Identification of Reassortment of Orthotospovirus citrullomaculosi in Jiangxi Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus Disease Investigation and Sampling
2.2. Total RNA Extraction and RT-PCR Detection
2.3. High-Throughput Sequencing for Complete Genome Determination
2.4. Multiple-Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Recombination and Reassortment Analysis
2.6. Validation of Reassortment
3. Results
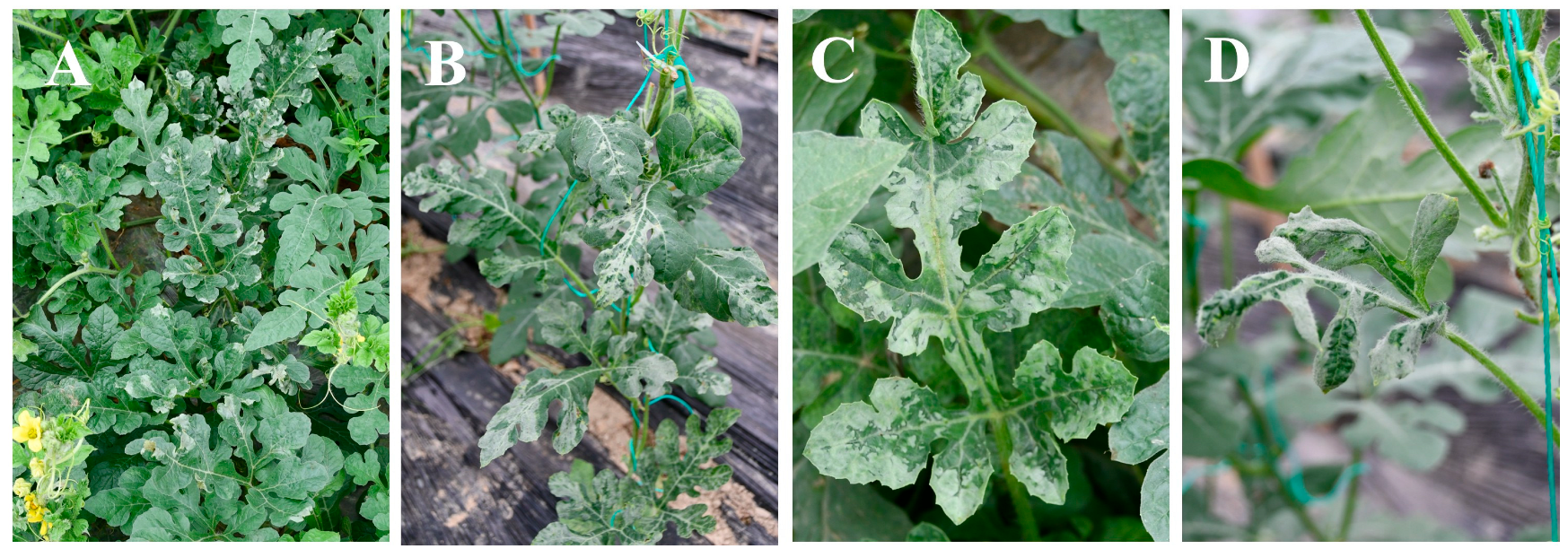
3.1. Occurrence and Symptoms
3.2. RT-PCR Detection
3.3. Complete Genome of WSMoV
3.4. Multiple-Sequence Alignment and Clustering of Complete Genome
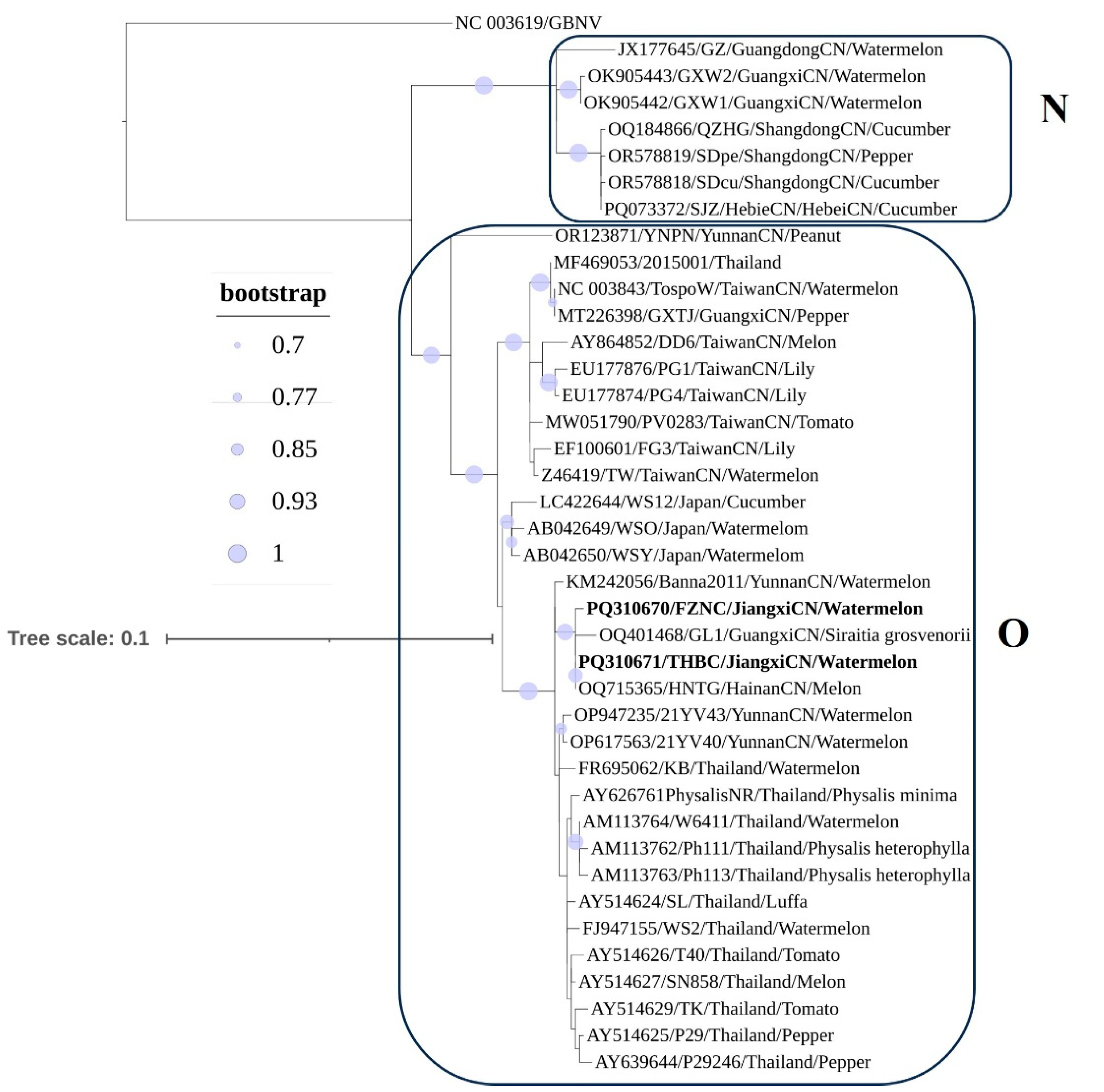
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
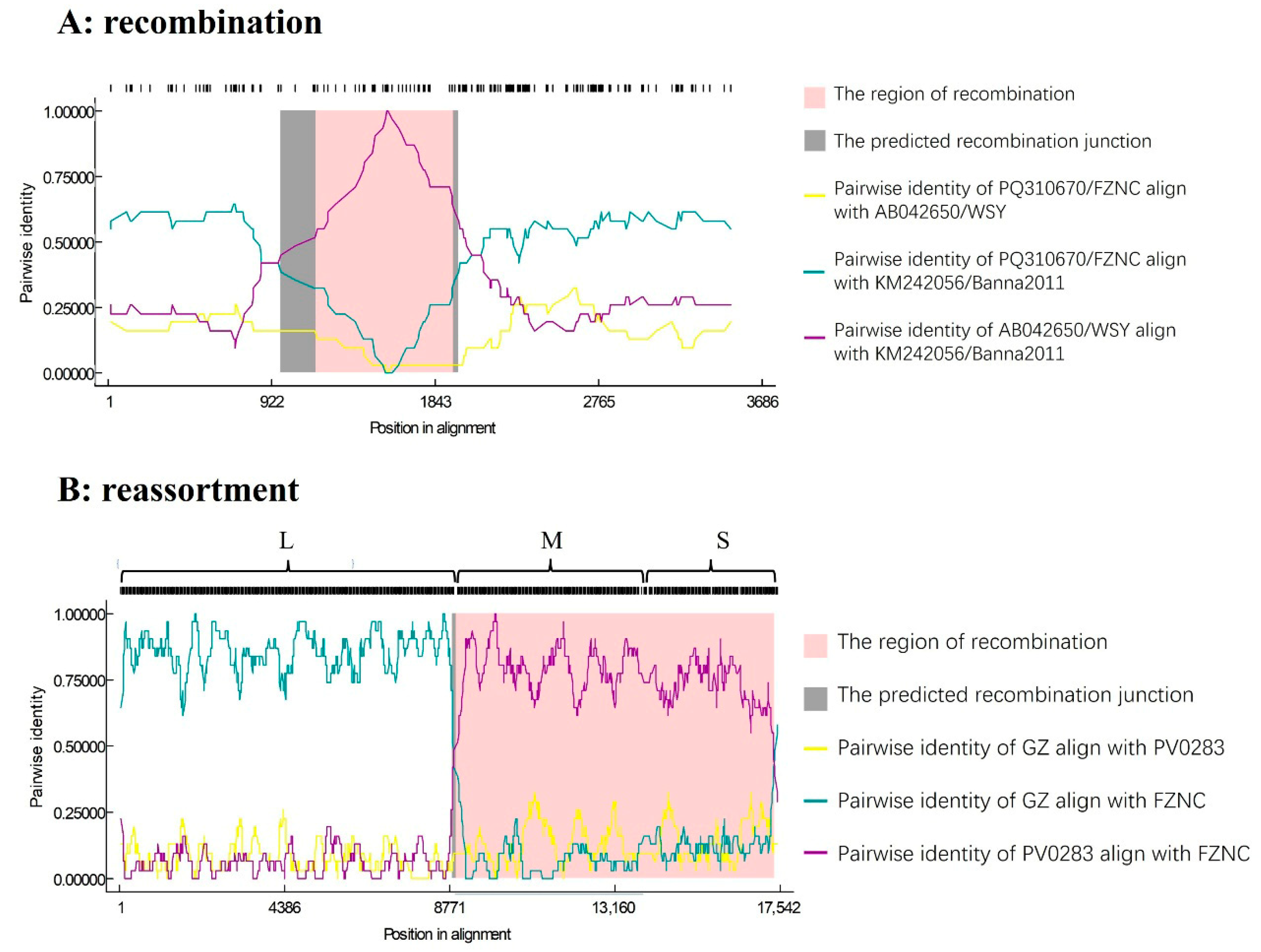
3.6. Recombination and Reassortment Analysis
3.7. RT-PCR Validation of Reassortment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, F.; Chao, C.; Chung, M.; Chen, C.; Yeh, S. Completion of the genome sequence of Watermelon silver mottle virus and utilization of degenerate primers for detecting tospoviruses in five serogroups. Phytopathology 2001, 91, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaki, M.; Honda, Y.; Hanada, K.; Tochihara, H.; Yonaha, T.; Hokama, K.; Yokoyama, T. Silver mottle disease of watermelon caused by tomato spotted wilt virus. Plant Dis. 1984, 68, 1006–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, S.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Jih, C.; Chen, M.; Chen, C. Identification of tomato spotted wilt-like virus on watermelon in Taiwan. Plant Dis. 1992, 76, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiemsombat, P.; Gajanandana, O.; Warin, N.; Hongprayoon, R.; Bhunchoth, A.; Pongsapich, P. Biological and molecular characterization of tospoviruses in Thailand. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y. First report of natural infection of watermelon by Watermelon silver mottle virus in China. New Dis. Rep. 2011, 24, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; He, Z. First Report of Watermelon silver mottle virus Infecting Pepper in Guangdong Province. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2015, 42, 2261–2266. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, T.; Li, H.; Guo, M.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Ding, M. Identification of Watermelon silver mottle virus infecting watermelon in Yunnan. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2016, 46, 461–468. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Qin, B.; Xie, H.; Cui, L.; Chen, Q.; Cai, J. Identification of watermelon silver mottle virus on watermelon and melon and sequence analysis of S RNA of isolates from Guangxi Province. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2023, 53, 534–538. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Cui, L.; Qin, B.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Cai, J. Molecular identification of watermelon silver mottle virus infecting sweet pepper in Guangxi. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2021, 51, 474–477. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.-G.; Nong, Y.; Farooq, T.; Tang, Y.-F.; She, X.-M.; Yu, L.; Lan, G.-B.; Zhou, X.-P.; He, Z.-F. Small RNA deep sequencing reveals the presence of multiple viral infections in cucurbit crops in Guangdong, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Xu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wang, M. Identification and analysis of melon virus disease pathogen in winter and spring at Hainan area. China Veg. 2023, 6, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, M.; Yan, Y.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, C.; Gao, C.; Kang, B.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; et al. Identification of watermelon silver mottle virus on watermelon in Zhejiang and Shandong province. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2024, 54, 877–880. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zeng, C.; Lou, B.; Pang, Q.; Su, Y.; Song, Y.; Lei, C.; Li, Y.; Wen, Y. First report of Watermelon silver mottle orthotospovirus infecting Siraitia grosvenorii in China. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Xu, Z.; Wei, Z.; Huang, Y.; Guo, C.; Chen, J.; Sun, Z. Occurrence of Watermelon Silver Mottle Virus in Peanut in China. Plant Dis. 2024, 108, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, N.; Jiang, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Chi, W.; Li, S.; Zhu, X.; Sun, X. A Sequencing-Based Phylogenetic Analysis of Various Strains of Watermelon Silver Mottle Virus in Northern China and Their One-Step Detection Using Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Plant Dis. 2024, 108, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Kang, B.; Wu, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Fei, Z.; Hong, N.; Gu, Q. Detection and genome characterization of a novel member of the genus Polerovirus from zucchini (Cucurbita pepo) in China. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2187–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Salse, J.; Lucas, W.J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Mao, L.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Z. The draft genome of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) and resequencing of 20 diverse accessions. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Gao, S.; Padmanabhan, C.; Li, R.; Galvez, M.; Gutierrez, D.; Fuentes, S.; Ling, K.-S.; Kreuze, J.; Fei, Z. VirusDetect: An automated pipeline for efficient virus discovery using deep sequencing of small RNAs. Virology 2017, 500, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar]
- Muhire, B.M.; Varsani, A.; Martin, D.P. SDT: A virus classification tool based on pairwise sequence alignment and identity calculation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108277. [Google Scholar]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; Von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijaykrishna, D.; Mukerji, R.; Smith, G.J. RNA virus reassortment: An evolutionary mechanism for host jumps and immune evasion. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004902. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, E.C. Influenza virus. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 809–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tentchev, D.; Verdin, E.; Marchal, C.; Jacquet, M.; Aguilar, J.M.; Moury, B. Evolution and structure of Tomato spotted wilt virus populations: Evidence of extensive reassortment and insights into emergence processes. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Isolate | Location | Year | Host | GenBank Accessions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FZNC | Jiangxi, China | 2023 | WM | L: PQ310674, M: PQ310672, S: PQ310670 |
| THBC | Jiangxi, China | 2023 | WM | L: PQ310675, M: PQ310673, S: PQ310671 |
| GZ | Guangdong, China | 2011 | WM | L: JX177647, M: JX177646, S: JX177645 |
| SJZ | Hebei, China | 2023 | Cu | L: JX177647, M: PQ073373, S: PQ073372 |
| YNPN | Yunnan, China | 2022 | Pe | L: OR123870, M: OR123869, S: OR123871 |
| PV0283 | Taiwan, China | 2020 | To | L: MW051788, M: MW051789, S: MW051790 |
| W2015 | Thailand | 2015 | NC | L: MF469051, M: MF469052, S: MF469053 |
| Taiwan | Taiwan, China | 1988 | WM | L: NC_003832, M: NC_003841, S: NC_003843 |
| GL1 | Guangxi, China | NC | SG | L: OQ401466, M: OQ401467, S: OQ401468 |
| TW | Taiwan, China | 1992 | M | L: AY863200, |
| QZHG | Shandong, China | 2022 | Cu | S: OQ184866 |
| GXW1 | Guangxi, China | 2016 | WM | S: OK905442 |
| GXW2 | Guangxi, China | 2016 | WM | S: OK905443 |
| DD6 | Taiwan, China | NC | M | M: AY864852, S: DQ157768 |
| WS | NC | NC | NC | S: Z46419 |
| WSO | Japan | 1982 | WM | S: AB042649 |
| WSY | Japan | 1982 | WM | S: AB042650 |
| Banna2011 | Yunnan, China | 2011 | WM | S: KM242056 |
| Methods of Detection | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Recombination | Reassortment | |
| RDP | 4.93 × 10−6 | 1.35 × 10−151 |
| GENECONV | 4.14 × 10−9 | 6.09 × 10−136 |
| BootScan | 4.18 × 10−6 | 1.96 × 10−134 |
| MaxChi | 1.07 × 10−7 | 5.18 × 10−62 |
| Chimaera | 2.04 × 10−6 | 2.74 × 10−64 |
| SiScan | 5.82 × 10−10 | 1.37 × 10−68 |
| 3Seq | 7.14 × 10−6 | 3.73 × 10−14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, B.; Zhang, X.; Cao, N.; Yan, C.; Li, F.; Zhu, F. Identification of Reassortment of Orthotospovirus citrullomaculosi in Jiangxi Province, China. Viruses 2025, 17, 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111448
Peng B, Zhang X, Cao N, Yan C, Li F, Zhu F. Identification of Reassortment of Orthotospovirus citrullomaculosi in Jiangxi Province, China. Viruses. 2025; 17(11):1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111448
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Bin, Xinlong Zhang, Na Cao, Chengpu Yan, Fangshu Li, and Fanghong Zhu. 2025. "Identification of Reassortment of Orthotospovirus citrullomaculosi in Jiangxi Province, China" Viruses 17, no. 11: 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111448
APA StylePeng, B., Zhang, X., Cao, N., Yan, C., Li, F., & Zhu, F. (2025). Identification of Reassortment of Orthotospovirus citrullomaculosi in Jiangxi Province, China. Viruses, 17(11), 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111448




