Fc-Effector-Independent in vivo Activity of a Potent Influenza B Neuraminidase Broadly Neutralizing Antibody
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
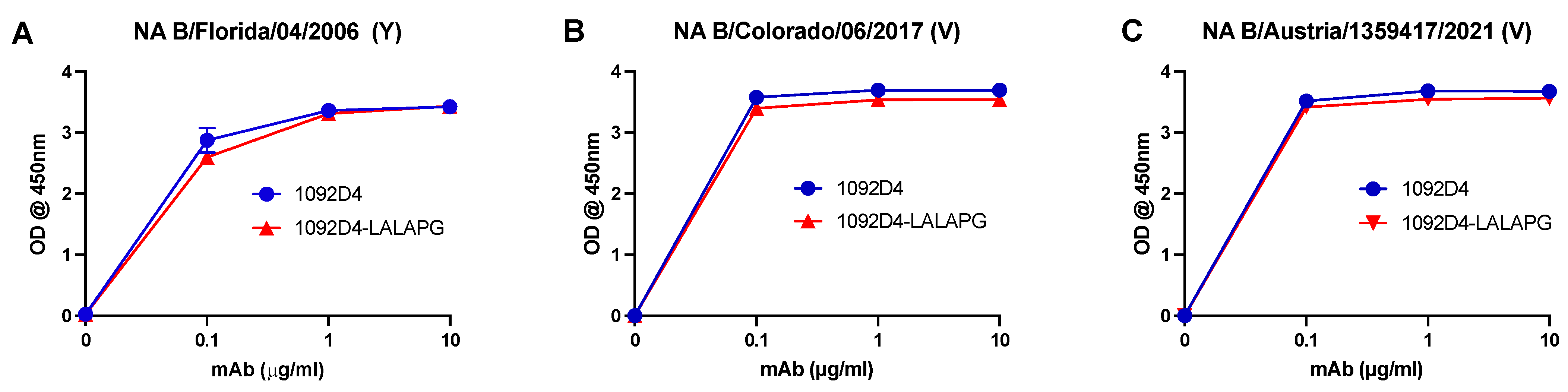
3.1. 1092D4–LALAPG Has Comparable Binding to IBV NA
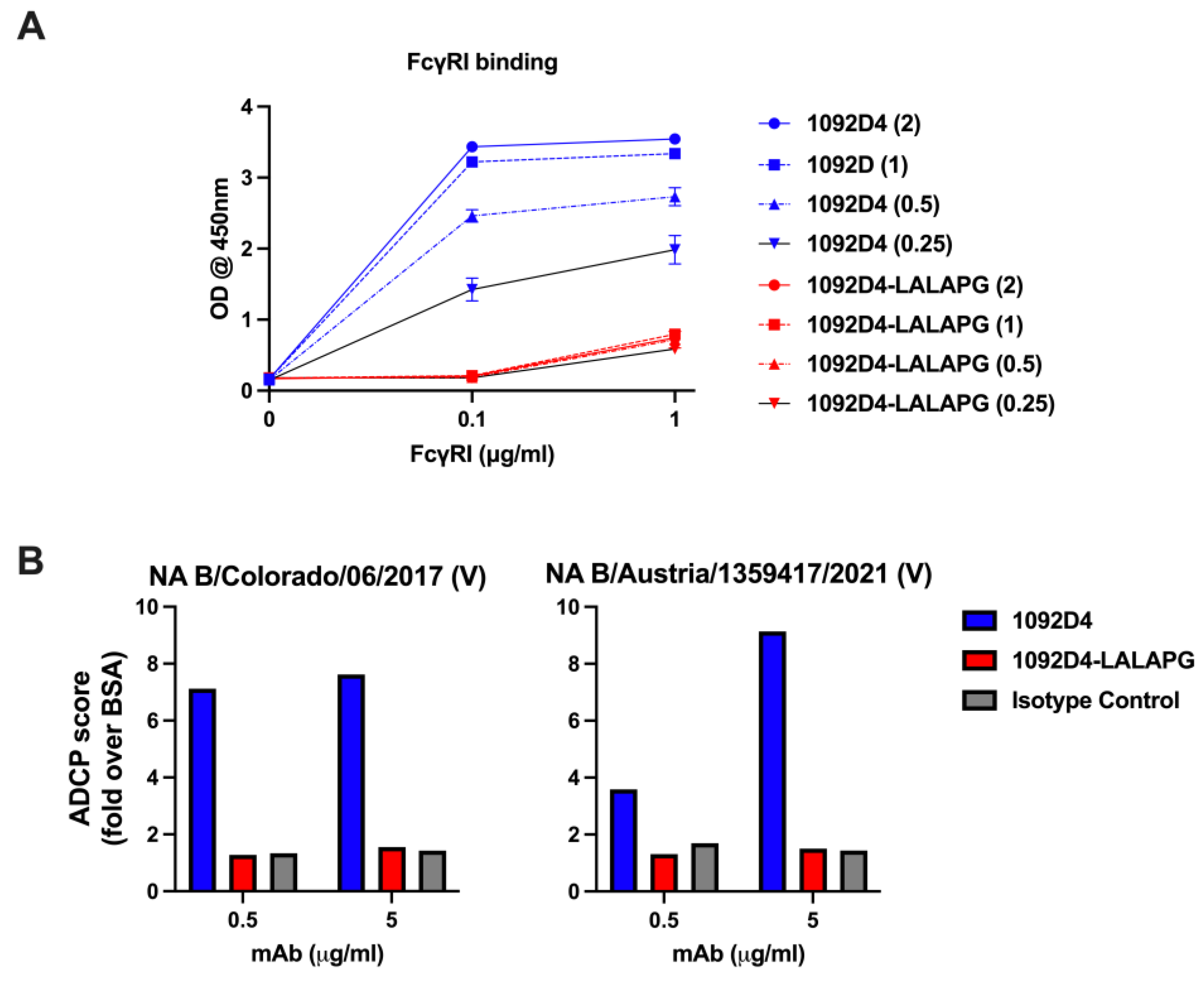
3.2. 1092D4–LALAPG Reduces FcγRI Binding and Antibody-Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis
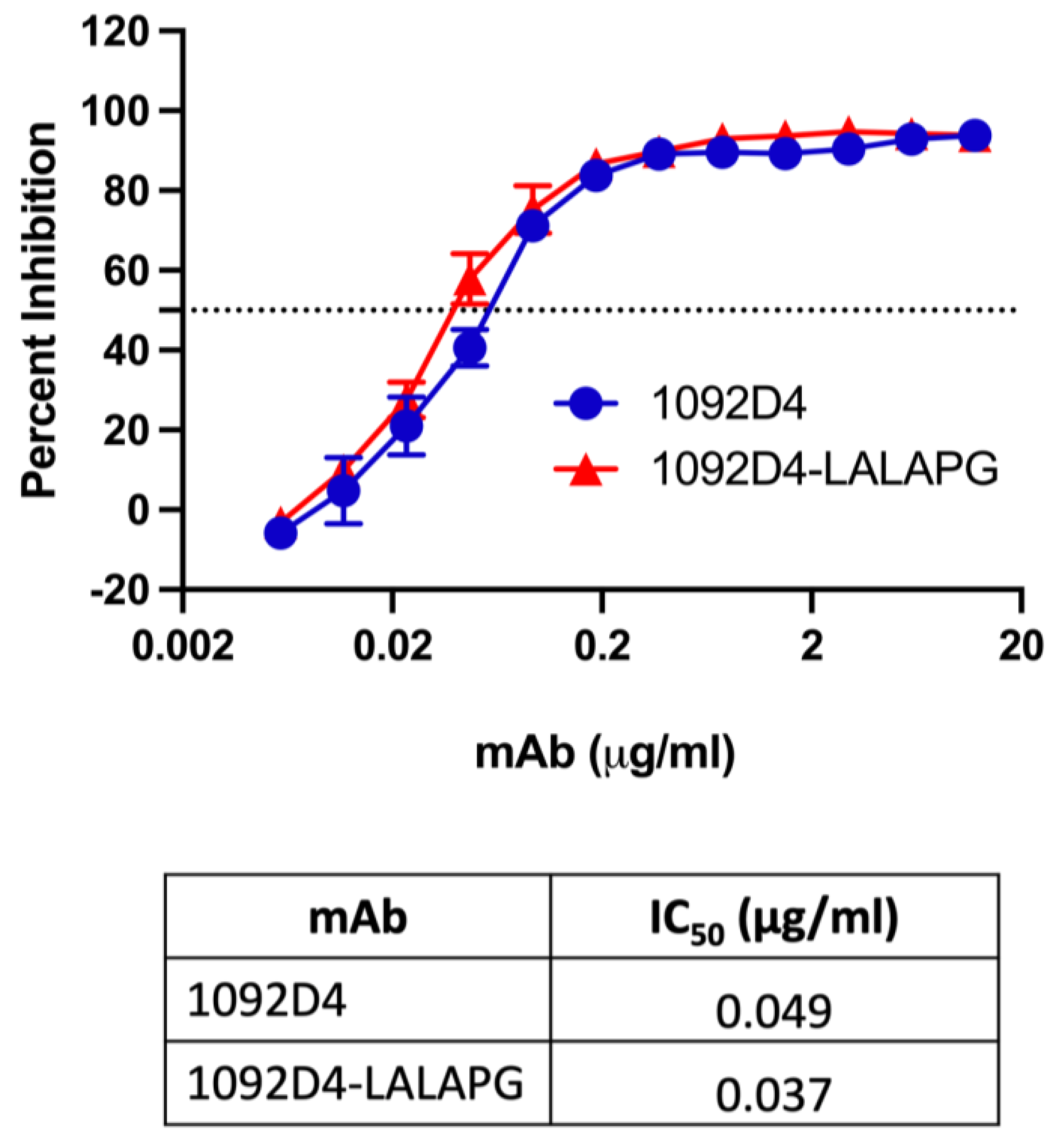
3.3. 1092D4–LALAPG Retains Ability to Inhibit NA Enzymatic Activity
3.4. 1092D4 and 1092D4–LALAPG Potently Neutralize Diverse IBV
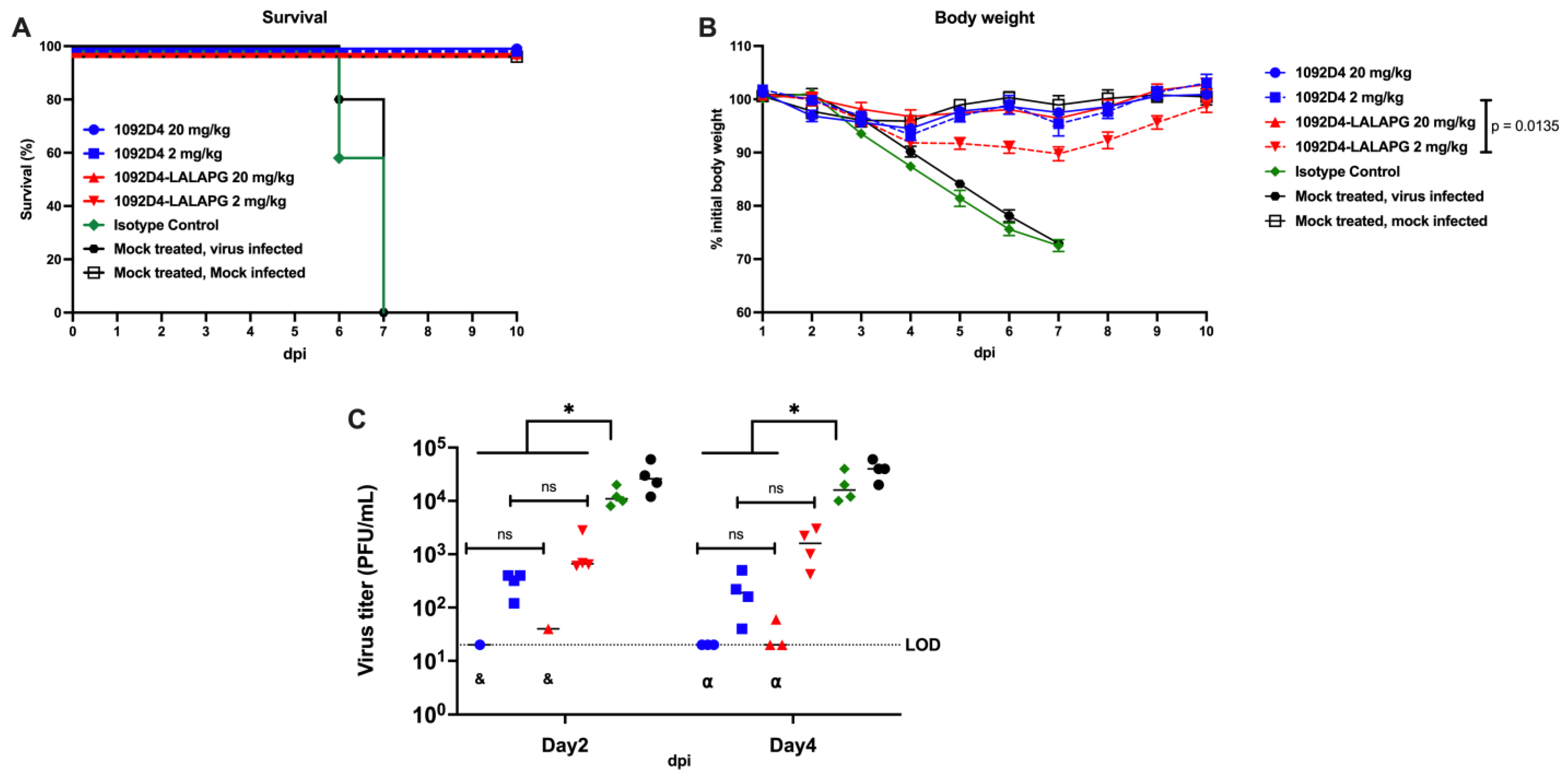
3.5. 1092D4–LALAPG Protects from Lethal IBV Infection
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merced-Morales, A.; Daly, P.; Elal, A.I.A.; Ajayi, N.; Annan, E.; Budd, A.; Barnes, J.; Colon, A.; Cummings, C.N.; Iuliano, A.D.; et al. Influenza Activity and Composition of the 2022–23 Influenza Vaccine—United States, 2021–2022 Season. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekaran, V.; Sullivan, S.; Edwards, K.M.; Xie, R.; Khvorov, A.; Valkenburg, S.A.; Cowling, B.J.; Barr, I.G. Human seasonal influenza under COVID-19 and the potential consequences of influenza lineage elimination. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Y.R. Influenza B infections in children: A review. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2020, 9, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.K.; Chan, M.C.; Cheung, J.L.; Lee, N.; Leung, T.F.; Yeung, A.C.; Wong, M.C.; Ngai, K.L.; Nelson, E.A.; Hui, D.S. Influenza B lineage circulation and hospitalization rates in a subtropical city, Hong Kong, 2000–2010. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skowronski, D.M.; Chambers, C.; De Serres, G.; Sabaiduc, S.; Winter, A.L.; Dickinson, J.A.; Gubbay, J.B.; Fonseca, K.; Drews, S.J.; Charest, H.; et al. Age-Related Differences in Influenza B Infection by Lineage in a Community-Based Sentinel System, 2010–2011 to 2015–2016, Canada. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, D.; Vaudry, W.; Moore, D.; Bettinger, J.A.; Halperin, S.A.; Scheifele, D.W.; Jadvji, T.; Lee, L.; Mersereau, T.; members of the Canadian Immunization Monitoring Program Active. Hospitalization for Influenza A versus B. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20154643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shang, M.; Blanton, L.; Brammer, L.; Olsen, S.J.; Fry, A.M. Influenza-Associated Pediatric Deaths in the United States, 2010–2016. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20172918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noshi, T.; Kitano, M.; Taniguchi, K.; Yamamoto, A.; Omoto, S.; Baba, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Ishida, K.; Kushima, Y.; Hattori, K.; et al. In vitro characterization of baloxavir acid, a first-in-class cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor of the influenza virus polymerase PA subunit. Antivir. Res. 2018, 160, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrukee, R.; Tai, C.M.; Oh, D.Y.; Anderson, D.E.; Gunalan, V.; Hibberd, M.; Lau, G.Y.; Barr, I.G.; Messling, V.V.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; et al. Utilising animal models to evaluate oseltamivir efficacy against influenza A and B viruses with reduced in vitro susceptibility. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S. Emerging antiviral therapies and drugs for the treatment of influenza. Expert. Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2022, 27, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, R.A. The Structure, Function, and Pathobiology of the Influenza A and B Virus Ion Channels. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2020, 10, a038505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinno, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Kawakami, K. Association Between Baloxavir Marboxil Prescription for Children with Influenza B Infections and Short-Term Healthcare Consumption in Japan During the 2018-2019 Influenza Season. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2022, 11, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saim-Mamoun, A.; Abed, Y.; Carbonneau, J.; Boivin, G. Generation and Characterization of Drug-Resistant Influenza B Viruses Selected In Vitro with Baloxavir Acid. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascua, P.N.Q.; Jones, J.C.; Webby, R.J.; Govorkova, E.A. Effect of E23G/K, F36V, N37T, E119D, and E199G polymerase acidic protein substitutions on the replication and baloxavir susceptibility of influenza B viruses. Antivir. Res. 2022, 208, 105455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnham, A.J.; Baranovich, T.; Govorkova, E.A. Neuraminidase inhibitors for influenza B virus infection: Efficacy and resistance. Antivir. Res. 2013, 100, 520–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boudreau, C.M.; Alter, G. Extra-Neutralizing FcR-Mediated Antibody Functions for a Universal Influenza Vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DiLillo, D.J.; Tan, G.S.; Palese, P.; Ravetch, J.V. Broadly neutralizing hemagglutinin stalk-specific antibodies require FcgammaR interactions for protection against influenza virus in vivo. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DiLillo, D.J.; Palese, P.; Wilson, P.C.; Ravetch, J.V. Broadly neutralizing anti-influenza antibodies require Fc receptor engagement for in vivo protection. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegaskanda, S. The Potential Role of Fc-Receptor Functions in the Development of a Universal Influenza Vaccine. Vaccines 2018, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Widge, A.T.; Hofstetter, A.R.; Houser, K.V.; Awan, S.F.; Chen, G.L.; Florez, M.C.B.; Berkowitz, N.M.; Mendoza, F.; Hendel, C.S.; Holman, L.A.; et al. An influenza hemagglutinin stem nanoparticle vaccine induces cross-group 1 neutralizing antibodies in healthy adults. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eade4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, K.V.; Chen, G.L.; Carter, C.; Crank, M.C.; Nguyen, T.A.; Florez, M.C.B.; Berkowitz, N.M.; Mendoza, F.; Hendel, C.S.; Gordon, I.J.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a ferritin nanoparticle H2 influenza vaccine in healthy adults: A phase 1 trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Job, E.R.; Ysenbaert, T.; Smet, A.; Van Hecke, A.; Meuris, L.; Kleanthous, H.; Saelens, X.; Vogel, T.U. Fcgamma Receptors Contribute to the Antiviral Properties of Influenza Virus Neuraminidase-Specific Antibodies. mBio 2019, 10, e01667-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yasuhara, A.; Yamayoshi, S.; Kiso, M.; Sakai-Tagawa, Y.; Koga, M.; Adachi, E.; Kikuchi, T.; Wang, I.H.; Yamada, S.; Kawaoka, Y. Antigenic drift originating from changes to the lateral surface of the neuraminidase head of influenza A virus. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchuk, I.M.; Bangaru, S.; Gilchuk, P.; Irving, R.P.; Kose, N.; Bombardi, R.G.; Thornburg, N.J.; Creech, C.B.; Edwards, K.M.; Li, S.; et al. Influenza H7N9 Virus Neuraminidase-Specific Human Monoclonal Antibodies Inhibit Viral Egress and Protect from Lethal Influenza Infection in Mice. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 715–728 e718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepenbrink, M.S.; Nogales, A.; Basu, M.; Fucile, C.F.; Liesveld, J.L.; Keefer, M.C.; Rosenberg, A.F.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Kobie, J.J. Broad and Protective Influenza B Virus Neuraminidase Antibodies in Humans after Vaccination and their Clonal Persistence as Plasma Cells. mBio 2019, 10, e00066-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sondermann, P.; Huber, R.; Oosthuizen, V.; Jacob, U. The 3.2-A crystal structure of the human IgG1 Fc fragment-Fc gammaRIII complex. Nature 2000, 406, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idusogie, E.E.; Presta, L.G.; Gazzano-Santoro, H.; Totpal, K.; Wong, P.Y.; Ultsch, M.; Meng, Y.G.; Mulkerrin, M.G. Mapping of the C1q binding site on rituxan, a chimeric antibody with a human IgG1 Fc. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 4178–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alegre, M.L.; Collins, A.M.; Pulito, V.L.; Brosius, R.A.; Olson, W.C.; Zivin, R.A.; Knowles, R.; Thistlethwaite, J.R.; Jolliffe, L.K.; Bluestone, J.A. Effect of a single amino acid mutation on the activating and immunosuppressive properties of a “humanized” OKT3 monoclonal antibody. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 3461–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wines, B.D.; Powell, M.S.; Parren, P.W.; Barnes, N.; Hogarth, P.M. The IgG Fc contains distinct Fc receptor (FcR) binding sites: The leukocyte receptors Fc gamma RI and Fc gamma RIIa bind to a region in the Fc distinct from that recognized by neonatal FcR and protein A. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 5313–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, J.; Winter, G.; Jones, P.T.; Pound, J.D.; Tanaka, T.; Walker, M.R.; Artymiuk, P.J.; Arata, Y.; Burton, D.R.; Jefferis, R.; et al. Human Fc gamma RI and Fc gamma RII interact with distinct but overlapping sites on human IgG. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 2657–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, K.O. Conceptual Approaches to Modulating Antibody Effector Functions and Circulation Half-Life. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Alegre, M.L.; Varga, S.S.; Rothermel, A.L.; Collins, A.M.; Pulito, V.L.; Hanna, L.S.; Dolan, K.P.; Parren, P.W.; Bluestone, J.A.; et al. In vitro characterization of five humanized OKT3 effector function variant antibodies. Cell. Immunol. 2000, 200, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, M.; Kim, H.S.; Tong, R.K.; Bainbridge, T.W.; Vernes, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.L.; Chung, S.; Dennis, M.S.; Zuchero, Y.J.; et al. Effector-attenuating Substitutions That Maintain Antibody Stability and Reduce Toxicity in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 3900–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nogales, A.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, I.; Monte, K.; Lenschow, D.J.; Perez, D.R.; Martinez-Sobrido, L. Replication-competent fluorescent-expressing influenza B virus. Virus Res. 2016, 213, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ackerman, M.E.; Moldt, B.; Wyatt, R.T.; Dugast, A.S.; McAndrew, E.; Tsoukas, S.; Jost, S.; Berger, C.T.; Sciaranghella, G.; Liu, Q.; et al. A robust, high-throughput assay to determine the phagocytic activity of clinical antibody samples. J. Immunol. Methods 2011, 366, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piepenbrink, M.S.; Park, J.G.; Deshpande, A.; Loos, A.; Ye, C.; Basu, M.; Sarkar, S.; Khalil, A.M.; Chauvin, D.; Woo, J.; et al. Potent universal beta-coronavirus therapeutic activity mediated by direct respiratory administration of a Spike S2 domain-specific human neutralizing monoclonal antibody. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, M.C.; Waldock, J.; Commandeur, S.; Strauss, L.; Trombetta, C.M.; Marchi, S.; Zhou, F.; van de Witte, S.; van Amsterdam, P.; Ho, S.; et al. Validation of a Harmonized Enzyme-Linked-Lectin-Assay (ELLA-NI) Based Neuraminidase Inhibition Assay Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for Quantification of N1 Influenza Antibodies and the Use of a Calibrator to Improve the Reproducibility of the ELLA-NI With Reverse Genetics Viral and Recombinant Neuraminidase Antigens: A FLUCOP Collaborative Study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 909297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappel, M.S.; Isenman, D.E.; Everett, M.; Xu, Y.Y.; Dorrington, K.J.; Klein, M.H. Identification of the Fc gamma receptor class I binding site in human IgG through the use of recombinant IgG1/IgG2 hybrid and point-mutated antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 9036–9040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, I.; Anderson, S.; Fry, J.; Julien, L.A.; Neville, D.; Qureshi, O.; Watts, G.; Hale, G. Fc-engineered antibodies with immune effector functions completely abolished. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Ding, N.; Li, Y.; Shao, J.; Zhu, M.; Xie, Z.; Sun, K. Vaccine based on antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity epitope on the H1N1 influenza virus increases mortality in vaccinated mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 1874–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.W.; Yuan, S.; Poon, K.M.; Wen, L.; Yang, D.; Sun, Z.; Li, C.; Hu, M.; Shuai, H.; Zhou, J.; et al. Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Epitopes on the Hemagglutinin Head Region of Pandemic H1N1 Influenza Virus Play Detrimental Roles in H1N1-Infected Mice. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.; Zhao, G.; Liu, C.; Wu, X.; Guo, Y.; Yu, H.; Song, H.; Du, L.; Jiang, S.; Guo, R.; et al. Inhibition of complement activation alleviates acute lung injury induced by highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus infection. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khurana, S.; Loving, C.L.; Manischewitz, J.; King, L.R.; Gauger, P.C.; Henningson, J.; Vincent, A.L.; Golding, H. Vaccine-induced anti-HA2 antibodies promote virus fusion and enhance influenza virus respiratory disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 200ra114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, K.K.; Zhang, A.J.; Hung, I.F.; Xu, T.; Ip, W.C.; Wong, R.T.; Ng, J.C.; Chan, J.F.; Chan, K.H.; Yuen, K.Y. High titer and avidity of nonneutralizing antibodies against influenza vaccine antigen are associated with severe influenza. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monsalvo, A.C.; Batalle, J.P.; Lopez, M.F.; Krause, J.C.; Klemenc, J.; Hernandez, J.Z.; Maskin, B.; Bugna, J.; Rubinstein, C.; Aguilar, L.; et al. Severe pandemic 2009 H1N1 influenza disease due to pathogenic immune complexes. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winarski, K.L.; Tang, J.; Klenow, L.; Lee, J.; Coyle, E.M.; Manischewitz, J.; Turner, H.L.; Takeda, K.; Ward, A.B.; Golding, H.; et al. Antibody-dependent enhancement of influenza disease promoted by increase in hemagglutinin stem flexibility and virus fusion kinetics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 15194–15199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Motsoeneng, B.M.; Dhar, N.; Nunes, M.C.; Krammer, F.; Madhi, S.A.; Moore, P.L.; Richardson, S.I. Influenza Vaccination Results in Differential Hemagglutinin Stalk-Specific Fc-Mediated Functions in Individuals Living With or Without HIV. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 873191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tan, H.X.; Koutsakos, M.; Jegaskanda, S.; Esterbauer, R.; Tilmanis, D.; Aban, M.; Kedzierska, K.; Hurt, A.C.; Kent, S.J.; et al. Cross-lineage protection by human antibodies binding the influenza B hemagglutinin. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rijal, P.; Wang, B.B.; Tan, T.K.; Schimanski, L.; Janesch, P.; Dong, T.; McCauley, J.W.; Daniels, R.S.; Townsend, A.R.; Huang, K.A. Broadly Inhibiting Antineuraminidase Monoclonal Antibodies Induced by Trivalent Influenza Vaccine and H7N9 Infection in Humans. J. Virol. 2020, 94, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, Y.T.; Park, S.; Jung, Y.J.; Lee, Y.; Ko, E.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Li, X.; Kang, S.M. Neuraminidase expressing virus-like particle vaccine provides effective cross protection against influenza virus. Virology 2019, 535, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Chromikova, V.; O’Dell, G.; Sordillo, E.M.; Simon, V.; van Bakel, H.; Krammer, F.; McMahon, M. Murine Broadly Reactive Antineuraminidase Monoclonal Antibodies Protect Mice from Recent Influenza B Virus Isolates and Partially Inhibit Virus Transmission in the Guinea Pig Model. mSphere 2022, 7, e0092721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Neutralization (NT50 μg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Virus | 1092D4 | 1092D4–LALAPG |
| B/Malaysia/2506/04 | 0.39 | 0.39 |
| B/Florida/04/06 | 0.39 | 0.39 |
| B/Brisbane/60/2008 | 0.04 | 0.15 |
| B/New York/PV00081/18 | 0.63 | 0.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalil, A.M.; Piepenbrink, M.S.; Markham, I.; Basu, M.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Kobie, J.J. Fc-Effector-Independent in vivo Activity of a Potent Influenza B Neuraminidase Broadly Neutralizing Antibody. Viruses 2023, 15, 1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071540
Khalil AM, Piepenbrink MS, Markham I, Basu M, Martinez-Sobrido L, Kobie JJ. Fc-Effector-Independent in vivo Activity of a Potent Influenza B Neuraminidase Broadly Neutralizing Antibody. Viruses. 2023; 15(7):1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071540
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalil, Ahmed M., Michael S. Piepenbrink, Ian Markham, Madhubanti Basu, Luis Martinez-Sobrido, and James J. Kobie. 2023. "Fc-Effector-Independent in vivo Activity of a Potent Influenza B Neuraminidase Broadly Neutralizing Antibody" Viruses 15, no. 7: 1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071540
APA StyleKhalil, A. M., Piepenbrink, M. S., Markham, I., Basu, M., Martinez-Sobrido, L., & Kobie, J. J. (2023). Fc-Effector-Independent in vivo Activity of a Potent Influenza B Neuraminidase Broadly Neutralizing Antibody. Viruses, 15(7), 1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071540







