Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Disease Outcomes in Children and Adolescents Hospitalized Due to COVID-19 Infection in Tunisia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Source
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Baseline Variables and Study Outcomes
2.4. Complete Genome Sequencing and Genome Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Study Outcomes
3.2.1. Clinical Presentation
3.2.2. Disease Severity
3.2.3. Description of the Deceased Population
3.2.4. Incidence Rate of Hospitalization and Inpatient Case Fatality Rate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Talmoudi, K.; Safer, M.; Letaief, H.; Hchaichi, A.; Harizi, C.; Dhaouadi, S.; Derouiche, S.; Bouaziz, I.; Gharbi, D.; Najar, N.; et al. Estimating transmission dynamics and serial interval of the first wave of COVID-19 infections under different control measures: A statistical analysis in Tunisia from 29 February to 5 May 2020. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ONMNE Tunisia|Ministry of Health, COVID-19 in Numbers. Available online: https://onmne.tn/ (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- WHO. Tunisia: WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard with Vaccination Data. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/region/emro/country/tn (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Baggio, S.; L’Huillier, A.G.; Yerly, S.; Bellon, M.; Wagner, N.; Rohr, M.; Huttner, A.; Blanchard-Rohner, G.; Loevy, N.; Kaiser, L.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Viral Load in the Upper Respiratory Tract of Children and Adults With Early Acute Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, G.P.; Bottino, I.; Rocchi, A.; Marchisio, P.; Elli, S.; Agostoni, C.; Costantino, G. Frequency of Children vs Adults Carrying Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Asymptomatically. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Interim Statement on COVID-19 Vaccination for Children. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/11-08-2022-interim-statement-on-covid-19-vaccination-for-children (accessed on 16 May 2023).
- COVID-19 Confrmed Cases and Deaths. United Nations Children’s Fund. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/resources/covid-19-confrmed-cases-and-deaths-dashboard/ (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Chen, F.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Y. The role of children in household transmission of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 122, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Mo, X.; Hu, Y.; Qi, X.; Jiang, F.; Jiang, Z.; Tong, S. Epidemiology of COVID-19 Among Children in China. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20200702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinardi, J.; Dantas, A.C.; Carballo, C.; Thakkar, K.; Akoury, N.A.; Kyaw, M.H.; Del Carmen Morales Castillo, G.; Srivastava, A.; Sáfadi, M.A.P. Narrative Review of the Evolution of COVID-19 Vaccination Recommendations in Countries in Latin America, Africa and the Middle East, and Asia. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2023, 12, 1237–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO SAGE Roadmap on Uses of COVID-19 Vaccines in the Context of OMICRON and Substantial Population Immunity: An Approach to Optimize the Global Impact of COVID-19 Vaccines at a Time When Omicron and Its Sub-Lineages are the Dominant Circulating Variants of Concern, Based on Public Health Goals, Evolving Epidemiology, and Increasing Population-Level Immunity, First Issued 20 October 2020, Updated: 13 November 2020, Updated: 16 July 2021, Update: 21 January 2022, Latest Update: 30 March 2023. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/366671 (accessed on 3 August 2023).
- WHO. Highlights from the Meeting of the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) on Immunization. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/immunization/sage/2023/march-2023/sage_march_2023_meeting_highlights.pdf?sfvrsn=a8e5be9_4 (accessed on 3 August 2023).
- Tezer, H.; Bedir Demirdag, T. Novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in children. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 50, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgi, A.; Louati, A.; Miraoui, A.; Lahmar, L.; Ayari, A.; Hajji, A.; Bouziri, A.; Menif, K.; Smaoui, H.; Jaballah, N.B. Critically ill infants with SARS-CoV-2 delta variant infection. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2023, 64, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouikha, A.; Fares, W.; Laamari, A.; Haddad-Boubaker, S.; Belaiba, Z.; Ghedira, K.; Kammoun Rebai, W.; Ayouni, K.; Khedhiri, M.; Ben Halima, S.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 in Tunisia (North Africa) through Several Successive Waves of COVID-19. Viruses 2022, 14, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemiri, H.; Mangone, I.; Gdoura, M.; Mefteh, K.; Chouikha, A.; Fares, W.; Lorusso, A.; Ancora, M.; Pasquale, A.D.; Cammà, C.; et al. Dynamic of SARS-CoV-2 variants circulation in Tunisian pediatric population, during successive waves, from March 2020 to September 2022. Virus Res. 2024, 344, 199353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Tirupathi, R.; Sule, A.A.; Aldali, J.; Mutair, A.A.; Alhumaid, S.; Muzaheed; Gupta, N.; Koritala, T.; Adhikari, R.; et al. Viral Dynamics and Real-Time RT-PCR Ct Values Correlation with Disease Severity in COVID-19. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Youssef, F.; Hechaichi, A.; Safer, M.; Letaief, H.; Dhaouadi, S.; Mziou, E.; Bougatef, S.; Bouabid, L.; Derouiche, S.; ép Ben Alaya, N.B. Epidemiological profile of children and adolescents with COVID-19 in Tunisia, Mars 2020–August 2022. Popul. Med. 2023, 5, A508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, K.J.; Whitaker, M.; Agathis, N.T.; Anglin, O.; Milucky, J.; Patel, K.; Pham, H.; Kirley, P.D.; Kawasaki, B.; Meek, J.; et al. Hospitalization of Infants and Children Aged 0–4 Years with Laboratory-Confirmed COVID-19-COVID-NET, 14 States, March 2020–February 2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Chorath, K.; Rajasekaran, K.; Burmeister, F.; Ahmed, M.; Moreira, A. Demographic predictors of hospitalization and mortality in US children with COVID-19. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, R.C.; Campbell, A.P.; Taylor, C.A.; Chai, S.J.; Kawasaki, B.; Meek, J.; Anderson, E.J.; Weigel, A.; Monroe, M.L.; Reeg, L.; et al. Risk Factors for Severe COVID-19 in Children. Pediatrics 2022, 149, e2021053418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariah, P.; Johnson, C.L.; Halabi, K.C.; Ahn, D.; Sen, A.I.; Fischer, A.; Banker, S.L.; Giordano, M.; Manice, C.S.; Diamond, R.; et al. Epidemiology, Clinical Features, and Disease Severity in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in a Children’s Hospital in New York City, New York. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, e202430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, L.R.; Tenforde, M.W.; Friedman, K.G.; Newhams, M.; Rose, E.B.; Dapul, H.; Soma, V.L.; Maddux, A.B.; Mourani, P.M.; Bowens, C.; et al. Characteristics and Outcomes of US Children and Adolescents With Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Compared With Severe Acute COVID-19. JAMA 2021, 325, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalala, U.S.; Gist, K.M.; Tripathi, S.; Boman, K.; Kumar, V.K.; Retford, L.; Chiotos, K.; Blatz, A.M.; Dapul, H.; Verma, S.; et al. Characterization and Outcomes of Hospitalized Children With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Report From a Multicenter, Viral Infection and Respiratory Illness Universal Study (Coronavirus Disease 2019) Registry. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 50, e40–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladhani, S.N.; Amin-Chowdhury, Z.; Davies, H.G.; Aiano, F.; Hayden, I.; Lacy, J.; Sinnathamby, M.; de Lusignan, S.; Demirjian, A.; Whittaker, H.; et al. COVID-19 in children: Analysis of the first pandemic peak in England. Arch. Dis. Child. 2020, 105, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parri, N.; Magistà, A.M.; Marchetti, F.; Cantoni, B.; Arrighini, A.; Romanengo, M.; Felici, E.; Urbino, A.; Da Dalt, L.; Verdoni, L.; et al. Characteristic of COVID-19 infection in pediatric patients: Early findings from two Italian Pediatric Research Networks. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2020, 179, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulou, G.B.; Maltezou, H.C. COVID-19 in Children: Where do we Stand? Arch. Med. Res. 2022, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lota-Salvado, R.; Padua, J.R.; Agrupis, K.A.; Malijan, G.M.; Sayo, A.R.; Suzuki, S.; Go, G.D.; Smith, C. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of children with confirmed COVID-19 infection in a tertiary referral hospital in Manila, Philippines. Trop. Med. Health 2023, 51, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.U.; Stiboy, E.; Hassan, M.Z.; Chan, M.; Islam, M.S.; Haider, N.; Jaffe, A.; Homaira, N. Epidemiology of COVID-19 infection in young children under five years: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vaccine 2021, 39, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolewska-Pilarczyk, M.; Pokorska-Śpiewak, M.; Stachowiak, A.; Marczyńska, M.; Talarek, E.; Ołdakowska, A.; Kucharek, I.; Sybilski, A.; Mania, A.; Figlerowicz, M.; et al. COVID-19 infections in infants. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, N.; Santesmasses, D.; Kerepesi, C.; Gladyshev, V.N. COVID-19 mortality rate in children is U-shaped. Aging 2021, 13, 19954–19962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimolai, N. COVID-19 among infants: Key clinical features and remaining controversies. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2024, 67, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbo, O.; Ray, G.T.; Fireman, B.; Layefsky, E.; Goddard, K.; Lewis, E.; Ross, P.; Omer, S.; Greenberg, M.; Klein, N. Maternal SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Infant Protection Against SARS-CoV-2 During the First 6 Months of Life. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.H.; Kim, H.W.; Kang, J.M.; Kim, D.H.; Cho, E.Y. Epidemiology and clinical features of coronavirus disease 2019 in children. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2020, 63, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Du, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.Y.; Qu, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Bao, S.; Li, Y.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1663–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götzinger, F.; Santiago-García, B.; Noguera-Julián, A.; Lanaspa, M.; Lancella, L.; Calò Carducci, F.I.; Gabrovska, N.; Velizarova, S.; Prunk, P.; Osterman, V.; et al. COVID-19 in children and adolescents in Europe: A multinational, multicentre cohort study. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopsack, K.H.; Mucci, L.A.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Nelson, P.S.; Kantoff, P.W. TMPRSS2 and COVID-19: Serendipity or Opportunity for Intervention? Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeimi, R.; Sepidarkish, M.; Mollalo, A.; Parsa, H.; Mahjour, S.; Safarpour, F.; Almukhtar, M.; Mechaal, A.; Chemaitelly, H.; Sartip, B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in children worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 56, 101786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyaolu, A.; Okorie, C.; Marinkovic, A.; Patidar, R.; Younis, K.; Desai, P.; Hosein, Z.; Padda, I.; Mangat, J.; Altaf, M. Comorbidity and its Impact on Patients with COVID-19. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preston, L.E.; Chevinsky, J.R.; Kompaniyets, L.; Lavery, A.M.; Kimball, A.; Boehmer, T.K.; Goodman, A.B. Characteristics and Disease Severity of US Children and Adolescents Diagnosed With COVID-19. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e215298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biharie, A.; Keuning, M.W.; Wolthers, K.C.; Pajkrt, D. Comorbidities, clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 in pediatric patients in a tertiary medical center in the Netherlands. World J. Pediatr. 2022, 18, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsankov, B.K.; Allaire, J.M.; Irvine, M.A.; Lopez, A.A.; Sauvé, L.J.; Vallance, B.A.; Jacobson, K. Severe COVID-19 Infection and Pediatric Comorbidities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 103, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, I.; Delle Cave, F.; Guarracino, C.; De Filippo, M.; Votto, M.; Licari, A.; Pistone, C.; Tondina, E. Obesity and COVID-19 in children and adolescents: A double pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2022, 93, e2022195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Karim, F.; Fernandez Bowman, A.; Antonetti, C.R. Obesity as a Risk Factor for Severe Illness From COVID-19 in the Pediatric Population. Cureus 2021, 13, e14825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.Y.; Derespina, K.R.; Herold, B.C.; Goldman, D.L.; Aldrich, M.; Weingarten, J.; Ushay, H.M.; Cabana, M.D.; Medar, S.S. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Hospitalized and Critically Ill Children and Adolescents with Coronavirus Disease 2019 at a Tertiary Care Medical Center in New York City. J. Pediatr. 2020, 223, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havers, F.; Fry, A.M.; Chen, J.; Christensen, D.; Moore, C.; Peacock, G.; Finelli, L.; Reed, C. Hospitalizations Attributable to Respiratory Infections among Children with Neurologic Disorders. J. Pediatr. 2016, 170, 135–141.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren, R.; Zaoutis, T.E.; Bridges, C.B.; Herrera, G.; Watson, B.M.; Wheeler, A.B.; Licht, D.J.; Luan, X.Q.; Coffin, S.E. Neurological and neuromuscular disease as a risk factor for respiratory failure in children hospitalized with influenza infection. JAMA 2005, 294, 2188–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valderas, C.; Mendez, G.; Echeverria, A.; Suarez, N.; Julio, K.; Sandoval, F. COVID-19 and neurologic manifestations: A synthesis from the child neurologist’s corner. World J. Pediatr. 2022, 18, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chekhlabi, N.; El Kettani, C.; Haoudar, A.; Bahlaoui, A.; Mahi, M.; Ettair, S.; Dini, N. The epidemiological and clinical profile of COVID-19 in children: Moroccan experience of the Cheikh Khalifa University Center. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2020, 35 (Suppl. S2), 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
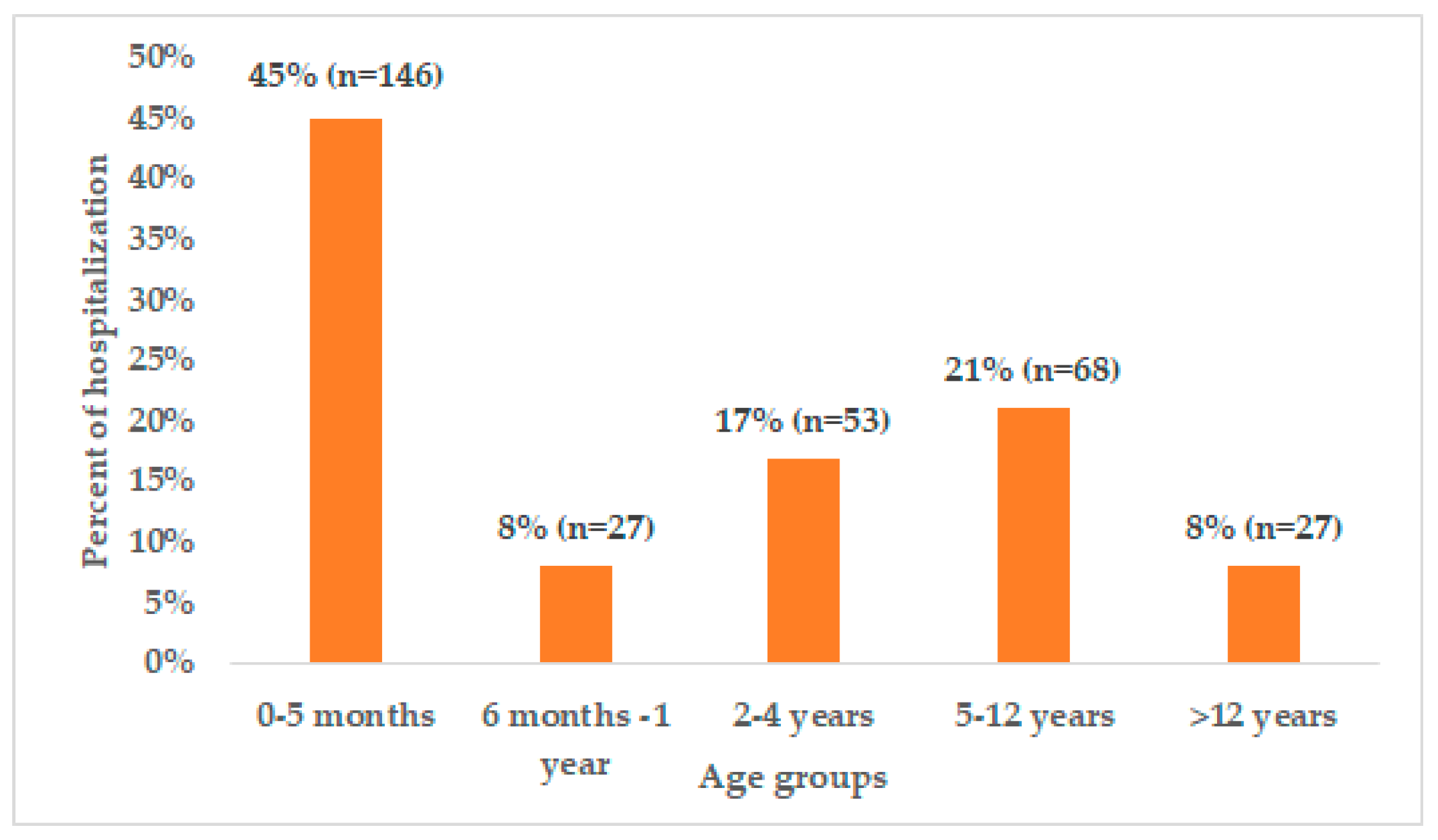

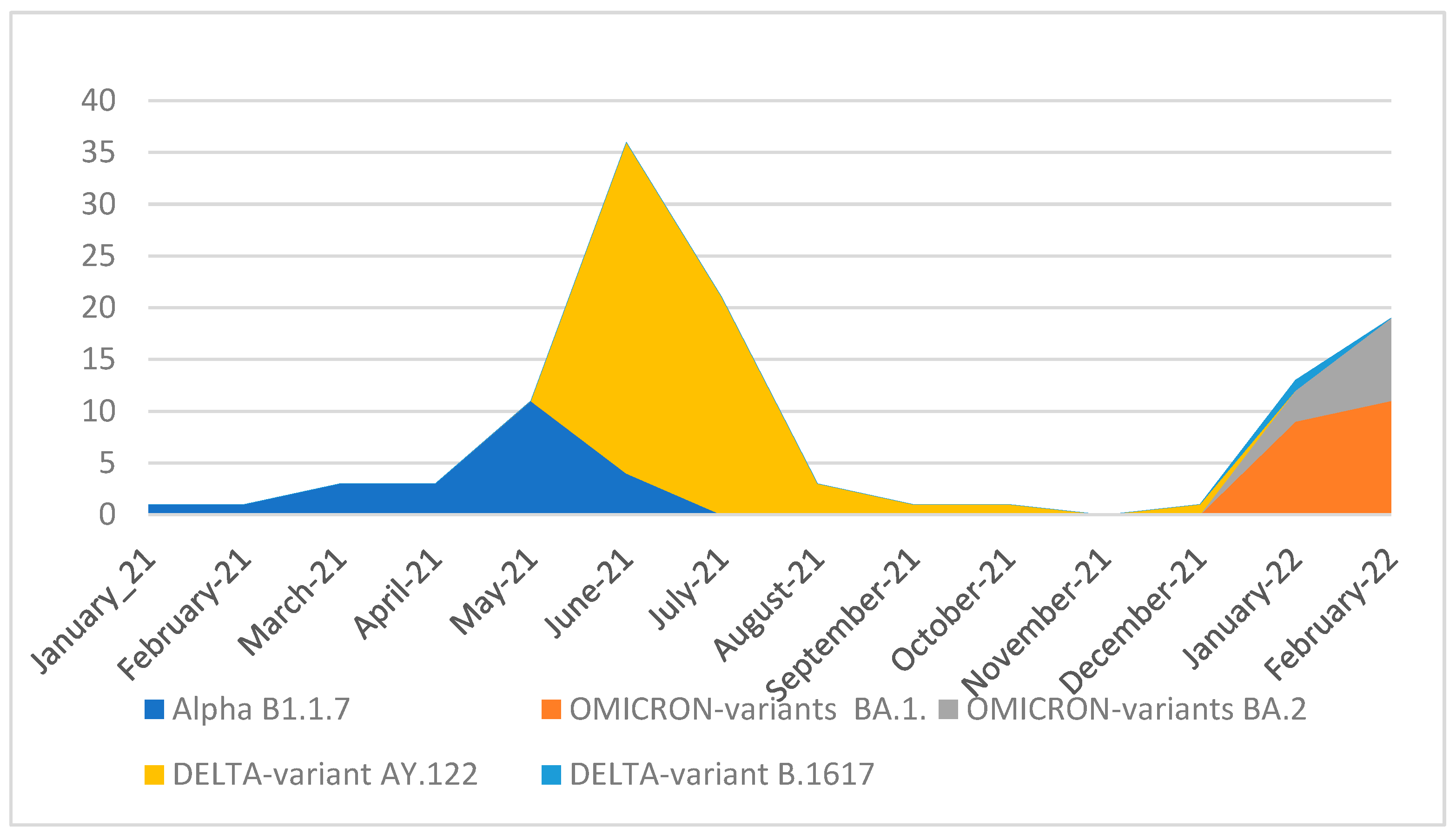
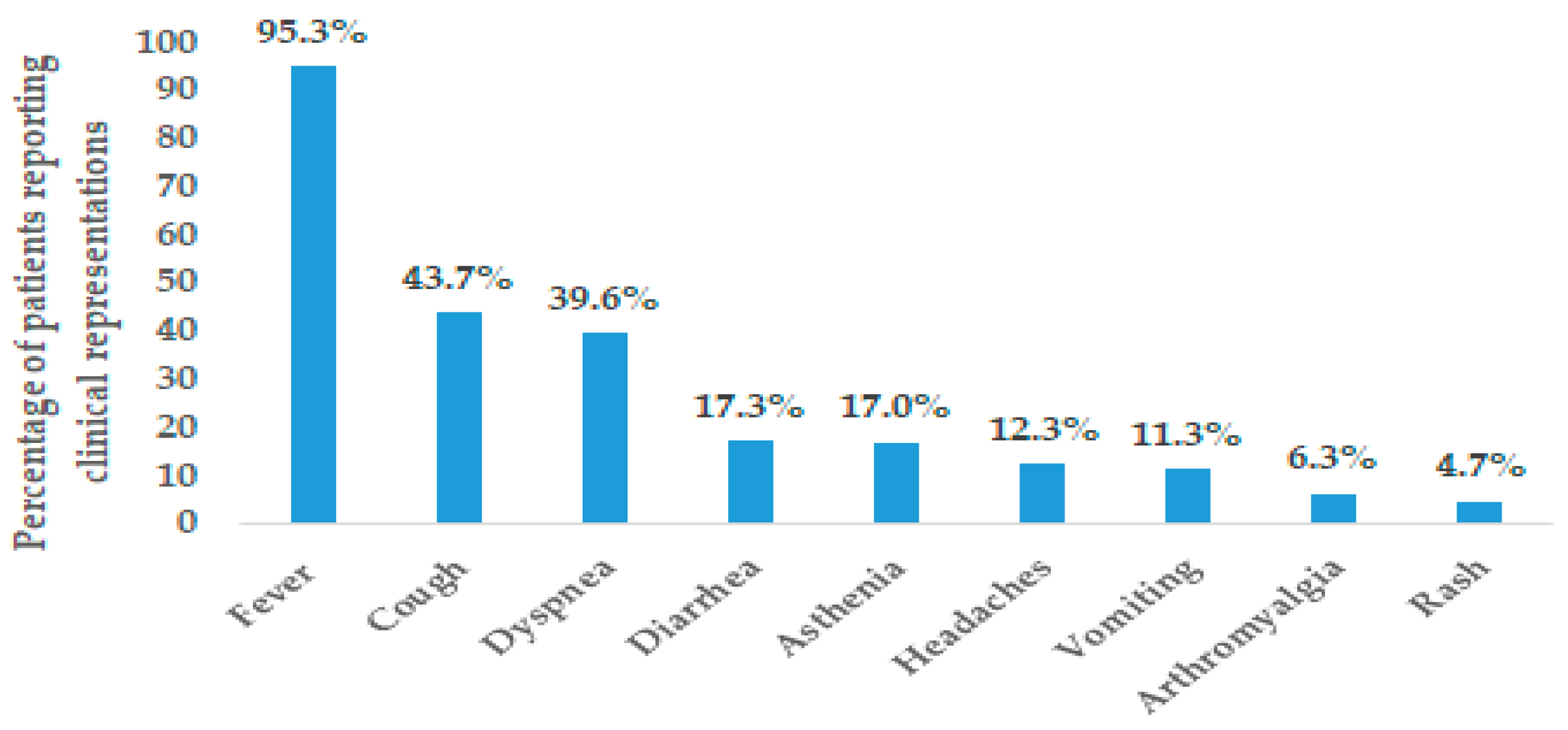
| Characteristics | All Cases (N = 327) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | |
| Mean (SD) | 3.3 (4.53) |
| Median [25, 75] | 0.8 [0.14; 5.5] |
| Gender, n (%) | |
| Female | 140 (43) |
| Male | 187 (57) |
| Residence Governorate, n (%) | |
| Tunis | 209 (64) |
| Ariana | 33 (10) |
| Ben Arous | 26 (7.9) |
| Mannouba | 20 (6.1) |
| Nabeul | 10 (3) |
| Beja | 7 (2.1) |
| Bizerte | 5 (1.5) |
| Siliana | 4 (1.2) |
| Zaghouan | 4 (1.2) |
| Jendouba | 4 (1.2) |
| Kasserine | 3 (0.9) |
| Elkef | 1 (0.3) |
| Kairouan | 1 (0.3) |
| Comorbidities *, n (%) | |
| Neurological disease | 17 (20) |
| Asthma | 14 (16.47) |
| Congenital heart disease | 14 (16.47) |
| Obesity | 9 (10.59) |
| Diabetes | 7 (8.24) |
| Others ** | 47 (55.29) |
| Reasons for hospitalization, n (%) | |
| Fever | 157 (49) |
| Respiratory problems | 103 (32) |
| Seizures | 17 (5) |
| Gastric problems | 15 (5) |
| Cardiovascular problems | 5 (2) |
| Glycemic problems | 4 (1) |
| Others | 29 (9) |
| 0–5 Months | 6 Months–1 Year | 2–4 Years | 5–12 Years | >12 Years | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 23 | 10 | 3 | 6 | 1 |
| Deaths | 5 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Comorbidities * | |||||
| Obesity | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 1 |
| Neurological disease | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Heart disease | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Asthma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Diabetes | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Liver disease | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Inherited metabolic disease | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borgi, A.; Meftah, K.; Trabelsi, I.; Kyaw, M.H.; Zaghden, H.; Bouafsoun, A.; Mezghani, F.; Missaoui, N.; Abdel Ali, A.; Essaddam, L.; et al. Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Disease Outcomes in Children and Adolescents Hospitalized Due to COVID-19 Infection in Tunisia. Viruses 2024, 16, 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050779
Borgi A, Meftah K, Trabelsi I, Kyaw MH, Zaghden H, Bouafsoun A, Mezghani F, Missaoui N, Abdel Ali A, Essaddam L, et al. Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Disease Outcomes in Children and Adolescents Hospitalized Due to COVID-19 Infection in Tunisia. Viruses. 2024; 16(5):779. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050779
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorgi, Aida, Khaoula Meftah, Ines Trabelsi, Moe H. Kyaw, Hela Zaghden, Aida Bouafsoun, Fatma Mezghani, Nada Missaoui, Alya Abdel Ali, Leila Essaddam, and et al. 2024. "Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Disease Outcomes in Children and Adolescents Hospitalized Due to COVID-19 Infection in Tunisia" Viruses 16, no. 5: 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050779
APA StyleBorgi, A., Meftah, K., Trabelsi, I., Kyaw, M. H., Zaghden, H., Bouafsoun, A., Mezghani, F., Missaoui, N., Abdel Ali, A., Essaddam, L., Khemiri, H., Haddad-Boubaker, S., Boussetta, K., Khemiri, M., Ben Becher, S., Boukthir, S., Triki, H., Menif, K., & Smaoui, H. (2024). Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Disease Outcomes in Children and Adolescents Hospitalized Due to COVID-19 Infection in Tunisia. Viruses, 16(5), 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050779







