Molecular Characteristics of Enterovirus B83 Strain Isolated from a Patient with Acute Viral Myocarditis and Global Transmission Dynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection, Viral Isolation, and Primary Identification
2.2. Viral RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription
2.3. Full-Length Genome Amplification
2.4. Nucleotide Sequencing
2.5. EV-B83 Dataset Construction
2.6. Bayesian Temporal Dynamics Analysis
2.7. Recombination Analysis
2.8. Bayesian Phylogeographic Analysis
2.9. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Number
3. Results
3.1. Whole-Genome Sequences Analysis of Strain S17
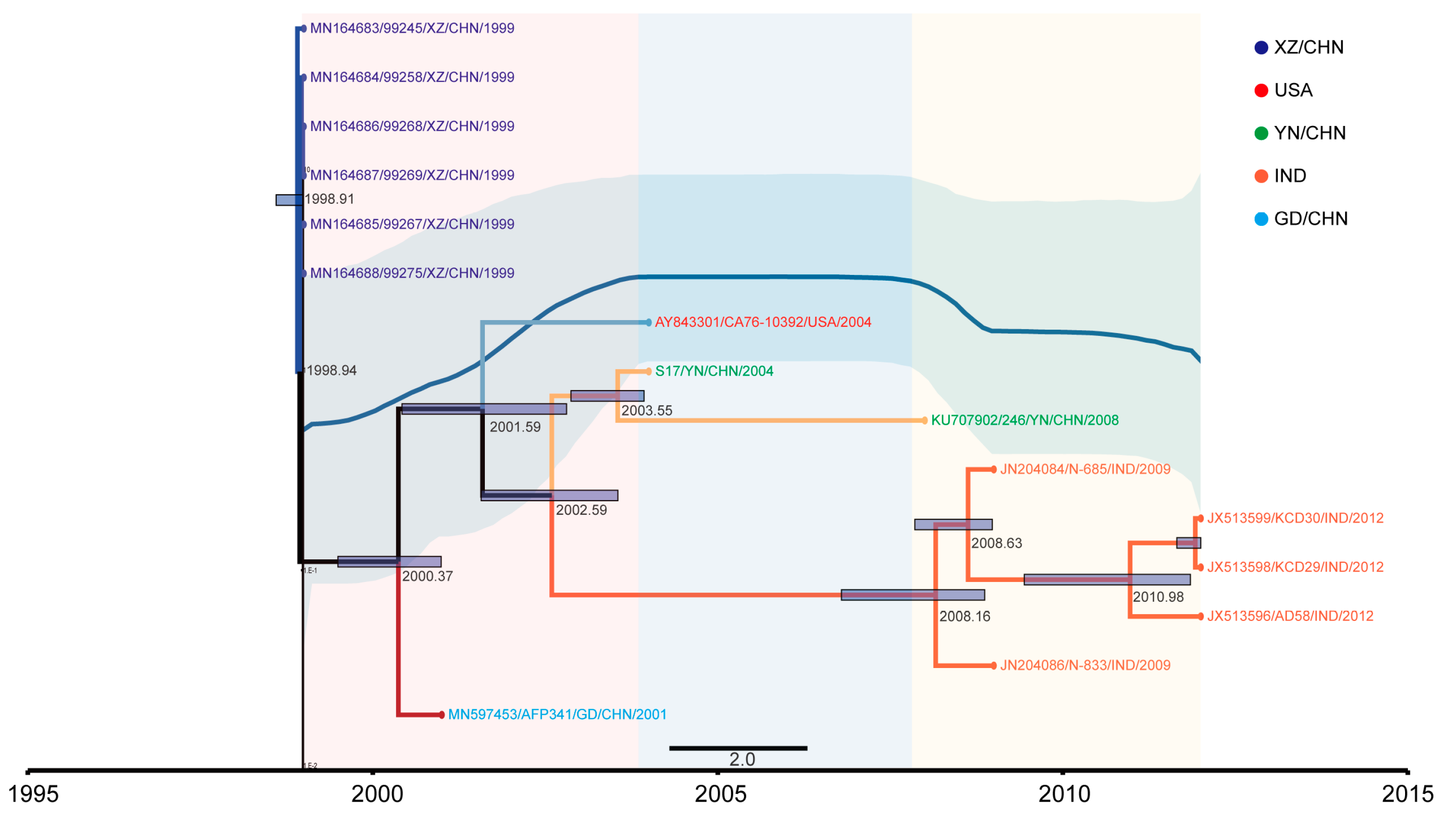
3.2. The Evolutionary Dynamics of EV-B83
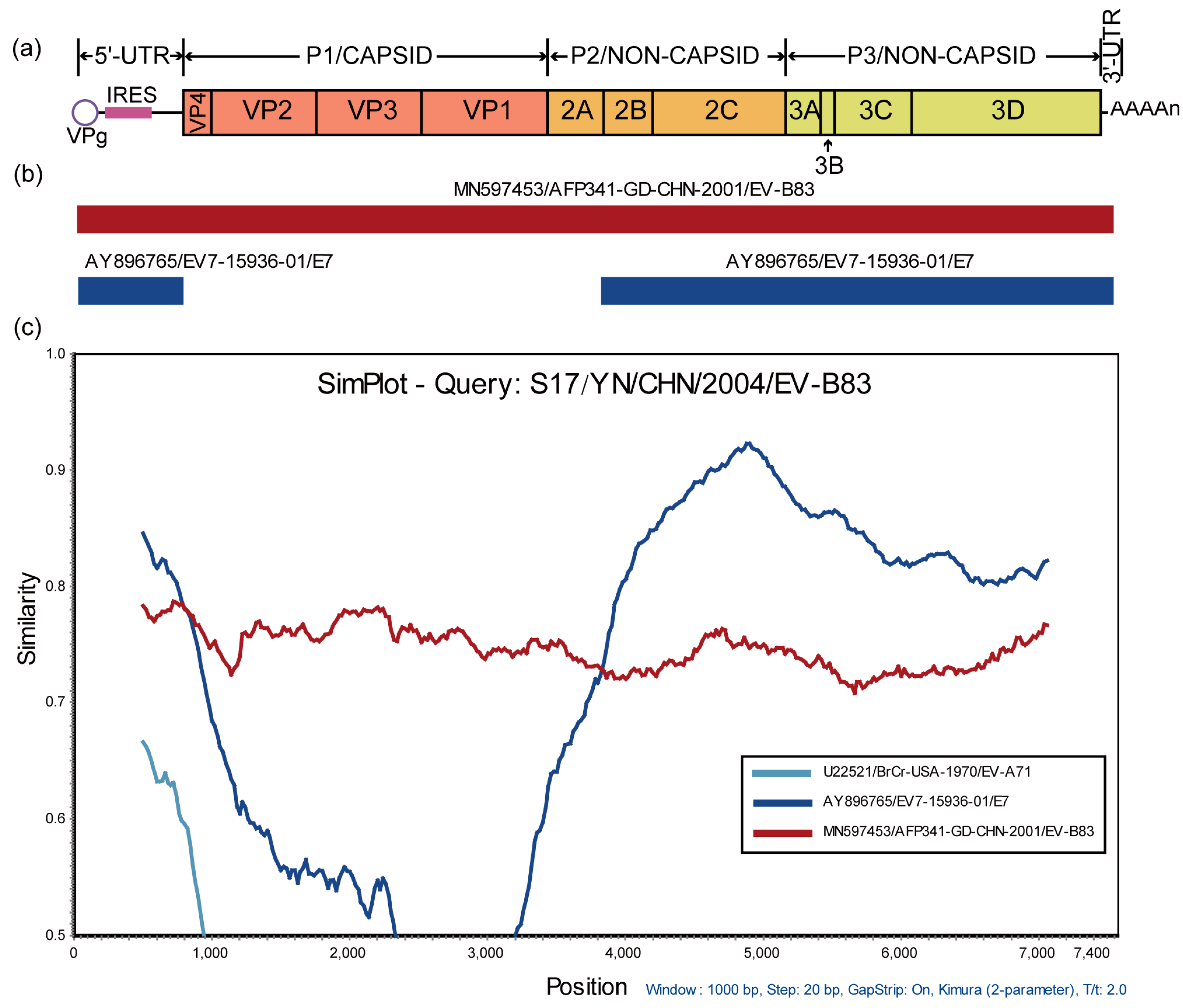
3.3. Recombination Analysis of S17
3.4. EV-B83 Phylogeographic Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knowles, N.J.; Hovi, T.; Hyypiä, T.; King, A.M.Q.; Lindberg, M.; Pallansch, M.A.; Palmenberg, A.C.; Simmonds, P.; Skern, T.; Stanway, G.; et al. Picornaviridae. In Virus Taxonomy: Classification and Nomenclature of Viruses: Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; King, A.M.Q., Adams, M.J., Carstens, E.B., Lefkowitz, E.J.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 855–880. [Google Scholar]
- Arbustini, E.; Porcu, E.; Bellini, O.; Grasso, M.; Pilotto, A.; Dal Bello, B.; Morbini, P.; Diegoli, M.; Gavazzi, A.; Specchia, G.; et al. Enteroviral infection causing fatal myocarditis and subclinical myopathy. Heart 2000, 83, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.S.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, K.M.; Gong, Y.N.; Shih, S.R. Enterovirus and Encephalitis. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkosi, N.; Preiser, W.; van Zyl, G.; Claassen, M.; Cronje, N.; Maritz, J.; Newman, H.; McCarthy, K.; Ntshoe, G.; Essel, V.; et al. Molecular characterisation and epidemiology of enterovirus-associated aseptic meningitis in the Western and Eastern Cape Provinces, South Africa 2018–2019. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 139, 104845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogle, J.M.; Chow, M.; Filman, D.J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science 1985, 229, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, L.; DeSantis, E.R. Treatment of viral myocarditis caused by coxsackievirus B. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2008, 65, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olejniczak, M.; Schwartz, M.; Webber, E.; Shaffer, A.; Perry, T.E. Viral Myocarditis-Incidence, Diagnosis and Management. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2020, 34, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberste, M.S.; Maher, K.; Nix, W.A.; Michele, S.M.; Uddin, M.; Schnurr, D.; al-Busaidy, S.; Akoua-Koffi, C.; Pallansch, M.A. Molecular identification of 13 new enterovirus types, EV79-88, EV97, and EV100-101, members of the species Human Enterovirus B. Virus. Res. 2007, 128, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henquell, C.; Mirand, A.; Richter, J.; Schuffenecker, I.; Bottiger, B.; Diedrich, S.; Terletskaia-Ladwig, E.; Christodoulou, C.; Peigue-Lafeuille, H.; Bailly, J.L. Phylogenetic patterns of human coxsackievirus B5 arise from population dynamics between two genogroups and reveal evolutionary factors of molecular adaptation and transmission. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 12249–12259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.C.; Reddy, H.; Sudheendra, K.; Raghavendra, A.; Varadharaj, V.; Edula, S.; Goparaju, R.; Ratnakar, B.; Srinivasa Rao, A.S.; Maiya, P.P.; et al. Non-polio enterovirus association with persistent diarrhea in children as revealed by a follow-up study of an Indian cohort during the first two years of life. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 61, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.C.; Ananda Babu, M.; Raghavendra, A.; Dhananjaya, D.; Kumar, S.; Maiya, P.P. Non-polio enteroviruses and their association with acute diarrhea in children in India. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 17, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxmivandana, R.; Yergolkar, P.; Gopalkrishna, V.; Chitambar, S.D. Characterization of the non-polio enterovirus infections associated with acute flaccid paralysis in South-Western India. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, C.D.; Yergolkar, P.; Shankarappa, K.S. Antigenic diversity of enteroviruses associated with nonpolio acute flaccid paralysis, India, 2007-2009. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberste, M.S.; Feeroz, M.M.; Maher, K.; Nix, W.A.; Engel, G.A.; Hasan, K.M.; Begum, S.; Oh, G.; Chowdhury, A.H.; Pallansch, M.A.; et al. Characterizing the picornavirus landscape among synanthropic nonhuman primates in Bangladesh, 2007 to 2008. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, V.; Mey, C.; Eloit, M.; Zhu, H.; Danet, L.; Huang, Z.; Zou, G.; Tarantola, A.; Cheval, J.; Perot, P.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of human enterovirus 71 at the origin of an epidemic of fatal hand, foot and mouth disease cases in Cambodia. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2016, 5, e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingjun, T.; Yoshida, H.; Yan, W.; Lin, L.; Tsuji, T.; Shimizu, H.; Miyamura, T. Molecular typing and epidemiology of non-polio enteroviruses isolated from Yunnan Province, the People’s Republic of China. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 80, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, Q.; Tian, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, K.; Ding, Z.; Lu, L. Complete Genome Analysis of an Enterovirus EV-B83 Isolated in China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, M.; Han, Z.; Zhang, M.; Song, Y.; Yan, D.; Zhu, S.; Xu, W. Phylogenetic characteristics and molecular epidemiological analysis of novel enterovirus EV-B83 isolated from Tibet, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Polio Laboratory Manual, 4th ed.; Document World Health Oraganization/IVB/04.10: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.F.; Naguib, T.; Yang, S.J.; Nasr, E.; Jorba, J.; Ahmed, N.; Campagnoli, R.; van der Avoort, H.; Shimizu, H.; Yoneyama, T.; et al. Circulation of endemic type 2 vaccine-derived poliovirus in Egypt from 1983 to 1993. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 8366–8377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiko, H.; Shimada, Y.; Yonaha, M.; Hashimoto, O.; Hayashi, A.; Sakae, K.; Takeda, N. Molecular diagnosis of human enteroviruses by phylogeny-based classification by use of the VP4 sequence. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberste, M.S.; Maher, K.; Kilpatrick, D.R.; Pallansch, M.A. Molecular evolution of the human enteroviruses: Correlation of serotype with VP1 sequence and application to picornavirus classification. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1941–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Lam, T.T.; Max Carvalho, L.; Pybus, O.G. Exploring the temporal structure of heterochronous sequences using TempEst (formerly Path-O-Gen). Virus. Evol. 2016, 2, vew007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goss, E.M.; Tabima, J.F.; Cooke, D.E.; Restrepo, S.; Fry, W.E.; Forbes, G.A.; Fieland, V.J.; Cardenas, M.; Grünwald, N.J. The Irish potato famine pathogen Phytophthora infestans originated in central Mexico rather than the Andes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8791–8796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior Summarization in Bayesian Phylogenetics Using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus. Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lole, K.S.; Bollinger, R.C.; Paranjape, R.S.; Gadkari, D.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Novak, N.G.; Ingersoll, R.; Sheppard, H.W.; Ray, S.C. Full-length human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes from subtype C-infected seroconverters in India, with evidence of intersubtype recombination. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.; Rambaut, A.; Pybus, O.G. Correlating viral phenotypes with phylogeny: Accounting for phylogenetic uncertainty. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2008, 8, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemey, P.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A. Bayesian phylogeography finds its roots. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielejec, F.; Rambaut, A.; Suchard, M.A.; Lemey, P. SPREAD: Spatial phylogenetic reconstruction of evolutionary dynamics. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2910–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Liu, X.; Du, Z.; Hou, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Yang, J. Bayesian phylodynamic analysis reveals the dispersal patterns of tobacco mosaic virus in China. Virology 2019, 528, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muslin, C.; Joffret, M.L.; Pelletier, I.; Blondel, B.; Delpeyroux, F. Evolution and Emergence of Enteroviruses through Intra- and Inter-species Recombination: Plasticity and Phenotypic Impact of Modular Genetic Exchanges in the 5’ Untranslated Region. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muslin, C.; Mac Kain, A.; Bessaud, M.; Blondel, B.; Delpeyroux, F. Recombination in Enteroviruses, a Multi-Step Modular Evolutionary Process. Viruses 2019, 11, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Miao, Y.; Zheng, C.; Luo, D.; Sun, J.; Hu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. A Single Mutation in the VP1 Gene of Enterovirus 71 Enhances Viral Binding to Heparan Sulfate and Impairs Viral Pathogenicity in Mice. Viruses 2020, 12, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseligka, E.D.; Sobo, K.; Stoppini, L.; Cagno, V.; Abdul, F.; Piuz, I.; Meylan, P.; Huang, S.; Constant, S.; Tapparel, C. A VP1 mutation acquired during an enterovirus 71 disseminated infection confers heparan sulfate binding ability and modulates ex vivo tropism. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volle, R.; Razafindratsimandresy, R.; Joffret, M.L.; Bessaud, M.; Rabemanantsoa, S.; Andriamamonjy, S.; Raharinantoanina, J.; Blondel, B.; Heraud, J.M.; Bailly, J.L.; et al. High Permissiveness for Genetic Exchanges between Enteroviruses of Species A, including Enterovirus 71, Favors Evolution through Intertypic Recombination in Madagascar. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01667-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukashev, A.N.; Shumilina, E.Y.; Belalov, I.S.; Ivanova, O.E.; Eremeeva, T.P.; Reznik, V.I.; Trotsenko, O.E.; Drexler, J.F.; Drosten, C. Recombination strategies and evolutionary dynamics of the Human enterovirus A global gene pool. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberste, M.S.; Maher, K.; Kilpatrick, D.R.; Flemister, M.R.; Brown, B.A.; Pallansch, M.A. Typing of human enteroviruses by partial sequencing of VP1. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberste, M.S.; Maher, K.; Flemister, M.R.; Marchetti, G.; Kilpatrick, D.R.; Pallansch, M.A. Comparison of classic and molecular approaches for the identification of untypeable enteroviruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1170–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnaji, F.G.; Bentley, K.; Pearson, A.; Woodman, A.; Moore, J.; Fox, H.; Macadam, A.J.; Evans, D.J. Generated Randomly and Selected Functionally? The Nature of Enterovirus Recombination. Viruses 2022, 14, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaidis, M.; Mimouli, K.; Kyriakopoulou, Z.; Tsimpidis, M.; Tsakogiannis, D.; Markoulatos, P.; Amoutzias, G.D. Large-scale genomic analysis reveals recurrent patterns of intertypic recombination in human enteroviruses. Virology 2019, 526, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annoni, G.; De Rienzo, F.; Nonini, S.; Pugni, L.; Marianeschi, S.M.; Mauri, L.; Gatelli, I.; Mauri, L.; Aresta, F.; Bramerio, M.; et al. Enterovirus fulminant myocarditis as cause of acute heart failure in a newborn. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2022, 42, 101093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairweather, D.; Stafford, K.A.; Sung, Y.K. Update on coxsackievirus B3 myocarditis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2012, 24, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, L.; Sauter, M.; Seebohm, G.; Klingel, K. In Vitro Model Systems of Coxsackievirus B3-Induced Myocarditis: Comparison of Commonly Used Cell Lines and Characterization of CVB3-Infected iCell((R)) Cardiomyocytes. Viruses 2021, 13, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuzawa, N.; Harada, N.; Hatori, T.; Imai, K.; Kitahara, Y.; Sakurai, S.; Kurabayashi, M. Myocarditis, hepatitis, and pancreatitis in a patient with coxsackievirus A4 infection: A case report. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.A.; Thaker, H.M.; Racaniello, V.R. Transgenic mouse model for echovirus myocarditis and paralysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15906–15911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primer | Nucleotide Position (nt) | Primer Sequence | Orientation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0001S48 a | GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTTTAAAACAGCTCTGGGGTT | Forward | [20] | |
| EV/PCR-1 | 539–564 | ACACGGACACCCAAAGTAGTCGGTCC | Reverse | [20] |
| EVP4 | 541–560 | CTACTTTGGGTGTCCGTGTT | Forward | [21] |
| OL68-1 | 1178–1197 | GGTAAYTTCCACCACCANCC | Reverse | [21] |
| S17-936Y | 936–955 | CTACCCGCATTGAACTCACC | Forward | This study |
| S17-1716Z | 1697–1716 | GAGGCGCAATCCATTGTACT | Reverse | This study |
| S17-1586Y | 1586–1605 | CCGGTCATTACAACTTCACC | Forward | This study |
| S17-2567Z | 2548–2567 | ATGGTGTCGCTGGGAACTAC | Reverse | This study |
| 008 | 2411–2430 | GCRTGCAATGAYTTCTCWGT | Forward | [22] |
| 011 | 3389–3408 | GCICCIGAYTGITGICCRAA | Reverse | [22] |
| S17-3167Y | 3167–3186 | GCCCACCACGTCTCTGTAAT | Forward | This study |
| S17-4245Z | 4226–4245 | TGAGGGTGCACTCTGCTCTA | Reverse | This study |
| S17-3981Y | 3981–4000 | GCGTTGGCTCAAACAAAAAG | Forward | This study |
| S17-4970Z | 4951–4970 | AACATTTCGGTCACGAGCAT | Reverse | This study |
| S17-4437Y | 4437–4456 | TGGAAAATCAGTGGCAACAA | Forward | This study |
| S17-5423Z | 5404–5423 | TATTCGGTTTTCACGGTGCT | Reverse | This study |
| S17-5277Y | 5277–5296 | GTTTGCAGGTTTCCAAGGAG | Forward | This study |
| S17-6348Z | 6329–6348 | TTTGTCCATGCACTCCTTCA | Reverse | This study |
| S17-6219Y | 6219–6238 | TGAAGGCCTAGAAGCACTGG | Forward | This study |
| S17-7353Z | 7334–7353 | GTTCGGTGAGTGTGGTAGGG | Reverse | This study |
| S17-6777Y | 6777–6796 | GTGTTCTGGGACCAGCATTT | Forward | This study |
| 7500A a | GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGG(T)24 | Reverse | [20] |
| Genome Region | Position (nt) | Length (nt) | S17 vs. CA76-10392 (%) | S17 vs. Other EV-B Strains (%) | Note a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleotide | Amino Acid | Nucleotide | Amino Acid | ||||
| 5′-UTR | 1–743 | 743 | 83.3 | / | 67.7–89.0 | / | One Deletion, Two Insertions |
| VP4 | 744–950 | 207 | 77.7 | 91.3 | 70.5–77.2 | 73.9–94.2 | |
| VP2 | 951–1727 | 777 | 79.9 | 98.0 | 66.2–71.7 | 73.6–84.2 | |
| VP3 | 1728–2438 | 711 | 78.8 | 97.4 | 63.2–72.8 | 65.8–82.7 | |
| VP1 | 2439–3290 | 852 | 74.9 | 94.0 | 52.7–65.8 | 54.6–69.3 | |
| 2A | 3291–3740 | 450 | 79.7 | 95.3 | 74.8–82.8 | 90.0–96.0 | |
| 2B | 3741–4037 | 297 | 81.4 | 96.9 | 74.4–87.2 | 91.9–96.9 | |
| 2C | 4038–5024 | 987 | 80.8 | 96.9 | 79.0–86.6 | 96.3–98.4 | |
| 3A | 5025–5291 | 267 | 77.5 | 96.6 | 74.1–87.2 | 92.1–100.0 | |
| 3B | 5292–5357 | 66 | 75.7 | 90.9 | 68.1–86.3 | 81.8–95.4 | |
| 3C | 5358–5906 | 549 | 79.5 | 95.6 | 75.5–86.1 | 92.8–98.9 | |
| 3D | 5907–7292 | 1386 | 78.6 | 95.0 | 76.8–86.3 | 94.1–98.0 | |
| 3′-UTR | 7296–7396 | 101 | 88.1 | / | 79.2–97.0 | / | one insertion |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.; Lu, H.; Ma, L.; Zhu, S.; Yan, D.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y. Molecular Characteristics of Enterovirus B83 Strain Isolated from a Patient with Acute Viral Myocarditis and Global Transmission Dynamics. Viruses 2023, 15, 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061360
Song J, Lu H, Ma L, Zhu S, Yan D, Han J, Zhang Y. Molecular Characteristics of Enterovirus B83 Strain Isolated from a Patient with Acute Viral Myocarditis and Global Transmission Dynamics. Viruses. 2023; 15(6):1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061360
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Juan, Huanhuan Lu, Lin Ma, Shuangli Zhu, Dongmei Yan, Jun Han, and Yong Zhang. 2023. "Molecular Characteristics of Enterovirus B83 Strain Isolated from a Patient with Acute Viral Myocarditis and Global Transmission Dynamics" Viruses 15, no. 6: 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061360
APA StyleSong, J., Lu, H., Ma, L., Zhu, S., Yan, D., Han, J., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Molecular Characteristics of Enterovirus B83 Strain Isolated from a Patient with Acute Viral Myocarditis and Global Transmission Dynamics. Viruses, 15(6), 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061360







