Bacteriophage-Associated Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Brazilian Poultry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Escherichia coli Isolation
2.3. Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Molecular Confirmation
2.4. Species Confirmation by Sequencing
2.5. Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
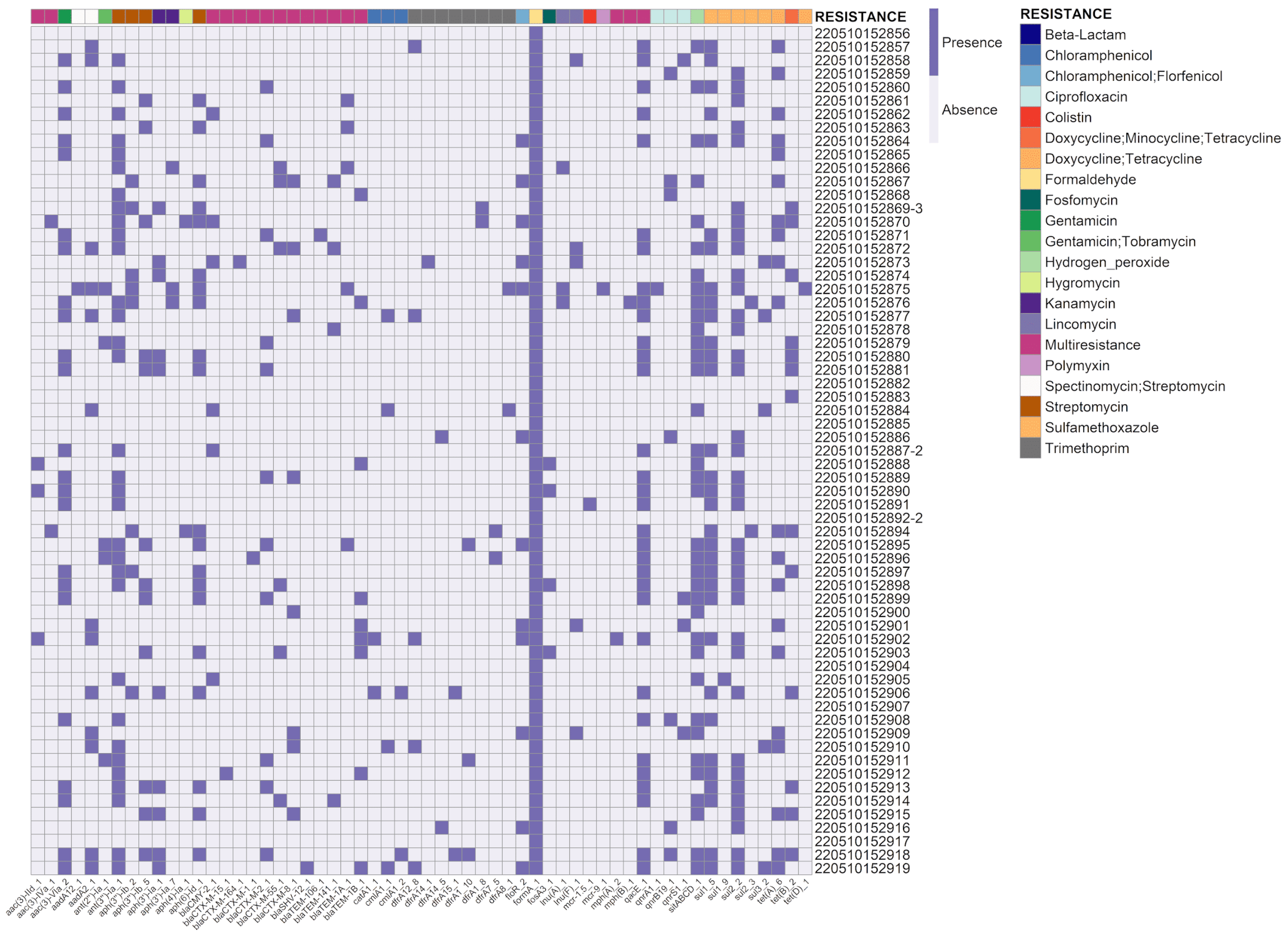
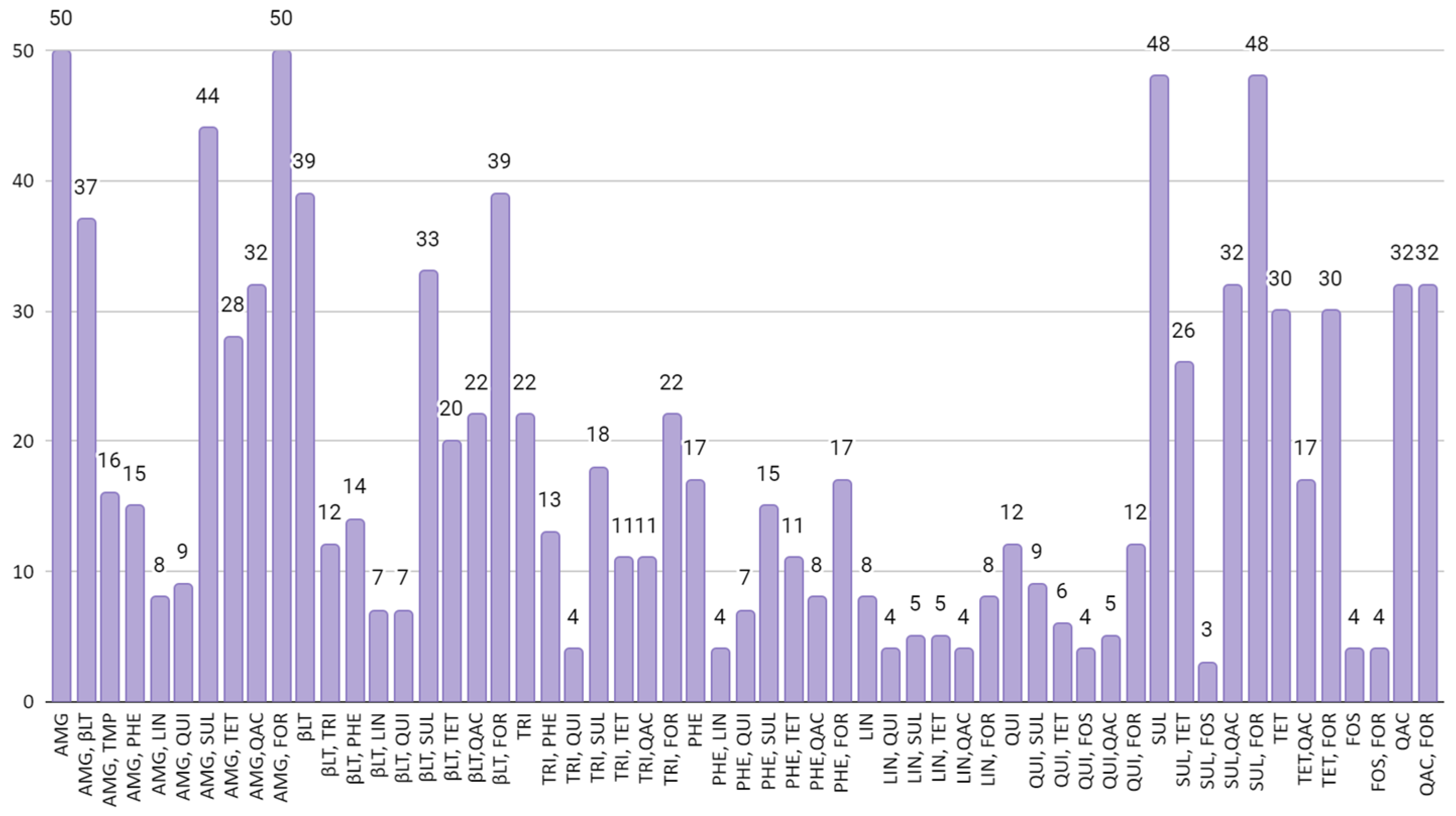
3. Results
3.1. E. coli and APEC Confirmation
3.2. Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ABPA (Associação Brasileira de Proteína Animal). 2023 Relatório Anual; ABPA: São Paulo, Brazil, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, P.H.W.; Rehman, M.A.; Kiarie, E.G.; Topp, E.; Diarra, M.S. Production Systems and Important Antimicrobial Resistant-Pathogenic Bacteria in Poultry: A Review. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, H.; Bachmeier, J.; Bisgaard, M. New Strategies to Prevent and Control Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC). Avian Pathol. 2021, 50, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Miller, E.A.; Flores-Figueroa, C.; Munoz-Aguayo, J.; Cardona, C.; Fransen, K.; Lighty, M.; Gonder, E.; Nezworski, J.; Haag, A.; et al. Refining the Definition of the Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Pathotype through Inclusion of High-Risk Clonal Groups. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 102009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, L.K.; Vaillancourt, J.; Barbieri, N.L.; Logue, C.M. Colibacillosis. In Diseases of Poultry; Swayne, D.E., Boulianne, M., Logue, C.M., McDougald, L.R., Nair, V., Suarez, D.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 770–830. [Google Scholar]
- Dho-Moulin, M.; Fairbrother, J.M. Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC). Vet. Res. 1999, 30, 299–316. [Google Scholar]
- La Ragione, R.M.; Woodward, M.J. Virulence Factors of Escherichia coli Serotypes Associated with Avian Colisepticaemia. Res. Vet. Sci. 2002, 73, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landoni, M.F.; Albarellos, G. The Use of Antimicrobial Agents in Broiler Chickens. Vet. J. 2015, 205, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.A.; Cryer, T.L.; Lafi, S.Q.; Basha, E.A.; Good, L.; Tarazi, Y.H. Identification of Escherichia coli from Broiler Chickens in Jordan, Their Antimicrobial Resistance, Gene Characterization and the Associated Risk Factors. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathayat, D.; Lokesh, D.; Ranjit, S.; Rajashekara, G. Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC): An Overview of Virulence and Pathogenesis Factors, Zoonotic Potential, and Control Strategies. Pathogens 2021, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, B.M.; Levy, S.B. Food Animals and Antimicrobials: Impacts on Human Health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Kehrenberg, C.; Walsh, T.R. Use of Antimicrobial Agents in Veterinary Medicine and Food Animal Production. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2001, 17, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, N.; Käsbohrer, A.; Mayrhofer, S.; Zitz, U.; Hofacre, C.; Domig, K.J. The Application of Antibiotics in Broiler Production and the Resulting Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli: A Global Overview. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 1791–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambi, L.; Crippa, C.; Lucchi, A.; De Cesare, A.; Parisi, A.; Manfreda, G.; Pasquali, F. The Resistome of Commensal Escherichia coli Isolated from Broiler Carcasses “Produced without the Use of Antibiotics”. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVey, S.; Kennedy, M.; Chengappa, M.M. Veterinary Microbiology, 3rd ed.; Koogan, G., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; ISBN 9788527726641. [Google Scholar]
- MacGowan, A.; Macnaughton, E. Antibiotic Resistance. Medicine 2017, 45, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Barceló, C. The Disparate Effects of Bacteriophages on Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collett, S.R.; Smith, J.A.; Boulianne, M.; Owen, R.L.; Gingerich, E.; Singer, R.S.; Johnson, T.J.; Hofacre, C.L.; Berghaus, R.D.; Stewart-Brown, B. Principles of Disease Prevention, Diagnosis, and Control. In Diseases of Poultry; Swayne, D.E., Boulianne, M., Logue, C.M., McDougald, L.R., Nair, V., Suarez, D.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–78. [Google Scholar]
- Brown-Jaque, M.; Calero-Cáceres, W.; Muniesa, M. Transfer of Antibiotic-Resistance Genes via Phage-Related Mobile Elements. Plasmid 2015, 79, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clokie, M.R.J.; Millard, A.D.; Letarov, A.V.; Heaphy, S. Phages in Nature. Bacteriophage 2011, 1, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, P.; Aiewsakun, P. Virus Classification—Where Do You Draw the Line? Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2037–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, Z.; Abedon, S.T. Diversity of Phage Infection Types and Associated Terminology: The Problem with ‘Lytic or Lysogenic’. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnw047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, L.K.; Silva, E.C.; Campos, W.F.; Del Fiol, F.S.; Vila, M.; Dąbrowska, K.; Krylov, V.N.; Balcão, V.M. Biotechnological Applications of Bacteriophages: State of the Art. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 212–213, 38–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.L. Bacteriophage-Mediated Horizontal Gene Transfer: Transduction. In Bacteriophages; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 151–192. [Google Scholar]
- Rogovski, P.; Cadamuro, R.D.; da Silva, R.; de Souza, E.B.; Bonatto, C.; Viancelli, A.; Michelon, W.; Elmahdy, E.M.; Treichel, H.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, D.; et al. Uses of Bacteriophages as Bacterial Control Tools and Environmental Safety Indicators. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elois, M.A.; da Silva, R.; Pilati, G.V.T.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, D.; Fongaro, G. Bacteriophages as Biotechnological Tools. Viruses 2023, 15, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canchaya, C.; Fournous, G.; Chibani-Chennoufi, S.; Dillmann, M.-L.; Brüssow, H. Phage as Agents of Lateral Gene Transfer. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüssow, H.; Canchaya, C.; Hardt, W.-D. Phages and the Evolution of Bacterial Pathogens: From Genomic Rearrangements to Lysogenic Conversion. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 560–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Doetkott, C.; Johnson, S.J.; Rosenberger, S.C.; Nolan, L.K. Identification of Minimal Predictors of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Virulence for Use as a Rapid Diagnostic Tool. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3987–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Siek, K.E.; Giddings, C.W.; Doetkott, C.; Johnson, T.J.; Nolan, L.K. Characterizing the APEC Pathotype**. Vet. Res. 2005, 36, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coil, D.; Jospin, G.; Darling, A.E. A5-Miseq: An Updated Pipeline to Assemble Microbial Genomes from Illumina MiSeq Data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality Assessment Tool for Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R.; Oliver Glöckner, F.; Peplies, J. JSpeciesWS: A Web Server for Prokaryotic Species Circumscription Based on Pairwise Genome Comparison. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of Acquired Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, P.; Jenner, R.; Norris, J.; Page, S.; Browning, G. Antimicrobial Prescribing Guidelines for Poultry. Aust. Vet. J. 2021, 99, 181–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, M.L.; Reid, C.J.; Roy Chowdhury, P.; Bushell, R.N.; Esbert, N.; Tivendale, K.A.; Noormohammadi, A.H.; Islam, S.; Marenda, M.S.; Browning, G.F.; et al. Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of Australian Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli That Carry the Class 1 Integrase Gene. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Mohsin, M.; Johnson, T.J.; Smith, E.A.; Johnson, A.; Umair, M.; Saleemi, M.K.; Sajjad-ur-Rahman. Genomic Landscape of Multi-Drug Resistant Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Recovered from Broilers. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 247, 108766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomrongsuwannakij, T.; Narinthorn, R.; Mahawan, T.; Blackall, P.J. Molecular and Phenotypic Characterization of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Commercial Broilers and Native Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinheinz, K.A.; Joensen, K.G.; Larsen, M.V. Applying the ResFinder and VirulenceFinder Web-Services for Easy Identification of Acquired Antibiotic Resistance and E. coli Virulence Genes in Bacteriophage and Prophage Nucleotide Sequences. Bacteriophage 2014, 4, e27943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, E.; Variatza, E.; Balcázar, J.L. Bacteriophages as a Reservoir of Extended-Spectrum β -Lactamase and Fluoroquinolone Resistance Genes in the Environment. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O456–O459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shousha, A.; Awaiwanont, N.; Sofka, D.; Smulders, F.J.M.; Paulsen, P.; Szostak, M.P.; Humphrey, T.; Hilbert, F. Bacteriophages Isolated from Chicken Meat and the Horizontal Transfer of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4600–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, P.; Zhou, Q.; Tao, W.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, Z. Estimating the Contribution of Bacteriophage to the Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Pig Feces. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gómez, C.; Blanco-Picazo, P.; Brown-Jaque, M.; Quirós, P.; Rodríguez-Rubio, L.; Cerdà-Cuellar, M.; Muniesa, M. Infectious Phage Particles Packaging Antibiotic Resistance Genes Found in Meat Products and Chicken Feces. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, X.; Tang, M.; Liu, J.; Tuo, H.; Gu, J.; Tang, Y.; Lei, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, A. Exploring the Profile of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes Harboring by Bacteriophage in Chicken Feces. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, E.; Bonnin, R.A.; Rocha, E.P.C. Phage-Plasmids Spread Antibiotic Resistance Genes through Infection and Lysogenic Conversion. mBio 2022, 13, e01851-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, E.; Tilocca, B.; Roncada, P. Antimicrobial Resistance in Veterinary Medicine: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colomer-Lluch, M.; Jofre, J.; Muniesa, M. Antibiotic Resistance Genes in the Bacteriophage DNA Fraction of Environmental Samples. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, T.; Bera, B.C.; Vaid, R.K.; Barua, S.; Riyesh, T.; Virmani, N.; Hussain, M.; Singh, R.K.; Tripathi, B.N. Abundance of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Environmental Bacteriophages. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 3458–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Picazo, P.; Fernández-Orth, D.; Brown-Jaque, M.; Miró, E.; Espinal, P.; Rodríguez-Rubio, L.; Muniesa, M.; Navarro, F. Unravelling the Consequences of the Bacteriophages in Human Samples. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Picazo, P.; Gómez-Gómez, C.; Aguiló-Castillo, S.; Fernández-Orth, D.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Muniesa, M.; Rodríguez-Rubio, L. Chicken Liver Is a Potential Reservoir of Bacteriophages and Phage-derived Particles Containing Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Microb. Biotechnol. 2022, 15, 2464–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Gu, J.; Song, Z.; Hu, T.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H. Profiles and Key Drivers of Bacteria/Phage Co-Mediated Antibiotic Resistance Genes during Swine Manure Composting Amended with Humic Acid. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 374, 128721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Organization for Animal Health (OIE). OIE Annual Report on Antimicrobial Agents Intended for Use in Animals, 5th ed.; World Organization for Animal Health (OIE): Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- van Duijkeren, E.; Schwarz, C.; Bouchard, D.; Catry, B.; Pomba, C.; Baptiste, K.E.; Moreno, M.A.; Rantala, M.; Ružauskas, M.; Sanders, P.; et al. The Use of Aminoglycosides in Animals within the EU: Development of Resistance in Animals and Possible Impact on Human and Animal Health: A Review. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 2480–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechner, V.; Sofka, D.; Paulsen, P.; Hilbert, F. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli and Resistance Genes in Coliphages from a Small Animal Clinic and in a Patient Dog with Chronic Urinary Tract Infection. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Target Gene | Primer Sequence | Amplicon Size | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| iroN | 5′-AAGTCAAAGCAGGGGTTGCCCG-3′ | 667 bp | [30] |
| 5′-GATCGCCGACATTAAGACGCAG-3′ | |||
| ompT | 5′-TCATCCCGGAAGCCTCCCTCACTACTAT-3′ | 496 bp | [29] |
| 5′-TAGCGTTTGCTGCACTGGCTTCTGATAC-3′ | |||
| hlyF | 5′-GGCCACAGTCGTTTAGGGTGCTTACC-3′ | 450 bp | [29] |
| 5′-GGCGGTTTAGGCATTCCGATACTCA-3′ | |||
| iss | 5′-CAGCAACCCGAACCACTTGATG-3′ | 323 bp | [30] |
| 5′-AGCATTGCCAGAGCGGCAGAA-3′ | |||
| iutA | 5′-GGCTGGACATCATGGGAACTGG-3′ | 302 bp | [29] |
| 5′-CGTCGGGAACGGGTAGAATCG-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pilati, G.V.T.; Cadamuro, R.D.; Filho, V.B.; Dahmer, M.; Elois, M.A.; Savi, B.P.; Salles, G.B.C.; Muniz, E.C.; Fongaro, G. Bacteriophage-Associated Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Brazilian Poultry. Viruses 2023, 15, 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071485
Pilati GVT, Cadamuro RD, Filho VB, Dahmer M, Elois MA, Savi BP, Salles GBC, Muniz EC, Fongaro G. Bacteriophage-Associated Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Brazilian Poultry. Viruses. 2023; 15(7):1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071485
Chicago/Turabian StylePilati, Giulia Von Tönnemann, Rafael Dorighello Cadamuro, Vilmar Benetti Filho, Mariane Dahmer, Mariana Alves Elois, Beatriz Pereira Savi, Gleidson Biasi Carvalho Salles, Eduardo Correa Muniz, and Gislaine Fongaro. 2023. "Bacteriophage-Associated Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Brazilian Poultry" Viruses 15, no. 7: 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071485
APA StylePilati, G. V. T., Cadamuro, R. D., Filho, V. B., Dahmer, M., Elois, M. A., Savi, B. P., Salles, G. B. C., Muniz, E. C., & Fongaro, G. (2023). Bacteriophage-Associated Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Brazilian Poultry. Viruses, 15(7), 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071485






