Advancements in Research on Duck Tembusu Virus Infections
Abstract
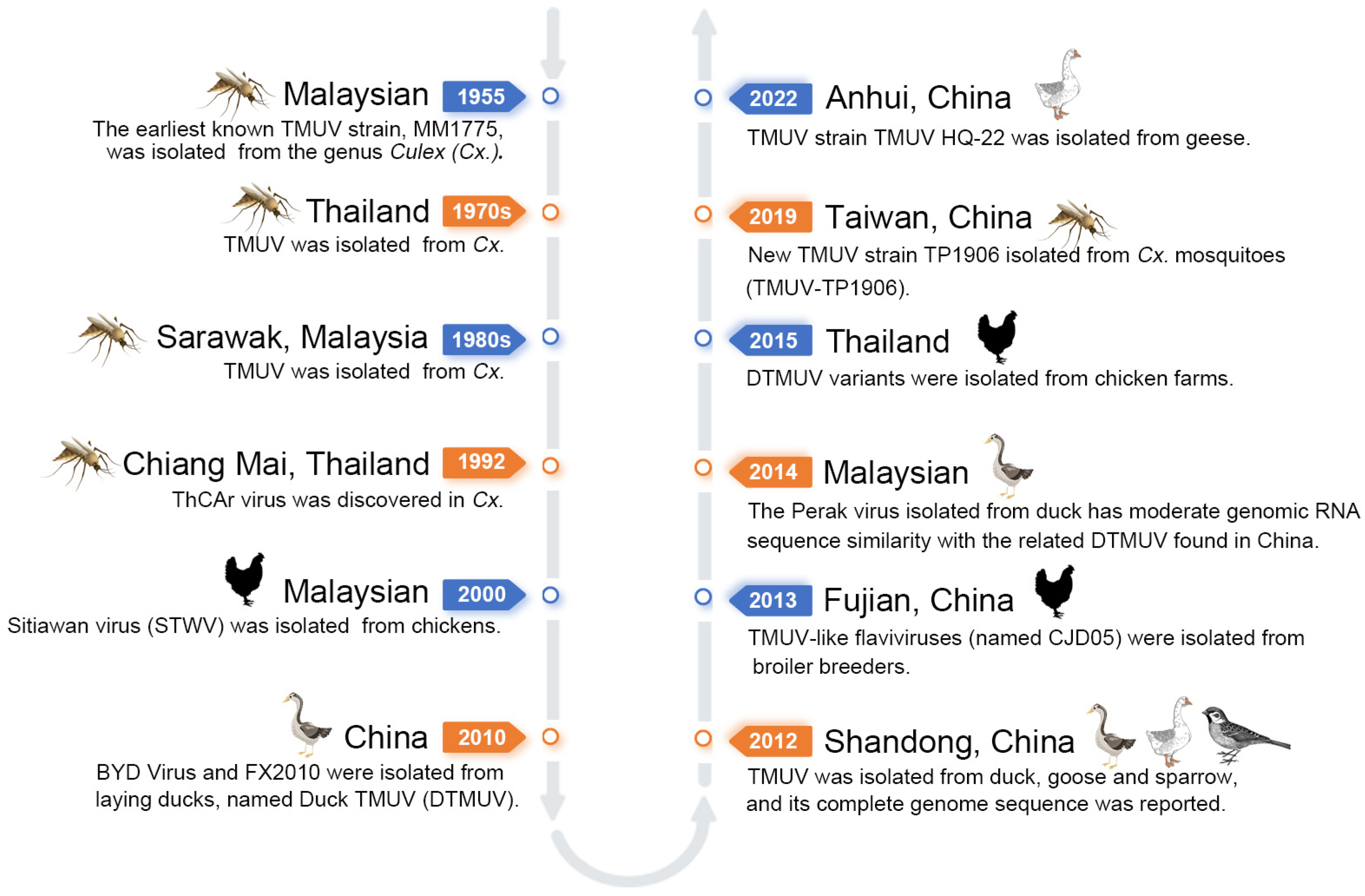
1. Introduction
2. Genomic Characteristics
2.1. Structural Proteins
2.2. Non-Structural Proteins
3. Diagnostic Methods
4. Vaccination
5. Innate Immune Responses
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Shi, Y.; Chu, X.; Ahmed, N.; Wu, J.; Chen, Q. Tembusu virus induced apoptosis in vacuolate spermatogenic cells is mediated by Cytc-mediated mitochondrial apoptotic signaling pathway. Theriogenology 2024, 215, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazear, H.M.; Stringer, E.M.; de Silva, A.M. The Emerging Zika Virus Epidemic in the Americas: Research Priorities. JAMA 2016, 315, 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, M.G.; Harris, E. Dengue. Lancet 2015, 385, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninvilai, P.; Limcharoen, B.; Tunterak, W.; Prakairungnamthip, D.; Oraveerakul, K.; Banlunara, W.; Thontiravong, A. Pathogenesis of Thai duck Tembusu virus in Cherry Valley ducks: The effect of age on susceptibility to infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 243, e108636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulmanausahakul, R.; Ketsuwan, K.; Jaimipuk, T.; Smith, D.R.; Auewarakul, P.; Songserm, T. Detection of antibodies to duck tembusu virus in human population with or without the history of contact with ducks. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; Mahalingam, S.; Wang, M.; Cheng, A. An updated review of avian-origin Tembusu virus: A newly emerging avian Flavivirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2413–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, R.; Phanitchat, T.; Wichit, S.; Morales Vargas, R.E.; Jaroenpool, J.; Diagne, C.T.; Pompon, J.; Misse, D. New Insights into the Biology of the Emerging Tembusu Virus. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, G.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. The spread of Tembusu virus in China from 2010 to 2019. Virus Res. 2021, 300, e198374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Ti, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Diao, Y. Evidence of possible vertical transmission of Tembusu virus in ducks. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 179, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Hang, T.; Yang, L.M.; Xue, J.B.; Fujita, R.; Feng, X.S.; Jiang, T.G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.Z.; Zhou, X.N. Long-distance spread of Tembusu virus, and its dispersal in local mosquitoes and domestic poultry in Chongming Island, China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2023, 12, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Twu, N.C.; Wu, M.C.; Fang, Z.S.; Dubruel, A.; Chang, S.C.; Wu, C.F.; Lo, D.Y.; Chen, H.W. A novel goose-origin Tembusu virus exhibits pathogenicity in day-old chicks with evidence of direct contact transmission. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, e103332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Teng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Z. Airborne Transmission of a Novel Tembusu Virus in Ducks. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2734–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, A.; Chen, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Yang, Q.; et al. Differential immune-related gene expression in the spleens of duck Tembusu virus-infected goslings. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 212, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Diao, Y.; Yu, C.; Gao, X.; Ju, X.; Xue, C.; Liu, X.; Ge, P.; Qu, J.; Zhang, D. Characterization of a Tembusu virus isolated from naturally infected house sparrows (Passer domesticus) in Northern China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2013, 60, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Ding, Y.; Yao, W.; Chen, S.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, L.; Bao, G.; Yang, K.; Fan, S.; Du, Q.; et al. Pathogenicity and Interspecies Transmission of Cluster 3 Tembusu Virus Strain TMUV HQ-22 Isolated from Geese. Viruses 2023, 15, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, S.; Yin, X.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y. Adapted Tembusu-like virus in chickens and geese in China. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2807–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, G.S.; Way, H.J.; Bowen, E.T.; Simpson, D.I.; Hill, M.N.; Kamath, S.; Bendell, P.J.; Heathcote, O.H. Arbovirus infections in Sarawak, October 1968–February 1970 Tembusu and Sindbis virus isolations from mosquitoes. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1975, 69, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Williams, D.T. The zoonotic flaviviruses of southern, south-eastern and eastern Asia, and Australasia: The potential for emergent viruses. Zoonoses Public Health 2009, 56, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.D.; Karabatsos, N.; Cropp, B.; Tagaki, M.; Tsuda, Y.; Ichinose, A.; Igarashi, A. Identification of a flavivirus isolated from mosquitos in Chiang Mai Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1999, 30, 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Kono, Y.; Tsukamoto, K.; Abd Hamid, M.; Darus, A.; Lian, T.C.; Sam, L.S.; Yok, C.N.; Di, K.B.; Lim, K.T.; Yamaguchi, S.; et al. Encephalitis and retarded growth of chicks caused by Sitiawan virus, a new isolate belonging to the genus Flavivirus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 63, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Li, S.; Hu, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Lu, X.; Zhang, G.; Hu, X.; Liu, D.; et al. Duck egg-drop syndrome caused by BYD virus, a new Tembusu-related flavivirus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Dai, X.; Teng, Q.; Yan, L.; Zhou, J.; Ji, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. An infectious disease of ducks caused by a newly emerged Tembusu virus strain in mainland China. Virology 2011, 417, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, T.; Zhang, D.; Ma, X.; Cao, Z.; Chen, L.; Ni, Z.; Ye, W.; Yu, B.; Hua, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Complete genome sequence of a novel flavivirus, duck tembusu virus, isolated from ducks and geese in China. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3406–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Lin, F.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Huang, M.; Zheng, M. Isolation and characterization of a Chinese strain of Tembusu virus from Hy-Line Brown layers with acute egg-drop syndrome in Fujian, China. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homonnay, Z.G.; Kovacs, E.W.; Banyai, K.; Albert, M.; Feher, E.; Mato, T.; Tatar-Kis, T.; Palya, V. Tembusu-like flavivirus (Perak virus) as the cause of neurological disease outbreaks in young Pekin ducks. Avian Pathol. 2014, 43, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thontiravong, A.; Ninvilai, P.; Tunterak, W.; Nonthabenjawan, N.; Chaiyavong, S.; Angkabkingkaew, K.; Mungkundar, C.; Phuengpho, W.; Oraveerakul, K.; Amonsin, A. Tembusu-Related Flavivirus in Ducks, Thailand. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 2164–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.H.; Su, C.L.; Chang, M.C.; Hu, H.C.; Yang, S.L.; Shu, P.Y. Genome Analysis of a Novel Tembusu Virus in Taiwan. Viruses 2020, 12, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Jiao, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, P.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Wu, Q.; Cao, S.; Lu, H.; et al. Duck Tembusu virus infection activates the MKK3/6-p38 MAPK signaling pathway to promote virus replication. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 288, e109951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, S. Innate immune responses to duck Tembusu virus infection. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Ma, B.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Jin, H.; Luo, R. Epidemiology, genetic diversity, and evolutionary dynamics of Tembusu virus. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, e262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Dong, X.; Fu, R.; Su, X.; Xu, B.; Teng, Q.; Yuan, C.; et al. The emergence of a disease caused by a mosquito origin Cluster 3.2 Tembusu virus in chickens in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 272, e109500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, R.; Vargas, R.E.M.; Rajonhson, D.M.; Yamanaka, A.; Jaroenpool, J.; Wichit, S.; Misse, D.; Kritiyakan, A.; Chaisiri, K.; Morand, S.; et al. Identification of the Tembusu Virus in Mosquitoes in Northern Thailand. Viruses 2023, 15, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninvilai, P.; Tunterak, W.; Oraveerakul, K.; Amonsin, A.; Thontiravong, A. Genetic characterization of duck Tembusu virus in Thailand, 2015–2017: Identification of a novel cluster. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1982–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Diao, Y.; Gao, X.; Yu, C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, D. Analysis of the complete genome of Tembusu virus, a flavivirus isolated from ducks in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2012, 59, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Jia, R.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Zhu, D.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; et al. Ultrastructure of duck Tembusu virus observed by electron microscopy with negative staining. Acta Virol. 2018, 62, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Liu, X.; Yan, D.; Teng, Q.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z. Generation and characterization of chimeric Tembusu viruses containing pre-membrane and envelope genes of Japanese encephalitis virus. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, e1140141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Saleemi, M.K.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhou, D.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, B.; Li, Q.; Cao, S.; et al. Decanoyl-Arg-Val-Lys-Arg-Chloromethylketone: An Antiviral Compound That Acts against Flaviviruses through the Inhibition of Furin-Mediated prM Cleavage. Viruses 2019, 11, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzarti, E.; Linden, A.; Desmecht, D.; Garigliany, M. Mosquito-borne epornitic flaviviruses: An update and review. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Sheng, Z.Z.; Huang, B.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Yuan, X.; Qin, Z.; Wang, D.; Chakravarty, S.; Li, F.; et al. Structural, antigenic, and evolutionary characterizations of the envelope protein of newly emerging Duck Tembusu Virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerold, G.; Bruening, J.; Weigel, B.; Pietschmann, T. Protein Interactions during the Flavivirus and Hepacivirus Life Cycle. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2017, 16 (Suppl. S1), S75–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khromykh, A.A.; Westaway, E.G. RNA binding properties of core protein of the flavivirus Kunjin. Arch. Virol. 1996, 141, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Mao, L.; Hu, T.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; et al. Assembly-defective Tembusu virus ectopically expressing capsid protein is an approach for live-attenuated flavivirus vaccine development. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, K.; Allison, S.L.; Schalich, J.; Heinz, F.X. Proteolytic activation of tick-borne encephalitis virus by furin. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 8475–8481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. Development and biochemical characteristics of a monoclonal antibody against prM protein of Tembusu virus. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, e103065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, S.L.; Stadler, K.; Mandl, C.W.; Kunz, C.; Heinz, F.X. Synthesis and secretion of recombinant tick-borne encephalitis virus protein E in soluble and particulate form. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 5816–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Q.; Wu, L.; He, X.; Chen, H. The vaccine efficacy of recombinant duck enteritis virus expressing secreted E with or without PrM proteins of duck tembusu virus. Vaccine 2014, 32, 5271–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rossmann, M.G. A structural perspective of the flavivirus life cycle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Lu, H.; Li, S.; Moureau, G.; Deng, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, T.; de Lamballerie, X.; Qin, C.F.; et al. Genomic and antigenic characterization of the newly emerging Chinese duck egg-drop syndrome flavivirus: Genomic comparison with Tembusu and Sitiawan viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 2158–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Lv, P.; Wang, P.; Li, N.; Wang, F. Bacillus subtilis expressing duck Tembusu virus E protein induces immune protection in ducklings. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 185, 106419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Yun, T.; Chen, L.; Ye, W.; Hua, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, C. Study on the Protective Immunity Induced by Pseudotyped Baculovirus Expressing the E Protein of Tembusu Virus in Ducklings. Genes 2023, 14, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, F.X.; Stiasny, K. Flaviviruses and flavivirus vaccines. Vaccine 2012, 30, 4301–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yan, D.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, L.; Shi, X.; Ma, T.; Li, X.; Teng, Q.; et al. 326K at E Protein Is Critical for Mammalian Adaption of TMUV. Viruses 2023, 15, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Wang, B.; Shi, Y.; Ni, X.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Su, X.; Teng, Q.; et al. A Single Mutation at Position 120 in the Envelope Protein Attenuates Tembusu Virus in Ducks. Viruses 2022, 14, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brien, J.D.; Austin, S.K.; Sukupolvi-Petty, S.; O’Brien, K.M.; Johnson, S.; Fremont, D.H.; Diamond, M.S. Genotype-specific neutralization and protection by antibodies against dengue virus type 3. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 10630–10643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliphant, T.; Nybakken, G.E.; Engle, M.; Xu, Q.; Nelson, C.A.; Sukupolvi-Petty, S.; Marri, A.; Lachmi, B.E.; Olshevsky, U.; Fremont, D.H.; et al. Antibody recognition and neutralization determinants on domains I and II of West Nile Virus envelope protein. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 12149–12159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crill, W.D.; Roehrig, J.T. Monoclonal antibodies that bind to domain III of dengue virus E glycoprotein are the most efficient blockers of virus adsorption to Vero cells. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 7769–7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpio, K.L.; Barrett, A.D.T. Flavivirus NS1 and Its Potential in Vaccine Development. Vaccines 2021, 9, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, G.; Randolph, V.B.; Cleaves, G.R.; Ryan, T.E.; Stollar, V. Evidence that the mature form of the flavivirus nonstructural protein NS1 is a dimer. Virology 1988, 162, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khromykh, A.A.; Sedlak, P.L.; Westaway, E.G. cis- and trans-acting elements in flavivirus RNA replication. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 3253–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, W.; Yu, T.; Wang, M.; Liu, M.; Zhu, D.; Chen, S.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.; et al. NS1: A promising novel target antigen with strong immunogenicity and protective efficacy for avian flavivirus vaccine development. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, e103469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Zhang, S.; Tan, W.; Hu, T.; He, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; et al. Linear epitope identification of monoclonal antibodies against the duck Tembusu virus NS1. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, e102926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Gayen, S.; Kang, C.; Yuan, Z.; Shi, P.Y. Membrane topology and function of dengue virus NS2A protein. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4609–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Zhang, W.; Liu, P.; Yang, C.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.; et al. The prokaryotic expression, polyclonal antibody preparation, and subcellular localization of the transmembrane protein NS2A of the duck Tembusu virus. Acta Virol. 2020, 64, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Chen, H.B.; Wang, X.J.; Huang, H.; Khromykh, A.A. Analysis of adaptive mutations in Kunjin virus replicon RNA reveals a novel role for the flavivirus nonstructural protein NS2A in inhibition of beta interferon promoter-driven transcription. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 12225–12235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerer, B.M.; Rice, C.M. Mutations in the yellow fever virus nonstructural protein NS2A selectively block production of infectious particles. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 4773–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossmann, S.; Wieseler, J.; Kerber, R.; Kummerer, B.M. A basic cluster in the N terminus of yellow fever virus NS2A contributes to infectious particle production. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4951–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.J.; Chen, H.B.; Khromykh, A.A. Molecular and functional analyses of Kunjin virus infectious cDNA clones demonstrate the essential roles for NS2A in virus assembly and for a nonconservative residue in NS3 in RNA replication. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 7804–7813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phoo, W.W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, M.Y.; Loh, Y.R.; Tan, Y.B.; Ng, E.Y.; Lescar, J.; Kang, C.; Luo, D. Structure of the NS2B-NS3 protease from Zika virus after self-cleavage. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, e13410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Phoo, W.W.; Loh, Y.R.; Zhang, Z.; Ng, E.Y.; Wang, W.; Keller, T.H.; Luo, D.; Kang, C. Structural characterization of the linked NS2B-NS3 protease of Zika virus. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 2338–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Hu, T.; Chen, W.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Q.; et al. The G92 NS2B mutant of Tembusu virus is involved in severe defects in progeny virus assembly. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 267, e109396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Pan, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, D.; Tong, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Ji, Y.; Wu, Z.; et al. The Evolution, Genomic Epidemiology, and Transmission Dynamics of Tembusu Virus. Viruses 2022, 14, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Vasudevan, S.G.; Lescar, J. The flavivirus NS2B-NS3 protease-helicase as a target for antiviral drug development. Antivir. Res. 2015, 118, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.; Liu, G.; Yang, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Gong, S.; Wei, F.; Diao, Y.; Tang, Y. Specific High-Sensitivity Enzymatic Molecular Detection System Termed RPA-Based CRISPR-Cas13a for Duck Tembusu Virus Diagnostics. Bioconjug. Chem. 2022, 33, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yon, C.; Teramoto, T.; Mueller, N.; Phelan, J.; Ganesh, V.K.; Murthy, K.H.; Padmanabhan, R. Modulation of the nucleoside triphosphatase/RNA helicase and 5′-RNA triphosphatase activities of Dengue virus type 2 nonstructural protein 3 (NS3) by interaction with NS5, the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 27412–27429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Lima, C.D. Enzymology of RNA cap synthesis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2010, 1, 152–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, T.; Sugrue, R.J.; Xu, Q.; Lee, A.K.; Chan, Y.C.; Fu, J. Recombinant dengue virus type 1 NS3 protein exhibits specific viral RNA binding and NTPase activity regulated by the NS5 protein. Virology 1998, 246, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Xu, T.; Watson, R.P.; Scherer-Becker, D.; Sampath, A.; Jahnke, W.; Yeong, S.S.; Wang, C.H.; Lim, S.P.; Strongin, A.; et al. Insights into RNA unwinding and ATP hydrolysis by the flavivirus NS3 protein. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 3209–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhard, L.G.; Kaufman, S.B.; Gamarnik, A.V. Novel ATP-independent RNA annealing activity of the dengue virus NS3 helicase. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanyi-Nagy, R.; Darlix, J.L. Reprint of: Core protein-mediated 5′-3′ annealing of the West Nile virus genomic RNA in vitro. Virus Res. 2012, 169, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelo, E.; Bolognesi, M.; Milani, M. Flaviviral helicase: Insights into the mechanism of action of a motor protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, J.E.; Wudzinska, A.; Datan, E.; Quaglino, D.; Zakeri, Z. Flavivirus NS4A-induced autophagy protects cells against death and enhances virus replication. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 22147–22159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Jiang, B.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Q.; et al. Identification of duck GSDME: Tissue distribution, proteolysis and cellular location. Cytokine 2022, 156, e155925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Yao, H.; Duan, X.; Lu, X.; Liu, Y. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein influences negative strand RNA synthesis of dengue virus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 385, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartenschlager, R.; Lohmann, V.; Wilkinson, T.; Koch, J.O. Complex formation between the NS3 serine-type proteinase of the hepatitis C virus and NS4A and its importance for polyprotein maturation. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 7519–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Wu, C.; Wang, R.; Yao, X.; Nie, K.; Lv, Q.; Fu, S.; Yin, Q.; Su, W.; Li, F.; et al. Persistence of Tembusu Virus in Culex tritaeniorhynchus in Yunnan Province, China. Pathogens 2023, 12, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.; Sparacio, S.; Bartenschlager, R. Subcellular localization and membrane topology of the Dengue virus type 2 Non-structural protein 4B. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8854–8863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.D.; Seeger, C. Differential effects of mutations in NS4B on West Nile virus replication and inhibition of interferon signaling. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 11809–11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, S.; Li, T.; McCune, B.T.; Edeling, M.A.; Fremont, D.H.; Cristea, I.M.; Diamond, M.S. Evidence for a genetic and physical interaction between nonstructural proteins NS1 and NS4B that modulates replication of West Nile virus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7360–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Takeda, K.; Markoff, L. Protein-protein interactions among West Nile non-structural proteins and transmembrane complex formation in mammalian cells. Virology 2013, 446, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umareddy, I.; Chao, A.; Sampath, A.; Gu, F.; Vasudevan, S.G. Dengue virus NS4B interacts with NS3 and dissociates it from single-stranded RNA. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 2605–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Xie, X.; Wang, Q.Y.; Dong, H.; Lee, M.Y.; Kang, C.; Yuan, Z.; Shi, P.Y. Characterization of dengue virus NS4A and NS4B protein interaction. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3455–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Gong, P. Crystal Structure of the full-length Japanese encephalitis virus NS5 reveals a conserved methyltransferase-polymerase interface. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, B.; Lu, T.; Hu, T.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; et al. Role of the homologous MTase-RdRp interface of flavivirus intramolecular NS5 on duck tembusu virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 269, e109433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, B.; Zeng, M.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; et al. Motif C in nonstructural protein 5 of duck Tembusu virus is essential for viral proliferation. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 262, e109224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Duan, Y.; Jiang, B.; Pan, X.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; et al. Nuclear localization of duck Tembusu virus NS5 protein attenuates viral replication in vitro and NS5-NS2B3 interaction. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 262, e109239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Pan, Y.; Luo, W.; Cheng, A.; Wang, M.; Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Sun, D.; et al. NS5 hijacks TRAF3 to inhibit type I interferon signaling during duck Tembusu virus infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 286, e109894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninvilai, P.; Tunterak, W.; Prakairungnamthip, D.; Oraveerakul, K.; Thontiravong, A. Development and Validation of a Universal One-Step RT-PCR Assay for Broad Detection of Duck Tembusu Virus. Avian Dis. 2020, 64, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wan, C.; Wang, Z.; Tan, J.; Tan, M.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, J.; Huang, Y.; Su, Q.; Kang, Z.; et al. Rapid diagnosis of duck Tembusu virus and goose astrovirus with TaqMan-based duplex real-time PCR. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, e1146241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Hong, W.; Wang, A.; Zuo, W. A multiplex PCR for detection of six viruses in ducks. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 248, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.W.; Xiong, C.; Shi, K.C.; Xie, S.Y.; Long, F.; Li, J.; Zheng, M.; Wei, X.K.; Feng, S.; Qu, S.; et al. Development and application of a multiplex qPCR assay for the detection of duck circovirus, duck Tembusu virus, Muscovy duck reovirus, and new duck reovirus. Virus Genes 2023, 59, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Xiong, C.; Shi, K.; Long, F.; Feng, S.; Qu, S.; Lu, W.; Huang, M.; Lin, C.; Sun, W.; et al. Multiplex digital PCR: A superior technique to qPCR for the simultaneous detection of duck Tembusu virus, duck circovirus, and new duck reovirus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, e1222789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, J.; Shaozhou, W.; Bai, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hua, R.; Liu, J.H.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y. Epitope Identification and Application for Diagnosis of Duck Tembusu Virus Infections in Ducks. Viruses 2016, 8, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Bi, Z.; Yin, D.; Gu, X.; Xu, Z.; Huang, R.; Xing, X.; Qi, K.; Wang, G. Development and application of an indirect ELISA for the serological detection of duck Tembusu virus infection based on the NS1 protein antigen. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Jin, H.; Hu, X.; Su, J. Development and application of a monoclonal antibody-based blocking ELISA for detection of antibodies to Tembusu virus in multiple poultry species. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunterak, W.; Ninvilai, P.; Prakairungnamthip, D.; Oraveerakul, K.; Sasipreeyajan, J.; Thontiravong, A. Evaluation and comparison of hemagglutination inhibition and indirect immunofluorescence tests for the detection of antibodies against duck Tembusu virus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e1693–e1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Yu, X.; Yang, G.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. A Novel Diagnostic Method to Detect Duck Tembusu Virus: A Colloidal Gold-Based Immunochromatographic Assay. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, e1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Huang, X.; Yang, J.; An, F.; Li, Y. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Duck Ovarian Follicles Infected with Duck Tembusu Virus by Label-Free LC-MS. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, e463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wanzhe, Y.; Jianuan, L.; Peng, L.; Jiguo, S.; Ligong, C.; Juxiang, L. Development of a nano-particle-assisted PCR assay for detection of duck tembusu virus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, B.; He, P.; Yang, Z.; Duan, H.; Xie, J.; Zou, L.; Zhao, J.; et al. Efficacy Evaluation of an Inactivated Duck Tembusu Virus Vaccine. Avian Dis. 2015, 59, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, M.; Li, S.; Su, W.; Hu, X.; He, W.; Su, J. Efficacy assessment of an inactivated Tembusu virus vaccine candidate in ducks. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 110, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Yin, D.; Wang, R.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, X.; Xing, X.; Liu, H.M.; Liu, G.; Wang, G. A recombinant adenovirus expressing the E protein of duck Tembusu virus induces protective immunity in duck. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Ren, X.; Zhang, S.; Song, H.; Guo, X.; Jia, H.; Xin, T.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, S. Interleukin-2 shows high adjuvanticity for an inactivated vaccine against duck Tembusu virus disease. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 6454–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Gao, X.; Fang, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, W.; Jia, H.; Guo, X.; Xin, T.; et al. pUC18-CpG Is an Effective Adjuvant for a Duck Tembusu Virus Inactivated Vaccine. Viruses 2020, 12, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Gao, X.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, S.; Peng, S.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, X.; et al. Development of a live attenuated vaccine candidate against duck Tembusu viral disease. Virology 2014, 450–451, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. Development of an attenuated live vaccine candidate of duck Tembusu virus strain. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 231, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, M.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Zhu, D.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, S.; et al. A novel live attenuated duck Tembusu virus vaccine targeting N7 methyltransferase protects ducklings against pathogenic strains. Vet. Res. 2023, 54, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, P.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Jin, H.; Luo, R. Identification of a linear epitope within domain I of Duck Tembusu virus envelope protein using a novel neutralizing monoclonal antibody. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 115, e103906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Sun, M.; Cao, Y. The truncated E protein of DTMUV provide protection in young ducks. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 240, e108508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Jia, R.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Zhu, D.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Q.; et al. Heterologous prime-boost: An important candidate immunization strategy against Tembusu virus. Virol. J. 2020, 17, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Bi, Z.; Ding, M.; Yin, D.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; Miao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, G. Immunization with a suicidal DNA vaccine expressing the E glycoprotein protects ducklings against duck Tembusu virus. Virol. J. 2018, 15, e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhehui, Q.; Xiwen, Z.; Xiaoqiu, G.; Zhuoyan, L.; Wenjing, Y.; Shuoshuo, L.; Wen, Z.; Fengchao, J.; Shuhai, H.; Shaofang, L. Self-Assembled Nanoparticles with E Protein Domains I and II of Duck Tembusu Virus Can Induce a More Comprehensive Immune Response Against the Duck Tembusu Virus Challenge. Avian Dis. 2023, 67, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Wu, X.; Guo, X.; Han, H.; Zhang, P.; Wang, M.; Song, Y.; Jiao, F.; He, S.; Lu, S.; et al. Self-assembled nanoparticle with E protein domain III of DTMUV based on ferritin as carrier can induce a more comprehensive immune response and against DTMUV challenge in duck. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 284, e109820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.; Chen, C.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Fu, Q.; Wan, C.; Shi, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, W. Comparative analysis of transcriptional profiles of retinoic-acid-induced gene I-like receptors and interferons in seven tissues from ducks infected with avian Tembusu virus. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; An, D.; Fan, Y.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. Effect of TMUV on immune organs of TMUV infected ducklings. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 255, e109033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Y.; Liu, S.; Chai, T.; Wei, L. Immune responses of ducks infected with duck Tembusu virus. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, e425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thontiravong, A.; Nedumpun, T.; Ninvilai, P.; Tunterak, W.; Techakriengkrai, N.; Banlunara, W.; Suradhat, S. Dynamics of cellular and humoral immune responses following duck Tembusu virus infection in ducks. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e1365–e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Huang, J.; Cui, M.; Wu, X.; Wang, M.; Zhu, D.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Y.; et al. Duck Tembusu Virus Inhibits Type I Interferon Production through the JOSD1-SOCS1-IRF7 Negative-Feedback Regulation Pathway. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0093022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Ni, J.; Bi, D.; Luo, R.; Jin, H. Functional characterization of duck TBK1 in IFN-beta induction. Cytokine 2018, 111, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Yang, Z.; Xiong, T.; Wang, T.; Yang, J.; Huang, M.; Liu, D.; Chen, R. Avian IRF1 and IRF7 Play Overlapping and Distinct Roles in Regulating IFN-Dependent and -Independent Antiviral Responses to Duck Tembusu Virus Infection. Viruses 2022, 14, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Cheng, A.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Y.; Wang, M.; Huang, J.; Zhu, D.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; et al. DEF Cell-Derived Exosomal miR-148a-5p Promotes DTMUV Replication by Negative Regulating TLR3 Expression. Viruses 2020, 12, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Deng, K.; Wei, L.; Cai, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, S. Molecular identification of duck DDX3X and its potential role in response to Tembusu virus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 106, e103599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Luo, G.; Yang, Z.; Lin, S.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Goraya, M.U.; Chi, X.; Zeng, X.; Chen, J.L. Avian Tembusu virus infection effectively triggers host innate immune response through MDA5 and TLR3-dependent signaling pathways. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Ma, L.; Rao, Z.; Li, Y.; Zheng, H.; He, Q.; Luo, R. Duck Tembusu Virus Infection Promotes the Expression of Duck Interferon-Induced Protein 35 to Counteract RIG-I Antiviral Signaling in Duck Embryo Fibroblasts. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, e711517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wang, N.; Cui, L.; Chen, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, H. Avian Flavivirus Infection of Monocytes/Macrophages by Extensive Subversion of Host Antiviral Innate Immune Responses. J. Virol. 2019, 93, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.Y.; Suthar, M.S. Mechanisms of innate immune evasion in re-emerging RNA viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 12, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lei, C.Q.; Ji, Y.; Zhou, H.; Ren, Y.; Peng, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Jia, Y.; Ge, J.; Zhong, B.; et al. Duck Tembusu Virus Nonstructural Protein 1 Antagonizes IFN-beta Signaling Pathways by Targeting VISA. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 4704–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, B.; Zeng, M.; Lu, T.; Hu, T.; Guo, J.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; et al. Decreased virulence of duck Tembusu virus harboring a mutant NS2A with impaired interaction with STING and IFNbeta induction. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 265, e109312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, B.; Zeng, M.; Duan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; et al. Binding of Duck Tembusu Virus Nonstructural Protein 2A to Duck STING Disrupts Induction of Its Signal Transduction Cascade To Inhibit Beta Interferon Induction. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01850-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, W.; Bai, J.; Tian, M.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Cao, T.; Song, L.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Construction, expression and antiviral activity analysis of recombinant adenovirus expressing human IFITM3 in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Y.; Wang, T.; Wu, S.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; et al. Binding of the Duck Tembusu Virus Protease to STING Is Mediated by NS2B and Is Crucial for STING Cleavage and for Impaired Induction of IFN-beta. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 3374–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaberi, D.; Bahlstrom, A.; Chinthakindi, P.K.; Nyman, T.; Sandstrom, A.; Jarhult, J.D.; Palanisamy, N.; Lundkvist, A.; Lennerstrand, J. Targeting the NS2B-NS3 protease of tick-borne encephalitis virus with pan-flaviviral protease inhibitors. Antiviral. Res. 2021, 190, e105074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, A.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, W.; Jin, H.; Jongkaewwattana, A.; He, Q.; Luo, R. Tembusu Virus Nonstructural Protein 2B Antagonizes Type I Interferon Production by Targeting MAVS for Degradation. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0081622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Hu, T.; Chen, W.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Q.; et al. The autophagy-related degradation of MDA5 by Tembusu virus nonstructural 2B disrupts IFNbeta production. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zeng, M.; Jiang, B.; Lu, T.; Guo, J.; Hu, T.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; et al. Amelioration of Beta Interferon Inhibition by NS4B Contributes to Attenuating Tembusu Virus Virulence in Ducks. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, e671471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Pan, Y.; Huang, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, M.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Zhu, D.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Y.; et al. The substitution at residue 218 of the NS5 protein methyltransferase domain of Tembusu virus impairs viral replication and translation and may triggers RIG-I-like receptor signaling. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, e102017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Tang, M.; Li, W.; Feng, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, S.; Shan, F.; et al. Development of a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification based clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats Cas12a assay for duck Tembusu virus. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, e1301653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.Y.; Tang, H.; Xiong, W.J.; Liu, T.N.; Li, J.Y.; Xia, J.Y.; Xiao, C.T. Isolation and characterization of a novel goose ovaritis-associated cluster 3 Tembusu virus. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, e102867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Product Name | Approval Time | Research and Development Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Inactivated vaccine of Duck Tembusu virus disease (HB strain) | 5 May 2016 | Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences (Beijing, China), Reipu (Baoding) Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Baoding, Hebei, China), Yangzhou Unibio Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Yangzhou, Jiangsu, China), and so on. |
| Live vaccine of Duck Tembusu virus disease (WF100 strain) | 27 June 2016 | Qilu Animal Health Products Co., Ltd. (Jinan, Shandong, China). |
| Live vaccine of Duck Tembusu virus disease (FX2010-180P strain) | 15 October 2018 | Shanghai Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Shanghai, China), Jilin ZhenyeBiologic Products Co., Ltd. (Jilin, China), Qingdao Yibang Bioengineering Co., Ltd. (Qingdao, Shandong, China), and so on. |
| Inactivated vaccine of Duck Tembusu virus disease (DF2 strain) | 26September 2021 | Huazhong Agricultural University (Wuhan, Hubei, China), Wuhan Kexin Bio-Engineering Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, Hubei, China). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Y.; Wang, R.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, A.; Wu, Z.; Sun, F.; Zhu, S. Advancements in Research on Duck Tembusu Virus Infections. Viruses 2024, 16, 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050811
Cheng Y, Wang R, Wu Q, Chen J, Wang A, Wu Z, Sun F, Zhu S. Advancements in Research on Duck Tembusu Virus Infections. Viruses. 2024; 16(5):811. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050811
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Yuting, Ruoheng Wang, Qingguo Wu, Jinying Chen, Anping Wang, Zhi Wu, Fang Sun, and Shanyuan Zhu. 2024. "Advancements in Research on Duck Tembusu Virus Infections" Viruses 16, no. 5: 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050811
APA StyleCheng, Y., Wang, R., Wu, Q., Chen, J., Wang, A., Wu, Z., Sun, F., & Zhu, S. (2024). Advancements in Research on Duck Tembusu Virus Infections. Viruses, 16(5), 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050811





