Interferon-α for Immune Modulation in Chronic Hepatitis B Toward Functional Cure
Abstract
1. Role of the Immune System and IFN in Controlling HBV Infection
2. Immune Modulatory Role of IFN-I in Innate Immune Cell Responses
2.1. Modulatory Role of IFN-I in NK Cell Responses
2.2. Modulatory Role of IFN-I in Dendritic Cells
2.3. Modulatory Role of IFN-I in Macrophages
2.4. Modulatory Role of IFN-I in Neutrophils
3. Immune Modulatory Role of IFN-I in T and B Cell Responses
3.1. Modulatory Role of IFN-I in CD8+ T Cell Responses
3.2. Modulatory Role of IFN-I in CD4+ T Cell Responses
3.3. Modulatory Role of IFN-I in B Cell Responses
4. Strategies to Enhance HBV Specific Immune Response of IFN-I
4.1. IFN-Based Cytokine Engineering
4.2. IFN Subtype-Specific Effects
| IFN-α Subtypes | Antiviral Effects | Immunomodulatory Effects | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBV [157] | HCV [148] | HIV [155] | IAV [149] | SARS-CoV-2 [150] | ||
| IFN-α1/13 | +++ | + | +++ | - | - | / |
| IFN-α2 | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | Enhanced T cell motility [147]; Higher frequencies of GranzymeB and CD107a positive CD8+ T cells [155]; |
| IFN-α4 | + | + | + | + | ++ | / |
| IFN-α5 | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | / |
| IFN-α6 | +++ | + | +++ | + | - | / |
| IFN-α7 | ++ | +++ | ++ | + | + | / |
| IFN-α8 | ++ | +++ | + | - | +++ | Enhanced expression of IFN-γ, IL-2 and IL-4 by CD4+ T cells [159]; |
| IFN-α10 | ++ | ++ | + | + | - | Enhanced expression of IFN-γ, IL-2 and IL-4 by CD4+ T cells [159]; |
| IFN-α14 | +++ | ++ | +++ | + | +++ | Increased innate immunity and higher frequencies of TRAIL+ NK cells [155]; Resulted in a lower naive to effector CD8+ T cell ratio and associated with fewer indicators of T cell dysfunction [156]; |
| IFN-α16 | + | + | + | +++ | - | / |
| IFN-α17 | ++ | +++ | +++ | + | + | / |
| IFN-α21 | ++ | ++ | ++ | - | + | / |
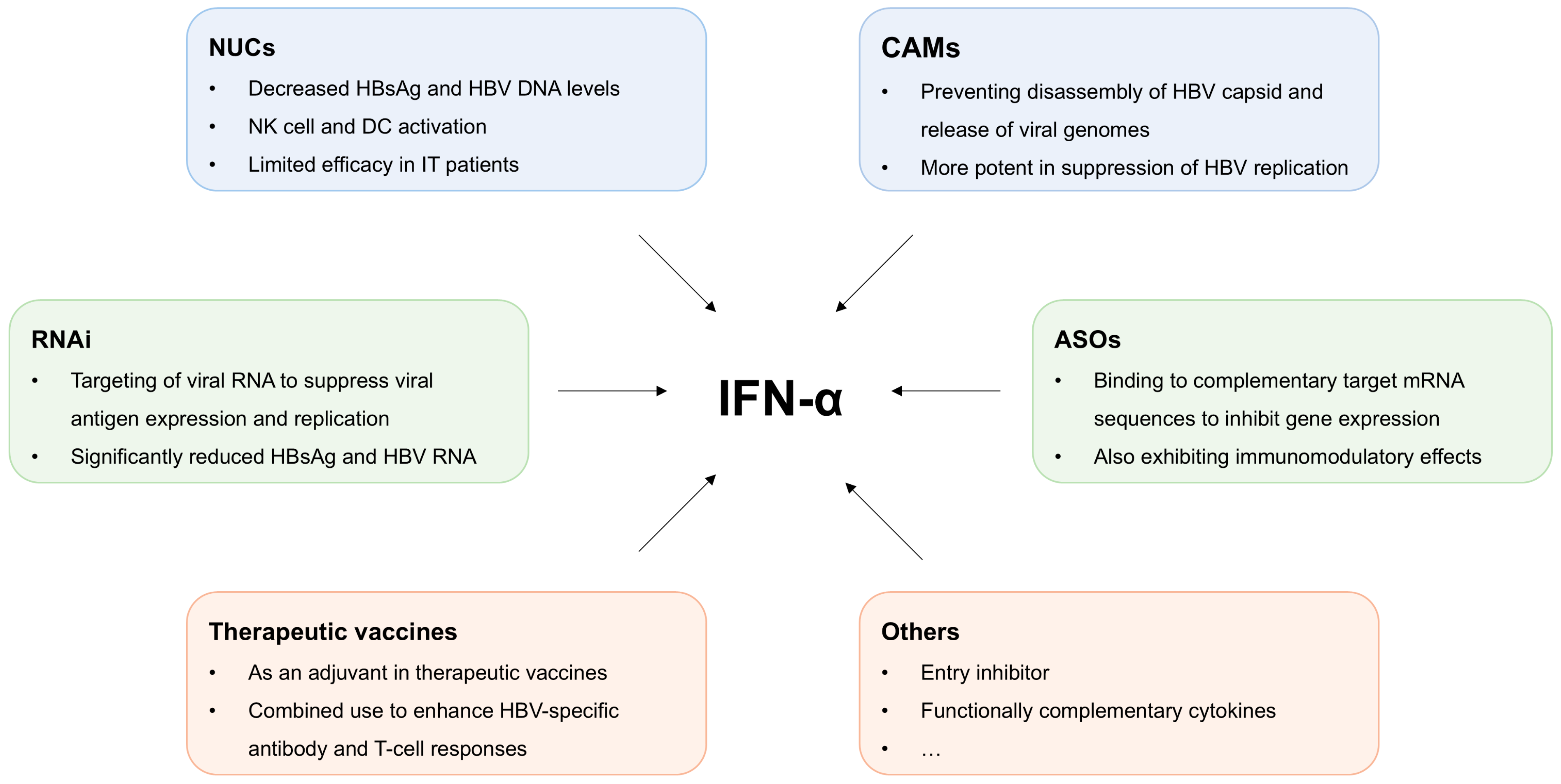
4.3. Combination Therapy
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iannacone, M.; Guidotti, L.G. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 22, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Hepatitis Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; Available online: https://www.globalhep.org/sites/default/files/content/resources/files/2024-04/2024%20Global%20Hepatitis%20Report%20-%20WHO.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Boehmer, D.; Zanoni, I. Interferons in health and disease. Cell 2025, 188, 4480–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNab, F.; Mayer-Barber, K.; Sher, A.; Wack, A.; O’Garra, A. Type I interferons in infectious disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghany, M.G.; Buti, M.; Lampertico, P.; Lee, H.M. Guidance on treatment endpoints and study design for clinical trials aiming to achieve cure in chronic hepatitis B and D: Report from the 2022 AASLD-EASL HBV-HDV Treatment Endpoints Conference. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1254–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.-H.; Hsu, C.-W.; Chang, M.-L.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lai, M.-W.; Yeh, C.-T. Peginterferon Is Superior to Nucleos(t)ide Analogues for Prevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoggins, J.W.; Wilson, S.J.; Panis, M.; Murphy, M.Y.; Jones, C.T.; Bieniasz, P.; Rice, C.M. A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature 2011, 472, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, M.; Zang, T.M.; Rihn, S.J.; Zhang, F.; Kueck, T.; Alim, M.; Schoggins, J.; Rice, C.M.; Wilson, S.J.; Bieniasz, P.D. Identification of Interferon-Stimulated Genes with Antiretroviral Activity. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, D.; Cai, D.; Levy, J.M.; Cuconati, A.; Block, T.M.; Guo, J.-T.; Guo, H. Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Mediates the Antiviral Effect of Gamma Interferon against Hepatitis B Virus in Human Hepatocyte-Derived Cells. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoletti, A.; Ferrari, C. Innate and adaptive immune responses in chronic hepatitis B virus infections: Towards restoration of immune control of viral infection. Gut 2012, 61, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maini, M.K.; Gehring, A.J. The role of innate immunity in the immunopathology and treatment of HBV infection. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S60–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, K.; Sagar; Sogukpinar, Ö.; Llewellyn-Lacey, S.; Price, D.A.; Emmerich, F.; Kraft, A.R.M.; Cornberg, M.; Kielbassa, S.; Knolle, P.; et al. Attenuated effector T cells are linked to control of chronic HBV infection. Nat. Immunol. 2024, 25, 1650–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, G.C.; Zoulim, F.; Hou, J.; Bertoletti, A. Therapeutic strategies for hepatitis B virus infection: Towards a cure. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thimme, R.; Dandri, M. Dissecting the divergent effects of interferon-alpha on immune cells: Time to rethink combination therapy in chronic hepatitis B? J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Luo, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Feng, X.; Yang, X.; Sutter, K.; Dittmer, U.; et al. A systematic comparison reveals dynamic differences in early adaptive immune responses of acute—resolving versus chronic HBV replication. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thimme, R.; Bertoletti, A.; Iannacone, M. Beyond exhaustion: The unique characteristics of CD8+ T cell dysfunction in chronic HBV infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 775–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, M.; Kallin, N.; Donakonda, S.; Zhang, J.D.; Wintersteller, H.; Hegenbarth, S.; Heim, K.; Ramirez, C.; Fürst, A.; Lattouf, E.I.; et al. A liver immune rheostat regulates CD8 T cell immunity in chronic HBV infection. Nature 2024, 631, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutgehetmann, M.; Bornscheuer, T.; Volz, T.; Allweiss, L.; Bockmann, J.H.; Pollok, J.M.; Lohse, A.W.; Petersen, J.; Dandri, M. Hepatitis B virus limits response of human hepatocytes to interferon-alpha in chimeric mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 2074–2083.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Guan, S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z. Induction of interleukin 6 impairs the anti-HBV efficiency of IFN-alpha in human hepatocytes through upregulation of SOCS3. J. Med. Virol. 2019, 91, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.L.H.; Gane, E.; Lok, A.S.F. How to achieve functional cure of HBV: Stopping NUCs, adding interferon or new drug development? J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, H.L.A.; van Zonneveld, M.; Senturk, H.; Zeuzem, S.; Akarca, U.S.; Cakaloglu, Y.; Simon, C.; So, T.M.K.; Gerken, G.; de Man, R.A.; et al. Pegylated interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: A randomised trial. Lancet 2005, 365, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouse, J.; Kalinke, U.; Oxenius, A. Regulation of antiviral T cell responses by type I interferons. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidlund, M.; Orn, A.; Wigzell, H.; Senik, A.; Gresser, I. Enhanced NK cell activity in mice injected with interferon and interferon inducers. Nature 1978, 273, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y. Direct action of type I IFN on NK cells is required for their activation in response to vaccinia viral infection in vivo. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 1592–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudreau, J.E.; Stephenson, K.B.; Wang, F.; Ashkar, A.A.; Mossman, K.L.; Lenz, L.L.; Rosenthal, K.L.; Bramson, J.L.; Lichty, B.D.; Wan, Y. IL-15 and type I interferon are required for activation of tumoricidal NK cells by virus-infected dendritic cells. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranek, T.; Manh, T.P.; Alexandre, Y.; Maqbool, M.A.; Cabeza, J.Z.; Tomasello, E.; Crozat, K.; Bessou, G.; Zucchini, N.; Robbins, S.H.; et al. Differential responses of immune cells to type I interferon contribute to host resistance to viral infection. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.B.; Salazar-Mather, T.P.; Dalod, M.Y.; Van Deusen, J.B.; Wei, X.Q.; Liew, F.Y.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Durbin, J.E.; Biron, C.A. Coordinated and distinct roles for IFN-alpha beta, IL-12, and IL-15 regulation of NK cell responses to viral infection. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 4279–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, C.; Brunetto, M.; Reynolds, G.; Christophides, T.; Kennedy, P.T.; Lampertico, P.; Das, A.; Lopes, A.R.; Borrow, P.; Williams, K.; et al. Cytokines induced during chronic hepatitis B virus infection promote a pathway for NK cell-mediated liver damage. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagi, T.; Gil, M.P.; Wang, X.; Louten, J.; Chu, W.M.; Biron, C.A. High basal STAT4 balanced by STAT1 induction to control type 1 interferon effects in natural killer cells. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2383–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micco, L.; Peppa, D.; Loggi, E.; Schurich, A.; Jefferson, L.; Cursaro, C.; Panno, A.M.; Bernardi, M.; Brander, C.; Bihl, F.; et al. Differential boosting of innate and adaptive antiviral responses during pegylated-interferon-alpha therapy of chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, A.; Bolte, F.J.; Takeda, K.; Park, N.; Yu, Z.X.; Park, H.; Valdez, K.; Ghany, M.G.; Rehermann, B. Clearance of pegylated interferon by Kupffer cells limits NK cell activation and therapy response of patients with HBV infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eaba6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, U.S.; Peppa, D.; Micco, L.; Singh, H.D.; Carey, I.; Foster, G.R.; Maini, M.K.; Kennedy, P.T. Interferon Alpha Induces Sustained Changes in NK Cell Responsiveness to Hepatitis B Viral Load Suppression In Vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Huang, D.; Wu, D.; Chen, Y.; Ma, K.; Han, M.; Luo, X.; Yan, W.; Ning, Q. Pegylated Interferon-a (IFN-a) Enhances the Inhibitory Effect of Natural Killer Cells on Regulatory T Cells via IFN-gamma in Chronic Hepatitis B. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 1878–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luft, T.; Pang, K.C.; Thomas, E.; Hertzog, P.; Hart, D.N.J.; Trapani, J.; Cebon, J. Type I IFNs Enhance the Terminal Differentiation of Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cella, M.; Salio, M.; Sakakibara, Y.; Langen, H.; Julkunen, I.; Lanzavecchia, A. Maturation, activation, and protection of dendritic cells induced by double-stranded RNA. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, M.; Schiavoni, G.; Mattei, F.; Gresser, I.; Belardelli, F.; Borrow, P.; Tough, D.F. Type I interferons produced by dendritic cells promote their phenotypic and functional activation. Blood 2002, 99, 3263–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Amakawa, R.; Inaba, M.; Ikehara, S.; Inaba, K.; Fukuhara, S. Differential regulation of human blood dendritic cell subsets by IFNs. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 2961–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, B.; Trifilo, M.J.; Zuniga, E.I.; Oldstone, M.B. Viruses evade the immune system through type I interferon-mediated STAT2-dependent, but STAT1-independent, signaling. Immunity 2005, 22, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bon, A.; Etchart, N.; Rossmann, C.; Ashton, M.; Hou, S.; Gewert, D.; Borrow, P.; Tough, D.F. Cross-priming of CD8+ T cells stimulated by virus-induced type I interferon. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bon, A.; Durand, V.; Kamphuis, E.; Thompson, C.; Bulfone-Paus, S.; Rossmann, C.; Kalinke, U.; Tough, D.F. Direct stimulation of T cells by type I IFN enhances the CD8+ T cell response during cross-priming. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 4682–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadaro, F.; Lapenta, C.; Donati, S.; Abalsamo, L.; Barnaba, V.; Belardelli, F.; Santini, S.M.; Ferrantini, M. IFN-alpha enhances cross-presentation in human dendritic cells by modulating antigen survival, endocytic routing, and processing. Blood 2012, 119, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, E.; Fessenden, T.B.; Lutz, E.; Dinter, T.; Yim, L.; Blatt, S.; Bhutkar, A.; Wittrup, K.D.; Spranger, S. Type I interferon activates MHC class I-dressed CD11b+ conventional dendritic cells to promote protective anti-tumor CD8+ T cell immunity. Immunity 2022, 55, 308–323.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlato, S.; Santini, S.M.; Lapenta, C.; Di Pucchio, T.; Logozzi, M.; Spada, M.; Giammarioli, A.M.; Malorni, W.; Fais, S.; Belardelli, F. Expression of CCR-7, MIP-3beta, and Th-1 chemokines in type I IFN-induced monocyte-derived dendritic cells: Importance for the rapid acquisition of potent migratory and functional activities. Blood 2001, 98, 3022–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouzaut, A.; Garasa, S.; Teijeira, A.; Gonzalez, I.; Martinez-Forero, I.; Suarez, N.; Larrea, E.; Alfaro, C.; Palazon, A.; Dubrot, J.; et al. Dendritic cells adhere to and transmigrate across lymphatic endothelium in response to IFN-alpha. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 3054–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, D.; Yao, J.; Zhang, H.; Jin, L.; Shi, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.S. Increased infiltration of intrahepatic DC subsets closely correlate with viral control and liver injury in immune active pediatric patients with chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 122, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonejima, A.; Mizukoshi, E.; Tamai, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Kitahara, M.; Yamashita, T.; Arai, K.; Terashima, T.; Iida, N.; Fushimi, K.; et al. Characteristics of Impaired Dendritic Cell Function in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Hepatology 2019, 70, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, D.; Yao, J.; Fu, J.; Jin, L.; Wang, F.S. Response to interferon-alpha treatment correlates with recovery of blood plasmacytoid dendritic cells in children with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2007, 47, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, W.; Xu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, W.; Shi, B.; Wan, S.; Liu, J.; et al. Hepatitis B virus surface antigen drives T cell immunity through non-canonical antigen presentation in mice. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Xia, Y.; Serti, E.; Block, P.D.; Chung, M.; Chayama, K.; Rehermann, B.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B virus evades innate immunity of hepatocytes but activates cytokine production by macrophages. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Han, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Xu, C.; Wei, L.; Jiang, J.D.; Block, T.M.; Guo, J.T.; et al. STING agonists induce an innate antiviral immune response against hepatitis B virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, M.; Meng, Z.; Trippler, M.; Broering, R.; Szczeponek, A.; Krux, F.; Dittmer, U.; Roggendorf, M.; Gerken, G.; et al. Toll-like receptor-mediated control of HBV replication by nonparenchymal liver cells in mice. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Pan, T.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; et al. Exosomes mediate the cell-to-cell transmission of IFN-α-induced antiviral activity. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, D.T.; Negash, A.; Chen, J.; Crochet, N.; Sinha, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guedj, J.; Holder, S.; Saito, T.; Lemon, S.M.; et al. Innate immune tolerance and the role of kupffer cells in differential responses to interferon therapy among patients with HCV genotype 1 infection. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 402–413.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleetwood, A.J.; Dinh, H.; Cook, A.D.; Hertzog, P.J.; Hamilton, J.A. GM-CSF- and M-CSF-dependent macrophage phenotypes display differential dependence on type I interferon signaling. J. Leukoc Biol. 2009, 86, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.S.; Janssen, H.L.; Boonstra, A. Type I and III interferons enhance IL-10R expression on human monocytes and macrophages, resulting in IL-10-mediated suppression of TLR-induced IL-12. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 2431–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, K.; Frenz, T.; Spanier, J.; Tegtmeyer, P.K.; Chhatbar, C.; Skerra, J.; Ghita, L.; Namineni, S.; Lienenklaus, S.; Koster, M.; et al. Type I interferon receptor signaling delays Kupffer cell replenishment during acute fulminant viral hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minayoshi, Y.; Maeda, H.; Yanagisawa, H.; Hamasaki, K.; Mizuta, Y.; Nishida, K.; Kinoshita, R.; Enoki, Y.; Imafuku, T.; Chuang, V.T.G.; et al. Development of Kupffer cell targeting type-I interferon for the treatment of hepatitis via inducing anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory actions. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanguez, E.; Garcia-Culebras, A.; Frau, A.; Llompart, C.; Knobeloch, K.P.; Gutierrez-Erlandsson, S.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Esteban, M.; Nieto, A.; Guerra, S. ISG15 regulates peritoneal macrophages functionality against viral infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldanta, S.; Fernandez-Escobar, M.; Acin-Perez, R.; Albert, M.; Camafeita, E.; Jorge, I.; Vazquez, J.; Enriquez, J.A.; Guerra, S. ISG15 governs mitochondrial function in macrophages following vaccinia virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Qin, B.; Xiao, C.; Lu, X.; Chen, L. Cell-type specific interferon stimulated gene staining in liver underlies response to interferon therapy in chronic HBV infected patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 2355–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirafuji, N.; Matsuda, S.; Ogura, H.; Tani, K.; Kodo, H.; Ozawa, K.; Nagata, S.; Asano, S.; Takaku, F. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor stimulates human mature neutrophilic granulocytes to produce interferon-alpha. Blood 1990, 75, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einhorn, S.; Jarstrand, C. Functions of human neutrophilic granulocytes after in vivo exposure to interferon alpha. Infect Immun. 1984, 43, 1054–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazzolla, G.; Giannelli, G.; Antonelli, G.; Tortorella, C.; Jirillo, E.; Schiraldi, O.; Antonaci, S. Effects of interferon-alpha treatment on neutrophil oxidative metabolism, lymphocyte proliferation and monocyte HLA class I antigen expression in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 1996, 18, 529–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, A.; Kobayashi, H.; Teramura, K.; Yoshimoto, S.; Ohsawa, N. Effects of interferon-alpha on peripheral neutrophil counts and serum granulocyte colony-stimulating factor levels in chronic hepatitis C patients. Cytokines Cell Mol. Ther. 2000, 6, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jablonowska, E.; Wojcik, K.; Kur, B.; Lewkowicz, P.; Nocun, M. Neutrophil function and apoptosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with pegylated interferon alpha and ribavirin. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2012, 60, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, S.; Kimura, K.; Nagaki, M.; Satake, S.; Kakimi, K.; Moriwaki, H. Blockade of neutrophil elastase attenuates severe liver injury in hepatitis B transgenic mice. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 15142–15150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, T.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, S.; Deng, H.; Zhong, B. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) are associated with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, X.; Jiang, J.; Yang, L.; Xin, J.; Shi, D.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Ren, K.; Hassan, H.M.; et al. PBMC transcriptomics identifies immune-metabolism disorder during the development of HBV-ACLF. Gut 2022, 71, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Ren, H.; Li, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, J.; Chen, Z.; et al. Circulating Neutrophil Dysfunction in HBV-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 620365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtsinger, J.M.; Valenzuela, J.O.; Agarwal, P.; Lins, D.; Mescher, M.F. Type I IFNs provide a third signal to CD8 T cells to stimulate clonal expansion and differentiation. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 4465–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervas-Stubbs, S.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Gonzalez, I.; Mancheno, U.; Dubrot, J.; Azpilicueta, A.; Gabari, I.; Palazon, A.; Aranguren, A.; Ruiz, J.; et al. Effects of IFN-alpha as a signal-3 cytokine on human naive and antigen-experienced CD8+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolumam, G.A.; Thomas, S.; Thompson, L.J.; Sprent, J.; Murali-Krishna, K. Type I interferons act directly on CD8 T cells to allow clonal expansion and memory formation in response to viral infection. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.J.; Kolumam, G.A.; Thomas, S.; Murali-Krishna, K. Innate inflammatory signals induced by various pathogens differentially dictate the IFN-I dependence of CD8 T cells for clonal expansion and memory formation. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 1746–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starbeck-Miller, G.R.; Xue, H.H.; Harty, J.T. IL-12 and type I interferon prolong the division of activated CD8 T cells by maintaining high-affinity IL-2 signaling in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimeno, R.; Lee, C.K.; Schindler, C.; Levy, D.E. Stat1 and Stat2 but not Stat3 arbitrate contradictory growth signals elicited by alpha/beta interferon in T lymphocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 5456–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, Y.; Nishibori, T.; Su, L.; Arduini, R.M.; Baker, D.P.; David, M. Cutting edge: Role of STAT1, STAT3, and STAT5 in IFN-alpha beta responses in T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.B.; Cousens, L.P.; Doughty, L.A.; Pien, G.C.; Durbin, J.E.; Biron, C.A. Interferon alpha/beta-mediated inhibition and promotion of interferon gamma: STAT1 resolves a paradox. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.B.; Watford, W.T.; Salomon, R.; Hofmann, S.R.; Pien, G.C.; Morinobu, A.; Gadina, M.; O’Shea, J.J.; Biron, C.A. Critical role for STAT4 activation by type 1 interferons in the interferon-gamma response to viral infection. Science 2002, 297, 2063–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.K.; Daffis, S.; Brien, J.D.; Gainey, M.D.; Yokoyama, W.M.; Sheehan, K.C.; Murphy, K.M.; Schreiber, R.D.; Diamond, M.S. A temporal role of type I interferon signaling in CD8+ T cell maturation during acute West Nile virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Swiecki, M.; Cella, M.; Alber, G.; Schreiber, R.D.; Gilfillan, S.; Colonna, M. Timing and magnitude of type I interferon responses by distinct sensors impact CD8 T cell exhaustion and chronic viral infection. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 11, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Du, Y.; Huang, S.; Chen, M.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Han, M.; Li, J.; Yu, Q.; et al. Simultaneous or Prior Activation of Intrahepatic Type I Interferon Signaling Leads to Hepatitis B Virus Persistence in a Mouse Model. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0003421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovich, B.A.; Li, J.; Shannon, J.; Hurren, R.; Chalupny, J.; Cosman, D.; Miller, R.G. Activated, but not resting, T cells can be recognized and killed by syngeneic NK cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3572–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soderquest, K.; Walzer, T.; Zafirova, B.; Klavinskis, L.S.; Polic, B.; Vivier, E.; Lord, G.M.; Martin-Fontecha, A. Cutting edge: CD8+ T cell priming in the absence of NK cells leads to enhanced memory responses. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 3304–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppa, D.; Gill, U.S.; Reynolds, G.; Easom, N.J.; Pallett, L.J.; Schurich, A.; Micco, L.; Nebbia, G.; Singh, H.D.; Adams, D.H.; et al. Up-regulation of a death receptor renders antiviral T cells susceptible to NK cell-mediated deletion. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouse, J.; Bedenikovic, G.; Wiesel, M.; Ibberson, M.; Xenarios, I.; Von Laer, D.; Kalinke, U.; Vivier, E.; Jonjic, S.; Oxenius, A. Type I interferons protect T cells against NK cell attack mediated by the activating receptor NCR1. Immunity 2014, 40, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.C.; Grusdat, M.; Pandyra, A.A.; Polz, R.; Huang, J.; Sharma, P.; Deenen, R.; Kohrer, K.; Rahbar, R.; Diefenbach, A.; et al. Type I interferon protects antiviral CD8+ T cells from NK cell cytotoxicity. Immunity 2014, 40, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimme, R.; Wieland, S.; Steiger, C.; Ghrayeb, J.; Reimann, K.A.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. CD8+ T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Pegylated interferon α-2b up-regulates specific CD8+ T cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wu, D.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, W.; Hu, D.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tao, R.; Xiao, F.; et al. End-of-treatment HBcrAg and HBsAb levels identify durable functional cure after Peg-IFN-based therapy in patients with CHB. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Jia, H.; Qian, X.; Tang, T.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yu, G.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the immunoregulatory roles of PegIFN-α in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2024, 79, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, K.; Isogawa, M.; Onishi, M.; Baudi, I.; Saito, S.; Nakajima, A.; Fujita, T.; Tanaka, Y. Restoration of type I interferon signaling in intrahepatically primed CD8+ T cells promotes functional differentiation. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e145761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, S.; Zhao, X.; Chen, M.; Lin, Y.; Xia, Y.; Sun, C.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. Poly(I:C) treatment leads to interferon-dependent clearance of hepatitis B virus in a hydrodynamic injection mouse model. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10421–10431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Li, Q.; Wen, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, Z.; Ye, G.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Interferon alpha facilitates anti-HBV cellular immune response in a B cell-dependent manner. Antivir. Res. 2022, 207, 105420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.T.; Hoang, L.T.; Chin, D.; Rasmussen, E.; Lopatin, U.; Hart, S.; Bitter, H.; Chu, T.; Gruenbaum, L.; Ravindran, P.; et al. Reduction of HBV replication prolongs the early immunological response to IFNalpha therapy. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penna, A.; Laccabue, D.; Libri, I.; Giuberti, T.; Schivazappa, S.; Alfieri, A.; Mori, C.; Canetti, D.; Lampertico, P.; Vigano, M.; et al. Peginterferon-alpha does not improve early peripheral blood HBV-specific T-cell responses in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, K.; Isogawa, M.; Hamada-Tsutsumi, S.; Baudi, I.; Saito, S.; Nakajima, A.; Tanaka, Y. Type I Interferon Signaling Prevents Hepatitis B Virus-Specific T Cell Responses by Reducing Antigen Expression. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01099-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allweiss, L.; Volz, T.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Giersch, K.; Bornscheuer, T.; Lohse, A.W.; Petersen, J.; Ma, H.; Klumpp, K.; Fletcher, S.P.; et al. Immune cell responses are not required to induce substantial hepatitis B virus antigen decline during pegylated interferon-alpha administration. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, A.; Veeraswamy, R.; Pekosz, A.; Kanagawa, O.; Unanue, E.R.; Colonna, M.; Cella, M. Interferon-producing cells fail to induce proliferation of naive T cells but can promote expansion and T helper 1 differentiation of antigen-experienced unpolarized T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, H.J.; Davis, A.M.; George, T.C.; Farrar, J.D. IFN-alpha is not sufficient to drive Th1 development due to lack of stable T-bet expression. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 3792–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giovanni, M.; Cutillo, V.; Giladi, A.; Sala, E.; Maganuco, C.G.; Medaglia, C.; Di Lucia, P.; Bono, E.; Cristofani, C.; Consolo, E.; et al. Spatiotemporal regulation of type I interferon expression determines the antiviral polarization of CD4+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osokine, I.; Snell, L.M.; Cunningham, C.R.; Yamada, D.H.; Wilson, E.B.; Elsaesser, H.J.; de la Torre, J.C.; Brooks, D. Type I interferon suppresses de novo virus-specific CD4 Th1 immunity during an established persistent viral infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7409–7414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havenar-Daughton, C.; Kolumam, G.A.; Murali-Krishna, K. Cutting Edge: The direct action of type I IFN on CD4 T cells is critical for sustaining clonal expansion in response to a viral but not a bacterial infection. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 3315–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corre, B.; Perrier, J.; El Khouri, M.; Cerboni, S.; Pellegrini, S.; Michel, F. Type I interferon potentiates T-cell receptor mediated induction of IL-10-producing CD4+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 2730–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, S.; Russo, V.; Dettori, B.; Palombi, C.; Baev, D.; Proietti, E.; Le Bon, A.; Belardelli, F.; Pace, L. Type I interferons induce peripheral T regulatory cell differentiation under tolerogenic conditions. Int. Immunol. 2021, 33, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Koch, M.A.; Pepper, M.; Campbell, D.J. Type I interferons directly inhibit regulatory T cells to allow optimal antiviral T cell responses during acute LCMV infection. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 961–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangaplara, A.; Martens, C.; Dahlstrom, E.; Metidji, A.; Gokhale, A.S.; Glass, D.D.; Lopez-Ocasio, M.; Baur, R.; Kanakabandi, K.; Porcella, S.F.; et al. Type I interferon signaling attenuates regulatory T cell function in viral infection and in the tumor microenvironment. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narmada, B.C.; Khakpoor, A.; Shirgaonkar, N.; Narayanan, S.; Kim Aw, P.P.; Singh, M.; Ong, K.H.; Owino, C.O.; Ting Ng, J.W.; Yew, H.C.; et al. Single cell landscape of functionally cured chronic hepatitis B patients reveals activation of innate and altered CD4-CTL-driven adaptive immunity. J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri-Aria, K.T.; Alexander, G.J.; Magrin, S.; Anderson, M.G.; Eddleston, A.L.; Williams, R. Differential effect of alpha-interferons on CD4- and CD8-positive lymphocytes in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers. J. Hepatol. 1988, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, M.A.; Quiroga, J.A.; Subira, D.; Castanon, S.; Esteban, J.M.; Pardo, M.; Carreno, V. Hepatitis B virus-specific T-cell proliferation and cytokine secretion in chronic hepatitis B e antibody-positive patients treated with ribavirin and interferon alpha. Hepatology 2001, 33, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.Y.; Jin, H.; Piao, X.X.; Piao, F.S. Ribavirin and IFN-alpha combination therapy induces CD4+ T-cell proliferation and Th1 cytokine secretion in patients with chronic hepatitis B. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 5440–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coro, E.S.; Chang, W.L.; Baumgarth, N. Type I IFN receptor signals directly stimulate local B cells early following influenza virus infection. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 4343–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, K.; Lang, K.S.; Manjarrez-Orduno, N.; Junt, T.; Senn, B.M.; Holdener, M.; Akira, S.; Zinkernagel, R.M.; Hengartner, H. Early type I interferon-mediated signals on B cells specifically enhance antiviral humoral responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 2094–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groof, A.; Ducreux, J.; Aleva, F.; Long, A.J.; Ferster, A.; van der Ven, A.; van de Veerdonk, F.; Houssiau, F.A.; Lauwerys, B.R. STAT3 phosphorylation mediates the stimulatory effects of interferon alpha on B cell differentiation and activation in SLE. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bon, A.; Schiavoni, G.; D’Agostino, G.; Gresser, I.; Belardelli, F.; Tough, D.F. Type i interferons potently enhance humoral immunity and can promote isotype switching by stimulating dendritic cells in vivo. Immunity 2001, 14, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bon, A.; Thompson, C.; Kamphuis, E.; Durand, V.; Rossmann, C.; Kalinke, U.; Tough, D.F. Cutting edge: Enhancement of antibody responses through direct stimulation of B and T cells by type I IFN. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 2074–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Q.; Langston, H.; Cooper, M.D. Resident bone marrow macrophages produce type 1 interferons that can selectively inhibit interleukin-7-driven growth of B lineage cells. Immunity 1995, 3, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseman, E.A.; Wu, T.; de la Torre, J.C.; Schwartzberg, P.L.; McGavern, D.B. Type I interferon suppresses virus-specific B cell responses by modulating CD8+ T cell differentiation. Sci. Immunol. 2016, 1, eaah3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.; Fu, R.; Lei, X.; He, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Guo, X.; Chen, F.; et al. Therapeutic vaccine-induced plasma cell differentiation is defective in the presence of persistently high HBsAg levels. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, 714–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.R.; Pallett, L.J.; McCoy, L.E.; Suveizdyte, K.; Amin, O.E.; Swadling, L.; Alberts, E.; Davidson, B.R.; Kennedy, P.T.F.; Gill, U.S.; et al. Circulating and intrahepatic antiviral B cells are defective in hepatitis B. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4588–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bert, N.; Salimzadeh, L.; Gill, U.S.; Dutertre, C.-A.; Facchetti, F.; Tan, A.; Hung, M.; Novikov, N.; Lampertico, P.; Fletcher, S.P.; et al. Comparative characterization of B cells specific for HBV nucleocapsid and envelope proteins in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanwolleghem, T.; Groothuismink, Z.M.A.; Kreefft, K.; Hung, M.; Novikov, N.; Boonstra, A. Hepatitis B core-specific memory B cell responses associate with clinical parameters in patients with chronic HBV. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Q.; Tan, L.; Gan, W.Q.; Mo, Z.S.; Chen, D.B.; Wang, P.P.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Xie, D.Y.; Gao, Z.L. The relationship between the clearance of HBsAg and the remodeling of B cell subsets in CHB patients treated with Peg-IFN-alpha. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspord, C.; Bruder Costa, J.; Jacob, M.C.; Dufeu-Duchesne, T.; Bertucci, I.; Pouget, N.; Brevot-Lutton, O.; Zoulim, F.; Bourliere, M.; Plumas, J.; et al. Remodeling of B-Cell Subsets in Blood during Pegylated IFNalpha-2a Therapy in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Yu, K.; Dong, M.; Wang, J.; Yang, F.; Zhu, H.; Yu, J.; Yang, J.; Xie, W.; Mitra, B.; et al. Intrahepatic transcriptomics reveals gene signatures in chronic hepatitis B patients responded to interferon therapy. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1876–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Hu, X.; Yu, L.; Ji, H.; Li, W.; Cai, Y.; Cheng, G.; Jiang, Y. T follicular helper cells improve the response of patients with chronic hepatitis B to interferon by promoting HBsAb production. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 57, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-W.; Lai, R.-M.; Wang, L.-F.; Wang, S.-L.; Xue, H.-X.; Li, C.; Zheng, Z.-Z.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.-Y.; Zeng, D.-W.; et al. Varied immune responses of HBV-specific B cells in patients undergoing pegylated interferon-alpha treatment for chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Wan, Y.; Issa, R.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Mao, M.; Li, M.; Tong, X.; Tian, C.; et al. The presence of baseline HBsAb-Specific B cells can predict HBsAg or HBeAg seroconversion of chronic hepatitis B on treatment. Emerg. Microbes Infect 2023, 12, 2259003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Wang, D.; Shen, X.; Guo, C.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Sun, R.; Li, J.; Tian, Z.; Wei, H. Immunomodulation Induced During Interferon-alpha Therapy Impairs the Anti-HBV Immune Response Through CD24(+)CD38(hi) B Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 591269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R. Development and Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2a (40 kD). Semin. Liver Dis. 2004, 24, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooksley, W.G.; Piratvisuth, T.; Lee, S.D.; Mahachai, V.; Chao, Y.C.; Tanwandee, T.; Chutaputti, A.; Chang, W.Y.; Zahm, F.E.; Pluck, N. Peginterferon alpha-2a (40 kDa): An advance in the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. J. Viral Hepat. 2003, 10, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramon, J.; Saez, V.; Baez, R.; Aldana, R.; Hardy, E. PEGylated interferon-alpha2b: A branched 40K polyethylene glycol derivative. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 1374–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooksley, W.G. Treatment with interferons (including pegylated interferons) in patients with hepatitis B. Semin. Liver Dis. 2004, 24 (Suppl. S1), 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Schlapschy, M.; Morath, V.; Roeder, N.; Vogt, E.I.; Stadler, D.; Cheng, X.; Dittmer, U.; Sutter, K.; Heikenwalder, M.; et al. PASylated interferon alpha efficiently suppresses hepatitis B virus and induces anti-HBs seroconversion in HBV-transgenic mice. Antivir. Res. 2019, 161, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, P.; Gao, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, M.; Peng, H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J. VEGFR2-targeted antibody fused with IFN alpha mut regulates the tumor microenvironment of colorectal cancer and exhibits potent anti-tumor and anti-metastasis activity. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Yan, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, L.; Xue, X.; Li, M.; Li, W.; Hao, Q.; Wan, Y.; Qin, X.; et al. High-yield expression, purification and characterization of tumor-targeted IFN-alpha2a. Cytotherapy 2007, 9, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, C.; Steward, K.K.; Timmerman, J.M.; Morrison, S.L. Targeted delivery of interferon-alpha via fusion to anti-CD20 results in potent antitumor activity against B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2010, 115, 2864–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, C.Y.; Sun, S.; Liang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, F.S.; Fu, Y.X.; Peng, H. Engineered anti-PDL1 with IFNalpha targets both immunoinhibitory and activating signals in the liver to break HBV immune tolerance. Gut 2022, 72, 1544–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulstock, E.; Sosabowski, J.; Ovecka, M.; Prince, R.; Goodall, L.; Mudd, C.; Sepp, A.; Davies, M.; Foster, J.; Burnet, J.; et al. Liver-targeting of interferon-alpha with tissue-specific domain antibodies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Sastry, K.S.; Tiefenthaler, G.; Cano, J.; Tang, T.; Ho, Z.Z.; Teoh, D.; Bohini, S.; Chen, A.; Sankuratri, S.; et al. Targeted delivery of interferon-alpha to hepatitis B virus-infected cells using T-cell receptor-like antibodies. Hepatology 2012, 56, 2027–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Wang, J.; Shen, W.C. Lipidization of human interferon-alpha: A new approach toward improving the delivery of protein drugs. J. Control. Release 2008, 129, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioravanti, J.; Gonzalez, I.; Medina-Echeverz, J.; Larrea, E.; Ardaiz, N.; Gonzalez-Aseguinolaza, G.; Prieto, J.; Berraondo, P. Anchoring interferon alpha to apolipoprotein A-I reduces hematological toxicity while enhancing immunostimulatory properties. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeytin, H.; Reali, E.; Zaharoff, D.A.; Rogers, C.J.; Schlom, J.; Greiner, J.W. Targeted delivery of murine IFN-gamma using a recombinant fowlpox virus: NK cell recruitment to regional lymph nodes and priming of tumor-specific host immunity. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2008, 28, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotz, C.; Wagenaar, T.R.; Gieseke, F.; Bangari, D.S.; Callahan, M.; Cao, H.; Diekmann, J.; Diken, M.; Grunwitz, C.; Hebert, A.; et al. Local delivery of mRNA-encoded cytokines promotes antitumor immunity and tumor eradication across multiple preclinical tumor models. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabc7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar, G.; Moi, D.; Ranghetti, A.; Ozkal-Baydin, P.; Squadrito, M.L.; Kajaste-Rudnitski, A.; Bondanza, A.; Gentner, B.; De Palma, M.; Mazzieri, R.; et al. Genetic engineering of hematopoiesis for targeted IFN-alpha delivery inhibits breast cancer progression. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 217ra213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutter, K.; Dickow, J.; Dittmer, U. Interferon alpha subtypes in HIV infection. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018, 40, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilkens, C.M.; Schlaak, J.F.; Kerr, I.M. Differential responses to IFN-alpha subtypes in human T cells and dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 5255–5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.R.; Masri, S.H.; David, R.; Jones, M.; Datta, A.; Lombardi, G.; Runkell, L.; de Dios, C.; Sizing, I.; James, M.J.; et al. IFN-alpha subtypes differentially affect human T cell motility. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, A.; Francois, C.; Descamps, V.; Fournier, C.; Wychowski, C.; Dubuisson, J.; Castelain, S.; Duverlie, G. Enhanced anti-HCV activity of interferon alpha 17 subtype. Virol. J. 2009, 6, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, A.D.R.; Wunderlich, K.; Schloer, S.; Schughart, K.; Geffers, R.; Seders, M.; Witt, M.; Christersson, A.; Wiewrodt, R.; Wiebe, K.; et al. Antiviral potential of human IFN-alpha subtypes against influenza A H3N2 infection in human lung explants reveals subtype-specific activities. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 1763–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhenn, J.; Meister, T.L.; Todt, D.; Bracht, T.; Schork, K.; Billaud, J.N.; Elsner, C.; Heinen, N.; Karakoese, Z.; Haid, S.; et al. Differential interferon-alpha subtype induced immune signatures are associated with suppression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2111600119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, M.S.; Guo, K.; Gibbert, K.; Lee, E.J.; Dillon, S.M.; Barrett, B.S.; McCarter, M.D.; Hasenkrug, K.J.; Dittmer, U.; Wilson, C.C.; et al. Interferon-alpha Subtypes in an Ex Vivo Model of Acute HIV-1 Infection: Expression, Potency and Effector Mechanisms. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Shen, G.; Kibbie, J.; Gonzalez, T.; Dillon, S.M.; Smith, H.A.; Cooper, E.H.; Lavender, K.; Hasenkrug, K.J.; Sutter, K.; et al. Qualitative Differences Between the IFNalpha subtypes and IFNbeta Influence Chronic Mucosal HIV-1 Pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauzin, A.; Espinosa Ortiz, A.; Blake, O.; Soundaramourty, C.; Joly-Beauparlant, C.; Nicolas, A.; Droit, A.; Dutrieux, J.; Estaquier, J.; Mammano, F. Differential Inhibition of HIV Replication by the 12 Interferon Alpha Subtypes. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0231120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, S.; Choi, J.G.; Ortega, N.M.; Zhang, J.; Shankar, P.; Swamy, N.M. Gene therapy with plasmids encoding IFN-beta or IFN-alpha14 confers long-term resistance to HIV-1 in humanized mice. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 78412–78420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavender, K.J.; Gibbert, K.; Peterson, K.E.; Van Dis, E.; Francois, S.; Woods, T.; Messer, R.J.; Gawanbacht, A.; Muller, J.A.; Munch, J.; et al. Interferon Alpha Subtype-Specific Suppression of HIV-1 Infection In Vivo. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6001–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rout, S.S.; Di, Y.; Dittmer, U.; Sutter, K.; Lavender, K.J. Distinct effects of treatment with two different interferon-alpha subtypes on HIV-1-associated T-cell activation and dysfunction in humanized mice. AIDS 2022, 36, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Lai, F.; Wang, Y.; Sutter, K.; Dittmer, U.; Ye, J.; Zai, W.; Liu, M.; Shen, F.; et al. Functional Comparison of Interferon-alpha Subtypes Reveals Potent Hepatitis B Virus Suppression by a Concerted Action of Interferon-alpha and Interferon-gamma Signaling. Hepatology 2021, 73, 486–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harari, D.; Abramovich, R.; Zozulya, A.; Smith, P.; Pouly, S.; Koster, M.; Hauser, H.; Schreiber, G. Bridging the species divide: Transgenic mice humanized for type-I interferon response. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillyer, P.; Raviv, N.; Gold, D.M.; Dougherty, D.; Liu, J.; Johnson, T.R.; Graham, B.S.; Rabin, R.L. Subtypes of type I IFN differentially enhance cytokine expression by suboptimally stimulated CD4+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 3197–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, N.; Gibbert, K.; Alter, C.; Nair, S.; Zelinskyy, G.; James, C.M.; Dittmer, U. Anti-retroviral effects of type I IFN subtypes in vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickow, J.; Francois, S.; Kaiserling, R.L.; Malyshkina, A.; Drexler, I.; Westendorf, A.M.; Lang, K.S.; Santiago, M.L.; Dittmer, U.; Sutter, K. Diverse Immunomodulatory Effects of Individual IFNalpha Subtypes on Virus-Specific CD8+ T Cell Responses. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Karakoese, Z.; Ablikim, D.; Ickler, J.; Schuhenn, J.; Zeng, X.; Feng, X.; Yang, X.; Dittmer, U.; Yang, D.; et al. IFNalpha subtype-specific susceptibility of HBV in the course of chronic infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1017753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ashuo, A.; Hao, M.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Liu, J.; Hua, T.; Fang, Z.; Li, J.; Yuan, Z.; et al. An extracellular humanized IFNAR immunocompetent mouse model for analyses of human interferon alpha and subtypes. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2287681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruder Costa, J.; Dufeu-Duchesne, T.; Leroy, V.; Bertucci, I.; Bouvier-Alias, M.; Pouget, N.; Brevot-Lutton, O.; Bourliere, M.; Zoulim, F.; Plumas, J.; et al. Pegylated Interferon alpha-2a Triggers NK-Cell Functionality and Specific T-Cell Responses in Patients with Chronic HBV Infection without HBsAg Seroconversion. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcellin, P.; Ahn, S.H.; Ma, X.; Caruntu, F.A.; Tak, W.Y.; Elkashab, M.; Chuang, W.-L.; Lim, S.-G.; Tabak, F.; Mehta, R.; et al. Combination of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate and Peginterferon α-2a Increases Loss of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 134–144.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feld, J.J.; Terrault, N.A.; Lin, H.H.S.; Belle, S.H.; Chung, R.T.; Tsai, N.; Khalili, M.; Perrillo, R.; Cooper, S.L.; Ghany, M.G.; et al. Entecavir and Peginterferon Alfa-2a in Adults with Hepatitis B e Antigen–Positive Immune-Tolerant Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2338–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, P.; Ling, S.C.; Belle, S.H.; Murray, K.F.; Rodriguez-Baez, N.; Schwarzenberg, S.J.; Teckman, J.; Lin, H.H.S.; Schwarz, K.B. Combination of Entecavir/Peginterferon Alfa-2a in Children with Hepatitis B e Antigen–Positive Immune Tolerant Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2326–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Qu, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Qi, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Yang, F.; Shen, Z.; Guo, Y.; et al. PegIFN alpha-2a reduces relapse in HBeAg-negative patients after nucleo(s)tide analogue cessation: A randomized-controlled trial. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogomolov, P.; Alexandrov, A.; Voronkova, N.; Macievich, M.; Kokina, K.; Petrachenkova, M.; Lehr, T.; Lempp, F.A.; Wedemeyer, H.; Haag, M.; et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis D with the entry inhibitor myrcludex B: First results of a phase Ib/IIa study. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukutomi, K.; Hikita, H.; Murai, K.; Nakabori, T.; Shimoda, A.; Fukuoka, M.; Yamai, T.; Higuchi, Y.; Miyakawa, K.; Suemizu, H.; et al. Capsid Allosteric Modulators Enhance the Innate Immune Response in Hepatitis B Virus-Infected Hepatocytes During Interferon Administration. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klumpp, K.; Shimada, T.; Allweiss, L.; Volz, T.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Hartman, G.; Flores, O.A.; Lam, A.M.; Dandri, M. Efficacy of NVR 3-778, Alone and In Combination with Pegylated Interferon, vs Entecavir In uPA/SCID Mice with Humanized Livers and HBV Infection. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 652–662.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.F.; Schiefke, I.; Yoon, J.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Heo, J.; Kim, J.H.; Lik Yuen Chan, H.; Yoon, K.T.; Klinker, H.; Manns, M.; et al. RNA Interference Therapy with ARC-520 Results in Prolonged Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Response in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. Hepatology 2020, 72, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoulim, F. Does siRNA-based therapy require pegylated interferon-alfa-2a to cure HBV infection? Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 1069–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.F.; Lim, Y.S.; Yoon, K.T.; Lim, T.H.; Heo, J.; Tangkijvanich, P.; Tak, W.Y.; Thanawala, V.; Cloutier, D.; Mao, S.; et al. VIR-2218 (elebsiran) plus pegylated interferon-alfa-2a in participants with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A phase 2 study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Q.; Hua, R.; Tang, H.; Morano Amado, L.E.; Yang, S.-S.; Peng, C.-Y.; Su, W.-W.; Chuang, W.-L.; et al. Xalnesiran with or without an Immunomodulator in Chronic Hepatitis B. New Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 2098–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buti, M.; Heo, J.; Tanaka, Y.; Andreone, P.; Atsukawa, M.; Cabezas, J.; Chak, E.; Coffin, C.S.; Fujiwara, K.; Gankina, N.; et al. Sequential Peg-IFN after bepirovirsen may reduce post-treatment relapse in chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miquilena-Colina, M.E.; Lozano-Rodríguez, T.; García-Pozo, L.; Sáez, A.; Rizza, P.; Capone, I.; Rapicetta, M.; Chionne, P.; Capobianchi, M.; Selleri, M.; et al. Recombinant interferon-α2b improves immune response to hepatitis B vaccination in haemodialysis patients: Results of a randomised clinical trial. Vaccine 2009, 27, 5654–5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Lim, T.H.; Leerapun, A.; Weltman, M.; Jia, J.; Lim, Y.S.; Tangkijvanich, P.; Sukeepaisarnjaroen, W.; Ji, Y.; Le Bert, N.; et al. Therapeutic vaccine BRII-179 restores HBV-specific immune responses in patients with chronic HBV in a phase Ib/IIa study. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Scala, M.; Otano, I.; Gil-Farina, I.; Vanrell, L.; Hommel, M.; Olague, C.; Vales, A.; Galarraga, M.; Guembe, L.; Ortiz de Solorzano, C.; et al. Complementary Effects of Interleukin-15 and Alpha Interferon Induce Immunity in Hepatitis B Virus Transgenic Mice. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 8563–8574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Fu, B.; Shen, X.; Guo, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, R.; Ye, Y.; Li, J.; Tian, Z.; et al. Restoration of HBV-specific CD8+ T-cell responses by sequential low-dose IL-2 treatment in non-responder patients after IFN-alpha therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.K.; Wu, X.; Qian, J.; Ma, X.P.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, R.; Sun, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, P.; et al. Genetic variation in STAT4 predicts response to interferon-α therapy for hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2016, 63, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, J.; Zhou, B.; Xie, Q.; Liang, X.; Fan, R.; Conran, C.; Xu, J.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Variants in STAT4 Associated with Cure of Chronic HBV Infection in HBeAg-positive Patients Treated with Pegylated Interferon-alpha. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 196–204.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastard, P.; Gervais, A.; Le Voyer, T.; Rosain, J.; Philippot, Q.; Manry, J.; Michailidis, E.; Hoffmann, H.-H.; Eto, S.; Garcia-Prat, M.; et al. Autoantibodies neutralizing type I IFNs are present in ~4% of uninfected individuals over 70 years old and account for ~20% of COVID-19 deaths. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabl4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaycox, J.R.; Dai, Y.; Ring, A.M. Decoding the autoantibody reactome. Science 2024, 383, 705–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, M.A.; Feld, J.B.; Lin, H.-H.S.; Mosa, A.I.; Salimzadeh, L.; Perrillo, R.P.; Chung, R.T.; Schwarz, K.B.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Gehring, A.J.; et al. Neutralizing antibodies to interferon alfa arising during peginterferon therapy of chronic hepatitis B in children and adults: Results from the HBRN Trials. Hepatology 2025, 81, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Objectives | Reagents | Approaches and Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prolonged half-life | Pegylated IFNs | Covalent attachment of an inert polyethylene glycol (PEG) polymer to the interferon molecule to produce a larger molecule with prolonged half-life. | [130,131,132] |
| PAS-mIFNα | With the help of PASylation technology that adds a polypeptide comprising Proline, Alanine and Serine (PAS), mIFNα11 was fused with a 600 amino acid PAS chain to increase plasma half-life. | [133] | |
| Tissue targeting | IFN-α2a-NGR | Coupled a cyclic NGR peptide with the C terminus of IFN-α2a, in which the NGR (Asn-Gly-Arg) peptide is a tumor-homing peptide. | [135] |
| anti-CD20-mIFNα | The N-terminus of mIFNα1 or hIFNα2a was fused via a Gly4Ser linker to the C-terminus of the heavy chain of anti-CD20 to generate the more potent fusion proteins. | [136] | |
| anti-PDL1-IFNα | High level of PDL1 was observed in liver infected with HBV, and anti-PDL1-IFNα heterodimeric fusion protein could allow targeted delivery of IFNα into the liver. | [137] | |
| mIFNα2-ASGPR dAb fusion protein | mIFNα2 was fused to a domain antibody (dAb) specifc to a hepatocyte restricted antigen, asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR), to specifically targets the liver. | [138] | |
| TCR-L/IFNα fusion proteins | TCR-like antibodies (TCR-L) able to selectively recognize HBV peptides were generated, and each antibody was genetically linked to two IFNα molecules to produce liver-targeted fusion proteins. | [139] | |
| Enhanced half-life with targeting | anti-VEGFR2-IFNα (mut) | IFNα(mut) was fused with anti-VEGFR2 antibody through G4S linker to yield a novel fused antibody that showed increased half-life and significant anti-cancer activity. | [134] |
| PAL-IFN | IFN-α containing two disulfide bonds was reduced and modified with a reversible lipidization agent. IFN was then slowly released from PAL-IFN into blood circulation upon reduction of the disulfide bonds in vivo (~8 h). | [140] | |
| ApoA-I-IFN | Systemic administration of plasmid encoding IFNα linked to ApoA-I (IA) resulted in longer half-life than IFNα and exhibited hepatic tropism. | [141] | |
| Novel delivery platform | rF-MuIFN-γ | A replication-deficient recombinant avian (fowlpox) virus was generated to express the murine IFN-γ gene, which was able to deliver concentrated levels of the cytokine to a local tissue microenvironment. | [142] |
| mRNA-encoding cytokines | Intratumoral administration of saline-formulated mRNA encoding four cytokines including IFN-α could minimize the potential for off-target effects and adverse reactions potentially associated with carrier material. | [143] | |
| hTIE2-IFN-mirT | Developed a gene transfer strategy into hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) to target IFN-α transgene expression to tumor-infiltrating monocytes/macrophages. | [144] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ashuo, A.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, J. Interferon-α for Immune Modulation in Chronic Hepatitis B Toward Functional Cure. Viruses 2025, 17, 1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101358
Ashuo A, Liu J, Yuan Z, Chen J. Interferon-α for Immune Modulation in Chronic Hepatitis B Toward Functional Cure. Viruses. 2025; 17(10):1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101358
Chicago/Turabian StyleAshuo, Asha, Jia Liu, Zhenghong Yuan, and Jieliang Chen. 2025. "Interferon-α for Immune Modulation in Chronic Hepatitis B Toward Functional Cure" Viruses 17, no. 10: 1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101358
APA StyleAshuo, A., Liu, J., Yuan, Z., & Chen, J. (2025). Interferon-α for Immune Modulation in Chronic Hepatitis B Toward Functional Cure. Viruses, 17(10), 1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101358






