Recent Advances in the Study of the Immune Escape Mechanism of SFTSV and Its Therapeutic Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Viral Evasion of Immunization Modes
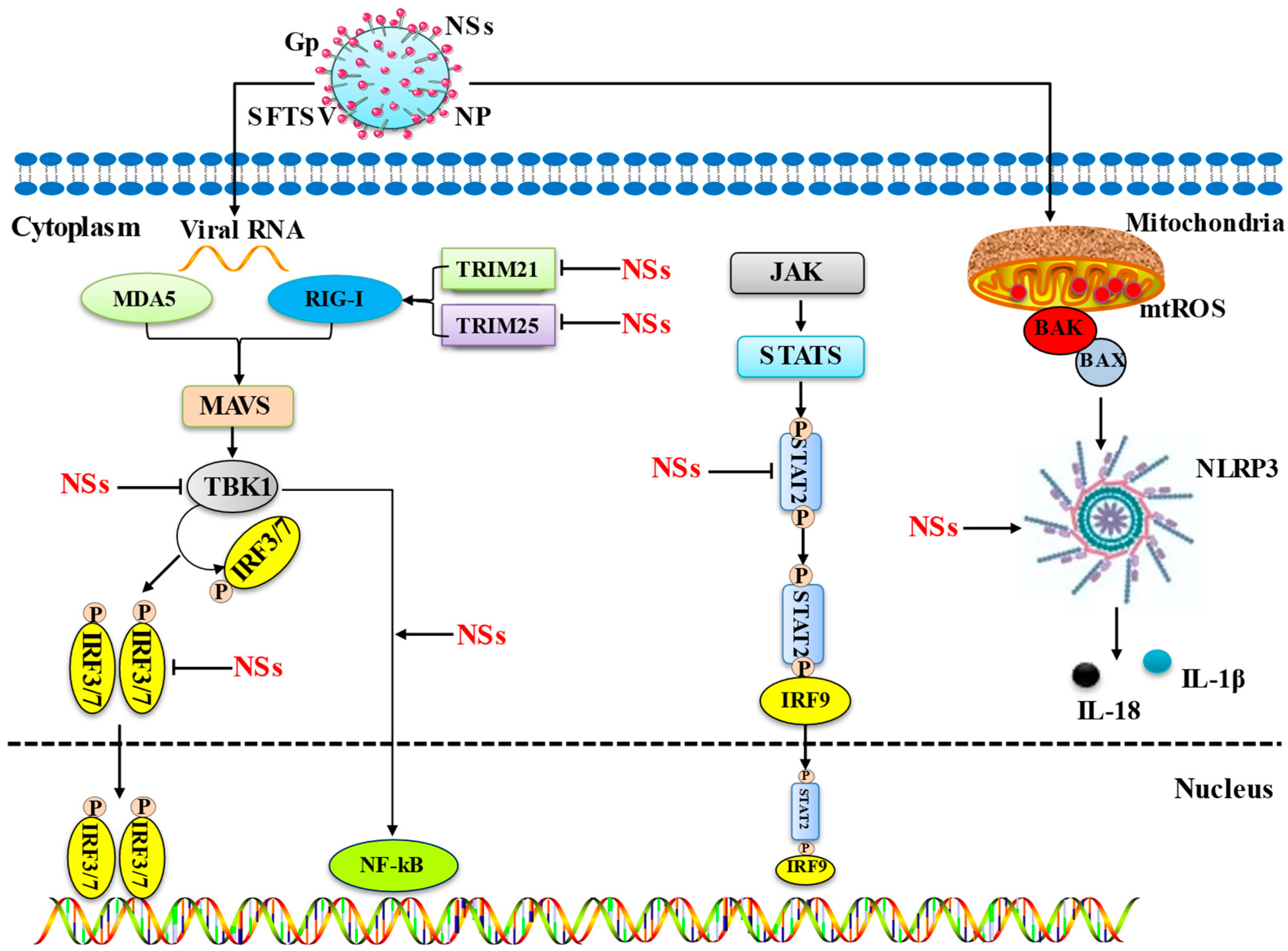
3. Innate Immunity
4. Adapt Immunity
5. Study of Antiviral Drugs against SFTSV
5.1. Ribavilin 1-β-d-Nuclear Furanyl-1,2,4-Triazole-3 Carboxamide
5.2. Favipiravir T-705 (6-Fluoro-3-Hydroxy-2-Pyrazine Carboxamide)
5.3. Hexachlorophenol (Hexachlorophene)
5.4. Ion Channel Blockers
5.5. IFN-γ
5.6. 2′-Fluoro-2′-Deoxycytidine
5.7. Caffeic Acid (CA)
5.8. Amodiaquine (Amodiaquine)
5.9. Immunotherapy
- (1)
- Glucocorticoids
- (2)
- Plasma exchange
- (3)
- New therapeutic approaches
5.10. Vaccine
6. Chinese Medicinal Ingredients against SFTSV Virus
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, X.J.; Liang, M.F.; Zhang, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.D.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.F.; Popov, V.L.; Li, C.; et al. Fever with Thrombocytopenia Associated with a Novel Bunyavirus in China. N. Eng. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, C.; Shinohara, N.; Furuta, R.A.; Tanishige, N.; Shimojima, M.; Matsubayashi, K.; Nagai, T.; Tsubaki, K.; Satake, M. Investigation of antibody to severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) in blood samples donated in a SFTS-endemic area in Japan. Vox Sang. 2018, 113, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.R.; Yun, Y.; Bae, S.G.; Park, D.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.M.; Cho, N.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, K.H. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection, South Korea, 2010. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2103–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zohaib, A.; Zhang, J.; Saqib, M.; Athar, M.A.; Hussain, M.H.; Chen, J.; Sial, A.U.; Tayyab, M.H.; Batool, M.; Khan, S.; et al. Serologic Evidence of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus and Related Viruses in Pakistan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, X.C.; Yun, Y.; Van An, L.; Kim, S.H.; Thao, N.T.P.; Man, P.K.C.; Yoo, J.R.; Heo, S.T.; Cho, N.H.; Lee, K.H. Endemic Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome, Vietnam. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1029–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.L.; Wang, X.J.; Li, J.D.; Ding, S.J.; Zhang, Q.F.; Qu, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Wu, W.; Jiang, M.; et al. Isolation, identification and characterization of SFTS bunyavirus from ticks collected on the surface of domestic animals. Bing Xue Bao Chin. J. Virol. 2012, 28, 252–257. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, L.; Sun, Y.; Cui, X.M.; Tang, F.; Hu, J.G.; Wang, L.Y.; Cui, N.; Yang, Z.D.; Huang, D.D.; Zhang, X.A.; et al. Transmission of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus by Haemaphysalis longicornis Ticks, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.S.; Shimojima, M.; Nagata, N.; Ami, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Iwata-Yoshikawa, N.; Fukushi, S.; Watanabe, S.; Kurosu, T.; Kataoka, M.; et al. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Phlebovirus causes lethal viral hemorrhagic fever in cats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Z.T.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, M.F.; Jin, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, C.B.; Li, C.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Bian, P.F.; et al. Clinical progress and risk factors for death in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Liu, R.; Lu, Q.B.; Wang, L.Y.; Qin, S.L.; Yang, Z.D.; Zhuang, L.; Liu, K.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.A.; et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus-related human encephalitis. J. Infect. 2015, 70, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefkowitz, E.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Hendrickson, R.C.; Orton, R.J.; Siddell, S.G.; Smith, D.B. Virus taxonomy: The database of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D708–D717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, C.T.; Barr, J.N. Recent advances in the molecular and cellular biology of bunyaviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92 Pt 11, 2467–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brault, A.C.; Savage, H.M.; Duggal, N.K.; Eisen, R.J.; Staples, J.E. Heartland Virus Epidemiology, Vector Association, and Disease Potential. Viruses 2018, 10, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.Q.; Shi, C.; Yao, T.; Feng, K.; Mo, Q.; Deng, F.; Wang, H.; Ning, Y.J. The Nonstructural Protein of Guertu Virus Disrupts Host Defenses by Blocking Antiviral Interferon Induction and Action. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMullan, L.K.; Folk, S.M.; Kelly, A.J.; MacNeil, A.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Metcalfe, M.G.; Batten, B.C.; Albariño, C.G.; Zaki, S.R.; Rollin, P.E.; et al. A new phlebovirus associated with severe febrile illness in Missouri. N. Eng. J. Med. 2012, 367, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Ouyang, S.; Liang, M.; Niu, F.; Shaw, N.; Wu, W.; Ding, W.; Jin, C.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Structure of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus nucleocapsid protein in complex with suramin reveals therapeutic potential. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6829–6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, J.; Kato, H.; Fujita, T. The Role of Non-Structural Protein NSs in the Pathogenesis of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Viruses 2021, 13, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Qi, X.; Liang, M.; Li, C.; Cardona, C.J.; Li, D.; Xing, Z. Roles of viroplasm-like structures formed by nonstructural protein NSs in infection with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2014, 28, 2504–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Qi, X.; Wu, X.; Liang, M.; Li, C.; Cardona, C.J.; Xu, W.; Tang, F.; Li, Z.; Wu, B.; et al. Suppression of the interferon and NF-κB responses by severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 8388–8401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, J.; Weber, F.; Cusack, S. Bunyaviridae RNA polymerases (L-protein) have an N-terminal, influenza-like endonuclease domain, essential for viral cap-dependent transcription. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, D.; Thorkelsson, S.R.; Quemin, E.R.J.; Meier, K.; Kouba, T.; Gogrefe, N.; Busch, C.; Reindl, S.; Günther, S.; Cusack, S.; et al. Structural and functional characterization of the severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus L protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 5749–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Tang, B.; Hu, L.; Deng, F.; Wang, H.; Pang, D.W.; Hu, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y. Single-Particle Tracking Reveals the Sequential Entry Process of the Bunyavirus Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus. Small 2019, 15, e1803788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carty, M.; Guy, C.; Bowie, A.G. Detection of Viral Infections by Innate Immunity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 183, 114316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazear, H.M.; Schoggins, J.W.; Diamond, M.S. Shared and Distinct Functions of Type I and Type III Interferons. Immunity 2019, 50, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Shimojima, M.; Narita, R.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Kato, H.; Saijo, M.; Fujita, T. RIG-I-Like Receptor and Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways Cause Aberrant Production of Inflammatory Cytokines/Chemokines in a Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection Mouse Model. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02246-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilli, M.; Arko-Mensah, J.; Ponpuak, M.; Roberts, E.; Master, S.; Mandell, M.A.; Dupont, N.; Ornatowski, W.; Jiang, S.; Bradfute, S.B.; et al. TBK-1 promotes autophagy-mediated antimicrobial defense by controlling autophagosome maturation. Immunity 2012, 37, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Shin, O.S. Nonstructural Protein of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Phlebovirus Inhibits TBK1 to Evade Interferon-Mediated Response. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Bai, M.; Qi, X.; Li, C.; Liang, M.; Li, D.; Cardona, C.J.; Xing, Z. Suppression of the IFN-α and -β Induction through Sequestering IRF7 into Viral Inclusion Bodies by Nonstructural Protein NSs in Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Bunyavirus Infection. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 841–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, W.M.; Chevillotte, M.D.; Rice, C.M. Interferon-stimulated genes: A complex web of host defenses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, Y.; Sakai, M.; Shimojima, M.; Saijo, M.; Itoh, M.; Gotoh, B. Nonstructural protein of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome phlebovirus targets STAT2 and not STAT1 to inhibit type I interferon-stimulated JAK-STAT signaling. Microbes Infect. 2018, 20, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ye, H.; Li, S.; Jiao, B.; Wu, J.; Zeng, P.; Chen, L. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus inhibits exogenous Type I IFN signaling pathway through its NSs invitro. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172744. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa, R.; Sakabe, S.; Urata, S.; Yasuda, J. Species-Specific Pathogenicity of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Is Determined by Anti-STAT2 Activity of NSs. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e02226-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowen, B.B.; Westover, J.B.; Miao, J.; Van Wettere, A.J.; Rigas, J.D.; Hickerson, B.T.; Jung, K.H.; Li, R.; Conrad, B.L.; Nielson, S.; et al. Modeling Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection in Golden Syrian Hamsters: Importance of STAT2 in Preventing Disease and Effective Treatment with Favipiravir. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01942-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatakeyama, S. TRIM Family Proteins: Roles in Autophagy, Immunity, and Carcinogenesis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017, 42, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niida, M.; Tanaka, M.; Kamitani, T. Downregulation of active IKK beta by Ro52-mediated autophagy. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 2378–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Shin, W.J.; Jung, J.U. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus NSs Interacts with TRIM21 To Activate the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01684-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gack, M.U.; Albrecht, R.A.; Urano, T.; Inn, K.S.; Huang, I.C.; Carnero, E.; Farzan, M.; Inoue, S.; Jung, J.U.; García-Sastre, A. Influenza A virus NS1 targets the ubiquitin ligase TRIM25 to evade recognition by the host viral RNA sensor RIG-I. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 5, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, Y.Q.; Ning, Y.J.; Wang, H.; Deng, F. A RIG-I-like receptor directs antiviral responses to a bunyavirus and is antagonized by virus-induced blockade of TRIM25-mediated ubiquitination. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 9691–9711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonczyk, A.; Krist, B.; Sajek, M.; Michalska, A.; Piaszyk-Borychowska, A.; Plens-Galaska, M.; Wesoly, J.; Bluyssen, H.A.R. Direct Inhibition of IRF-Dependent Transcriptional Regulatory Mechanisms Associated With Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, M.; Igarashi, M.; Koshiba, T.; Irie, T.; Takada, A.; Ichinohe, T. Two Conserved Amino Acids within the NSs of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Phlebovirus Are Essential for Anti-interferon Activity. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00706-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Guan, Y.; Jiang, N.; Zheng, N.; Wu, Z. Nonstructural Protein NSs Hampers Cellular Antiviral Response through LSm14A during Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection. J. Immunol. 2021, 207, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, J.; Yamada, S.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Abe, H.; Shimojima, M.; Kato, H.; Fujita, T. The Non-structural Protein NSs of SFTSV Causes Cytokine Storm Through the Hyper-activation of NF-κB. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 41, e00542-20. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Jin, C.; Zhu, L.; Liang, M.; Li, C.; Cardona, C.J.; Li, D.; Xing, Z. Host Responses and Regulation by NFκB Signaling in the Liver and Liver Epithelial Cells Infected with A Novel Tick-borne Bunyavirus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.W.; Chu, M.; Jiao, Y.J.; Zhou, C.M.; Qi, R.; Yu, X.J. SFTSV Infection Induced Interleukin-1β Secretion Through NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 595140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vince, J.E.; De Nardo, D.; Gao, W.; Vince, A.J.; Hall, C.; McArthur, K.; Simpson, D.; Vijayaraj, S.; Lindqvist, L.M.; Bouillet, P.; et al. The Mitochondrial Apoptotic Effectors BAX/BAK Activate Caspase-3 and -7 to Trigger NLRP3 Inflammasome and Caspase-8 Driven IL-1β Activation. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 2339–2353.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xin, Q.L.; Guan, Z.Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.A.; Li, X.K.; Xiao, G.F.; Lozach, P.Y.; et al. SFTSV Infection Induces BAK/BAX-Dependent Mitochondrial DNA Release to Trigger NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 4370–4385.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Yu, Y.; Wen, C.; Li, Z.; Ding, H.; Qi, X.; Cardona, C.J.; Xing, Z. Nonstructural Protein NSs Activates Inflammasome and Pyroptosis through Interaction with NLRP3 in Human Microglial Cells Infected with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Bandavirus. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0016722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Hu, K.; Yi, Z.; Ma, H.; Li, X.; Guo, W.; Xu, B.; Huang, X. Changes in peripheral blood cytokines in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 4704–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Kang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Hou, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T. The Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus NSs Protein Interacts with CDK1 To Induce G(2) Cell Cycle Arrest and Positively Regulate Viral Replication. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01575-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.M.; Zhang, W.K.; Yan, L.N.; Jiao, Y.J.; Zhou, C.M.; Yu, X.J. Bunyavirus SFTSV exploits autophagic flux for viral assembly and egress. Autophagy 2022, 18, 1599–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.Y.; Yu, X.J.; Zhou, C.M. SAFA initiates innate immunity against cytoplasmic RNA virus SFTSV infection. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1010070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.K.; Zhang, S.F.; Xu, W.; Xing, B.; Lu, Q.B.; Zhang, P.H.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.C.; Chen, W.W.; et al. Vascular endothelial injury in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome caused by the novel bunyavirus. Virology 2018, 520, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Zheng, N.; Liu, Y.; Tian, C.; Wu, X.; Ma, X.; Chen, D.; Zou, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; et al. Deficient humoral responses and disrupted B-cell immunity are associated with fatal SFTSV infection. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Jie, S. Circulating regulatory T cells in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Infect. Dis. 2015, 47, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, A.; Park, S.J.; Jung, K.L.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, Y.I.; Foo, S.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.G.; Yu, K.M.; et al. Molecular Signatures of Inflammatory Profile and B-Cell Function in Patients with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. mBio 2021, 12, e02583-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Sato, Y.; Sano, K.; Arashiro, T.; Katano, H.; Nakajima, N.; Shimojima, M.; Kataoka, M.; Takahashi, K.; Wada, Y.; et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus targets B cells in lethal human infections. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, Y.; Wang, H.; Guan, Y.; Zhu, W.; Guo, M.; Zheng, N.; Wu, Z. Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus-Induced Macrophage Differentiation Is Regulated by miR-146. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, A.; Michel, T.; Thérésine, M.; Andrès, E.; Hentges, F.; Zimmer, J. CD56bright natural killer (NK) cells: An important NK cell subset. Immunology 2009, 126, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xiong, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, S.; Zou, C.; Liang, B.; Lu, M.; et al. Depletion but Activation of CD56(dim)CD16(+) NK Cells in Acute Infection with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graci, J.D.; Cameron, C.E. Mechanisms of action of ribavirin against distinct viruses. Rev. Med. Virol. 2006, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lu, Q.B.; Cui, N.; Li, H.; Wang, L.Y.; Liu, K.; Yang, Z.D.; Wang, B.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; et al. Case-fatality ratio and effectiveness of ribavirin therapy among hospitalized patients in china who had severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2013, 57, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łagocka, R.; Dziedziejko, V.; Kłos, P.; Pawlik, A. Favipiravir in Therapy of Viral Infections. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Jiang, X.M.; Cui, N.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, S.F.; Lu, Q.B.; Yang, Z.D.; Xin, Q.L.; Song, Y.B.; Zhang, X.A.; et al. Clinical effect and antiviral mechanism of T-705 in treating severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, H.; Shimojima, M.; Fukushi, S.; Yoshikawa, T.; Fukuma, A.; Taniguchi, S.; Morikawa, S.; Saijo, M. Characterization of Glycoprotein-Mediated Entry of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 5292–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Chen, Z.; Li, W. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) treated with a novel antiviral medication, favipiravir (T-705). Infection 2020, 48, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suemori, K.; Saijo, M.; Yamanaka, A.; Himeji, D.; Kawamura, M.; Haku, T.; Hidaka, M.; Kamikokuryo, C.; Kakihana, Y.; Azuma, T.; et al. A multicenter non-randomized, uncontrolled single arm trial for evaluation of the efficacy and the safety of the treatment with favipiravir for patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Lu, Q.B.; Yao, W.S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.A.; Cui, N.; Yuan, C.; Yang, T.; Peng, X.F.; Lv, S.M.; et al. Clinical efficacy and safety evaluation of favipiravir in treating patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. EBioMedicine 2021, 72, 103591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Chan, J.F.; Ye, Z.W.; Wen, L.; Tsang, T.G.; Cao, J.; Huang, J.; Chan, C.C.; Chik, K.K.; Choi, G.K.; et al. Screening of an FDA-Approved Drug Library with a Two-Tier System Identifies an Entry Inhibitor of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, L.K.; Li, S.F.; Zhang, S.F.; Wan, W.W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xin, Q.L.; Dai, K.; Hu, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.B.; et al. Calcium channel blockers reduce severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) related fatality. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hover, S.; Foster, B.; Barr, J.N.; Mankouri, J. Viral dependence on cellular ion channels—An emerging anti-viral target? J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hover, S.; King, B.; Hall, B.; Loundras, E.A.; Taqi, H.; Daly, J.; Dallas, M.; Peers, C.; Schnettler, E.; McKimmie, C.; et al. Modulation of Potassium Channels Inhibits Bunyavirus Infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 3411–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kursunel, M.A.; Esendagli, G. The untold story of IFN-γ in cancer biology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 31, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thäle, C.; Kiderlen, A.F. Sources of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) in early immune response to Listeria monocytogenes. Immunobiology 2005, 210, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlrab, F.; Jamieson, A.T.; Hay, J.; Mengel, R.; Guschlbauer, W. The effect of 2′-fluoro-2′-deoxycytidine on herpes virus growth. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gene Struct. Expr. 1985, 824, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smee, D.F.; Jung, K.-H.; Westover, J.; Gowen, B.B. 2′-Fluoro-2′-deoxycytidine is a broad-spectrum inhibitor of bunyaviruses in vitro and in phleboviral disease mouse models. Antivir. Res. 2018, 160, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, M.; Shirasago, Y.; Tanida, I.; Kakuta, S.; Uchiyama, Y.; Shimojima, M.; Hanada, K.; Saijo, M.; Fukasawa, M. Structural basis of antiviral activity of caffeic acid against severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. J. Infect. Chemother. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Chemother. 2021, 27, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.-P.; Tsui, K.-H.; Chang, K.-S.; Sung, H.-C.; Hsu, S.-Y.; Lin, Y.-H.; Yang, P.-S.; Chen, C.-L.; Feng, T.-H.; Juang, H.-H. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester inhibits the growth of bladder carcinoma cells by upregulating growth differentiation factor 15. Biomed. J. 2022, 45, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Xiaokaiti, Y.; Fan, S.; Pan, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X. Direct interaction between caffeic acid phenethyl ester and human neutrophil elastase inhibits the growth and migration of PANC-1 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3019–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yin, X.; Liu, X.; Xuan, H. Ethanol extract of propolis and its constituent caffeic acid phenethyl ester inhibit breast cancer cells proliferation in inflammatory microenvironment by inhibiting TLR4 signal pathway and inducing apoptosis and autophagy. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanida, I.; Shirasago, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Abe, R.; Wakita, T.; Hanada, K.; Fukasawa, M. Inhibitory Effects of Caffeic Acid, a Coffee-Related Organic Acid, on the Propagation of Hepatitis C Virus. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 68, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Yamashita, A.; Nakakoshi, M.; Yokoe, H.; Sudo, M.; Kasai, H.; Tanaka, T.; Fujimoto, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Kato, N.; et al. Inhibitory Effects of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester Derivatives on Replication of Hepatitis C Virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, M.; Shirasago, Y.; Ando, S.; Shimojima, M.; Saijo, M.; Fukasawa, M. Caffeic acid, a coffee-related organic acid, inhibits infection by severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in vitro. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWald, L.E.; Johnson, J.C.; Gerhardt, D.M.; Torzewski, L.M.; Postnikova, E.; Honko, A.N.; Janosko, K.; Huzella, L.; Dowling, W.E.; Eakin, A.E.; et al. In Vivo Activity of Amodiaquine against Ebola Virus Infection. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Mesplède, T.; Xu, H.; Quan, Y.; Wainberg, M.A. The antimalarial drug amodiaquine possesses anti-ZIKA virus activities. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, M.; Toyama, M.; Sakakibara, N.; Okamoto, M.; Arima, N.; Saijo, M. Establishment of an antiviral assay system and identification of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus inhibitors. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2017, 25, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.R.; Kim, T.J.; Heo, S.T.; Hwang, K.A.; Oh, H.; Ha, T.; Ko, H.K.; Baek, S.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, J.H.; et al. IL-6 and IL-10 Levels, Rather Than Viral Load and Neutralizing Antibody Titers, Determine the Fate of Patients With Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection in South Korea. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 711847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Yi, J.; Kim, G.; Choi, S.J.; Jun, K.I.; Kim, N.H.; Choe, P.G.; Kim, N.J.; Lee, J.K.; Oh, M.D. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1892–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Azuma, M.; Maruhashi, T.; Sogabe, K.; Sumitani, R.; Uemura, M.; Iwasa, M.; Fujii, S.; Miki, H.; Kagawa, K.; et al. Steroid pulse therapy in patients with encephalopathy associated with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.R.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.R.; Lee, K.H.; Oh, W.S.; Heo, S.T. Application of therapeutic plasma exchange in patients having severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2019, 34, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, V. An Overview of Monoclonal Antibodies. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2019, 35, 150927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Du, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhan, L.; Yang, B.; Huang, X.; Xu, B.; Morita, K.; Yu, F. Development of monoclonal antibody based IgG and IgM ELISA for diagnosis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 26, 102386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, S.; Posadas-Herrera, G.; Aoki, K.; Morita, K.; Hayasaka, D. Therapeutic effect of post-exposure treatment with antiserum on severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) in a mouse model of SFTS virus infection. Virology 2015, 482, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Taniguchi, S.; Kato, H.; Iwata-Yoshikawa, N.; Tani, H.; Kurosu, T.; Fujii, H.; Omura, N.; Shibamura, M.; Watanabe, S.; et al. A highly attenuated vaccinia virus strain LC16m8-based vaccine for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1008859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, J.E.; Kim, Y.I.; Park, S.J.; Yu, M.A.; Kwon, H.I.; Eo, S.; Kim, T.S.; Seok, J.; Choi, W.S.; Jeong, J.H.; et al. Development of a SFTSV DNA vaccine that confers complete protection against lethal infection in ferrets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ye, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Peng, K. Screening of a Small Molecule Compound Library Identifies Toosendanin as an Inhibitor Against Bunyavirus and SARS-CoV-2. Front. Pharm. 2021, 12, 735223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Chen, T.; Li, R.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, Y. Recent Advances in the Study of the Immune Escape Mechanism of SFTSV and Its Therapeutic Agents. Viruses 2023, 15, 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040940
Chen L, Chen T, Li R, Xu Y, Xiong Y. Recent Advances in the Study of the Immune Escape Mechanism of SFTSV and Its Therapeutic Agents. Viruses. 2023; 15(4):940. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040940
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lei, Tingting Chen, Ruidong Li, Yingshu Xu, and Yongai Xiong. 2023. "Recent Advances in the Study of the Immune Escape Mechanism of SFTSV and Its Therapeutic Agents" Viruses 15, no. 4: 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040940
APA StyleChen, L., Chen, T., Li, R., Xu, Y., & Xiong, Y. (2023). Recent Advances in the Study of the Immune Escape Mechanism of SFTSV and Its Therapeutic Agents. Viruses, 15(4), 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040940





