Long-Term Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Variant-Specific Neutralizing Antibodies Following mRNA Vaccination and Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
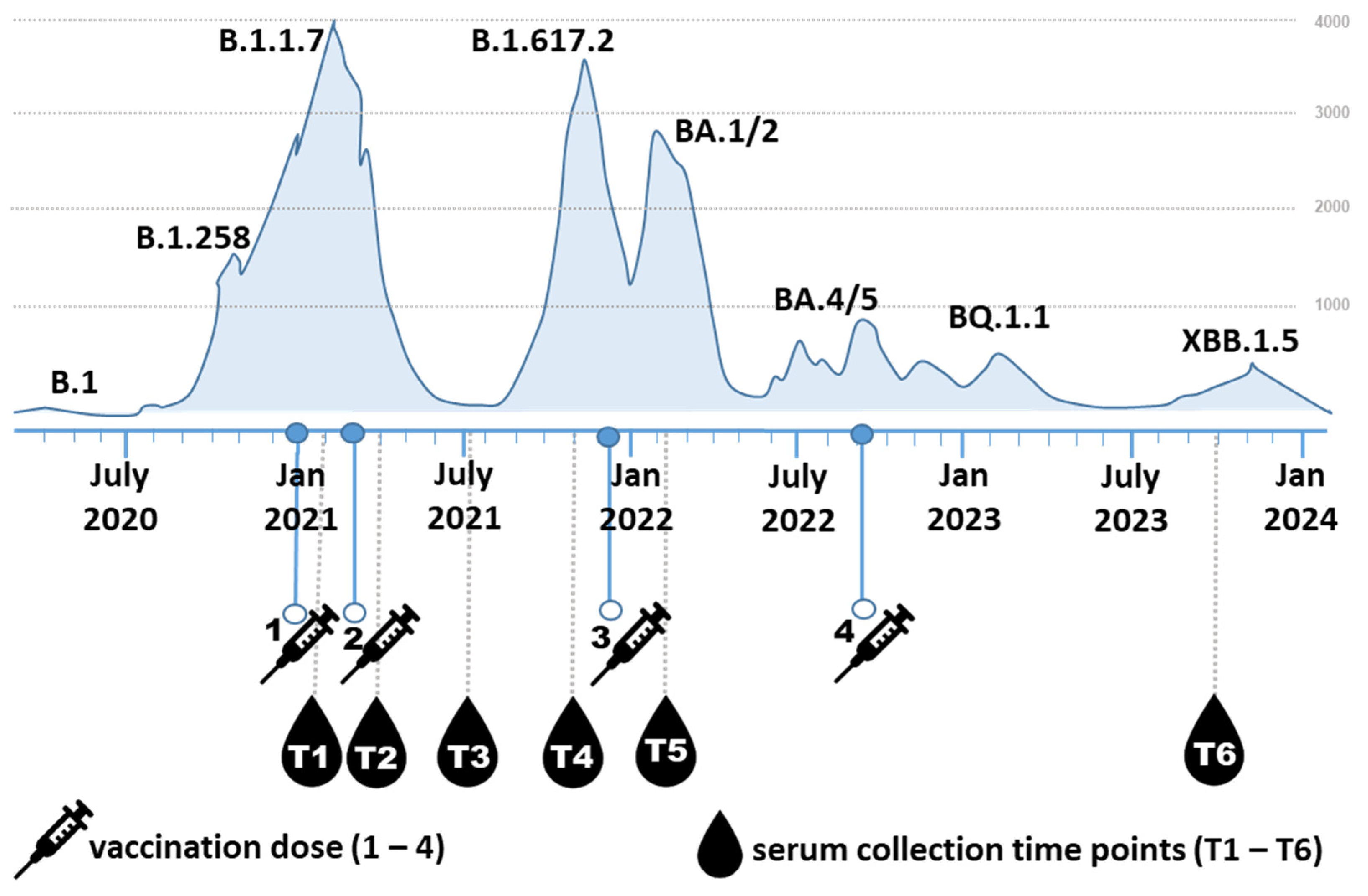
2.1. Participants
2.2. Plasmids
2.3. Cell Lines
2.4. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Pseudotype-Based Neutralization Assay
2.5. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 IgG Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
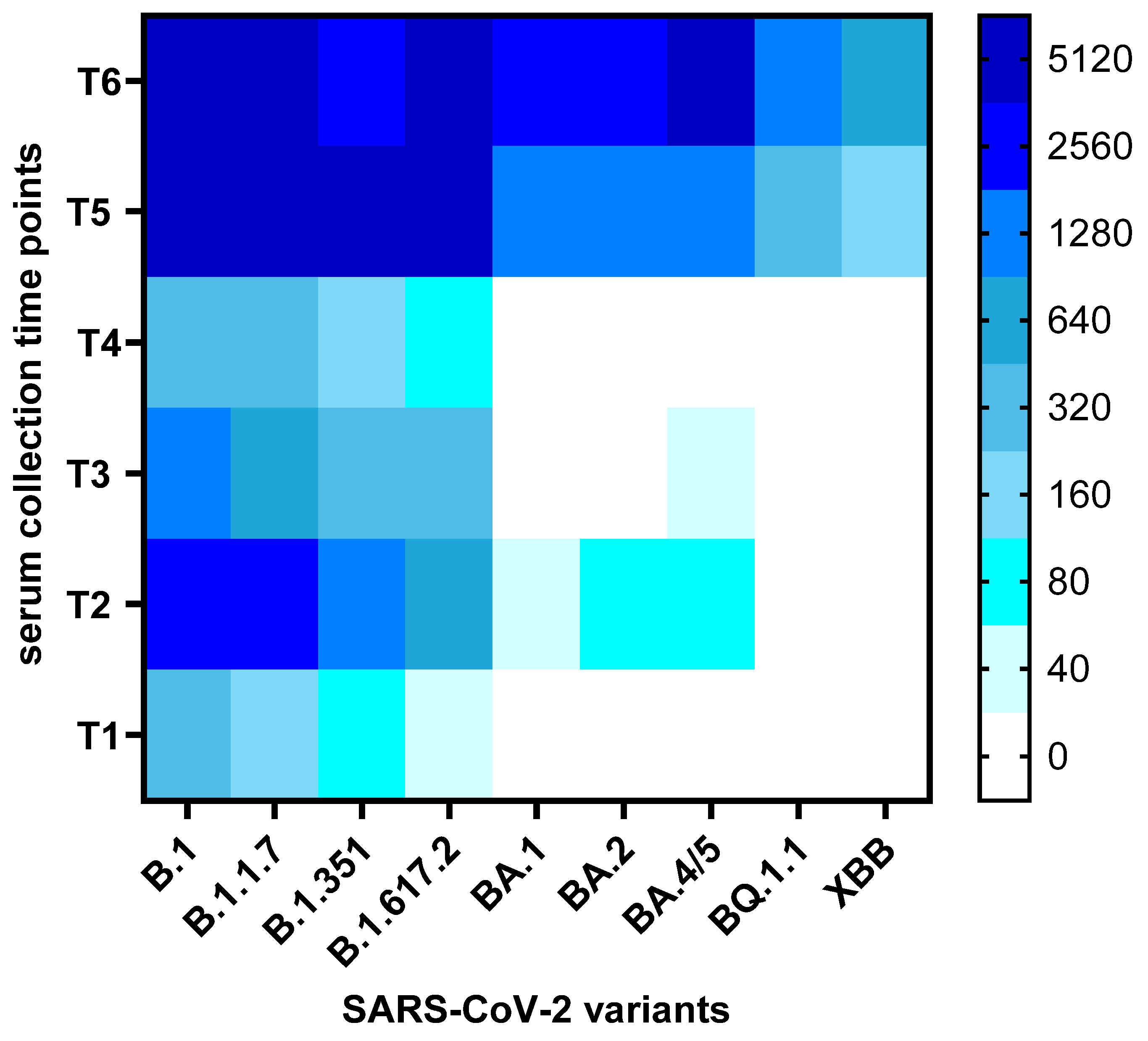
3. Results
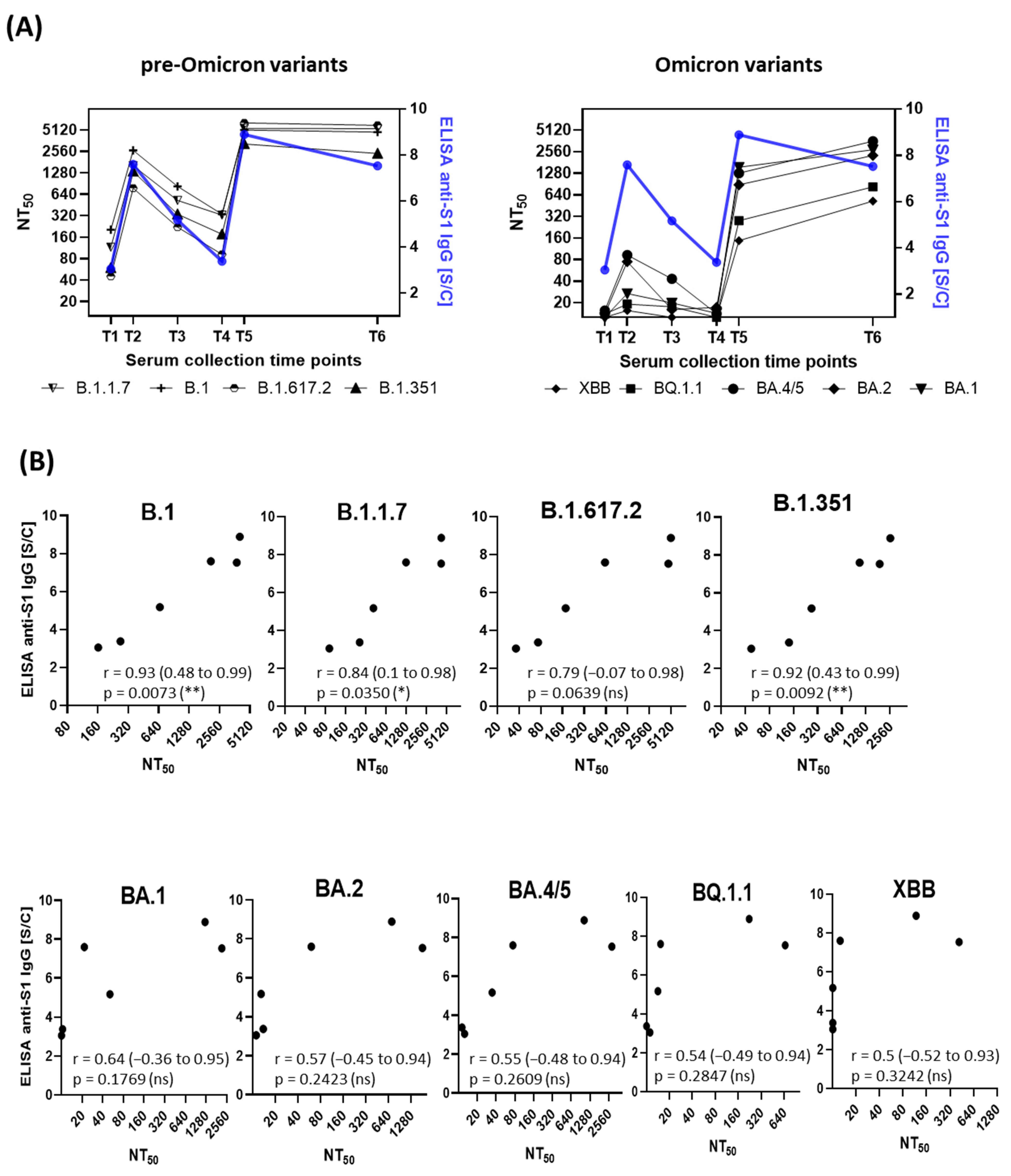
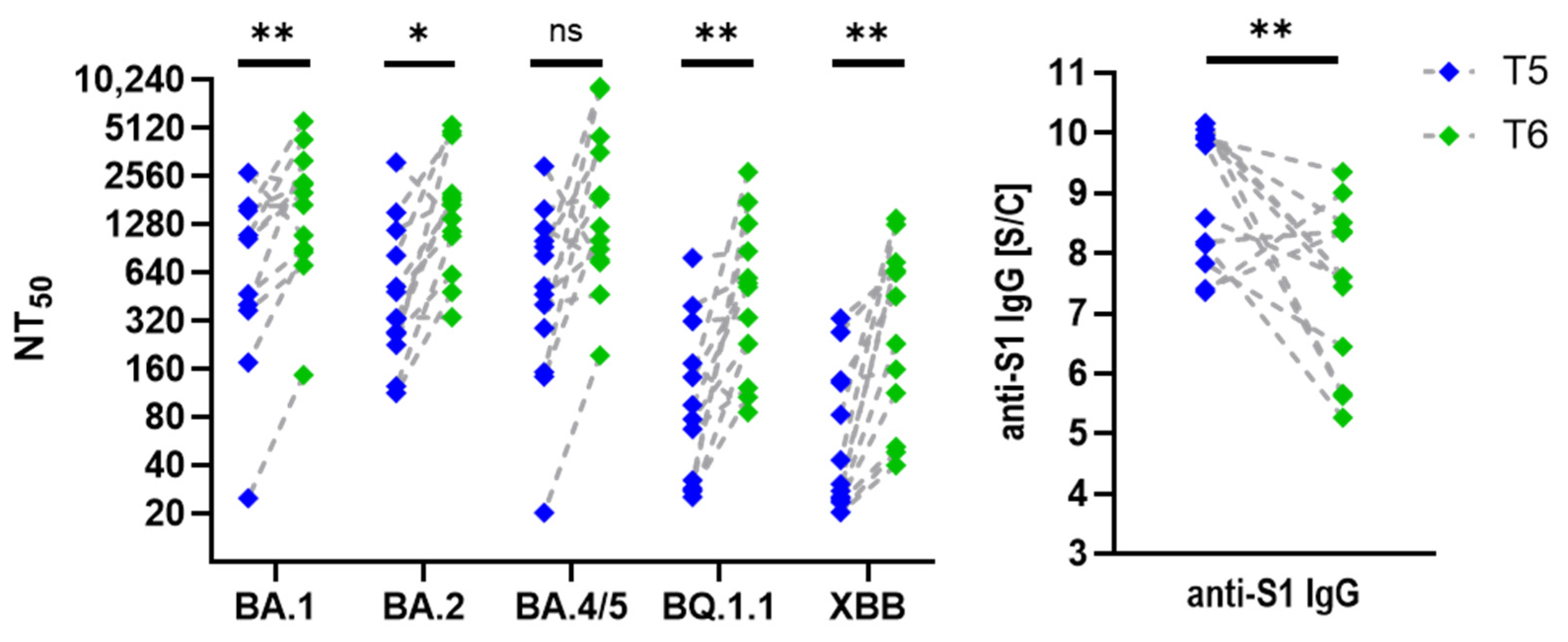
3.1. Correlation of Anti-SARS-CoV-2-S1 IgG Antibodies with Neutralization Titers
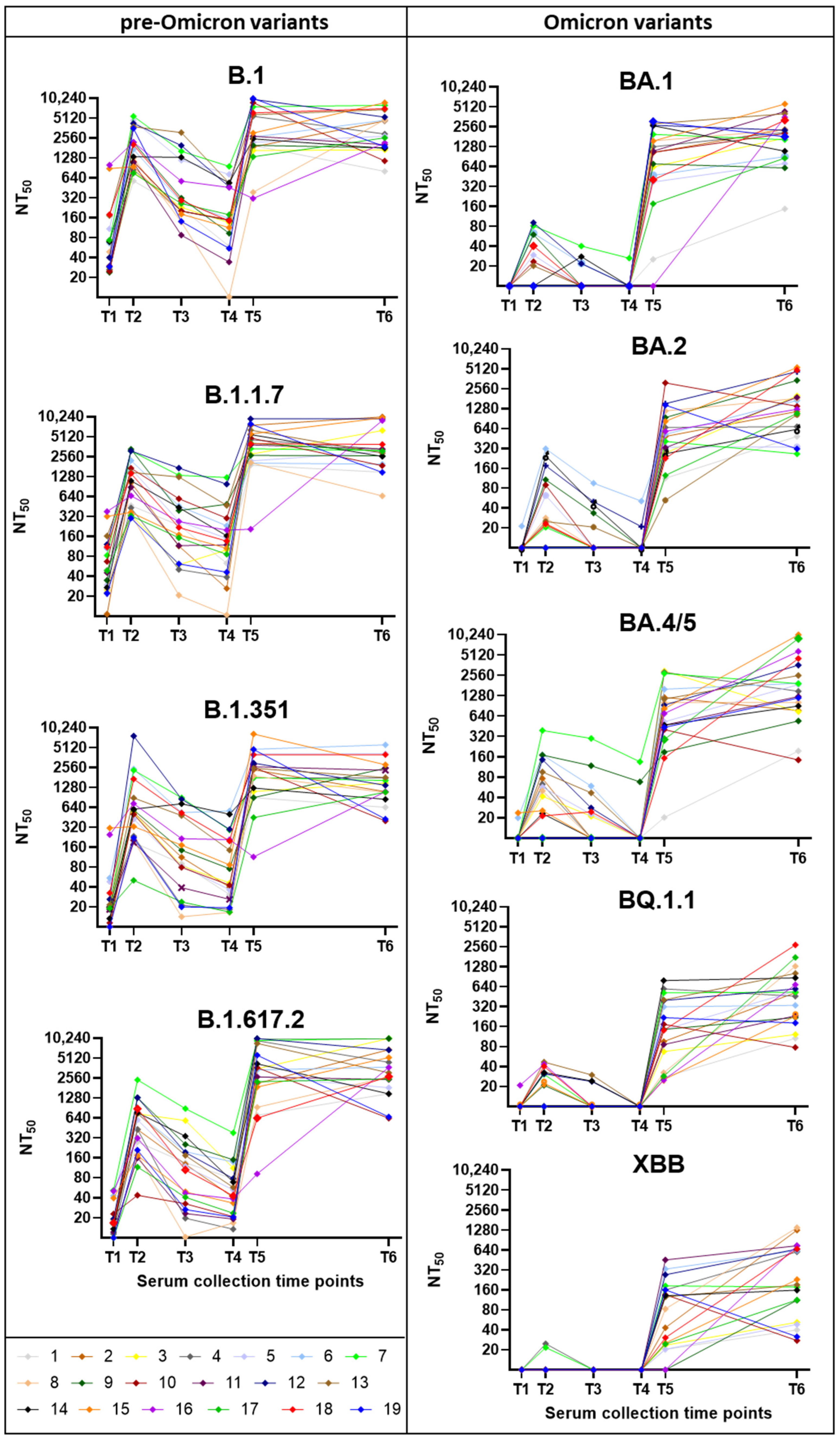
3.2. Neutralization Trends Across Virus Variants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhama, K.; Khan, S.; Tiwari, R.; Sircar, S.; Bhat, S.; Malik, Y.S.; Singh, K.P.; Chaicumpa, W.; Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J. Coronavirus Disease 2019—COVID-19. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anamika; Khanka, S.; Chandra, G.; Singh, K.; Jamloki, D.; Naaz, F.; Gupta, B. Review on Various Type of Vaccines for Controlling Infectious Disease. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 3, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleem, B.; Zareef, R.; Bitar, F.; Arabi, M. Myocarditis in COVID-19: A Focus on the Pediatric Population. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 13, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Sette, A.; Crotty, S. Immunological Memory to SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Vaccines. Immunol. Rev. 2022, 310, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, J.M.; Mateus, J.; Kato, Y.; Hastie, K.M.; Yu, E.D.; Faliti, C.E.; Grifoni, A.; Ramirez, S.I.; Haupt, S.; Frazier, A.; et al. Immunological Memory to SARS-CoV-2 Assessed for up to 8 Months after Infection. Science 2021, 371, eabf4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.S.; O’Halloran, J.A.; Kalaidina, E.; Kim, W.; Schmitz, A.J.; Zhou, J.Q.; Lei, T.; Thapa, M.; Chen, R.E.; Case, J.B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines Induce Persistent Human Germinal Centre Responses. Nature 2021, 596, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, K.W.; Linderman, S.L.; Moodie, Z.; Czartoski, J.; Lai, L.; Mantus, G.; Norwood, C.; Nyhoff, L.E.; Edara, V.V.; Floyd, K.; et al. Longitudinal Analysis Shows Durable and Broad Immune Memory after SARS-CoV-2 Infection with Persisting Antibody Responses and Memory B and T Cells. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murin, C.D.; Wilson, I.A.; Ward, A.B. Antibody Responses to Viral Infections: A Structural Perspective across Three Different Enveloped Viruses. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Liao, G.; Chen, Y.; Hu, C.-H. Patterns of IgG and IgM Antibody Response in COVID-19 Patients. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, M.S. Durability of Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Vaccination. Semin. Immunol. 2024, 73, 101884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Huillier, A.G.; Meyer, B.; Andrey, D.O.; Arm-Vernez, I.; Baggio, S.; Didierlaurent, A.; Eberhardt, C.S.; Eckerle, I.; Grasset-Salomon, C.; Huttner, A.; et al. Antibody Persistence in the First 6 Months Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Hospital Workers: A Prospective Longitudinal Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 784.e1–784.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, D.; Nyhoff, L.E.; Zarnitsyna, V.I.; Moreno, A.; Manning, K.; Linderman, S.; Burrell, A.R.; Stephens, K.; Norwood, C.; Mantus, G.; et al. Infants and Young Children Generate More Durable Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection than Adults. iScience 2023, 26, 107967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shook, L.L.; Atyeo, C.G.; Yonker, L.M.; Fasano, A.; Gray, K.J.; Alter, G.; Edlow, A.G. Durability of Anti-Spike Antibodies in Infants After Maternal COVID-19 Vaccination or Natural Infection. JAMA 2022, 327, 1087–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Du, L. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein: A Key Target for Eliciting Persistent Neutralizing Antibodies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Shan, C.; Duan, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, P.; Song, J.; Song, T.; Bi, X.; Han, C.; Wu, L.; et al. A Human Neutralizing Antibody Targets the Receptor-Binding Site of SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 584, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affeldt, P.; Koehler, F.C.; Brensing, K.A.; Adam, V.; Burian, J.; Butt, L.; Gies, M.; Grundmann, F.; Hinrichs, S.; Johannis, W.; et al. Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Vaccination in Dialysis Patients and Kidney Transplant Recipients. Microorganisms 2021, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo-Herrera, M.; Rincón-Orozco, B.; González-Escobar, J.M.; Herrera-Arévalo, S.M.; Carrasquilla-Agudelo, E.; Serna-Ortega, P.A.; Quiceno-García, S.; Palacio-Muñoz, N.; Rosero-López, B.; Mondol-Miranda, E.; et al. Longitudinal Follow-Up of the Specific Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Colombia. J. Med. Virol. 2025, 97, e70133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, B.; Richter, E.; Büning, A.; Baum, M.; Breuer, A.; Zorn, J.; König, J.; Geiger, M.; Eschbach-Bludau, M.; Heuser, J.; et al. A Longitudinal Study on SARS-CoV-2 Seroconversion, Reinfection and Neutralisation Spanning Several Variant Waves and Vaccination Campaigns, Heinsberg, Germany, April 2020 to November 2022. Eurosurveillance 2024, 29, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tworek, A.; Jaroń, K.; Cicha, M.; Rydzewski, A.; Wierzba, W.; Zaczyński, A.; Król, Z.; Rydzewska, G. The Persistence of SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizingantibodies after COVID-19: A One-Yearobservation. Is a SARS-CoV-2 Vaccinationbooster Dose Necessary? Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 48, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiano, F.; Ireland, G.; Baawuah, F.; Beckmann, J.; Okike, I.O.; Ahmad, S.; Garstang, J.; Brent, A.J.; Brent, B.; Borrow, R.; et al. Antibody Persistence After Primary SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Protection Against Future Variants Including Omicron in Adolescents: National, Prospective Cohort Study. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2023, 42, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunathilake, R.P.; Kumara, R.A.; Karunathilaka, A.; Wazil, A.W.M.; Nanayakkara, N.; Bandara, C.K.; Abeysekera, R.A.; Noordeen, F.; Gawarammana, I.B.; Ratnatunga, C.N. 18-Month Longitudinal SARS COV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Dynamics in Haemodialysis Patients Receiving Heterologous 3-Dose Vaccination (AZD-1222- AZD-1222- BNT162b2) in a Lower Middle Income Setting. BMC Nephrol. 2024, 25, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitt, M.A. Generation of VSV Pseudotypes Using Recombinant ΔG-VSV for Studies on Virus Entry, Identification of Entry Inhibitors, and Immune Responses to Vaccines. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 169, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhao, C.; Hao, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Nie, L.; Qin, H.; Wang, M.; et al. Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody by a Pseudotyped Virus-Based Assay. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 3699–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condor Capcha, J.M.; Lambert, G.; Dykxhoorn, D.M.; Salerno, A.G.; Hare, J.M.; Whitt, M.A.; Pahwa, S.; Jayaweera, D.T.; Shehadeh, L.A. Generation of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Pseudotyped Virus for Viral Entry and Neutralization Assays: A 1-Week Protocol. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 7, 618651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCZI.sk. Available online: https://Covid-19.Nczisk.Sk/Sk (accessed on 13 November 2024).
- Kowarz, E.; Löscher, D.; Marschalek, R. Optimized Sleeping Beauty Transposons Rapidly Generate Stable Transgenic Cell Lines. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yewdell, J.W.; Li, T.; Kang, I.; Hu, Z.; Gibbs, J.; Ye, C.; Kosik, I.; Shi, G.; Holly, J.; Kosikova, M.; et al. Syncytia Formation Promotes Virus Resistance to Interferon and Neutralizing Antibodies 2024. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-3846435/v1 (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Xiong, H.-L.; Wu, Y.-T.; Cao, J.-L.; Yang, R.; Liu, Y.-X.; Ma, J.; Qiao, X.-Y.; Yao, X.-Y.; Zhang, B.-H.; Zhang, Y.-L.; et al. Robust Neutralization Assay Based on SARS-CoV-2 S-Protein-Bearing Vesicular Stomatitis Virus (VSV) Pseudovirus and ACE2-Overexpressing BHK21 Cells. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2105–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, C.; Baty, F.; Streibig, J.C.; Gerhard, D. Dose-Response Analysis Using R. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0146021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2. WIREs Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, B.T.; Bryan, A.; Fink, S.L.; Goecker, E.A.; Roychoudhury, P.; Huang, M.-L.; Zhu, H.; Chaudhary, A.; Madarampalli, B.; Lu, J.Y.C.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Levels Measured by the AdviseDx SARS-CoV-2 Assay Are Concordant with Previously Available Serologic Assays but Are Not Fully Predictive of Sterilizing Immunity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e00989-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajanova, I.; Lukacikova, L.; Jelenska, L.; Grossmannova, K.; Radikova, Z.; Vlcek, M.; Klempa, B.; Kollar, R.; Bodova, K.; Kopacek, J.; et al. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 IgG Antibodies in the Staff of the Slovak Academy of Sciences in Response to COVID-19 and/or Vaccination: Situation in August 2021. Acta Virol. 2022, 65, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Ito, J.; Uriu, K.; Zahradnik, J.; Kida, I.; Anraku, Y.; Nasser, H.; Shofa, M.; Oda, Y.; Lytras, S.; et al. Virological Characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 XBB Variant Derived from Recombination of Two Omicron Subvariants. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, J.; Ardizzone, C.M.; Khanna, M.; Trauth, A.J.; Hagensee, M.E.; Ramsay, A.J. Dynamics of Serum-Neutralizing Antibody Responses in Vaccinees through Multiple Doses of the BNT162b2 Vaccine. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Phillips, D.J.; White, T.; Sayal, H.; Aley, P.K.; Bibi, S.; Dold, C.; Fuskova, M.; Gilbert, S.C.; Hirsch, I.; et al. Correlates of Protection against Symptomatic and Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 2032–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing Antibody Levels Are Highly Predictive of Immune Protection from Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaebler, C.; Wang, Z.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Muecksch, F.; Finkin, S.; Tokuyama, M.; Cho, A.; Jankovic, M.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Oliveira, T.Y.; et al. Evolution of Antibody Immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 591, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, A.; Chappert, P.; Barba-Spaeth, G.; Roeser, A.; Fourati, S.; Azzaoui, I.; Vandenberghe, A.; Fernandez, I.; Meola, A.; Bouvier-Alias, M.; et al. Maturation and Persistence of the Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Memory B Cell Response. Cell 2021, 184, 1201–1213.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreano, E.; Paciello, I.; Piccini, G.; Manganaro, N.; Pileri, P.; Hyseni, I.; Leonardi, M.; Pantano, E.; Abbiento, V.; Benincasa, L.; et al. Hybrid Immunity Improves B Cells and Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Nature 2021, 600, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, R.R.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Painter, M.M.; Mathew, D.; Pattekar, A.; Kuthuru, O.; Gouma, S.; Hicks, P.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; et al. Distinct Antibody and Memory B Cell Responses in SARS-CoV-2 Naïve and Recovered Individuals Following mRNA Vaccination. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabi6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrovitz, N.; Ware, H.; Ma, X.; Li, Z.; Hosseini, R.; Cao, C.; Selemon, A.; Whelan, M.; Premji, Z.; Issa, H.; et al. Protective Effectiveness of Previous SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Hybrid Immunity against the Omicron Variant and Severe Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas, D.; Bruel, T.; Staropoli, I.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Porrot, F.; Maes, P.; Grzelak, L.; Prot, M.; Mougari, S.; Planchais, C.; et al. Resistance of Omicron Subvariants BA.2.75.2, BA.4.6, and BQ.1.1 to Neutralizing Antibodies. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Iketani, S.; Guo, Y.; Chan, J.F.-W.; Wang, M.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Chu, H.; Huang, Y.; Nair, M.S.; et al. Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2022, 602, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatatos, L.; Czartoski, J.; Wan, Y.-H.; Homad, L.J.; Rubin, V.; Glantz, H.; Neradilek, M.; Seydoux, E.; Jennewein, M.F.; MacCamy, A.J.; et al. mRNA Vaccination Boosts Cross-Variant Neutralizing Antibodies Elicited by SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Science 2021, 372, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Iketani, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Bowen, A.D.; Liu, M.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; et al. Alarming Antibody Evasion Properties of Rising SARS-CoV-2 BQ and XBB Subvariants. Cell 2023, 186, 279–286.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, B.; Sun, J.; Zou, L.; Yi, L.; Lin, H.; Zhou, P.; Liang, C.; Zeng, L.; Zhuang, X.; et al. Immune Evasion after SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.5 and XBB.1.9 Endemic Observed from Guangdong Province, China from 2022 to 2023. Virol. J. 2024, 21, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreano, E.; Paciello, I.; Marchese, S.; Donnici, L.; Pierleoni, G.; Piccini, G.; Manganaro, N.; Pantano, E.; Abbiento, V.; Pileri, P.; et al. Anatomy of Omicron BA.1 and BA.2 Neutralizing Antibodies in COVID-19 mRNA Vaccinees. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruell, H.; Vanshylla, K.; Tober-Lau, P.; Hillus, D.; Schommers, P.; Lehmann, C.; Kurth, F.; Sander, L.E.; Klein, F. mRNA Booster Immunization Elicits Potent Neutralizing Serum Activity against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterle, M.E.; Haslwanter, D.; Bortz, R.H.; Wirchnianski, A.S.; Lasso, G.; Vergnolle, O.; Abbasi, S.A.; Fels, J.M.; Laudermilch, E.; Florez, C.; et al. A Replication-Competent Vesicular Stomatitis Virus for Studies of SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Mediated Cell Entry and Its Inhibition. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 486–496.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholukh, A.M.; Fiore-Gartland, A.; Ford, E.S.; Miner, M.D.; Hou, Y.J.; Tse, L.V.; Kaiser, H.; Zhu, H.; Lu, J.; Madarampalli, B.; et al. Evaluation of Cell-Based and Surrogate SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Assays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0052721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettl, F.; Meister, T.L.; Vollmer, T.; Fischer, B.; Steinmann, J.; Krawczyk, A.; V’kovski, P.; Todt, D.; Steinmann, E.; Pfaender, S.; et al. Rapid Quantification of SARS-CoV-2-Neutralizing Antibodies Using Propagation-Defective Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Pseudotypes. Vaccines 2020, 8, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoni, D.; Wilkie, C.; Bentley, E.M.; Mayora-Neto, M.; Wright, E.; Scott, S.; Ray, S.; Castillo-Olivares, J.; Heeney, J.L.; Mattiuzzo, G.; et al. Correlation between Pseudotyped Virus and Authentic Virus Neutralisation Assays, a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1184362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Apice, L.; Trovato, M.; Gramigna, G.; Colavita, F.; Francalancia, M.; Matusali, G.; Meschi, S.; Lapa, D.; Bettini, A.; Mizzoni, K.; et al. Comparative Analysis of the Neutralizing Activity against SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan-Hu-1 Strain and Variants of Concern: Performance Evaluation of a Pseudovirus-Based Neutralization Assay. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 981693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolah, A.M.K.; Sohrab, S.S.; Tolah, K.M.K.; Hassan, A.M.; El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Azhar, E.I. Evaluation of a Pseudovirus Neutralization Assay for SARS-CoV-2 and Correlation with Live Virus-Based Micro Neutralization Assay. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torán-Monserrat, P.; Lamonja-Vicente, N.; Costa-Garrido, A.; Carrasco-Ribelles, L.A.; Quirant, B.; Boigues, M.; Molina, X.; Chacón, C.; Dacosta-Aguayo, R.; Arméstar, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Risk by Vaccine Doses and Prior Infections Over 24 Months: ProHEpiC-19 Longitudinal Study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024, 10, e56926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, K.; Carreño, J.M.; Gleason, C.; Monahan, B.; Singh, G.; Abbad, A.; Tcheou, J.; Raskin, A.; Kleiner, G.; Van Bakel, H.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-Infection- and Vaccine-Induced Antibody Responses Are Long Lasting with an Initial Waning Phase Followed by a Stabilization Phase. Immunity 2024, 57, 587–599.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvidt, A.K.; Guo, H.; Andersen, R.; Lende, S.S.F.; Vibholm, L.K.; Søgaard, O.S.; Schleimann, M.H.; Russell, V.; Cheung, A.M.-W.; Paramithiotis, E.; et al. Long-Term Humoral and Cellular Immunity after Primary SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A 20-Month Longitudinal Study. BMC Immunol. 2023, 24, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaňová, V.; Náhliková, J.; Ličková, M.; Sláviková, M.; Kajanová, I.; Lukáčiková, Ľ.; Sabo, M.; Rádiková, Ž.; Pastoreková, S.; Klempa, B. Long-Term Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Variant-Specific Neutralizing Antibodies Following mRNA Vaccination and Infection. Viruses 2025, 17, 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050675
Vaňová V, Náhliková J, Ličková M, Sláviková M, Kajanová I, Lukáčiková Ľ, Sabo M, Rádiková Ž, Pastoreková S, Klempa B. Long-Term Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Variant-Specific Neutralizing Antibodies Following mRNA Vaccination and Infection. Viruses. 2025; 17(5):675. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050675
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaňová, Veronika, Jana Náhliková, Martina Ličková, Monika Sláviková, Ivana Kajanová, Ľubomíra Lukáčiková, Miroslav Sabo, Žofia Rádiková, Silvia Pastoreková, and Boris Klempa. 2025. "Long-Term Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Variant-Specific Neutralizing Antibodies Following mRNA Vaccination and Infection" Viruses 17, no. 5: 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050675
APA StyleVaňová, V., Náhliková, J., Ličková, M., Sláviková, M., Kajanová, I., Lukáčiková, Ľ., Sabo, M., Rádiková, Ž., Pastoreková, S., & Klempa, B. (2025). Long-Term Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Variant-Specific Neutralizing Antibodies Following mRNA Vaccination and Infection. Viruses, 17(5), 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050675





