Activation of IRE1 Endonuclease Activity Regulates Zika Virus Replication and Antiviral Response During Infection in Human Microglia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Virus Infection
2.2. Viral Production and Propagation
2.3. PCR and RT-qPCR
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Flow Cytometry and Cytometric Bead Array
2.6. Pharmacological Treatment
2.7. Indirect Immunofluorescence
2.8. RNA Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. ZIKV Infection Triggers ER Stress and a Pro-Inflammatory Response in Human Microglia
3.2. ZIKV Infection Induces Activation of the IRE1 Endonuclease Domain in Human Microglia
3.3. IRE1 Endonuclease Activity Regulates ZIKV Replication in Human Microglia
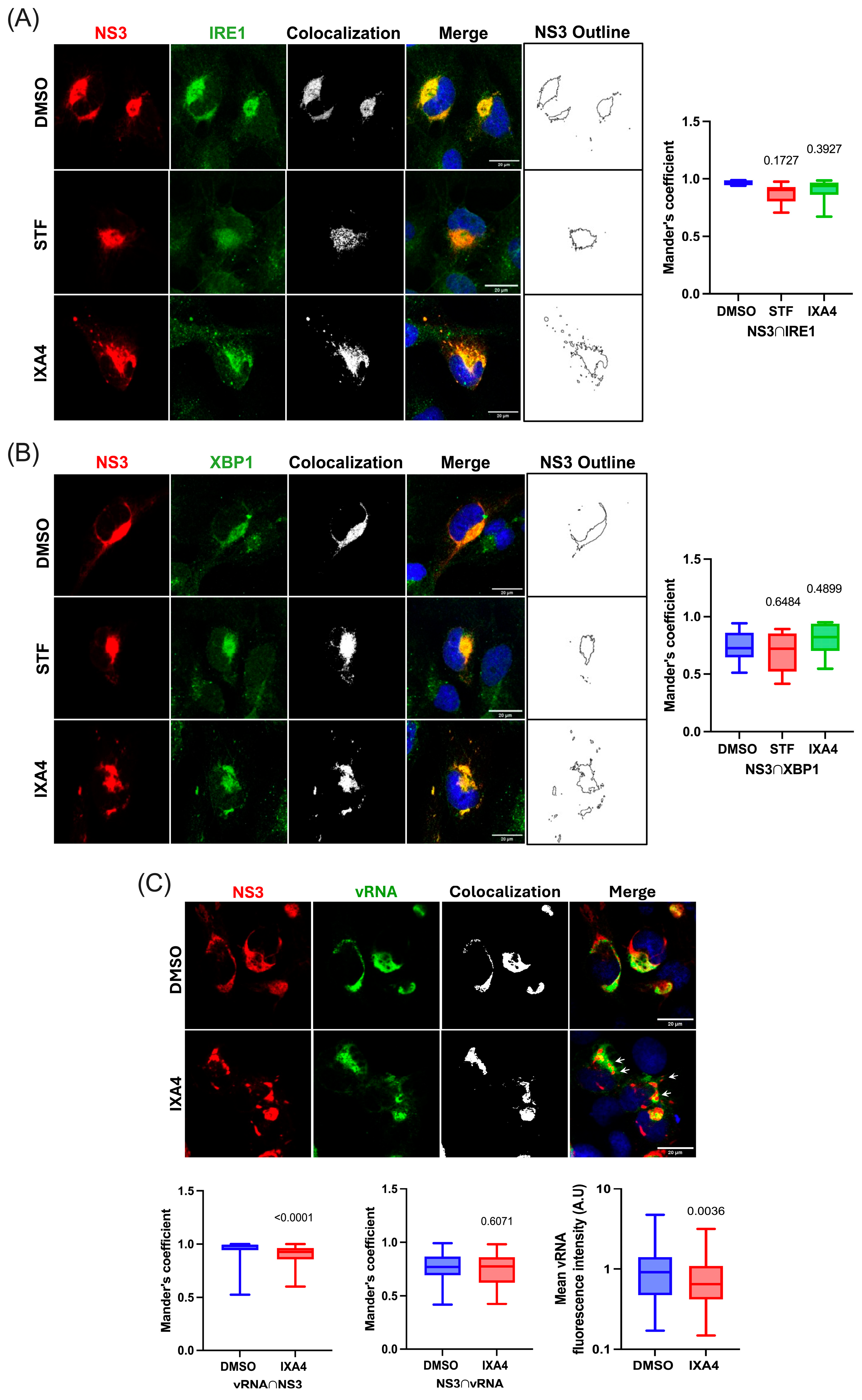
3.4. Hyperactivation of the IRE1 Endonuclease Activity Induces the Appereance of Cytoplasmic Structures Derived from the ER
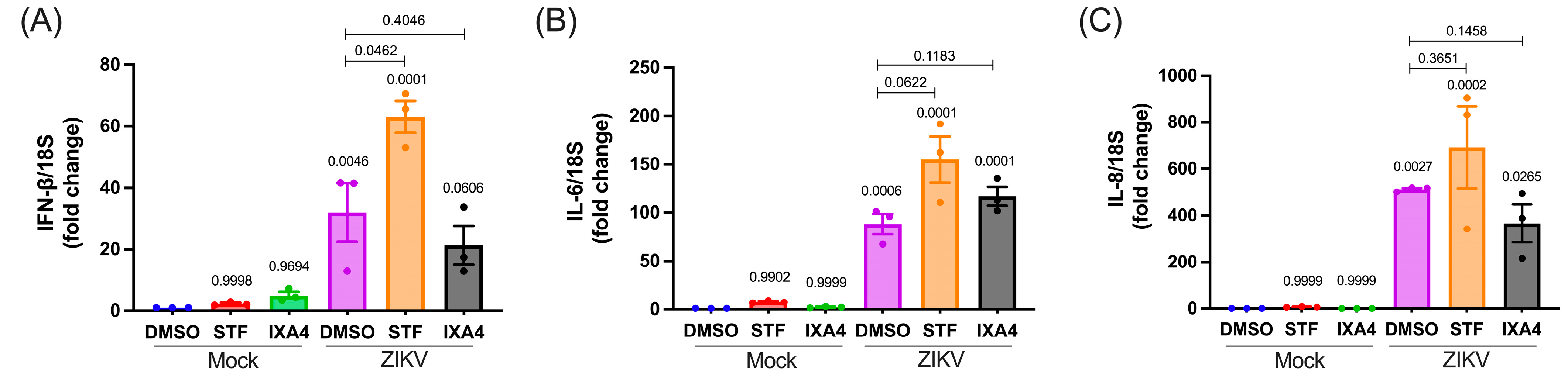
3.5. The IRE1 Endonuclease Activity Regulates the Antiviral Response Triggered by ZIKV in Human Microglia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATF6 | Activating Transcription Factor 6 |
| BiP | Binding immunoglobulin protein |
| cDC | Conventional dendritic cell |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| ER | Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| FISH | Fluorescent in situ hybridization |
| IFN-I | Interferon (Type I) |
| IRF3 | Interferon regulatory factor 3 |
| IL | Interleukin (6 or 8) |
| IRE1 | Inositol-requiring enzyme 1 |
| NS3 | Nonstructural protein 3 |
| PAMP | Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns |
| PERK | Endoplasmic Reticulum Kinase |
| PRR | Pattern Recognition Receptors |
| RIDD | Regulated IRE1α-dependent decay |
| TBK1 | TANK-binding kinase 1 |
| Tn | Tunicamycin |
| UPR | Unfolded Protein Response |
| VRC | Viral Replication Compartments |
| vRNA | Viral RNA |
| XBP1 | X-box Binding Protein 1 |
| ZIKV | Zika virus |
References
- Ukoaka, B.M.; Okesanya, O.J.; Daniel, F.M.; Ahmed, M.M.; Udam, N.G.; Wagwula, P.M.; Adigun, O.A.; Udoh, R.A.; Peter, I.G.; Lawal, H. Updated WHO list of emerging pathogens for a potential future pandemic: Implications for public health and global preparedness. Infez. Med. 2024, 32, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plourde, A.R.; Bloch, E.M. A Literature Review of Zika Virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ling, L.; Zhang, Z.; Marin-Lopez, A. Current Advances in Zika Vaccine Development. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.Y.; Yang, S.; Lu, H.Z.; Wang, L.M.; Li, N.; Zhang, H.T.; Xing, S.Y.; Du, Y.N.; Deng, S.Q. A review on Zika vaccine development. Pathog. Dis. 2024, 82, ftad036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Q.; Ashraf, U.; Yang, M.; Zhu, W.; Gu, J.; Chen, Z.; Gu, C.; Si, Y.; Cao, S.; et al. Zika virus causes placental pyroptosis and associated adverse fetal outcomes by activating GSDME. eLife 2022, 11, e73792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynoso, G.V.; Gordon, D.N.; Kalia, A.; Aguilar, C.C.; Malo, C.S.; Aleshnick, M.; Dowd, K.A.; Cherry, C.R.; Shannon, J.P.; Vrba, S.M.; et al. Zika virus spreads through infection of lymph node-resident macrophages. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, P.; Cochet, M.; Hamel, R.; Gladwyn-Ng, I.; Alfano, C.; Diop, F.; Garcia, D.; Talignani, L.; Montero-Menei, C.N.; Nougairede, A.; et al. Zika virus differentially infects human neural progenitor cells according to their state of differentiation and dysregulates neurogenesis through the Notch pathway. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veilleux, C.; Eugenin, E.A. Mechanisms of Zika astrocyte infection and neuronal toxicity. NeuroImmune Pharm. Ther. 2023, 2, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Shan, C.; Dunn, T.J.; Xie, X.; Xia, H.; Gao, J.; Labastida, J.A.; Zou, J.; Villarreal, P.P.; Schlagal, C.R.; et al. Role of microglia in the dissemination of Zika virus from mother to fetal brain. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, C.; Whitmore, L.S.; Moreno, D.; Malhotra, K.; Tisoncik-Go, J.; Tran, E.; Wren, N.; Glass, I.A.; Research, L.B.D.; Young, J.E.; et al. The human neural cell atlas of Zika virus infection in developing brain tissue. Cell Rep. Med. 2025, 6, 102189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, S.; Farahani, A.V.; Ardekani, O.S.; Seyedi, S.; Tayebi, Z.; Kami, M.; Aghaei, F.; Hosseini, T.M.; Nia, M.M.K.; Soheili, R.; et al. Zika virus tropism and pathogenesis: Understanding clinical impacts and transmission dynamics. Virol. J. 2024, 21, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiyarom, B.; Giannakopoulos, S.; Strange, D.P.; Panova, N.; Gale, M., Jr.; Verma, S. RIG-I and MDA5 are modulated by bone morphogenetic protein (BMP6) and are essential for restricting Zika virus infection in human Sertoli cells. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1062499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plociennikowska, A.; Frankish, J.; Moraes, T.; Del Prete, D.; Kahnt, F.; Acuna, C.; Slezak, M.; Binder, M.; Bartenschlager, R. TLR3 activation by Zika virus stimulates inflammatory cytokine production which dampens the antiviral response induced by RIG-I-like receptors. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e01050-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, M.; Bridgeman, A.; Gray, N.; Hertzog, J.; Hublitz, P.; Kohl, A.; Rehwinkel, J. RIG-I Plays a Dominant Role in the Induction of Transcriptional Changes in Zika Virus-Infected Cells, which Protect from Virus-Induced Cell Death. Cells 2020, 9, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Rastogi, M.; Singh, S.K. Zika virus NS1 suppresses the innate immune responses via miR-146a in human microglial cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193 (Pt B), 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Gao, C.; Wen, C.; Zou, P.; Qi, X.; Cardona, C.J.; Xing, Z. Intrinsic features of Zika Virus non-structural proteins NS2A and NS4A in the regulation of viral replication. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Luo, Z.; Zeng, J.; Chen, W.; Foo, S.S.; Lee, S.A.; Ge, J.; Wang, S.; Goldman, S.A.; Zlokovic, B.V.; et al. Zika Virus NS4A and NS4B Proteins Deregulate Akt-mTOR Signaling in Human Fetal Neural Stem Cells to Inhibit Neurogenesis and Induce Autophagy. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ropidi, M.I.M.; Khazali, A.S.; Rashid, N.N.; Yusof, R. Endoplasmic reticulum: A focal point of Zika virus infection. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyaud, E.; Ranadheera, C.; Cheng, D.; Goncalves, J.; Dyakov, B.J.A.; Laurent, E.M.N.; St-Germain, J.; Pelletier, L.; Gingras, A.C.; Brumell, J.H.; et al. Global Interactomics Uncovers Extensive Organellar Targeting by Zika Virus. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2018, 17, 2242–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignol, E.D.; Peters, K.N.; Connor, J.H.; Bullitt, E. Zika virus induced cellular remodelling. Cell Microbiol. 2017, 19, e12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.K.M.; Moriarty, K.P.; Cardoen, B.; Gao, G.; Vogl, A.W.; Jean, F.; Hamarneh, G.; Nabi, I.R. Super resolution microscopy and deep learning identify Zika virus reorganization of the endoplasmic reticulum. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraj, P.G.; Sahoo, P.K.; Kraus, M.; Bruett, T.; Annamalai, A.S.; Pattnaik, A.; Pattnaik, A.K.; Byrareddy, S.N.; Natarajan, S.K. Zika virus infection induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in placental trophoblasts. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Sun, J.; Fu, Z.; Ke, X.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Q.; et al. ZIKV infection activates the IRE1-XBP1 and ATF6 pathways of unfolded protein response in neural cells. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mufrrih, M.; Chen, B.; Chan, S.W. Zika Virus Induces an Atypical Tripartite Unfolded Protein Response with Sustained Sensor and Transient Effector Activation and a Blunted BiP Response. mSphere 2021, 6, e0036121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, C.; Gladwyn-Ng, I.; Couderc, T.; Lecuit, M.; Nguyen, L. The Unfolded Protein Response: A Key Player in Zika Virus-Associated Congenital Microcephaly. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ron, D.; Walter, P. Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, C.; Zhang, K.; Kaufman, R.J. Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, P.; Ron, D. The unfolded protein response: From stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 2011, 334, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.M.; Kang, T.I.; So, J.S. Roles of XBP1s in Transcriptional Regulation of Target Genes. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinon, F.; Chen, X.; Lee, A.H.; Glimcher, L.H. TLR activation of the transcription factor XBP1 regulates innate immune responses in macrophages. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Turner, M.J.; DeLay, M.L.; Klenk, E.I.; Sowders, D.P.; Colbert, R.A. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response are linked to synergistic IFN-beta induction via X-box binding protein 1. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 1194–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirone, M. ER Stress, UPR Activation and the Inflammatory Response to Viral Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.L.; Sims, S.G.; Nowery, J.D.; Meares, G.P. Endoplasmic reticulum stress differentially modulates the IL-6 family of cytokines in murine astrocytes and macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mesa, Y.; Jay, T.R.; Checkley, M.A.; Luttge, B.; Dobrowolski, C.; Valadkhan, S.; Landreth, G.E.; Karn, J.; Alvarez-Carbonell, D. Immortalization of primary microglia: A new platform to study HIV regulation in the central nervous system. J. Neurovirol. 2017, 23, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutso, M.; Saul, S.; Rausalu, K.; Susova, O.; Zusinaite, E.; Mahalingam, S.; Merits, A. Reverse genetic system, genetically stable reporter viruses and packaged subgenomic replicon based on a Brazilian Zika virus isolate. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2712–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz, M. Zika Virus Isolation, Purification, and Titration. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2142, 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Guha, P.; Kaptan, E.; Gade, P.; Kalvakolanu, D.V.; Ahmed, H. Tunicamycin induced endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by activating mTORC1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68191–68207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandjean, J.M.D.; Madhavan, A.; Cech, L.; Seguinot, B.O.; Paxman, R.J.; Smith, E.; Scampavia, L.; Powers, E.T.; Cooley, C.B.; Plate, L.; et al. Pharmacologic IRE1/XBP1s activation confers targeted ER proteostasis reprogramming. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papandreou, I.; Denko, N.C.; Olson, M.; Van Melckebeke, H.; Lust, S.; Tam, A.; Solow-Cordero, D.E.; Bouley, D.M.; Offner, F.; Niwa, M.; et al. Identification of an Ire1alpha endonuclease specific inhibitor with cytotoxic activity against human multiple myeloma. Blood 2011, 117, 1311–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lum, F.M.; Low, D.K.; Fan, Y.; Tan, J.J.; Lee, B.; Chan, J.K.; Renia, L.; Ginhoux, F.; Ng, L.F. Zika Virus Infects Human Fetal Brain Microglia and Induces Inflammation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shi, S.; Xia, F.; Shan, C.; Ha, Y.; Zou, J.; Adam, A.; Zhang, M.; Wang, T.; Liu, H.; et al. Zika virus induces neuronal and vascular degeneration in developing mouse retina. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpikova, E.P.; Tronco, A.R.; Hartigh, A.B.D.; Jackson, K.J.; Iwawaki, T.; Fink, S.L. IRE1alpha Promotes Zika Virus Infection via XBP1. Viruses 2020, 12, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Huo, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhou, S.; Ma, X.; Gao, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, X.; He, J.; et al. Inositol-Requiring Enzyme 1alpha Promotes Zika Virus Infection through Regulation of Stearoyl Coenzyme A Desaturase 1-Mediated Lipid Metabolism. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01229-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, R.J.; Cao, S. Inositol-requiring 1/X-box-binding protein 1 is a regulatory hub that links endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis with innate immunity and metabolism. EMBO Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Doroudgar, S. IRE1/XBP1 and endoplasmic reticulum signaling—from basic to translational research for cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Physiol 2022, 28, 100552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Liu, Y.P.; Sha, H.; Chen, H.; Qi, L.; Smith, J.A. XBP-1 couples endoplasmic reticulum stress to augmented IFN-beta induction via a cis-acting enhancer in macrophages. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 2324–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhong, D.; Li, G. The role of microglia in viral encephalitis: A review. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez Viedma, M.D.P.; Pickett, B.E. Characterizing the Different Effects of Zika Virus Infection in Placenta and Microglia Cells. Viruses 2018, 10, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, K.; Dumas, A.A.; Prinz, M. Microglia: Immune; non-immune functions. Immunity 2021, 54, 2194–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.B.C.; Freire, V.; Coelho, S.V.A.; Meuren, L.M.; Palmeira, J.D.F.; Cardoso, A.L.; Neves, F.A.R.; Ribeiro, B.M.; Arganaraz, G.A.; Arruda, L.B.; et al. ZIKV Strains Elicit Different Inflammatory and Anti-Viral Responses in Microglia Cells. Viruses 2023, 15, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manet, C.; Mansuroglu, Z.; Conquet, L.; Bortolin, V.; Comptdaer, T.; Segrt, H.; Bourdon, M.; Menidjel, R.; Stadler, N.; Tian, G.; et al. Zika virus infection of mature neurons from immunocompetent mice generates a disease-associated microglia and a tauopathy-like phenotype in link with a delayed interferon beta response. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, M.J.; Caine, E.A.; Zaitsev, K.; Begley, M.C.; Weger-Lucarelli, J.; Uccellini, M.B.; Tripathi, S.; Morrison, J.; Yount, B.L.; Dinnon, K.H.; et al. An Immunocompetent Mouse Model of Zika Virus Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 672–685.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studencka-Turski, M.; Cetin, G.; Junker, H.; Ebstein, F.; Kruger, E. Molecular Insight Into the IRE1alpha-Mediated Type I Interferon Response Induced by Proteasome Impairment in Myeloid Cells of the Brain. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman-Rodriguez, M.; Hernandez-Diaz, T.; Lisboa, P.; Lopez-Schettini, J.; Sanhueza, S.; Leyton, L.; Iwawaki, T.; Soto-Rifo, R.; Osorio, F. The IRE1/XBP1s Axis Regulates Innate Immune Responses in Conventional Dendritic Cells During ZIKV Infection. FASEB J. 2025, 39, e71025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Target | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| vRNA | GTCTTGGAACATGGAGG | TTCACCTTGTGTTGGGC |
| IFN-β | TCTCCTGTTGTGCTTCTCCAC | GCCTCCCATTCAATTGCCAC |
| IL-6 | GCCCAGCTATGAACTCCTTCT | GAAGGCAGCAGGCAACAC |
| IL-8 | GACCACACTGCGCCAACAC | CTTCTCCACAACCCTCTGCAC |
| XBP1s | AAGAACACGCTTGGGAATGG | CTGCACCTGCTGCGGAC |
| XBP1u | GACAGAGAGTCAAACTAACGTGG | GTCCAGCAGGCAAGAAGGT |
| Bloc1s1 | CCCAATTTGCCAAGCAGACA | CATCCCCAATTTCCTTGAGTGC |
| Per1 | TATACCCTGGAGGAGCTGGA | AGGAAGGAGACAGCCACTGA |
| Scara3 | CGCTGCCAGAAGAACCTATC | AACCAGAGAGGCCAACACAG |
| Erjd4 | TGGTGGTTCCAGTAGACAAAGG | CTTCGTTGAGTGACAGTCCTGC |
| Edem1 | TTCCCTCCTGGTGGAATTTG | AGGCCACTCTGCTTTCCAAC |
| 18S | TGTGCCGCTAGAGGTGAAATT | TGGCAAATGCTTTCGCTTT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Díaz, T.; Oyarzún-Arrau, A.; Gaete-Argel, A.; López-Palma, D.; López-Schettini, J.; Fernández, D.; Valiente-Echeverría, F.; Osorio, F.; Soto-Rifo, R. Activation of IRE1 Endonuclease Activity Regulates Zika Virus Replication and Antiviral Response During Infection in Human Microglia. Viruses 2025, 17, 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101291
Hernández-Díaz T, Oyarzún-Arrau A, Gaete-Argel A, López-Palma D, López-Schettini J, Fernández D, Valiente-Echeverría F, Osorio F, Soto-Rifo R. Activation of IRE1 Endonuclease Activity Regulates Zika Virus Replication and Antiviral Response During Infection in Human Microglia. Viruses. 2025; 17(10):1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101291
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Díaz, Tomás, Aarón Oyarzún-Arrau, Aracelly Gaete-Argel, Delia López-Palma, Javier López-Schettini, Dominique Fernández, Fernando Valiente-Echeverría, Fabiola Osorio, and Ricardo Soto-Rifo. 2025. "Activation of IRE1 Endonuclease Activity Regulates Zika Virus Replication and Antiviral Response During Infection in Human Microglia" Viruses 17, no. 10: 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101291
APA StyleHernández-Díaz, T., Oyarzún-Arrau, A., Gaete-Argel, A., López-Palma, D., López-Schettini, J., Fernández, D., Valiente-Echeverría, F., Osorio, F., & Soto-Rifo, R. (2025). Activation of IRE1 Endonuclease Activity Regulates Zika Virus Replication and Antiviral Response During Infection in Human Microglia. Viruses, 17(10), 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101291






