Mechanisms of Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA and Minichromosome Formation and HBV Gene Transcription
Abstract
1. Introduction
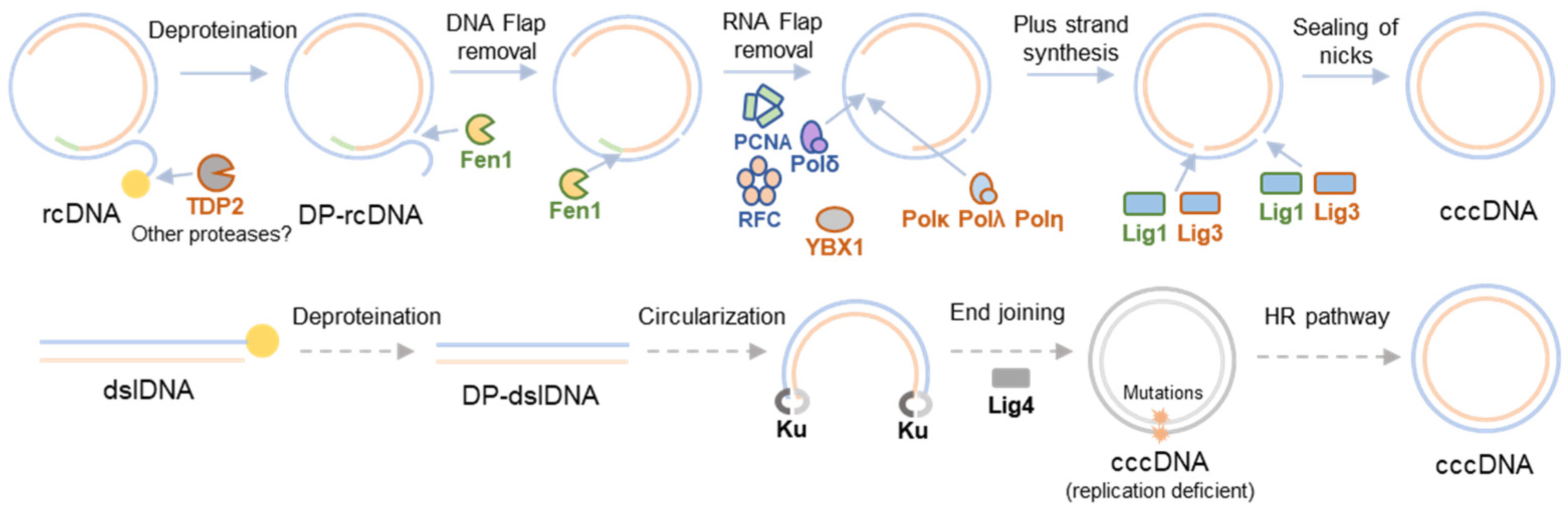
2. HBV cccDNA Formation
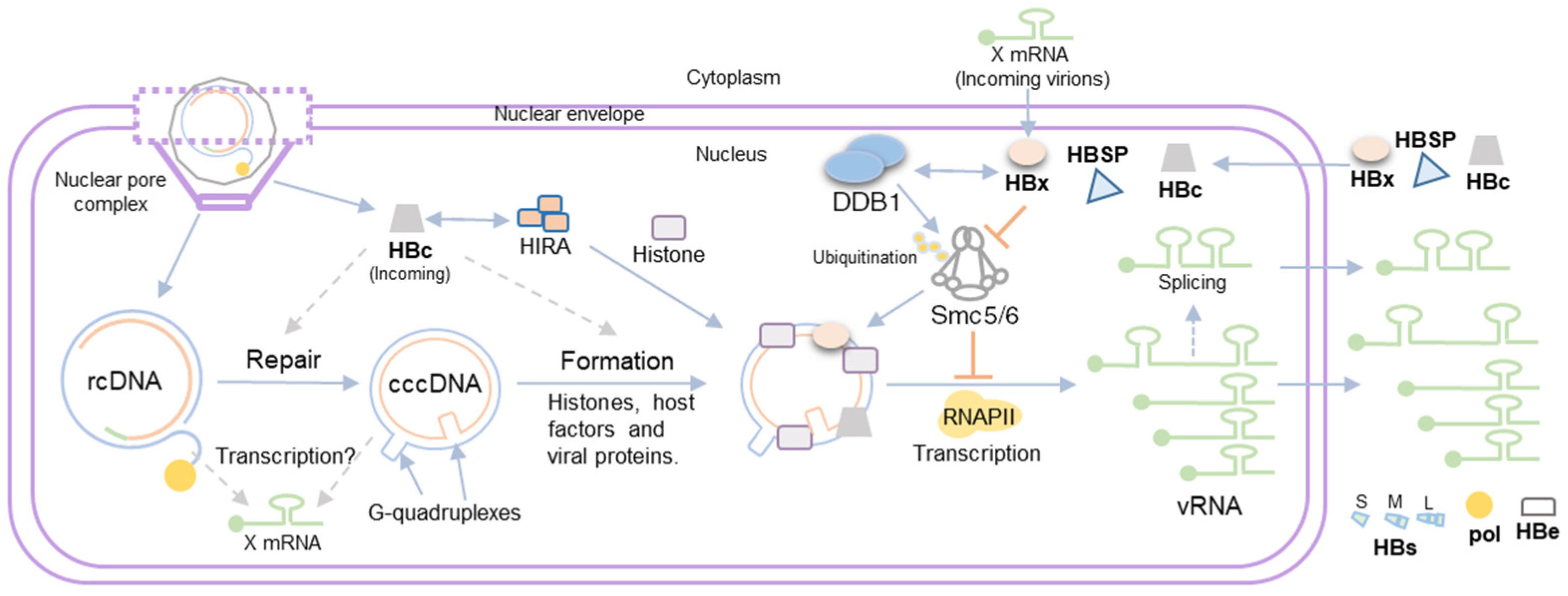
3. HBV Minichromosome Formation
4. Viral Gene Expression from the HBV Minichromosome
5. Role of HBV Proteins in cccDNA Transcription
6. HBV Post-Transcriptional Modifications
7. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chisari, F.V.; Ferrari, C. Hepatitis B Virus Immunopathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1995, 13, 29–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, B.Y.; Ploss, A. Determinants of Hepatitis B and Delta Virus Host Tropism. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 13, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, J.J.; Stevens, G.A.; Groeger, J.; Wiersma, S.T. Global Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection: New Estimates of Age-Specific HBsAg Seroprevalence and Endemicity. Vaccine 2012, 30, 2212–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeger, C.; Mason, W.S. Molecular Biology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Virology 2015, 479–480, 672–686. [Google Scholar]
- Ozer, A.; Khaoustov, V.I.; Mearns, M.; Lewis, D.E.; Genta, R.M.; Darlington, G.J.; Yoffe, B. Effect of Hepatocyte Proliferation and Cellular DNA Synthesis on Hepatitis B Virus Replication. Gastroenterology 1996, 110, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, J.; Mason, W.S. Replication of the Genome of a Hepatitis B-like Virus by Reverse Transcription of an RNA Intermediate. Cell 1982, 29, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, A.; Gripon, P.; Urban, S. Hepatitis B Virus Infection Initiates with a Large Surface Protein-Dependent Binding to Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide Is a Functional Receptor for Human Hepatitis B and D Virus. eLife 2012, 2012, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, M.; Saso, W.; Sugiyama, R.; Ishii, K.; Ohki, M.; Nagamori, S.; Suzuki, R.; Aizaki, H.; Ryo, A.; Yun, J.-H.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Is a Host-Entry Cofactor Triggering Hepatitis B Virus Internalization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8487–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Chang, W.-C.; Tao, M.-H.; Huang, C. Entry of Hepatitis B Virus into Immortalized Human Primary Hepatocytes by Clathrin-Dependent Endocytosis. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 9443–9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, B.; Vlachou, A.; Panté, N.; Helenius, A.; Kann, M. Nuclear Import of Hepatitis B Virus Capsids and Release of the Viral Genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9849–9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, Z.; Gruebele, M.; Tajkhorshid, E. Molecular Mechanism of Capsid Disassembly in Hepatitis B Virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2102530118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newbold, J.E.; Xin, H.; Tencza, M.; Sherman, G.; Dean, J.; Bowden, S.; Locarnini, S. The Covalently Closed Duplex Form of the Hepadnavirus Genome Exists in Situ as a Heterogeneous Population of Viral Minichromosomes. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 3350–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartenschlager, R.; Schaller, H. Hepadnaviral Assembly Is Initiated by Polymerase Binding to the Encapsidation Signal in the Viral RNA Genome. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 3413–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Seeger, C. Expression and Characterization of Hepadnavirus Reverse Transcriptases. Methods Enzymol. 1996, 275, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staprans, S.; Loeb, D.D.; Ganem, D. Mutations Affecting Hepadnavirus Plus-Strand DNA Synthesis Dissociate Primer Cleavage from Translocation and Reveal the Origin of Linear Viral DNA. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttleman, J.S.; Pourcel, C.; Summers, J. Formation of the Pool of Covalently Closed Circular Viral DNA in Hepadnavirus-Infected Cells. Cell 1986, 47, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Sorensen, E.M.; Naito, A.; Schott, M.; Kim, S.; Ahlquist, P. Involvement of Host Cellular Multivesicular Body Functions in Hepatitis B Virus Budding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10205–10210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, X.; Nguyen, D.; Mentzer, L.; Adams, C.; Lee, H.; Ashley, R.; Hafenstein, S.; Hu, J. Secretion of Genome-Free Hepatitis B Virus--Single Strand Blocking Model for Virion Morphogenesis of Para-Retrovirus. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.T.; Billaud, J.N.; Sällberg, M.; Guidotti, L.G.; Chisari, F.V.; Jones, J.; Hughes, J.; Milich, D.R. A Function of the Hepatitis B Virus Precore Protein Is to Regulate the Immune Response to the Core Antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14913–14918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlandschoot, P.; Leroux-Roels, G. Viral Apoptotic Mimicry: An Immune Evasion Strategy Developed by the Hepatitis B Virus? Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.; Budzinska, M.A.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S. HBV DNA Integration: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Viruses 2017, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Ploss, A. Mechanism of Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA Formation. Viruses 2021, 13, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KöNiger, C.; Wingert, I.; Marsmann, M.; Rösler, C.; Beck, J.; Nassal, M. Involvement of the Host DNA-Repair Enzyme TDP2 in Formation of the Covalently Closed Circular DNA Persistence Reservoir of Hepatitis B Viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4244–E4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, K.; Que, L.; Shimadu, M.; Koura, M.; Ishihara, Y.; Wakae, K.; Nakamura, T.; Watashi, K.; Wakita, T.; Muramatsu, M. Flap Endonuclease 1 Is Involved in CccDNA Formation in the Hepatitis B Virus. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Ploss, A. Core Components of DNA Lagging Strand Synthesis Machinery Are Essential for Hepatitis B Virus CccDNA Formation. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis B Virus CccDNA Is Formed through Distinct Repair Processes of Each Strand. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Gao, Z.; Xu, G.; Peng, B.; Liu, C.; Yan, H.; Yao, Q.; Sun, G.; Liu, Y.; Tang, D.; et al. DNA Polymerase κ Is a Key Cellular Factor for the Formation of Covalently Closed Circular DNA of Hepatitis B Virus. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrier, E.R.; Ligat, G.; Heydmann, L.; Doernbrack, K.; Miller, J.; Maglott-Roth, A.; Jühling, F.; El Saghire, H.; Heuschkel, M.J.; Fujiwara, N.; et al. Cell-Based CccDNA Reporter Assay Combined with Functional Genomics Identifies YBX1 as HBV CccDNA Host Factor and Antiviral Candidate Target. Gut 2022, 72, 1745–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Summers, J. Illegitimate Replication of Linear Hepadnavirus DNA through Nonhomologous Recombination. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 4029–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Summers, J. Infection of Ducklings with Virus Particles Containing Linear Double-Stranded Duck Hepatitis B Virus DNA: Illegitimate Replication and Reversion. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 8710–8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Xu, C.; Zhou, T.; Block, T.M.; Guo, J.T. Characterization of the Host Factors Required for Hepadnavirus Covalently Closed Circular (Ccc) DNA Formation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieber, M.R. The Mechanism of Double-Strand DNA Break Repair by the Nonhomologous DNA End-Joining Pathway. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 181–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Summers, J. Integration of Hepadnavirus DNA in Infected Liver: Evidence for a Linear Precursor. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9710–9717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, C.T.; Schwinn, S.; Locarnini, S.; Fyfe, J.; Manns, M.P.; Trautwein, C.; Zentgraf, H. Structural Organization of the Hepatitis B Virus Minichromosome. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 307, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrisani, O. Epigenetic Mechanisms in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatoma Res. 2021, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandri, M. Epigenetic Modulation in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Semin. Immunopathol. 2020, 42, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, M.; Quivy, J.-P.; Chapus, F.; Michelet, M.; Fresquet, J.; Maadadi, S.; Aberkane, A.N.; Diederichs, A.; Lucifora, J.; Rivoire, M.; et al. HIRA Supports Hepatitis B Virus Minichromosome Establishment and Transcriptional Activity in Infected Hepatocytes. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 14, 527–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagami, H.; Ray-Gallet, D.; Almouzni, G.; Nakatani, Y. Histone H3.1 and H3.3 Complexes Mediate Nucleosome Assembly Pathways Dependent or Independent of DNA Synthesis. Cell 2004, 116, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray-Gallet, D.; Woolfe, A.; Vassias, I.; Pellentz, C.; Lacoste, N.; Puri, A.; Schultz, D.C.; Pchelintsev, N.A.; Adams, P.D.; Jansen, L.E.T.; et al. Dynamics of Histone H3 Deposition In Vivo Reveal a Nucleosome Gap-Filling Mechanism for H3.3 to Maintain Chromatin Integrity. Mol. Cell 2011, 44, 928–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, T.S.; Glass, M.; Cole, J.J.; Rather, M.I.; Marsden, M.; Neilson, M.; Brock, C.; Humphreys, I.R.; Everett, R.D.; Adams, P.D. Histone Chaperone HIRA Deposits Histone H3.3 onto Foreign Viral DNA and Contributes to Anti-Viral Intrinsic Immunity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 11673–11683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, S.; Polo, S.E.; Almouzni, G. Transcription Recovery after DNA Damage Requires Chromatin Priming by the H3.3 Histone Chaperone HIRA. Cell 2013, 155, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Astudillo, F.; Garrido, D.; Varas-Godoy, M.; Gutiérrez, J.L.; Villanueva, R.A.; Loyola, A. The Histone Variant H3.3 Regulates the Transcription of the Hepatitis B Virus. Ann. Hepatol. 2021, 21, 100261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucifora, J.; Pastor, F.; Charles, É.; Pons, C.; Auclair, H.; Fusil, F.; Rivoire, M.; Cosset, F.-L.; Durantel, D.; Salvetti, A. Evidence for Long-Term Association of Virion-Delivered HBV Core Protein with CccDNA Independently of Viral Protein Production. JHEP reports Innov. Hepatol. 2021, 3, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Yuan, Y.; Yuan, H.; Yun, H.; Sun, M.; Bu, Y.; Liu, L.; et al. HAT1 Signaling Confers to Assembly and Epigenetic Regulation of HBV CccDNA Minichromosome. Theranostics 2019, 9, 7345–7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vachon, A.; Seo, G.E.; Patel, N.H.; Coffin, C.S.; Marinier, E.; Eyras, E.; Osiowy, C. Hepatitis B Virus Serum RNA Transcript Isoform Composition and Proportion in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients by Nanopore Long-Read Sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1233178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.S.; Sozzi, V.; Littlejohn, M.; Yuen, L.K.W.; Warner, N.; Betz-Stablein, B.; Luciani, F.; Revill, P.A.; Brown, C.M. Quantitative Analysis of the Splice Variants Expressed by the Major Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremsdorf, D.; Lekbaby, B.; Bablon, P.; Sotty, J.; Augustin, J.; Schnuriger, A.; Pol, J.; Soussan, P. Alternative Splicing of Viral Transcripts: The Dark Side of HBV. Gut 2021, 70, 2373–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, N.; Nakashima, K.; Sun, S.; Ito, M.; Suzuki, T. Cell Type Diversity in Hepatitis B Virus RNA Splicing and Its Regulation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussan, P.; Tuveri, R.; Nalpas, B.; Garreau, F.; Zavala, F.; Masson, A.; Pol, S.; Brechot, C.; Kremsdorf, D. The Expression of Hepatitis B Spliced Protein (HBSP) Encoded by a Spliced Hepatitis B Virus RNA Is Associated with Viral Replication and Liver Fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozzi, V.; McCoullough, L.; Mason, H.; Littlejohn, M.; Revill, P.A. The in Vitro Replication Phenotype of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Splice Variant Sp1. Virology 2022, 574, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.-Y.; Sun, C.-P.; Tao, M.-H.; Wu, H.-L.; Wang, S.-H.; Yeh, S.-H.; Zheng, Q.-B.; Yuan, Q.; Xia, N.-S.; Ogawa, K.; et al. Major HBV Splice Variant Encoding a Novel Protein Important for Infection. J. Hepatol. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, K.; Fang, B.A.M.; Wu, H.; Li, F.; Xiang, X.; Tang, W.; Zhao, G.; Lin, L.; Bao, S.; et al. Identification of Acetyltransferase Genes (HAT1 and KAT8) Regulating HBV Replication by RNAi Screening. Cell Biosci. 2015, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcon, V.; Hernández, S.; Rubio, L.; Alvarez, F.; Flores, Y.; Varas-Godoy, M.; De Ferrari, G.V.; Kann, M.; Villanueva, R.A.; Loyola, A. The Enzymes LSD1 and Set1A Cooperate with the Viral Protein HBx to Establish an Active Hepatitis B Viral Chromatin State. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhenda, S.; Ducroux, A.; Rivière, L.; Sobhian, B.; Ward, M.D.; Dion, S.; Hantz, O.; Protzer, U.; Michel, M.-L.; Benkirane, M.; et al. Methyltransferase PRMT1 Is a Binding Partner of HBx and a Negative Regulator of Hepatitis B Virus Transcription. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4360–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decorsière, A.; Mueller, H.; Van Breugel, P.C.; Abdul, F.; Gerossier, L.; Beran, R.K.; Livingston, C.M.; Niu, C.; Fletcher, S.P.; Hantz, O.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Identifies the Smc5/6 Complex as a Host Restriction Factor. Nature 2016, 531, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivekanandan, P.; Thomas, D.; Torbenson, M. Hepatitis B Viral DNA Is Methylated in Liver Tissues. J. Viral Hepat. 2008, 15, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Xie, W. The Role of 3D Genome Organization in Development and Cell Differentiation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Y.; Peng, B.; Gao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Duan, J.; Qi, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Transcriptionally Inactive Hepatitis B Virus Episome DNA Preferentially Resides in the Vicinity of Chromosome 19 in 3D Host Genome upon Infection. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, C.; Livingston, C.M.; Li, L.; Beran, R.K.; Daffis, S.; Ramakrishnan, D.; Burdette, D.; Peiser, L.; Salas, E.; Ramos, H.; et al. The Smc5/6 Complex Restricts HBV When Localized to ND10 without Inducing an Innate Immune Response and Is Counteracted by the HBV X Protein Shortly after Infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Peng, B.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, D.; He, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. SLF2 Interacts with the SMC5/6 Complex to Direct Hepatitis B Virus Episomal DNA to Promyelocytic Leukemia Bodies for Transcriptional Repression. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0032823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, F.; Diman, A.; Baechler, B.; Ramakrishnan, D.; Kornyeyev, D.; Beran, R.K.; Fletcher, S.P.; Strubin, M. Smc5/6 Silences Episomal Transcription by a Three-Step Function. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2022, 29, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppert, J.L. Four-Stranded Nucleic Acids: Structure, Function and Targeting of G-Quadruplexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraud, G.; Rodà, M.; Huchon, P.; Michelet, M.; Maadadi, S.; Jutzi, D.; Montserret, R.; Ruepp, M.-D.; Parent, R.; Combet, C.; et al. G-Quadruplexes Control Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Promoting CccDNA Transcription and Phase Separation in Hepatocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 52, 2290–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Escribano, P.; Hormeño, S.; Madariaga-Marcos, J.; Solé-Soler, R.; O’Reilly, F.J.; Morris, K.; Aicart-Ramos, C.; Aramayo, R.; Montoya, A.; Kramer, H.; et al. Purified Smc5/6 Complex Exhibits DNA Substrate Recognition and Compaction. Mol. Cell 2020, 80, 1039–1054.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belloni, L.; Pollicino, T.; De Nicola, F.; Guerrieri, F.; Raffa, G.; Fanciulli, M.; Raimondo, G.; Levrero, M. Nuclear HBx Binds the HBV Minichromosome and Modifies the Epigenetic Regulation of CccDNA Function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19975–19979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, T.; Zehnder, B.; Qu, B.; Urban, S. De Novo Synthesis of Hepatitis B Virus Nucleocapsids Is Dispensable for the Maintenance and Transcriptional Regulation of CccDNA. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Wu, C.; Xu, Z.; Teng, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Zhan, Q.; Zhu, C.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Core Protein Is Not Required for Covalently Closed Circular DNA Transcriptional Regulation. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0136222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, C.; Shi, B.; Fang, Z.; Qin, B.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Z. A Novel Recombinant CccDNA-Based Mouse Model with Long Term Maintenance of RcccDNA and Antigenemia. Antivir. Res. 2020, 180, 104826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Zhou, B.; Cai, D.; Zong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Mercier, A.; Guo, H.; Hou, J.; Colonno, R.; et al. Rapid Turnover of Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA Indicated by Monitoring Emergence and Reversion of Signature-Mutation in Treated Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Hepatology 2021, 73, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornyeyev, D.; Ramakrishnan, D.; Voitenleitner, C.; Livingston, C.M.; Xing, W.; Hung, M.; Kwon, H.J.; Fletcher, S.P.; Beran, R.K. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein in Primary Human Hepatocytes. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Breugel, P.C.; Robert, E.I.; Mueller, H.; Decorsière, A.; Zoulim, F.; Hantz, O.; Strubin, M. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Stimulates Gene Expression Selectively from Extrachromosomal DNA Templates. Hepatology 2012, 56, 2116–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leupin, O.; Bontron, S.; Schaeffer, C.; Strubin, M. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Stimulates Viral Genome Replication via a DDB1-Dependent Pathway Distinct from That Leading to Cell Death. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 4238–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angers, S.; Li, T.; Yi, X.; MacCoss, M.J.; Moon, R.T.; Zheng, N. Molecular Architecture and Assembly of the DDB1-CUL4A Ubiquitin Ligase Machinery. Nature 2006, 443, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadelmayer, B.; Diederichs, A.; Chapus, F.; Rivoire, M.; Neveu, G.; Alam, A.; Fraisse, L.; Carter, K.; Testoni, B.; Zoulim, F. Full-Length 5′RACE Identifies All Major HBV Transcripts in HBV-Infected Hepatocytes and Patient Serum. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, D.; Cordero, G.; Kawamura, R.; Sverzhinsky, A.; Sarker, M.; Roy, S.; Malo, C.; Pascal, J.M.; Marko, J.F.; D’Amours, D. The Smc5/6 Core Complex Is a Structure-Specific DNA Binding and Compacting Machine. Mol. Cell 2020, 80, 1025–1038.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berggren, K.A.; Schwartz, R.E.; Kleiner, R.E.; Ploss, A. The Impact of Epitranscriptomic Modifications on Liver Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 35, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roundtree, I.A.; Evans, M.E.; Pan, T.; He, C. Dynamic RNA Modifications in Gene Expression Regulation. Cell 2017, 169, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Liu, J.; He, C. RNA N6-Methyladenosine Methylation in Post-Transcriptional Gene Expression Regulation. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imam, H.; Khan, M.; Gokhale, N.S.; McIntyre, A.B.R.; Kim, G.-W.; Jang, J.Y.; Kim, S.-J.; Mason, C.E.; Horner, S.M.; Siddiqui, A. N6-Methyladenosine Modification of Hepatitis B Virus RNA Differentially Regulates the Viral Life Cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 8829–8834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-W.; Moon, J.-S.; Siddiqui, A. N6-Methyladenosine Modification of the 5′ Epsilon Structure of the HBV Pregenome RNA Regulates Its Encapsidation by the Viral Core Protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2120485119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-W.; Siddiqui, A. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Recruits Methyltransferases to Affect Cotranscriptional N6-Methyladenosine Modification of Viral/Host RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2019455118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Kitamura, K.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Chowdhury, S.; Fu, W.; Koura, M.; Wakae, K.; Honjo, T.; Muramatsu, M. RNA Editing of Hepatitis B Virus Transcripts by Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2246–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Vilchez, S.; Lara-Pezzi, E.; Trapero-Marugán, M.; Moreno-Otero, R.; Sanz-Cameno, P. The Molecular and Pathophysiological Implications of Hepatitis B X Antigen in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Rev. Med. Virol. 2011, 21, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, S.; Zlotnick, A. Asymmetric Modification of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Genomes by an Endogenous Cytidine Deaminase inside HBV Cores Informs a Model of Reverse Transcription. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez-Moreno, A.; Ploss, A. Mechanisms of Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA and Minichromosome Formation and HBV Gene Transcription. Viruses 2024, 16, 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040609
Gómez-Moreno A, Ploss A. Mechanisms of Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA and Minichromosome Formation and HBV Gene Transcription. Viruses. 2024; 16(4):609. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040609
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez-Moreno, Andoni, and Alexander Ploss. 2024. "Mechanisms of Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA and Minichromosome Formation and HBV Gene Transcription" Viruses 16, no. 4: 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040609
APA StyleGómez-Moreno, A., & Ploss, A. (2024). Mechanisms of Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA and Minichromosome Formation and HBV Gene Transcription. Viruses, 16(4), 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040609





