Cytomegalovirus Colitis in Adult Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Risk Factors Contributing to CMV Colitis
2.1. Demographic Factors
2.2. Disease-Specific Factors
2.3. Patient-Specific Factors and Laboratory Findings
2.4. Use of Immunosuppressants
3. Pathophysiology
4. Clinical Features
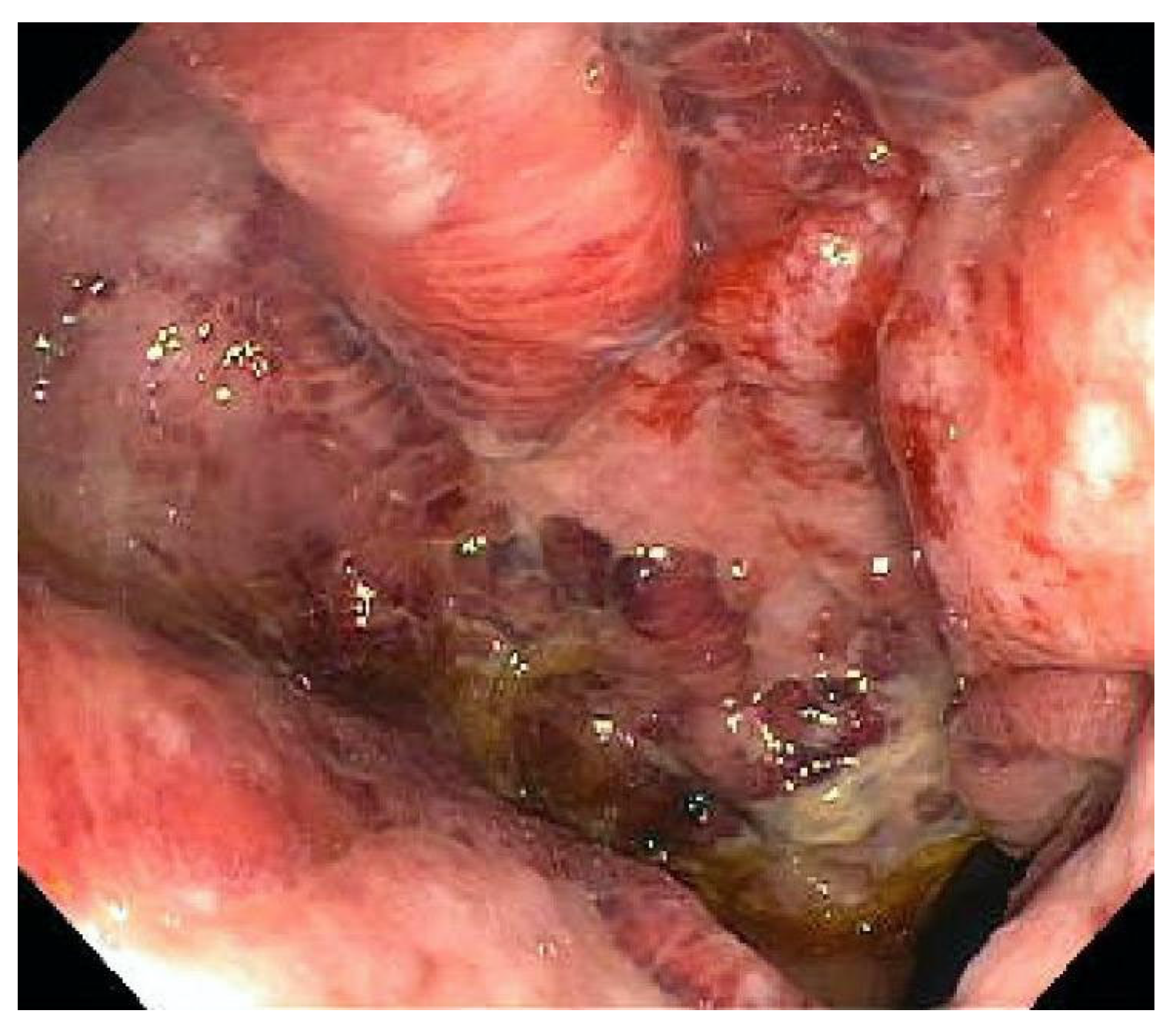
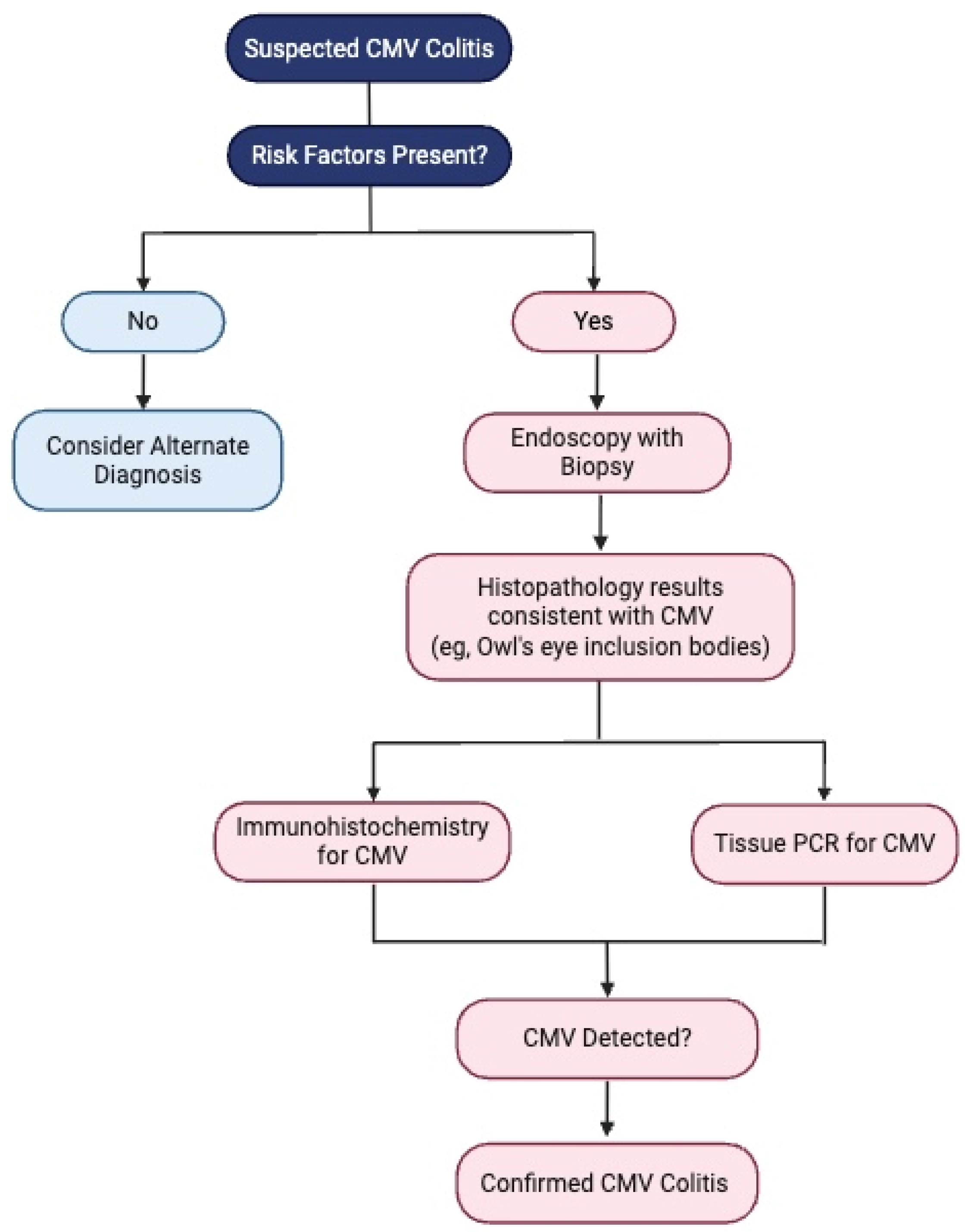
5. Diagnosis
6. Treatment Strategies for CMV in UC Patients
6.1. Role of Immunosuppressants and Biologics
6.2. Antiviral Therapy
6.3. Prophylaxis
7. Prognosis and Negative Prognostic Factors
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACG | American College of Gastroenterology |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CD | Crohn’s Disease |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
| ECCO | European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation |
| G-CSF | Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IBD | Inflammatory Bowel Disease |
| IFN-ɣ | Interferon-gamma |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PPV | Positive Predictive Value |
| TNF-ɑ | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| UC | Ulcerative Colitis |
References
- Flanders, W.D.; Lally, C.; Dilley, A.; Diaz-Decaro, J. Estimated cytomegalovirus seroprevalence in the general population of the United States and Canada. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, M.K.; Khanna, R. Human cytomegalovirus: Clinical aspects, immune regulation, and emerging treatments. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2004, 4, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dioverti, M.V.; Razonable, R.R. Cytomegalovirus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungman, P.; Chemaly, R.F.; Khawaya, F.; Alain, S.; Avery, R.; Badshah, C.; Boeckh, M.; Fournier, M.; Hodowanec, A.; Komatsu, T.; et al. Consensus definitions of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection and disease in transplant patients including resistant and refractory CMV for use in clinical trials: 2024 update from the Transplant Associated Virus Infections Forum. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 79, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kandiel, A.; Lashner, B. Cytomegalovirus colitis complicating inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 2857–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharzik, T.; Ellul, P.; Greuter, T.; Rahier, J.F.; Verstockt, B.; Abreu, C.; Albuquerque, A.; Allocca, M.; Esteve, M.; Farraye, F.A.; et al. ECCO guidelines on the prevention, diagnosis, and management of infections in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Crohns Colitis. 2021, 15, 879–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.-Q.; Meng, Z.-M.; Zhang, T.; Jing, X.-T.; Gan, H.-T. Opportunistic infection in hospitalised patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2020, 30, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, T.; Higashida-Konishi, M.; Izumi, K.; Hama, S.; Oshige, T.; Oshima, H.; Okano, Y. Risk factors associated with cytomegalovirus reactivation in patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy for rheumatic diseases: A retrospective study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kishore, J.; Ghoshal, U.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Krishnani, N.; Kumar, S.; Singh, M.; Ayyagari, A. Infection with cytomegalovirus in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Prevalence, clinical significance and outcome. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53 Pt 11, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Wang, G.; Kong, D.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; Qin, H.; Wang, H. Risk factors of cytomegalovirus reactivation in ulcerative colitis patients: A meta-analysis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hirayama, Y.; Ando, T.; Hirooka, Y.; Watanabe, O.; Miyahara, R.; Nakamura, M.; Yamamura, T.; Goto, H. Characteristic endoscopic findings and risk factors for cytomegalovirus-associated colitis in patients with active ulcerative colitis. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 8, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, H.-S.; Park, S.H.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, J.-M.; Kwak, M.S.; Hwang, S.W.; et al. Risk factors and clinical outcomes associated with cytomegalovirus colitis in patients with acute severe ulcerative colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.-R.; Wu, R.-C.; Kuo, C.-J.; Yeh, P.-J.; Yeh, Y.-M.; Chen, C.-L.; Chiu, C.-H.; Pan, Y.-B.; Tsou, Y.-K.; Le, P.-H. Adequate antiviral treatment lowers overall complications of cytomegalovirus colitis among inpatients with inflammatory bowel diseases. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alotaibi, Y.; AlLehibi, A.; Almtawa, A.; Alotaibi, N.; Alghamdi, A.; Alrajhi, S.; AlQutub, A.; AlEid, A.; Alamr, A.; Al Ibrahim, B.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors of cytomegalovirus colitis in inflammatory bowel disease patients in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: A tertiary center experience. Saudi J. Med. Med. Sci. 2023, 11, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ramos, G.P.; Papadakis, K.A. Mechanisms of disease: Inflammatory bowel diseases. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jentzer, A.; Veyrard, P.; Roblin, X.; Saint-Sardos, P.; Rochereau, N.; Paul, S.; Bourlet, T.; Pozzetto, B.; Pillet, S. Cytomegalovirus and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) with a special focus on the link with ulcerative colitis (UC). Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Humar, A.; St Louis, P.; Mazzulli, T.; McGeer, A.; Lipton, J.; Messner, H.; Macdonald, K.S. Elevated serum cytokines are associated with cytomegalovirus infection and disease in bone marrow transplant recipients. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 179, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maidji, E.; Somsouk, M.; Rivera, J.M.; Hunt, P.W.; Stoddart, C.A. Replication of CMV in the gut of HIV-infected individuals and epithelial barrier dysfunction. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- de Souza, H.S.P.; Fiocchi, C. Immunopathogenesis of IBD: Current state of the art. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue-Toyoda, M.; Kato, K.; Nagata, K.; Yoshikawa, H. Glucocorticoids facilitate the transcription from the human cytomegalovirus major immediate early promoter in glucocorticoid receptor- and nuclear factor-I-like protein-dependent manner. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Damme, E.; Sauviller, S.; Lau, B.; Kesteleyn, B.; Griffiths, P.; Burroughs, A.; Emery, V.; Sinclair, J.; Van Loock, M. Glucocorticosteroids trigger reactivation of human cytomegalovirus from latently infected myeloid cells and increase the risk for HCMV infection in D + R + liver transplant patients. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96 Pt 1, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hookey, L.; Depew, W.; Boag, A.; Vanner, S. 6-mercaptopurine and inflammatory bowel disease: Hidden ground for the cytomegalovirus. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 17, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shukla, T.; Singh, S.; Tandon, P.; McCurdy, J.D. Corticosteroids and thiopurines, but not tumor necrosis factor antagonists, are associated with cytomegalovirus reactivation in inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 51, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, R.B.; Taylor, K.M.; Morrissey, C.O.; Gardiner, B.J. Cytomegalovirus in inflammatory bowel disease: A clinical approach. Intern. Med. J. 2022, 52, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criscuoli, V.; Rizzuto, M.R.; Gallo, E.; Orlando, A.; Cottone, M. Toxic megacolon and human cytomegalovirus in a series of severe ulcerative colitis patients. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 66, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, J.S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Park, S.J.; Cheon, J.H.; Ye, B.D.; Jung, S.-A.; Park, Y.S.; Choi, C.H.; et al. Long-term outcomes of cytomegalovirus reactivation in patients with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis: A multicenter study. Gut Liver 2014, 8, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Suzuki, H.; Kato, J.; Kuriyama, M.; Hiraoka, S.; Kuwaki, K.; Yamamoto, K. Specific endoscopic features of ulcerative colitis complicated by cytomegalovirus infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oh, S.J.; Lee, C.K.; Kim, Y.-W.; Jeong, S.J.; Park, Y.M.; Oh, C.H.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, H.J. True cytomegalovirus colitis is a poor prognostic indicator in patients with ulcerative colitis flares: The 10-year experience of an academic referral inflammatory bowel disease center. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Rennie, M.; Krasovec, A.; Nagubandi, S.; Liu, S.; Ge, E.; Khehra, B.; Au, M.; Sivagnanam, S.; Kwan, V.; et al. Impact of cytomegalovirus on outcomes in acute severe ulcerative colitis: A retrospective observational study. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2024, 15, 20406223241233203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, W.-X.; Ma, C.-Y.; Zhang, J.-G.; He, F.; Liu, Q.-M.; Cheng, A.; Liu, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Bu, X.; et al. Effects of cytomegalovirus infection on the prognosis of inflammatory bowel disease patients. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 3287–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- Wu, X.-W.; Wu, L.; Ji, H.-Z.; Wang, F.-Y. Relationship between cytomegalovirus infection and steroid resistance in inflammatory bowel disease: A meta-analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 3203–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tandon, P.; James, P.; Cordeiro, E.; Mallick, R.; Shukla, T.; McCurdy, J.D. Diagnostic accuracy of blood-based tests and histopathology for cytomegalovirus reactivation in inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCurdy, J.D.; Enders, F.T.; Jones, A.; Killian, J.M.; Loftus, E.V.; Bruining, D.H.; Smyrk, T.C. Detection of cytomegalovirus in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Where to biopsy and how many biopsies? Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2833–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, E.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, E.J.; Song, E.H.; Chong, Y.P.; Lee, S.; Choi, S.; Woo, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S. Diagnostic performance of the cytomegalovirus (CMV) antigenemia assay in patients with CMV gastrointestinal disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, e121–e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, G.; Picardi, A.; Capobianchi, A.; Spagnoli, A.; Cudillo, L.; Dentamaro, T.; Tendas, A.; Cupelli, L.; Ciotti, M.; Volpi, A.; et al. A prospective study comparing quantitative cytomegalovirus (CMV) polymerase chain reaction in plasma and pp65 antigenemia assay in monitoring patients after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. BMC Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- King, W.; Richhart, R.; Gonzalo, D.H.; Zimmermann, E. Cytomegaloviral colitis in primary CMV viraemia in a young immunocompetent adult. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e249891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surapatpichai, M.; Taeudomkul, S.; Jiragawasan, C.; Laohawetwanit, T. Cytomegalovirus colitis in an immunocompromised patient presenting with massive lower gastrointestinal bleeding. IDCases 2022, 28, e01500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sanat, Z.M.; Siami, Z.; Alatab, S.; Vahedi, H.; Fanni, Z. Cytomegalovirus infection in adult patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A literature review. Arch. Iran Med. 2024, 27, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, H. Practical updates in clinical antiviral resistance testing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2024, 62, e0072823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Matsuoka, K.; Iwao, Y.; Mori, T.; Sakuraba, A.; Yajima, T.; Hisamatsu, T.; Okamoto, S.; Morohoshi, Y.; Izumiya, M.; Ichikawa, H.; et al. Cytomegalovirus is frequently reactivated and disappears without antiviral agents in ulcerative colitis patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maconi, G.; Lombardini, M.; Furfaro, F.; Bezzio, C.; Zerbi, P.; Ardizzone, S. Long-term outcome of inflammatory bowel diseases with cytomegalovirus colitis: Effect of antiviral treatment. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 26, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Krishna, S.G.; Hinton, A.; Arsenescu, R.; Levine, E.J.; Conwell, D.L. Cytomegalovirus-related hospitalization is associated with adverse outcomes and increased health-care resource utilization in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jones, A.; McCurdy, J.D.; Loftus, E.V.; Bruining, D.H.; Enders, F.T.; Killian, J.M.; Smyrk, T.C. Effects of antiviral therapy for patients with inflammatory bowel disease and a positive intestinal biopsy for cytomegalovirus. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, T.; Singh, S.; Loftus, E.V.; Bruining, D.H.; McCurdy, J.D. Antiviral therapy in steroid-refractory ulcerative colitis with cytomegalovirus: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2718–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillet, S.; Jarlot, C.; Courault, M.; Del Tedesco, E.; Chardon, R.; Saint-Sardos, P.; Presles, E.; Phelip, J.-M.; Berthelot, P.; Pozzetto, B.; et al. Infliximab does not worsen outcomes during flare-ups associated with cytomegalovirus infection in patients with ulcerative colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, M.; Ohta, M.; Ohkura, T.; Ando, T.; Ohmiya, N.; Niwa, Y.; Goto, H. Cytomegalovirus infection in severe ulcerative colitis patients undergoing continuous intravenous cyclosporine treatment in Japan. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyant, T.; Fedyk, E.; Abhyankar, B. An overview of the mechanism of action of the monoclonal antibody vedolizumab. J. Crohns Colitis 2016, 10, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawa-Gołębiewska, A.; Lenarcik, M.; Zagórowicz, E. Resolution of CMV infection in the bowel on vedolizumab therapy. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 1234–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hommel, C.; Pillet, S.; Rahier, J.F. Comment on: ‘Resolution of CMV infection in the bowel on vedolizumab therapy’. J. Crohns Colitis 2020, 14, 148–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, R.S.; McClure, E.L.; Pruce, J.C.; Allegretti, J.R. S731 Cytomegalovirus colitis is rarely observed after initiation of infliximab, adalimumab, or vedolizumab in biologic-naïve patients with ulcerative colitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, S334–S335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeralam, Y.; Al Qurashi, B.; Al Masoudi, A.; Alhejaili, T.L.; Khayat, M.; Aljoaid, A.M.; Harti, W.A.; Hafiz, W.A.; Shariff, M.K. Cytomegalovirus colitis in a patient with ulcerative colitis on vedolizumab monotherapy. Cureus 2023, 15, e35439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Weisshof, R.; Golan, M.A.; Sossenheimer, P.H.; El Jurdi, K.; Ollech, J.E.; Pekow, J.; Cohen, R.D.; Sakuraba, A.; Dalal, S.; Rubin, D.T. Real-world experience with tofacitinib in IBD at a tertiary center. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Panés, J.; D’Haens, G.R.; Sands, B.E.; Su, C.; Moscariello, M.; Jones, T.; Pedersen, R.; Friedman, G.S.; Lawendy, N.; et al. Safety of tofacitinib for treatment of ulcerative colitis, based on 4.4 years of data from global clinical trials. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 1541–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Feagan, B.G.; Danese, S.; O’Brien, C.D.; Ott, E.; Marano, C.; Baker, T.; Zhou, Y.; Volger, S.; Tikhonov, I.; et al. Safety of ustekinumab in inflammatory bowel disease: Pooled safety analysis of results from phase 2/3 studies. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2021, 27, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, C.A.; Kennedy, N.A.; Raine, T.; Hendy, P.A.; Smith, P.J.; Limdi, J.K.; Hayee, B.; Lomer, M.C.E.; Parkes, G.C.; Selinger, C.; et al. British Society of Gastroenterology consensus guidelines on the management of inflammatory bowel disease in adults. Gut 2019, 68 (Suppl. 3), s1–s106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zagórowicz, E.; Bugajski, M.; Wieszczy, P.; Pietrzak, A.; Magdziak, A.; Mróz, A. Cytomegalovirus infection in ulcerative colitis is related to severe inflammation and a high count of cytomegalovirus-positive cells in biopsy is a risk factor for colectomy. J. Crohns Colitis 2016, 10, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walti, C.S.; Khanna, N.; Avery, R.K.; Helanterä, I. New treatment options for refractory/resistant CMV infection. Transpl. Int. 2023, 36, 11785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rahier, J.F.; Magro, F.; Abreu, C.; Armuzzi, A.; Ben-Horin, S.; Chowers, Y.; Cottone, M.; de Ridder, L.; Doherty, G.; Ehehalt, R.; et al. Second European evidence-based consensus on the prevention, diagnosis and management of opportunistic infections in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2014, 8, 443–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Category | Risk Factors |
|---|---|
| Demographic factors |
|
| Disease severity |
|
| Clinical features |
|
| Immunosuppressants |
|
| Colonoscopy findings |
|
| Other risk factors |
|
| Investigation | Findings | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Endoscopy | Punched-out ulcers, erosions, mucosal inflammation | Unable to distinguish between CMV colitis and IBD flare |
| Histology | Owl’s eye inclusions | Pathognomonic, gold standard |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | CMV antigens in tissues | Sensitive and specific, gold standard |
| Tissue PCR | CMV DNA in tissues | Quantitative PCR preferred, high viral load correlated with active disease |
| Whole-blood PCR and pp65 antigenemia | CMV DNA and pp65 antigen in blood | Assesses systemic viremia, poor correlation with CMV colitis |
| Viral culture | Grows viable virus | High specificity, low sensitivity, slow turnaround time |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soni, K.; Puing, A. Cytomegalovirus Colitis in Adult Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Viruses 2025, 17, 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060752
Soni K, Puing A. Cytomegalovirus Colitis in Adult Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Viruses. 2025; 17(6):752. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060752
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoni, Kriti, and Alfredo Puing. 2025. "Cytomegalovirus Colitis in Adult Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease" Viruses 17, no. 6: 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060752
APA StyleSoni, K., & Puing, A. (2025). Cytomegalovirus Colitis in Adult Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Viruses, 17(6), 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060752






