Replication Characteristics of African Swine Fever Virus (ASFV) Genotype I E70 and ASFV Genotype II Belgium 2018/1 in Perivenous Macrophages Using Established Vein Explant Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Animals and Collection of Tissues
2.2. Virus
2.3. Inoculation of the Explants
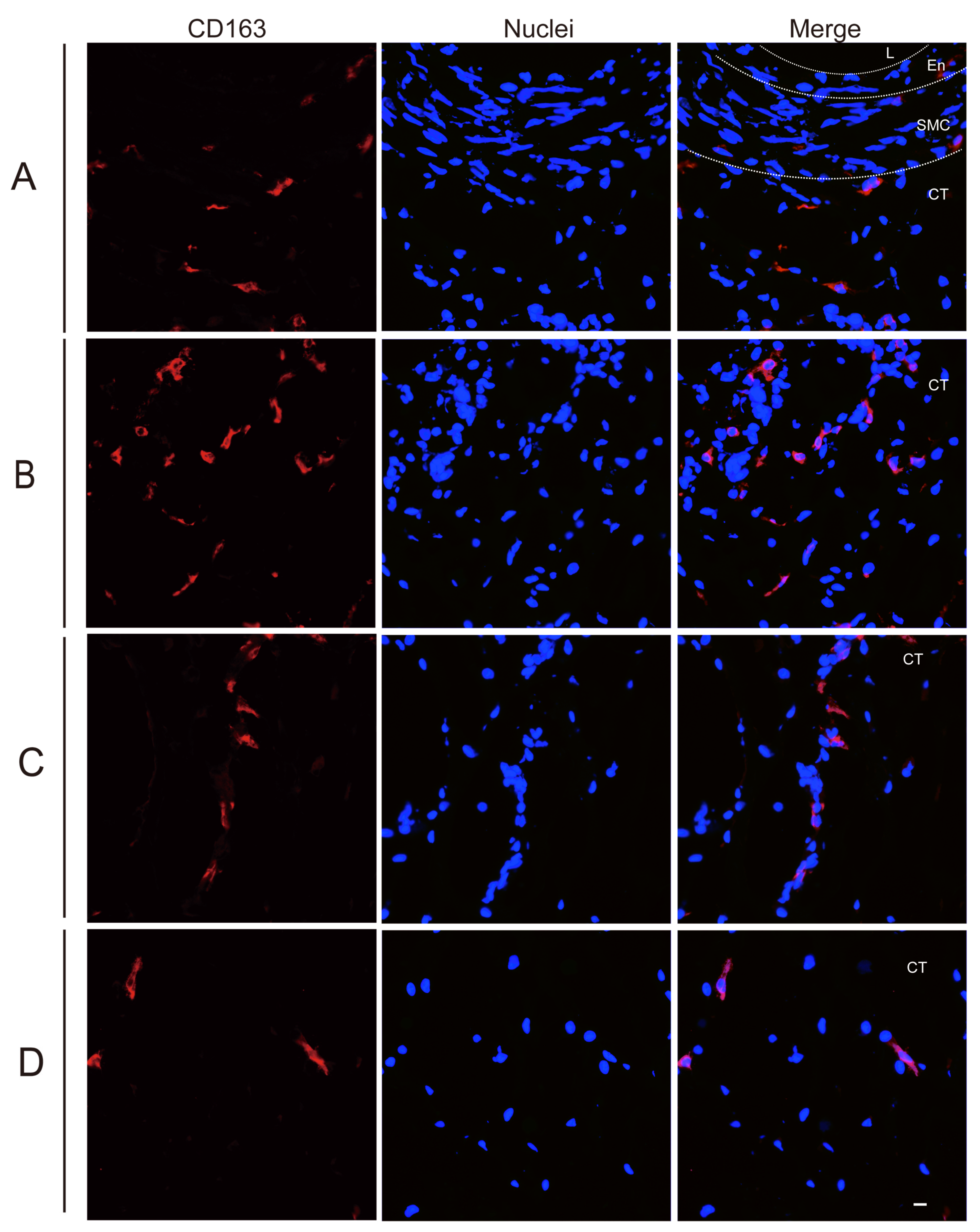
2.4. Analysis of Perivenous Macrophages Using Immunofluorescence (IF) Staining
2.5. Further Identification of ASFV Susceptible Cells by IF Staining
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Explant Viability of Ear and Leg Vein Explants
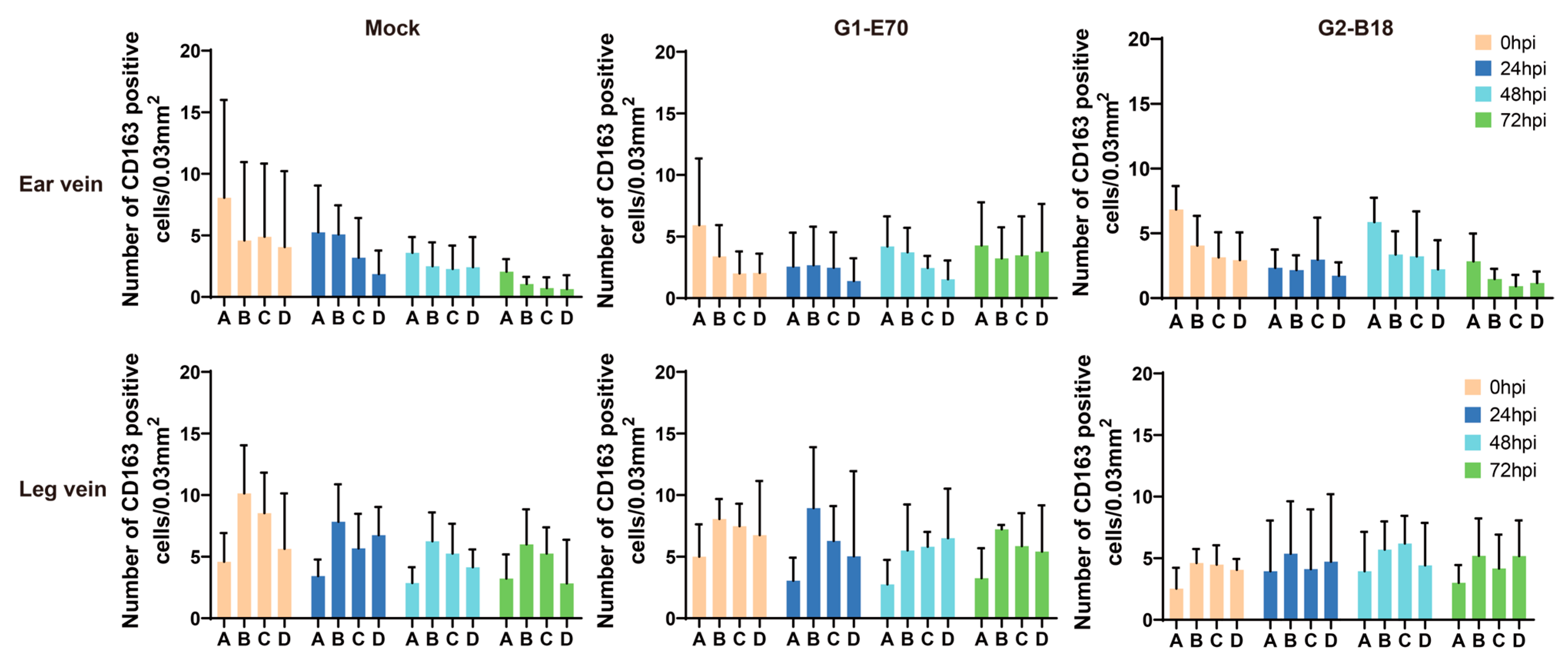
3.2. Quantitation of Perivenous Macrophages in Ear and Leg Vein Explants
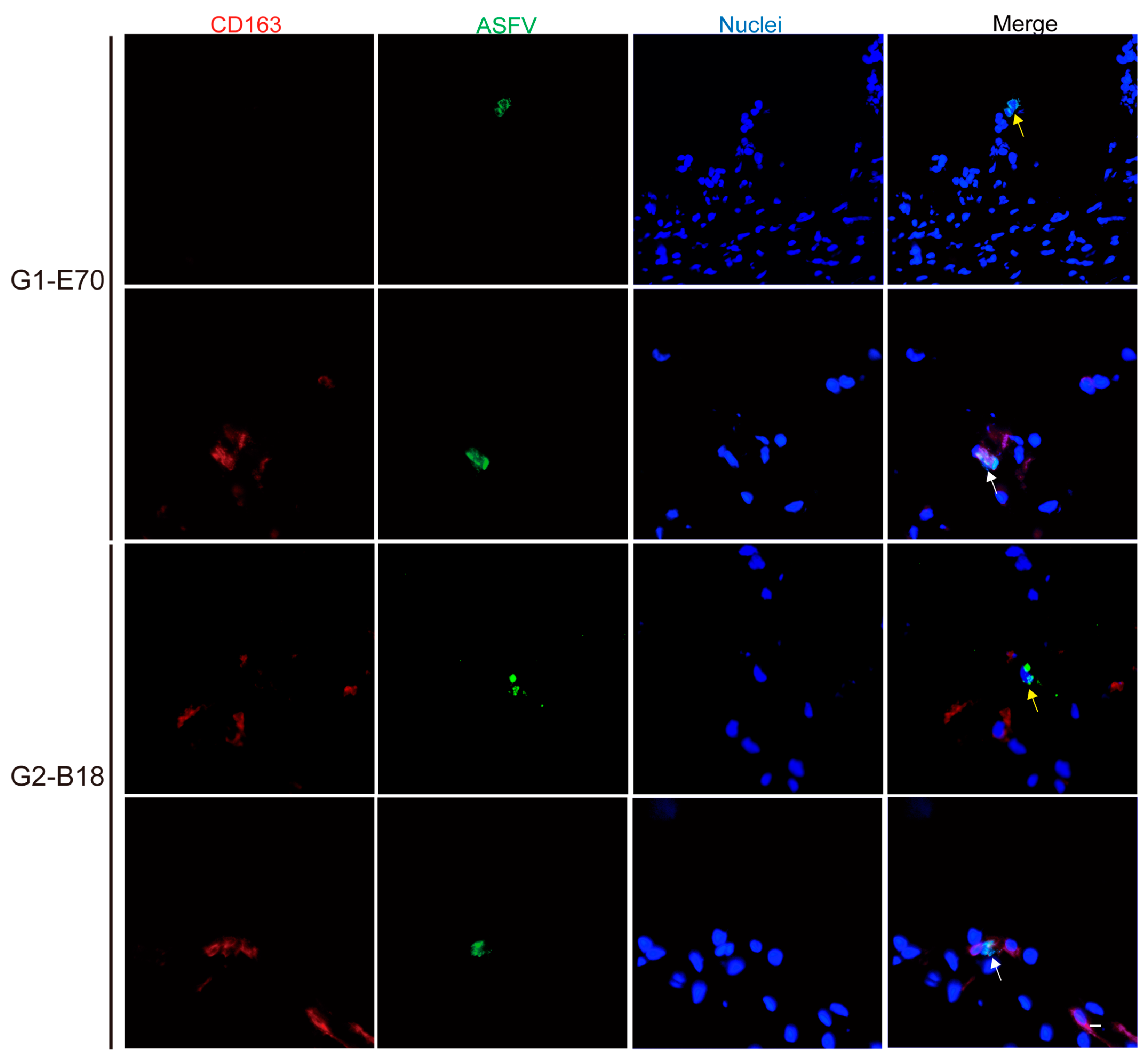
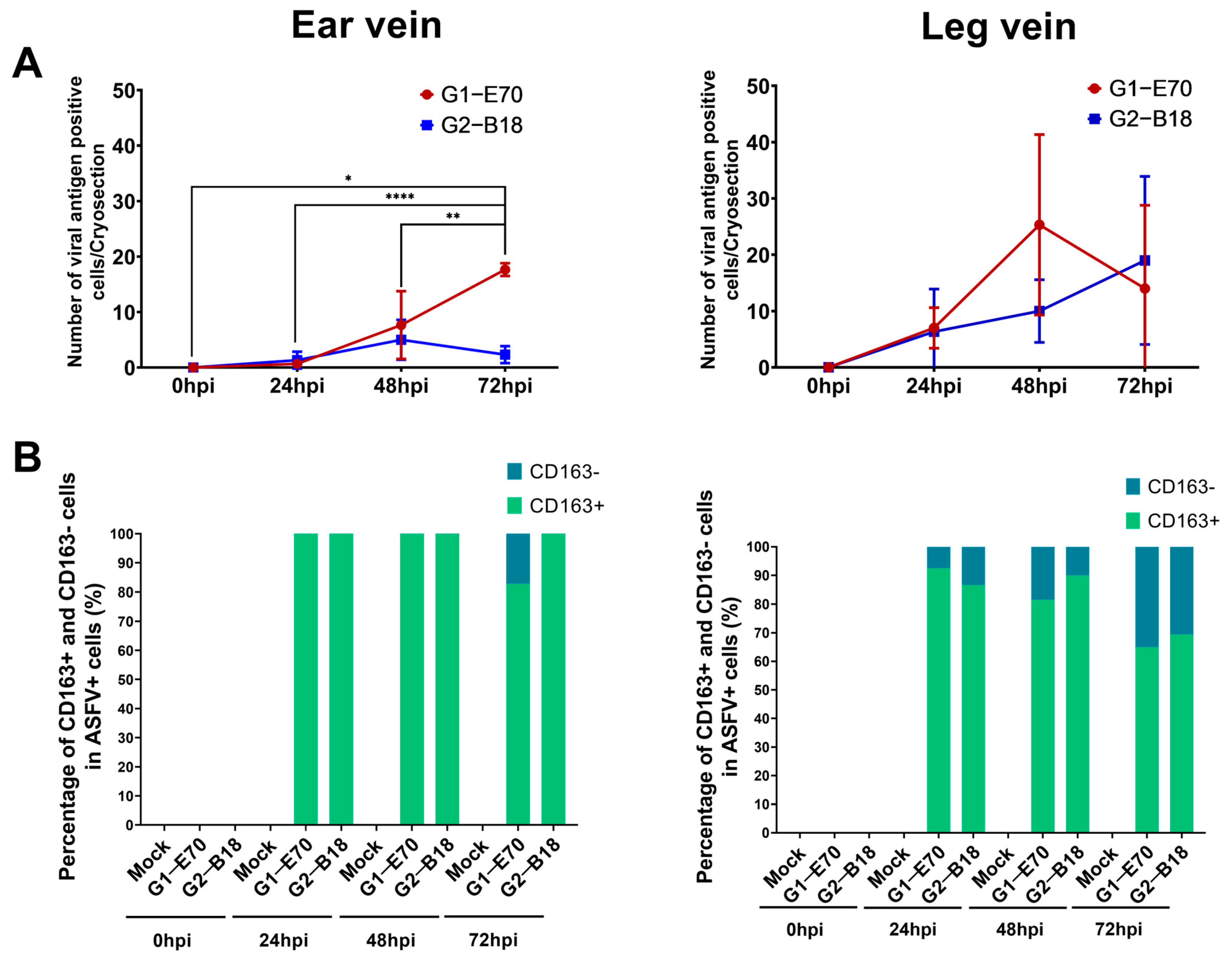
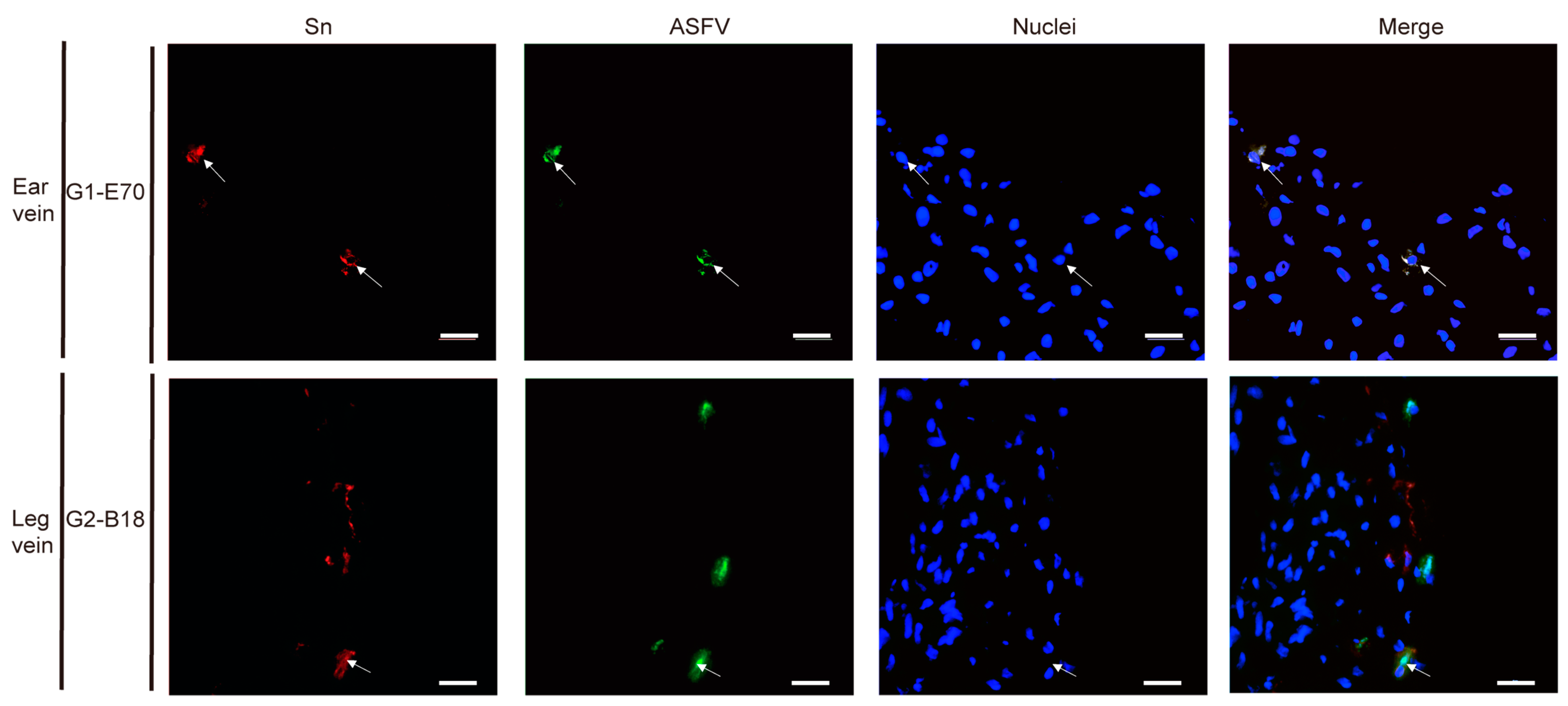
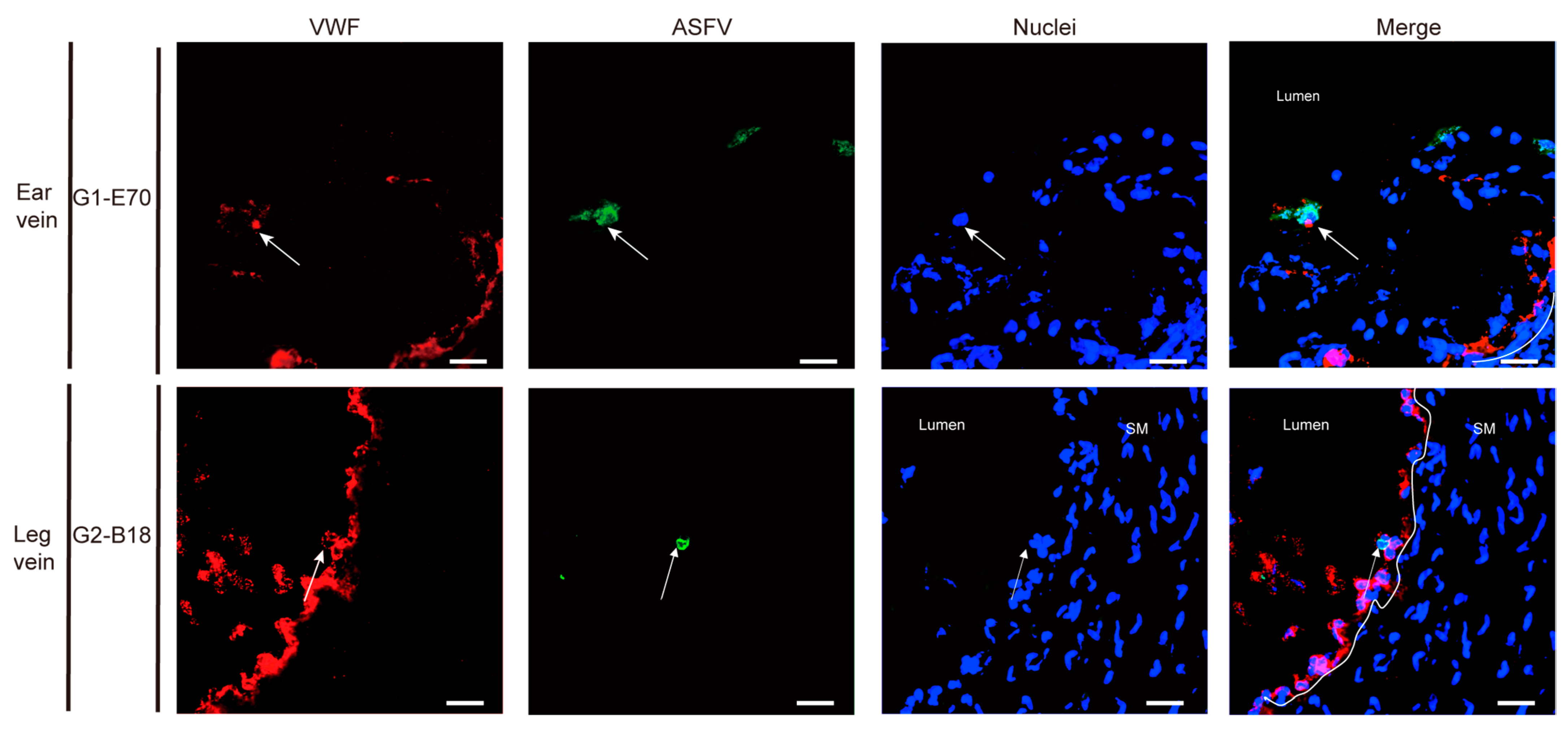
3.3. Quantitation and Identification of ASFV-Infected Cells in Ear and Leg Vein Explants
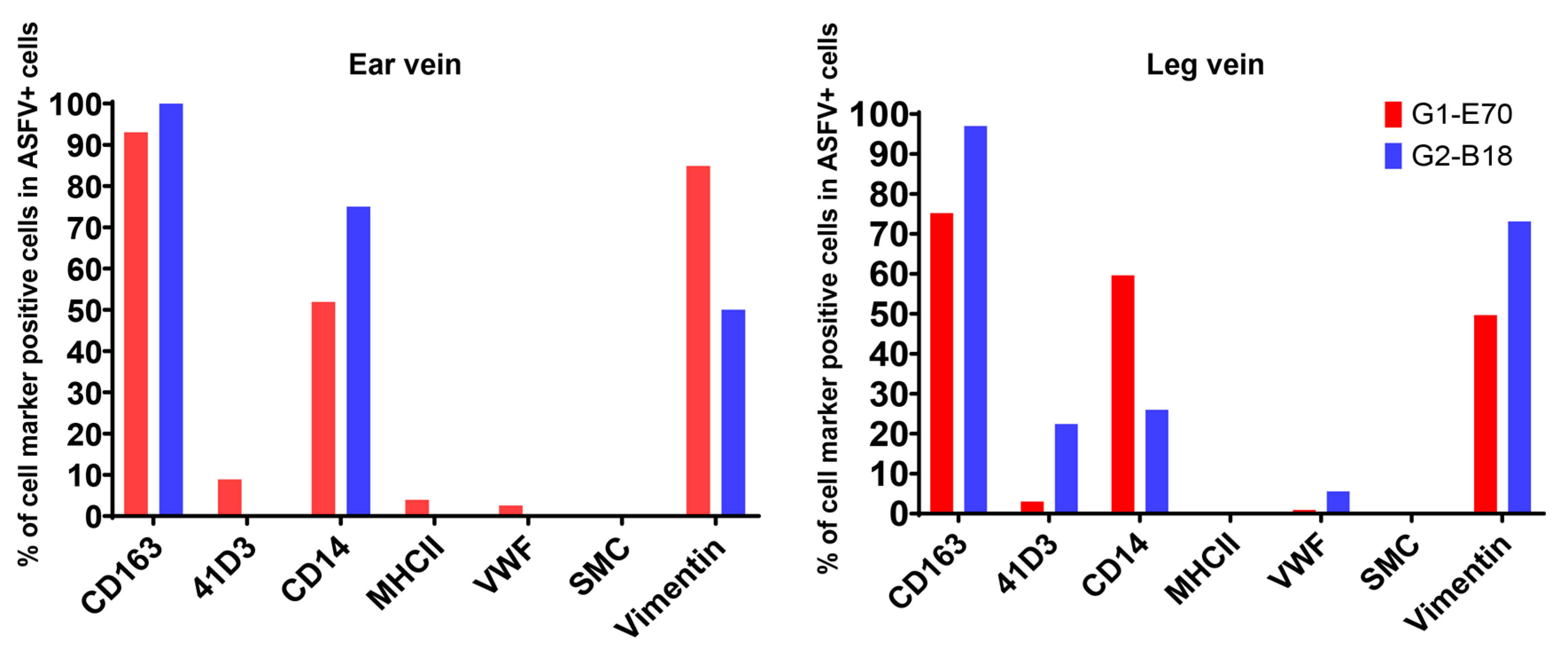
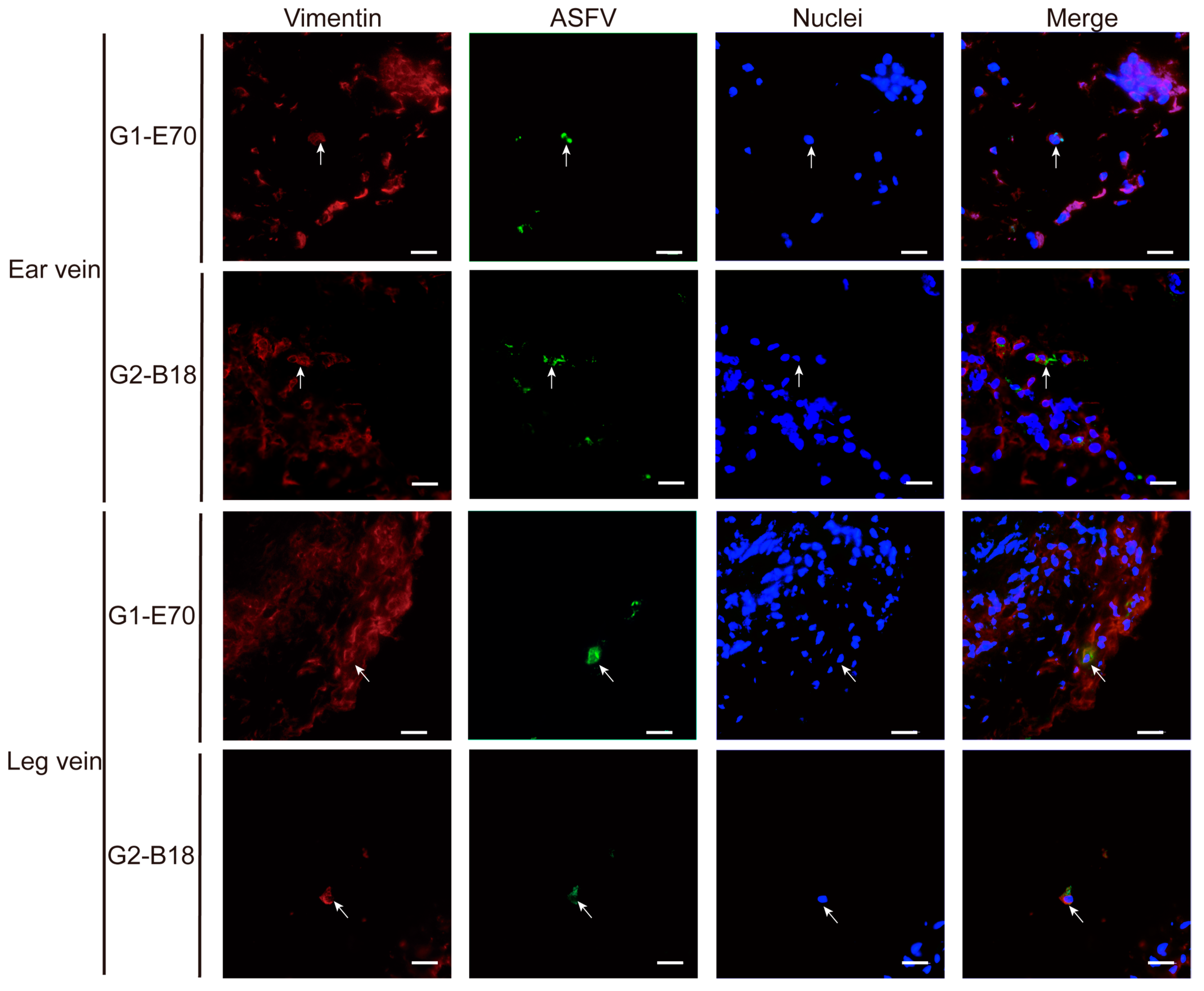
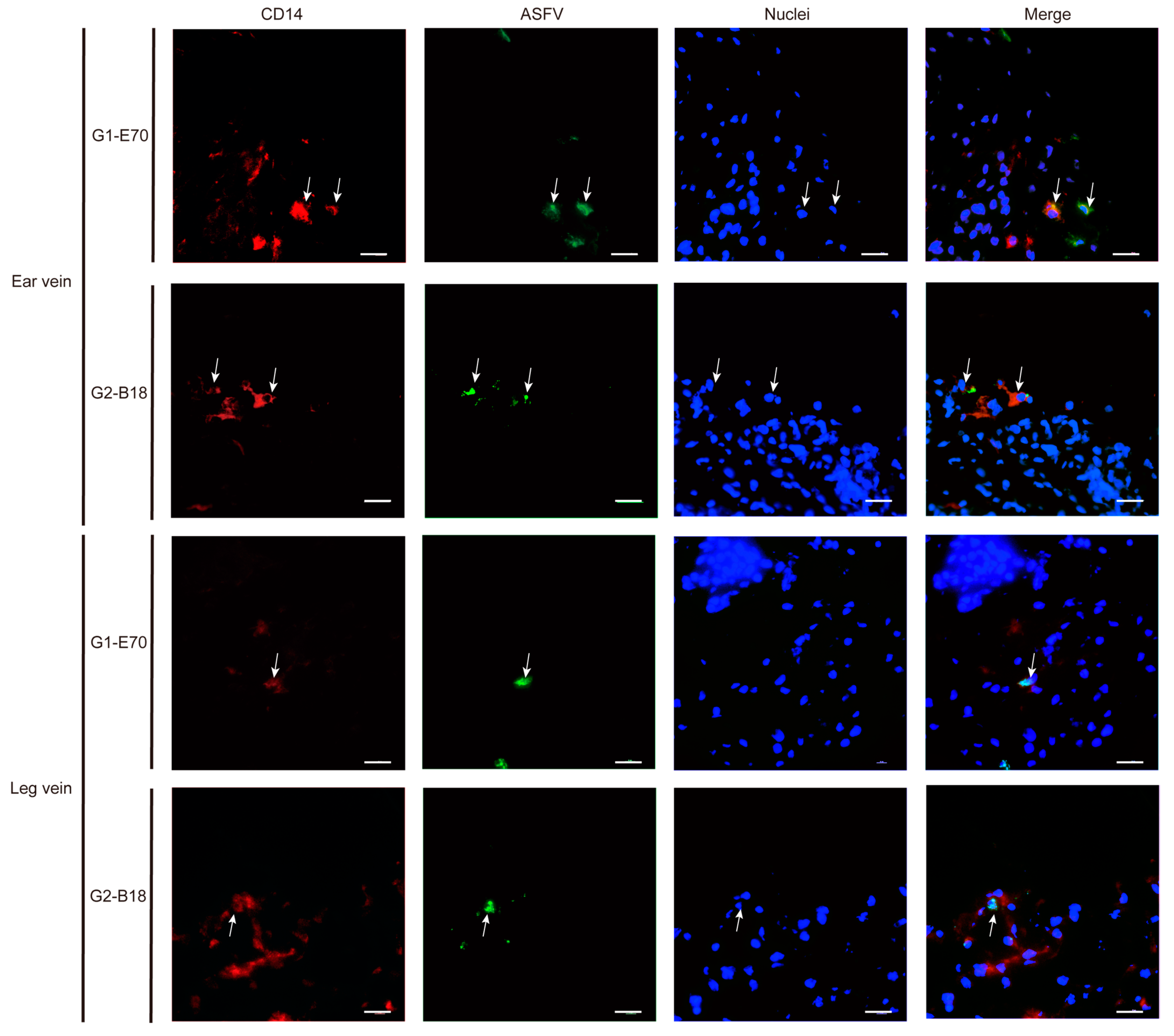
3.4. Characterization of ASFV Susceptible Cells with Other Cell Markers in Vein Explants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martins, C.; Boinas, F.; Iacolina, L.; Ruiz-Fons, F.; Gavier-Widén, D. African swine fever (ASF), the pig health challenge of the century. In Understanding and Combatting African Swine Fever: A European Perspective; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Urbano, A.; Forth, J.; Olesen, A.; Dixon, L.; Rasmussen, T.; Cackett, G.; Werner, F.; Karger, A.; Andrés, G.; Wang, X. African swine fever virus: Cellular and molecular aspects. In Understanding and Combatting African Swine Fever: A European Perspective; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 25–61. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Kang, W.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Zheng, H. Structure of African Swine Fever Virus and Associated Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Infection and Immunosuppression: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 715582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, A.; García-Barreno, B.; Nogal, M.L.; Viñuela, E.; Enjuanes, L. Monoclonal antibodies specific for African swine fever virus proteins. J. Virol. 1985, 54, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastre, P.; Gallardo, C.; Monedero, A.; Ruiz, T.; Arias, M.; Sanz, A.; Rueda, P. Development of a novel lateral flow assay for detection of African swine fever in blood. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinhobl, M.; Spinard, E.; Tesler, N.; Birtley, H.; Signore, A.; Ambagala, A.; Masembe, C.; Borca, M.V.; Gladue, D.P. Reclassification of ASFV into 7 Biotypes Using Unsupervised Machine Learning. Viruses 2023, 16, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, H.; Ge, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z. A systematic review of genotypes and serogroups of African swine fever virus. Virus genes 2022, 58, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, A.; Licoppe, A.; Volpe, R.; Paternostre, J.; Lesenfants, C.; Cassart, D.; Garigliany, M.; Tignon, M.; van den Berg, T.; Desmecht, D.; et al. Summer 2018: African swine fever virus hits north-western Europe. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 54–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garigliany, M.; Desmecht, D.; Tignon, M.; Cassart, D.; Lesenfant, C.; Paternostre, J.; Volpe, R.; Cay, A.B.; van den Berg, T.; Linden, A. Phylogeographic Analysis of African Swine Fever Virus, Western Europe, 2018. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licoppe, A.; De Waele, V.; Malengreaux, C.; Paternostre, J.; Van Goethem, A.; Desmecht, D.; Herman, M.; Linden, A. Management of a Focal Introduction of ASF Virus in Wild Boar: The Belgian Experience. Pathogens 2023, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikalo, J.; Schoder, M.E.; Sehl, J.; Breithaupt, A.; Tignon, M.; Cay, A.B.; Gager, A.M.; Fischer, M.; Beer, M.; Blome, S. The African swine fever virus isolate Belgium 2018/1 shows high virulence in European wild boar. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1654–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Villamandos, J.C.; Bautista, M.J.; Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Carrasco, L. Pathology of African swine fever: The role of monocyte-macrophage. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Villamandos, J.C.; Carrasco, L.; Bautista, M.J.; Sierra, M.A.; Quezada, M.; Hervas, J.; Chacón Mde, L.; Ruiz-Villamor, E.; Salguero, F.J.; Sónchez-Cordón, P.J.; et al. African swine fever and classical swine fever: A review of the pathogenesis. DTW Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2003, 110, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blome, S.; Gabriel, C.; Beer, M. Pathogenesis of African swine fever in domestic pigs and European wild boar. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco, L.; de Lara, F.C.; Gómez-Villamandos, J.C.; Bautista, M.J.; Villeda, C.J.; Wilkinson, P.J.; Sierra, M.A. The pathogenic role of pulmonary intravascular macrophages in acute African swine fever. Res. Vet. Sci. 1996, 61, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Breedam, W.; Delputte, P.L.; Van Gorp, H.; Misinzo, G.; Vanderheijden, N.; Duan, X.; Nauwynck, H.J. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus entry into the porcine macrophage. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.J.; Ramanathan, P.; Bishop, E.A.; O’Donnell, V.; Gladue, D.P.; Borca, M.V. Mechanisms of African swine fever virus pathogenesis and immune evasion inferred from gene expression changes in infected swine macrophages. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudreault, N.N.; Richt, J.A. Subunit Vaccine Approaches for African Swine Fever Virus. Vaccines 2019, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.; Xie, J.; Vanderheijden, N.; Nauwynck, H.J. Isolation and characterization of a new population of nasal surface macrophages and their susceptibility to PRRSV-1 subtype 1 (LV) and subtype 3 (Lena). Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkard, C.; Opriessnig, T.; Mileham, A.J.; Stadejek, T.; Ait-Ali, T.; Lillico, S.G.; Whitelaw, C.B.A.; Archibald, A.L. Pigs Lacking the Scavenger Receptor Cysteine-Rich Domain 5 of CD163 Are Resistant to Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus 1 Infection. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Torres, C.; Gómez-Puertas, P.; Gómez-del-Moral, M.; Alonso, F.; Escribano, J.M.; Ezquerra, A.; Domínguez, J. Expression of porcine CD163 on monocytes/macrophages correlates with permissiveness to African swine fever infection. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 2307–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, L.; Gaudreault, N.N.; Whitworth, K.M.; Murgia, M.V.; Nietfeld, J.C.; Mileham, A.; Samuel, M.; Wells, K.D.; Prather, R.S.; Rowland, R.R.R. Genetically edited pigs lacking CD163 show no resistance following infection with the African swine fever virus isolate, Georgia 2007/1. Virology 2017, 501, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor-Vaknin, N.; Punturieri, A.; Sitwala, K.; Markovitz, D.M. Vimentin is secreted by activated macrophages. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanovic, S.; Windsor, M.; Nagata, K.I.; Inagaki, M.; Wileman, T. Vimentin rearrangement during African swine fever virus infection involves retrograde transport along microtubules and phosphorylation of vimentin by calcium calmodulin kinase II. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11766–11775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, B.; Zhang, T.; Shi, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, D.; Yan, W.; Chen, L.; et al. Identification and analysis of the interaction network of African swine fever virus D1133L with host proteins. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1037346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, M.A.; Carrasco, L.; Gómez-Villamandos, J.C.; Martin de las Mulas, J.; Méndez, A.; Jover, A. Pulmonary intravascular macrophages in lungs of pigs inoculated with African swine fever virus of differing virulence. J. Comp. Pathol. 1990, 102, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, M.A.; Bernabe, A.; Mozos, E.; Mendez, A.; Jover, A. Ultrastructure of the liver in pigs with experimental African swine fever. Vet. Pathol. 1987, 24, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.; Han, S.; Tignon, M.; Balmelle, N.; Cay, A.B.; Griffioen, F.; Droesbeke, B.; Nauwynck, H.J. Differential infection behavior of African swine fever virus (ASFV) genotype I and II in the upper respiratory tract. Vet. Res. 2023, 54, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, P.W.; Holinka, L.G.; O’Donnell, V.; Reese, B.; Sanford, B.; Fernandez-Sainz, I.; Gladue, D.P.; Arzt, J.; Rodriguez, L.; Risatti, G.R.; et al. The progressive adaptation of a georgian isolate of African swine fever virus to vero cells leads to a gradual attenuation of virulence in swine corresponding to major modifications of the viral genome. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2324–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoni, G.; Petrini, S.; Mészáros, I.; Dei Giudici, S.; Righi, C.; Olasz, F.; Zinellu, S.; Tamás, V.; Pela, M.; Gallardo, C.; et al. Evaluation of Haematological and Immunological Parameters of the ASFV Lv17/WB/Rie1 Strain and Its Derived Mutant Lv17/WB/Rie1/d110-11L against ASFV Challenge Infection in Domestic Pigs. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borca, M.V.; Ramirez-Medina, E.; Silva, E.; Vuono, E.; Rai, A.; Pruitt, S.; Holinka, L.G.; Velazquez-Salinas, L.; Zhu, J.; Gladue, D.P. Development of a Highly Effective African Swine Fever Virus Vaccine by Deletion of the I177L Gene Results in Sterile Immunity against the Current Epidemic Eurasia Strain. J. Virol. 2020, 94, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, X.H.; Le, T.T.P.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Do, T.T.; Nguyen, V.D.; Gay, C.G.; Borca, M.V.; Gladue, D.P. African swine fever virus vaccine candidate ASFV-G-ΔI177L efficiently protects European and native pig breeds against circulating Vietnamese field strain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e497–e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brake, D.A. African Swine Fever Modified Live Vaccine Candidates: Transitioning from Discovery to Product Development through Harmonized Standards and Guidelines. Viruses 2022, 14, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Oh, D.; Xie, J.; Nauwynck, H.J. Susceptibility of perivenous macrophages to PRRSV-1 subtype 1 LV and PRRSV-1 subtype 3 Lena using a new vein explant model. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1223530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A Simple Method of Estimating Fifty Per Cent Endpoints12. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauwynck, H.J.; Pensaert, M.B. Effect of specific antibodies on the cell-associated spread of pseudorabies virus in monolayers of different cell types. Arch. Virol. 1995, 140, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Nauwynck, H.J.; Favoreel, H.; Pensaert, M.B. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection of alveolar macrophages can be blocked by monoclonal antibodies against cell surface antigens. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1998, 440, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, E.; Summerfield, A.; McCullough, K.; Ezquerra, A.; Dominguez, J.; Alonso, F.; Lunney, J.; Sinkora, J.; Haverson, K. Summary of workshop findings for porcine myelomonocytic markers. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2001, 80, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Hashimoto, M. Pathogenic role of monocytes/macrophages in large vessel vasculitis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 859502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scruggs, D.W.; Sorden, S.D. Proliferative vasculopathy and cutaneous hemorrhages in porcine neonates infected with the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Vet. Pathol. 2001, 38, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.; Do, D.T.; Vo, H.V.; Kwon, H.I.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, M.H.; Nguyen, D.T.T.; Le, Q.T.V.; Tran, T.M.; Nguyen, T.T.; et al. The Isolation and Replication of African Swine Fever Virus in Primary Renal-Derived Swine Macrophages. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 645456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulford, K.; Micklem, K.; McCarthy, S.; Cordell, J.; Jones, M.; Mason, D.Y. A monocyte/macrophage antigen recognized by the four antibodies GHI/61, Ber-MAC3, Ki-M8 and SM4. Immunology 1992, 75, 588–595. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, B.F.; Tseng, L.C.; Hosler, G.A.; Teske, N.M.; Zhang, S.; Karp, D.R.; Olsen, N.J.; Mohan, C. A subset of CD163+ macrophages displays mixed polarizations in discoid lupus skin. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzoni, G.; Dei Giudici, S.; Oggiano, A. Infection, modulation and responses of antigen-presenting cells to African swine fever viruses. Virus Res. 2018, 258, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, C.; Soler, A.; Nurmoja, I.; Cano-Gómez, C.; Cvetkova, S.; Frant, M.; Woźniakowski, G.; Simón, A.; Pérez, C.; Nieto, R.; et al. Dynamics of African swine fever virus (ASFV) infection in domestic pigs infected with virulent, moderate virulent and attenuated genotype II ASFV European isolates. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 2826–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, L.K.; Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Galindo, I.; Alonso, C. Investigations of Pro- and Anti-Apoptotic Factors Affecting African Swine Fever Virus Replication and Pathogenesis. Viruses 2017, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhou, L.; Wu, J.; Weng, W.; Wang, H.; Ye, M.; Qu, Y.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, X.; et al. Riding apoptotic bodies for cell-cell transmission by African swine fever virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2309506120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraco, G.; Park, L.; Anrather, J.; Iadecola, C. Brain perivascular macrophages: Characterization and functional roles in health and disease. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basler, C.F. Molecular pathogenesis of viral hemorrhagic fever. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoni, G.; Pedrera, M.; Sánchez-Cordón, P.J. African Swine Fever Virus Infection and Cytokine Response In Vivo: An Update. Viruses 2023, 15, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulovic, E.; Mehinagic, K.; Wüthrich, T.; Hilty, M.; Posthaus, H.; Summerfield, A.; Ruggli, N.; Benarafa, C. The baseline immunological and hygienic status of pigs impact disease severity of African swine fever. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithgow, P.; Takamatsu, H.; Werling, D.; Dixon, L.; Chapman, D. Correlation of cell surface marker expression with African swine fever virus infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascosa, A.L.; Bustos, M.J.; Galindo, I.; Viñuela, E. Virus-specific cell receptors are necessary, but not sufficient, to confer cell susceptibility to African swine fever virus. Arch. Virol. 1999, 144, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landmann, R.; Müller, B.; Zimmerli, W. CD14, new aspects of ligand and signal diversity. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Yu, C.; Yang, X.F.; Wang, H. Monocyte and macrophage differentiation: Circulation inflammatory monocyte as biomarker for inflammatory diseases. Biomark. Res. 2014, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannhorst, K.; Carlson, J.; Hölper, J.E.; Grey, F.; Baillie, J.K.; Höper, D.; Wöhnke, E.; Franzke, K.; Karger, A.; Fuchs, W.; et al. The non-classical major histocompatibility complex II protein SLA-DM is crucial for African swine fever virus replication. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, A.; Perez, J.; Carrasco, L.; Bautista, M.J.; Sanchez-Vizcaino, J.M.; Sierra, M.A. Distribution of ASFV antigens in pig tissues experimentally infected with two different Spanish virus isolates. Zentralblatt Fur Veterinarmedizin. Reihe B J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 1992, 39, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salguero, F.J. Comparative Pathology and Pathogenesis of African Swine Fever Infection in Swine. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Villamandos, J.C.; Hervás, J.; Méndez, A.; Carrasco, L.; Villeda, C.J.; Sierra, M.A.; Wilkonson, P.J. A pathological study of the perisinusoidal unit of the liver in acute African swine fever. Res. Vet. Sci. 1995, 59, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Matos, A.P.; Carvalho, Z.G. African swine fever virus interaction with microtubules. Biol. Cell 1993, 78, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouvenet, N.; Windsor, M.; Rietdorf, J.; Hawes, P.; Monaghan, P.; Way, M.; Wileman, T. African swine fever virus induces filopodia-like projections at the plasma membrane. Cell Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1803–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallée, I.; Tait, S.W.; Powell, P.P. African swine fever virus infection of porcine aortic endothelial cells leads to inhibition of inflammatory responses, activation of the thrombotic state, and apoptosis. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 10372–10382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primary Antibodies 1 | Primary Antibodies 2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Host | Target Cells | Clone | Isotype | Dilution | Company | |
| Anti-VP72, IgG2a | Anti-CD163 mAb | mouse | macrophages | 2A10/11 | IgG1 | 1:200 | Bio-rad |
| Anti-Sialoadhesin mAb | mouse | macrophages | 41D3 | IgG1 | 1:50 | [37] | |
| Anti-vimentin mAb | mouse | mesenchymal cells | V9 | IgG1 | 1:50 | Bio-rad | |
| Anti-VP72, IgG1 | Anti-CD14 mAb | mouse | monocytes | MIL2 | IgG2b | 1:100 | [38] |
| Anti-MHCII mAb | mouse | APCs | MSA3 | IgG2a | 1:200 | Kingfisher Biotech | |
| Anti-smooth muscle actin mAb | mouse | smooth muscle cells | 1A4 | IgG2a | 1:50 | Dako | |
| Anti-von willebrand factor pAb | rabbit | endothelial cells | IgG | 1:50 | Dako |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, S.; Oh, D.; Balmelle, N.; Cay, A.B.; Ren, X.; Droesbeke, B.; Tignon, M.; Nauwynck, H. Replication Characteristics of African Swine Fever Virus (ASFV) Genotype I E70 and ASFV Genotype II Belgium 2018/1 in Perivenous Macrophages Using Established Vein Explant Model. Viruses 2024, 16, 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101602
Han S, Oh D, Balmelle N, Cay AB, Ren X, Droesbeke B, Tignon M, Nauwynck H. Replication Characteristics of African Swine Fever Virus (ASFV) Genotype I E70 and ASFV Genotype II Belgium 2018/1 in Perivenous Macrophages Using Established Vein Explant Model. Viruses. 2024; 16(10):1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101602
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Shaojie, Dayoung Oh, Nadège Balmelle, Ann Brigitte Cay, Xiaolei Ren, Brecht Droesbeke, Marylène Tignon, and Hans Nauwynck. 2024. "Replication Characteristics of African Swine Fever Virus (ASFV) Genotype I E70 and ASFV Genotype II Belgium 2018/1 in Perivenous Macrophages Using Established Vein Explant Model" Viruses 16, no. 10: 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101602
APA StyleHan, S., Oh, D., Balmelle, N., Cay, A. B., Ren, X., Droesbeke, B., Tignon, M., & Nauwynck, H. (2024). Replication Characteristics of African Swine Fever Virus (ASFV) Genotype I E70 and ASFV Genotype II Belgium 2018/1 in Perivenous Macrophages Using Established Vein Explant Model. Viruses, 16(10), 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101602







