Gonadocorticoids Have Different Effects on the Expression of Toll-like Receptors When Infected with Various HIV-1 Subtypes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBLs)
2.2. Ethical Aspects
2.3. HIV-Infection
2.4. Hormone Treatment
2.5. Assessment of Virus Replication
2.6. Assessment of Toll-like Receptor (TLR) and C-C Chemokine Receptor (CCR) Gene Expression
2.7. Statistical Analysis
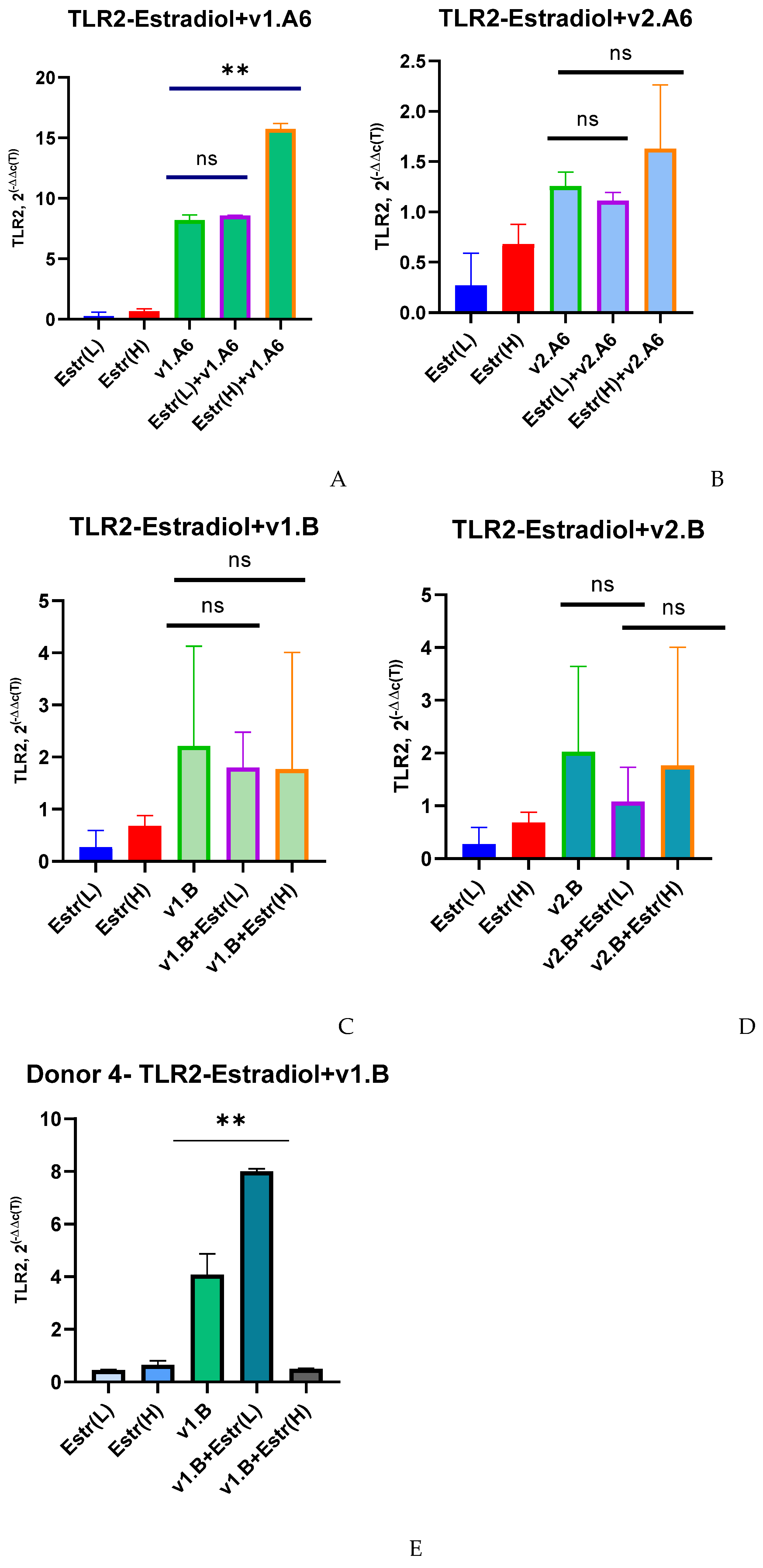
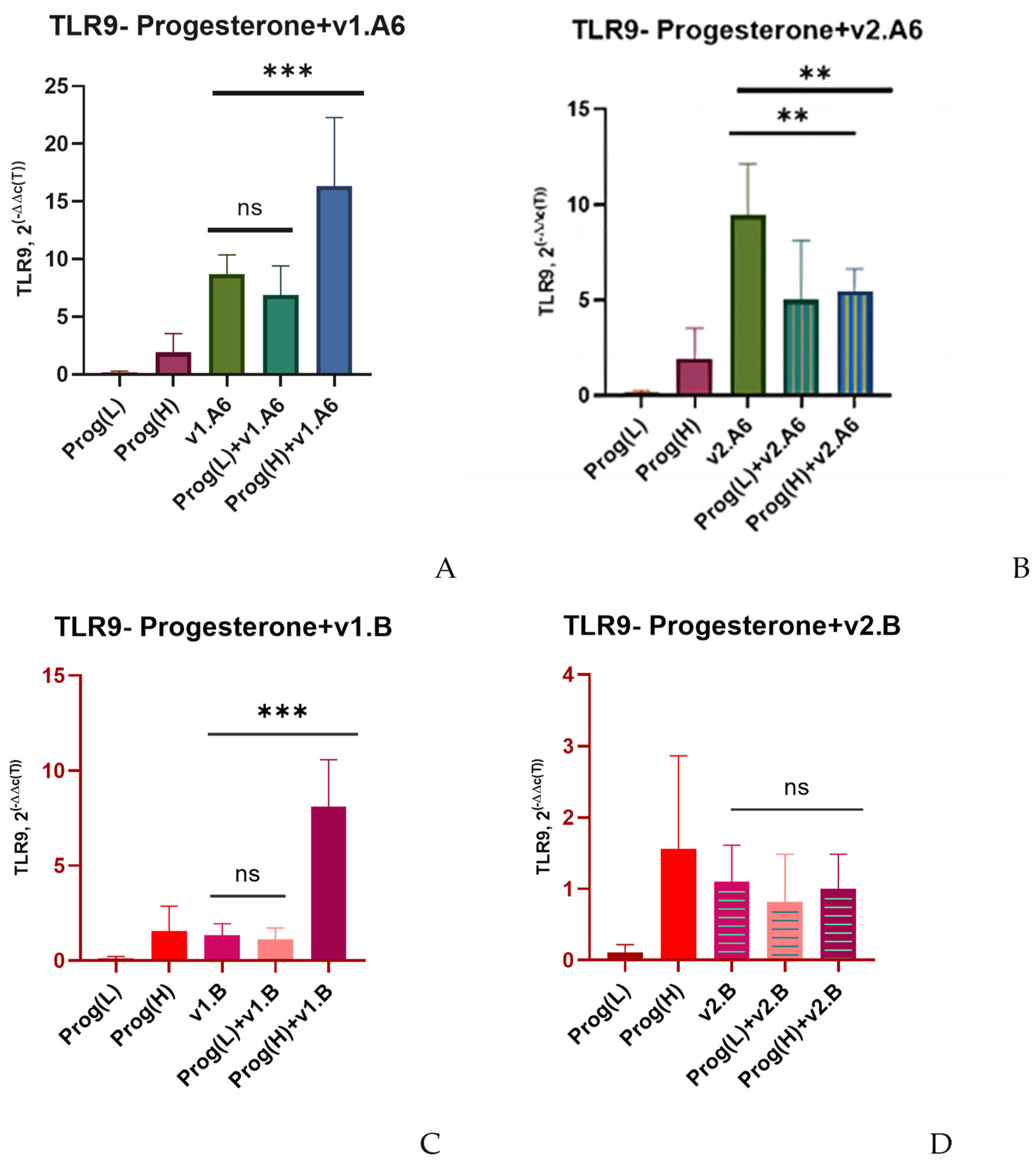
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PBMCs | Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| TLRs | Toll-like receptors |
| Estr | Estradiol |
| Prog | Progesterone |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
References
- Global HIV & AIDS Statistics—Fact Sheet|UNAIDS. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet (accessed on 17 September 2025).
- Katz, I.T.; Maughan-Brown, B. Improved Life Expectancy of People Living with HIV: Who Is Left Behind? Lancet HIV 2017, 4, e324–e326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trickey, A.; Sabin, C.A.; Burkholder, G.; Crane, H.; d’Arminio Monforte, A.; Egger, M.; Gill, M.J.; Grabar, S.; Guest, J.L.; Jarrin, I.; et al. Life Expectancy after 2015 of Adults with HIV on Long-Term Antiretroviral Therapy in Europe and North America: A Collaborative Analysis of Cohort Studies. Lancet HIV 2023, 10, e295–e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, T.; Cao, W.; Li, T. HIV-Related Immune Activation and Inflammation: Current Understanding and Strategies. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 7316456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appay, V.; Sauce, D. Immune Activation and Inflammation in HIV-1 Infection: Causes and Consequences. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streeck, H.; Maestri, A.; Habermann, D.; Crowell, T.A.; Esber, A.L.; Son, G.; Eller, L.A.; Eller, M.A.; Parikh, A.P.; Horn, P.A.; et al. Dissecting Drivers of Immune Activation in Chronic HIV-1 Infection. EBioMedicine 2022, 83, 104182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozman, M.; Zidovec-Lepej, S.; Jambrosic, K.; Babić, M.; Drmić Hofman, I. Role of TLRs in HIV-1 Infection and Potential of TLR Agonists in HIV-1 Vaccine Development and Treatment Strategies. Pathogens 2023, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Ikegawa, M.; Ori, D.; Akira, S. Decoding Toll-like Receptors: Recent Insights and Perspectives in Innate Immunity. Immunity 2024, 57, 649–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakad, P.K.; Mishra, R.; Mishra, I. Toll-like Receptor Expression during Inflammatory Processes in Human Diseases. Rheumatol. Autoimmun. 2025, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Gazy, N.; Venketaraman, V. A Role of Intracellular Toll-Like Receptors (3, 7, and 9) in Response to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and Co-Infection with HIV. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, E.P. The Role of Toll-Like Receptors in Retroviral Infection. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, G.; Vashishtha, R.; Verma, C.; Sharma, S.; Yadav, R.N. Role of Toll-Like Receptors (Tlrs) in HIV Disease Progression. In Recent Trends in Diabetes and Cancer Research and Its Management; Kolay, S.R., Pandey, A.K., Kumar, S., Saxena, P., Kumari, A., Shachi, K., Eds.; Iterative International Publishers: Chikkamagaluru, India; Selfypage Developers Pvt Ltd.: Chikkamagaluru, India, 2024; pp. 557–580. ISBN 978-1-68576-521-7. [Google Scholar]
- Vignuzzi, M.; López, C.B. Defective Viral Genomes Are Key Drivers of the Virus–Host Interaction. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, N.; Liu, S.; Huang, H. Sex Difference in Human Diseases: Mechanistic Insights and Clinical Implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, J.A.; Turner, S.R.; Marsden, M.D. Contribution of Sex Differences to HIV Immunology, Pathogenesis, and Cure Approaches. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 905773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, A.; Addo, M.M.; Dahlke, C. Sex Differences in Immunity: Implications for the Development of Novel Vaccines Against Emerging Pathogens. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 601170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addo, M.M.; Altfeld, M. Sex-Based Differences in HIV Type 1 Pathogenesis. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209 (Suppl. S3), S86–S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.L. Sex Differences in Prophylaxis and Therapeutic Treatments for Viral Diseases. In Sex and Gender Differences in Pharmacology; Regitz-Zagrosek, V., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 499–522. ISBN 978-3-642-30726-3. [Google Scholar]
- Falcinelli, S.D.; Shook-Sa, B.E.; Dewey, M.G.; Sridhar, S.; Read, J.; Kirchherr, J.; James, K.S.; Allard, B.; Ghofrani, S.; Stuelke, E.; et al. Impact of Biological Sex on Immune Activation and Frequency of the Latent HIV Reservoir During Suppressive Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, E.P. Sex Differences in HIV Infection. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2018, 15, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galligan, C.L.; Fish, E.N. Sex Differences in the Immune Response. In Sex and Gender Differences in Infection and Treatments for Infectious Diseases; Klein, S.L., Roberts, C.W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–29. ISBN 978-3-319-16438-0. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, J.; Jung, N.; Robinson, N.; Lehmann, C. Sex Differences in Immune Responses to Infectious Diseases. Infection 2015, 43, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, S.; Altfeld, M. Sex Differences in HIV-1-Mediated Immunopathology. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2016, 11, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wira, C.R.; Rodriguez-Garcia, M.; Patel, M.V. The Role of Sex Hormones in Immune Protection of the Female Reproductive Tract. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapgood, J.P.; Kaushic, C.; Hel, Z. Hormonal Contraception and HIV-1 Acquisition: Biological Mechanisms. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 36–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Garcia, M.; Connors, K.; Ghosh, M. HIV Pathogenesis in the Human Female Reproductive Tract. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2021, 18, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosik, M.N.; Bystritskaya, E.P.; Ryzhov, K.A.; Berezhnaya, E.V.; Lobach, O.A.; Kiseleva, I.A.; Kireev, D.E.; Kuzina, A.V.; Kostyuchenko, E.P.; Vasileva, V.E.; et al. Impact of Female Sex Hormones on the Expression of CCR5/CCR8 Co-Receptor Genes and Virus Replication in HIV-1 Infection. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2025, 179, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, M.; Kapembwa, M.S.; Gotch, F.; Patterson, S. Oral Contraceptive Use Induces Upregulation of the CCR5 Chemokine Receptor on CD4+ T Cells in the Cervical Epithelium of Healthy Women. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2002, 54, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciaranghella, G.; Wang, C.; Hu, H.; Anastos, K.; Merhi, Z.; Nowicki, M.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Greenblatt, R.M.; Cohen, M.; Golub, E.T.; et al. CCR5 Expression Levels in HIV-Uninfected Women Receiving Hormonal Contraception. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1397–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritz, M.F.; Ray, R.M.; Bick, A.J.; Tomasicchio, M.; Woodland, J.G.; Govender, Y.; Avenant, C.; Hapgood, J.P. Medroxyprogesterone Acetate, Unlike Norethisterone, Increases HIV-1 Replication in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells and an Indicator Cell Line, via Mechanisms Involving the Glucocorticoid Receptor, Increased CD4/CD8 Ratios and CCR5 Levels. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampah, M.E.S.; Laird, G.M.; Blankson, J.N.; Siliciano, R.F.; Coleman, J.S. Medroxyprogesterone Acetate Increases HIV-1 Infection of Unstimulated Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Vitro. AIDS 2015, 29, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Muñoz, E.; Fuentes-Romero, L.L.; Zamora-Chávez, J.; Camacho-Arroyo, I.; Soto-Ramírez, L.E. Effects of Progesterone on the Content of CCR5 and CXCR4 Coreceptors in PBMCs of Seropositive and Exposed but Uninfected Mexican Women to HIV-1. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 132, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosik, M.; Berezhnya, E.; Bystritskaya, E.; Kiseleva, I.; Lobach, O.; Kireev, D.; Svitich, O. Female Sex Hormones Upregulate the Replication Activity of HIV-1 Sub-Subtype A6 and CRF02_AG but Not HIV-1 Subtype B. Pathogens 2023, 12, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, J.S.; Wendel, G.D.; McIntire, D.D.; Norgard, M.V. The Effect of Progesterone Levels and Pregnancy on HIV-1 Coreceptor Expression. Reprod. Sci. 2009, 16, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, F.; Pellicer, A.; Simon, C. The Chemokine Connection: Hormonal and Embryonic Regulation at the Human Maternal-Embryonic Interface-A Review. Placenta 2003, 24 (Suppl. B), S48–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, E.; Origoni, M.; Taccagni, G.; Ferrari, D.; Doglioni, C.; Nava, A.; Lisco, A.; Grivel, J.-C.; Margolis, L.; Poli, G. Productive HIV-1 Infection of Human Cervical Tissue Ex Vivo Is Associated with the Secretory Phase of the Menstrual Cycle. Mucosal Immunol. 2013, 6, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asin, S.N.; Eszterhas, S.K.; Rollenhagen, C.; Heimberg, A.M.; Howell, A.L. HIV Type 1 Infection in Women: Increased Transcription of HIV Type 1 in Ectocervical Tissue Explants. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monis, C.N.; Tetrokalashvili, M. Proliferative and Follicular Phases of the Menstrual Cycle. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri, D.; Hayashi, H.; Victoriano, A.F.B.; Okamoto, T.; Onozaki, K. Estrogen Stimulates Transcription of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1). Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donninelli, G.; Gessani, S.; Del Cornò, M. Interplay between HIV-1 and Toll-like Receptors in Human Myeloid Cells: Friend or Foe in HIV-1 Pathogenesis? J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.C.; Stevenson, M.; Latz, E.; Urcuqui-Inchima, S. HIV Type 1 Infection Up-Regulates TLR2 and TLR4 Expression and Function in Vivo and in Vitro. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2012, 28, 1313–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heggelund, L.; Müller, F.; Lien, E.; Yndestad, A.; Ueland, T.; Kristiansen, K.I.; Espevik, T.; Aukrust, P.; Frøland, S.S. Increased Expression of Toll-like Receptor 2 on Monocytes in HIV Infection: Possible Roles in Inflammation and Viral Replication. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolduc, J.-F.; Ouellet, M.; Hany, L.; Tremblay, M.J. Toll-Like Receptor 2 Ligation Enhances HIV-1 Replication in Activated CCR6+ CD4+ T Cells by Increasing Virus Entry and Establishing a More Permissive Environment to Infection. J. Virol. 2017, 91, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Equils, O.; Schito, M.L.; Karahashi, H.; Madak, Z.; Yarali, A.; Michelsen, K.S.; Sher, A.; Arditi, M. Toll-like Receptor 2 (TLR2) and TLR9 Signaling Results in HIV-Long Terminal Repeat Trans-Activation and HIV Replication in HIV-1 Transgenic Mouse Spleen Cells: Implications of Simultaneous Activation of TLRs on HIV Replication. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5159–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordone, S.K.; Ignacio, G.A.; Su, L.; Sempowski, G.D.; Golenbock, D.T.; Li, L.; Dean, G.A. Failure of TLR4-Driven NF-Kappa B Activation to Stimulate Virus Replication in Models of HIV Type 1 Activation. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2007, 23, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, A.; Molina-Pinelo, S.; de Felipe, B.; Abad-Fernández, M.; González-Escribano, M.F.; Leal, M.; Soriano-Sarabia, N. Brief Report: Toll-like Receptor 9-1635A/G Polymorphism Is Associated With HIV-1 Rebound After Four Weeks of Interruption of Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Acquir. Immune. Defic. Syndr. 2020, 85, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampathkumar, R.; Shadabi, E.; Luo, M. Interplay between HIV-1 and Host Genetic Variation: A Snapshot into Its Impact on AIDS and Therapy Response. Adv. Virol. 2012, 2012, 508967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, R.M.; Shen, T.; Gnanakaran, S.; Derdeyn, C.A. Appreciating HIV Type 1 Diversity: Subtype Differences in Env. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2009, 25, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ssemwanga, D.; Nsubuga, R.N.; Mayanja, B.N.; Lyagoba, F.; Magambo, B.; Yirrell, D.; Van der Paal, L.; Grosskurth, H.; Kaleebu, P. Effect of HIV-1 Subtypes on Disease Progression in Rural Uganda: A Prospective Clinical Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, B.T.; Leitner, T.; Paraskevis, D.; Peeters, M. Primate Immunodeficiency Virus Classification and Nomenclature: Review. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 46, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.M.; Perno, C.F. HIV-1 Genetic Variability and Clinical Implications. ISRN Microbiol. 2013, 2013, 481314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeeninga, R.E.; Hoogenkamp, M.; Armand-Ugon, M.; de Baar, M.; Verhoef, K.; Berkhout, B. Functional Differences between the Long Terminal Repeat Transcriptional Promoters of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Subtypes A through G. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 3740–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonova, A.A.; Lebedev, A.V.; Kazennova, E.V.; Kim, K.V.; Ozhmegova, E.N.; Tumanov, A.S.; Munchak, Y.M.; Orlova-Morozova, E.A.; Pronin, A.Y.; Prilipov, A.G.; et al. Variability of VPU Protein in HIV-1 Sub-Subtype A6 in Patients with Different Stages of HIV Infection. HIV Infect. Immunosuppr. Disord. 2024, 16, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhov, K.A.; Nosik, M.N.; Kravtchenko, A.V. A study of the HIV-1 regulatory genes using the polymerase chain reaction. Probl. Virol. 2015, 60, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, J.K.; Byakwaga, H.; Kuang, X.T.; Le, A.Q.; Brumme, C.J.; Mwimanzi, P.; Omarjee, S.; Martin, E.; Lee, G.Q.; Baraki, B.; et al. Ability of HIV-1 Nef to Downregulate CD4 and HLA Class I Differs among Viral Subtypes. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.I.; Gromov, K.B.; Kireev, D.E.; Shlykova, A.V.; Lopatukhin, A.E.; Kazennova, E.V.; Lebedev, A.V.; Tumanov, A.S.; Kim, K.V.; Bobkova, M.R. Analysis of Tat protein characteristics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 sub-subtype A6 (Retroviridae: Orthoretrovirinae: Lentivirus: Human immunodeficiency virus-1). Probl. Virol. 2021, 66, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromov, K.B.; Kazennova, E.V.; Kireev, D.E.; Murzakova, A.V.; Lopatukhin, A.E.; Bobkova, M.R. Analysis of HIV-1 (Human immunodeficiency virus-1, Lentivirus, Orthoretrovirinae, Retroviridae) Nef protein polymorphism of variants circulating in the former USSR countries. Probl. Virol. 2019, 64, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devadas, K.; Biswas, S.; Haleyurgirisetty, M.; Wood, O.; Ragupathy, V.; Lee, S.; Hewlett, I. Analysis of Host Gene Expression Profile in HIV-1 and HIV-2 Infected T-Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tough, R.H.; McLaren, P.J. Interaction of the Host and Viral Genome and Their Influence on HIV Disease. Front. Genet. 2019, 9, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, P.J.; Fellay, J. HIV-1 and Human Genetic Variation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, P.J.; Coulonges, C.; Bartha, I.; Lenz, T.L.; Deutsch, A.J.; Bashirova, A.; Buchbinder, S.; Carrington, M.N.; Cossarizza, A.; Dalmau, J.; et al. Polymorphisms of Large Effect Explain the Majority of the Host Genetic Contribution to Variation of HIV-1 Virus Load. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14658–14663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellay, J. Host Genetics Influences on HIV Type-1 Disease. Antivir. Ther. 2009, 14, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Huda, S.; Babu, S.P.S. Toll-like Receptor Polymorphism in Host Immune Response to Infectious Diseases: A Review. Scand. J. Immunol. 2019, 90, e12771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skevaki, C.; Pararas, M.; Kostelidou, K.; Tsakris, A.; Routsias, J.G. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of Toll-like Receptors and Susceptibility to Infectious Diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 180, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beima-Sofie, K.M.; Bigham, A.W.; Lingappa, J.R.; Wamalwa, D.; Mackelprang, R.D.; Bamshad, M.J.; Maleche-Obimbo, E.; Richardson, B.A.; John-Stewart, G.C. Toll-like Receptor Variants Are Associated with Infant HIV-1 Acquisition and Peak Plasma HIV-1 RNA Level. AIDS 2013, 27, 2431–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackelprang, R.D.; Bigham, A.W.; Celum, C.; de Bruyn, G.; Beima-Sofie, K.; John-Stewart, G.; Ronald, A.; Mugo, N.R.; Buckingham, K.J.; Bamshad, M.J.; et al. Toll-like Receptor Polymorphism Associations with HIV-1 Outcomes among Sub-Saharan Africans. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, R.T.; Yao, X.-D.; Ball, T.B.; McKinnon, L.R.; Kaul, R.; Wachihi, C.; Jaoko, W.; Plummer, F.A.; Rosenthal, K.L. Toll-like Receptor Expression and Responsiveness Are Increased in Viraemic HIV-1 Infection. AIDS 2008, 22, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller Sanders, C.; Cruse, J.M.; Lewis, R.E. Toll-like Receptor and Chemokine Receptor Expression in HIV-Infected T Lymphocyte Subsets. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2010, 88, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.J.; Lacas, A.; Lindsay, R.J.; Doyle, E.H.; Axten, K.L.; Pereyra, F.; Rosenberg, E.S.; Walker, B.D.; Allen, T.M.; Altfeld, M. Differential Regulation of Toll-like Receptor Pathways in Acute and Chronic HIV-1 Infection. AIDS 2012, 26, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pine, S.O.; McElrath, M.J.; Bochud, P.-Y. Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptor 4 and Toll-like Receptor 9 Influence Viral Load in a Seroincident Cohort of HIV-1-Infected Individuals. AIDS 2009, 23, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, E.; Malacrida, S.; Zanchetta, M.; Mosconi, I.; Montagna, M.; Giaquinto, C.; De Rossi, A. Toll-like Receptor 9 Polymorphisms Influence Mother-to-Child Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1. J. Transl. Med. 2010, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teräsjärvi, J.; Kainulainen, L.; Peltola, V.; Mertsola, J.; Hakanen, A.; He, Q. Genetic polymorphisms of TLR1, TLR2, TLR3 and TLR4 in patients with recurrent or severe infections. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2024, 51, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royo, J.L.; Alarcón-Martín, E.; Díaz-Fuentes, J.; Colmenero, J.D.; Bravo, M.J. Discordance in TLR2 (−196 to −174) Polymorphism Effect on HIV Infection Risk. J. Gene Med. 2018, 20, e3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidyant, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Agarwal, V.; Dhole, T.N. Susceptibility to HIV-1 Infection Is Influenced by Toll like Receptor-2 (−196 to −174) Polymorphism in a North Indian Population. J. Gene Med. 2017, 19, e2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-C.; Jeong, B.-H. Strong Association of the Rs4986790 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) of the Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Gene with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection: A Meta-Analysis. Genes 2020, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidyant, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Dhole, T. A Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism in TLR4 Is Linked with the Risk of HIV-1 Infection. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 76, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano-Sarabia, N.; Vallejo, A.; Ramírez-Lorca, R.; del Mar Rodríguez, M.; Salinas, A.; Pulido, I.; Sáez, M.E.; Leal, M. Influence of the Toll-like Receptor 9 1635A/G Polymorphism on the CD4 Count, HIV Viral Load, and Clinical Progression. J. Acquir. Immune. Defic. Syndr. 2008, 49, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, C.M.; Cruse, J.M.; Lewis, R.E. Toll-like Receptors, Cytokines and HIV-1. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2008, 84, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayesh, M.E.H.; Kohara, M.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K. Toll-like Receptor Response to Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 or Co-Infection with Hepatitis B or C Virus: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nosik, M.; Ryzhov, K.; Berezhnaya, E.; Bystritskaya, E.; Lobach, O.; Kiseleva, I.; Kostyuchenko, E.; Kuzina, A.; Meremianina, E.; Kireev, D.; et al. Gonadocorticoids Have Different Effects on the Expression of Toll-like Receptors When Infected with Various HIV-1 Subtypes. Viruses 2025, 17, 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111512
Nosik M, Ryzhov K, Berezhnaya E, Bystritskaya E, Lobach O, Kiseleva I, Kostyuchenko E, Kuzina A, Meremianina E, Kireev D, et al. Gonadocorticoids Have Different Effects on the Expression of Toll-like Receptors When Infected with Various HIV-1 Subtypes. Viruses. 2025; 17(11):1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111512
Chicago/Turabian StyleNosik, Marina, Konstantin Ryzhov, Elena Berezhnaya, Elizaveta Bystritskaya, Olga Lobach, Irina Kiseleva, Elizaveta Kostyuchenko, Anna Kuzina, Ekaterina Meremianina, Dmitry Kireev, and et al. 2025. "Gonadocorticoids Have Different Effects on the Expression of Toll-like Receptors When Infected with Various HIV-1 Subtypes" Viruses 17, no. 11: 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111512
APA StyleNosik, M., Ryzhov, K., Berezhnaya, E., Bystritskaya, E., Lobach, O., Kiseleva, I., Kostyuchenko, E., Kuzina, A., Meremianina, E., Kireev, D., & Svitich, O. (2025). Gonadocorticoids Have Different Effects on the Expression of Toll-like Receptors When Infected with Various HIV-1 Subtypes. Viruses, 17(11), 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111512




