Single Amino Acid Residue W33 of tva Receptor Is Critical for Viral Entry and High-Affinity Binding of Avian Leukosis Virus Subgroup K
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Replication-Competent Avian Retroviruses
2.3. Construction, Production, and Transduction of tva Expression Vectors
2.4. Infection and Spinoculation Assay
2.5. Immunoadhesin
2.6. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.7. Sensitivity Calculation
2.8. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and qRT-PCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
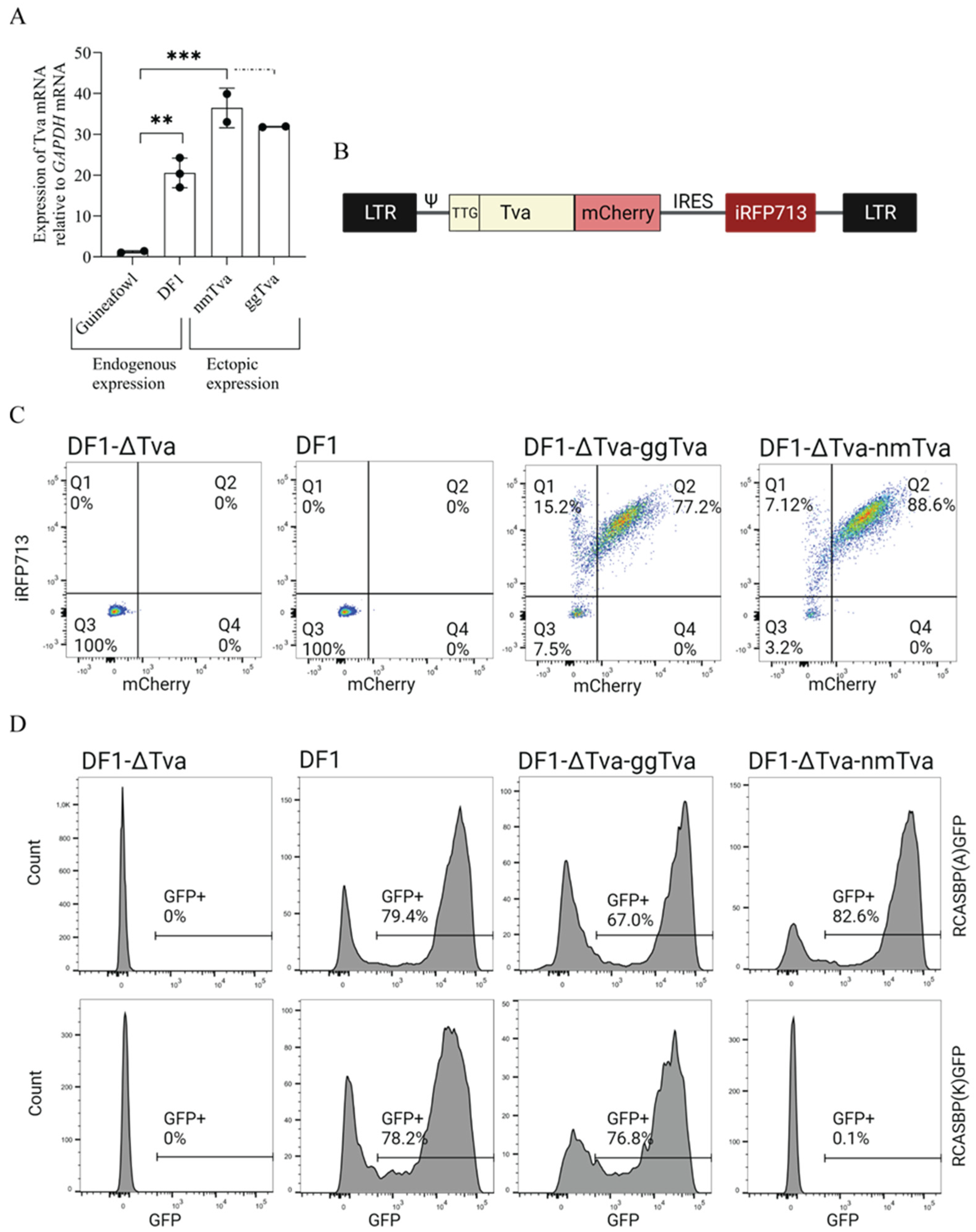
3.1. Experimental Design and Generation of Retroviral Vector for Ectopic tva Expression
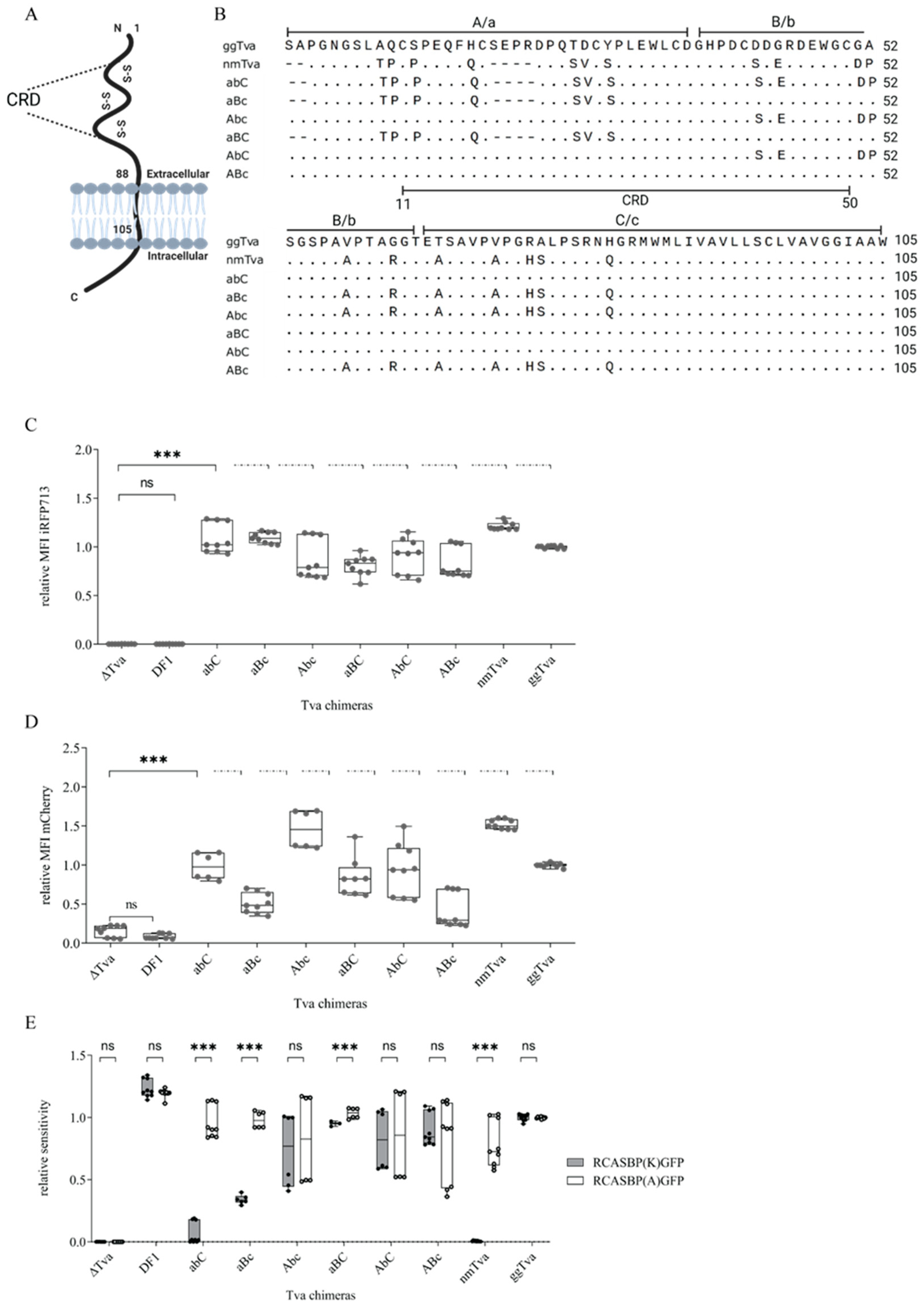
3.2. Cysteine-Rich Domain of tva Is Important for Sensitivity to ALV-K
3.3. Resistance of Guineafowl tva to ALV-K Depends on a Combination of Polymorphic Amino Acid Residues in CRD
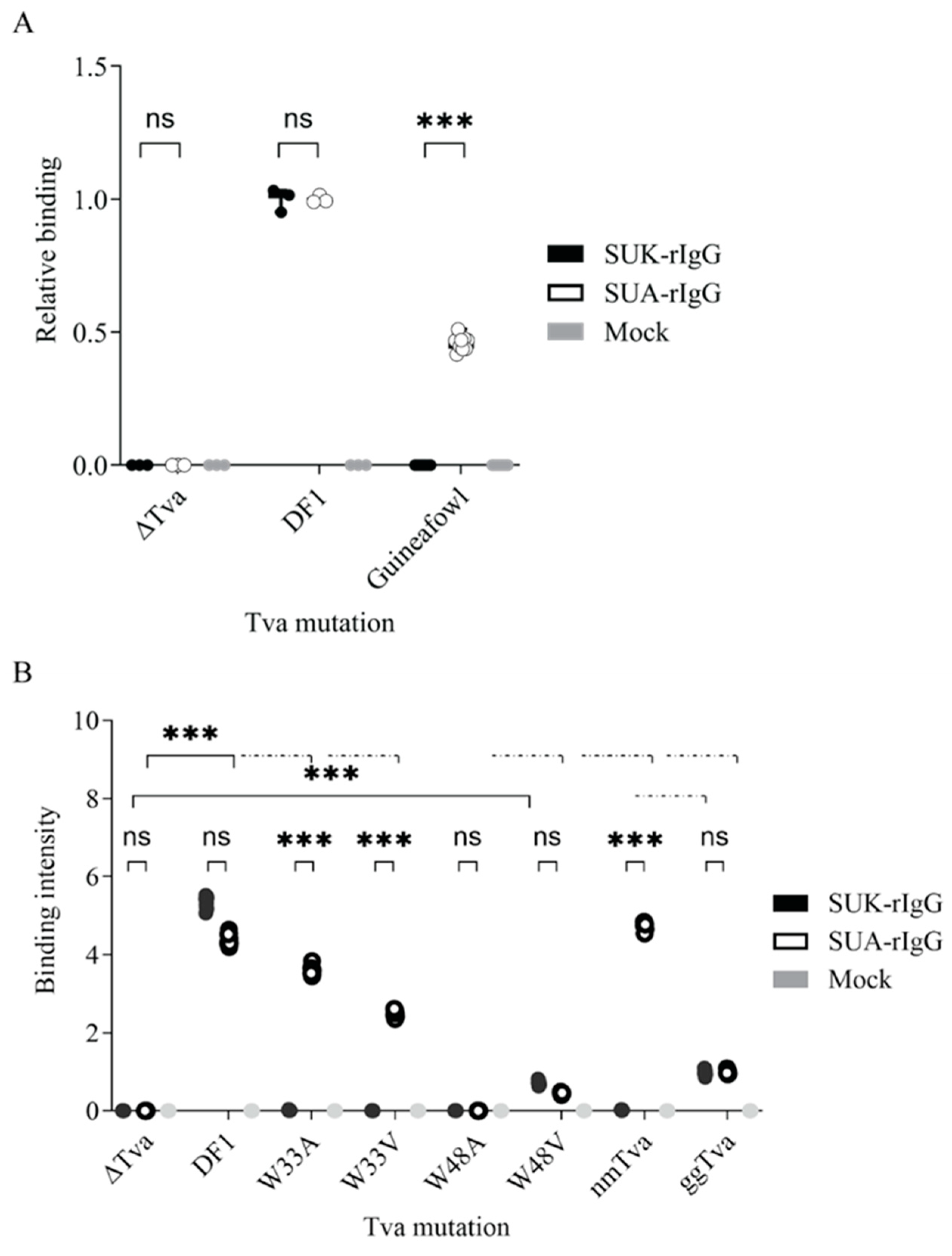
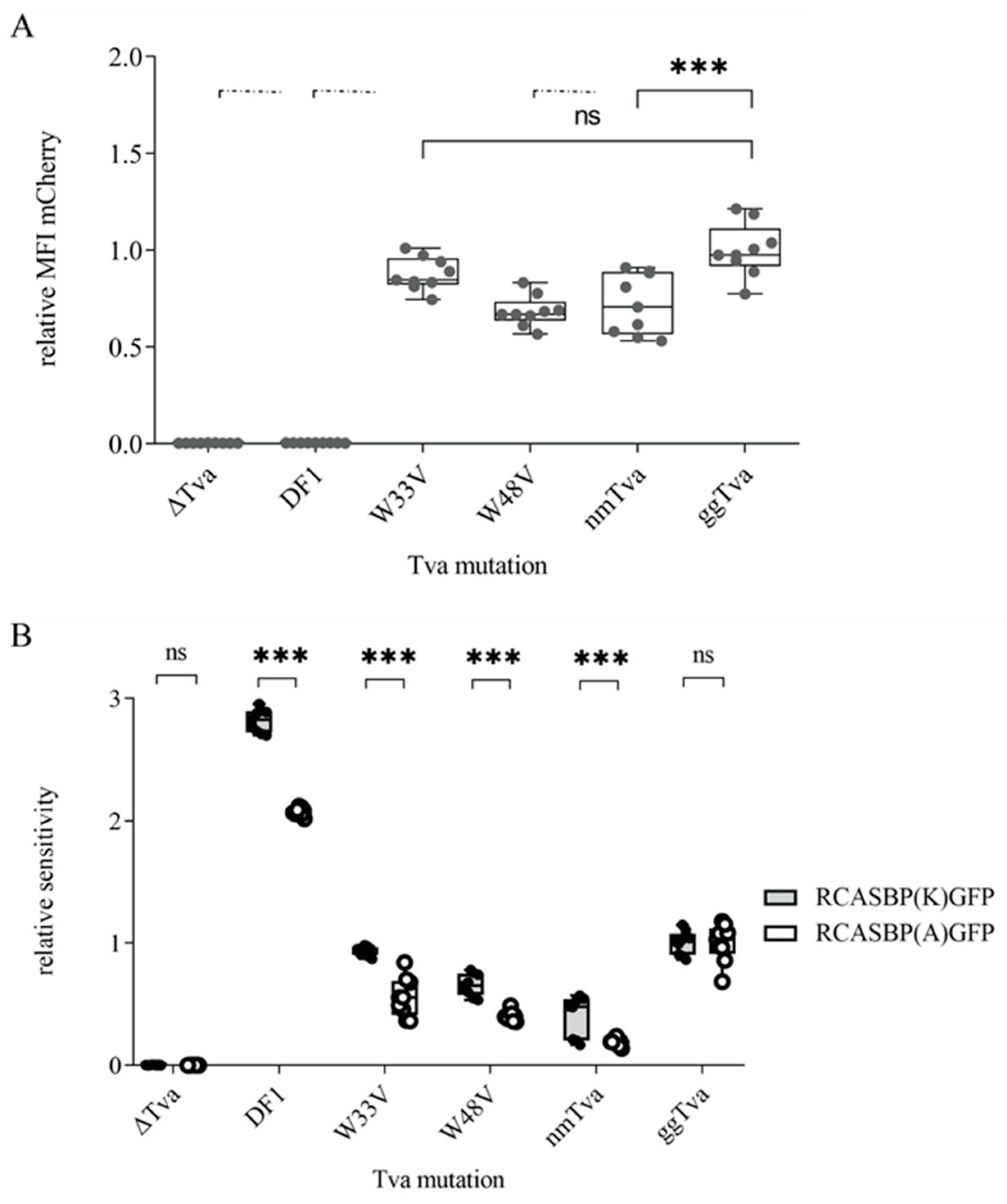
3.4. Tryptophan 33 in tva CRD Is Critical for ALV-K Binding and Infection
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Payne, L.N.; Nair, V. The long view: 40 years of avian leukosis research. Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federspiel, M.J. Reverse Engineering Provides Insights on the Evolution of Subgroups A to E Avian Sarcoma and Leukosis Virus Receptor Specificity. Viruses 2019, 11, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorner, A.J.; Stoye, J.P.; Coffin, J.M. Molecular basis of host range variation in avian retroviruses. J. Virol. 1985, 53, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Ma, M.; Chang, F.; Muhammad, F.; Yu, M.; Ren, C.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, A.; et al. Molecular characteristic and pathogenicity analysis of a novel multiple recombinant ALV-K strain. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 260, 109184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fandiño, S.; Gomez-Lucia, E.; Benítez, L.; Doménech, A. Avian Leukosis: Will We Be Able to Get Rid of It? Animals 2023, 13, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Li, X.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chang, S.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, H.; Chen, F.; Xie, Q. Molecular epidemiology of J-subgroup avian leukosis virus isolated from meat-type chickens in southern China between 2013 and 2014. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 3039–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Su, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, X.; Cui, Z. Genomic sequence analysis and biological characteristics of a rescued clone of avian leukosis virus strain JS11C1, isolated from indigenous chickens. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2512–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Přikryl, D.; Plachý, J.; Kučerová, D.; Koslová, A.; Reinišová, M.; Šenigl, F.; Hejnar, J. The Novel Avian Leukosis Virus Subgroup K Shares Its Cellular Receptor with Subgroup A. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00580-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, P.; Young, J.A.; Varmus, H.E. A receptor for subgroup A Rous sarcoma virus is related to the low density lipoprotein receptor. Cell 1993, 74, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.A.; Bates, P.; Varmus, H.E. Isolation of a chicken gene that confers susceptibility to infection by subgroup A avian leukosis and sarcoma viruses. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 1811–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krchlíková, V.; Mikešová, J.; Geryk, J.; Bařinka, C.; Nexo, E.; Fedosov, S.N.; Kosla, J.; Kučerová, D.; Reinišová, M.; Hejnar, J.; et al. The avian retroviral receptor tva mediates the uptake of transcobalamin bound vitamin B12 (cobalamin). J. Virol. 2021, 95, e02136-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koslová, A.; Trefil, P.; Mucksová, J.; Reinišová, M.; Plachý, J.; Kalina, J.; Kučerová, D.; Geryk, J.; Krchlíková, V.; Lejčková, B.; et al. Precise CRISPR/Cas9 editing of the NHE1 gene renders chickens resistant to the J subgroup of avian leukosis virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 2108–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elleder, D.; Melder, D.C.; Trejbalová, K.; Svoboda, J.; Federspiel, M.J. Two different molecular defects in the tva receptor gene explain the resistance of two tvar lines of chickens to infection by subgroup A avian sarcoma and leukosis viruses. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 13489–13500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinišová, M.; Plachý, J.; Trejbalová, K.; Šenigl, F.; Kučerová, D.; Geryk, J.; Svoboda, J.; Hejnar, J. Intronic deletions that disrupt mRNA splicing of the tva receptor gene result in decreased susceptibility to infection by avian sarcoma and leukosis virus subgroup A. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2021–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Chang, S.; Shu, D.; Zhang, H.; Chen, F.; Xie, Q. Intronic deletions of tva receptor gene decrease the susceptibility to infection by avian sarcoma and leukosis virus subgroup A. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koslová, A.; Trefil, P.; Mucksová, J.; Krchlíková, V.; Plachý, J.; Krijt, J.; Reinišová, M.; Kučerová, D.; Geryk, J.; Kalina, J.; et al. Knock-Out of Retrovirus Receptor Gene in the Chicken Confers Resistance to Avian Leukosis Virus Subgroups A and K and Affects Cobalamin (Vitamin B)-Dependent Level of Methylmalonic Acid. Viruses 2021, 13, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melder, D.C.; Pike, G.M.; VanBrocklin, M.W.; Federspiel, M.J. Model of the TVA receptor determinants required for efficient infection by subgroup A avian sarcoma and leukosis viruses. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2136–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Edinger, A.; Bates, P. Role of basic residues in the subgroup-determining region of the subgroup A avian sarcoma and leukosis virus envelope in receptor binding and infection. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 3458–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingler, K.; Young, J.A. Residue Trp-48 of tva is critical for viral entry but not for high-affinity binding to the SU glycoprotein of subgroup A avian leukosis and sarcoma viruses. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 7510–7516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Yu, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, P.; Meng, L.; Guo, R.; Feng, X.; Hu, M.; He, T.; et al. Residues E53, L55, H59, and G70 of the cellular receptor protein tva mediate cell binding and entry of the novel subgroup K avian leukosis virus. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 102962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koslová, A.; Kučerová, D.; Reinišová, M.; Geryk, J.; Trefil, P.; Hejnar, J. Genetic Resistance to Avian Leukosis Viruses Induced by CRISPR/Cas9 Editing of Specific Receptor Genes in Chicken Cells. Viruses 2018, 10, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federspiel, M.J.; Hughes, S.H. Retroviral gene delivery. Methods Cell Biol. 1997, 52, 179–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Štafl, K.; Trávníček, M.; Kučerová, D.; Pecnová, Ľ.; Krchlíková, V.; Gáliková, E.; Stepanets, V.; Hejnar, J.; Trejbalová, K. Heterologous avian system for quantitative analysis of Syncytin-1 interaction with ASCT2 receptor. Retrovirology 2021, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmen, S.L.; Salter, D.W.; Payne, W.S.; Dodgson, J.B.; Hughes, S.H.; Federspiel, M.J. Soluble Forms of the Subgroup A Avian Leukosis Virus [ALV(A)] Receptor tva Significantly Inhibit ALV(A) Infection In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 10051–10060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainey, G.J.A.; Natonson, A.; Maxfield, L.F.; Coffin, J.M. Mechanisms of avian retroviral host range extension. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6709–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-Y.; Huang, W.; Dolmer, K.; Gettins, P.G.W.; Rong, L. Solution structure of the viral receptor domain of tva and its implications in viral entry. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 2848–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Yu, M.; Liu, P.; Meng, L.; Guo, R.; Feng, X.; Liu, A.; Qi, X.; et al. Residues L55 and W69 of tva Mediate Entry of Subgroup A Avian Leukosis Virus. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0067822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kučerová, D.; Plachý, J.; Reinišová, M.; Šenigl, F.; Trejbalová, K.; Geryk, J.; Hejnar, J. Nonconserved tryptophan 38 of the cell surface receptor for subgroup J avian leukosis virus discriminates sensitive from resistant avian species. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 8399–8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Doherty, U.; Swiggard, W.J.; Malim, M.H. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 spinoculation enhances infection through virus binding. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10074–10080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmen, S.L.; Federspiel, M.J. Selection of a subgroup A avian leukosis virus ALV(A) envelope resistant to soluble ALV(A) surface glycoprotein. Virology 2000, 273, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melder, D.C.; Pankratz, V.S.; Federspiel, M.J. Evolutionary pressure of a receptor competitor selects different subgroup a avian leukosis virus escape variants with altered receptor interactions. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 0504–10514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brojatsch, J.; Naughton, J.; Rolls, M.M.; Zingler, K.; Young, J.A. CAR1, a TNFR-related protein, is a cellular receptor for cytopathic avian leukosis-sarcoma viruses and mediates apoptosis. Cell 1996, 87, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adkins, H.B.; Brojatsch, J.; Naughton, J.; Rolls, M.M.; Pesola, J.M.; Young, J.A. Identification of a cellular receptor for subgroup E avian leukosis virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 11617–11622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adkins, H.B.; Brojatsch, J.; Young, J.A.T. Identification and characterization of a shared TNFR-related receptor for subgroup B, D, and E avian leukosis viruses reveal cysteine residues required specifically for subgroup E viral entry. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 3572–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adkins, H.B.; Blacklow, S.C.; Young, J.A. Two functionally distinct forms of a retroviral receptor explain the nonreciprocal receptor interference among subgroups B, D, and E avian leukosis viruses. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 3520–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauss, D.J.; Young, J.A. A fifteen-amino-acid TVB peptide serves as a minimal soluble receptor for subgroup B avian leukosis and sarcoma viruses. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 5404–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klucking, S.; Young, J.A.T. Amino acid residues Tyr-67, Asn-72, and Asp-73 of the TVB receptor are important for subgroup E avian sarcoma and leukosis virus interaction. Virology 2004, 318, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachý, J.; Reinišová, M.; Kučerová, D.; Šenigl, F.; Stepanets, V.; Hron, T.; Trejbalová, K.; Elleder, D.; Hejnar, J. Identification of New World Quails Susceptible to Infection with Avian Leukosis Virus Subgroup J. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02002-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoušková, M.; Plachý, J.; Kučerová, D.; Pecnová, Ľ.; Reinišová, M.; Geryk, J.; Karafiát, V.; Hron, T.; Hejnar, J. Rapid adaptive evolution of avian leukosis virus subgroup J in response to biotechnologically induced host resistance. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| NO. | Sequence 5′-3′ |
|---|---|
| gg/nmtva-TTG-FW | ATACCAATTGCCACCTTGGTGCGGTTGTTGGAGC |
| gg/nmtva-TTG-RV | TGCGGATCAAGCTAGCAAGCCGTC |
| Segment_A-FW | CCGCTGCCCACCCCCA |
| Segment_A-RV | GTCGCAGAGCCACTCCAGC |
| Segment_B-FW | GCTGGAGTGGCTCTGCGAC |
| Segment_B-RV | CGGGGCTCCCGCTCG |
| Segment_C-FW | CGAGCGGGAGCCCCG |
| Segment_C-RV | GATAGCCCGCATAGTCAGGAACATC |
| ggtva-S12P-FW | ACTGCTCGGGCGGGCACTGCG |
| ggtva-S12P-RV | CGCAGTGCCCGCCCGAGCAGT |
| ggtva-H17Q-RV | GCTCCGAACACTGGAACTGCTCGG |
| ggtva-H17Q-FW | CCGAGCAGTTCCAGTGTTCGGAGC |
| ggtva-Δ19-23aa-FW | GCGGGTAGCAGTCGGTTTGGGGATCACAGTG-GAACTGCTCGGGTGAG |
| ggtva-Δ19-23aa-RV | CTCACCCGAGCAGTTCCACTGTGATCCCCAAAC-CGACTGCTACCCGC |
| ggtva-T26S-FW | GATCCCCAATCCGACTGCTACCCG |
| ggtva-T26S-RV | CGGGTAGCAGTCGGATTGGGGATC |
| ggtva-D27V-FW | CAGCGGGTAGCAGACGGTTTGGGG |
| ggtva-D27V-RV | CCCCAAACCGTCTGCTACCCGCTG |
| ggtva-Y29S-FW | CTCCAGCGGGGAGCAGTCGGTTTG |
| ggtva-Y29S-RV | CAAACCGACTGCTCCCCGCTGGAG |
| ggtva-D42S-FW | GTCCCGTCCATCGCTGCAGTCGG |
| ggtva-D42S-RV | CCGACTGCAGCGATGGACGGGAC |
| ggtva-G44E-FW | CCACTCGTCCCTTTCATCGTCGCA |
| ggtva-G44E-RV | TGCGACGATGAAAGGGACGAGTGG |
| ggtva-W48A-FW | ACGGGACGAGGCTtGGCTGCGGAGCGAGCGGG |
| ggtva-W48A-RV | GTCGCAGAGAGCCTCCAGCGGGTAGCAGTC |
| ggtva-W48V-FW | ACGGGACGAGGTTGGCTGCGGAGCGAGCGGG |
| ggtva-W48V-RV | CTCCGCAGCCAACCTCGTCCCGTCCATCGTCGC |
| ggtva-W33A-FW | CCCGCTGGAGGCTCTCTGCGACGGGCATCC |
| ggtva-W33A-RV | TCGCAGAGAGCCTCCAGCGGGTAGCAGTC |
| ggtva-W33V-FW | CCCGCTGGAGGTTCTCTGCGACGGGCATCC |
| ggtva-W33V-RV | GTCGCAGAGAACcCTCCAGCGGGTAGCAGTC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gáliková, E.; Přikryl, D.; Prost, S.; Kučerová, D.; Trejbalová, K.; Hejnar, J. Single Amino Acid Residue W33 of tva Receptor Is Critical for Viral Entry and High-Affinity Binding of Avian Leukosis Virus Subgroup K. Viruses 2025, 17, 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050709
Gáliková E, Přikryl D, Prost S, Kučerová D, Trejbalová K, Hejnar J. Single Amino Acid Residue W33 of tva Receptor Is Critical for Viral Entry and High-Affinity Binding of Avian Leukosis Virus Subgroup K. Viruses. 2025; 17(5):709. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050709
Chicago/Turabian StyleGáliková, Eliška, David Přikryl, Salomé Prost, Dana Kučerová, Kateřina Trejbalová, and Jiří Hejnar. 2025. "Single Amino Acid Residue W33 of tva Receptor Is Critical for Viral Entry and High-Affinity Binding of Avian Leukosis Virus Subgroup K" Viruses 17, no. 5: 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050709
APA StyleGáliková, E., Přikryl, D., Prost, S., Kučerová, D., Trejbalová, K., & Hejnar, J. (2025). Single Amino Acid Residue W33 of tva Receptor Is Critical for Viral Entry and High-Affinity Binding of Avian Leukosis Virus Subgroup K. Viruses, 17(5), 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050709






