Isolation and Pathogenicity of a Natural Recombinant Pig Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus in Northeast China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Genome Sequencing
2.2. Sequence Analysis and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Isolation and Identification
2.4. Animal Experiments
2.5. Serological Testing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
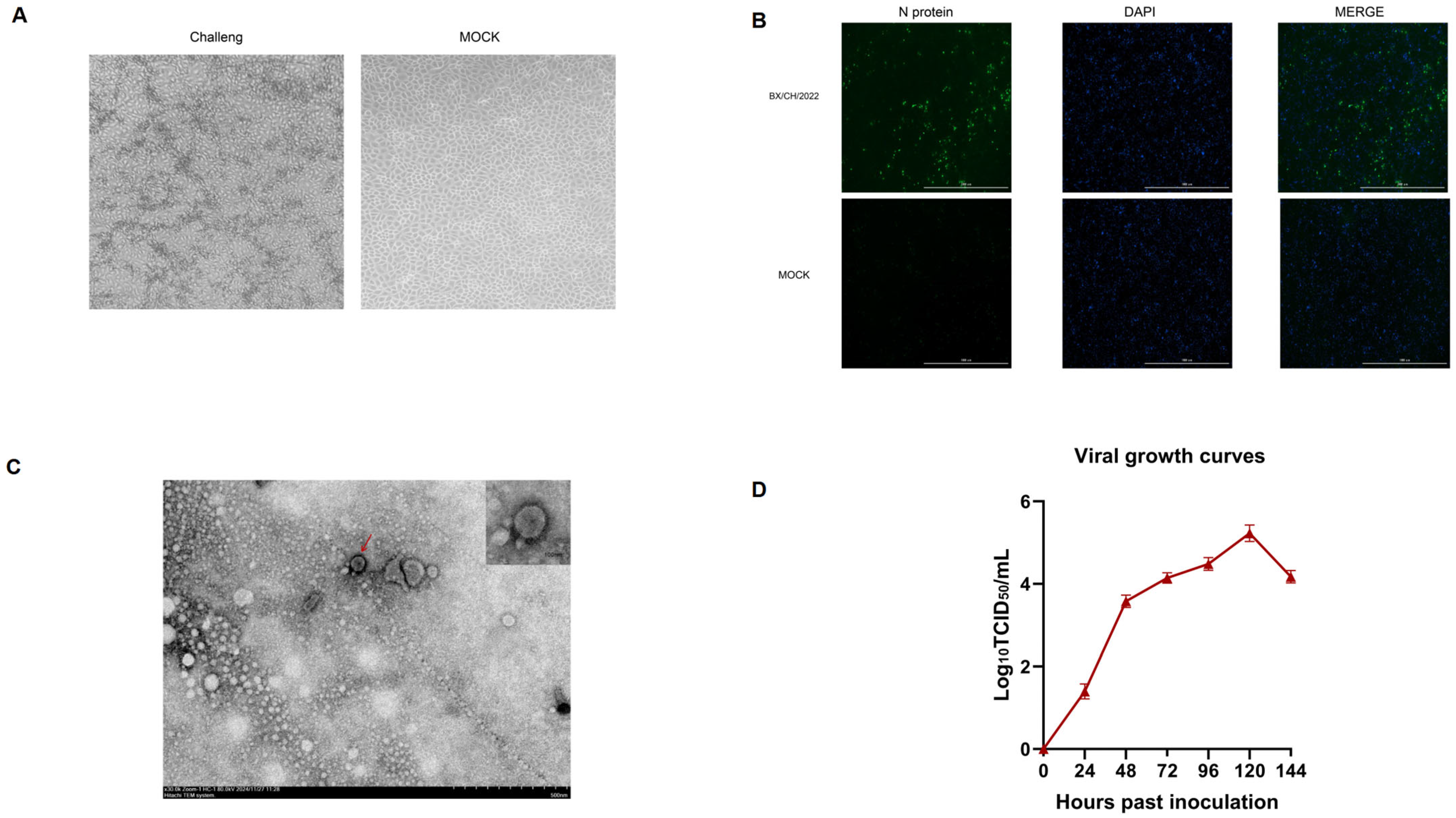
3.1. Virus Isolation and Identification
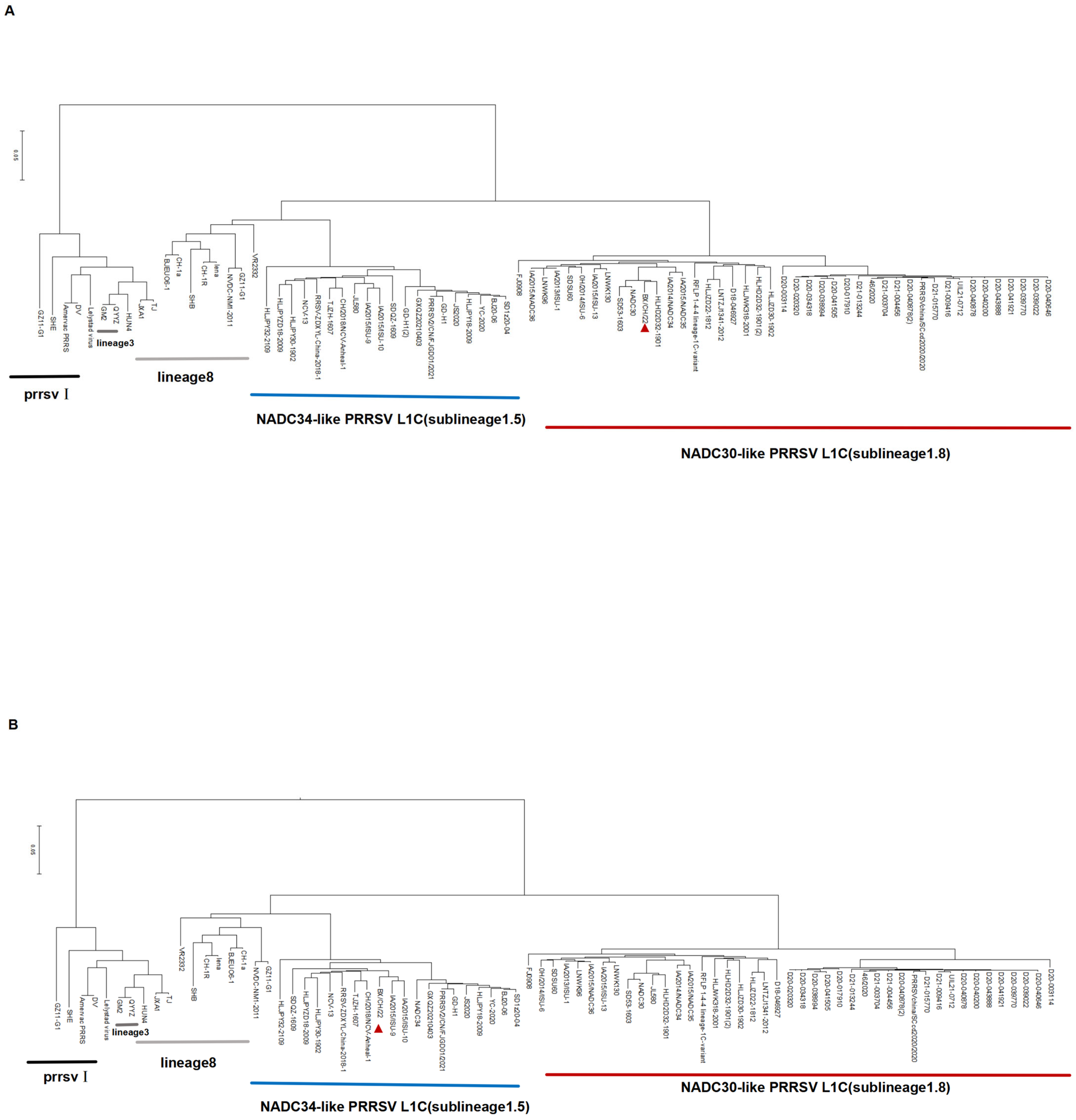
3.2. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
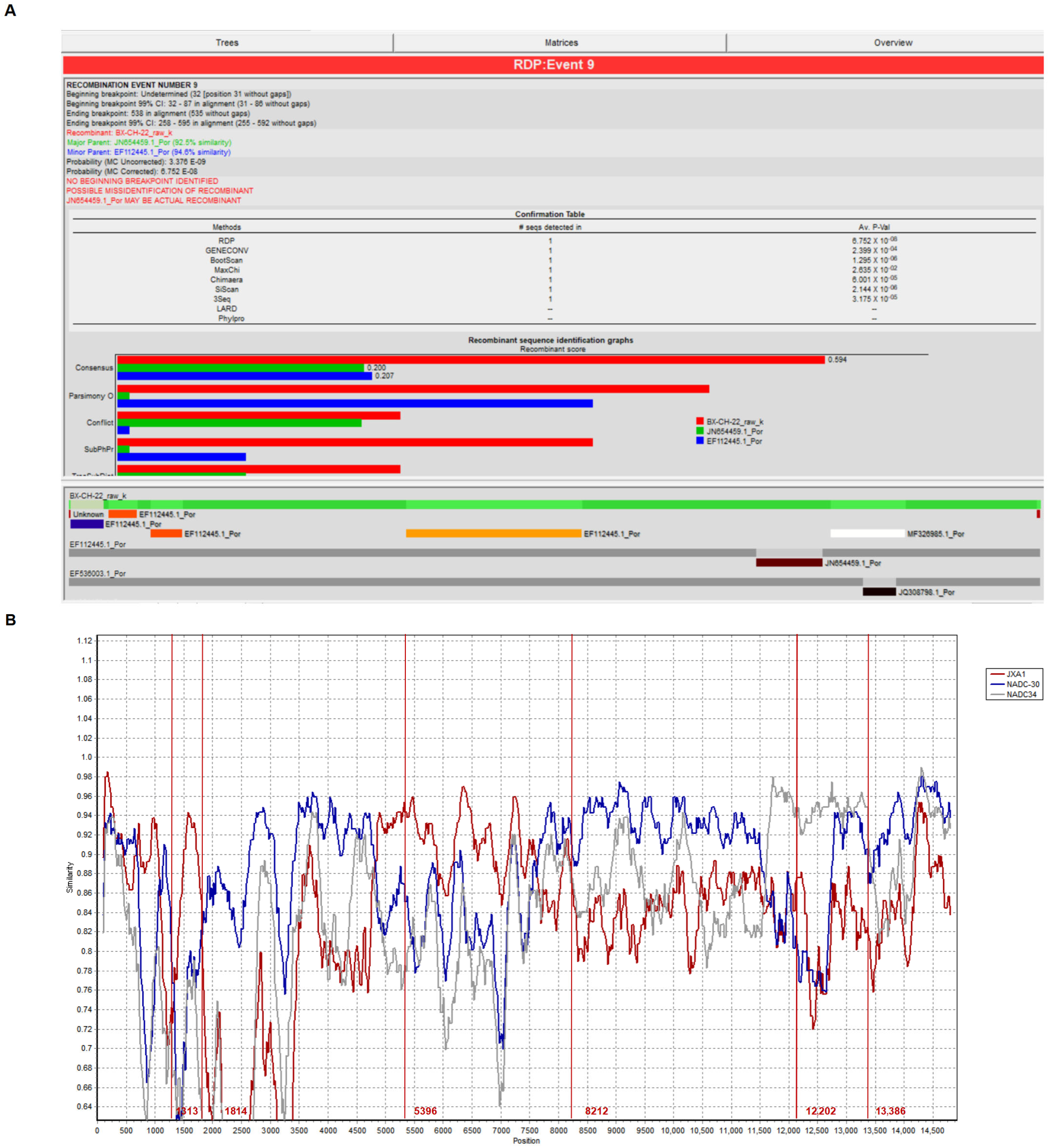
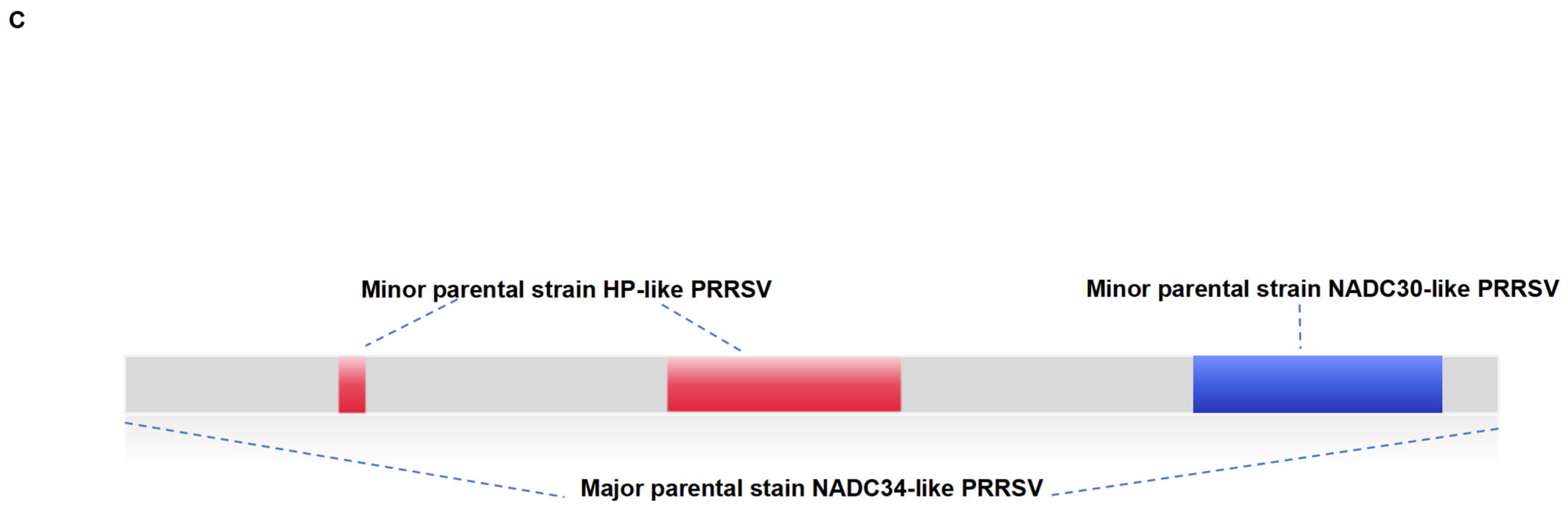
3.3. Recombination Analysis
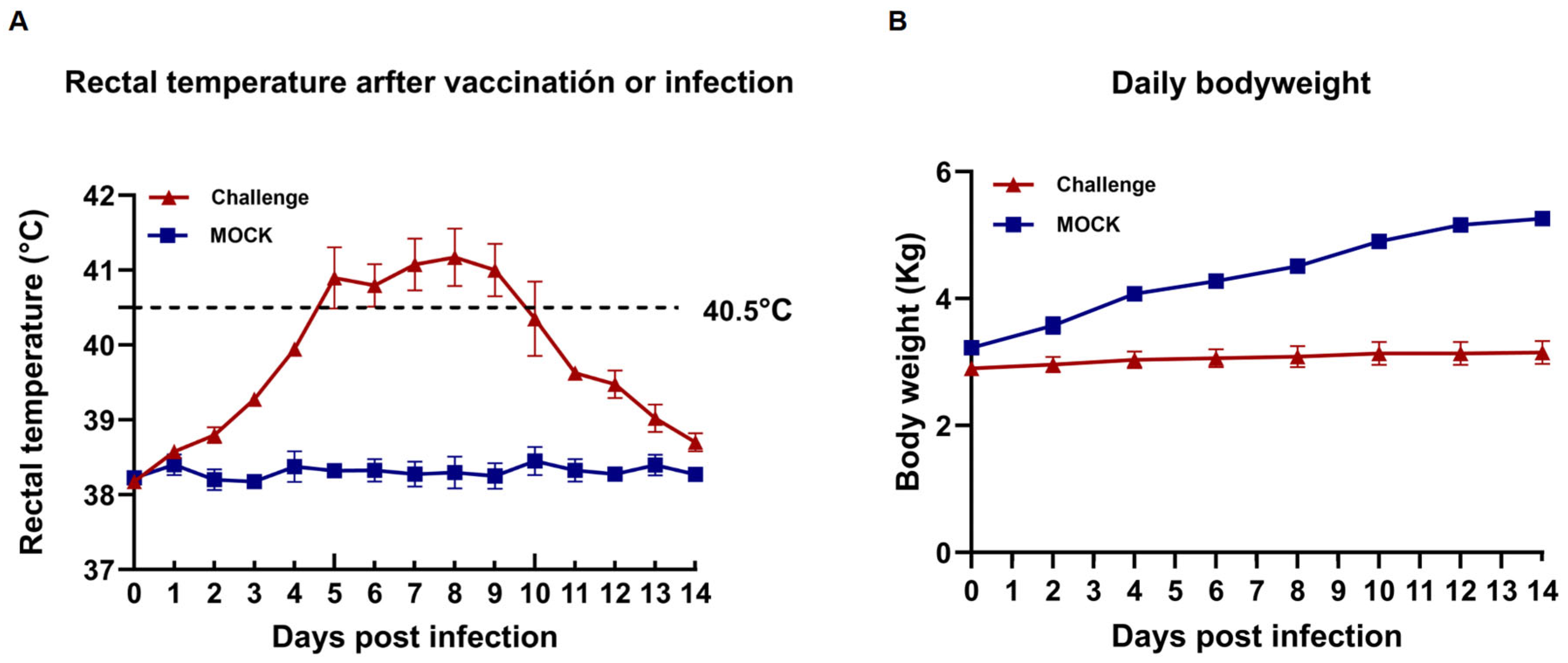
3.4. Clinical Signs
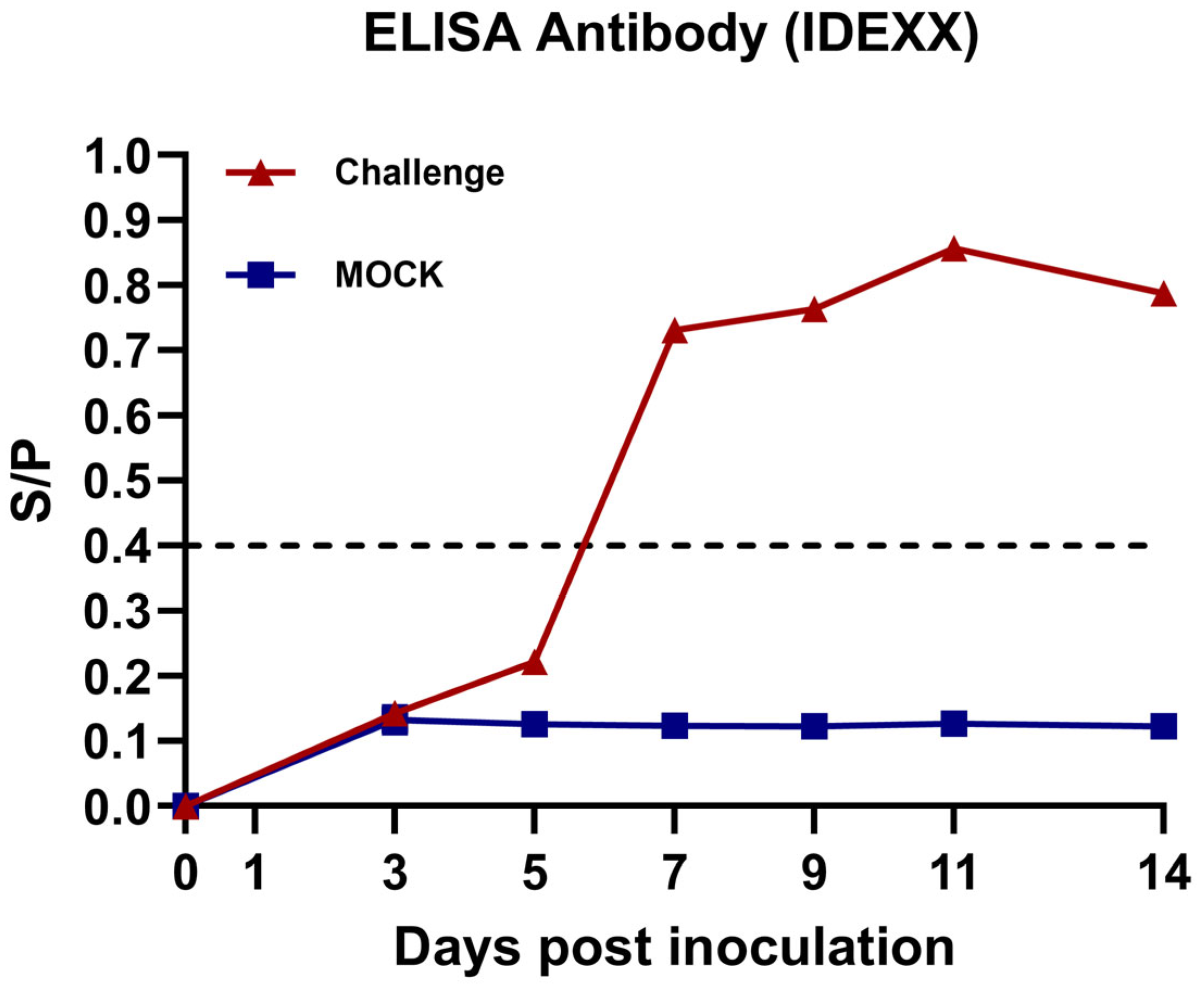
3.5. Anti-PRRSV Antibody Detection
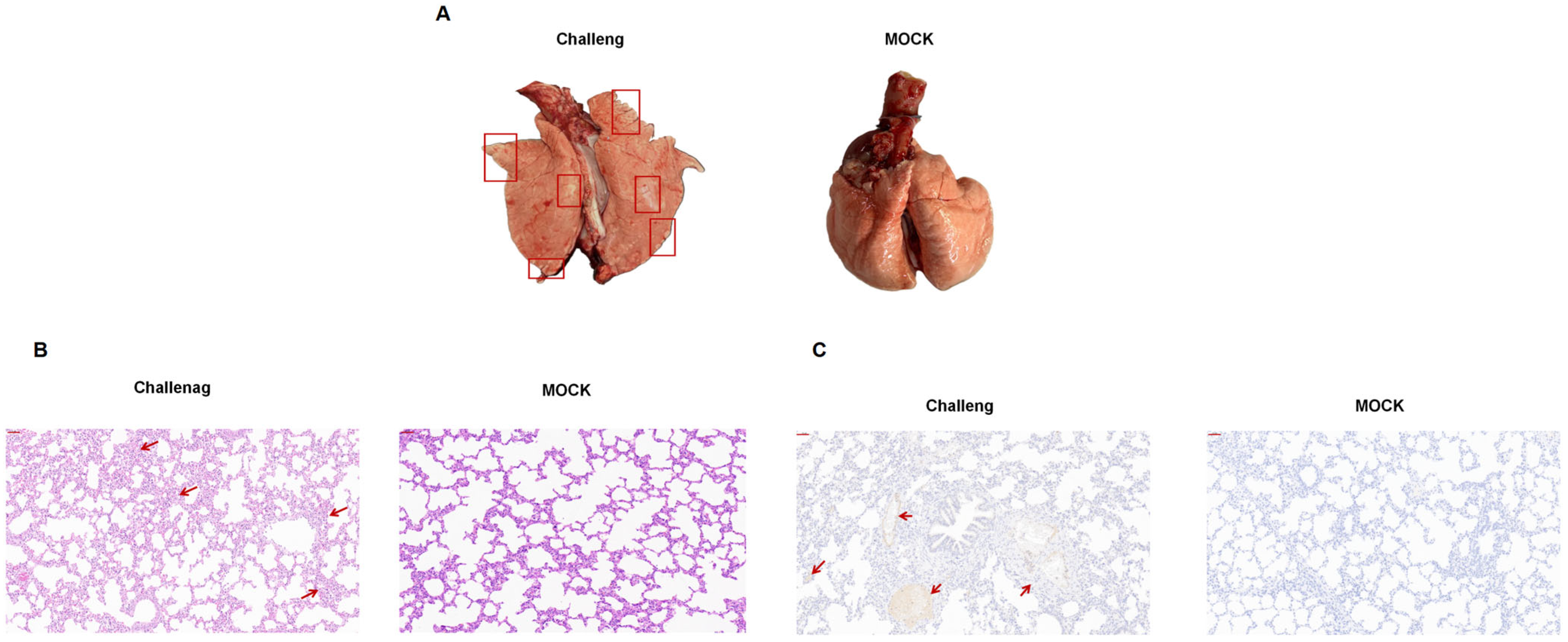
3.6. Gross Pathology and Histopathology
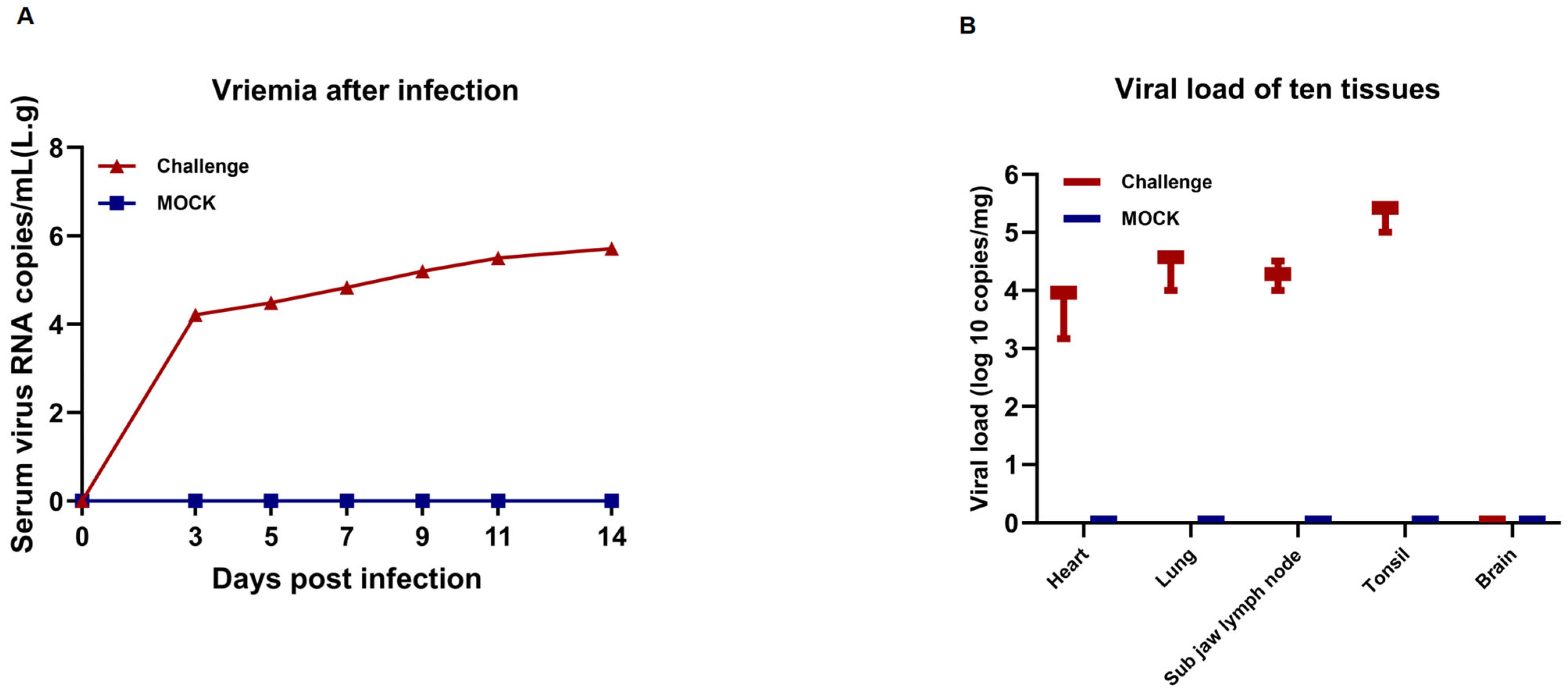
3.7. Assessment of Viremia and Viral Loads in Tissue and Serum
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| CPE | cytopathic effect |
| dpi | days post-infection |
| H & E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| hpi | hours post-infection |
| NSP | non-structural protein |
| ORF | open reading frame |
| PRRSV | porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus |
| PRV | pseudorabies virus |
| CSFV | classical swine fever virus |
| RT-PCR | real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| TCID50 | 50% tissue culture infectious dose |
References
- Kappes, M.A.; Faaberg, K.S. PRRSV structure, replication and recombination: Origin of phenotype and genotype diversity. Virology 2015, 479–480, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Xu, H.; Wang, K.; He, F. Emergence of two different recombinant PRRSV strains with low neutralizing antibody susceptibility in China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Lei, K.; Xu, H.; He, F. Genetic characterization of a novel recombinant PRRSV2 from lineage 8, 1 and 3 in China with significant variation in replication efficiency and cytopathic effects. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaner-Tarbes, S.; Del Portillo, H.A.; Montoya, M.; Fraile, L. Key gaps in the knowledge of the porcine respiratory reproductive syndrome virus (PRRSV). Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.W.; Li, L.; Yin, M.; Wang, Q.; Luo, W.T.; Ma, Y.; Pu, Z.H.; Zhou, J.L. Cloning and molecular characterization of the ORF5 gene from a PRRSV-SN strain from Southwest China. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 112, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Li, X. Emergence and spread of NADC34-like PRRSV in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 3005–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Peng, O.; Xu, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Lin, L.; Zhou, Q.; Cai, X.; Hu, G.; He, Z.; et al. Characterization and pathogenicity of two novel PRRSVs recombined by NADC30-like and NADC34-like strains in China. Viruses 2022, 14, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim-im, W.; Anderson, T.K.; Paploski, I.A.D.; VanderWaal, K.; Gauger, P.; Krueger, K.; Shi, M.; Main, R.; Zhang, J. Refining PRRSV-2 genetic classification based on global ORF5 sequences and investigation of their geographic distributions and temporal changes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e02916-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, G.; Yu, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Tong, W.; Liu, C.; Gao, F.; Tong, G. Genetic diversity of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) from 1996 to 2017 in China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Han, J.; Yang, H. Evolution and Diversity of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 298, 110252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, S.; Guo, Z.; Li, C.; Gong, B.; Li, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, M.; Xiang, L.; et al. Novel characterization of NADC30-like and NADC34-like PRRSV strains in China: Epidemiological status and pathogenicity analysis of L1A variants. J. Integr. Agric. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Du, C.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, D.; Luo, Y.; Yao, X.; Yang, Z.; Ren, M.; et al. Isolation, identification, recombination analysis and pathogenicity experiment of a PRRSV recombinant strain in Sichuan Province, China. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1362471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Zheng, J.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, Q.; Wu, Q.; Lin, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, Q.; Gong, L.; et al. Isolation, identification, and pathogenicity of a NADC30-like porcine reproductive and respiratory disorder syndrome virus strain affecting sow production. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1207189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Feng, H.; Lee, J.; Ning Chen, W. Comparative proteomics profile of lipid-cumulating oleaginous yeast: An iTRAQ-coupled 2-D LC-MS/MS analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Zou, C.; Zeng, S.; Peng, O.; Hu, G.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Hu, F.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, H. In Vivo Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Porcine Alveolar Macrophages in PRRSV-Infected Pigs. Virol. Sin. 2025, 40, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Su, G.; Duan, C.; Fang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, S. Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Infection Manipulates Central Carbon Metabolism. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 279, 109674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Techakriengkrai, N.; Nedumpun, T.; Suradhat, S. Abrogation of PRRSV infectivity by CRISPR-Cas13b-mediated viral RNA cleavage in mammalian cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Carvajal, J.M.; Ruedas-Torres, I.; Carrasco, L.; Pallarés, F.J.; Mateu, E.; Rodríguez-Gómez, I.M.; Gómez-Laguna, J. Activation of regulated cell death in the lung of piglets infected with virulent PRRSV-1 Lena strain occurs earlier and mediated by cleaved Caspase-8. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson-Corley, K.N.; Olivier, A.K.; Meyerholz, D.K. Principles for valid histopathologic scoring in research. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 50, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, X.X.; Li, X.; Qiao, S.; Deng, R.; Zhang, G. Prevalence and genetic characteristics of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in central China during 2016–2017: NADC30-like PRRSVs are predominant. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 135, 103657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiao, D.; Jing, Y.; He, Y.; Han, W.; Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, S. Genetic characterization and pathogenicity of a novel recombinant PRRSV from lineage 1, 8 and 3 in China failed to infect MARC-145 cells. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 165, 105469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhai, J.; Wei, C.; Dai, A.; Yang, X.; Luo, M. Recombination in JXA1-R vaccine and NADC30-like strain of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 204, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Losada, M.; Arenas, M.; Galán, J.C.; Palero, F.; González-Candelas, F. Recombination in viruses: Mechanisms, methods of study, and evolutionary consequences. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 30, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.J.; Xie, W.; Chen, X.X.; Qiao, S.; Zhao, M.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, B.L.; Zhang, G. Molecular epidemiology of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in Central China since 2014: The prevalence of NADC30-like PRRSVs. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 109, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Rouzine, I.M.; Bianco, S.; Acevedo, A.; Goldstein, E.F.; Farkov, M.; Brodsky, L.; Andino, R. RNA recombination enhances adaptability and is required for virus spread and virulence. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, L.; Xu, Z.; Deng, H.; Li, F.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, L. Emergence and spread of NADC34-like PRRSV in Southwest China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e3416–e3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, G.; Chang, T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Xia, D.; Qi, X.; Zhu, X.; Wei, Z.; Tian, X.; et al. Recombinant characterization and pathogenicity of a novel L1C RFLP-1-4-4 variant of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in China. Vet. Res. 2024, 55, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Tan, X.; Lao, M.; Wu, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, S.; Yu, J.; Zhu, J.; Yu, L.; Tong, W.; et al. The Novel PRRSV Strain HBap4-2018 with a unique recombinant pattern is highly pathogenic to piglets. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 1611–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Z.; Li, Q.; Xu, L.; Liang, D.; Li, Y.; Shi, Z.; Luo, L.; Jin, J.; Huo, X.; Dong, X.; et al. Isolation and Pathogenicity of a Natural Recombinant Pig Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus in Northeast China. Viruses 2025, 17, 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050729
Tian Z, Li Q, Xu L, Liang D, Li Y, Shi Z, Luo L, Jin J, Huo X, Dong X, et al. Isolation and Pathogenicity of a Natural Recombinant Pig Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus in Northeast China. Viruses. 2025; 17(5):729. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050729
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Zhixin, Qiwei Li, Luxiang Xu, Dexin Liang, Yuan Li, Ziqi Shi, Lingzhi Luo, Jiechao Jin, Xiaoyi Huo, Xiumei Dong, and et al. 2025. "Isolation and Pathogenicity of a Natural Recombinant Pig Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus in Northeast China" Viruses 17, no. 5: 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050729
APA StyleTian, Z., Li, Q., Xu, L., Liang, D., Li, Y., Shi, Z., Luo, L., Jin, J., Huo, X., Dong, X., & Zhou, H. (2025). Isolation and Pathogenicity of a Natural Recombinant Pig Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus in Northeast China. Viruses, 17(5), 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050729







