Probenecid Inhibits Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) Replication In Vitro and in BALB/c Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
2.3. HMPV Plaque Assay
2.4. Probenecid Treatment and HMPV Replication
2.5. Mice
2.6. BAL Cytokines and Chemokines
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
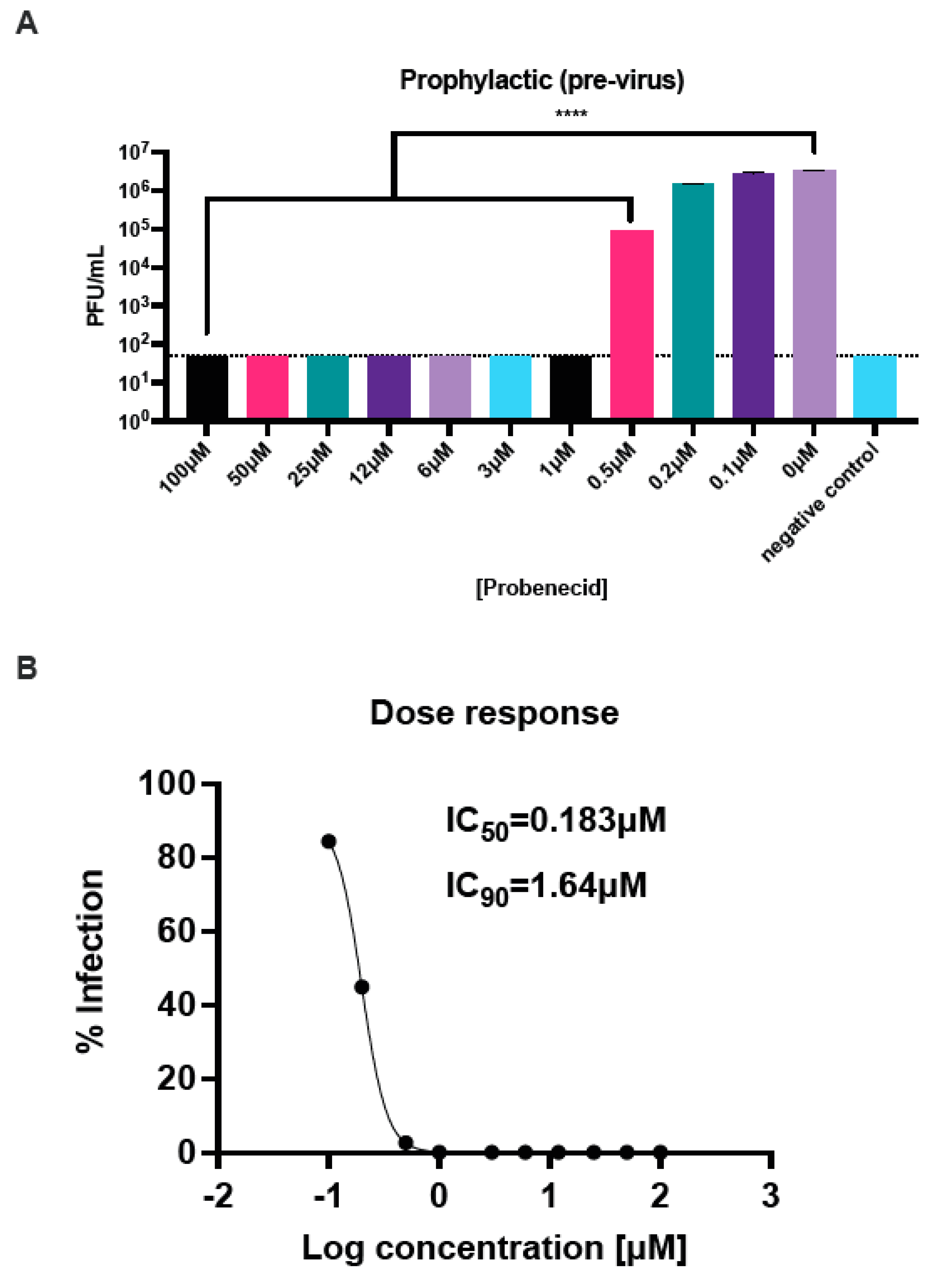
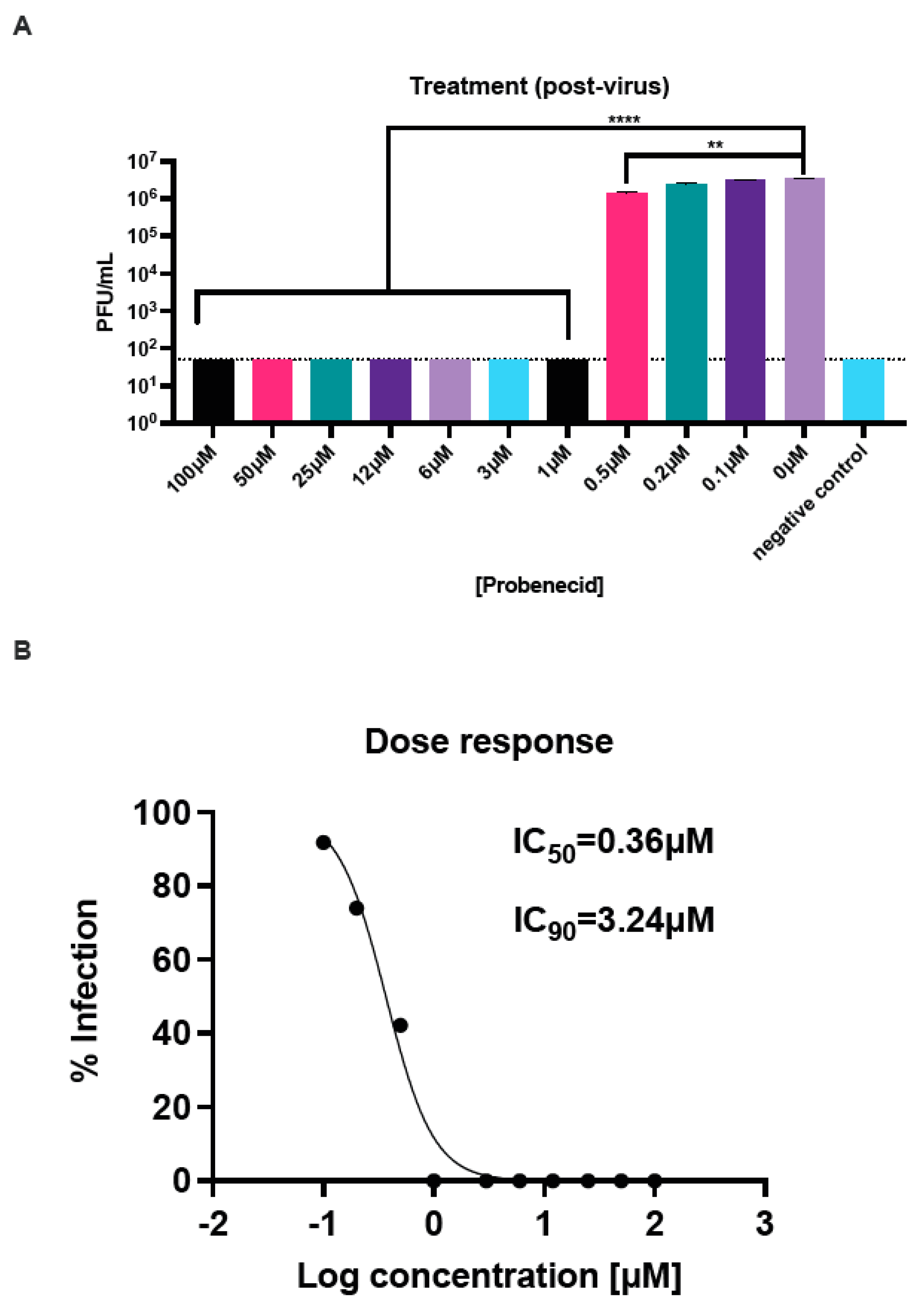
3.1. Probenecid Inhibits HMPV In Vitro
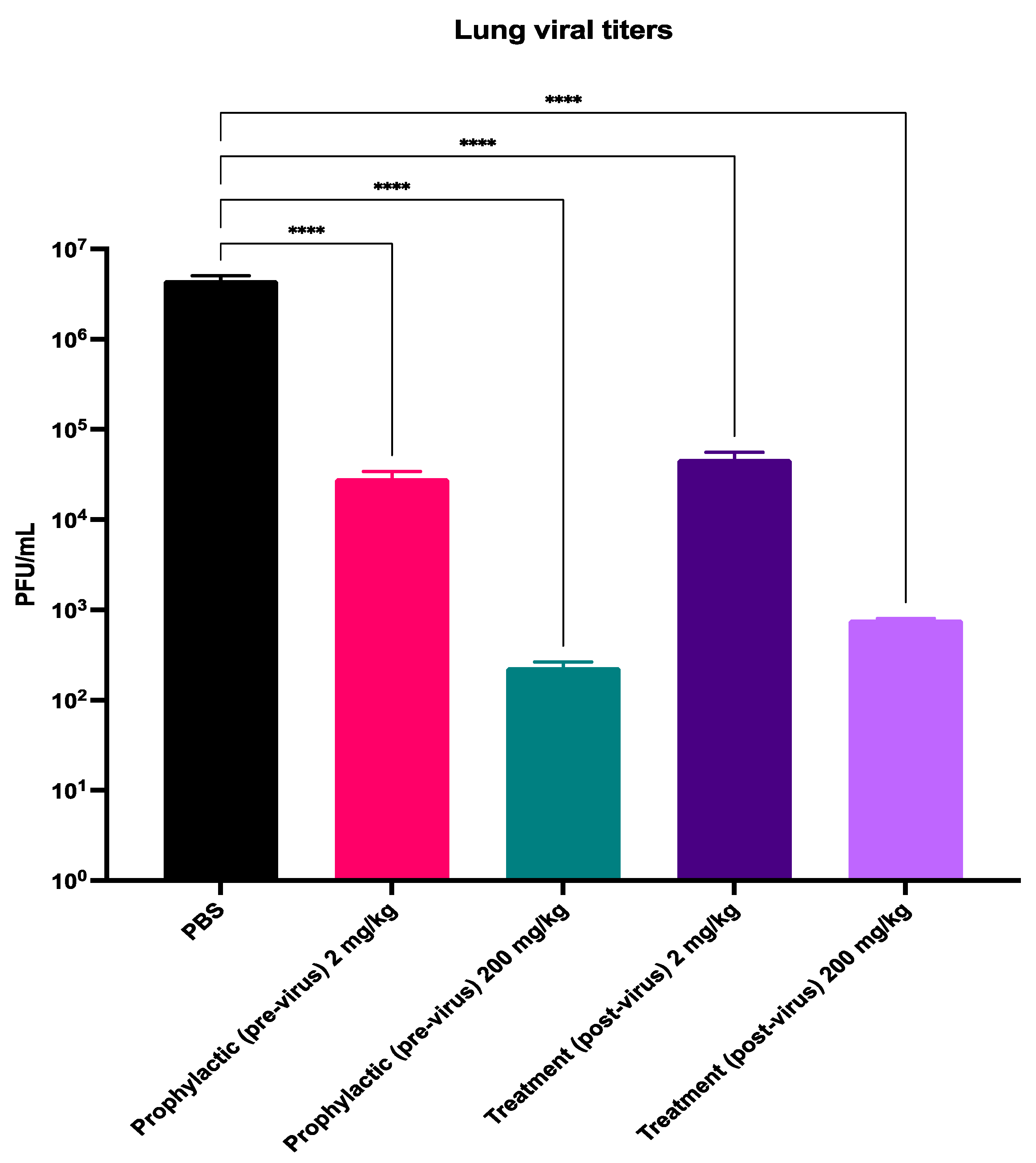
3.2. Probenecid Inhibits HMPV In Vivo
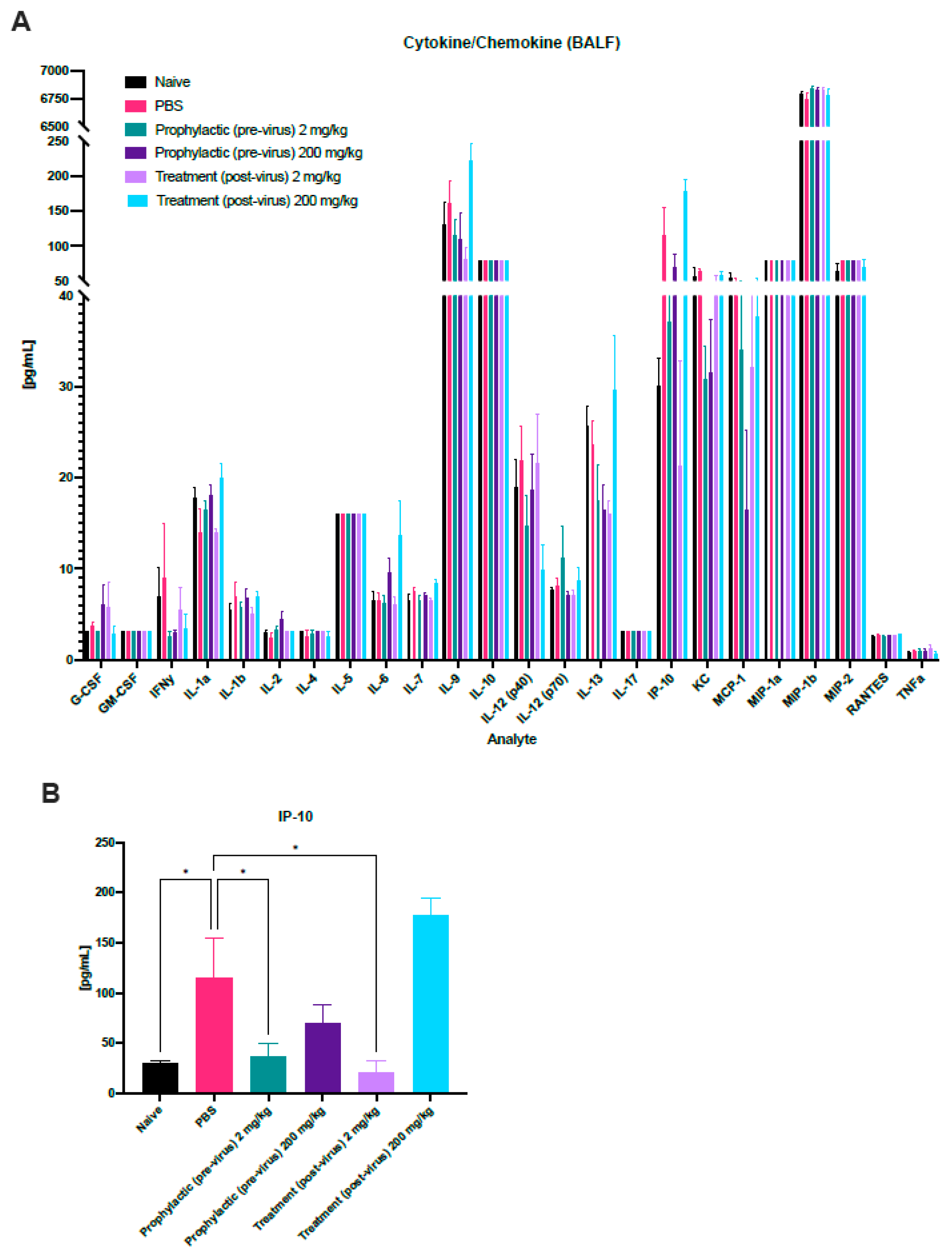
3.3. Immune Profiling during HMPV Challenge and Probenecid Treatment
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, P.; Srivastava, M. Prophylactic and therapeutic approaches for human metapneumovirus. Virusdisease 2018, 29, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, S.; Thomas, M. Human Metapneumovirus; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, P.E.; Frutos, M.C.; Adamo, M.P.; Cuffini, C.; Camara, J.A.; Paglini, M.G.; Moreno, L.; Camara, A. Human Metapneumovirus: Epidemiology and genotype diversity in children and adult patients with respiratory infection in Cordoba, Argentina. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Deloria-Knoll, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Cohen, C.; Ali, A.; Basnet, S.; Bassat, Q.; Brooks, W.A.; Chittaganpitch, M.; et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infection associated with human metapneumovirus in children under 5 years in 2018: A systematic review and modelling study. Lancet Glob Health 2021, 9, e33–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, S.; Mastrolia, M.V. Metapneumovirus Infections and Respiratory Complications. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 37, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinder, J.T.; Moncman, C.L.; Barrett, C.; Jin, H.; Kallewaard, N.; Dutch, R.E. Respiratory Syncytial Virus and Human Metapneumovirus Infections in Three-Dimensional Human Airway Tissues Expose an Interesting Dichotomy in Viral Replication, Spread, and Inhibition by Neutralizing Antibodies. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01068-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.Y.; Renaud, C.; Ficken, E.; Thomson, B.; Kuypers, J.; Englund, J.A. Respiratory Tract Infections Due to Human Metapneumovirus in Immunocompromised Children. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. Soc. 2014, 3, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, A.; Masante, C.; Buchholz, U.J.; Dutch, R.E. Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) binding and infection are mediated by interactions between the HMPV fusion protein and heparan sulfate. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3230–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Huang, J.; Rush, S.A.; Murray, J.; Gingerich, A.D.; Royer, F.; Hsieh, C.L.; Tripp, R.A.; McLellan, J.S.; Mousa, J.J. Structural basis for ultrapotent antibody-mediated neutralization of human metapneumovirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2203326119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cseke, G.; Wright, D.W.; Tollefson, S.J.; Johnson, J.E.; Crowe, J.E., Jr.; Williams, J.V. Human metapneumovirus fusion protein vaccines that are immunogenic and protective in cotton rats. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Mujica, P.; Illanes-Gonzalez, J.; Lopez, A.; Vargas, C.; Saez, J.C.; Gonzalez-Jamett, A.; Ardiles, A.O. Probenecid, an Old Drug with Potential New Uses for Central Nervous System Disorders and Neuroinflammation. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.; Bergeron, H.C.; Jones, L.P.; Reener, Z.B.; Martin, D.E.; Sancilio, F.D.; Tripp, R.A. Probenecid Inhibits Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Replication. Viruses 2022, 14, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perwitasari, O.; Yan, X.; Johnson, S.; White, C.; Brooks, P.; Tompkins, S.M.; Tripp, R.A. Targeting organic anion transporter 3 with probenecid as a novel anti-influenza a virus strategy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.; Martin, D.E.; Hosking, S.; Orr-Burks, N.; Hogan, R.J.; Tripp, R.A. Probenecid Inhibits Influenza A(H5N1) and A(H7N9) Viruses In Vitro and in Mice. Viruses 2024, 16, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.; Hogan, R.J.; Martin, D.E.; Blahunka, K.; Sancilio, F.D.; Balyan, R.; Lovern, M.; Still, R.; Tripp, R.A. Probenecid inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in vivo and in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosli, S.; Kirby, F.J.; Lawlor, K.E.; Rainczuk, K.; Drummond, G.R.; Mansell, A.; Tate, M.D. Repurposing drugs targeting the P2X7 receptor to limit hyperinflammation and disease during influenza virus infection. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 3834–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.E.; Pandey, N.; Chavda, P.; Singh, G.; Sutariya, R.; Sancilio, F.; Tripp, R.A. Oral Probenecid for Nonhospitalized Adults with Symptomatic Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19. Viruses 2023, 15, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripp, R.A.; Mark Tompkins, S. Antiviral effects of inhibiting host gene expression. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 386, 459–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripp, R.A.; Mejias, A.; Ramilo, O. Host gene expression and respiratory syncytial virus infection. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 372, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perwitasari, O.; Bakre, A.; Tompkins, S.M.; Tripp, R.A. siRNA Genome Screening Approaches to Therapeutic Drug Repositioning. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 124–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meliopoulos, V.A.; Andersen, L.E.; Birrer, K.F.; Simpson, K.J.; Lowenthal, J.W.; Bean, A.G.; Stambas, J.; Stewart, C.R.; Tompkins, S.M.; van Beusechem, V.W.; et al. Host gene targets for novel influenza therapies elucidated by high-throughput RNA interference screens. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 1372–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripp, R.A.; Tompkins, S.M. Therapeutic applications of RNAi for silencing virus replication. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 555, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.; Martin, D.E.; Sancilio, F.D.; Tripp, R.A. Antiviral Activity of Probenecid and Oseltamivir on Influenza Virus Replication. Viruses 2023, 15, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Khandelwal, N.; Thachamvally, R.; Tripathi, B.N.; Barua, S.; Kashyap, S.K.; Maherchandani, S.; Kumar, N. Role of MAPK/MNK1 signaling in virus replication. Virus Res. 2018, 253, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caly, L.; Li, H.M.; Bogoyevitch, M.A.; Jans, D.A. c-Jun N-terminal kinase activity is required for efficient respiratory syncytial virus production. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ye, C.; Wan, C.; Li, G.; Peng, L.; Peng, Y.; Fang, R. The Roles of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) in Infectious Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J.; Kang, E.; Seo, J.; Cho, S. Phosphorylation Dynamics of JNK Signaling: Effects of Dual-Specificity Phosphatases (DUSPs) on the JNK Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, V.; Ram, P.T. Network Motifs in JNK Signaling. Genes. Cancer 2013, 4, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H. Crosstalk of HNF4alpha with extracellular and intracellular signaling pathways in the regulation of hepatic metabolism of drugs and lipids. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.T.; An, J.X.; Xu, J.Y.; Tuo, B.G. Overview of organic anion transporters and organic anion transporter polypeptides and their roles in the liver. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 3915–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigam, S.K.; Granados, J.C. OAT, OATP, and MRP Drug Transporters and the Remote Sensing and Signaling Theory. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 63, 637–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhras, N.; Weinberg, J.B.; Newton, D. Human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus: Subtle differences but comparable severity. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2010, 2, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peret, T.C.; Boivin, G.; Li, Y.; Couillard, M.; Humphrey, C.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Erdman, D.D.; Anderson, L.J. Characterization of human metapneumoviruses isolated from patients in North America. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, 1660–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Peled, Y.; Diaz, D.; Pena-Briseno, A.; Murray, J.; Huang, J.; Tripp, R.A.; Mousa, J.J. A Potent Neutralizing Site III-Specific Human Antibody Neutralizes Human Metapneumovirus In Vivo. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00342-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Williams, J.V. Development and optimization of a direct plaque assay for trypsin-dependent human metapneumovirus strains. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 259, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deffrasnes, C.; Cote, S.; Boivin, G. Analysis of replication kinetics of the human metapneumovirus in different cell lines by real-time PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 488–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.V.; Edwards, K.M.; Weinberg, G.A.; Griffin, M.R.; Hall, C.B.; Zhu, Y.; Szilagyi, P.G.; Wang, C.K.; Yang, C.F.; Silva, D.; et al. Population-based incidence of human metapneumovirus infection among hospitalized children. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 1890–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G. Animal models of respiratory syncytial virus infection. Vaccine 2017, 35, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schildgen, O.; Simon, A.; Williams, J. Animal models for human metapneumovirus (HMPV) infections. Vet. Res. 2007, 38, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Chopra, P.; Liu, L.; Nagy, T.; Murray, J.; Tripp, R.A.; Boons, G.J.; Mousa, J.J. Structure, Immunogenicity, and Conformation-Dependent Receptor Binding of the Postfusion Human Metapneumovirus F Protein. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0059321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.M.; Liu, C.C.; Wang, H.C.; Su, I.J.; Wang, J.R. Human metapneumovirus infection among children in Taiwan: A comparison of clinical manifestations with other virus-associated respiratory tract infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fausther-Bovendo, H.; Hamelin, M.E.; Carbonneau, J.; Venable, M.C.; Checkmahomed, L.; Lavoie, P.O.; Ouellet, M.E.; Boivin, G.; D’Aoust, M.A.; Kobinger, G.P. A Candidate Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibody Inhibits Both HRSV and HMPV Replication in Mice. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Li, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; Sun, M. Neutralising antibodies against human metapneumovirus. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e732–e744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, K.C.; Mousa, J.J.; Blanco, J.C.G.; Kim, S.; Boukhvalova, M.S. Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) Infection and MPV467 Treatment in Immunocompromised Cotton Rats Sigmodon hispidus. Viruses 2023, 15, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Shu, Z.; Qin, X.; Dou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X. A live attenuated human metapneumovirus vaccine strain provides complete protection against homologous viral infection and cross-protection against heterologous viral infection in BALB/c mice. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsey, A.R.; Erdman, D.; Anderson, L.J.; Walsh, E.E. Human metapneumovirus infections in young and elderly adults. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Bergh, A.; Bailly, B.; Guillon, P.; von Itzstein, M.; Dirr, L. Antiviral strategies against human metapneumovirus: Targeting the fusion protein. Antivir. Res. 2022, 207, 105405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, N.; Koch, S.E.; Tranter, M.; Rubinstein, J. The history and future of probenecid. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2012, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagos, F.T.; Daood, M.J.; Ocque, J.A.; Nolin, T.D.; Bayir, H.; Poloyac, S.M.; Kochanek, P.M.; Clark, R.S.; Empey, P.E. Probenecid, an organic anion transporter 1 and 3 inhibitor, increases plasma and brain exposure of N-acetylcysteine. Xenobiotica 2017, 47, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripp, R.A.; Martin, D.E. Repurposing Probenecid to Inhibit SARS-CoV-2, Influenza Virus, and Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Replication. Viruses 2022, 14, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Tang, W.; Zeng, H.; Peng, Y.; Yu, X.; Yan, F.; Cao, S. Probenecid-Blocked Pannexin-1 Channel Protects Against Early Brain Injury via Inhibiting Neuronal AIM2 Inflammasome Activation After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 854671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Box, H.J.; Sharp, J.; Pennington, S.H.; Kijak, E.; Tatham, L.; Caygill, C.H.; Lopeman, R.C.; Jeffreys, L.N.; Herriott, J.; Neary, M.; et al. Lack of antiviral activity of probenecid in vitro and in Syrian golden hamsters. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2024, 79, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Plata, A.; Casola, A.; Suarez, G.; Yu, X.; Spetch, L.; Peeples, M.E.; Garofalo, R.P. Differential response of dendritic cells to human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 34, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamelin, M.E.; Yim, K.; Kuhn, K.H.; Cragin, R.P.; Boukhvalova, M.; Blanco, J.C.; Prince, G.A.; Boivin, G. Pathogenesis of human metapneumovirus lung infection in BALB/c mice and cotton rats. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8894–8903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huck, B.; Neumann-Haefelin, D.; Schmitt-Graeff, A.; Weckmann, M.; Mattes, J.; Ehl, S.; Falcone, V. Human metapneumovirus induces more severe disease and stronger innate immune response in BALB/c mice as compared with respiratory syncytial virus. Respir. Res. 2007, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bergeron, H.C.; Crabtree, J.; Nagy, T.; Martin, D.E.; Tripp, R.A. Probenecid Inhibits Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) Replication In Vitro and in BALB/c Mice. Viruses 2024, 16, 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16071087
Bergeron HC, Crabtree J, Nagy T, Martin DE, Tripp RA. Probenecid Inhibits Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) Replication In Vitro and in BALB/c Mice. Viruses. 2024; 16(7):1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16071087
Chicago/Turabian StyleBergeron, Harrison C., Jackelyn Crabtree, Tamas Nagy, David E. Martin, and Ralph A. Tripp. 2024. "Probenecid Inhibits Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) Replication In Vitro and in BALB/c Mice" Viruses 16, no. 7: 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16071087
APA StyleBergeron, H. C., Crabtree, J., Nagy, T., Martin, D. E., & Tripp, R. A. (2024). Probenecid Inhibits Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) Replication In Vitro and in BALB/c Mice. Viruses, 16(7), 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16071087










