Three Distinct Circovirids Identified in a Tapeworm Recovered from a Bobcat (Lynx rufus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extractions and Metagenomics
2.3. Mitochondrial Sequence Analyses
2.4. Circovirus Sequence Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
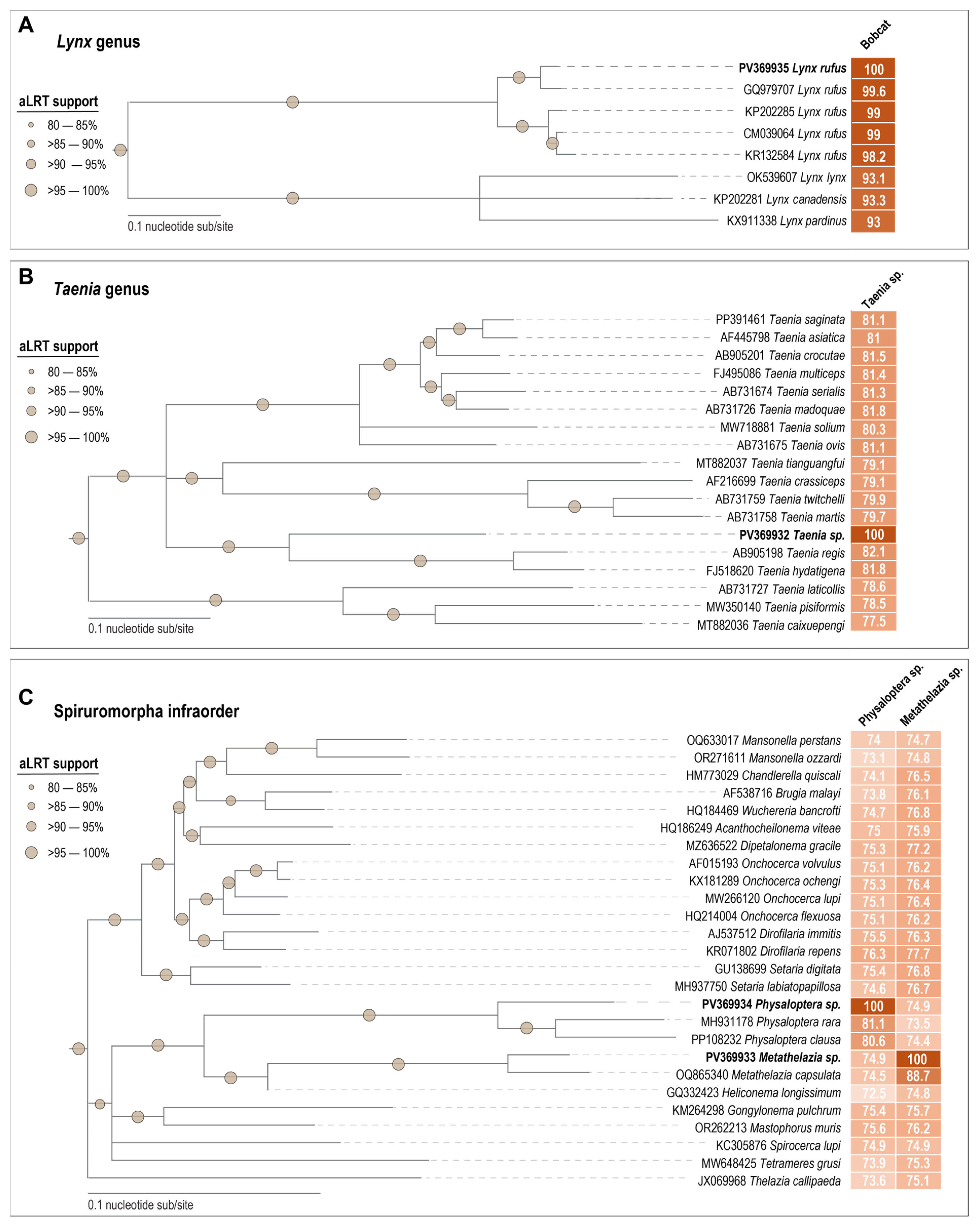
3.1. Bobcat Mitochondrial Genome
3.2. Helminth Mitochondrial Genomes
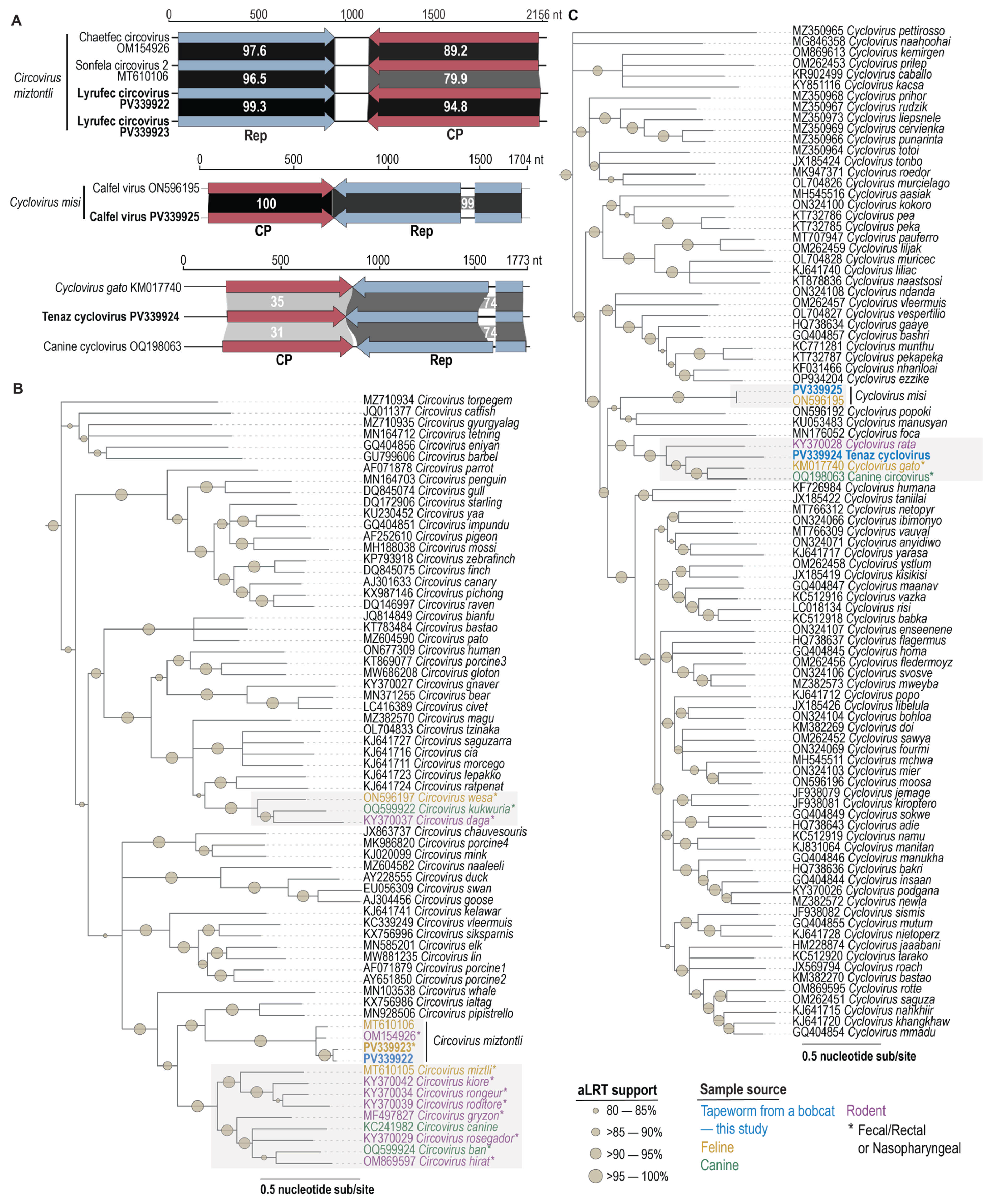
3.3. Circovirid Genomes
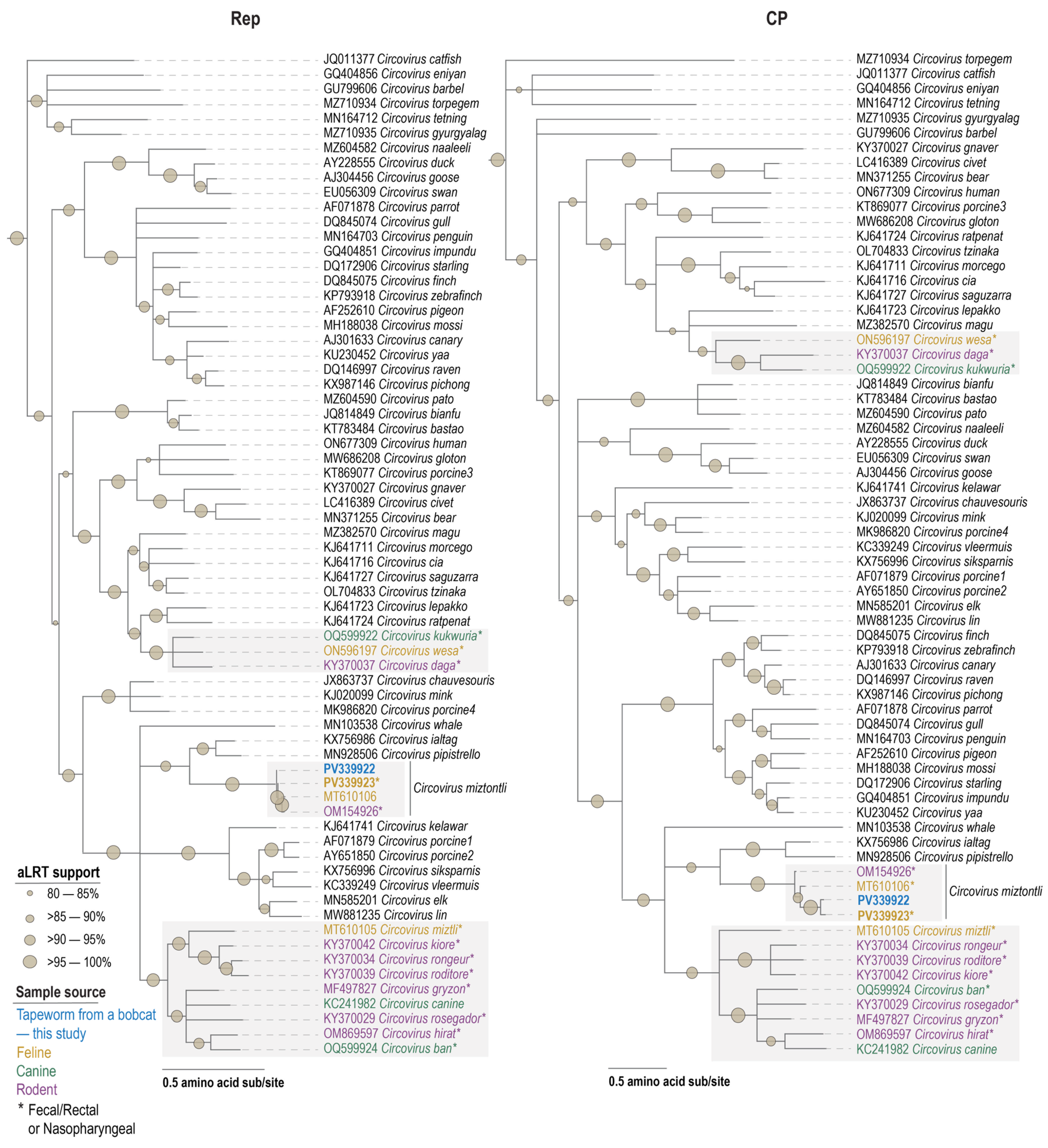
3.4. Circovirus
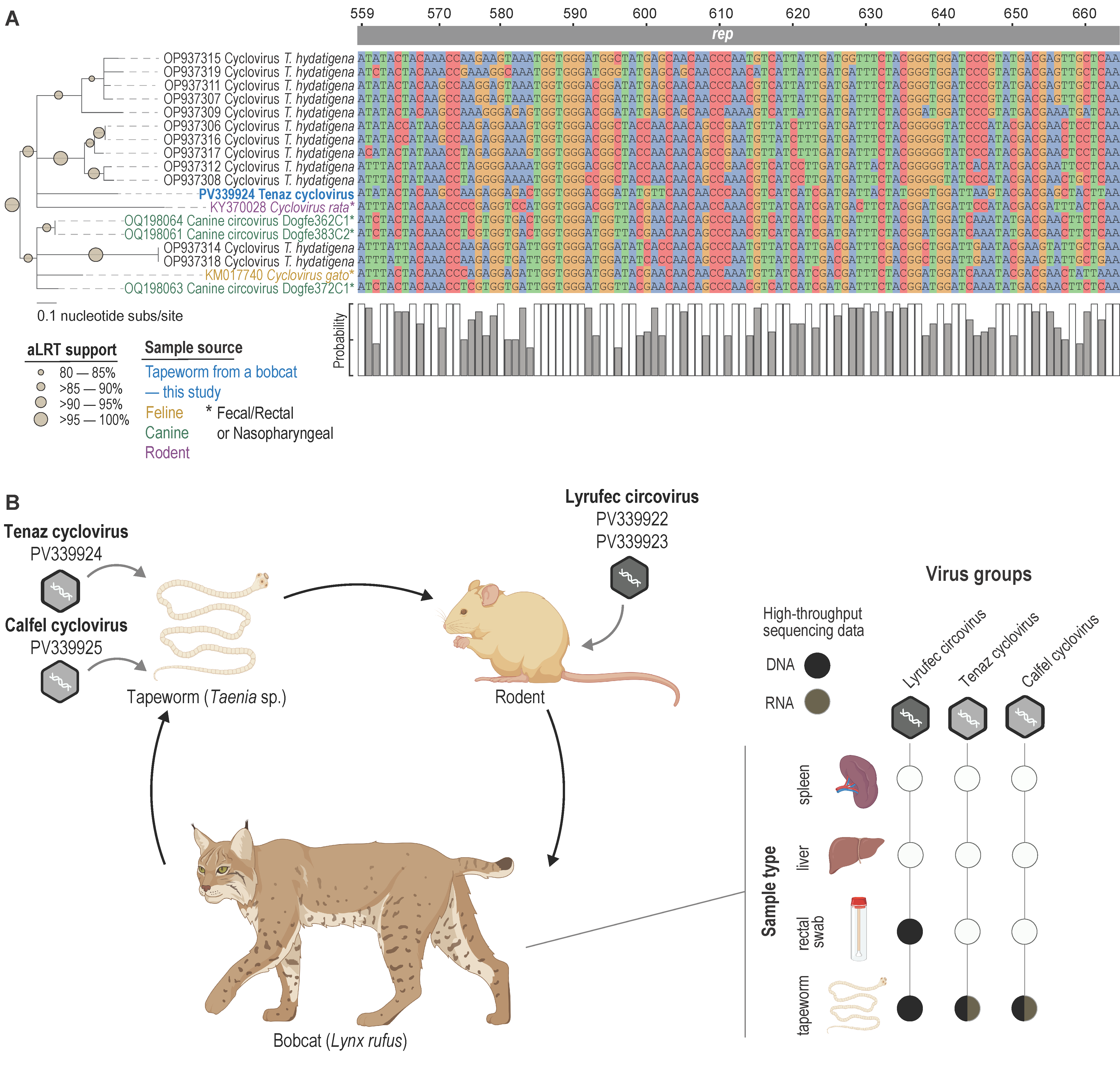
3.5. Cyclovirus
3.6. Circovirid Host
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larivière, S.; Walton, L.R. Lynx rufus . Mamm. Species 1997, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, N.M.; Crimmins, S.M. Bobcat population status and management in North America: Evidence of large-scale population increase. J. Fish Wildl. Manag. 2010, 1, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.; Morin, D.; Lopez-Gonzalez, C. Lynx rufus . In The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; 2016: e. T12521A50655874; World Conservation Union: Gland, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Litvaitis, J.A.; Reed, G.C.; Carroll, R.P.; Litvaitis, M.K.; Tash, J.; Mahard, T.; Broman, D.J.; Callahan, C.; Ellingwood, M. Bobcats (Lynx rufus) as a model organism to investigate the effects of roads on wide-ranging carnivores. Environ. Manag. 2015, 55, 1366–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, S.P.; Sauvajot, R.M.; Fuller, T.K.; York, E.C.; Kamradt, D.A.; Bromley, C.; Wayne, R.K. Effects of urbanization and habitat fragmentation on bobcats and coyotes in southern California. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, G.M.; Jennings, M.K.; Smith, J.G.; Boydston, E.E.; Lyren, L.M.; Lewison, R.L. Bobcats in southern California respond to urbanization at multiple scales. Biol. Conserv. 2023, 278, 109849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, V.D.; Kenyon, M.; Brown, R.K.; Dyck, M.A.; Prange, S.; Peterman, W.E.; Dennison, C. Habitat connectivity and resource selection in an expanding bobcat (Lynx rufus) population. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakiewicz, C.P.; Burridge, C.P.; Funk, W.C.; Craft, M.E.; Crooks, K.R.; Fisher, R.N.; Fountain-Jones, N.M.; Jennings, M.K.; Kraberger, S.J.; Lee, J.S. Does the virus cross the road? Viral phylogeographic patterns among bobcat populations reflect a history of urban development. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 1806–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branney, A.B.; Dutt, A.M.V.; Wardle, Z.M.; Tanner, E.P.; Tewes, M.E.; Cherry, M.J. Scale of effect of landscape patterns on resource selection by bobcats (Lynx rufus) in a multi-use rangeland system. Landsc. Ecol. 2024, 39, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, J.; Rodgers, T.; Young, J.K. Beating the heat: Ecology of desert bobcats. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2022, 22, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, S.J.; Tornabene, B.J.; DeBlieux, T.S.; Pochini, K.M.; Chislock, M.F.; Compton, Z.A.; Eiler, L.K.; Verble, K.M.; Hoverman, J.T. Healthy but smaller herds: Predators reduce pathogen transmission in an amphibian assemblage. J. Anim. Ecol. 2019, 88, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olival, K.J.; Hosseini, P.R.; Zambrana-Torrelio, C.; Ross, N.; Bogich, T.L.; Daszak, P. Host and viral traits predict zoonotic spillover from mammals. Nature 2017, 546, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.E.; Pence, D.B. Ecology of helminth parasitism in the bobcat from West Texas. J. Parasitol. 1978, 64, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiestand, S.J.; Nielsen, C.K.; Jiménez, F.A. Epizootic and zoonotic helminths of the bobcat (Lynx rufus) in Illinois and a comparison of its helminth component communities across the American Midwest. Parasite 2014, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiekotter, K.L. Helminth species diversity and biology in the bobcat, Lynx rufus (Schreber), from Nebraska. J. Parasitol. 1985, 71, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolph, C.B.; Peregrine, A.S. Tapeworms. In Greene’s Infectious Diseases of the Dog and Cat; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 1455–1484. [Google Scholar]
- McAllister, C.T.; Robison, H.W.; Woodyard, E.T.; Rosser, T.G. Selected Helminth Parasites (Cestoda, Nematoda) of Bobcat, Lynx rufus (Carnivora: Felidae), in Northeastern Arkansas. J. Ark. Acad. Sci. 2021, 75, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichard, M.V.; Caudell, D.L.; Kocan, A.A. Survey of helminth lung parasites of bobcats (Lynx rufus) from Alabama, Kansas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Virginia, USA. Comp. Parasitol. 2004, 71, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanasundaram, A.; Henry, C.; Brym, M.Z.; Kendall, R.J. Molecular identification of Physaloptera sp. from wild northern bobwhite (Colinus virginianus) in the Rolling Plains ecoregion of Texas. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 2963–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcenillas-Hernández, I.; Aleix-Mata, G.; Sánchez-Baca, A.; Martínez-Carrasco, C.; de Ybáñez, M.R. First report of Metathelazia capsulata in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Europe and new contributions to its identification. Res. Vet. Sci. 2023, 155, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraberger, S.; Serieys, L.E.; Richet, C.; Fountain-Jones, N.M.; Baele, G.; Bishop, J.M.; Nehring, M.; Ivan, J.S.; Newkirk, E.S.; Squires, J.R. Complex evolutionary history of felid anelloviruses. Virology 2021, 562, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, N.; Combrink, L.; Kraberger, S.; Fontenele, R.S.; Schmidlin, K.; Cassaigne, I.; Culver, M.; Varsani, A.; Van Doorslaer, K. DNA virome composition of two sympatric wild felids, bobcat (Lynx rufus) and puma (Puma concolor) in Sonora, Mexico. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1126149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerna, G.M.; Serieys, L.E.; Riley, S.P.; Richet, C.; Kraberger, S.; Varsani, A. A Circovirus and Cycloviruses identified in feces of bobcats (Lynx rufus) in California. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, C.C.; Sweanor, L.L.; Wilson-Henjum, G.; Kays, R.W.; Moreno, R.; VandeWoude, S.; Troyer, R.M. Identification of novel gammaherpesviruses in Ocelots (Leopardus pardalis) and Bobcats (Lynx rufus) in Panama and Colorado, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troyer, R.M.; Beatty, J.A.; Stutzman-Rodriguez, K.R.; Carver, S.; Lozano, C.C.; Lee, J.S.; Lappin, M.R.; Riley, S.P.; Serieys, L.E.; Logan, K.A. Novel gammaherpesviruses in North American domestic cats, bobcats, and pumas: Identification, prevalence, and risk factors. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3914–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rector, A.; Lemey, P.; Tachezy, R.; Mostmans, S.; Ghim, S.-J.; Van Doorslaer, K.; Roelke, M.; Bush, M.; Montali, R.J.; Joslin, J. Ancient papillomavirus-host co-speciation in Felidae. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoust, P.-Y.; McBurney, S.R.; Godson, D.L.; Van De Bildt, M.W.; Osterhaus, A.D. Canine distemper virus–associated encephalitis in free-living lynx (Lynx canadensis) and bobcats (Lynx rufus) of eastern Canada. J. Wildl. Dis. 2009, 45, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, A.B.; Kohler, D.J.; Ortega, A.; Hoover, E.A.; Grove, D.M.; Holmes, E.C.; Parrish, C.R. Host-specific parvovirus evolution in nature is recapitulated by in vitro adaptation to different carnivore species. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraberger, S.; Serieys, L.E.; Riley, S.P.; Schmidlin, K.; Newkirk, E.S.; Squires, J.R.; Buck, C.B.; Varsani, A. Novel polyomaviruses identified in fecal samples from four carnivore species. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, S.; Troyer, J.; Terwee, J.; Lyren, L.; Boyce, W.; Riley, S.; Roelke, M.; Crooks, K.; Vandewoude, S. Frequent transmission of immunodeficiency viruses among bobcats and pumas. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10961–10969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Bevins, S.N.; Serieys, L.E.; Vickers, W.; Logan, K.A.; Aldredge, M.; Boydston, E.E.; Lyren, L.M.; McBride, R.; Roelke-Parker, M. Evolution of puma lentivirus in bobcats (Lynx rufus) and mountain lions (Puma concolor) in North America. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7727–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleeman, J.M.; Keane, J.M.; Johnson, J.S.; Brown, R.J.; Woude, S.V. Feline leukemia virus in a captive bobcat. J. Wildl. Dis. 2001, 37, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Villa, A.; Reeder, S.A.; Orciari, L.A.; Yager, P.A.; Franka, R.; Blanton, J.D.; Zuckero, L.; Hunt, P.; Oertli, E.H.; Robinson, L.E. Enzootic rabies elimination from dogs and reemergence in wild terrestrial carnivores, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraberger, S.; Serieys, L.; Fountain-Jones, N.; Packer, C.; Riley, S.; Varsani, A. Novel smacoviruses identified in the faeces of two wild felids: North American bobcat and African lion. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2395–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varsani, A.; Harrach, B.; Roumagnac, P.; Benkő, M.; Breitbart, M.; Delwart, E.; Franzo, G.; Kazlauskas, D.; Rosario, K.; Segalés, J. 2024 taxonomy update for the family Circoviridae. Arch. Virol. 2024, 169, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitbart, M.; Delwart, E.; Rosario, K.; Segalés, J.; Varsani, A.; Consortium, I.R. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Circoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1997–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, K.; Breitbart, M.; Harrach, B.; Segalés, J.; Delwart, E.; Biagini, P.; Varsani, A. Revisiting the taxonomy of the family Circoviridae: Establishment of the genus Cyclovirus and removal of the genus Gyrovirus. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pass, D.; Perry, R. The pathology of psittacine beak and feather disease. Aust. Vet. J. 1984, 61, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, B.W.; Niagro, F.D.; Latimer, K.S.; Steffens, W.; Pesti, D.; Ancona, J.; Lukert, P.D. Routes and prevalence of shedding of psittacine beak and feather disease virus. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1991, 52, 1804–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tischer, I.; Mields, W.; Wolff, D.; Vagt, M.; Griem, W. Studies on epidemiology and pathogenicity of porcine Circovirus. Arch. Virol. 1986, 91, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, G.; Meehan, B.; Todd, D.; Kennedy, S.; McNeilly, F.; Ellis, J.; Clark, E.; Harding, J.; Espuna, E.; Bother, A. Novel porcine Circoviruses from pigs with wasting disease syndromes. Vet. Rec. 1998, 142, 467–468. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, N.; Kraberger, S.; Fontenele, R.S.; Schmidlin, K.; Bergeman, M.H.; Cassaigne, I.; Culver, M.; Varsani, A.; Van Doorslaer, K. Novel Circoviruses detected in feces of sonoran felids. Viruses 2020, 12, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.-M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.-W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisza, M.J.; Belford, A.K.; Dominguez-Huerta, G.; Bolduc, B.; Buck, C.B. Cenote-Taker 2 democratizes virus discovery and sequence annotation. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veaa100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.i.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and high-performance computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöver, B.C.; Müller, K.F. TreeGraph 2: Combining and visualizing evidence from different phylogenetic analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W78–W82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D. jModelTest: Phylogenetic model averaging. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. ProtTest-HPC: ProtTest 3: Fast selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1164–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhire, B.M.; Varsani, A.; Martin, D.P. SDT: A virus classification tool based on pairwise sequence alignment and identity calculation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, C.L.; Chooi, Y.-H. Clinker & clustermap. js: Automatic generation of gene cluster comparison figures. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 2473–2475. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Davis, B.W.; Eizirik, E.; Murphy, W.J. Phylogenomic evidence for ancient hybridization in the genomes of living cats (Felidae). Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paijmans, J.L.; Fickel, J.; Courtiol, A.; Hofreiter, M.; Förster, D.W. Impact of enrichment conditions on cross-species capture of fresh and degraded DNA. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Escalona, M.; Sahasrabudhe, R.; Nguyen, O.; Beraut, E.; Buchalski, M.R.; Wayne, R.K. A reference genome assembly of the bobcat, Lynx rufus. J. Hered. 2022, 113, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, S.; Salavati, R.; Beech, R.; Babaei, Z.; Sharbatkhori, M.; Baneshi, M.; Hajialilo, E.; Shad, H.; Harandi, M. Molecular and morphological characterization of the tapeworm Taenia hydatigena (Pallas, 1766) in sheep from Iran. J. Helminthol. 2015, 89, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terefe, Y.; Hailemariam, Z.; Menkir, S.; Nakao, M.; Lavikainen, A.; Haukisalmi, V.; Iwaki, T.; Okamoto, M.; Ito, A. Phylogenetic characterisation of Taenia tapeworms in spotted hyenas and reconsideration of the “Out of Africa” hypothesis of Taenia in humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-H.; Lin, R.-Q.; Li, M.-W.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Z.-G.; Song, H.-Q.; Zhao, G.-H.; Zhang, K.-X.; Zhu, X.-Q. The complete mitochondrial genomes of three cestode species of Taenia infecting animals and humans. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 2249–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos-Frank, B. An up-date of Verster’s (1969) Taxonomic revision of the genus Taenia Linnaeus’(Cestoda) in table format. Syst. Parasitol. 2000, 45, 155–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.T.T.; Gabriel, S.; Abatih, E.N.; Dorny, P. A systematic review on the global occurrence of Taenia hydatigena in pigs and cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 226, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, I.; El-Alfy, E.-S.; Janecek-Erfurth, E.; Strube, C. Molecular characterization of Cysticercus tenuicollis isolates from sheep in the Nile Delta, Egypt and a review on Taenia hydatigena infections worldwide. Parasitology 2021, 148, 913–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, N.; Muqaddas, H.; Ashraf, A.; Aslam, M.; Khan, M.; Fatima, M.; Qadir, R.; Ibenmoussa, S.; Dawoud, T.M.; Ullah, M.I. Leading report regarding the molecular epidemiology of Taenia hydatigena from Pakistan and global overview of the genetic diversity and population structure of the parasite. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 114, 102248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng-Nguyen, D.; Van Nguyen, T.; Van Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Nguyen, V.-A.T. Prevalence and risk factors of Taenia hydatigena in dogs, pigs, and cattle in the Central Highlands of Vietnam. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 3245–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torten, M.; Beemer, A.; Van Der Hoeden, J. Physaloptera clausa, a possible new reservoir host for parasitic leptospires. Bull. World Health Organ. 1966, 35, 278. [Google Scholar]
- Poglayen, G.; Giannetto, S.; Brianti, E.; Scala, A.; Garippa, G.; Capelli, G.; Scaravelli, D.; Reeve, N. Helminths found in hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in three areas of Italy. Vet. Rec. 2003, 152, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, W. Endoparasiten beim igel. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2007, 3, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirak, V.Y.; Senlik, B.; Aydogdu, A.; Selver, M.; Akyol, V. Helminth parasites found in hedgehogs (Erinaceus concolor) from Turkey. Prev. Vet. Med. 2010, 97, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizgajska-Wiktor, H.; Jarosz, W.; Pilacinska, B.; Dziemian, S. Helminths of hedgehogs, Erinaceus europaeus and E. roumanicus from Poznan region, Poland-coprological study. Wiad. Parazytol. 2010, 56, 329–332. [Google Scholar]
- Gorgani, T.; Naem, S.; Farshid, A.A.; Otranto, D. Scanning electron microscopy observations of the hedgehog stomach worm, Physaloptera clausa (Spirurida: Physalopteridae). Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naem, S.; Asadi, R. Ultrastructural characterization of male and female Physaloptera rara (Spirurida: Physalopteridae): Feline stomach worms. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 1983–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pence, D.B.; Tewes, M.E.; Laack, L.L. Helminths of the ocelot from southern Texas. J. Wildl. Dis. 2003, 39, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Suzuki, K. Gastrointestinal helminths of feral raccoons (Procyon lotor) in Wakayama Prefecture, Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2006, 68, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridger, K.E.; Baggs, E.M.; Finney-Crawley, J. Endoparasites of the coyote (Canis latrans), a recent migrant to insular Newfoundland. J. Wildl. Dis. 2009, 45, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kates, K.C.; Soulsby, E.J.L. Textbook of veterinary clinical parasitology. Vol. I. Helminths. J. Parasitol. 1965, 52, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naem, S.; Abbass Farshid, A.; Tanhai Marand, V. Pathological findings on natural infection with Physaloptera praeputialis in cats. Vet. Arh. 2006, 76, 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Moraes, I.d.S.; Silva, V.L.d.B.; Andrade-Silva, B.E.d.; Gomes, A.P.N.; Urzedo, N.F.d.; Abolis, V.B.; Gonçalves, R.d.S.; Arpon, K.V.; Assis-Silva, Z.M.d.; Silva, L.F.d. Gastrointestinal Helminths in Wild Felids in the Cerrado and Pantanal: Zoonotic Bioindicators in Important Brazilian Biomes. Animals 2024, 14, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleix-Mata, G.; Arcenillas-Hernández, I.; de Ybáñez, M.R.R.; Martínez-Carrasco, C.; Montiel, E.E.; Sánchez, A. Complete mitochondrial genome of Metathelazia capsulata (Pneumospiruridae) and comparison with other Spiruromorpha species. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 123, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerichter, C.B. Three new species of the genus Metathelazia (Nematoda). J. Parasitol. 1948, 34, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pence, D.B.; DowLER, R.C. Helminth parasitism in the badger, Taxidea taxus (Schreber, 1778), from the western Great Plains. Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1979, 46, 245–253. [Google Scholar]
- Helm, J.; Morgan, E. Canine and feline lungworm infections in the UK. In Practice 2017, 39, 298–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabaud, A.G.; Bain, O. The evolutionary expansion of the Spirurida. Int. J. Parasitol. 1994, 24, 1179–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, F.A.; Rosas-Valdez, R.; Gardner, S.L. A new species of Metathelazia (Nematoda: Pneumospiruridae) from the lungs of a nine-banded armadillo in Central Mexico. Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2013, 84, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, K.; Duffy, S.; Breitbart, M. A field guide to eukaryotic circular single-stranded DNA viruses: Insights gained from metagenomics. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 1851–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, M.C.; Larsen, B.B.; Rowsey, D.M.; Otto, H.W.; Gryseels, S.; Kraberger, S.; Custer, J.M.; Steger, L.; Yule, K.M.; Harris, R.E. Using archived and biocollection samples towards deciphering the DNA virus diversity associated with rodent species in the families cricetidae and heteromyidae. Virology 2023, 585, 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Fan, K.; Liang, X.; Gong, W.; Chen, W.; He, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P. Virus diversity, wildlife-domestic animal circulation and potential zoonotic viruses of small mammals, pangolins and zoo animals. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lu, L.; Du, J.; Yang, L.; Ren, X.; Liu, B.; Jiang, J.; Yang, J.; Dong, J.; Sun, L. Comparative analysis of rodent and small mammal viromes to better understand the wildlife origin of emerging infectious diseases. Microbiome 2018, 6, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, S.C.; Weiss, K.C.; Custer, J.M.; Lewis, J.S.; Kraberger, S.; Varsani, A. Identification of small circular DNA viruses in coyote fecal samples from Arizona (USA). Arch. Virol. 2024, 169, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Kuang, G.; Pan, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Wu, W.-c.; Pan, H.; Wang, J.; Han, X.; Yang, L. Small mammals in a biodiversity hotspot harbor viruses of emergence risk. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, nwae463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Yuan, Z.-G.; Luo, S.; Sun, C.; Zhang, P.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Hua, Y.; Wang, G. The genetic diversity and Interspecific Transmission of Circovirus in Rhizomys sinensis in Guangdong, Southern China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2023, 2023, 6668569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccaria, G.; Malatesta, D.; Scipioni, G.; Di Felice, E.; Campolo, M.; Casaccia, C.; Savini, G.; Di Sabatino, D.; Lorusso, A. Circovirus in domestic and wild carnivores: An important opportunistic agent? Virology 2016, 490, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Dubovi, E.J.; Henriquez-Rivera, J.A.; Lipkin, W.I. Complete genome sequence of the first Canine circovirus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Villiers, L.; Molini, U.; Coetzee, L.M.; Visser, L.; Spangenberg, J.; de Villiers, M.; Berjaoui, S.; Khaiseb, S.; Lorusso, A.; Franzo, G. Molecular epidemiology of Canine circovirus in domestic dogs and wildlife in Namibia, Africa. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2023, 112, 105458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balboni, A.; Urbani, L.; Delogu, M.; Musto, C.; Fontana, M.C.; Merialdi, G.; Lucifora, G.; Terrusi, A.; Dondi, F.; Battilani, M. Integrated use of molecular techniques to detect and genetically characterise DNA viruses in Italian wolves (Canis lupus italicus). Animals 2021, 11, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Deng, X.; Kapusinszky, B.; Pesavento, P.A.; Delwart, E. Faecal virome of cats in an animal shelter. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2553–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, L.; Li, J.; Wu, C.; Tian, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y. A Diverse Virome Is Identified in Parasitic Flatworms of Domestic Animals in Xinjiang, China. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0070223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, Q.M.; Kraberger, S.; Martin, D.P.; Shero, M.R.; Beltran, R.S.; Kirkham, A.L.; Aleamotu’a, M.; Ainley, D.G.; Kim, S.; Burns, J.M. Circoviruses and Cycloviruses identified in Weddell seal fecal samples from McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 95, 105070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, T.P.; de Souza, W.M.; Marsile-Medun, S.; Singer, J.B.; Wilson, S.J.; Gifford, R.J. The evolution, distribution and diversity of endogenous circoviral elements in vertebrate genomes. Virus Res. 2019, 262, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, Y.; Li, B.; Yu, X.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Li, G.; Yi, X.; Jiang, D. Widespread horizontal gene transfer from circular single-stranded DNA viruses to eukaryotic genomes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheilly, N.M.; Lucas, P.; Blanchard, Y.; Rosario, K. A world of viruses nested within parasites: Unraveling viral diversity within parasitic flatworms (Platyhelminthes). Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0013822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsella, C.M.; Bart, A.; Deijs, M.; Broekhuizen, P.; Kaczorowska, J.; Jebbink, M.F.; van Gool, T.; Cotten, M.; Van der Hoek, L. Entamoeba and Giardia parasites implicated as hosts of CRESS viruses. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoa-Meng, M.; Semmar, R.; Antezack, A.; Penant, G.; La Scola, B.; Monnet-Corti, V.; Colson, P. Correlation of Redondovirus and Entamoeba gingivalis detections in the human oral cavity suggests that this Amoeba is possibly the Redondovirus host. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Virus | Accession | Motif I | Motif II | Motif III | Walker A | Walker B | Motif C | Arg Finger |
| Circovirus miztontli | Lyrufec circovirus | PV339922 | AFTLNN | PHLQG | DNKKYCSK | GPPGTGKSRECL | IMDDF | ITSN | ALFRRI |
| Circovirus miztontli | Lyrufec circovirus | PV339923 | AFTLNN | PHLQG | DNKKYCSK | GPPGTGKSRECL | IMDDF | ITSN | ALFRRI |
| Cyclovirus misi | Calfel cyclovirus | PV339925 | VFTHFN | KHLQG | DNQKYCSK | GEPGTGKSKTAL | IIDDF | ITSN | AIKRRC |
| unclassified | Tenaz cyclovirus | PV339924 | CFTLNN | PHLQG | QNRTYCSK | GPPGVGKSRRAY | IIDDY | ITSN | AIERRC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Žuštra, A.; Howard, A.; Schwartz, K.; Day, R.; Dietrich, J.; Sobotyk, C.; Kraberger, S.; Varsani, A. Three Distinct Circovirids Identified in a Tapeworm Recovered from a Bobcat (Lynx rufus). Viruses 2025, 17, 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060745
Žuštra A, Howard A, Schwartz K, Day R, Dietrich J, Sobotyk C, Kraberger S, Varsani A. Three Distinct Circovirids Identified in a Tapeworm Recovered from a Bobcat (Lynx rufus). Viruses. 2025; 17(6):745. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060745
Chicago/Turabian StyleŽuštra, Ayla, April Howard, Katie Schwartz, Ron Day, Jaclyn Dietrich, Caroline Sobotyk, Simona Kraberger, and Arvind Varsani. 2025. "Three Distinct Circovirids Identified in a Tapeworm Recovered from a Bobcat (Lynx rufus)" Viruses 17, no. 6: 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060745
APA StyleŽuštra, A., Howard, A., Schwartz, K., Day, R., Dietrich, J., Sobotyk, C., Kraberger, S., & Varsani, A. (2025). Three Distinct Circovirids Identified in a Tapeworm Recovered from a Bobcat (Lynx rufus). Viruses, 17(6), 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060745







