Neutralizing Antibodies Against the Porcine Endogenous Retroviruses (PERVs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rats, Normal Rat Sera and Cells
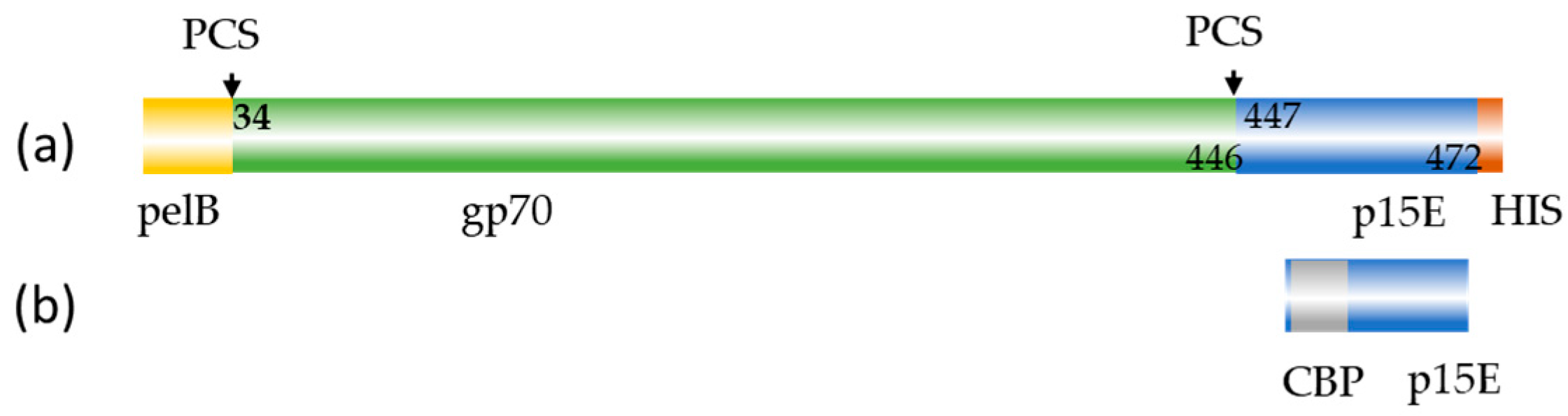
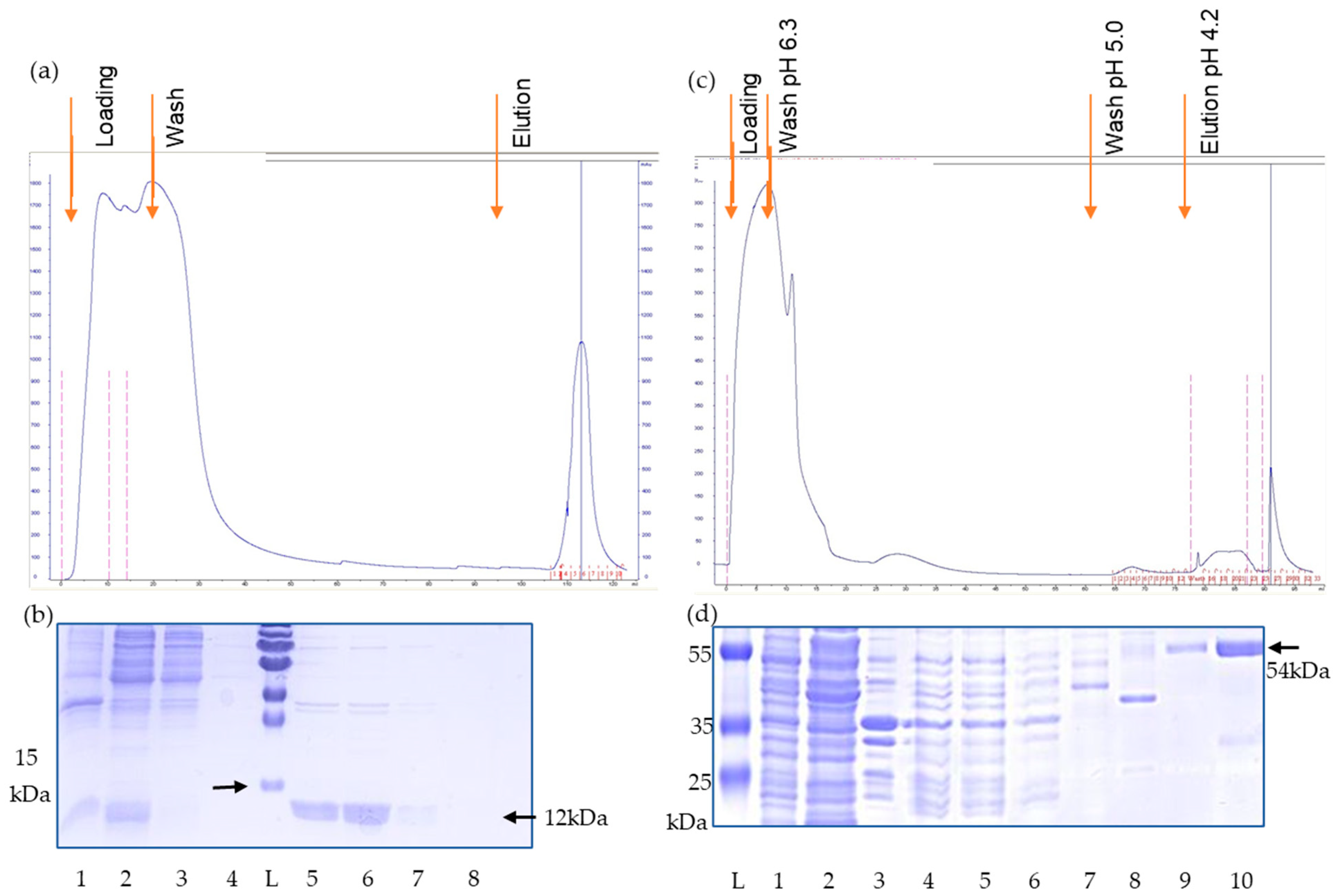
2.2. Cloning, Expression and Purification of the Recombinant Proteins
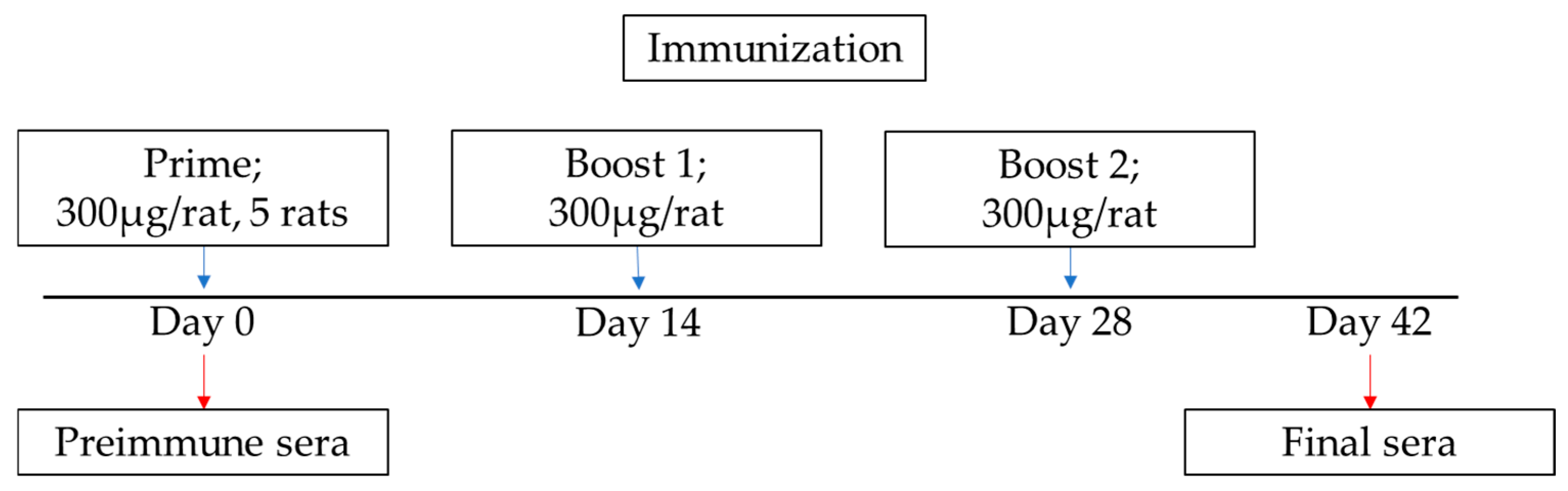
2.3. Immunization Schedule
2.4. SDS-PAGE
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. In Vitro Neutralization Assays
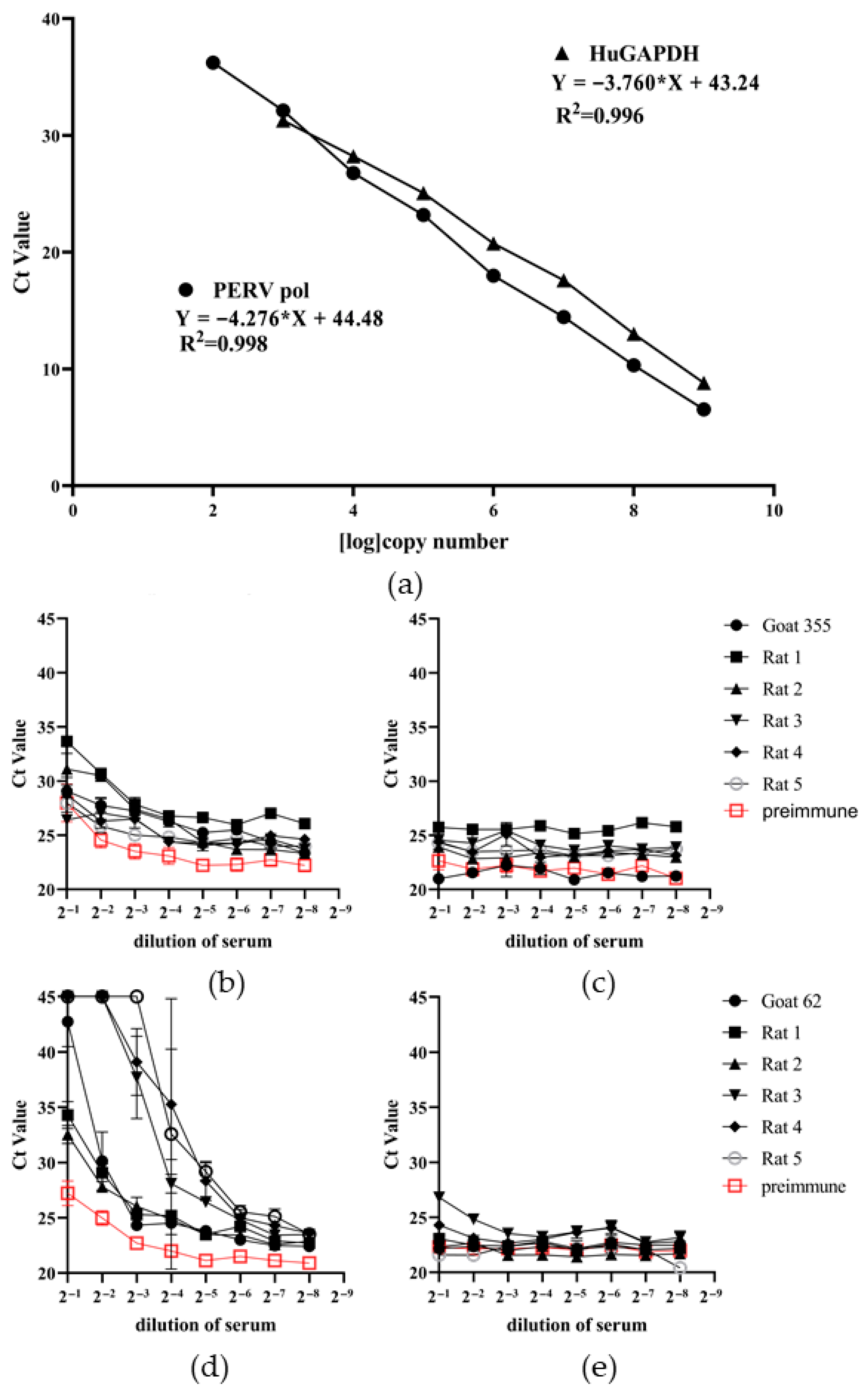
2.7. Duplex Real-Time PCR for the Detection of Provirus
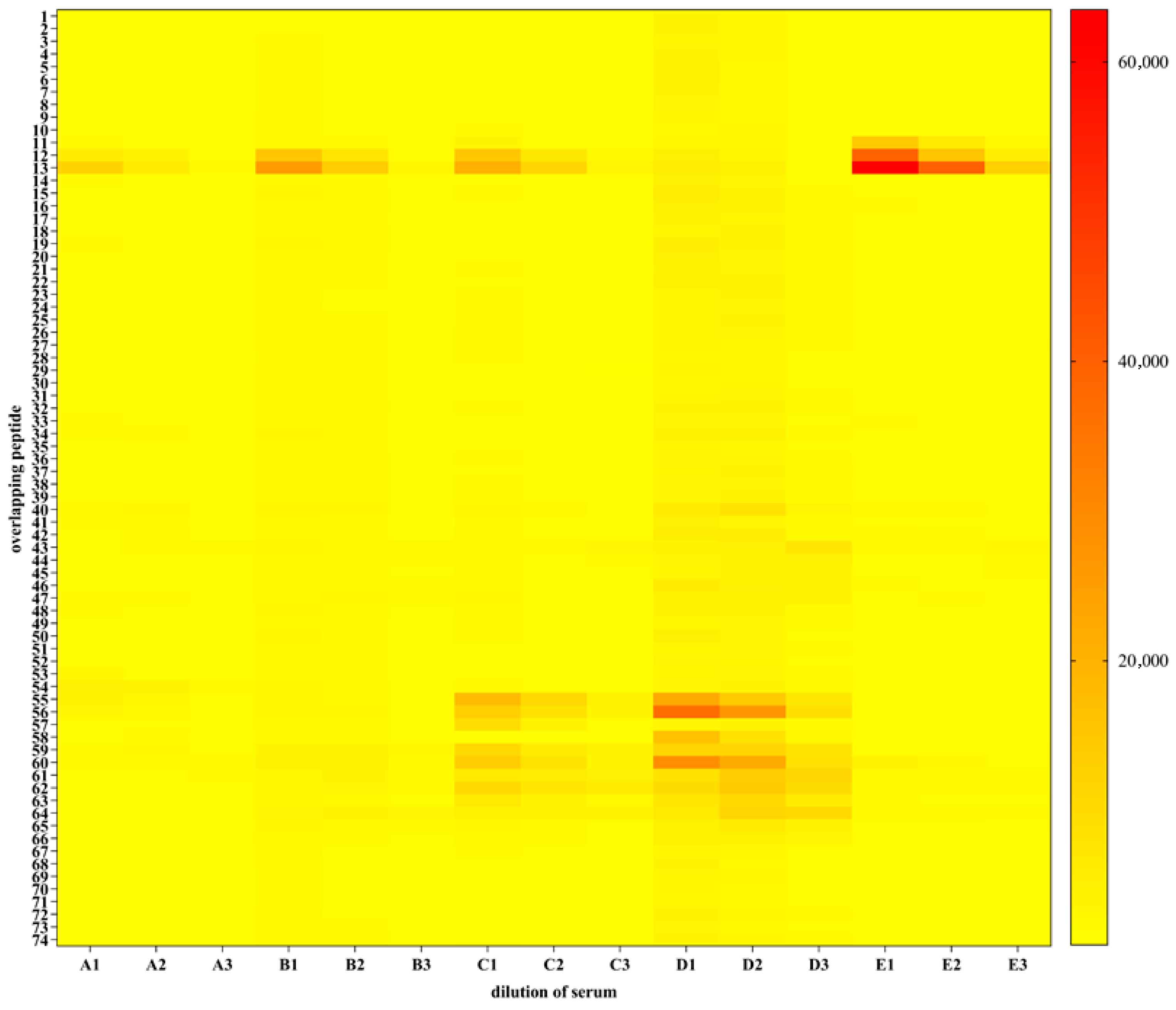
2.8. Epitope Mapping
3. Results
3.1. Production and Purification of the Antigens
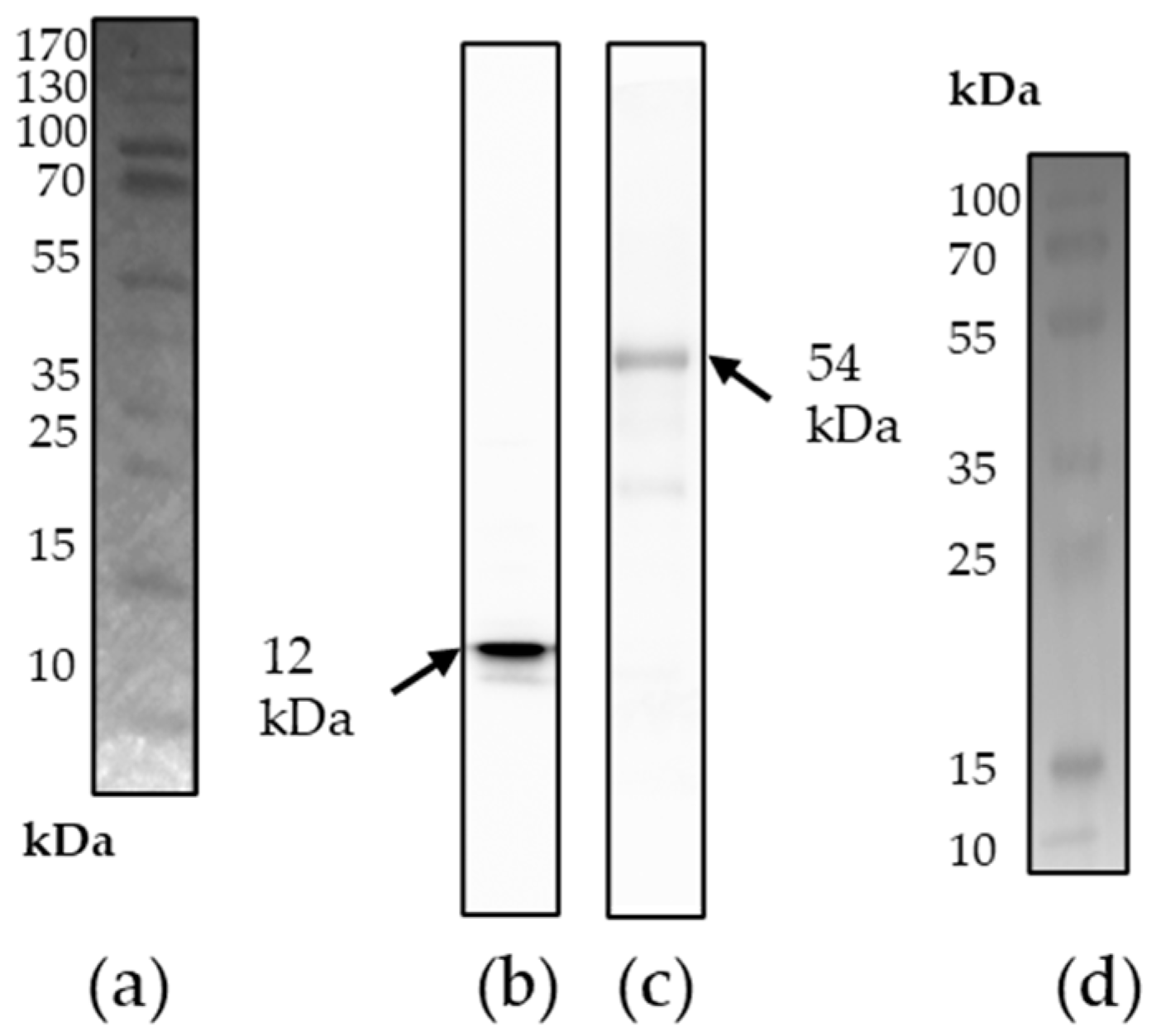
3.2. Characterization of the Antigens
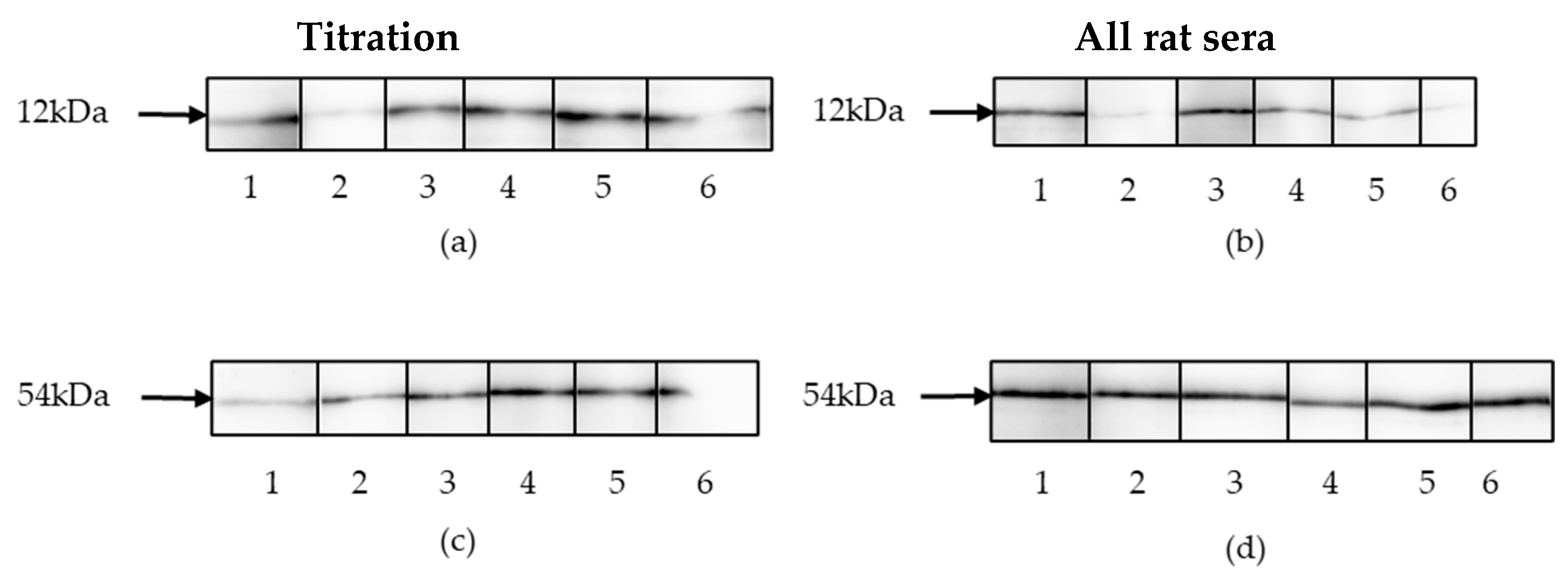
3.3. Detection of Binding Antibodies
3.4. Detection of Neutralizing Antibodies
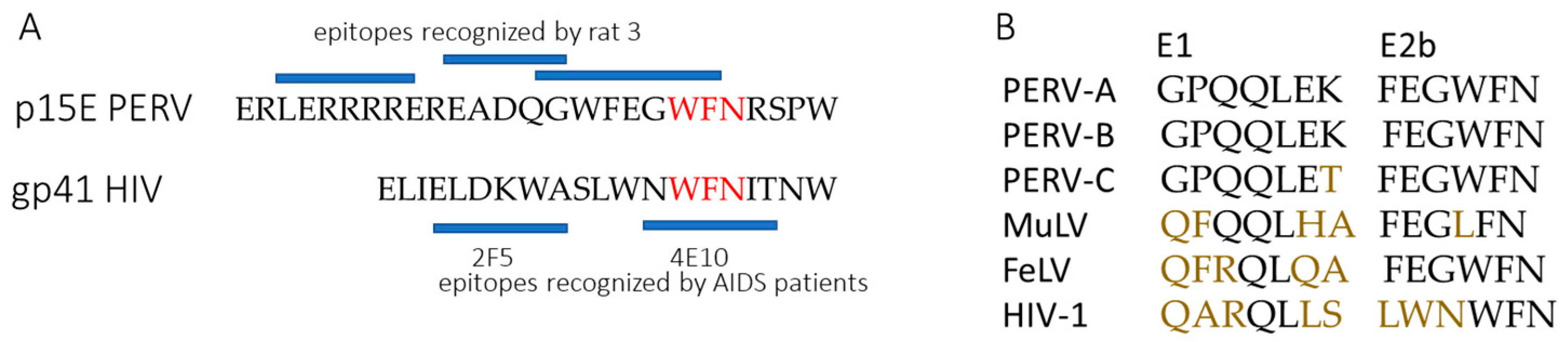
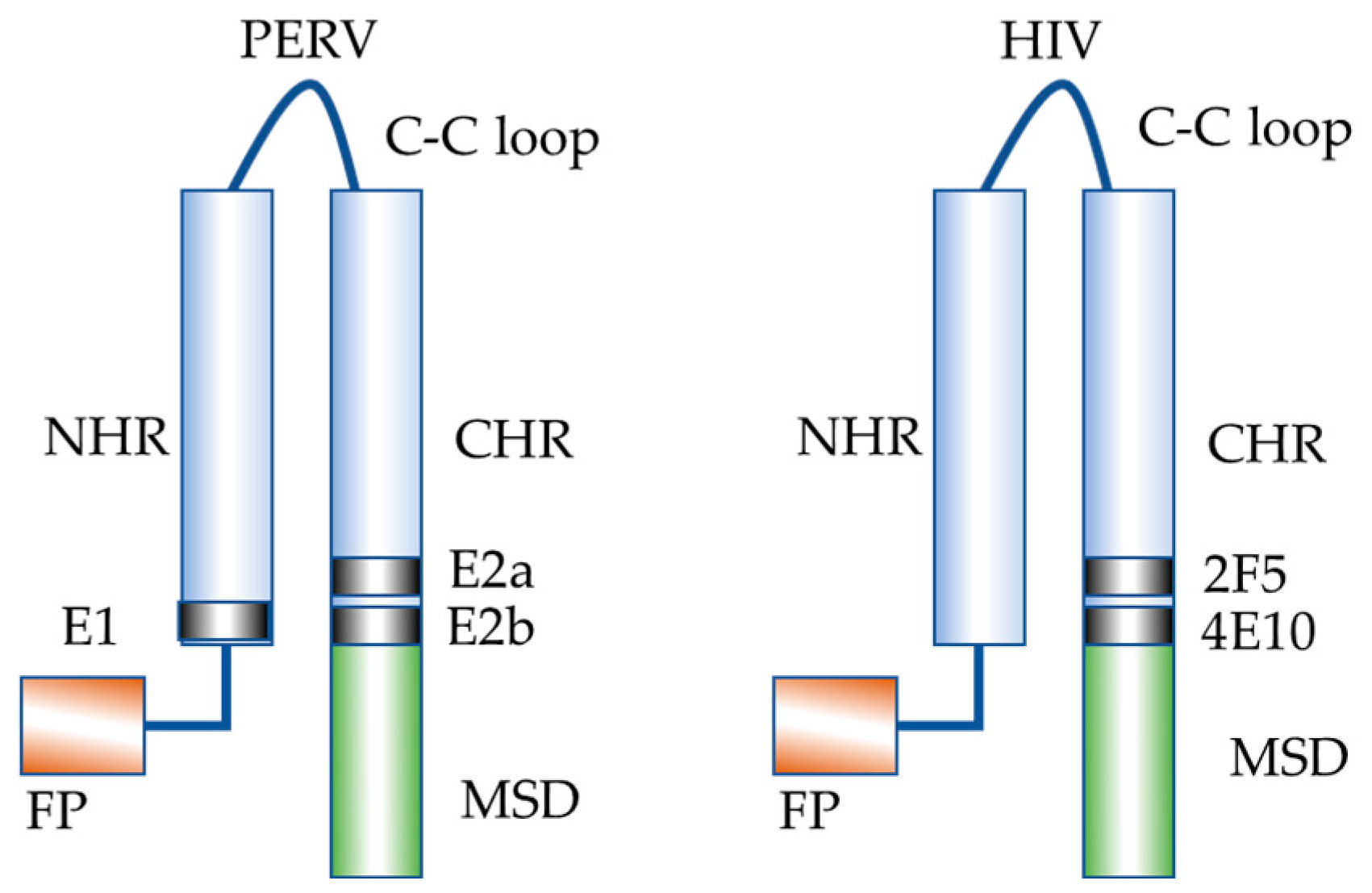
3.5. Results of the Epitope Mapping
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIDS | Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome |
| CHR | C-terminal helical region |
| CRISPR/Cas9 | Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated 9 |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium |
| FeLV | Feline leukemia virus |
| FPPR | Fusion peptide proximal region |
| LMU | Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich |
| MPER | Membrane proximal external region |
| MuLV | Murine leukemia virus |
| NHR | N-terminal helical region |
| PERV | Porcine endogenous retrovirus |
| PCMV/PRV | Porcine cytomegalovirus/porcine roseolovirus |
| SCNT | Somatic cell nuclear transfer |
| ZNF | Zinc finger nucleases |
References
- Cooper, D.K.C.; Pierson, R.N., 3rd. Milestones on the path to clinical pig organ xenotransplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2023, 23, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Kurome, M.; Kessler, B.; Kemter, E.; Wolf, E. What Genetic Modifications of Source Pigs Are Essential and Sufficient for Cell, Tissue, and Organ Xenotransplantation? Transpl. Int. 2024, 37, 13681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denner, J. Virus Safety of Xenotransplantation. Viruses 2022, 14, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, J.A. Prevention of infection in xenotransplantation: Designated pathogen-free swine in the safety equation. Xenotransplantation 2020, 27, e12595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, B.P.; Grazioli, A.; Singh, A.K.; Tully, A.; Galindo, J.; Saharia, K.K.; Shah, A.; Strauss, E.R.; Odonkor, P.N.; Williams, B.; et al. Transplantation of a genetically modified porcine heart into a live human. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Patience, C.; Magre, S.; Weiss, R.A.; Banerjee, P.T.; Le Tissier, P.; Stoye, J.P. Host range and interference studies of three classes of pig endogenous retrovirus. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 9986–9991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denner, J.; Tönjes, R.R. Infection barriers to successful xenotransplantation focusing on porcine endogenous retroviruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 318–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosch, B.; Stefanidis, D.; Myers, R.; Weiss, R.; Patience, C.; Takeuchi, Y. Evidence and consequence of porcine endogenous retrovirus recombination. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 13880–13890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denner, J. Why was PERV not transmitted during preclinical and clinical xenotransplantation trials and after inoculation of animals? Retrovirology 2018, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiebig, U.; Krüger, L.; Denner, J. Determination of the Copy Number of Porcine Endogenous Retroviruses (PERV) in Auckland Island Pigs Repeatedly Used for Clinical Xenotransplantation and Elimination of PERV-C. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, A.; Medugorac, I.; Ali, A.; Kessler, B.; Kurome, M.; Zakhartchenko, V.; Hammer, S.E.; Hauser, A.; Denner, J.; Dobenecker, B.; et al. Genetic diversity, growth and heart function of Auckland Island pigs, a potential source for organ xenotransplantation. Xenotransplantation 2024, 31, e12858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieckhoff, B.; Petersen, B.; Kues, W.A.; Kurth, R.; Niemann, H.; Denner, J. Knockdown of porcine endogenous retrovirus (PERV) expression by PERV-specific shRNA in transgenic pigs. Xenotransplantation 2008, 15, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsoondar, J.; Vaught, T.; Ball, S.; Mendicino, M.; Monahan, J.; Jobst, P.; Vance, A.; Duncan, J.; Wells, K.; Ayares, D. Production of transgenic pigs that express porcine endogenous retrovirus small interfering RNAs. Xenotransplantation 2009, 16, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semaan, M.; Kaulitz, D.; Petersen, B.; Niemann, H.; Denner, J. Long-term effects of PERV-specific RNA interference in transgenic pigs. Xenotransplantation 2012, 19, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semaan, M.; Ivanusic, D.; Denner, J. Cytotoxic Effects during Knock Out of Multiple Porcine Endogenous Retrovirus (PERV) Sequences in the Pig Genome by Zinc Finger Nucleases (ZFN). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Güell, M.; Niu, D.; George, H.; Lesha, E.; Grishin, D.; Aach, J.; Shrock, E.; Xu, W.; Poci, J.; et al. Genome-wide inactivation of porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERVs). Science 2015, 350, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, D.; Wei, H.J.; Lin, L.; George, H.; Wang, T.; Lee, I.H.; Zhao, H.Y.; Wang, Y.; Kan, Y.; Shrock, E.; et al. Inactivation of porcine endogenous retrovirus in pigs using CRISPR-Cas9. Science 2017, 357, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiser, C.; Schneider, J.; Bayer, H.; Hunsmann, G. Immunoprevention of Friend leukaemia virus-induced erythroleukaemia by vaccination with aggregated gp70. J. Gen. Virol. 1986, 67, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeras, T.; Schreiber, P.; Fournel, S.; Martin, V.; Nicolas, C.S.; Fontaine, C.; Lesbros, C.; Gueguen, S. Comparative efficacy of the Leucofeligen™ FeLV/RCP and Purevax™ RCP FeLV vaccines against infection with circulating feline Calicivirus. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebig, U.; Stephan, O.; Kurth, R.; Denner, J. Neutralizing antibodies against conserved domains of p15E of porcine endogenous retroviruses: Basis for a vaccine for xenotransplantation? Virology 2003, 307, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaulitz, D.; Fiebig, U.; Eschricht, M.; Wurzbacher, C.; Kurth, R.; Denner, J. Generation of neutralising antibodies against porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERVs). Virology 2011, 411, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denner, J.; Mihica, D.; Kaulitz, D.; Schmidt, C.M. Increased titers of neutralizing antibodies after immunization with both envelope proteins of the porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERVs). Virol. J. 2012, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waechter, A.; Eschricht, M.; Denner, J. Neutralization of porcine endogenous retrovirus by antibodies against the membrane-proximal external region of the transmembrane envelope protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waechter, A.; Denner, J. Novel neutralising antibodies targeting the N-terminal helical region of the transmembrane envelope protein p15E of the porcine endogenous retrovirus (PERV). Immunol. Res. 2014, 58, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, G.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Fang, J.H.; Hora, M. The adjuvant MF59: A 10-year perspective. In Vaccine Adjuvants: Preparation Methods and Research Protocols, Methods in Molecular Medicine; O’Hagan, D.T., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2000; Volume 42, pp. 211–228. [Google Scholar]
- Marciani, D.J.; Kensil, C.R.; Beltz, G.A.; Hung, C.H.; Cronier, J.; Aubert, A. Genetically-engineered subunit vaccine against feline leukaemia virus: Protective immune response in cats. Vaccine 1991, 9, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrendt, R.; Fiebig, U.; Norley, S.; Gürtler, L.; Kurth, R.; Denner, J. A neutralization assay for HIV-2 based on measurement of provirus integration by duplex real-time PCR. J. Virol. Methods 2009, 159, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denner, J.; Specke, V.; Thiesen, U.; Karlas, A.; Kurth, R. Genetic alterations of the long terminal repeat of an ecotropic porcine endogenous retrovirus during passage in human cells. Virology 2003, 314, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwick, M.B.; Labrijn, A.F.; Wang, M.; Spenlehauer, C.; Saphire, E.O.; Binley, J.M.; Moore, J.P.; Stiegler, G.; Katinger, H.; Burton, D.R.; et al. Broadly neutralizing antibodies targeted to the membrane-proximal external region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 glycoprotein gp41. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 10892–10905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhammer, S.; Hübner, J.; Kurth, R.; Denner, J. Antibodies neutralizing feline leukaemia virus (FeLV) in cats immunized with the transmembrane envelope protein p15E. Immunology 2006, 117, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Barroso, I.; Salzwedel, K.; Hunter, E.; Blumenthal, R. Role of the membrane-proximal domain in the initial stages of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein-mediated membrane fusion. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 6089–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzwedel, K.; West, J.T.; Hunter, E. A conserved tryptophan-rich motif in the membrane-proximal region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41 ectodomain is important for Env-mediated fusion and virus infectivity. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 2469–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coëffier, E.; Clément, J.M.; Cussac, V.; Khodaei-Boorane, N.; Jehanno, M.; Rojas, M.; Dridi, A.; Latour, M.; El Habib, R.; Barré-Sinoussi, F.; et al. Antigenicity and immunogenicity of the HIV-1 gp41 epitope ELDKWA inserted into permissive sites of the MalE protein. Vaccine 2000, 19, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, P.L.; Broder, C.C.; Long, D.; Lee, S.A.; Peterson, J.; Chakrabarti, S.; Doms, R.W.; Moss, B. Native oligomeric human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein elicits diverse monoclonal antibody reactivities. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 3015–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muster, T.; Guinea, R.; Trkola, A.; Purtscher, M.; Klima, A.; Steindl, F.; Palese, P. Cross-neutralizing activity against divergent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates induced by the gp41 sequence ELDKWAS. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 4031–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasz, N.; Morozov, V.A.; Kreutzberger, J.; Keller, M.; Eschricht, M.; Denner, J. Immunization with hybrid proteins containing the membrane proximal external region of HIV-1. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2014, 30, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustchina, E.; Li, M.; Louis, J.M.; Anderson, D.E.; Lloyd, J.; Frisch, C.; Bewley, C.A.; Gustchina, A.; Wlodawer, A.; Clore, G.M. Structural basis of HIV-1 neutralization by affinity matured Fabs directed against the internal trimeric coiled-coil of gp41. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.D.; Geleziunas, R.; Bianchi, E.; Lennard, S.; Hrin, R.; Zhang, H.; Lu, M.; An, Z.; Ingallinella, P.; Finotto, M.; et al. A human monoclonal antibody neutralizes diverse HIV-1 isolates by binding a critical gp41 epitope. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14759–14764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabin, C.; Corti, D.; Buzon, V.; Seaman, M.S.; Lutje Hulsik, D.; Hinz, A.; Vanzetta, F.; Agatic, G.; Silacci, C.; Mainetti, L.; et al. Crystal structure and size-dependent neutralization properties of HK20, a human monoclonal antibody binding to the highly conserved heptad repeat 1 of gp41. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhammer, S.; Hübner, J.; Jarrett, O.; Kurth, R.; Denner, J. Immunization with the transmembrane protein of a retrovirus, feline leukemia virus: Absence of antigenemia following challenge. Antivir. Res. 2011, 89, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langhammer, S.; Fiebig, U.; Kurth, R.; Denner, J. Increased neutralizing antibody response after simultaneous immunization with leucogen and the feline leukemia virus transmembrane protein. Intervirology 2011, 54, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Primer/Probe | Sequence 5′-3′ | Direction | Location (Nucleotide Number) | Accession Number | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PERV pol for | CGACTGCCCCAAGGGTTCAA | + | 3568–3587 | GenBank HM159246 | Yang et al. [16] |
| PERV pol rev | TCTCTCCTGCAAATCTGGGCC | − | 3783–3803 | ||
| PERV pol probe | 6FAM-CACGTACTGGAGGAGGGTCACCTG-BHQ1 | + | 3655–3678 | ||
| GAPDH for | GGCGATGCTGGCGCTGAGTAC | + | 365–385 | GenBank AF261085 | Behrendt et al. [27] |
| GAPDH rev | TGGTTCACACCCATGACGA | − | 495–513 | ||
| GAPDH probe | HEX-CTTCACCACCATGGAGAAGGCTGGG-BHQ1 | + | 407–430 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ban, J.; Krabben, L.; Kaufer, B.B.; Denner, J. Neutralizing Antibodies Against the Porcine Endogenous Retroviruses (PERVs). Viruses 2025, 17, 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111437
Ban J, Krabben L, Kaufer BB, Denner J. Neutralizing Antibodies Against the Porcine Endogenous Retroviruses (PERVs). Viruses. 2025; 17(11):1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111437
Chicago/Turabian StyleBan, Jinzhao, Ludwig Krabben, Benedikt B. Kaufer, and Joachim Denner. 2025. "Neutralizing Antibodies Against the Porcine Endogenous Retroviruses (PERVs)" Viruses 17, no. 11: 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111437
APA StyleBan, J., Krabben, L., Kaufer, B. B., & Denner, J. (2025). Neutralizing Antibodies Against the Porcine Endogenous Retroviruses (PERVs). Viruses, 17(11), 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111437








