Respiratory and Gut Microbiome Modification during Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Date Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.4. Date Synthesis and Analysis
3. Results
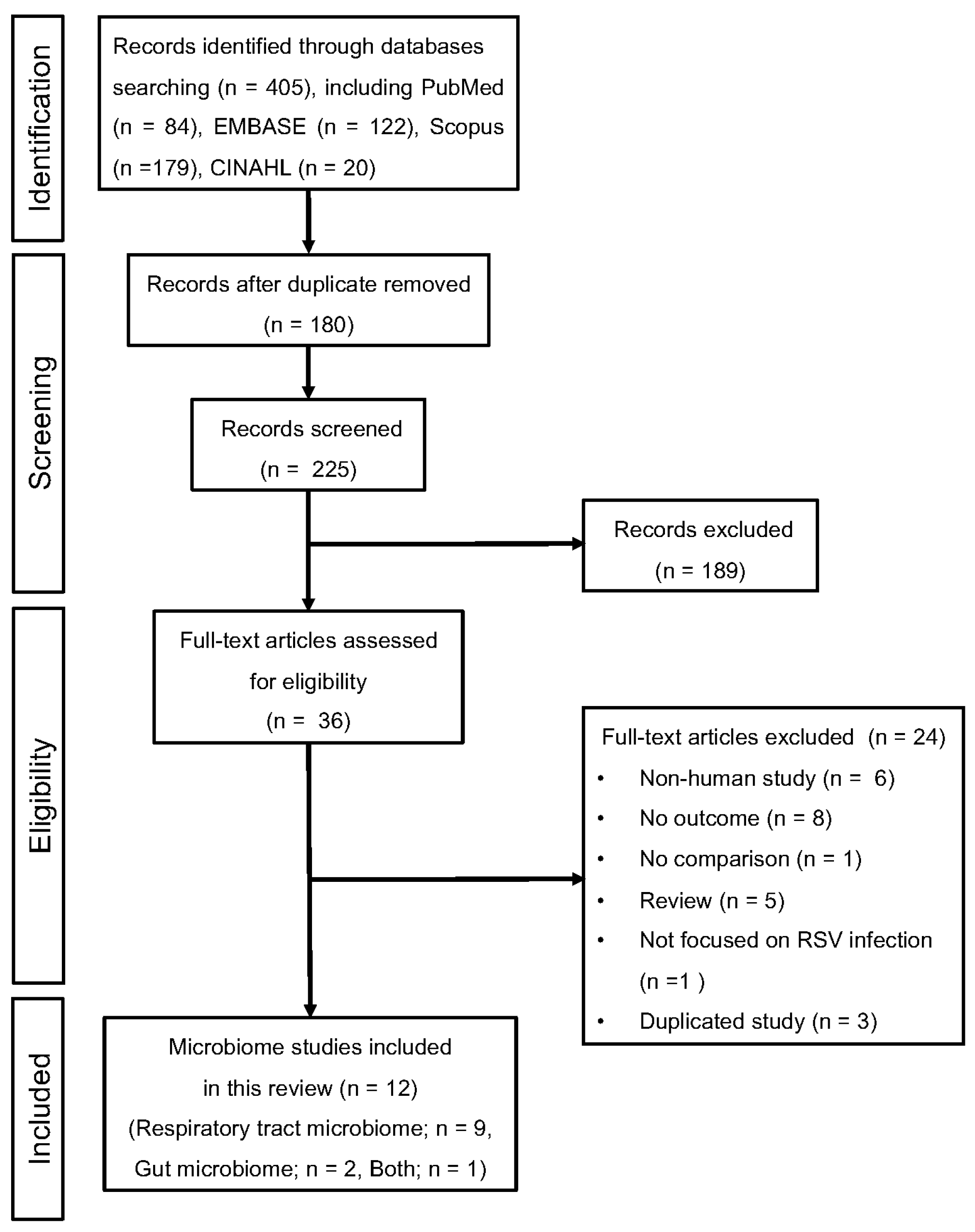
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Quality of Studies
3.3. Main Study Characteristics
3.4. Changes in Microbial Composition in the Respiratory Tract Associated with RSV Infection
3.4.1. Respiratory Tract Microbiome Compared to Healthy Controls
3.4.2. Respiratory Tract Microbiome Compared to Patients Other Than Healthy Controls
3.5. RSV Infection-Associated Changes in Microbial Composition in the Gut
3.6. Microbial Diversity in the Respiratory Tract Associated with RSV Infection
3.6.1. Alpha Diversity
3.6.2. Beta Diversity
3.7. Microbial Diversity in the Gut Associated with RSV Infection
3.7.1. Alpha Diversity
3.7.2. Beta Diversity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, T.; McAllister, D.A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Simoes, E.A.F.; Madhi, S.A.; Gessner, B.D.; Polack, F.P.; Balsells, E.; Acacio, S.; Aguayo, C.; et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2015: A systematic review and modelling study. Lancet 2017, 390, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurs, N.; Aljassim, F.; Kjellman, B.; Robinson, P.D.; Sigurbergsson, F.; Bjarnason, R.; Gustafsson, P.M. Asthma and allergy patterns over 18 years after severe RSV bronchiolitis in the first year of life. Thorax 2010, 65, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, H.; Nokes, D.J.; Gessner, B.D.; Dherani, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Singleton, R.J.; O’Brien, K.L.; Roca, A.; Wright, P.F.; Bruce, N.; et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, J.; Hilliard, T.N.; Sherriff, A.; Stalker, D.; Al Shammari, N.; Thomas, H.M. Hospitalization for RSV bronchiolitis before 12 months of age and subsequent asthma, atopy and wheeze: A longitudinal birth cohort study. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 16, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, L.; Sagfors, A.M.; Openshaw, P.J.; Culley, F.J. Immunity to RSV in Early-Life. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, R.F. Impact of respiratory syncytial virus in the United States. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2008, 65, S3–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberthal, A.S.; Bauchner, H.; Hall, C.B.; Johnson, D.W.; Kotagal, U.; Light, M.J.; Mason, W.; Meissner, H.C.; Phelan, K.J.; Zorc, J.J.; et al. Diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis. Pediatrics 2006, 118, 1774–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R.M.; Hartling, L. Glucocorticoids for acute viral bronchiolitis in infants and young children. JAMA 2014, 311, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.; Seo, J.; Yeun, J.; Choi, H.; Kim, Y.I.; Chang, S.Y. The role of mucosal barriers in human gut health. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2021, 44, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, W.L.; Mak, J.W.Y.; Wong, S.H.; Zhu, S.T.; Guo, S.L.; Chan, F.K.L.; Zhang, S.T.; Ng, S.C. Modulation of gut microbiota protects against viral respiratory tract infections: A systematic review of animal and clinical studies. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 4151–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, H.A.; Behieldin, A.; Edris, S. Gut microbiome skin axis in the development of atopic dermatitis. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2021, 71, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Are We Really Vastly Outnumbered? Revisiting the Ratio of Bacterial to Host Cells in Humans. Cell 2016, 164, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costea, P.I.; Hildebrand, F.; Arumugam, M.; Backhed, F.; Blaser, M.J.; Bushman, F.D.; de Vos, W.M.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Fraser, C.M.; Hattori, M.; et al. Enterotypes in the landscape of gut microbial community composition. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, Q.; Luo, M.; Xiong, L. Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 729346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, C.A.; Diaz-Arteche, C.; Eliby, D.; Schwartz, O.S.; Simmons, J.G.; Cowan, C.S.M. The gut microbiota in anxiety and depression—A systematic review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 83, 101943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, S.; Silvestre, M.P.; Vasques, M.; Araujo, J.R.; Morais, J.; Duarte, M.I.; Pestana, D.; Faria, A.; Pereira-Leal, J.B.; Vaz, J.; et al. A Pilot Study on the Metabolic Impact of Mediterranean Diet in Type 2 Diabetes: Is Gut Microbiota the Key? Nutrients 2021, 13, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulla, M.H.; Agarwal, D.; Singh, J.K.; Traiki, T.B.; Pandey, M.K.; Ahmad, R.; Srivastava, S.K. Association of the microbiome with colorectal cancer development (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 58, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.J.; Cao, N.W.; Zhou, H.Y.; Meng, X.; Guo, B.; Zhang, H.Y.; Li, B.Z. The oral and gut microbiome in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A systematic review. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Womble, J.T.; Gunsch, C.K.; Ingram, J.L. The Gut/Lung Microbiome Axis in Obesity, Asthma, and Bariatric Surgery: A Literature Review. Obesity 2021, 29, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enaud, R.; Prevel, R.; Ciarlo, E.; Beaufils, F.; Wieers, G.; Guery, B.; Delhaes, L. The Gut-Lung Axis in Health and Respiratory Diseases: A Place for Inter-Organ and Inter-Kingdom Crosstalks. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sencio, V.; Machado, M.G.; Trottein, F. The lung-gut axis during viral respiratory infections: The impact of gut dysbiosis on secondary disease outcomes. Mucosal Immunol. 2021, 14, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, F.; Wei, H.; Lian, Z.X.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z. Respiratory influenza virus infection induces intestinal immune injury via microbiota-mediated Th17 cell-dependent inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 2397–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, K.H.; Fachi, J.L.; de Paula, R.; da Silva, E.F.; Pral, L.P.; Dos Santos, A.A.; Dias, G.B.M.; Vargas, J.E.; Puga, R.; Mayer, F.Q.; et al. Microbiota-derived acetate protects against respiratory syncytial virus infection through a GPR43-type 1 interferon response. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raita, Y.; Perez-Losada, M.; Freishtat, R.J.; Harmon, B.; Mansbach, J.M.; Piedra, P.A.; Zhu, Z.; Camargo, C.A.; Hasegawa, K. Integrated omics endotyping of infants with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis and risk of childhood asthma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Chen, N.; Zhao, S.; He, Q. Airway microbiome, host immune response and recurrent wheezing in infants with severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 31, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, K.; Linnemann, R.W.; Mansbach, J.M.; Ajami, N.J.; Espinola, J.A.; Petrosino, J.F.; Piedra, P.A.; Stevenson, M.D.; Sullivan, A.F.; Thompson, A.D.; et al. The Fecal Microbiota Profile and Bronchiolitis in Infants. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20160218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.E.; Lee, Y.J.; Seo, H.J.; Sheen, S.S.; Hahn, S.; Jang, B.H.; Son, H.J. Testing a tool for assessing the risk of bias for nonrandomized studies showed moderate reliability and promising validity. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 66, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, C.; Aparicio, M.; Gonzalez-Martinez, F.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, M.I.; Perez-Moreno, J.; Toledo Del Castillo, B.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, R.; Fernandez, L. Nasal and Fecal Microbiota and Immunoprofiling of Infants with and without RSV Bronchiolitis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 667832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Steenhuijsen Piters, W.A.; Heinonen, S.; Hasrat, R.; Bunsow, E.; Smith, B.; Suarez-Arrabal, M.C.; Chaussabel, D.; Cohen, D.M.; Sanders, E.A.; Ramilo, O.; et al. Nasopharyngeal Microbiota, Host Transcriptome, and Disease Severity in Children with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ederveen, T.H.A.; Ferwerda, G.; Ahout, I.M.; Vissers, M.; de Groot, R.; Boekhorst, J.; Timmerman, H.M.; Huynen, M.A.; van Hijum, S.; de Jonge, M.I. Haemophilus is overrepresented in the nasopharynx of infants hospitalized with RSV infection and associated with increased viral load and enhanced mucosal CXCL8 responses. Microbiome 2018, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grier, A.; Gill, A.L.; Kessler, H.A.; Corbett, A.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Java, J.; Holden-Wiltse, J.; Falsey, A.R.; Topham, D.J.; Mariani, T.J.; et al. Temporal Dysbiosis of Infant Nasal Microbiota Relative to Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 1650–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, J.N.; Siefker, D.; Vu, L.; You, D.; DeVincenzo, J.; Pierre, J.F.; Cormier, S.A. Altered gut microbiota in infants is associated with respiratory syncytial virus disease severity. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansbach, J.M.; Hasegawa, K.; Henke, D.M.; Ajami, N.J.; Petrosino, J.F.; Shaw, C.A.; Piedra, P.A.; Sullivan, A.F.; Espinola, J.A.; Camargo, C.A., Jr. Respiratory syncytial virus and rhinovirus severe bronchiolitis are associated with distinct nasopharyngeal microbiota. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1909–1913.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansbach, J.M.; Luna, P.N.; Shaw, C.A.; Hasegawa, K.; Petrosino, J.F.; Piedra, P.A.; Sullivan, A.F.; Espinola, J.A.; Stewart, C.J.; Camargo, C.A., Jr. Increased Moraxella and Streptococcus species abundance after severe bronchiolitis is associated with recurrent wheezing. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 518–527.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopala, S.V.; Bakhoum, N.G.; Pakala, S.B.; Shilts, M.H.; Rosas-Salazar, C.; Mai, A.; Boone, H.H.; McHenry, R.; Yooseph, S.; Halasa, N.; et al. Metatranscriptomics to characterize respiratory virome, microbiome, and host response directly from clinical samples. Cell Rep. Methods 2021, 1, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas-Salazar, C.; Shilts, M.H.; Tovchigrechko, A.; Schobel, S.; Chappell, J.D.; Larkin, E.K.; Gebretsadik, T.; Halpin, R.A.; Nelson, K.E.; Moore, M.L.; et al. Nasopharyngeal Lactobacillus is associated with a reduced risk of childhood wheezing illnesses following acute respiratory syncytial virus infection in infancy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1447–1456.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, M.M.; Leimanis-Laurens, M.L.; Bu, S.; Kinney, G.A.; Teoh, S.T.; McKee, R.L.; Ferguson, K.; Winters, J.W.; Lunt, S.Y.; Prokop, J.W.; et al. Loss of Health Promoting Bacteria in the Gastrointestinal Microbiome of PICU Infants with Bronchiolitis: A Single-Center Feasibility Study. Children 2022, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippa, S.; Frassanito, A.; Marazzato, M.; Nenna, R.; Petrarca, L.; Neroni, B.; Bonfiglio, G.; Guerrieri, F.; Frasca, F.; Oliveto, G.; et al. Nasal Microbiota in RSV Bronchiolitis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Knittel, K.; Fuchs, B.M.; Ludwig, W.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. SILVA: A comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, D.; Price, M.N.; Goodrich, J.; Nawrocki, E.P.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Probst, A.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Hugenholtz, P. An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J. 2012, 6, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.L.; Leong, L.E.X.; Mobegi, F.M.; Choo, J.M.; Wesselingh, S.; Yang, I.A.; Upham, J.W.; Reynolds, P.N.; Hodge, S.; James, A.L.; et al. Long-Term Azithromycin Reduces Haemophilus influenzae and Increases Antibiotic Resistance in Severe Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.L.; Daly, J.; Baines, K.J.; Yang, I.A.; Upham, J.W.; Reynolds, P.N.; Hodge, S.; James, A.L.; Hugenholtz, P.; Willner, D.; et al. Airway dysbiosis: Haemophilus influenzae and Tropheryma in poorly controlled asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebre, M.A.; Pang, P.H.; Diver, S.; Desai, D.; Bafadhel, M.; Haldar, K.; Kebadze, T.; Cohen, S.; Newbold, P.; Rapley, L.; et al. Biological exacerbation clusters demonstrate asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease overlap with distinct mediator and microbiome profiles. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 2027–2036.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haldar, K.; George, L.; Wang, Z.; Mistry, V.; Ramsheh, M.Y.; Free, R.C.; John, C.; Reeve, N.F.; Miller, B.E.; Tal-Singer, R.; et al. The sputum microbiome is distinct between COPD and health, independent of smoking history. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, T.; Makino, A.; Ogata, R.; Nakamura, S.; Ito, T.; Nagata, K.; Terauchi, Y.; Oishi, T.; Fujieda, M.; Takahashi, Y.; et al. Respiratory syncytial virus infection exacerbates pneumococcal pneumonia via Gas6/Axl-mediated macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3021–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chonmaitree, T.; Owen, M.J.; Patel, J.A.; Hedgpeth, D.; Horlick, D.; Howie, V.M. Effect of viral respiratory tract infection on outcome of acute otitis media. J. Pediatr. 1992, 120, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.M.; Sandrini, S.; Datta, S.; Freestone, P.; Shafeeq, S.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Williams, G.; Glenn, S.M.; Kuipers, O.P.; Hirst, R.A.; et al. Respiratory syncytial virus increases the virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae by binding to penicillin binding protein 1a. A new paradigm in respiratory infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, F.W.; Pollard, K.M.; Parks, C.G.; Germolec, D.R.; Leung, P.S.; Selmi, C.; Humble, M.C.; Rose, N.R. Criteria for environmentally associated autoimmune diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2012, 39, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Brito-Zeron, P.; Kostov, B.; Siso-Almirall, A.; Bosch, X.; Buss, D.; Trilla, A.; Stone, J.H.; Khamashta, M.A.; Shoenfeld, Y. Google-driven search for big data in autoimmune geoepidemiology: Analysis of 394,827 patients with systemic autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gacesa, R.; Kurilshikov, A.; Vich Vila, A.; Sinha, T.; Klaassen, M.A.Y.; Bolte, L.A.; Andreu-Sanchez, S.; Chen, L.; Collij, V.; Hu, S.; et al. Environmental factors shaping the gut microbiome in a Dutch population. Nature 2022, 604, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durazzi, F.; Sala, C.; Castellani, G.; Manfreda, G.; Remondini, D.; De Cesare, A. Comparison between 16S rRNA and shotgun sequencing data for the taxonomic characterization of the gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Hofstaedter, C.E.; Zhao, C.; Mattei, L.; Tanes, C.; Clarke, E.; Lauder, A.; Sherrill-Mix, S.; Chehoud, C.; Kelsen, J.; et al. Optimizing methods and dodging pitfalls in microbiome research. Microbiome 2017, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faner, R.; Sibila, O.; Agusti, A.; Bernasconi, E.; Chalmers, J.D.; Huffnagle, G.B.; Manichanh, C.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Paredes, R.; Perez Brocal, V.; et al. The microbiome in respiratory medicine: Current challenges and future perspectives. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1602086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.J.; Ege, M.J.; von Mutius, E.; Ege, M.J.; von Mutius, E.; von Mutius, E. Challenges, impact and the future. ERS Monogr. 2019, 2019, 240–244. [Google Scholar]
- Carney, S.M.; Clemente, J.C.; Cox, M.J.; Dickson, R.P.; Huang, Y.J.; Kitsios, G.D.; Kloepfer, K.M.; Leung, J.M.; LeVan, T.D.; Molyneaux, P.L.; et al. Methods in Lung Microbiome Research. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 62, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| First Author (Year) | Country | Age Category | Number of Patients with RSV Infection | Number of Controls | Types of Samples | Diagnostic Method for RSV Infection | Microbiome Approach, Pipeline, and Database |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alba C et al. (2021) [29] | Spain | <2 years | 54 | 14 (Healthy control) | Nasal wash | PCR DFA | 16S rRNA (V3–V4) QIIME v. 1.9.1 [40] |
| Rajagopala SV et al. (2021) [36] | USA | <3 years | 43 | 22 (Healthy control) | Nasal swab | PCR | Metagenomics Trimmomatic v. 0.39 [41] SILVA [42] |
| Grier A et al. (2020) [32] | USA | <1 year | 89 (For the longitudinal cohort, 12) | 102 (Healthy control) (For the longitudinal cohort, 12) | Nasal swab | PCR | 16S rRNA (V1–V3) QIIME 2 [43] Greengenes [44] |
| Schippa S et al. (2020) [39] | Italy | <6 months | 48 (RSV positive) | 28 (Negative to other respiratory viruses) | Nasopharyngeal wash | PCR | 16S rRNA (V3–V4) Mothur v. 1.39.5 [45] SILVA v. 1.19 [42] |
| Ederveen THA et al. (2018) [31] | Netherlands | <6 months | 54 | 21 (Healthy control) | Nasopharyngeal aspirate | PCR | 16S rRNA (V3–V4) QIIME v.1.8 [40] RDP classifier v. 2.3 [46] |
| de Steenhuijsen Piters WAA et al. (2016) [30] | USA | <2 years | 106 (Outpatients, 22; Inpatients, 84) | 26 (Healthy control) | Nasopharyngeal swab | PCR Rapid antigen | 16S rRNA (V5–V7) QIIME v.1.8 [40] Greengenes [44] |
| First Author (Year) | Country | Age Category | Number of Patients with RSV Infection | Number of Controls | Samples | Diagnostic Method for RSV Infection | Microbiome Approach, Pipeline, and Database |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Russell MM et al. (2022) [38] | USA | <4 months | 20 | 9 (Healthy control) | Feces (peri-anal swab) | PCR | 16S rRNA (V4) SILVA release 102 [42] |
| Alba C et al. (2021) [29] | Spain | <2 years | 46 | 17 | Feces | PCR DFA | 16S rRNA (V3–V4) QIIME v. 1.9.1 [40] |
| Harding JN et al. (2020) [33] | USA | <1 year | 58 | 37 | Feces | PCR | 16S rRNA (V4) QIIME 2 [43] Greengenes [44] |
| Phylum | Class | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonadota corrig. phyl. nov. (Proteobacteria) ↑↑ Bacillota corrig. phyl. nov.(Firmicutes) ↓↓↑ Actinomycetota corrig. phyl. nov. (Actinobacteria) ↓↑ Phylum level → Bacteroidota corrig. phyl. nov. (Bacteroidetes) ↑ | Alphaproteobacteria ↑ Gammaproteobacteria ↑ Betaproteobacteria ↑ | Pseudomonadales ↑ Burkholderiales ↑ | Haemophilus ↑↑↑ Moraxella ↑ Streptococcus ↑ Corynebacterium ↓ Mannheimia ↑ Staphylococcus ↓ Pseudomonas ↑ Gluconacetobacter ↑ Alistipes ↓ Bacteroides ↓ Kineothrix ↓ Oscillibacter ↓ Pseudoflavonifractor ↓ Klebsiella Achromobacter ↑ | Haemophilus influenzae (Haemophilus sp.) ↑↑↑ Moraxella catarrhalis ↑ Streptococcus pneumoniae ↑↑ Delftia sp. ↑ Cutibacterium acnes ↑ [Eubacterium] Sireum ↓ Alistipes putredinis ↓ Bamasiella intestinihominis ↓ Kineothrix alysoides ↓ Oscillibacter ruminantium ↓ Prevotella oralis ↓ Pseudoflavonifractor phocaeensis ↓ Roseburia intestinalis ↓ Staphylococcus aureus ↑ |
| Phylum | Class | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S24_7 ↑ Odoribacteraceae ↑ Clostridiales ↑ Lactobacillaceae ↑ Actinomyces ↑ | Bifidobacterium ↑ Enterobactericeae unclassified ↑ Lachnospiraceae incertae sedis↑ Enterococcus ↑ Clostridiales Unclassified ↓ Porphyromonas ↓ Eggerthella ↑ Staphylococcus ↓ Haemophilus ↓ S24_7 ↑ Odoribacter ↑ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yagi, K.; Lukacs, N.W.; Huffnagle, G.B.; Kato, H.; Asai, N. Respiratory and Gut Microbiome Modification during Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection: A Systematic Review. Viruses 2024, 16, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16020220
Yagi K, Lukacs NW, Huffnagle GB, Kato H, Asai N. Respiratory and Gut Microbiome Modification during Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection: A Systematic Review. Viruses. 2024; 16(2):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16020220
Chicago/Turabian StyleYagi, Kazuma, Nicholas W. Lukacs, Gary B. Huffnagle, Hideo Kato, and Nobuhiro Asai. 2024. "Respiratory and Gut Microbiome Modification during Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection: A Systematic Review" Viruses 16, no. 2: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16020220
APA StyleYagi, K., Lukacs, N. W., Huffnagle, G. B., Kato, H., & Asai, N. (2024). Respiratory and Gut Microbiome Modification during Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection: A Systematic Review. Viruses, 16(2), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16020220







