Strain-Dependent Assessment of Powassan Virus Transmission to Ixodes scapularis Ticks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Virus Isolates Used in This Study
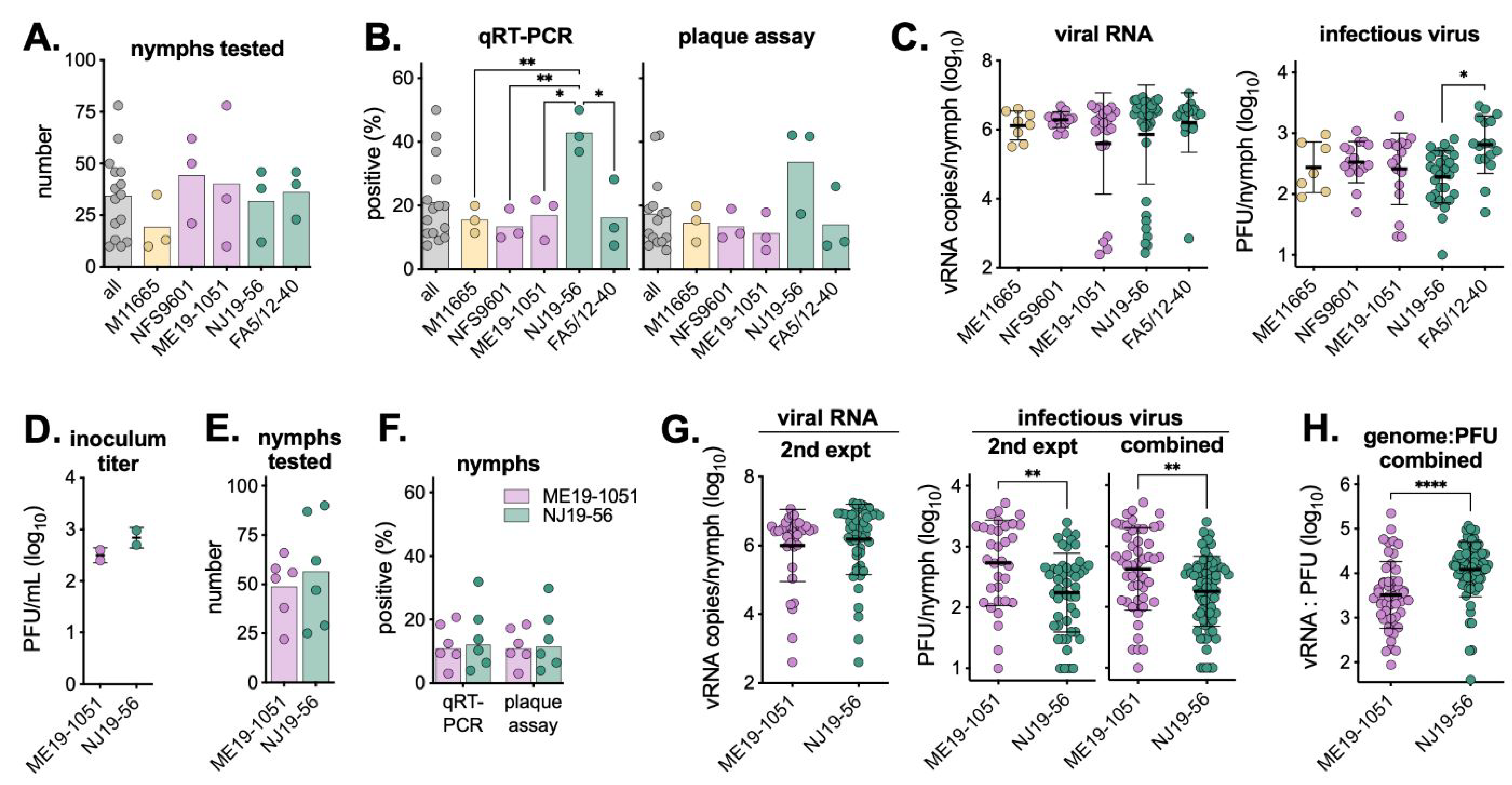
3.2. Viremic Transmission to Ticks
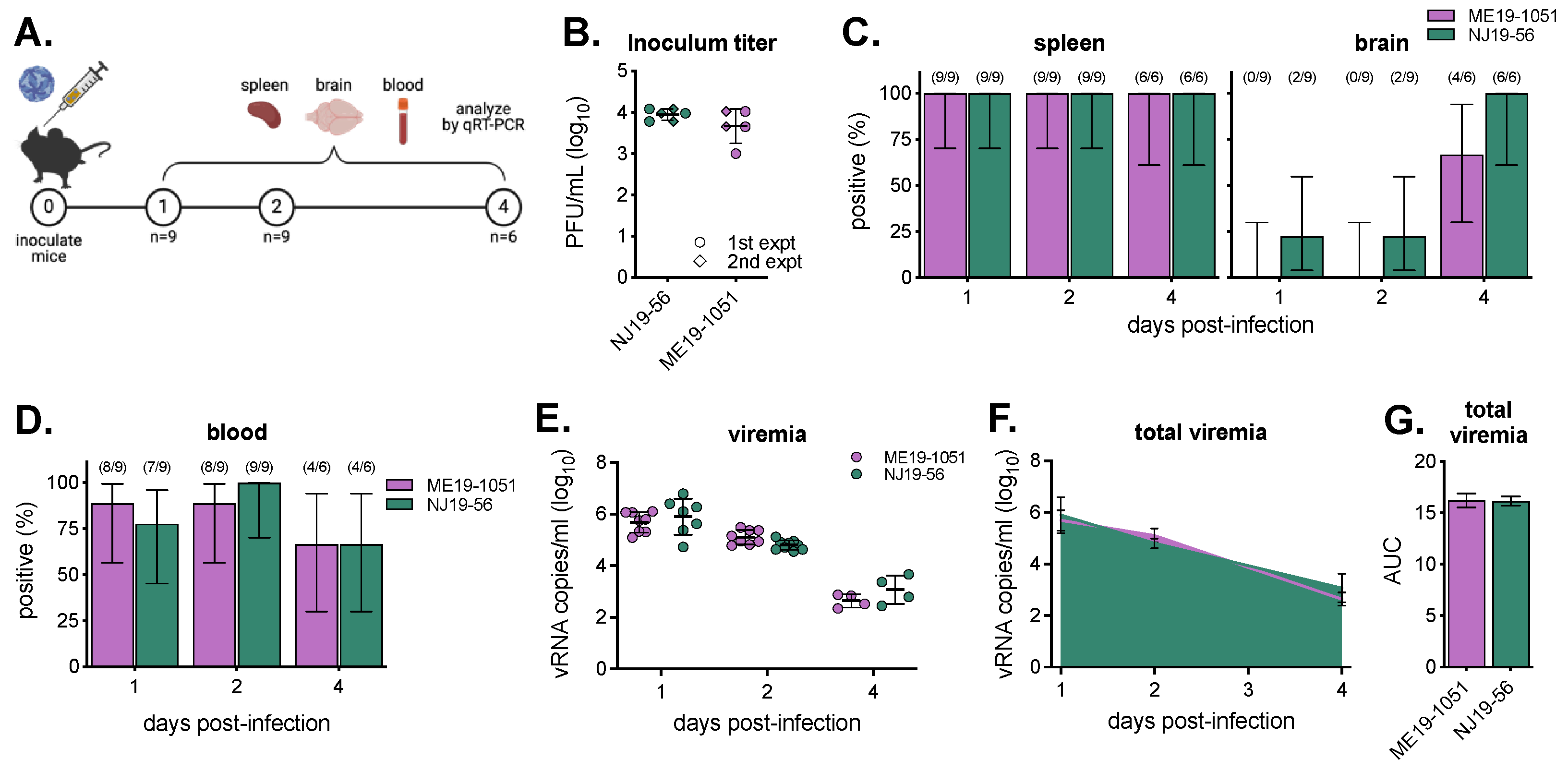
3.3. Viremia in BALB/c Mice
3.4. Artificial Infection of Ticks
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dennis, D.T.; Nekomoto, T.S.; Victor, J.C.; Paul, W.S.; Piesman, J. Reported distribution of Ixodes scapularis and Ixodes pacificus (Acari: Ixodidae) in the United States. J. Med. Entomol. 1998, 35, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisen, R.J.; Eisen, L. The Blacklegged Tick, Ixodes scapularis: An Increasing Public Health Concern. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonenshine, D.E. Range Expansion of Tick Disease Vectors in North America: Implications for Spread of Tick-Borne Disease. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebel, G.D. Update on Powassan virus: Emergence of a North American tick-borne flavivirus. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powassan Virus. 2023. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/powassan/data-maps/current-year-data.html (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Mc, L.D.; Donohue, W.L. Powassan virus: Isolation of virus from a fatal case of encephalitis. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1959, 80, 708–711. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, O.; Krause, P.J. The emergence of human Powassan virus infection in North America. Ticks Tick. Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telford, S.R., 3rd; Armstrong, P.M.; Katavolos, P.; Foppa, I.; Garcia, A.S.; Wilson, M.L.; Spielman, A. A new tick-borne encephalitis-like virus infecting New England deer ticks, Ixodes dammini. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1997, 3, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nofchissey, R.A.; Deardorff, E.R.; Blevins, T.M.; Anishchenko, M.; Bosco-Lauth, A.; Berl, E.; Lubelczyk, C.; Mutebi, J.P.; Brault, A.C.; Ebel, G.D.; et al. Seroprevalence of Powassan virus in New England deer, 1979–2010. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 88, 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliota, M.T.; Dupuis, A.P., 2nd; Wilczek, M.P.; Peters, R.J.; Ostfeld, R.S.; Kramer, L.D. The prevalence of zoonotic tick-borne pathogens in Ixodes scapularis collected in the Hudson Valley, New York State. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinepeter, K. Powassan Virus Identified in Ticks; Pennsylvania Department of Health: Harrisburg, PA, USA, 2022.
- Smalley, R.t.; Zafar, H.; Land, J.; Samour, A.; Hance, D.; Brennan, R.E. Detection of Borrelia miyamotoi and Powassan Virus Lineage II (Deer Tick Virus) from Odocoileus virginianus Harvested Ixodes scapularis in Oklahoma. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2022, 22, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumbie, A.N.; Whitlow, A.M.; Eastwood, G. First Evidence of Powassan Virus (Flaviviridae) in Ixodes scapularis in Appalachian Virginia, USA. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 106, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitlow, A.M.; Cumbie, A.N.; Eastwood, G. Pathogen prevalence in Amblyomma americanum and Ixodes scapularis ticks from central Appalachian Virginia, U.S.A. J. Vector Ecol. 2022, 47, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogels, C.B.F.; Brackney, D.E.; Dupuis, A.P., 2nd; Robich, R.M.; Fauver, J.R.; Brito, A.F.; Williams, S.C.; Anderson, J.F.; Lubelczyk, C.B.; Lange, R.E.; et al. Phylogeographic reconstruction of the emergence and spread of Powassan virus in the northeastern United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2218012120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMinn, R.J.; Langsjoen, R.M.; Bombin, A.; Robich, R.M.; Ojeda, E.; Normandin, E.; Goethert, H.K.; Lubelczyk, C.B.; Schneider, E.; Cosenza, D.; et al. Phylodynamics of deer tick virus in North America. Virus Evol. 2023, 9, vead008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackney, D.E.; Vogels, C.B.F. The known unknowns of Powassan virus ecology. J. Med. Entomol. 2023, 60, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.L.; Lafferty, K.D. Biodiversity and disease: A synthesis of ecological perspectives on Lyme disease transmission. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwasnik, M.; Rola, J.; Rozek, W. Tick-Borne Encephalitis-Review of the Current Status. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackney, D.E.; Pesko, K.N.; Brown, I.K.; Deardorff, E.R.; Kawatachi, J.; Ebel, G.D. West Nile virus genetic diversity is maintained during transmission by Culex pipiens quinquefasciatus mosquitoes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migne, C.V.; Honig, V.; Bonnet, S.I.; Palus, M.; Rakotobe, S.; Galon, C.; Heckmann, A.; Vyletova, E.; Devillers, E.; Attoui, H.; et al. Evaluation of two artificial infection methods of live ticks as tools for studying interactions between tick-borne viruses and their tick vectors. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos-Hernandez, L.; Rakotobe, S.; Defaye, B.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Simo, L. A Capsule-Based Model for Immature Hard Tick Stages Infestation on Laboratory Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 161, e61430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernesky, M.A.; McLean, D.M. Localization of Powassan virus in Dermacentor andersoni ticks by immunofluorescence. Can. J. Microbiol. 1969, 15, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Cozens, D.W.; Armstrong, P.M.; Brackney, D.E. Vector competence of human-biting ticks Ixodes scapularis, Amblyomma americanum and Dermacentor variabilis for Powassan virus. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raney, W.R.; Herslebs, E.J.; Langohr, I.M.; Stone, M.C.; Hermance, M.E. Horizontal and Vertical Transmission of Powassan Virus by the Invasive Asian Longhorned Tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis, Under Laboratory Conditions. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 923914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costero, A.; Grayson, M.A. Experimental transmission of Powassan virus (Flaviviridae) by Ixodes scapularis ticks (Acari:Ixodidae). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1996, 55, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, J.W.; Esser, H.J.; Sprong, H.; Godeke, G.J.; Hoornweg, T.E.; de Boer, W.F.; Pijlman, G.P.; Koenraadt, C.J.M. Differential susceptibility of geographically distinct Ixodes ricinus populations to tick-borne encephalitis virus and louping ill virus. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2321992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godsey, M.S.; Savage, H.M.; Burkhalter, K.L.; Bosco-Lauth, A.M.; Delorey, M.J. Transmission of Heartland Virus (Bunyaviridae: Phlebovirus) by Experimentally Infected Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2016, 53, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqbool, M.; Sajid, M.S.; Saqib, M.; Anjum, F.R.; Tayyab, M.H.; Rizwan, H.M.; Rashid, M.I.; Rashid, I.; Iqbal, A.; Siddique, R.M.; et al. Potential Mechanisms of Transmission of Tick-Borne Viruses at the Virus-Tick Interface. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 846884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brackney, D.E.; Armstrong, P.M. Transmission and evolution of tick-borne viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 21, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuttall, P.A.; Jones, L.D.; Labuda, M.; Kaufman, W.R. Adaptations of arboviruses to ticks. J. Med. Entomol. 1994, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonenshine, D.E.; Roe, R.M. Biology of Ticks, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lejal, E.; Moutailler, S.; Simo, L.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Pollet, T. Tick-borne pathogen detection in midgut and salivary glands of adult Ixodes ricinus. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, S.; Rajeevan, N.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.O.; Heisig, J.; Pan, J.; Eppler-Epstein, R.; Deponte, K.; Fish, D.; Fikrig, E. Gut microbiota of the tick vector Ixodes scapularis modulate colonization of the Lyme disease spirochete. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochwoto, M.; Offerdahl, D.K.; Leung, J.M.; Schwartz, C.L.; Long, D.; Rosenke, R.; Stewart, P.E.; Saturday, G.A.; Bloom, M.E. Cytoarchitecture of ex vivo midgut cultures of unfed Ixodes scapularis infected with a tick-borne flavivirus. Ticks Tick. Borne Dis. 2024, 15, 102301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.R.; Brunner, J.L.; Scoles, G.A.; Owen, J.P. Factors affecting larval tick feeding success: Host, density and time. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubaugh, N.D.; Ruckert, C.; Armstrong, P.M.; Bransfield, A.; Anderson, J.F.; Ebel, G.D.; Brackney, D.E. Transmission bottlenecks and RNAi collectively influence tick-borne flavivirus evolution. Virus Evol. 2016, 2, vew033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klasse, P.J. Molecular determinants of the ratio of inert to infectious virus particles. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2015, 129, 285–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjuan, R. Collective properties of viral infectivity. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 33, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokarz, R.; Lipkin, W.I. Discovery and Surveillance of Tick-Borne Pathogens. J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.F.; Armstrong, P.M. Prevalence and genetic characterization of Powassan virus strains infecting Ixodes scapularis in Connecticut. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 87, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermance, M.E.; Hart, C.E.; Esterly, A.T.; Reynolds, E.S.; Bhaskar, J.R.; Thangamani, S. Development of a small animal model for deer tick virus pathogenesis mimicking human clinical outcome. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasperse, B.A.; Mattocks, M.D.; Noll, K.E.; Ferris, M.T.; Heise, M.T.; Lazear, H.M. Neuroinvasive Flavivirus Pathogenesis Is Restricted by Host Genetic Factors in Collaborative Cross Mice, Independently of Oas1b. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0071523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, N.M.; Root, J.J.; Hartwig, A.E.; Bowen, R.A.; Bosco-Lauth, A.M. Powassan Virus Experimental Infections in Three Wild Mammal Species. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 104, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cull, B.; Wang, X.R. Methods for the Study of Ticks, Mosquitoes, and their Transmitted Pathogens: Toward a Greater Understanding of Vector Biology and Arthropod-Microbe Interactions. J. Vis. Exp. 2023, 193, e64986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia Guizzo, M.; Meneses, C.; Amado Cecilio, P.; Hessab Alvarenga, P.; Sonenshine, D.; Ribeiro, J.M. Optimizing tick artificial membrane feeding for Ixodes scapularis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, J.M.; Offerdahl, D.K.; Bloom, M.E. The Use of Ex Vivo Organ Cultures in Tick-Borne Virus Research. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochlin, I.; Chu, D.; Gmelin, M.; Le, J.; Furie, M.B.; Thanassi, D.G.; Keun Kim, H. Optimization of artificial membrane feeding system for lone star ticks, Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae), and experimental infection with Rickettsia amblyommatis (Rickettsiales: Rickettsiaceae). J. Med. Entomol. 2024, 61, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
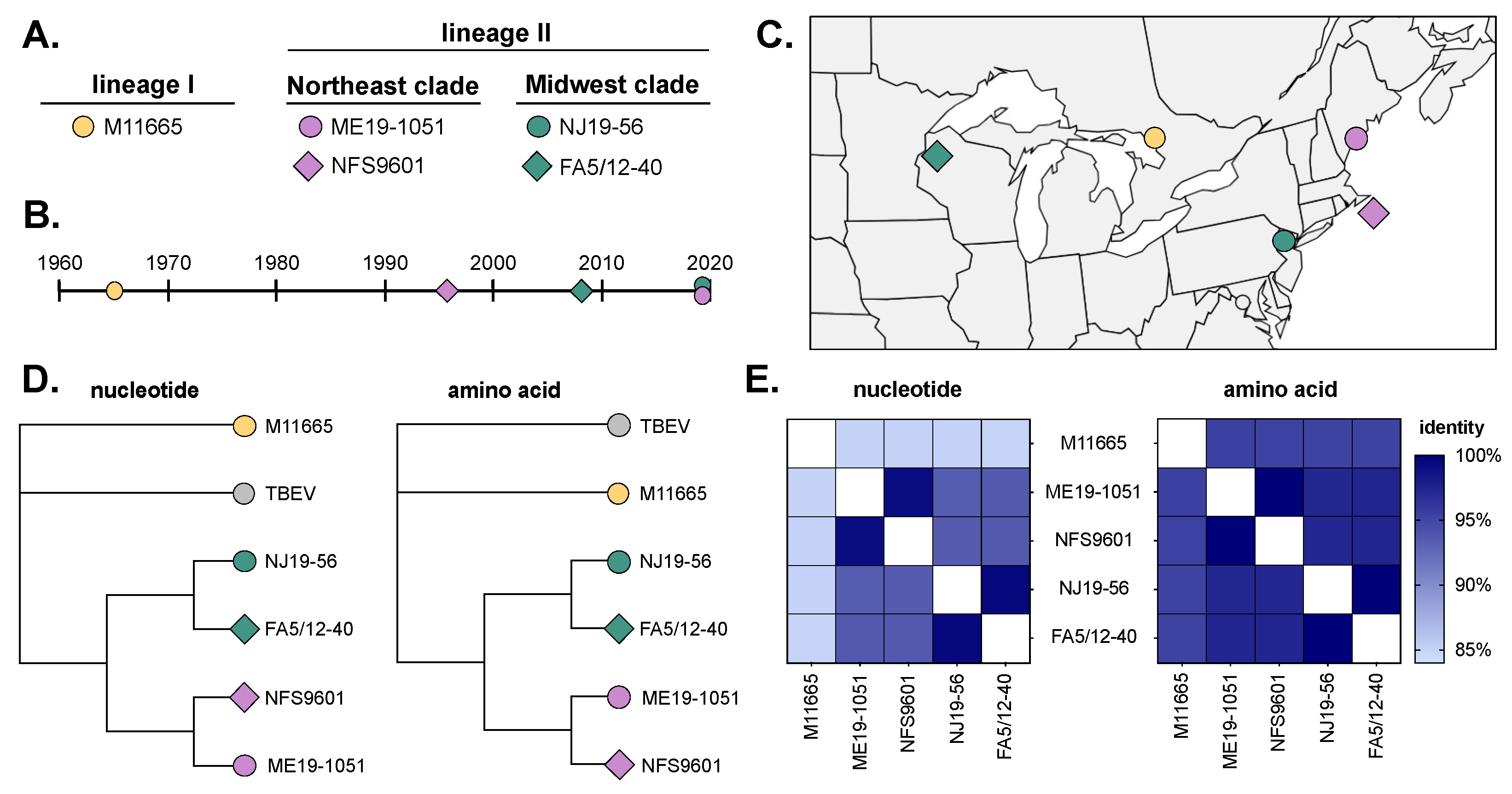

| Isolate ID | Lineage | Location | Year | Source | Passage History | GenBank Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M11665 | I | Ontario | 1965 | I. cookei | P1SM1V1B1 | OP823404 |
| NFS9601 | II | Nantucket, MA | 1996 | I. scapularis | SM1B2 | HM440559 |
| ME19-1051 | II | Cape Elizabeth, ME | 2019 | I. scapularis | B1 | OP823442 |
| FA5/12-40 | II | Spooner, WI | 2008 | I. scapularis | B2 | OP823475 |
| NJ19-56 | II | Hardwick, NJ | 2019 | I. scapularis | B1 | OP823460 |
| M11665 | I | Ontario | 1965 | I. cookei | P1SM1V1B1 | OP823404 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McMinn, R.J.; Gallichotte, E.N.; Courtney, S.; Telford, S.R.; Ebel, G.D. Strain-Dependent Assessment of Powassan Virus Transmission to Ixodes scapularis Ticks. Viruses 2024, 16, 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16060830
McMinn RJ, Gallichotte EN, Courtney S, Telford SR, Ebel GD. Strain-Dependent Assessment of Powassan Virus Transmission to Ixodes scapularis Ticks. Viruses. 2024; 16(6):830. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16060830
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcMinn, Rebekah J., Emily N. Gallichotte, Samantha Courtney, Sam R. Telford, and Gregory D. Ebel. 2024. "Strain-Dependent Assessment of Powassan Virus Transmission to Ixodes scapularis Ticks" Viruses 16, no. 6: 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16060830
APA StyleMcMinn, R. J., Gallichotte, E. N., Courtney, S., Telford, S. R., & Ebel, G. D. (2024). Strain-Dependent Assessment of Powassan Virus Transmission to Ixodes scapularis Ticks. Viruses, 16(6), 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16060830





