Nonenveloped Avian Reoviruses Released with Small Extracellular Vesicles Are Highly Infectious
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Vector
2.2. Viruses and Antibodies
2.3. EV Isolation
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Sandwich ELISA
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.7. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) Assay
2.8. Infectivity Assay
2.9. Mass Spectrometry
2.10. Cryo-Electron Microscopy
3. Results
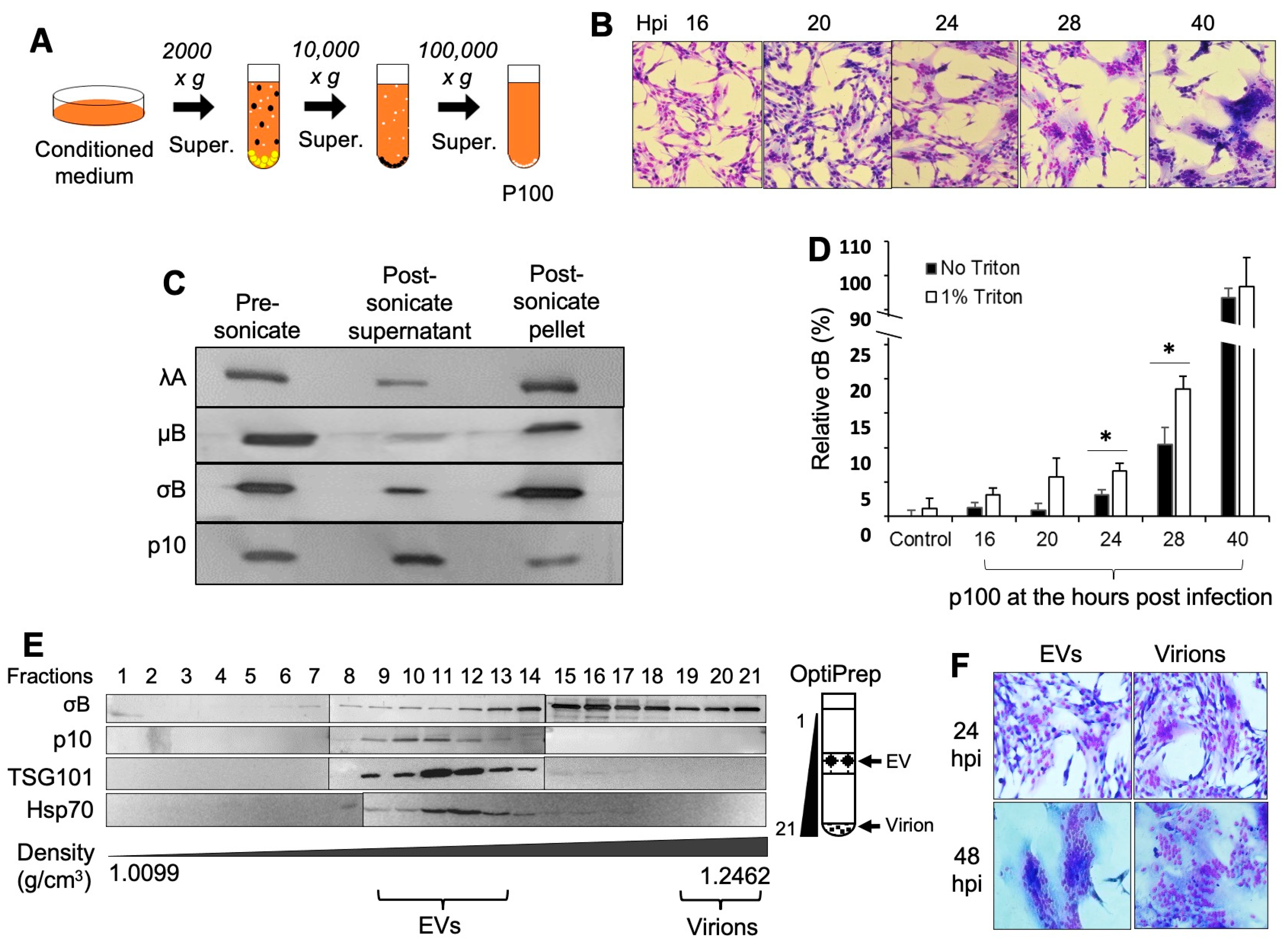
3.1. ARV-Infected Cells Release Viral Proteins in EVs and the EV Fractions Are Infectious
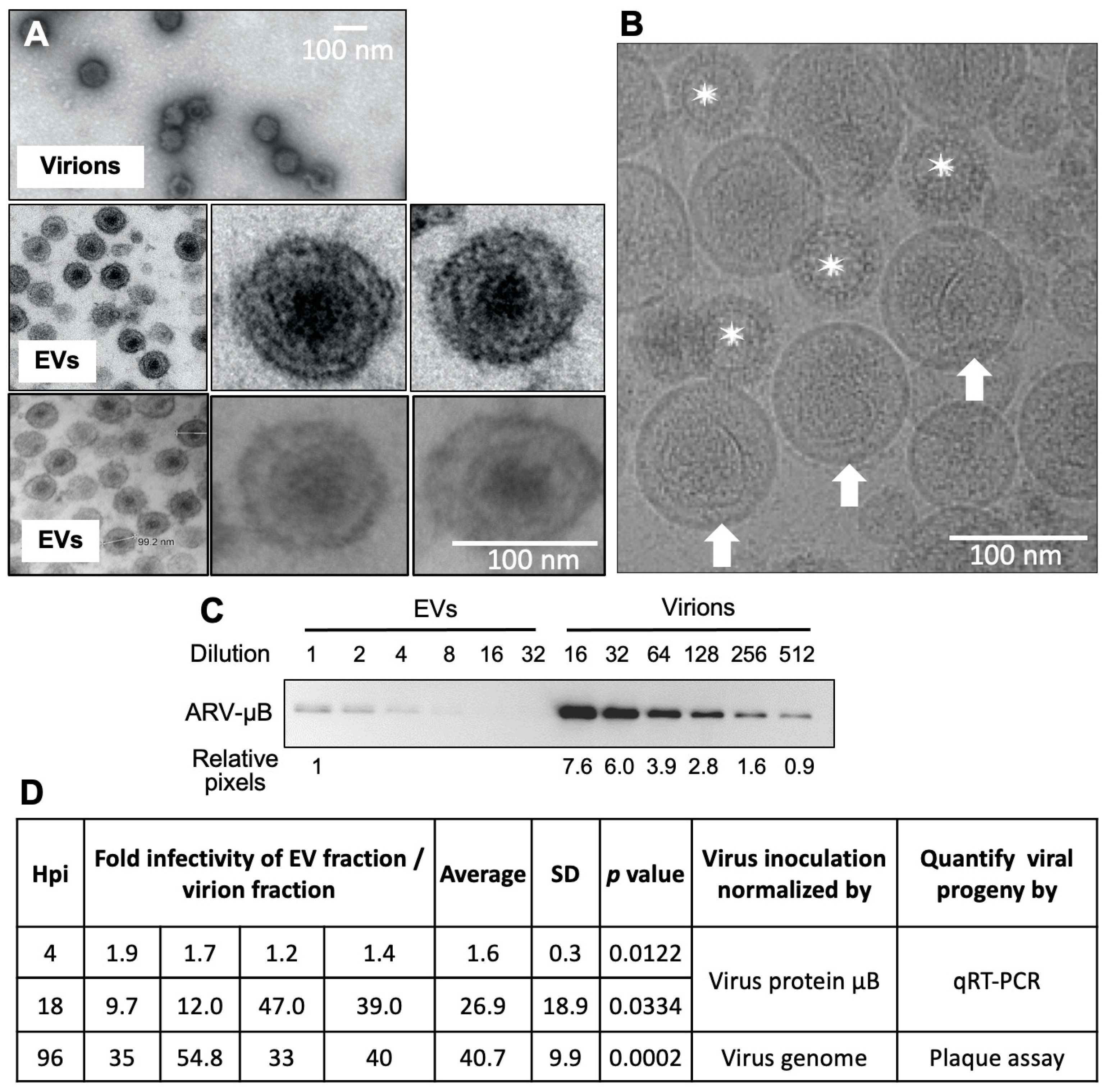
3.2. EV Fraction Is a Mixture of EVs and Virions and Is Highly Infectious
3.3. Viral Proteins and Full Virus Particles Exist in EV Fractions
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lai, F.W.; Lichty, B.D.; Bowdish, D.M. Microvesicles: Ubiquitous contributors to infection and immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 97, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, J.L.; Pan, H.; Lanza, G.M.; Wickline, S.A. Paracrine induction of endothelium by tumor exosomes. Lab. Investig. 2009, 89, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skog, J.; Würdinger, T.; Van Rijn, S.; Meijer, D.H.; Gainche, L.; Curry, W.T.; Carter, B.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.S.; Cho, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Choi, E.-J.; Rho, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, D.-S.; Kim, Y.-K.; Hwang, D. Colorectal cancer cell-derived microvesicles are enriched in cell cycle-related mRNAs that promote proliferation of endothelial cells. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meckes, D.G., Jr.; Raab-Traub, N. Microvesicles and viral infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 12844–12854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, M.T.; Graham, D.R.; Coren, L.V.; Trubey, C.M.; Bess, J.W., Jr.; Arthur, L.O.; Ott, D.E.; Lifson, J.D. Differential incorporation of CD45, CD80 (B7-1), CD86 (B7-2), and major histocompatibility complex class I and II molecules into human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions and microvesicles: Implications for viral pathogenesis and immune regulation. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 6173–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inal, J.M.; Jorfi, S. Coxsackievirus B transmission and possible new roles for extracellular vesicles. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-López, O.; Rivera-Serrano, E.E.; Hu, F.; Hensley, L.; McKnight, K.L.; Ren, J.; Stuart, D.I.; Fry, E.E.; Lemon, S.M. Redundant late domain functions of tandem VP2 YPX3L motifs in nonlytic cellular egress of quasi-enveloped hepatitis A virus. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, K.L.; Xie, L.; González-López, O.; Rivera-Serrano, E.E.; Chen, X.; Lemon, S.M. Protein composition of the hepatitis A virus quasi-envelope. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6587–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, S.W.; Kirkegaard, K. Escape of non-enveloped virus from intact cells. Virology 2015, 479, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, S.; Jirintai, S.; Takahashi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Kouki, T.; Yashiro, T.; Okamoto, H. Hepatitis E virus egress depends on the exosomal pathway, with secretory exosomes derived from multivesicular bodies. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2166–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iša, P.; Pérez-Delgado, A.; Quevedo, I.R.; López, S.; Arias, C.F. Rotaviruses associate with distinct types of extracellular vesicles. Viruses 2020, 12, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, D.; Rodríguez, L.-S.; Franco, M.A.; Angel, J.; Barreto, A. Caco-2 cells infected with rotavirus release extracellular vesicles that express markers of apoptotic bodies and exosomes. Cell Stress Chaperones 2015, 20, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiana, M.; Ghosh, S.; Ho, B.A.; Rajasekaran, V.; Du, W.-L.; Mutsafi, Y.; De Jésus-Diaz, D.A.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Levenson, E.A.; Parra, G.I. Vesicle-cloaked virus clusters are optimal units for inter-organismal viral transmission. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 208–220.e208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, N.; Maurice, M.; Delautier, D.; Quero, A.M.; Servin, A.L.; Trugnan, G. Rotavirus is released from the apical surface of cultured human intestinal cells through nonconventional vesicular transport that bypasses the Golgi apparatus. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 8268–8278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyatt, A.D.; Eaton, B.T.; Brookes, S.M. The release of bluetongue virus from infected cells and their superinfection by progeny virus. Virology 1989, 173, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirblich, C.; Bhattacharya, B.; Roy, P. Nonstructural protein 3 of bluetongue virus assists virus release by recruiting ESCRT-I protein Tsg101. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoltz, D.; Makkay, A. Co-replication of a reovirus and a polydnavirus in the ichneumonid parasitoid Hyposoter exiguae. Virology 2000, 278, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, J.; Sterner, F.; Botts, S.; Lee, K.; Margolin, A. In vitro and in vivo characterization of avian reoviruses. I. Pathogenicity and antigenic relatedness of several avian reovirus isolates. Avian Dis. 1989, 33, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, K.; Johnson, E.; Stehle, T.; Dermody, T. Attachment and cell entry of mammalian orthoreovirus. Reoviruses Entry Assem. Morphog. 2006, 309, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Attoui, H.; Billoir, F.; Biagini, P.; de Micco, P.; de Lamballerie, X. Complete sequence determination and genetic analysis of Banna virus and Kadipiro virus: Proposal for assignment to a new genus (Seadornavirus) within the family Reoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.W.; Stephenson, K.B.; Hanson, S.; Kucharczyk, M.; Duncan, R.; Bell, J.C.; Lichty, B.D. The p14 FAST protein of reptilian reovirus increases vesicular stomatitis virus neuropathogenesis. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salsman, J.; Top, D.; Boutilier, J.; Duncan, R. Extensive syncytium formation mediated by the reovirus FAST proteins triggers apoptosis-induced membrane instability. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8090–8100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, Y.; Kawagishi, T.; Sakai, Y.; Nouda, R.; Shimojima, M.; Saijo, M.; Matsuura, Y.; Kobayashi, T. Cell–cell fusion induced by reovirus FAST proteins enhances replication and pathogenicity of non-enveloped dsRNA viruses. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmulevitz, M.; Corcoran, J.; Salsman, J.; Duncan, R. Cell-cell fusion induced by the avian reovirus membrane fusion protein is regulated by protein degradation. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 5996–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shmulevitz, M.; Duncan, R. A new class of fusion-associated small transmembrane (FAST) proteins encoded by the non-enveloped fusogenic reoviruses. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, R.; Sullivan, K. Characterization of two avian reoviruses that exhibit strain-specific quantitative differences in their syncytium-inducing and pathogenic capabilities. Virology 1998, 250, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, R.; Chen, Z.; Walsh, S.; Wu, S. Avian reovirus-induced syncytium formation is independent of infectious progeny virus production and enhances the rate, but is not essential, for virus-induced cytopathology and virus egress. Virology 1996, 224, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wickline, S.A.; Hood, J.L. Magnetic resonance imaging of melanoma exosomes in lymph nodes. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 74, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onódi, Z.; Pelyhe, C.; Terézia Nagy, C.; Brenner, G.B.; Almási, L.; Kittel, Á.; Manček-Keber, M.; Ferdinandy, P.; Buzás, E.I.; Giricz, Z. Isolation of high-purity extracellular vesicles by the combination of iodixanol density gradient ultracentrifugation and bind-elute chromatography from blood plasma. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrich, B.M.; Liang, Y.; Fiandaca, M.S. Foetal bovine serum influence on in vitro extracellular vesicle analyses. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, R.; Corcoran, J.; Shou, J.; Stoltz, D. Reptilian reovirus: A new fusogenic orthoreovirus species. Virology 2004, 319, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeev-Ben-Mordehai, T.; Vasishtan, D.; Hernández Durán, A.; Vollmer, B.; White, P.; Prasad Pandurangan, A.; Siebert, C.A.; Topf, M.; Grünewald, K. Two distinct trimeric conformations of natively membrane-anchored full-length herpes simplex virus 1 glycoprotein B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 4176–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R. The low pH-dependent entry of avian reovirus is accompanied by two specific cleavages of the major outer capsid protein μ2C. Virology 1996, 219, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Teicher, C.; Haefliger, S.; Shmulevitz, M. Reduction of virion-associated σ1 fibers on oncolytic reovirus variants promotes adaptation toward tumorigenic cells. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4319–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.; Smiley, J.R.; Shmulevitz, M. Polymorphisms in the most oncolytic reovirus strain confer enhanced cell attachment, transcription, and single-step replication kinetics. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01937-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández de Castro, I.; Tenorio, R.; Ortega-González, P.; Knowlton, J.J.; Zamora, P.F.; Lee, C.H.; Fernández, J.J.; Dermody, T.S.; Risco, C. A modified lysosomal organelle mediates nonlytic egress of reovirus. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 219, e201910131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourís-Otero, F.; Cortez-San Martín, M.; Martínez-Costas, J.; Benavente, J. Avian reovirus morphogenesis occurs within viral factories and begins with the selective recruitment of sigmaNS and lambdaA to microNS inclusions. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 341, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcovski, J.; Goyal, S.M. Avian reovirus infections. In Diseases of Poultry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; Chapter 11; pp. 382–400. [Google Scholar]
- Top, D.; de Antueno, R.; Salsman, J.; Corcoran, J.; Mader, J.; Hoskin, D.; Touhami, A.; Jericho, M.H.; Duncan, R. Liposome reconstitution of a minimal protein-mediated membrane fusion machine. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 2980–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.; de Antueno, R.; Duncan, R.; Hoskin, D.W. Intracellular delivery of bovine lactoferricin’s antimicrobial core (RRWQWR) kills T-leukemia cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 388, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longatti, A.; Boyd, B.; Chisari, F.V. Virion-independent transfer of replication-competent hepatitis C virus RNA between permissive cells. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2956–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xie, F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Fang, M.; Zhou, F. The function and clinical application of extracellular vesicles in innate immune regulation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Boeuf, F.; Gebremeskel, S.; McMullen, N.; He, H.; Greenshields, A.L.; Hoskin, D.W.; Bell, J.C.; Johnston, B.; Pan, C.; Duncan, R. Reovirus FAST protein enhances vesicular stomatitis virus oncolytic virotherapy in primary and metastatic tumor models. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2017, 6, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Ma, P.; Deng, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Long, G. Hepatitis A virus structural protein pX interacts with ALIX and promotes the secretion of virions and foreign proteins through exosome-like vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1716513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Jirintai, S.; Tanaka, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Yasuda, J.; Okamoto, H. Tumour susceptibility gene 101 and the vacuolar protein sorting pathway are required for the release of hepatitis E virions. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2838–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenassi, M.; Cagney, G.; Liao, M.; Vaupotič, T.; Bartholomeeusen, K.; Cheng, Y.; Krogan, N.J.; Plemenitaš, A.; Peterlin, B.M. HIV Nef is secreted in exosomes and triggers apoptosis in bystander CD4+ T cells. Traffic 2010, 11, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckes, D.G., Jr.; Shair, K.H.; Marquitz, A.R.; Kung, C.-P.; Edwards, R.H.; Raab-Traub, N. Human tumor virus utilizes exosomes for intercellular communication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20370–20375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germano, J.F.; Sawaged, S.; Saadaeijahromi, H.; Andres, A.M.; Feuer, R.; Gottlieb, R.A.; Sin, J. Coxsackievirus B infection induces the extracellular release of miR-590-5p, a proviral microRNA. Virology 2019, 529, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; He, M.; He, H.; Kilby, K.; Antueno, R.d.; Castle, E.; McMullen, N.; Qian, Z.; Zeev-Ben-Mordehai, T.; Duncan, R.; et al. Nonenveloped Avian Reoviruses Released with Small Extracellular Vesicles Are Highly Infectious. Viruses 2023, 15, 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071610
Wang Z, He M, He H, Kilby K, Antueno Rd, Castle E, McMullen N, Qian Z, Zeev-Ben-Mordehai T, Duncan R, et al. Nonenveloped Avian Reoviruses Released with Small Extracellular Vesicles Are Highly Infectious. Viruses. 2023; 15(7):1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071610
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zuopei, Menghan He, Han He, Kyle Kilby, Roberto de Antueno, Elizabeth Castle, Nichole McMullen, Zhuoyu Qian, Tzviya Zeev-Ben-Mordehai, Roy Duncan, and et al. 2023. "Nonenveloped Avian Reoviruses Released with Small Extracellular Vesicles Are Highly Infectious" Viruses 15, no. 7: 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071610
APA StyleWang, Z., He, M., He, H., Kilby, K., Antueno, R. d., Castle, E., McMullen, N., Qian, Z., Zeev-Ben-Mordehai, T., Duncan, R., & Pan, C. (2023). Nonenveloped Avian Reoviruses Released with Small Extracellular Vesicles Are Highly Infectious. Viruses, 15(7), 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071610






