Differences in Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Transgenic hACE2-Hamster Founder Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Construction of a Gateway Expression Vector pmhyGNEIE-3-K18-hACE2
2.2. Isolation of Hamster Zygotes
2.3. Pronuclear Injection of pmhyGNEIE-3-K18-hACE2 Plasmid and Embryo Transfer
2.4. PCR Analysis of Transgene in hACE2-Hamster Pups
2.5. Animal Studies
2.6. SARS-CoV-2 Challenge Studies
2.7. Clinical Signs for Disease Scoring
2.8. Quantification of Virus in Hamster Tissue
2.9. Poly (I:C)] Treatment
2.10. Histopathological Analyses
2.11. Ethical Treatment of Animals
2.12. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
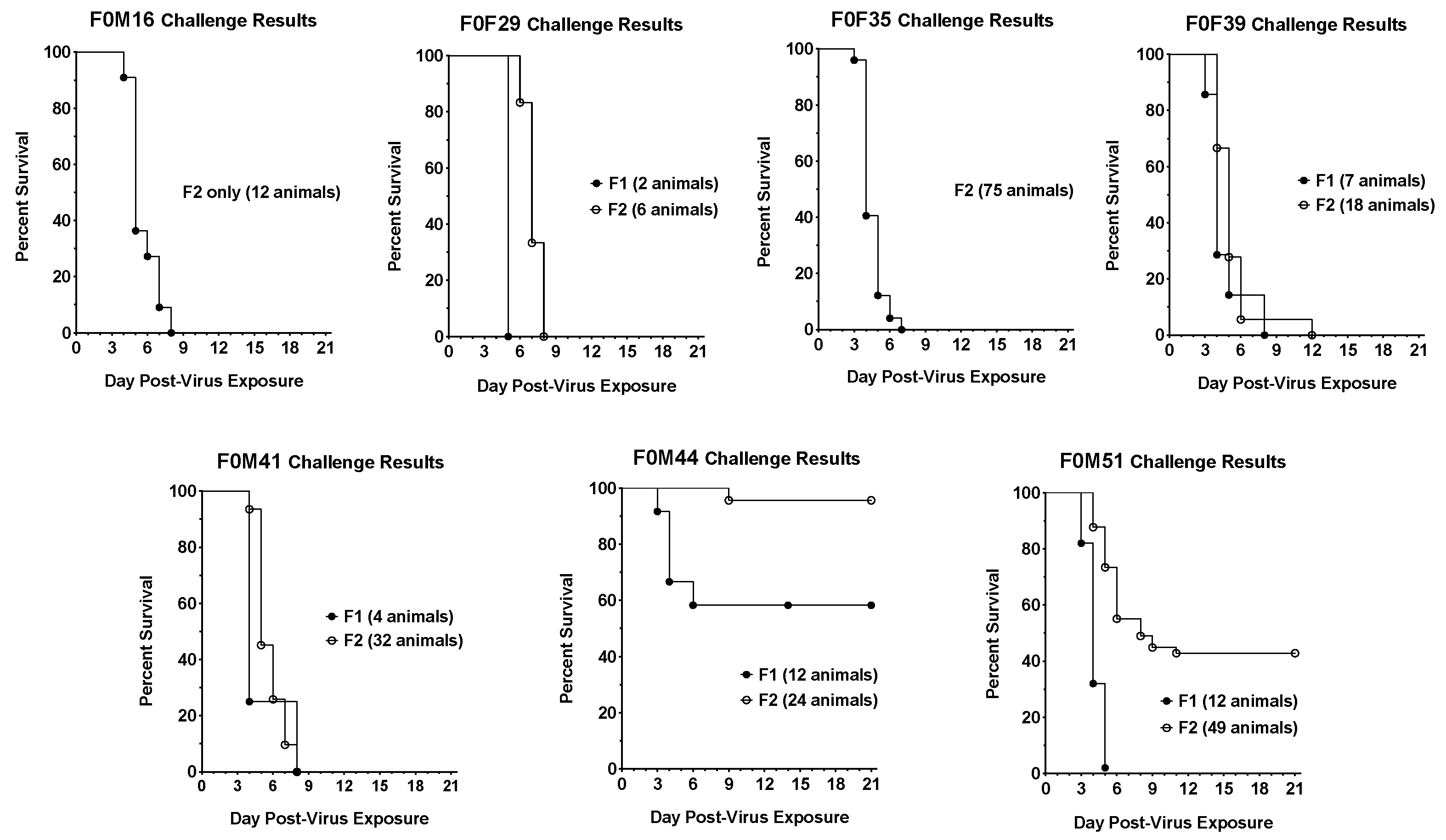
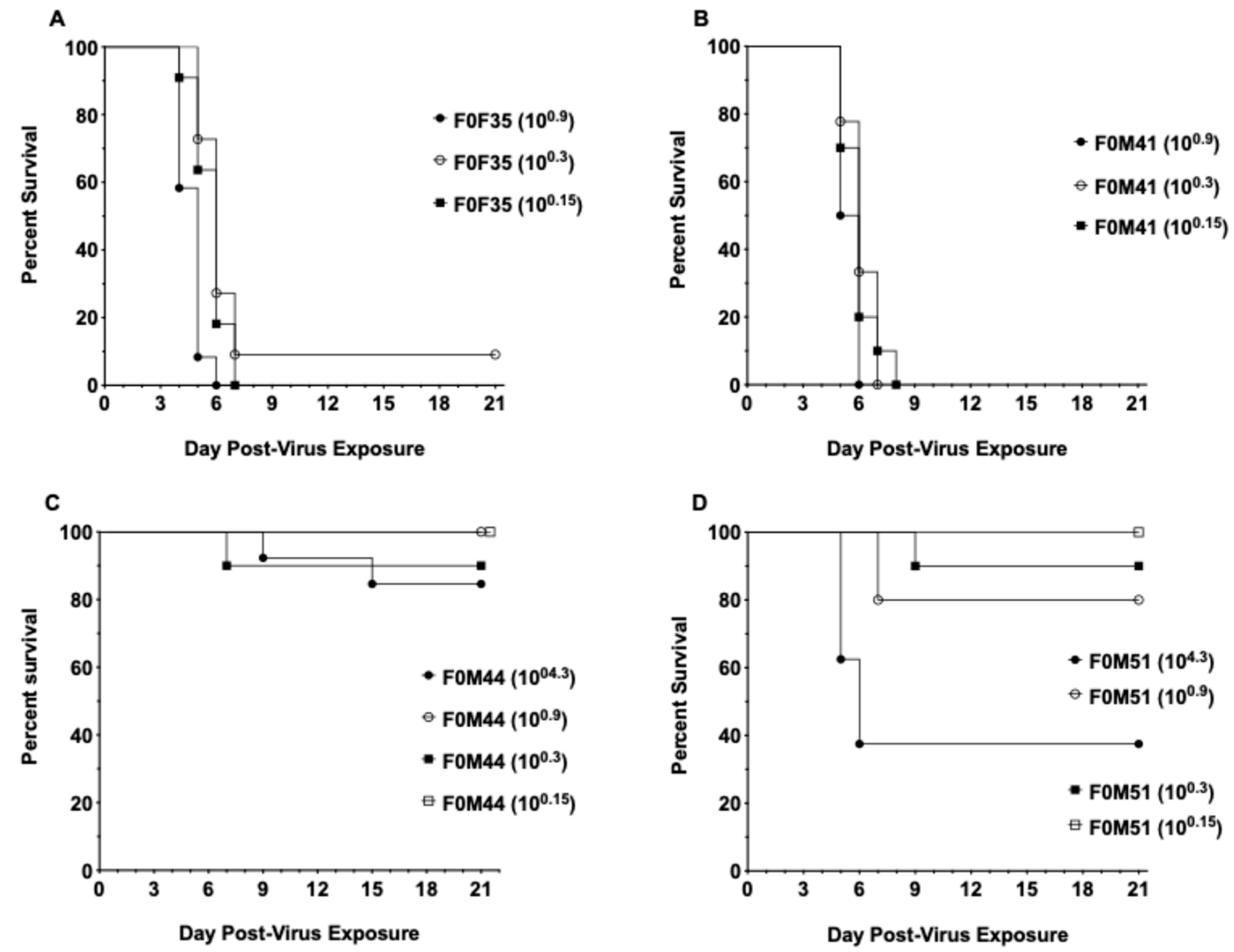
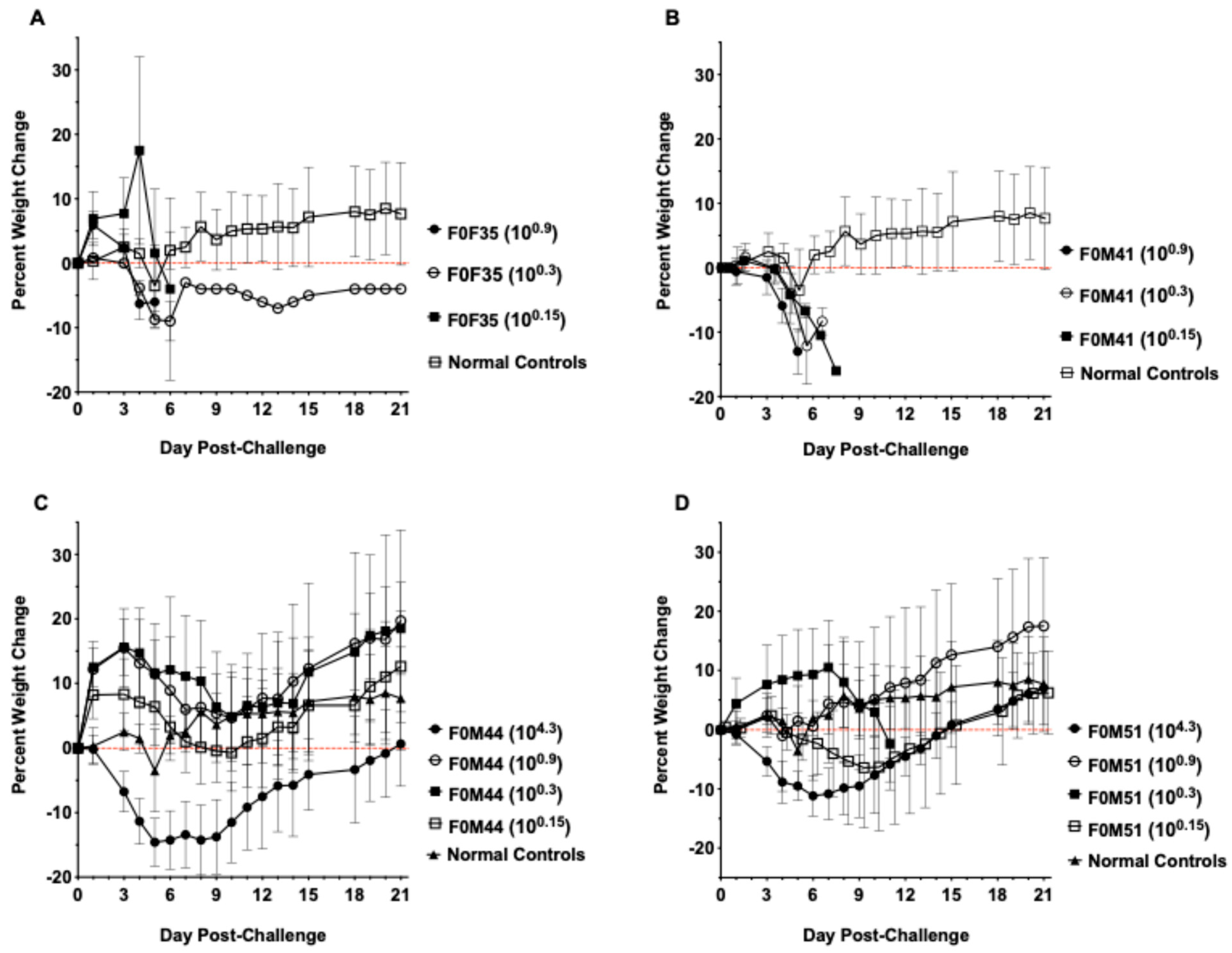
3.1. Virus Challenge of hACE2-Hamster Founder Lines
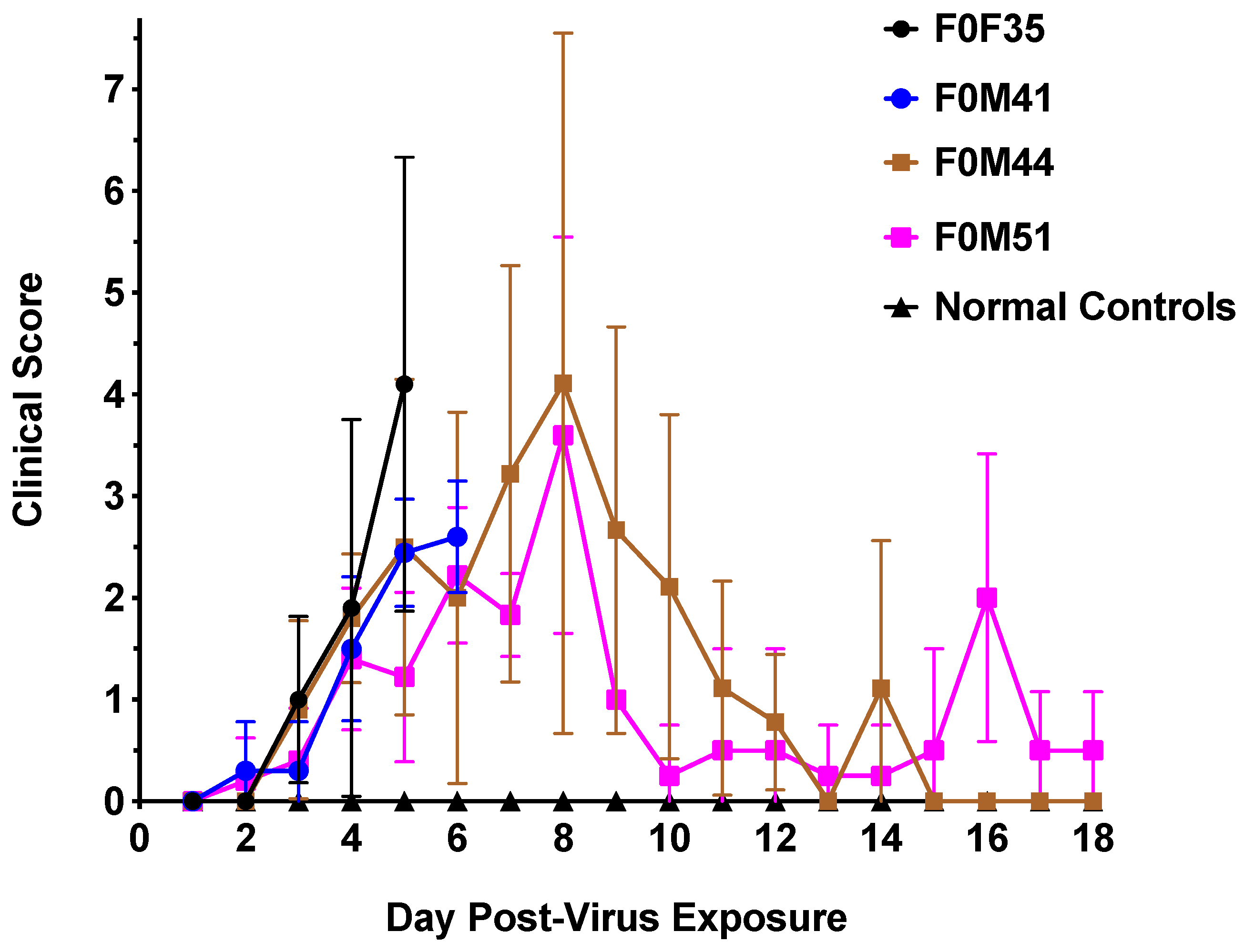
3.2. Clinical Signs Observed in hACE2-Hamsters After Virus Challenge
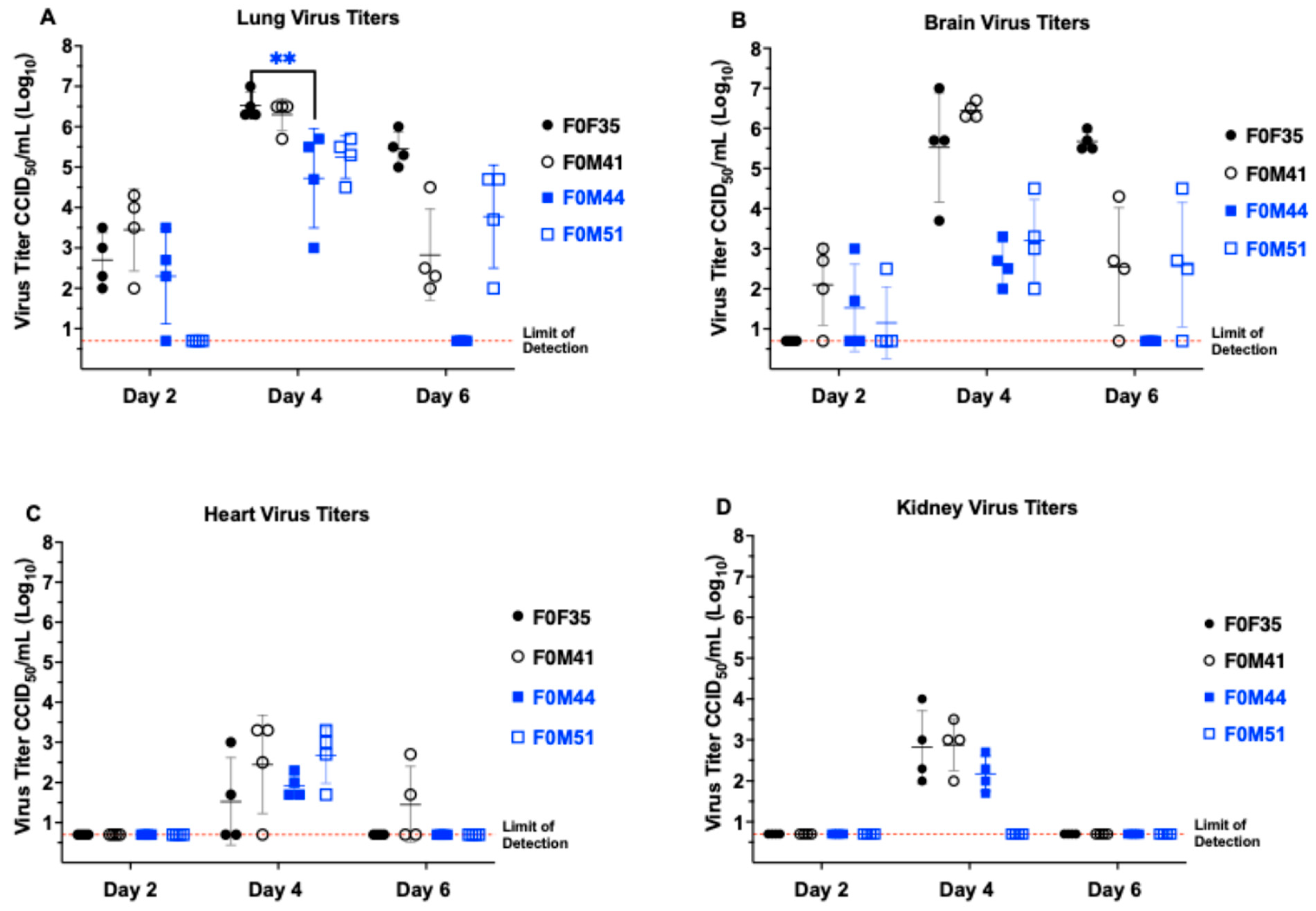
3.3. Virus Titers in Hamster Tissue
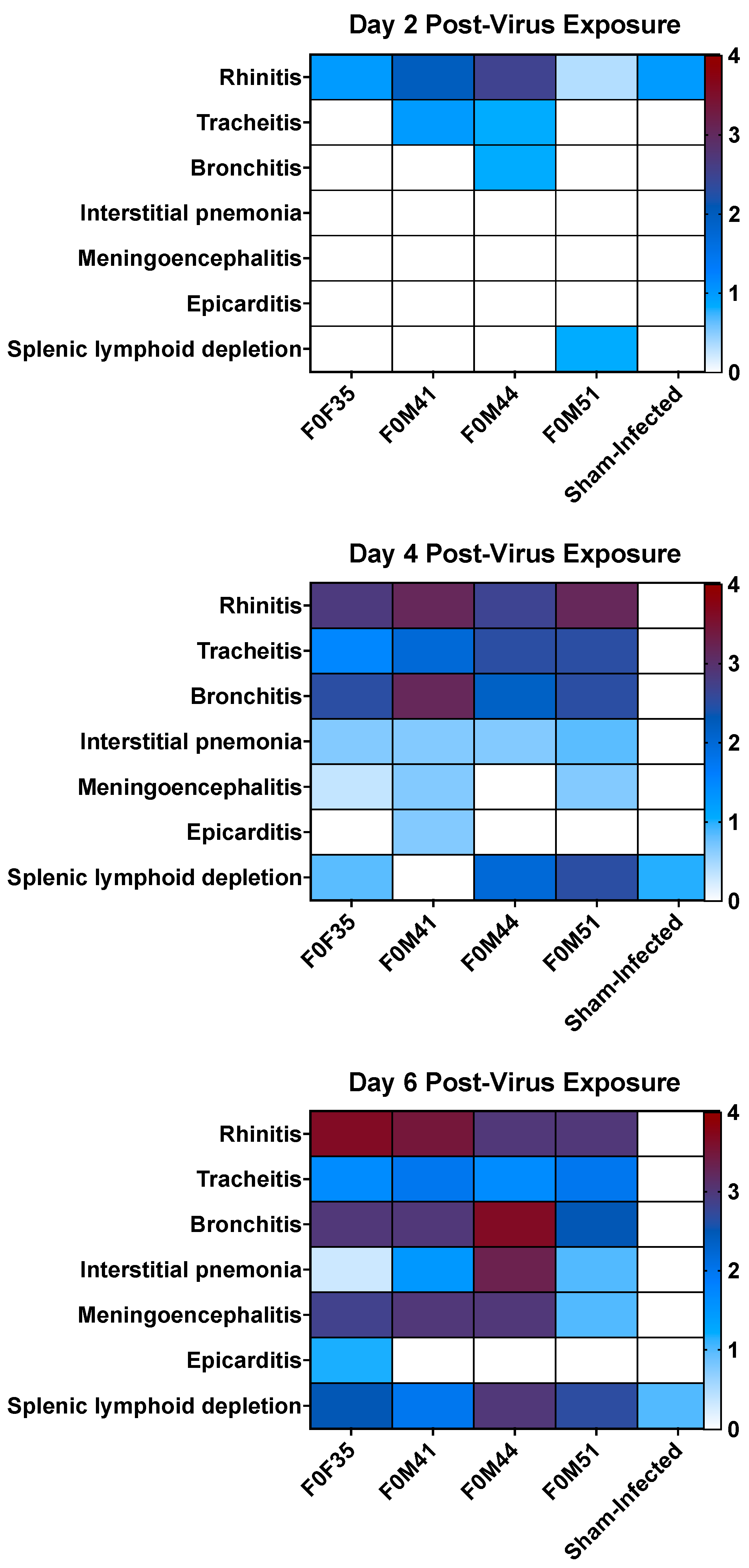
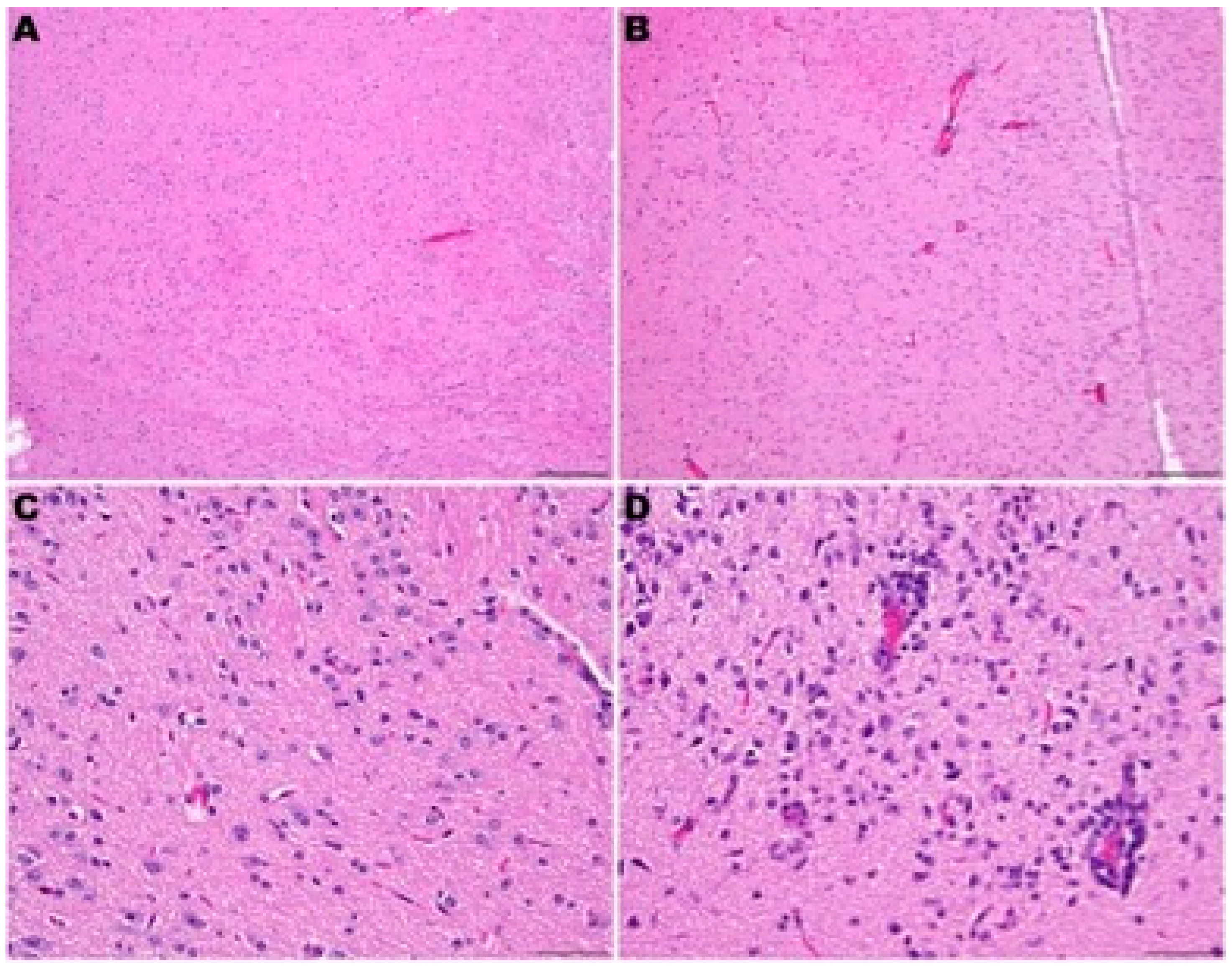
3.4. Histopathology in hACE2-Hamsters Infected with SARS-CoV-2
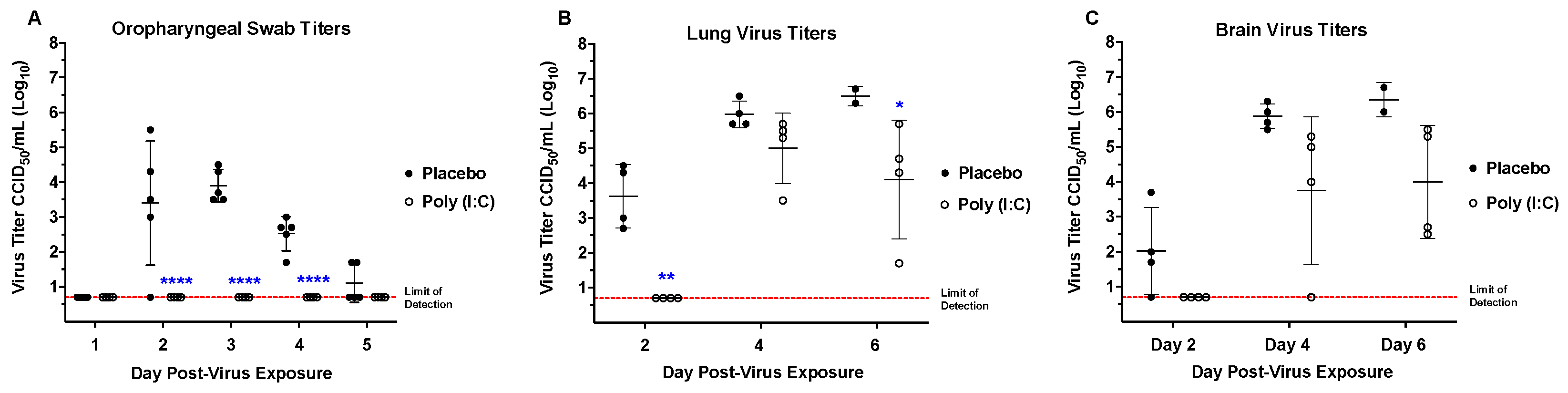
3.5. Poly (I:C) Treatment for a SARS-CoV-2 Infection in hACE2-Hamsters
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of 99 Cases of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A Descriptive Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollarves-Carrero, M.F.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.G.; Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J. Anosmia in a Healthcare Worker with COVID-19 in Madrid, Spain. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 35, 101666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Features of Patients Infected with 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsakos, M.; Kedzierska, K. A Race to Determine What Drives COVID-19 Severity. Nature 2020, 583, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemele, D.; Ķauķe, G.; Skrējāne, K.; Jaunozoliņa, L.; Karelis, G. A Fatal Case of COVID-19-Associated Acute Necrotizing Encephalopathy. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 3870–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tan, Y.; Ling, Y.; Lu, G.; Liu, F.; Yi, Z.; Jia, X.; Wu, M.; Shi, B.; Xu, S.; et al. Viral and Host Factors Related to the Clinical Outcome of COVID-19. Nature 2020, 583, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, G.; Townsend, L.; Savinelli, S.; Mallon, P.W.G.; Kenny, G. Long COVID: Clinical Characteristics, Proposed Pathogenesis and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1157651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, A.M. Deleterious Outcomes in Long-Hauler COVID-19: The Effects of SARS-CoV-2 on the CNS in Chronic COVID Syndrome. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 4017–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, N.K.; Ojha, S.; Jha, S.K.; Dureja, H.; Singh, S.K.; Shukla, S.D.; Chellappan, D.K.; Gupta, G.; Bhardwaj, S.; Kumar, N.; et al. Evidence of Coronavirus (CoV) Pathogenesis and Emerging Pathogen SARS-CoV-2 in the Nervous System: A Review on Neurological Impairments and Manifestations. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 71, 2192–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, R.W.; Brown, R.L.; Benjamin, L.; Nortley, R.; Wiethoff, S.; Bharucha, T.; Jayaseelan, D.L.; Kumar, G.; Raftopoulos, R.E.; Zambreanu, L.; et al. The Emerging Spectrum of COVID-19 Neurology: Clinical, Radiological and Laboratory Findings. Brain 2020, 143, 3104–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyiadji, N.; Shahin, G.; Noujaim, D.; Stone, M.; Patel, S.; Griffith, B. COVID-19-Associated Acute Hemorrhagic Necrotizing Encephalopathy: Imaging Features. Radiology 2020, 296, E119–E120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taquet, M.; Geddes, J.R.; Husain, M.; Luciano, S.; Harrison, P.J. 6-Month Neurological and Psychiatric Outcomes in 236 379 Survivors of COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using Electronic Health Records. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Jin, H.; Wang, M.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; He, Q.; Chang, J.; Hong, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. Neurologic Manifestations of Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, S.F.; Yan, L.M.; Chin, A.W.H.; Fung, K.; Choy, K.T.; Wong, A.Y.L.; Kaewpreedee, P.; Perera, R.A.P.M.; Poon, L.L.M.; Nicholls, J.M.; et al. Pathogenesis and Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in Golden Hamsters. Nature 2020, 583, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.D.; Liu, M.Q.; Chen, Y.; Shan, C.; Zhou, Y.W.; Shen, X.R.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Si, H.R.; et al. Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 in Transgenic Mice Expressing Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2. Cell 2020, 182, 50–58.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Deng, W.; Huang, B.; Gao, H.; Liu, J.; Ren, L.; Wei, Q.; Yu, P.; Xu, Y.; Qi, F.; et al. The Pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 in HACE2 Transgenic Mice. Nature 2020, 583, 830–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.F.W.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, A.J.; Poon, V.K.M.; Chan, C.C.S.; Lee, A.C.Y.; Fan, Z.; Li, C.; Liang, R.; Cao, J.; et al. Surgical Mask Partition Reduces the Risk of Noncontact Transmission in a Golden Syrian Hamster Model for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2139–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaki, Y.; Day, C.W.; Bailey, K.W.; Wandersee, M.K.; Wong, M.H.; Madsen, J.R.; Madsen, J.S.; Nelson, N.M.; Hoopes, J.D.; Woolcott, J.D.; et al. Induction of Interferon-γ-Inducible Protein 10 by SARS-CoV Infection, Interferon Alfacon 1 and Interferon Inducer in Human Bronchial Epithelial Calu-3 Cells and BALB/c Mice. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2010, 20, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, E. Interferon and Its Inducers—A Never-Ending Story: “Old” and “New” Data in a New Perspective. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, S19–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashi Bhushan, B.L.; Wanve, S.; Koradia, P.; Bhomia, V.; Soni, P.; Chakraborty, S.; Khobragade, A.; Joshi, S.; Mendiratta, S.K.; Kansagra, K.K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Pegylated Interferon-A2b in Moderate COVID-19: A Phase 3, Randomized, Comparator-Controlled, Open-Label Study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 111, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj, J.; Yatim, N.; Barnabei, L.; Corneau, A.; Boussier, J.; Smith, N.; Péré, H.; Charbit, B.; Bondet, V.; Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; et al. Impaired Type I Interferon Activity and Inflammatory Responses in Severe COVID-19 Patients. Science 2020, 369, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCray, P.B., Jr.; Pewe, L.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Hickey, M.; Manzel, L.; Shi, L.; Netland, J.; Jia, H.P.; Halabi, C.; Sigmund, C.D.; et al. Lethal infection of K18-hACE2 mice infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A Simple Method of Estimating Fifty per Cent Endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (US) Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fox, S.E.; Akmatbekov, A.; Harbert, J.L.; Li, G.; Quincy Brown, J.; Vander Heide, R.S. Pulmonary and cardiac pathology in African American patients with COVID-19: An autopsy series from New Orleans. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajanding, R.J.M. Comprehensive review of cardiovascular involvement in COVID-19. AACN Adv. Crit. Care 2021, 32, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslbauer, J.D.; Tzankov, A.; Mertz, K.D.; Schwab, N.; Nienhold, R.; Twerenbold, R.; Leibundgut, G.; Stalder, A.K.; Matter, M.; Glatz, K. Characterisation of cardiac pathology in 23 autopsies of lethal COVID-19. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2021, 7, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, J.W.; Li, R.; Cline, C.R.; Zeng, X.; Mucker, E.M.; Fuentes-Lao, A.J.; Spik, K.W.; Williams, J.A.; Twenhafel, N.; Davis, N.; et al. Hamsters Expressing Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Develop Severe Disease following Exposure to SARS-CoV-2. mBio 2022, 13, e0290621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Sato, S.; Hemmi, H.; Hoshino, K.; Kaisho, T.; Sanjo, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Sugiyama, M.; Okabe, M.; Takeda, K.; et al. Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Science 2003, 301, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vree, P.J.; de Wit, E.; Yilmaz, M.; van de Heijning, M.; Klous, P.; Verstegen, M.J.; Wan, Y.; Teunissen, H.; Krijger, P.H.; Geeven, G.; et al. Targeted sequencing by proximity ligation for comprehensive variant detection and local haplotyping. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Bao, L.; Yu, P.; Qi, F.; Gong, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, B.; Liu, M.; Han, Y.; Deng, W.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Causes a Systemically Multiple Organs Damages and Dissemination in Hamsters. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 618891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Rothan, H.A.; Natekar, J.P.; Stone, S.; Pathak, H.; Strate, P.G.; Arora, K.; Brinton, M.A.; Kumar, M. Neuroinvasion and Encephalitis Following Intranasal Inoculation of SARS-CoV-2 in K18-HACE2 Mice. Viruses 2021, 13, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaleva, L.M.; Cherniaev, A.L.; Samsonova, M.V.; Zayratyants, O.V.; Kakturskiy, L.V.; Vasyukova, O.A.; Birukov, A.E.; Kontorshchikov, A.S.; Sorokina, A.V.; Sinelnikov, M.Y. Pathological Features in 100 Deceased Patients with COVID-19 in Correlation with Clinical and Laboratory Data. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2021, 27, 1609900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Qie, S.; Liu, Z.; Ren, J.; Li, K.; Xi, J. Clinical Characteristics of Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Single Arm Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synowiec, A.; Szczepa, A.; Barreto-Duran, E.; Lie, L.K.; Pyrc, K. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): A Systemic Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e00133-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, G.B.; Burgess, S.L.; Sturek, J.M.; Donlan, A.N.; Petri, W.A.; Mann, B.J. Evaluation of K18-hACE2 mice as a model of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.D.; Firsching, T.C.; Trimpert, J.; Dietert, K. Hamster models of COVID-19 pneumonia reviewed: How human can they be? Vet. Pathol. 2021, 59, 528–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Perry, D.L.; Cooper, K.; Wang, H.; Dixit, S.; Liu, D.X.; Feuerstein, I.M.; Solomon, J.; Bartos, C.; et al. Longitudinal analyses using 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography with computed tomography as a measure of COVID-19 severity in the aged, young, and humanized ACE2 SARS-CoV-2 hamster models. Antivir. Res. 2023, 214, 105605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Drew, K.L. Mechanisms of innate preconditioning towards ischemia/anoxia tolerance: Lessons from mammalian hibernators. Cond. Med. 2019, 2, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, F.; Pretto, S.; Tagliabue, E.; Balsari, A.; Sfondrini, L. Exploiting poly(I:C) to induce cancer cell apoptosis. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfmann, P.J.; Iida, S.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Maemura, T.; Kiso, M.; Scheaffer, S.M.; Darling, T.L.; Joshi, A.; Loeber, S.; Singh, G.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron virus causes attenuated disease in mice and hamsters. Nature 2022, 603, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraki, R.; Kiso, M.; Iida, S.; Imai, M.; Takashita, E.; Kuroda, M.; Halfmann, P.J.; Loeber, S.; Maemura, T.; Yamayoshi, S.; et al. Characterization and antiviral susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2. Nature 2022, 607, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraki, R.; Halfmann, P.J.; Iida, S.; Yamayoshi, S.; Furusawa, Y.; Kiso, M.; Ito, M.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Mine, S.; Kuroda, M.; et al. Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 isolates in rodents. Nature 2022, 612, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraki, R.; Iida, S.; Halfmann, P.J.; Yamayoshi, S.; Hirata, Y.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Kiso, M.; Ito, M.; Furusawa, Y.; Ueki, H.; et al. Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2.75 clinical isolates. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfmann, P.J.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Kuroda, M.; Hirata, Y.; Yamayoshi, S.; Iida, S.; Uraki, R.; Ito, M.; Ueki, H.; Furusawa, Y.; et al. Characterization of Omicron BA.4.6, XBB, and BQ.1.1 subvariants in hamsters. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliland, T.; Dunn, M.; Liu, Y.; Alcorn, M.D.H.; Terada, Y.; Vasilatos, S.; Lundy, J.; Li, R.; Nambulli, S.; Larson, D.; et al. Transchromosomic bovine-derived anti-SARS-CoV-2 polyclonal human antibodies protects hACE2 transgenic hamsters against multiple variants. iScience 2023, 26, 107764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(− Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivcec, M.; Safronetz, D.; Haddock, E.; Feldmann, H.; Ebihara, H. Validation of assays to monitor immune responses in the Syrian golden hamster (Mesocricetus auratus). J. Immunol. Methods 2011, 368, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gibson, S.A.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Hurst, B.L.; Fan, Z.; Siddharthan, V.; Larson, D.P.; Sheesley, A.Y.; Stewart, R.; Kunzler, M.; et al. Differences in Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Transgenic hACE2-Hamster Founder Lines. Viruses 2024, 16, 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101625
Gibson SA, Liu Y, Li R, Hurst BL, Fan Z, Siddharthan V, Larson DP, Sheesley AY, Stewart R, Kunzler M, et al. Differences in Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Transgenic hACE2-Hamster Founder Lines. Viruses. 2024; 16(10):1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101625
Chicago/Turabian StyleGibson, Scott A., Yanan Liu, Rong Li, Brett L. Hurst, Zhiqiang Fan, Venkatraman Siddharthan, Deanna P. Larson, Ashley Y. Sheesley, Rebekah Stewart, Madelyn Kunzler, and et al. 2024. "Differences in Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Transgenic hACE2-Hamster Founder Lines" Viruses 16, no. 10: 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101625
APA StyleGibson, S. A., Liu, Y., Li, R., Hurst, B. L., Fan, Z., Siddharthan, V., Larson, D. P., Sheesley, A. Y., Stewart, R., Kunzler, M., Polejaeva, I. A., Van Wettere, A. J., Moisyadi, S., Morrey, J. D., Tarbet, E. B., & Wang, Z. (2024). Differences in Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Transgenic hACE2-Hamster Founder Lines. Viruses, 16(10), 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101625







