specificity of influenza B virus hemagglutinin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16874–16879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stray, S.J.; Pittman, L.B. Subtype- and antigenic site-specific differences in biophysical influences on evolution of influenza virus hemagglutinin. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, G.; Sun, F.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Q.; Ma, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, W.; et al. Seroprevalence of influenza viruses in Shandong, Northern China during the COVID-19 pandemic. Front. Med. 2022, 16, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaton, N.S.; Sachs, D.; Chen, C.-J.; Hai, R.; Palese, P. Genome-wide mutagenesis of influenza virus reveals unique plasticity of the hemagglutinin and NS1 proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20248–20253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, P.; Meng, F.; Ding, G.; Wu, J.; Song, S.; Sun, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Xing, W.; et al. Incidence, circulation, and spatiotemporal analysis of seasonal influenza in Shandong, China, 2008–2019: A retrospective study. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2022, 16, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, Y.; Su, Z.; Xie, C. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on influenza virus prevalence in children in Sichuan, China. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.J.; Azziz-Baumgartner, E.; Budd, A.P.; Brammer, L.; Sullivan, S.; Pineda, R.F.; Cohen, C.; Fry, A.M. Decreased influenza activity during the COVID-19 pandemic-United States, Australia, Chile, and South Africa, 2020. Am. J. Transpl. 2020, 20, 3681–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Du, X.; Chen, T.; Yang, L.; Wang, D.; Shu, Y. Nonpharmaceutical Interventions Used to Control COVID-19 Reduced Seasonal Influenza Transmission in China. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 1780–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.S.; Wood, T.; Jelley, L.; Jennings, T.; Jefferies, S.; Daniells, K.; Nesdale, A.; Dowell, T.; Turner, N.; Campbell-Stokes, P.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 nonpharmaceutical interventions on influenza and other respiratory viral infections in New Zealand. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Cowling, B.J.; Tsang, T.K. Influenza Resurgence after Relaxation of Public Health and Social Measures, Hong Kong, 2023. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 2556–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Walker, G.; Kim, K.W.; Stelzer-Braid, S.; Scotch, M.; Rawlinson, W.D. The resurgence of influenza A/H3N2 virus in Australia after the relaxation of COVID-19 restrictions during the 2022 season. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caini, S.; Meijer, A.; Nunes, M.C.; Henaff, L.; Zounon, M.; Boudewijns, B.; Del Riccio, M.; Paget, J. Probable extinction of influenza B/Yamagata and its public health implications: A systematic literature review and assessment of global surveillance databases. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, 100851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadalla, M.E.; Alkadi, H.; Alarjani, M.; Al-Anazi, A.E.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Alohali, T.A.; Enani, M.; Alturaiki, W.; Alosaimi, B. Moderately Low Effectiveness of the Influenza Quadrivalent Vaccine: Potential Mismatch between Circulating Strains and Vaccine Strains. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Song, J.Y.; Wie, S.-H.; Choi, W.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, S.H.; Park, K.-H.; et al. Real-world effectiveness of influenza vaccine over a decade during the 2011–2021 seasons-Implications of vaccine mismatch. Vaccine 2024, 42, 126381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorji, T.; Dorji, K.; Gyeltshen, S. Evolution of Influenza A(H3N2) Viruses in Bhutan for Two Consecutive Years, 2022 and 2023. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2024, 18, e70028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Xu, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, P.; Guo, X.; Zuo, Z.; Gao, L.; Jia, Z.; Xue, P.; Wang, J. An epidemiologic surveillance study based on wastewater and respiratory specimens reveals influenza a virus prevalence and mutations in Taiyuan, China during 2023–2024. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badar, N.; Ikram, A.; Salman, M.; Saeed, S.; Mirza, H.A.; Ahad, A.; Umair, M.; Farooq, U. Evolutionary analysis of seasonal influenza A viruses in Pakistan 2020–2023. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2024, 18, e13262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, R.P.; de Vries, E.; Martínez-Romero, C.; McBride, R.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Rottier, P.J.M.; García-Sastre, A.; Paulson, J.C.; de Haan, C.A.M. Evolution of the hemagglutinin protein of the new pandemic H1N1 influenza virus: Maintaining optimal receptor binding by compensatory substitutions. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 13868–13877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portnoff, A.D.; Patel, N.; Massare, M.J.; Zhou, H.; Tian, J.-H.; Zhou, B.; Shinde, V.; Glenn, G.M.; Smith, G. Influenza Hemagglutinin Nanoparticle Vaccine Elicits Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies against Structurally Distinct Domains of H3N2 HA. Vaccines 2020, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorquera, P.A.; Mishin, V.P.; Chesnokov, A.; Nguyen, H.T.; Mann, B.; Garten, R.; Barnes, J.; Hodges, E.; De La Cruz, J.; Xu, X.; et al. Insights into the antigenic advancement of influenza A(H3N2) viruses, 2011–2018. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowronski, D.M.; Leir, S.; Sabaiduc, S.; Chambers, C.; Zou, M.; Rose, C.; Olsha, R.; A Dickinson, J.; Winter, A.-L.; Jassem, A.; et al. Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness by A(H3N2) Phylogenetic Subcluster and Prior Vaccination History: 2016–2017 and 2017–2018 Epidemics in Canada. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 1387–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.C.; Xie, J.; Zheng, T.; Nycholat, C.M.; Grande, G.; Paulson, J.C.; Lerner, R.A.; Wilson, I.A. Diversity of Functionally Permissive Sequences in the Receptor-Binding Site of Influenza Hemagglutinin. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.D.; Ross, T.M. H3N2 influenza viruses in humans: Viral mechanisms, evolution, and evaluation. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2018, 14, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Kniss, K.; Mishin, V.P.; Merced-Morales, A.A.; Laplante, J.; George, K.S.; Blevins, P.; Chesnokov, A.; De La Cruz, J.A.; et al. Cluster of Oseltamivir-Resistant and Hemagglutinin Antigenically Drifted Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 Viruses, Texas, USA, January 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1953–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.; Saborio, S.; Kuan, G.; Gresh, L.; Sanchez, N.; Ojeda, S.; Harris, E.; Balmaseda, A.; Gordon, A. Association between Haemagglutination inhibiting antibodies and protection against clade 6B viruses in 2013 and 2015. Vaccine 2017, 35, 6202–6207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, A.; Mai, L.Q.; Thanh, L.T.; Wolbers, M.; Hang, N.L.K.; Thai, P.Q.; Yen, N.T.T.; Hoa, L.N.M.; Bryant, J.E.; Duong, T.N.; et al. Hemagglutination inhibiting antibodies and protection against seasonal and pandemic influenza infection. J. Infect. 2015, 70, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
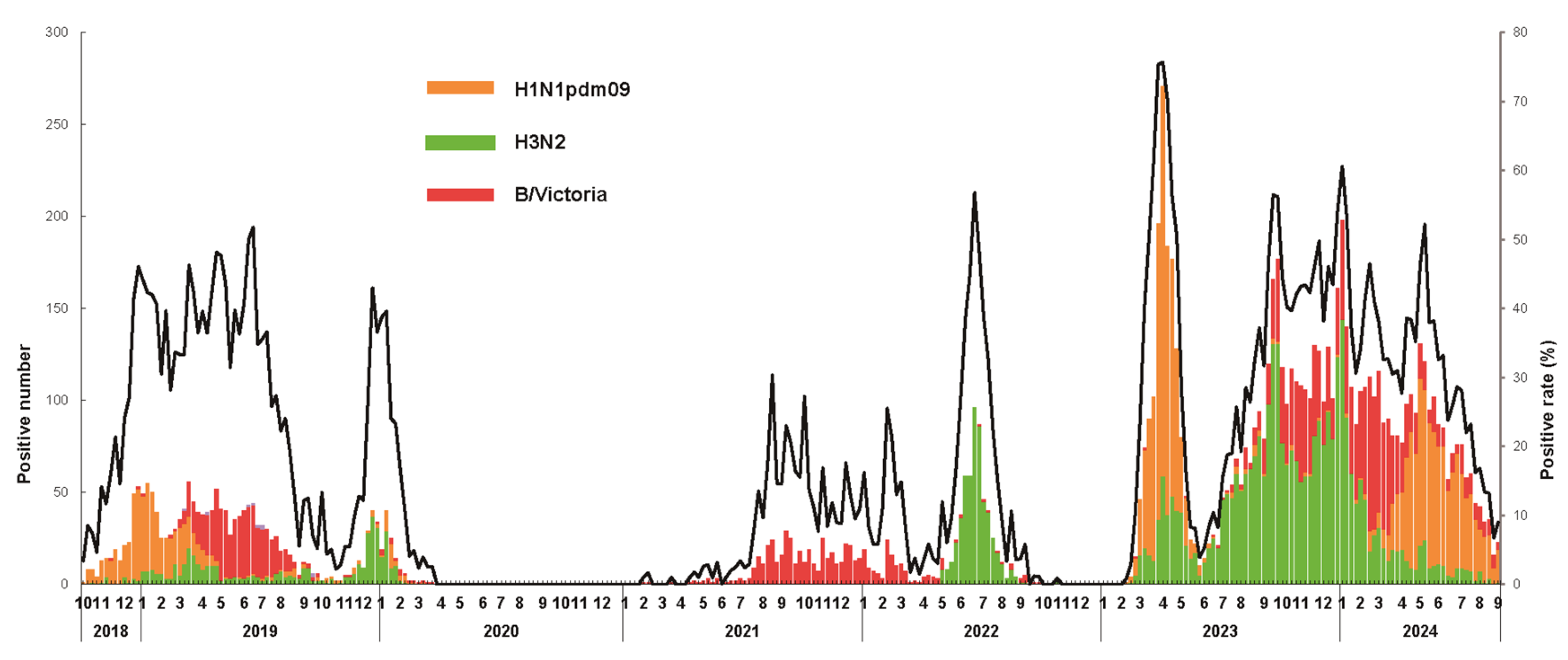
| Season | Sample Number | All Influenza Virus | H1N1pdm09 | H3N2 | B/Victoria | B/Yamagata |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive Number (Positive Rate %) | Positive Number (Positive Rate %) | Positive Number (Positive Rate %) | Positive Number (Positive Rate %) | Positive Number (Positive Rate %) | ||
| 2018.10–2019.09 | 4947 | 1481 (29.9%) | 604 (12.2%) | 258 (5.2%) | 610 (12.3%) | 9 (0.2%) |
| 2019.10–2020.09 | 3081 | 278 (9.0%) | 55 (1.8%) | 203 (6.6%) | 20 (0.7%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| 2020.10–2021.07 | 4150 | 53 (1.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 53 (1.3%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| 2021.08–2022.09 | 6653 | 1063 (16.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 541 (8.1%) | 522 (7.9%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| 2022.10–2023.05 | 5249 | 1473 (28.1%) | 1082 (20.6%) | 388 (7.4%) | 3 (0.1%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| 2023.06–2024.08 | 17,348 | 5722 (33.0%) | 1259 (7.3%) | 2800 (16.1%) | 1664 (9.6%) | 0 (0.0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Huang, S.; Qi, S.; Hu, Z.; Xu, X.; Jiang, H.; Duan, J.; et al. Analysis of Epidemiological and Evolutionary Characteristics of Seasonal Influenza Viruses in Shenzhen City from 2018 to 2024. Viruses 2025, 17, 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060798
Peng W, Liu H, Wang X, Li C, Huang S, Qi S, Hu Z, Xu X, Jiang H, Duan J, et al. Analysis of Epidemiological and Evolutionary Characteristics of Seasonal Influenza Viruses in Shenzhen City from 2018 to 2024. Viruses. 2025; 17(6):798. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060798
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Weiyu, Hui Liu, Xin Wang, Chao Li, Shunwu Huang, Shiyu Qi, Zhongnan Hu, Xiaoying Xu, Haihai Jiang, Jinyu Duan, and et al. 2025. "Analysis of Epidemiological and Evolutionary Characteristics of Seasonal Influenza Viruses in Shenzhen City from 2018 to 2024" Viruses 17, no. 6: 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060798
APA StylePeng, W., Liu, H., Wang, X., Li, C., Huang, S., Qi, S., Hu, Z., Xu, X., Jiang, H., Duan, J., Chen, H., Huang, M., Sun, Y., Wu, W., Jiang, M., Zou, X., & Fang, S. (2025). Analysis of Epidemiological and Evolutionary Characteristics of Seasonal Influenza Viruses in Shenzhen City from 2018 to 2024. Viruses, 17(6), 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060798






