A Novel Nobecovirus in an Epomophorus wahlbergi Bat from Nairobi, Kenya
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
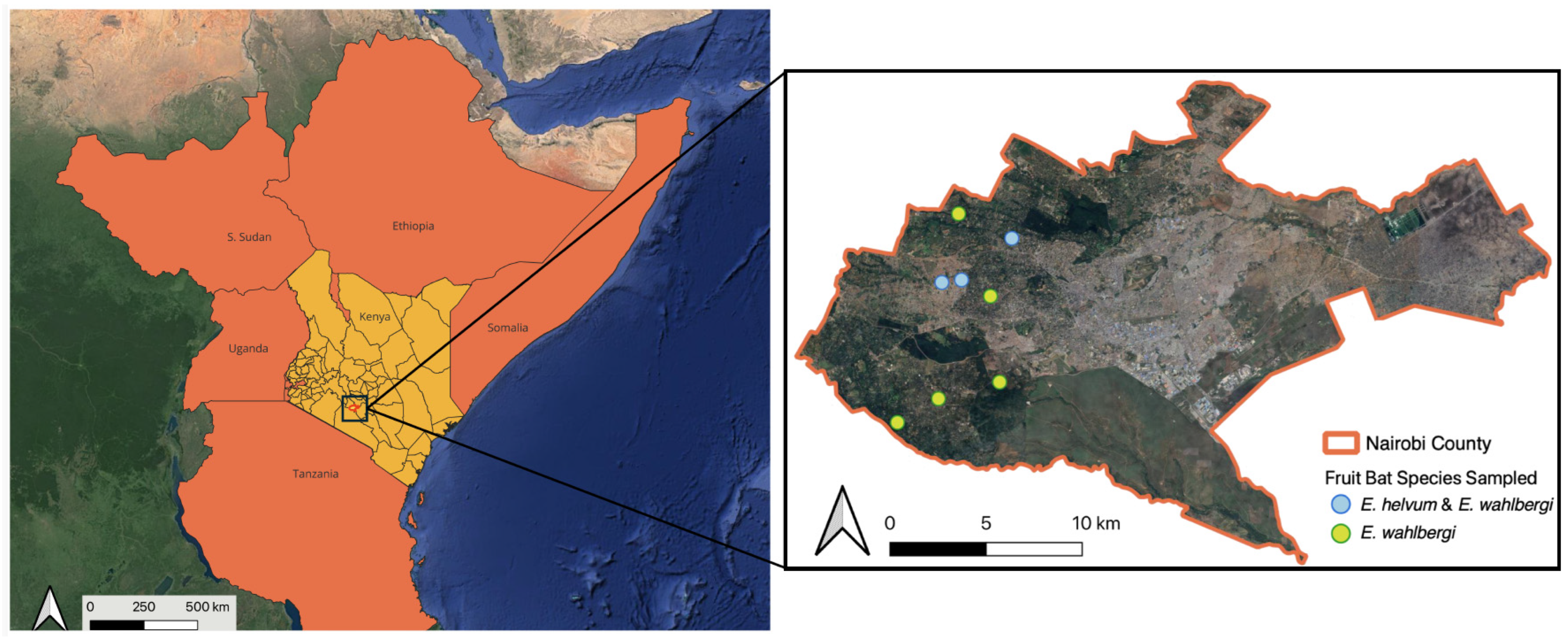
2.1. Study Area and Bat Sampling
2.2. Sample Processing and Library Preparation
2.3. Data Processing and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
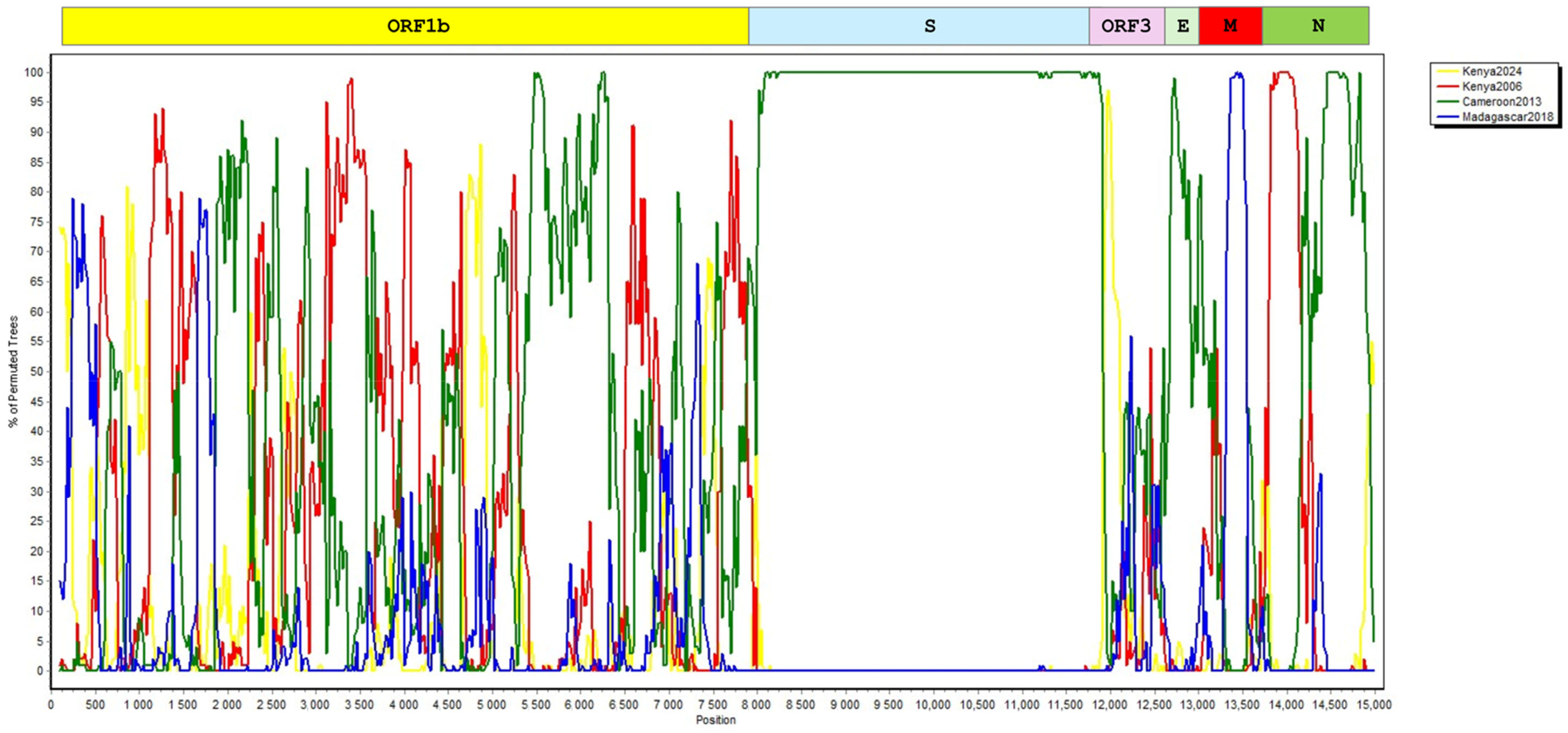
3.1. Genome Annotation and Phylogenetic and Recombination Analyses
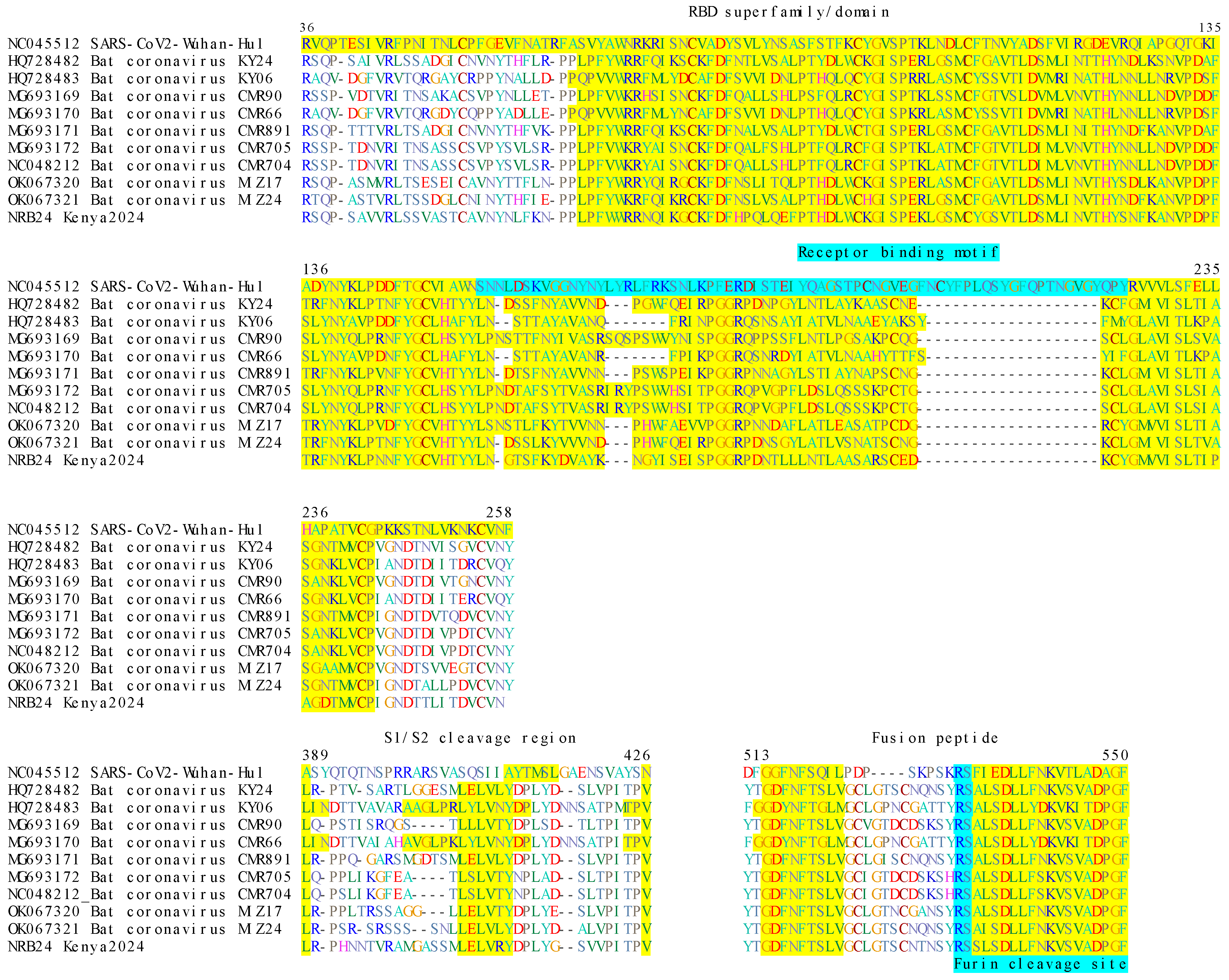
3.2. Analysis of Putative Viral Proteins
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plowright, R.K. Land Use-Induced Spillover: A Call to Action to Safeguard Environmental. Anim. Hum. Health 2021, 5, e237–e245. [Google Scholar]
- Plowright, R.K.; Parrish, C.R.; McCallum, H.; Hudson, P.J.; Ko, A.I.; Graham, A.L.; Lloyd-Smith, J.O. Pathways to Zoonotic Spillover. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, C.J.; Zipfel, C.M.; Garnier, R.; Bansal, S. Global Estimates of Mammalian Viral Diversity Accounting for Host Sharing. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olival, K.J.; Hosseini, P.R.; Zambrana-Torrelio, C.; Ross, N.; Bogich, T.L.; Daszak, P. Host and Viral Traits Predict Zoonotic Spillover from Mammals. Nature 2017, 546, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollentze, N.; Streicker, D.G. Viral Zoonotic Risk Is Homogenous among Taxonomic Orders of Mammalian and Avian Reservoir Hosts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9423–9430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.A.; Kramer, A.M.; Drake, J.M. Global Patterns of Zoonotic Disease in Mammals. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, C.E.; Dobson, A.P. Bats as ‘Special’ Reservoirs for Emerging Zoonotic Pathogens. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, M.; Anderson, D.E.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, C.W.; Lim, B.L.; Luko, K.; Wen, M.; Chia, W.N.; Mani, S.; Wang, L.C.; et al. Dampened NLRP3-Mediated Inflammation in Bats and Implications for a Special Viral Reservoir Host. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, C.E.; Boots, M.; Chandran, K.; Dobson, A.P.; Drosten, C.; Graham, A.L.; Grenfell, B.T.; Müller, M.A.; Ng, M.; Wang, L.-F.; et al. Accelerated Viral Dynamics in Bat Cell Lines, with Implications for Zoonotic Emergence. eLife 2020, 9, e48401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shi, Z.; Yu, M.; Ren, W.; Smith, C.; Epstein, J.H.; Wang, H.; Crameri, G.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. Bats Are Natural Reservoirs of SARS-Like Coronaviruses. Science 2005, 310, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytras, S.; Hughes, J.; Martin, D.; Swanepoel, P.; De Klerk, A.; Lourens, R.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Xia, W.; Jiang, X.; Robertson, D.L. Exploring the Natural Origins of SARS-CoV-2 in the Light of Recombination. Genome Biol. Evol. 2022, 14, evac018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytras, S.; Xia, W.; Hughes, J.; Jiang, X.; Robertson, D.L. The Animal Origin of SARS-CoV-2. Science 2021, 373, 968–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.K.; Hitchens, P.L.; Pandit, P.S.; Rushmore, J.; Evans, T.S.; Young, C.C.W.; Doyle, M.M. Global Shifts in Mammalian Population Trends Reveal Key Predictors of Virus Spillover Risk. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20192736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammal Diversity Database, Mammal Diversity Database (Version 2.0). Zenodo 2025. [CrossRef]
- Raven, P.H.; Gereau, R.E.; Phillipson, P.B.; Chatelain, C.; Jenkins, C.N.; Ulloa, C.U. The Distribution of Biodiversity Richness in the Tropics. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herkt, K.M.B.; Barnikel, G.; Skidmore, A.K.; Fahr, J. A High-Resolution Model of Bat Diversity and Endemism for Continental Africa. Ecol. Model. 2016, 320, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, B.D.; Webala, P. Keys to the Bats (Mammalia: Chiroptera) of East Africa. Fieldiana Life Earth Sci. 2012, 2012, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musila, S.; Monadjem, A.; Webala, P.W.; Patterson, B.D.; Hutterer, H.; De Jong, Y.A.; Butynski, T.M.; Mwangi, G.; Chen, Z.Z. An Annotated Checklist of Mammals of Kenya. Zool. Res. 2018, 40, 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassell, J.M.; Muloi, D.M.; VanderWaal, K.L.; Ward, M.J.; Bettridge, J.; Gitahi, N.; Ouko, T.; Imboma, T.; Akoko, J.; Karani, M.; et al. Epidemiological Connectivity between Humans and Animals across an Urban Landscape. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2218860120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrardy, C.; Tao, Y.; Kuzmin, I.V.; Niezgoda, M.; Agwanda, B.; Breiman, R.F.; Anderson, L.J.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Tong, S. Molecular Detection of Adenoviruses, Rhabdoviruses, and Paramyxoviruses in Bats from Kenya. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 91, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareinen, L.; Ogola, J.; Kivistö, I.; Smura, T.; Aaltonen, K.; Jääskeläinen, A.J.; Kibiwot, S.; Masika, M.M.; Nyaga, P.; Mwaengo, D.; et al. Range Expansion of Bombali Virus in Mops Condylurus Bats, Kenya, 2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 3007–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzmin, I.V.; Niezgoda, M.; Franka, R.; Agwanda, B.; Markotter, W.; Breiman, R.F.; Shieh, W.J.; Zaki, S.R. Marburg Virus in Fruit Bat, Kenya. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 352–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Tang, K.; Shi, M.; Conrardy, C.; Li, K.S.M.; Lau, S.K.P.; Anderson, L.J.; Tong, S. Genomic Characterization of Seven Distinct Bat Coronaviruses in Kenya. Virus Res. 2012, 167, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Conrardy, C.; Ruone, S.; Kuzmin, I.V.; Guo, X.; Tao, Y.; Niezgoda, M.; Haynes, L.; Agwanda, B.; Breiman, R.F.; et al. Detection of Novel SARS-like and Other Coronaviruses in Bats from Kenya. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waruhiu, C.; Ommeh, S.; Obanda, V.; Agwanda, B.; Gakuya, F.; Ge, X.-Y.; Yang, X.-L.; Wu, L.-J.; Zohaib, A.; Hu, B.; et al. Molecular Detection of Viruses in Kenyan Bats and Discovery of Novel Astroviruses, Caliciviruses and Rotaviruses. Virol. Sin. 2017, 32, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamau, J.; Ergunay, K.; Webala, P.W.; Justi, S.A.; Bourke, B.P.; Kamau, M.W.; Hassell, J.; Chege, M.N.; Mwaura, D.K.; Simiyu, C.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus and a Broad Range of Viruses in Kenyan Cave Bats. Viruses 2022, 14, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.; de Groot, R.; Haagmans, B.; Lau, S.; Neuman, B.; Perlman, S.; Sola, I.; van der Hoek, L.; Wong, A.; Yeh, S.-H. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Coronaviridae 2023. J. Gen. Virol. 2023, 104, 001843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zeng, L.-P.; Yang, X.-L.; Ge, X.-Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Xie, J.-Z.; Shen, X.-R.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Wang, N.; et al. Discovery of a Rich Gene Pool of Bat SARS-Related Coronaviruses Provides New Insights into the Origin of SARS Coronavirus. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, S.J.; Gilardi, K.; Menachery, V.D.; Goldstein, T.; Ssebide, B.; Mbabazi, R.; Navarrete-Macias, I.; Liang, E.; Wells, H.; Hicks, A.; et al. Further Evidence for Bats as the Evolutionary Source of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. mBio 2017, 8, e00373-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frutos, R.; Serra-Cobo, J.; Pinault, L.; López-Roig, M.; Devaux, C. Emergence of Bat-Related Betacoronaviruses: Hazard and Risks. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 591535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.C.P.; Li, X.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y. Global Epidemiology of Bat Coronaviruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muloi, D.M.; Wee, B.A.; McClean, D.M.H.; Ward, M.J.; Pankhurst, L.; Phan, H.; Ivens, A.C.; Kivali, V.; Kiyong’a, A.; Ndinda, C.; et al. Population Genomics of Escherichia Coli in Livestock-Keeping Households across a Rapidly Developing Urban Landscape. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- REDI-NET Consortium REDI-NET: SW-2 SWAB PROCESSING. protocols.io 2024. [CrossRef]
- REDI-NET Consortium REDI-NET: SW-4 SWAB TESTING. protocols.io 2024. [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Holt, K.E. Performance of Neural Network Basecalling Tools for Oxford Nanopore Sequencing. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coster, W.; D’Hert, S.; Schultz, D.T.; Cruts, M.; Van Broeckhoven, C. NanoPack: Visualizing and Processing Long-Read Sequencing Data. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2666–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve Years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise Alignment for Nucleotide Sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Reuter, K.; Drost, H. Sensitive Protein Alignments at Tree-of-Life Scale Using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, D.; Beier, S.; Flade, I.; Górska, A.; El-Hadidi, M.; Mitra, S.; Ruscheweyh, H.-J.; Tappu, R. MEGAN Community Edition—Interactive Exploration and Analysis of Large-Scale Microbiome Sequencing Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of Long, Error-Prone Reads Using Repeat Graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the Sensitivity of Progressive Multiple Sequence Alignment through Sequence Weighting, Position-Specific Gap Penalties and Weight Matrix Choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, A.; Birney, E.; Cerruti, L.; Ettwiller, L.; Eddy, S.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Howe, K.; Marshall, M.; Sonnhammer, E. The Pfam Protein Families Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Derbyshire, M.; Gonzales, N.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Geer, L.; Geer, R.; He, J.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.; et al. CDD: NCBI’s Conserved Domain Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 43, D222–D226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; Von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; Von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast Approximation for Phylogenetic Bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and Analysis of Recombination Patterns in Virus Genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lole, K.S.; Bollinger, R.C.; Paranjape, R.S.; Gadkari, D.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Novak, N.G.; Ingersoll, R.; Sheppard, H.W.; Ray, S.C. Full-Length Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Genomes from Subtype C-Infected Seroconverters in India, with Evidence of Intersubtype Recombination. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Zhu, Q.; Hohl, J.; Dong, A.; Schlick, T. Evolution of Coronavirus Frameshifting Elements: Competing Stem Networks Explain Conservation and Variability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2221324120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettenburg, G.; Kistler, A.; Ranaivoson, H.C.; Ahyong, V.; Andrianiaina, A.; Andry, S.; DeRisi, J.L.; Gentles, A.; Raharinosy, V.; Randriambolamanantsoa, T.H.; et al. Full Genome Nobecovirus Sequences from Malagasy Fruit Bats Define a Unique Evolutionary History for this Coronavirus Clade. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 786060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geldenhuys, M.; Mortlock, M.; Epstein, J.H.; Paweska, J.; Weyer, J.; Markotter, W. Overview of Bat and Wildlife Coronavirus Surveillance in Africa: A Framework for Global Investigations. Viruses 2021, 13, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.B.; Crameri, G.; Hyatt, A.; Yu, M.; Tompang, M.R.; Rosli, J.; McEachern, J.; Crameri, S.; Kumarasamy, V.; Eaton, B.T.; et al. A Previously Unknown Reovirus of Bat Origin is Associated with an Acute Respiratory Disease in Humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11424–11429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Liu, W.J.; Xu, W.; Jin, T.; Zhao, Y.; Song, J.; Shi, Y.; Ji, W.; Jia, H.; Zhou, Y.; et al. A Bat-Derived Putative Cross-Family Recombinant Coronavirus with a Reovirus Gene. PLOS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.C.P.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y. Interspecies Jumping of Bat Coronaviruses. Viruses 2021, 13, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Host | Epomophorus wahlbergi | Eidolon helvum | Rousettus aegyptiacus | Eidolon helvum | Rousettus madagascariensis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location, Year | Kenya, 2024 | Kenya 2006 | Kenya 2006 | Cameroon, 2013 | Madagascar, 2018 | ||||||
| Isolate | NRB24 | KY24 | KY06 | CMR900 | CMR66 | CMR891-892 | CMR705-P13 | CMR704-P12 | MIZ178 | MIZ240 | |
| GenBank Accession | PQ179293 | HQ728482.1 | HQ728483.1 | MG693169.1 | MG693170.1 | MG693171.1 | MG693172.1 | NC_048212.1 | OK067320.1 | OK067321.1 | |
| ORF1b | Size | 2579 | 2579 | 2588 | 2579 | 2588 | 2579 | 2579 | 2579 | 2579 | 2579 |
| Catalytic core—RNA polymerase (477363) | 1–823 | 1–823 | 1–823 | 1–823 | 1–823 | 1–823 | 1–823 | 1–823 | 1–823 | 1–823 | |
| Nsp13—zinc-binding domain (cl41714) | 824–918 | 824–918 | 824–918 | 824–918 | 824–918 | 824–918 | 824–918 | 824–918 | 824–918 | 824–918 | |
| Nsp13—stalk (cl41715) | 922–969 | 922–969 | 922–969 | 922–969 | 922–969 | 922–969 | 922–969 | 922–969 | 922–969 | 922–969 | |
| Nsp13—1B domain (cl41715) | 973–1051 | 973–1051 | 973–1051 | 973–1051 | 973–1051 | 973–1051 | 973–1051 | 973–1051 | 973–1051 | 973–1051 | |
| Nsp13—helicase domain (cl41748) | 1074–1413 | 1074–1413 | 1074–1413 | 1074–1413 | 1074–1413 | 1074–1413 | 1074–1413 | 1074–1413 | 1074–1413 | 1074–1413 | |
| Nsp14 (cl40464) | 1428–1950 | 1428–1951 | 1428–1952 | 1428–1951 | 1428–1952 | 1428–1951 | 1428–1951 | 1428–1951 | 1428–1951 | 1428–1951 | |
| Nsp15—N terminal domain (cl40469) | 1954–2014 | 1954–2014 | 1955–2015 | 1954–2014 | 1955–2015 | 1954–2014 | 1954–2014 | 1954–2014 | 1954–2014 | 1954–2014 | |
| Nsp15—M domain (cl41717) | 2018–2146 | 2018–2146 | 2019–2143 | 2018–2146 | 2019–2143 | 2018–2146 | 2018–2146 | 2018–2146 | 2018–2146 | 2018–2146 | |
| Nsp15—endoribonuclease domain (cl41718) | 2144–2292 | 2144–2292 | 2141–2289 | 2144–2292 | 2141–2289 | 2144–2292 | 2144–2292 | 2144–2292 | 2144–2292 | 2144–2292 | |
| Nsp16—methyltransferase (461919, cl41719) | 2297–2578 | 2323–2537 | 2297–2578 | 2323–2537 | 2297–2578 | 2323–2537 | 2323–2537 | 2323–2537 | 2297–2578 | 2323–2537 | |
| S | Size | 1274 | 1264 | 1278 | 1273 | 1278 | 1271 | 1269 | 1269 | 1256 | 1265 |
| S1—N terminal domain (cd21627) | 30–323 | 33–318 | 36–327 | 33–326 | 36–327 | 33–325 | 31–322 | 31–322 | 34–312 | 42–321 | |
| Receptor binding domain (cl09656) | 367–521 | 362–516 | 371–521 | 370–528 | 371–521 | 369–523 | 366–524 | 366–524 | 356–511 | 365–519 | |
| S1/S2 cleavage + S2 fusion domain (cd22381) | 538–1268 | 533–1258 | 538–1273 | 545–1267 | 538–1272 | 540–1265 | 541–1263 | 541–1263 | 528–1250 | 536–1259 | |
| ORF3 | Size | 232 | 238 | 220 | 238 | 220 | 238 | 239 | 239 | 238 | 238 |
| E | Size | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| Envelope protein (cl40474) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 4–63 | 4–63 | 4–63 | 4–63 | |
| M | Size | 222 | 221 | 222 | 221 | 223 | 221 | 221 | 221 | 221 | 221 |
| Matrix protein (cl40475) | 11–222 | 5–222 | 7–222 | 8–221 | 7–223 | 5–221 | 10–221 | 10–221 | 8–221 | 8–221 | |
| N | Size | 469 | 467 | 468 | 468 | 468 | 467 | 470 | 470 | 467 | 467 |
| Nucleocapsid protein (cl47612) | 53–396 | 53–374 | 54–375 | 54–375 | 54–395 | 54–375 | 54–375 | 54–375 | 53–374 | 53–374 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
VanAcker, M.C.; Ergunay, K.; Webala, P.W.; Kamau, M.; Mutura, J.; Lebunge, R.; Ochola, G.O.; Bourke, B.P.; McDermott, E.G.; Achee, N.L.; et al. A Novel Nobecovirus in an Epomophorus wahlbergi Bat from Nairobi, Kenya. Viruses 2025, 17, 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040557
VanAcker MC, Ergunay K, Webala PW, Kamau M, Mutura J, Lebunge R, Ochola GO, Bourke BP, McDermott EG, Achee NL, et al. A Novel Nobecovirus in an Epomophorus wahlbergi Bat from Nairobi, Kenya. Viruses. 2025; 17(4):557. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040557
Chicago/Turabian StyleVanAcker, Meredith C., Koray Ergunay, Paul W. Webala, Maureen Kamau, Janerose Mutura, Rashid Lebunge, Griphin Ochieng Ochola, Brian P. Bourke, Emily G. McDermott, Nicole L. Achee, and et al. 2025. "A Novel Nobecovirus in an Epomophorus wahlbergi Bat from Nairobi, Kenya" Viruses 17, no. 4: 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040557
APA StyleVanAcker, M. C., Ergunay, K., Webala, P. W., Kamau, M., Mutura, J., Lebunge, R., Ochola, G. O., Bourke, B. P., McDermott, E. G., Achee, N. L., Jiang, L., Grieco, J. P., Keter, E., Musanga, A., Murray, S., Stabach, J. A., Craft, M. E., Fèvre, E. M., Linton, Y.-M., & Hassell, J. (2025). A Novel Nobecovirus in an Epomophorus wahlbergi Bat from Nairobi, Kenya. Viruses, 17(4), 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040557







