Recombinant Sendai Virus Vectors as Novel Vaccine Candidates Against Animal Viruses
Abstract
1. The Clinical Need for New Generation Vaccines Against Animal Diseases
2. Virology of Sendai Virus
2.1. Taxonomy and Phylogeny of Sendai Virus
2.2. Genome and Virion Structure of Sendai Virus
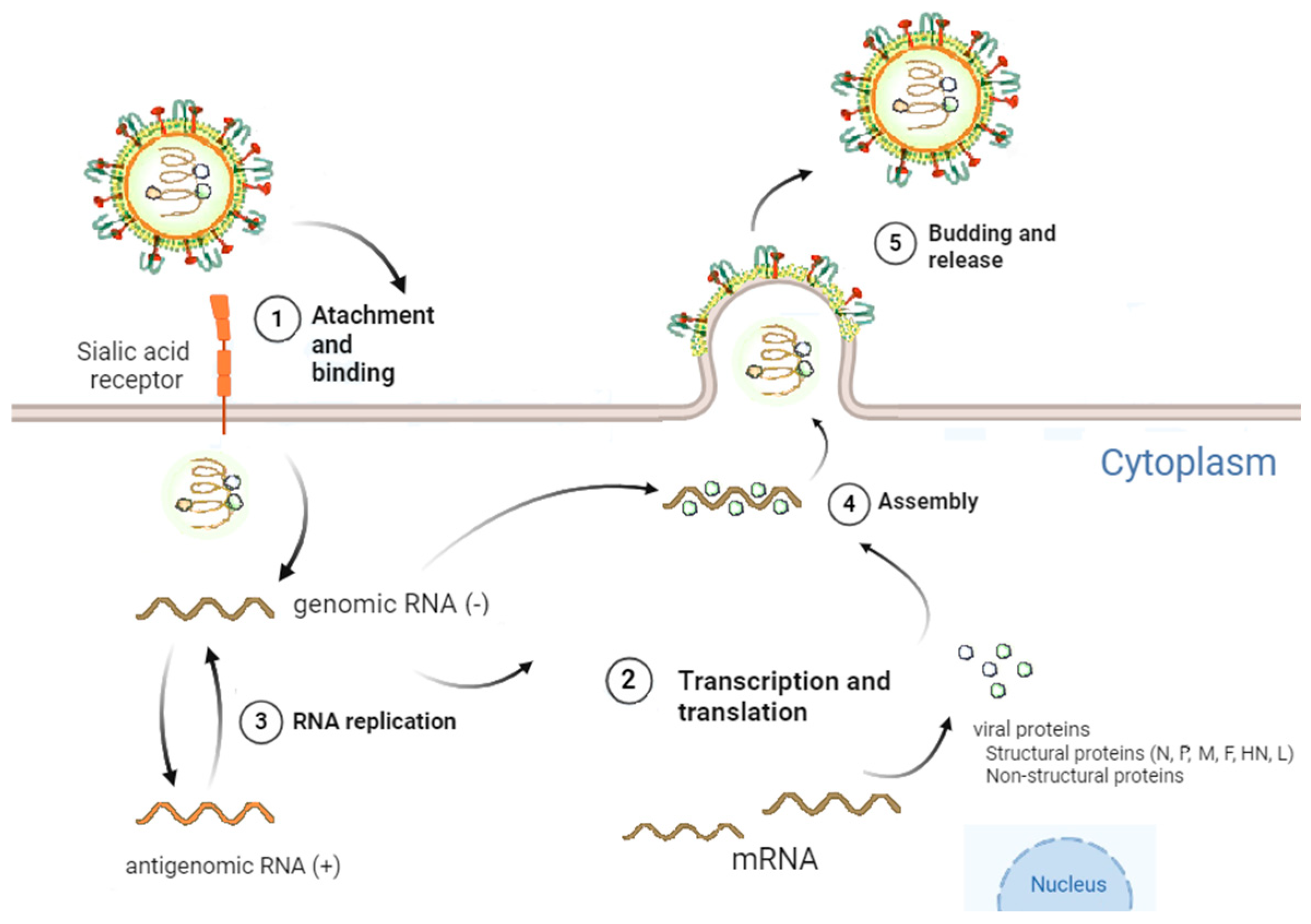
2.3. Viral Cycle of Sendai Virus
3. Sendai Virus as a Viral Vector
3.1. Generation and Rescue of Sendai Virus Vectors
3.2. Biodistribution of Sendai Virus Vectors
3.3. Foreign Gene Expression of Sendai Virus Vectors
3.4. Stimulation of Innate Immune Response by Sendai Virus Vectors
3.5. Stimulation of Adaptive Immune Response by Sendai Virus Vectors
4. Sendai Virus as a Vaccine Platform Against Animal Diseases
4.1. Sendai Virus Vector as a Vaccine Against Influenza
4.2. Sendai Virus Vector as a Vaccine Against Foot and Mouth Disease
4.3. Sendai Virus Vector as a Vaccine Against Animal Retroviruses
4.3.1. Sendai Virus Vector as a Vaccine Against Simian Immunodeficiency Virus
4.3.2. Sendai Virus Vector as a Vaccine Against Small Ruminant Lentiviruses
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AM | Alveolar macrophages |
| APCs | Antigen-presenting cells |
| APOBEC3/A3Z1 | Catalytic polypeptide-like 3 |
| ART | Antiretroviral therapy |
| BDM | Blood-derived macrophages |
| BPIV3 | Bovine parainfluenza virus 3 |
| CTLs | Cytotoxic T CD8+ cells |
| CV-1 cells | African Green Monkey Kidney Fibroblast Cells |
| F | Fusion |
| FMD | Foot-and-mouth disease |
| FMDV | Foot-and-mouth disease virus |
| HA | Hemagglutinin antigens |
| HAI | Hemagglutination inhibition |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| HN | Hemagglutinin-neuraminidase |
| HPIV1 | Human parainfluenza virus 1 |
| HPIV3 | Human parainfluenza virus 3 |
| IFIT2 | Interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 2 protein |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IFNAR | Interferon-α/β receptor |
| IRF-3 | Interferon regulatory factor 3 |
| ISGs | Interferon-stimulated genes |
| JAK-STAT | Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription |
| L | Large polymerase |
| M | Matrix |
| M2e | M2 protein |
| N | Nucleocapsid |
| OBST2/Tetherin | Ovine BST2 |
| OSF | Ovine skin fibroblasts |
| P | Phosphoprotein |
| RANTES | Regulated upon activation, normal T-cell expressed and presumably secreted |
| RIG-I | Retinoic acid-inducible gene I |
| rSeVv | Recombinant Sendai virus vectors |
| RSV | Respiratory syncytial virus |
| SAMHD1 | SAM domain and HD domain-containing protein 1 |
| SeV | Sendai virus |
| SHIV | Simian-human immunodeficiency virus |
| SIV | Simian immunodeficiency virus |
| SRLV | Small ruminant lentiviruses |
| TLR | Toll-like receptors |
| TRIM5α | Tripartite motif-containing protein 5 alpha |
| WD-PBEC | Primary pediatric bronchial epithelial cells |
References
- Rajput, A.S.; Rajawat, D.; Jisna, K.S.; Panwar, A.; Patra, M.K. Transient Impacts of Vaccination on Livestock Production: A Holistic Review. Indian J. Anim. Health 2024, 63, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, R.R.; Li, S. Antimicrobial Resistance in Livestock: Advances and Alternatives to Antibiotics. Anim. Front. 2018, 8, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, C.E.; Roth, J.A. Challenges in Having Vaccines Available to Control Transboundary Diseases of Livestock. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 42, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jogi, H.R.; Smaraki, N.; Rajak, K.K.; Yadav, A.K.; Bhatt, M.; Einstien, C.; Revathi, A.; Thakur, R.; Kamothi, D.J.; Dedeepya, P.V.S.S.; et al. Revolutionizing Veterinary Health with Viral Vector-Based Vaccines. Indian J. Microbiol. 2024, 64, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.-V.L.; Mironova, E.; Garcin, D.; Compans, R.W. Induction of Influenza-Specific Mucosal Immunity by an Attenuated Recombinant Sendai Virus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.G.; Chen, X.Y.; Qian, P.; Chen, H.C.; Li, X.M. Immunogenicity of a Recombinant Sendai Virus Expressing the Capsid Precursor Polypeptide of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus. Res. Vet. Sci. 2016, 104, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, M.; Matano, T.; Nakamura, H.; Takeda, A.; Kato, A.; Ariyoshi, K.; Mori, K.; Sata, T.; Nagai, Y. Elicitation of Protective Immunity against Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Infection by a Recombinant Sendai Virus Expressing the Gag Protein. AIDS 2000, 14, 1281–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, Á.; Glaria, I.; Moncayola, I.; Echeverría, I.; Arrizabalaga, J.; Rodríguez-Largo, A.; de Blas, I.; Lacasta, D.; Pérez, E.; Pérez, M.; et al. Characterization of a Recombinant Sendai Virus Vector Encoding the Small Ruminant Lentivirus Gag-P25: Antiviral Properties in Vitro and Transgene Expression in Sheep. Vet. Res. 2025, 56, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rima, B.; Balkema-Buschmann, A.; Dundon, W.G.; Duprex, P.; Easton, A.; Fouchier, R.; Kurath, G.; Lamb, R.; Lee, B.; Rota, P.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Paramyxoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1593–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, C.J.; Hurwitz, J.L. Sendai Virus-Vectored Vaccines That Express Envelope Glycoproteins of Respiratory Viruses. Viruses 2021, 13, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroya, M.; Ishida, N.; Shiratori, T. Newborn Virus Pneumonitis (Type Sendai). II. The Isolation of a New Virus. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1953, 58, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sealy, R.; Jones, B.G.; Surman, S.L.; Hurwitz, J.L. Robust IgA and IgG-Producing Antibody Forming Cells in the Diffuse-NALT and Lungs of Sendai Virus-Vaccinated Cotton Rats Associate with Rapid Protection against Human Parainfluenza Virus-Type 1. Vaccine 2010, 28, 6749–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akihiro, I.; Makoto, I. Chapter 3: Concept and Technology Underlying Sendai Virus (SeV) Vector Development. In Sendai Virus Vector: Advantages and Applications, 1st ed.; Yoshiyuki, N., Ed.; Springer Nature: Tokyo, Japan, 2013; pp. 69–90. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, J.C.; Reynolds, R.K. Natural History of Sendai Virus Infection in Mice. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1968, 88, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, N.; Homma, M. Sendai Virus. Adv. Virus Res. 1978, 23, 349–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobod, K.S.; Shenep, J.L.; Luján-Zilbermann, J.; Allison, K.; Brown, B.; Scroggs, R.A.; Portner, A.; Coleclough, C.; Hurwitz, J.L. Safety and Immunogenicity of Intranasal Murine Parainfluenza Virus Type 1 (Sendai Virus) in Healthy Human Adults. Vaccine 2004, 22, 3182–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurwitz, J.L.; Soike, K.F.; Sangster, M.Y.; Portner, A.; Sealy, R.E.; Dawson, D.H.; Coleclough, C. Intranasal Sendai Virus Vaccine Protects African Green Monkeys from Infection with Human Parainfluenza Virus-Type One. Vaccine 1997, 15, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesenbach, U.; McLachlan, G.; Owaki, T.; Somerton, L.; Shu, T.; Baker, A.; Tennant, P.; Gordon, C.; Vrettou, C.; Baker, E.; et al. Validation of Recombinant Sendai Virus in a Non-Natural Host Model. Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.J.; Goodman, S.J. Reassessing Conflicting Evolutionary Histories of the Paramyxoviridae and the Origins of Respiroviruses with Bayesian Multigene Phylogenies. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, J.; Chen-Harris, H.; Allen, J.E.; Hwang, M.; Elsheikh, M.; Mabery, S.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Zemla, A.T.; Bowen, R.A.; Borucki, M.K. Sendai Virus Intra-Host Population Dynamics and Host Immunocompetence Influence Viral Virulence during in Vivo Passage. Virus Evol. 2016, 2, vew008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, M.; Kawabata, R.; Morimoto, N.; Takeuchi, R.F.; Sakaguchi, T.; Irie, T.; Osakada, F. Evolutionary Engineering and Characterization of Sendai Virus Mutants Capable of Persistent Infection and Autonomous Production. Front. Virol. 2024, 4, 1363092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabayashi, K.; Compans, R.W. Functional Interaction of Paramyxovirus Glycoproteins: Identification of a Domain in Sendai Virus HN Which Promotes Cell Fusion. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 6112–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, H.; Ohta, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Yumine, N.; Nishio, M. Evidence That Receptor Destruction by the Sendai Virus Hemagglutinin-Neuraminidase Protein Is Responsible for Homologous Interference. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7640–7646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A.; Kiyotani, K.; Hasan, M.K.; Shioda, T.; Sakai, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Nagai, Y. Sendai Virus Gene Start Signals Are Not Equivalent in Reinitiation Capacity: Moderation at the Fusion Protein Gene. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9237–9246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, R.A.; Kolakofsky, D. Paramyxoviridae: The Viruses and Their Replication. In Fields Virology, 1st ed.; Fields, B.N., Knipe, D., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott-Raven Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Shioda, T.; Iwasaki, K.; Shibuta, H. Determination of the Complete Nucleotide Sequence of the Sendai Virus Genome RNA and the Predicted Amino Acid Sequences of the F, HN and L Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986, 14, 1545–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, L.; Tarbouriech, N.; Blackledge, M.; Timmins, P.; Burmeister, W.P.; Ruigrok, R.W.H.; Marion, D. Structure and Dynamics of the Nucleocapsid-Binding Domain of the Sendai Virus Phosphoprotein in Solution. Virology 2004, 319, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Kiyotani, K.; Sakai, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Shioda, T.; Nagai, Y. Importance of the Cysteine-Rich Carboxyl-Terminal Half of V Protein for Sendai Virus Pathogenesis. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 7266–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faísca, P.; Desmecht, D. Sendai Virus, the Mouse Parainfluenza Type 1: A Longstanding Pathogen That Remains up-to-Date. Res. Vet. Sci. 2007, 82, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calain, P.; Roux, L. The Rule of Six, a Basic Feature for Efficient Replication of Sendai Virus Defective Interfering RNA. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 4822–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwell, M.A.K.; Fredman, P.; Svennerholm, L. Receptor Ganglioside Content of Three Hosts for Sendai Virus. MDBK, HeLa, and MDCK Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1984, 775, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwell, M.A.K.; Moss, J.; Hom, B.E.; Fishman, P.H.; Svennerholm, L. Expression of Gangliosides as Receptors at the Cell Surface Controls Infection of NCTC 2071 Cells by Sendai Virus. Virology 1986, 155, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitzer, M.; Armeanu, S.; Lauer, U.M.; Neubert, W.J. Sendai Virus Vectors as an Emerging Negative-Strand RNA Viral Vector System. J. Gene. Med. 2003, 5, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgohain, M.P.; Haridhasapavalan, K.K.; Dey, C.; Adhikari, P.; Thummer, R.P. An Insight into DNA-Free Reprogramming Approaches to Generate Integration-Free Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells for Prospective Biomedical Applications. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2019, 15, 286–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calain, P.; Roux, L. Functional Characterisation of the Genomic and Antigenomic Promoters of Sendai Virus. Virology 1995, 212, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horikami, S.M.; Smallwood, S.; Moyer, S.A. The Sendai Virus V Protein Interacts with the NP Protein to Regulate Viral Genome RNA Replication. Virology 1996, 222, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.; Hong, P.; Won, S.T.; Thibault, P.A.; Vigant, F.; Oguntuyo, K.Y.; Taft, J.D.; Lee, B. Sendai Virus, an RNA Virus with No Risk of Genomic Integration, Delivers CRISPR/Cas9 for Efficient Gene Editing. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2016, 3, 16057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portner, A.; Marx, P.A.; Kingsbury, D.W. Isolation and Characterization of Sendai Virus Temperature-Sensitive Mutants. J. Virol. 1974, 13, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahle, L.; Garcin, D.; Kolakofsky, D. Sendai Virus Defective-Interfering Genomes and the Activation of Interferon-Beta. Virology 2006, 351, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.M.; Re, G.G.; Kingsbury, D.W. Complete Sequence of the Sendai Virus NP Gene from a Cloned Insert. Virology 1984, 135, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Nayak, D.P. Assembly of Sendai Virus: M Protein Interacts with F and HN Proteins and with the Cytoplasmic Tail and Transmembrane Domain of F Protein. Virology 2000, 276, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takimoto, T.; Murti, K.G.; Bousse, T.; Scroggs, R.A.; Portner, A. Role of Matrix and Fusion Proteins in Budding of Sendai Virus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11384–11391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takimoto, T.; Bousse, T.; Coronel, E.C.; Scroggs, R.A.; Portner, A. Cytoplasmic Domain of Sendai Virus HN Protein Contains a Specific Sequence Required for Its Incorporation into Virions. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 9747–9754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, C.A.; Neubert, W.J. Neuraminidase-Deficient Sendai Virus HN Mutants Provide Protection from Homologous Superinfection. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, M.J.; Mebatsion, T.; Conzelmann, K.K. Infectious Rabies Viruses from Cloned cDNA. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 4195–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcin, D.; Pelet, T.; Calain, P.; Roux, L.; Curran, J.; Kolakofsky, D. A Highly Recombinogenic System for the Recovery of Infectious Sendai Paramyxovirus from cDNA: Generation of a Novel Copy-Back Nondefective Interfering Virus. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 6087–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Griesenbach, U.; Shiraki-Iida, T.; Shu, T.; Hironaka, T.; Hou, X.; Williams, J.; Zhu, J.; Jeffery, P.K.; Geddes, D.M.; et al. A Defective Nontransmissible Recombinant Sendai Virus Mediates Efficient Gene Transfer to Airway Epithelium in Vivo. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 1659–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Kato, A.; Shioda, T.; Sakai, Y.; Yu, D.; Nagai, Y. Creation of an Infectious Recombinant Sendai Virus Expressing the Firefly Luciferase Gene from the 3’ Proximal First Locus. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 2813–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, C.; Shioda, T.; Tashiro, K.; Nagasawa, T.; Ikegawa, M.; Ohnishi, Y.; Kato, A.; Hu, H.; Xin, X.; Hasan, M.K.; et al. Large Quantity Production with Extreme Convenience of Human SDF-1alpha and SDF-1beta by a Sendai Virus Vector. FEBS Lett. 1998, 425, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-O.; Zhu, Y.-F.; Asakawa, M.; Kuma, H.; Hirata, T.; Ueda, Y.; Lee, Y.-S.; Fukumura, M.; Iida, A.; Kato, A.; et al. A Cytoplasmic RNA Vector Derived from Nontransmissible Sendai Virus with Efficient Gene Transfer and Expression. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6564–6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, S.; Okano, S.; Yonemitsu, Y.; Onimaru, M.; Sata, S.; Nagata-Takeshita, H.; Inoue, M.; Zhu, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Moroi, Y.; et al. Induction of Efficient Antitumor Immunity Using Dendritic Cells Activated by Recombinant Sendai Virus and Its Modulation by Exogenous IFN-β Gene. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 3564–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, I.; Yonemitsu, Y.; Komori, K.; Ueno, H.; Nakashima, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Fukumura, M.; Kato, A.; Hasan, M.K.; Nagai, Y.; et al. Recombinant Sendai Virus-Mediated Gene Transfer to Vasculature: A New Class of Efficient Gene Transfer Vector to the Vascular System. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 1294–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaki, N.; Ban, H.; Nishiyama, A.; Saeki, K.; Hasegawa, M. Efficient Induction of Transgene-Free Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Using a Vector Based on Sendai Virus, an RNA Virus That Does Not Integrate into the Host Genome. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2009, 85, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luongo, C.; Yang, L.; Winter, C.C.; Spann, K.M.; Murphy, B.R.; Collins, P.L.; Buchholz, U.J. Codon Stabilization Analysis of the “248” Temperature Sensitive Mutation for Increased Phenotypic Stability of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Candidates. Vaccine 2009, 27, 5667–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, J.; Tang, R.S.; Spaete, R.R.; Schickli, J.H. Optimization of Plasmid-Only Rescue of Highly Attenuated and Temperature-Sensitive Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine Candidates for Human Trials. J. Virol. Methods 2008, 153, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Tokusumi, Y.; Ban, H.; Kanaya, T.; Tokusumi, T.; Nagai, Y.; Iida, A.; Hasegawa, M. Nontransmissible Virus-like Particle Formation by F-Deficient Sendai Virus Is Temperature Sensitive and Reduced by Mutations in M and HN Proteins. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 3238–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Tokusumi, Y.; Ban, H.; Kanaya, T.; Shirakura, M.; Tokusumi, T.; Hirata, T.; Nagai, Y.; Iida, A.; Hasegawa, M. A New Sendai Virus Vector Deficient in the Matrix Gene Does Not Form Virus Particles and Shows Extensive Cell-to-Cell Spreading. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6419–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossow, S.; Schlecht, S.; Schubbert, R.; Pfeiffer, M.; Neubert, W.J.; Wiegand, M. Evaluation of Nucleocapsid and Phosphoprotein P Functionality as Critical Factors During the Early Phase of Paramyxoviral Infection. Open Virol. J. 2012, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizaki, M.; Hironaka, T.; Iwasaki, H.; Ban, H.; Tokusumi, Y.; Iida, A.; Nagai, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Inoue, M. Naked Sendai Virus Vector Lacking All of the Envelope-Related Genes: Reduced Cytopathogenicity and Immunogenicity. J. Gene Med. 2006, 8, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Suquilanda, E.; Zeledon, A.; Kacsinta, A.; Moore, A.; Seto, J.; McQueen, N. Mutations in Sendai Virus Variant F1-R That Correlate with Plaque Formation in the Absence of Trypsin. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 194, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Kiyotani, K.; Fukumura, M.; Asakawa, M.; Kato, A.; Shioda, T.; Yoshida, T.; Tanaka, A.; Hasegawa, M.; Nagai, Y. Accommodation of Foreign Genes into the Sendai Virus Genome: Sizes of Inserted Genes and Viral Replication. FEBS Lett. 1999, 456, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conzelmann, K.K. Reverse Genetics of Mononegavirales: The Rabies Virus Paradigm. In Sendai Virus Vector: Advantages and Applications, 1st ed.; Yoshiyuki, N., Ed.; Springer Nature: Tokyo, Japan, 2013; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller, C.K.; Cattaneo, R.; Schnell, M.J. Reverse Genetics of Mononegavirales: How They Work, New Vaccines, and New Cancer Therapeutics. Virology 2015, 479–480, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaty, S.M.; Park, A.; Won, S.T.; Hong, P.; Lyons, M.; Vigant, F.; Freiberg, A.N.; tenOever, B.R.; Duprex, W.P.; Lee, B. Efficient and Robust Paramyxoviridae Reverse Genetics Systems. MSphere 2017, 2, e00376-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takimoto, T.; Hurwitz, J.L.; Zhan, X.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Prouser, C.; Brown, B.; Coleclough, C.; Boyd, K.; Scroggs, R.A.; Portner, A.; et al. Recombinant Sendai Virus as a Novel Vaccine Candidate for Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Viral Immunol. 2005, 18, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, C.J.; Hurwitz, J.L. Sendai Virus as a Backbone for Vaccines against RSV and Other Human Paramyxoviruses. Expert. Rev. Vaccines 2016, 15, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pablo-Maiso, L.; Echeverría, I.; Rius-Rocabert, S.; Luján, L.; Garcin, D.; De Andrés, D.; Nistal-Villán, E.; Reina, R. Sendai Virus, a Strong Inducer of Anti-Lentiviral State in Ovine Cells. Vaccines 2020, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemitsu, Y.; Kitson, C.; Ferrari, S.; Farley, R.; Griesenbach, U.; Judd, D.; Steel, R.; Scheid, P.; Zhu, J.; Jeffery, P.K.; et al. Efficient Gene Transfer to Airway Epithelium Using Recombinant Sendai Virus. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesenbach, U.; Boyton, R.J.; Somerton, L.; Garcia, S.E.; Ferrari, S.; Owaki, T.; Ya-Fen, Z.; Geddes, D.M.; Hasegawa, M.; Altmann, D.M.; et al. Effect of Tolerance Induction to Immunodominant T-Cell Epitopes of Sendai Virus on Gene Expression Following Repeat Administration to Lung. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, M.; Seto, J.T.; Choosakul, S.; Yamakawa, M.; Klenk, H.D.; Rott, R. Budding Site of Sendai Virus in Polarized Epithelial Cells Is One of the Determinants for Tropism and Pathogenicity in Mice. Virology 1992, 187, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Yonemitsu, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Ishibashi, T.; Ueno, H.; Kato, A.; Nagai, Y.; Fukumura, M.; Inomata, H.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Recombinant Sendai virus-mediated gene transfer into adult rat retinal tissue: Efficient gene transfer by brief exposure. Exp. Eye Res. 2002, 75, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Yonemitsu, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Kondo, H.; Okano, S.; Kohno, R.I.; Miyazaki, M.; Inoue, M.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Newly-Developed Sendai Virus Vector for Retinal Gene Transfer: Reduction of Innate Immune Response via Deletion of All Envelope-Related Genes. J. Gene Med. 2008, 10, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Eguchi, A.; Okabe, J.; Harada, A.; Sasaki, K.; Ogiwara, N.; Inoue, Y.; Ito, T.; Matsuda, H.; Kataoka, K.; et al. Sendai Virus-Mediated Gene Delivery into Hepatocytes via Isolated Hepatic Perfusion. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, K.; Imamura, K.; Komatsu, K.; Mitani, K.; Aiba, K.; Nakatsuji, N.; Inoue, M.; Kawata, A.; Yamashita, H.; Takahashi, R.; et al. Simple Derivation of Spinal Motor Neurons from ESCs/IPSCs Using Sendai Virus Vectors. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2017, 4, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.H.; Kusuhara, K.; Yonemitsu, Y.; Nomura, A.; Okano, S.; Takeshita, H.; Hasegawa, M.; Sueishi, K.; Hara, T. Recombinant Sendai Virus Provides a Highly Efficient Gene Transfer into Human Cord Blood-Derived Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, H.; Nishishita, N.; Fusaki, N.; Tabata, T.; Saeki, K.; Shikamura, M.; Takada, N.; Inoue, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Kawamata, S.; et al. Efficient Generation of Transgene-Free Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (IPSCs) by Temperature-Sensitive Sendai Virus Vectors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14234–14239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiener, R.; Fleischmann, M.; Wiegand, M.A.; Lemmermann, N.A.W.; Schwegler, C.; Kaufmann, C.; Renzaho, A.; Thomas, S.; Felder, E.; Niller, H.H.; et al. Efficient Delivery of Human Cytomegalovirus T Cell Antigens by Attenuated Sendai Virus Vectors. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00569-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, A.; Kondoh, T.; Kosaka, H.; Suzuki, T.; Momota, H.; Masago, A.; Yoshida, T.; Taira, H.; Ishii-Watabe, A.; Okabe, J.; et al. Identification and Characterization of Cell Lines with a Defect in a Post-Adsorption Stage of Sendai Virus-Mediated Membrane Fusion. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17549–17555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiadopoulos, M.H.; Surman, S.R.; Riggs, J.M.; Elkins, W.R.; St. Claire, M.; Nishio, M.; Garcin, D.; Kolakofsky, D.; Collins, P.L.; Murphy, B.R. Sendai Virus, a Murine Parainfluenza Virus Type 1, Replicates to a Level Similar to Human PIV1 in the Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract of African Green Monkeys and Chimpanzees. Virology 2002, 297, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.G.; Sealy, R.E.; Rudraraju, R.; Traina-Dorge, V.L.; Finneyfrock, B.; Cook, A.; Takimoto, T.; Portner, A.; Hurwitz, J.L. Sendai Virus-Based RSV Vaccine Protects African Green Monkeys from RSV Infection. Vaccine 2012, 30, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikono, H.; Miyazaki, A.; Mase, M.; Inoue, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Saito, T. Induction of a Cross-Reactive Antibody Response to Influenza Virus M2 Antigen in Pigs by Using a Sendai Virus Vector. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2012, 146, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, C.; Horiba, S.; Kurihara, K.; Kamada, T.; Takahara, Y.; Inoue, M.; Iida, A.; Hara, H.; Shu, T.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Intranasal Sendai Viral Vector Vaccination Is More Immunogenic than Intramuscular under Pre-Existing Anti-Vector Antibodies. Vaccine 2011, 29, 8557–8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Griesenbach, U.; Iida, A.; Farley, R.; Wright, A.M.; Zhu, J.; Munkonge, F.M.; Smith, S.N.; You, J.; Ban, H.; et al. Sendai Virus-Mediated CFTR Gene Transfer to the Airway Epithelium. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, M.; Otsu, M. Development of Sendai Virus Vectors and Their Potential Applications in Gene Therapy and Regenerative Medicine. Curr. Gene Ther. 2012, 12, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokusumi, T.; Iida, A.; Hirata, T.; Kato, A.; Nagai, Y.; Hasegawa, M. Recombinant Sendai Viruses Expressing Different Levels of a Foreign Reporter Gene. Virus Res. 2002, 86, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homann, H.E.; Hofschneider, P.H.; Neubert, W.J. Sendai Virus Gene Expression in Lytically and Persistently Infected Cells. Virology 1990, 177, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownstein, D.G.; Weir, E.C. Immunostimulation in Mice Infected with Sendai Virus. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1987, 48, 1692–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertl, H.C.J.; Brown, E.G.; Finberg, R.W. Sendai Virus-Specific T Cell Clones II. Induction of Interferon Production by Sendai Virus-Specific T Helper Cell Clones. Eur. J. Immunol. 1982, 12, 1051–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yount, J.S.; Gitlin, L.; Moran, T.M.; López, C.B. MDA5 Participates in the Detection of Paramyxovirus Infection and Is Essential for the Early Activation of Dendritic Cells in Response to Sendai Virus Defective Interfering Particles. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 4910–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawski, M.R.; Bowen, G.N.; Cerny, A.M.; Anderson, L.J.; Haynes, L.M.; Tripp, R.A.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Finberg, R.W. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Activates Innate Immunity through Toll-Like Receptor 2. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, M.; Sareneva, T.; Julkunen, I.; Matikainen, S. IFNs Activate Toll-like Receptor Gene Expression in Viral Infections. Genes Immun. 2001, 2, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, K.J.; Koyama, S.; Nakagawa, A.; Coban, C.; Akira, S. Host Innate Immune Receptors and Beyond: Making Sense of Microbial Infections. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado-López, X.; Cotter, C.R.; Kim, W.K.; Sun, Y.; Muñoz, L.; Tapia, K.; López, C.B. Highly Immunostimulatory RNA Derived from a Sendai Virus Defective Viral Genome. Vaccine 2013, 31, 5713–5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensterl, V.; White, C.L.; Yamashita, M.; Sen, G.C. Novel Characteristics of the Function and Induction of Murine P56 Family Proteins. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 11045–11053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, M.S.; Farzan, M. The Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Functions of IFIT and IFITM Proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.L.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.J.; Wan, W.W.; Xin, Q.L.; Wang, W.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, L.K. Global Quantitative Proteomic Analysis Profiles Host Protein Expression in Response to Sendai Virus Infection. Proteomics 2017, 17, 1600239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaritsky, L.A.; Bedsaul, J.R.; Zoon, K.C. Virus Multiplicity of Infection Affects Type I Interferon Subtype Induction Profiles and Interferon-Stimulated Genes. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11534–11548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarino, A.V.; Kanno, Y.; Ferdinand, J.R.; O’Shea, J.J. Mechanisms of Jak/STAT Signaling in Immunity and Disease. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Yamashita, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sen, G.C. The IRF-3/Bax-Mediated Apoptotic Pathway, Activated by Viral Cytoplasmic RNA and DNA, Inhibits Virus Replication. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Sen, G.C. IRF-3 Activation by Sendai Virus Infection Is Required for Cellular Apoptosis and Avoidance of Persistence. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3500–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villenave, R.; Touzelet, O.; Thavagnanam, S.; Sarlang, S.; Parker, J.; Skibinski, G.; Heaney, L.G.; McKaigue, J.P.; Coyle, P.V.; Shields, M.D.; et al. Cytopathogenesis of Sendai Virus in Well-Differentiated Primary Pediatric Bronchial Epithelial Cells. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11718–11728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Doherty, P.C.; Zijlstra, M.; Jaenisch, R.; Katz, J.M. Delayed Clearance of Sendai Virus in Mice Lacking Class I MHC-Restricted CD8+ T Cells. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, G.A.; Katz, J.M.; Hogg, T.L.; Ryan, K.W.; Portner, A.; Woodland, D.L. Analysis of the Primary T-Cell Response to Sendai Virus Infection in C57BL/6 Mice: CD4+ T-Cell Recognition Is Directed Predominantly to the Hemagglutinin-Neuraminidase Glycoprotein. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 6863–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samieipour, Y.; Wiegand, M.; Willner, E.M.; Hoffmann, D.; Shameli, K.; Protzer, U.; Moeini, H. Replication-Deficient Sendai Virus Expressing Human Norovirus Capsid Protein Elicits Robust NoV-Specific Antibody and T-Cell Responses in Mice. Microbes Infect. 2024, 27, 105412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voges, B.; Vallbracht, S.; Zimmer, G.; Bossow, S.; Neubert, W.J.; Richter, K.; Hobeika, E.; Herrler, G.; Ehl, S. Recombinant Sendai Virus Induces T Cell Immunity against Respiratory Syncytial Virus That Is Protective in the Absence of Antibodies. Cell Immunol. 2007, 247, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, S.; Saeki, K.; Takeshita, M.; Hirano, K.; Shirakawa, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Ozawa, F.; Okano, H. Intranasal Sendai Virus-Based SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Using a Mouse Model. Genes Cells 2023, 28, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Gu, L.; Li, C.L.; Shu, T.; Lowrie, D.B.; Fan, X.Y. The Profile of T Cell Responses in Bacille Calmette-Guérin-Primed Mice Boosted by a Novel Sendai Virus Vectored Anti-Tuberculosis Vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 391066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, A.; Igarashi, H.; Nakamura, H.; Kano, M.; Iida, A.; Hirata, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Nagai, Y.; Matano, T. Protective Efficacy of an AIDS Vaccine, a Single DNA Priming Followed by a Single Booster with a Recombinant Replication-Defective Sendai Virus Vector, in a Macaque AIDS Model. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 9710–9715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Igarashi, H.; Takeda, A.; Sasaki, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Kano, M.; Sata, T.; Iida, A.; Hasegawa, M.; Horie, S.; et al. Induction of Gag-Specific T-Cell Responses by Therapeutic Immunization with a Gag-Expressing Sendai Virus Vector in Macaques Chronically Infected with Simian-Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Vaccine 2005, 23, 3166–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, M.; Gori-Savellini, G.; Martorelli, B.; Bossow, S.; Neubert, W.J.; Cusi, M.G. Evaluation of a Novel Immunogenic Vaccine Platform Based on a Genome Replication-Deficient Sendai Vector. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3888–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matano, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Igarashi, H.; Takeda, A.; Nakamura, H.; Kano, M.; Sugimoto, C.; Mori, K.; Iida, A.; Hirata, T.; et al. Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte–Based Control of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Replication in a Preclinical AIDS Vaccine Trial. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, K.; Takahara, Y.; Nomura, T.; Ishii, H.; Iwamoto, N.; Takahashi, N.; Inoue, M.; Iida, A.; Hara, H.; Shu, T.; et al. Immunogenicity of Repeated Sendai Viral Vector Vaccination in Macaques. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaggs Huang, F.; Bernstein, D.I.; Slobod, K.S.; Portner, A.; Takimoto, T.; Russell, C.J.; Meagher, M.; Jones, B.G.; Sealy, R.E.; Coleclough, C.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of an Intranasal Sendai Virus-Based Vaccine for Human Parainfluenza Virus Type I and Respiratory Syncytial Virus (SeVRSV) in Adults. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyn, D.; Mazanec, M.B.; Nedrud, J.G.; Portner, A. Location of Amino Acid Residues Important for the Structure and Biological Function of the Haemagglutinin-Neuraminidase Glycoprotein of Sendai Virus by Analysis of Escape Mutants. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, H.; Hironaka, T.; Inoue, M.; Iida, A.; Shu, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Nagai, Y.; Falsey, A.R.; Kamali, A.; Anzala, O.; et al. Prevalence of Specific Neutralizing Antibodies against Sendai Virus in Populations from Different Geographic Areas: Implications for AIDS Vaccine Development Using Sendai Virus Vectors. Hum. Vaccin. 2011, 7, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matano, T.; Kano, M.; Takeda, A.; Nakamura, H.; Nomura, N.; Furuta, Y.; Shioda, T.; Nagai, Y. No Significant Enhancement of Protection by Tat-Expressing Sendai Viral Vector-Booster in a Macaque AIDS Model. AIDS 2003, 17, 1392–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, T.; Takeda, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Kawada, M.; Matano, T. Impact of Cytotoxic-T-Lymphocyte Memory Induction without Virus-Specific CD4+ T-Cell Help on Control of a Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Challenge in Rhesus Macaques. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9339–9346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, N.; Takahashi, N.; Seki, S.; Nomura, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Inoue, M.; Shu, T.; Naruse, T.K.; Kimura, A.; Matano, T. Control of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Replication by Vaccine-Induced Gag- and Vif-Specific CD8+ T Cells. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, T.; Oshitani, H. Mucosal Immunity against Influenza Induced by Attenuated Recombinant Sendai Virus. Expert. Rev. Vaccines 2011, 10, 1393–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herniman, K.A.J.; Sellers, R.F. Protection of Guinea-Pigs against Foot-and-Mouth Disease by Simultaneous Inoculation of Sendai Virus and Inactivated Foot-and-Mouth Disease Vaccine. Arch. Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972, 37, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matano, T.; Kano, M.; Nakamura, H.; Takeda, A.; Nagai, Y. Rapid Appearance of Secondary Immune Responses and Protection from Acute CD4 Depletion after a Highly Pathogenic Immunodeficiency Virus Challenge in Macaques Vaccinated with a DNA Prime/Sendai Virus Vector Boost Regimen. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11891–11896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, M.; Igarashi, H.; Takeda, A.; Tsukamoto, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Dohki, S.; Takiguchi, M.; Matano, T. Involvement of Multiple Epitope-Specific Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Responses in Vaccine-Based Control of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Replication in Rhesus Macaques. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 1949–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, M.; Tsukamoto, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Iwamoto, N.; Kurihara, K.; Takeda, A.; Moriya, C.; Takeuchi, H.; Akari, H.; Matano, T. Gag-Specific Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Based Control of Primary Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Replication in a Vaccine Trial. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 10199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, A.; Igarashi, H.; Kawada, M.; Tsukamoto, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Inoue, M.; Iida, A.; Shu, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Matano, T. Evaluation of the Immunogenicity of Replication-Competent V-Knocked-out and Replication-Defective F-Deleted Sendai Virus Vector-Based Vaccines in Macaques. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6839–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura-Hoshi, M.; Takahara, Y.; Matsuoka, S.; Ishii, H.; Seki, S.; Nomura, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Sakawaki, H.; Miura, T.; Tokusumi, T.; et al. Therapeutic Vaccine-Mediated Gag-Specific CD8+ T-Cell Induction under Anti-Retroviral Therapy Augments Anti-Virus Efficacy of CD8+ Cells in Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Macaques. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.T.; Silvestri, G. Nonhuman Primate Models in AIDS Research. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2013, 8, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kestier, H.W.; Ringler, D.J.; Mori, K.; Panicali, D.L.; Sehgal, P.K.; Daniel, M.D.; Desrosiers, R.C. Importance of the Nef Gene for Maintenance of High Virus Loads and for Development of AIDS. Cell 1991, 65, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Pauza, C.D.; Lu, X.; Montefiori, D.C.; Miller, C.J. Rhesus Macaques That Become Systemically Infected with Pathogenic SHIV 89.6-PD after Intravenous, Rectal, or Vaginal Inoculation and Fail to Make an Antiviral Antibody Response Rapidly Develop AIDS. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. Hum. Retrovirol. 1998, 19, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargan, D.R.; Bennet, I.D.; Cousens, C.; Roy, D.J.; Blacklaws, B.A.; Dalziel Watt, R.G.N.J.; McConnell, I. Nucleotide Sequence of EV1, a British Isolate of Maedi-Visna Virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72, 1893–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pathogen | Vaccine Name | SeV Vector | Inserted Gene | Insertion Site | Host | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza A | GP42-SeV-H1 | GP42-SeV | HA (A/PR/8 (H1N1)) | M-F | C57BL/6 mice | [5] |
| SeV/ΔF/H5N1M2 | ΔF/SeV | M2 | Not specified | Guinea pigs and C57BL/6 mice | [81] | |
| FMDV | rSeV-P1 | ΔF/SeV | FMDV-P1 | N-P | BALB/c mice | [6] |
| SIV | SeV/SIV-Gag | ΔV/SeV | SIV-Gag | 5’-N | Cynomolgus and rhesus macaques | [7] |
| SeV-Tat | ΔV/SeV | HIV-Tat | 5’-N | Rhesus macaques | [116] | |
| F(-)SeV-Gag | ΔF/SeV | SIV-Gag | Not specified | Rhesus macaques | [108] | |
| F(-)SeV-Gag236-250-EGFP | ΔF/SeV | SIV-Gag236-250-EGFP | Not specified | Burmese rhesus macaques | [117] | |
| F(-)SeV-Vif | ΔF/SeV | Vif-opt | Not specified | Burmese rhesus macaques | [118] | |
| F(-)SeV-Nef | ΔF/SeV | Nef-G2A | Not specified | Burmese rhesus macaques | [118] | |
| SRLV | rSeV-GFP-P25 | ΔF-M/SeV | Gag-P25 | N-P | Lambs | [8] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez, Á.; Reina, R. Recombinant Sendai Virus Vectors as Novel Vaccine Candidates Against Animal Viruses. Viruses 2025, 17, 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050737
Gómez Á, Reina R. Recombinant Sendai Virus Vectors as Novel Vaccine Candidates Against Animal Viruses. Viruses. 2025; 17(5):737. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050737
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez, Álex, and Ramsés Reina. 2025. "Recombinant Sendai Virus Vectors as Novel Vaccine Candidates Against Animal Viruses" Viruses 17, no. 5: 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050737
APA StyleGómez, Á., & Reina, R. (2025). Recombinant Sendai Virus Vectors as Novel Vaccine Candidates Against Animal Viruses. Viruses, 17(5), 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050737





